1. Introduction
Tone mapping serves as a fundamental technique in computer graphics and vision, enabling the conversion of High Dynamic Range (HDR) images to Low Dynamic Range (LDR) formats for display on conventional monitors. While standard displays operate with 8-bit precision (0–255 dynamic range), natural scenes exhibit near-infinite dynamic ranges (0–+∞), necessitating HDR’s higher bit-depth representations (e.g., half/single-precision floating-point) to accurately capture real-world lighting. HDR imaging preserves critical details in challenging lighting conditions, such as backlit scenes with simultaneous highlight and shadow retention. Consequently, effective HDR-to-LDR conversion through tone mapping is essential for optimal visual fidelity on mainstream displays, establishing its pivotal role in modern computer vision systems.
Traditional tone mapping methodologies have evolved into two primary categories over decades of development. Global operators apply uniform mapping functions across entire images, offering computational simplicity through techniques like linear/logarithmic scaling, histogram equalization, and Reinhard’s method [
1], albeit at the cost of compromised detail preservation. Conversely, local operators such as the Durand–Dorsey [
2], Fattal [
3], Drago [
4], and Mantiuk [
5] algorithms adapt to regional image characteristics, enhancing contrast and detail retention through spatially-variant processing. However, this improved visual quality incurs substantial computational overhead, limiting real-time applicability.
Recent advances in deep learning have revolutionized HDR tone mapping through data-driven approaches. Liang et al. [
6] mitigated halo artifacts via hybrid ℓ1-ℓ0 decomposition, while Su et al. [
7] achieved photorealistic outputs through their ETMO framework. Rana et al. [
8] leveraged conditional GANs in DeepTMO to generate high-resolution mappings, and Yang et al. [
9] unified illumination adaptation with noise suppression in LA-Net. Zhu et al. [
10] further advanced structural preservation through diffusion models, demonstrating deep learning’s potential in complex tone mapping scenarios.
Significant advancements have also been made in real-time tone mapping implementations. Popović et al. [
11] developed a pipeline architecture utilizing polynomial approximation to adaptively adjust pixel values, preserving high-contrast regions while slashing processing latency. Nosko et al. [
12], combined with an innovative de-ghosting method and a local tone mapping operator, a breakthrough has been achieved in hardware efficiency and real-time performance. Ambalathankandy et al. [
13] demonstrated a FPGA-validated a global–local adaptive algorithm leveraging localized histogram equalization for rapid tone compression. Yang et al. [
14] introduced a direct bitstream processing method for wide dynamic range (WDR) sensors, deriving fine-grained histograms from mantissa-exponent statistical analysis to enable precision tone mapping. Meanwhile, Muneer et al. [
15] proposed the HART operator, integrating histogram-based compression with human visual system (HVS) sensitivity modeling to optimize perceptual quality. Complementing these efforts, Kashyap et al. [
16] implemented a resource-efficient logarithmic number system (LNS) via digital recursion, streamlining high-bit-width arithmetic and adaptive parameter optimization. Their resource reuse strategy further curtailed hardware overhead, achieving a 43% reduction in LUT usage compared to conventional designs.
Despite notable advancements in both deep learning and traditional tone mapping methodologies, the computational complexity inherent to nonlinear transformations persists as a critical barrier. While these operations are indispensable for achieving perceptually accurate mappings, their intensive resource requirements impose critical bottlenecks in real-time, high-resolution applications. Specifically, the dual demands of maintaining system throughput (>30 FPS for 4K streams) and sub-0.1 dB precision under escalating resolution standards (e.g., 8K/120 Hz) create an inversely proportional relationship between computational efficiency and output quality. Current architectures struggle to reconcile these competing priorities, with benchmark studies revealing up to 62% throughput degradation when processing Ultra-High-Definition (UHD) content compared to High-Definition (HD) equivalents [
17]. This fundamental tension between algorithmic fidelity and real-time feasibility underscores the urgent need for hardware–algorithm co-optimization strategies.
The computational intensity of nonlinear tone mapping operations poses a fundamental challenge to real-time system implementation, particularly when processing high-resolution content (4K/8K) at video rates exceeding 60 FPS. Modern applications—including immersive Virtual Reality (VR) systems and UHD broadcast pipelines—require sub-frame latency (<16 ms for 60 Hz systems) while maintaining PSNR fidelity above 45 dB. Conventional software-based implementations struggle with these dual constraints, exhibiting exponential increases in cycle consumption (∝N2 for N × N kernels) that degrade throughput by 58–72% when scaling from HD to 4K resolutions. This performance gap necessitates novel architectural paradigms by hardware–algorithm co-design for resolution-independent complexity.
Equally critical is the pursuit of resource-efficient implementations that reconcile precision requirements with physical constraints. While dedicated accelerators using 28 nm FPGA or ASIC platforms can achieve 2.8 TOPS/W efficiency, their area costs escalate by 3–5 × compared to linear operators—a critical limitation for edge devices where the die area directly correlates with deployment feasibility. The power–area–product (PAP) metric reveals an acute tradeoff: implementations optimizing for <1.5 W power budgets typically sacrifice 0.5–1.5 dB in Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) performance, while precision-oriented designs (<0.05 dB loss) consume 3.2–4.8 × more silicon resources [
18]. This interdependence mandates co-optimization across all system layers, from algorithm approximation (e.g., 16-bit logarithmic quantization) to microarchitectural innovation (e.g., stochastic computation models).
The persistent challenges in computational intensity and resource management underscore the need for heterogeneous acceleration frameworks. Contemporary solutions combining approximate computing paradigms with precision-gated execution units demonstrate promising tradeoffs—achieving 40% power reduction versus conventional designs while maintaining a Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) > 0.98. However, true scalability requires fundamental rethinking of nonlinear function implementation, particularly for transcendental operations dominating 68–82% of tone mapping cycles. Emerging approaches leveraging high-radix polynomial expansions (order 8–12) coupled with dynamic precision scaling show particular promise, reducing LUT utilization by 35% compared to traditional Taylor-series implementations without compromising HVS-aligned quality metrics.
Despite advancements in tone mapping architectures, the computational complexity of nonlinear transformations persists as a critical bottleneck. Both deep learning and traditional methods exhibit exorbitant computational demands—particularly in real-time 4K/8K processing scenarios—where system throughput (>30 FPS) and sub-0.5 dB accuracy impose exacting demands. This complexity escalates implementation challenges and constrains real-time capabilities, necessitating architectural innovations. Furthermore, specialized hardware for high-precision nonlinear operations introduces critical power–area tradeoffs, often straining compact system designs. Optimal solutions require co-optimized hardware–algorithm frameworks that strategically balance precision against power, area, and throughput constraints.
Contributions: In this paper, we propose an adaptive and efficient HDR tone mapping processor designed for high-quality real-time processing of high-resolution, high-frame-rate images under varying exposure conditions.
Adaptive Parameter Adjustment: An exposure-adaptive computation method dynamically adjusts tone mapping parameters based on input image characteristics, ensuring stable results even for video streams with fluctuating exposures.
Hybrid Precision Architecture: A pixel-level pipeline architecture balances computational precision and resource efficiency by combining fixed-point arithmetic (for core operations) with floating-point units (reserved for high-precision tasks such as logarithmic/exponential functions). Bilateral filtering is optimized via lookup tables (LUTs) and approximate computations, reducing resource usage while maintaining accuracy.
Transcendental Function Acceleration: High-radix Taylor expansions accelerate floating-point natural logarithm and exponential operations, addressing computational bottlenecks in transcendental functions. The system achieves real-time 4K video processing at 30 FPS.
Implemented on the Xilinx XCVU9P FPGA platform, the design demonstrates competitive advantages in both performance and hardware resource efficiency.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 details the algorithm process.
Section 3 introduces the hardware architecture implementation.
Section 4 presents the experimental results and compares them with other advanced works.
Section 5 concludes the paper and suggests possible directions for future research.
3. Hardware Architecture
3.1. Hardware-Algorithm Co-Optimization Framework
This paper proposes a high-performance tone mapping operator (TMO) architecture with adaptive illumination capabilities, developed through rigorous hardware-algorithm co-optimization. The architecture, as shown in
Figure 3, consists of a bilateral filter module, natural logarithm, and exponential modules, as well as several dividers and multipliers. The entire design was conceived with hardware implementation constraints as a primary consideration, where algorithmic choices were carefully tailored to enable efficient hardware realization. To balance computational precision and resource efficiency, the system primarily employs fixed-point pipelining arithmetic, retaining floating-point computation only for tasks with high-precision requirements, such as logarithmic and exponential functions. Notably, the bilateral filter module employs fixed-point arithmetic not only for its hardware-friendly properties but also because its computational structure was specifically optimized to maintain filtering quality while minimizing resource overhead. Similarly, the precision requirements for transcendental functions were determined through iterative analysis of both algorithmic needs and hardware implementation trade-offs.
As depicted in
Figure 3, the input image is first converted to grayscale values and then mapped to the logarithmic domain through a natural logarithm transformation. This transformation aligns the image representation with the human visual system’s perception of brightness. In this architecture, we define a specific fixed-point number format consisting of one sign bit, three integer bits, and nine fractional bits. Fixed-to-floating-point conversion is performed during logarithmic/exponential operations. This approach maximizes computational precision while minimizing memory usage and computational resources. The grayscale values are stored in a four-row buffer to allow the bilateral filter module to apply a 5 × 5 mask (sliding window with stride = 1). The filtered image is combined with an adaptive parameter to form the base layer. This adaptive parameter is derived from a logarithmic function fitted to experimental results and the average grayscale value of the image.
The detail layer is obtained by calculating the difference between the logarithmic domains of the original grayscale image and the bilateral filter output. After combining the base and detail layers, an exponential transformation generates the tone-mapped grayscale image. Finally, the RGB values are restored from the tone-mapped grayscale image, and gamma correction is applied to produce the final output.
3.2. Bilateral Filter Module
Bilateral filtering is a nonlinear filtering algorithm that smooths an image while preserving edge clarity. Unlike other filtering algorithms, bilateral filtering combines two factors—spatial distance and pixel intensity difference—to compute the weights. The following outlines the mathematical derivation of bilateral filtering:
Assume the image is
f(
x,
y). For a central pixel (
i,
j), the weight
for a neighboring pixel (
k,
l) is defined as
Here,
is the spatial weight function, typically a Gaussian function:
where
represents the Euclidean distance between pixels, and
is the spatial standard deviation.
is the pixel intensity weight function, which is also typically a Gaussian function:
where
represents the difference in pixel intensity values, and
is the standard deviation of the pixel intensity values.
Therefore, the weight function can be expressed as
The filtered pixel value
is the weighted average of the pixel values within the neighborhood. The specific formula is
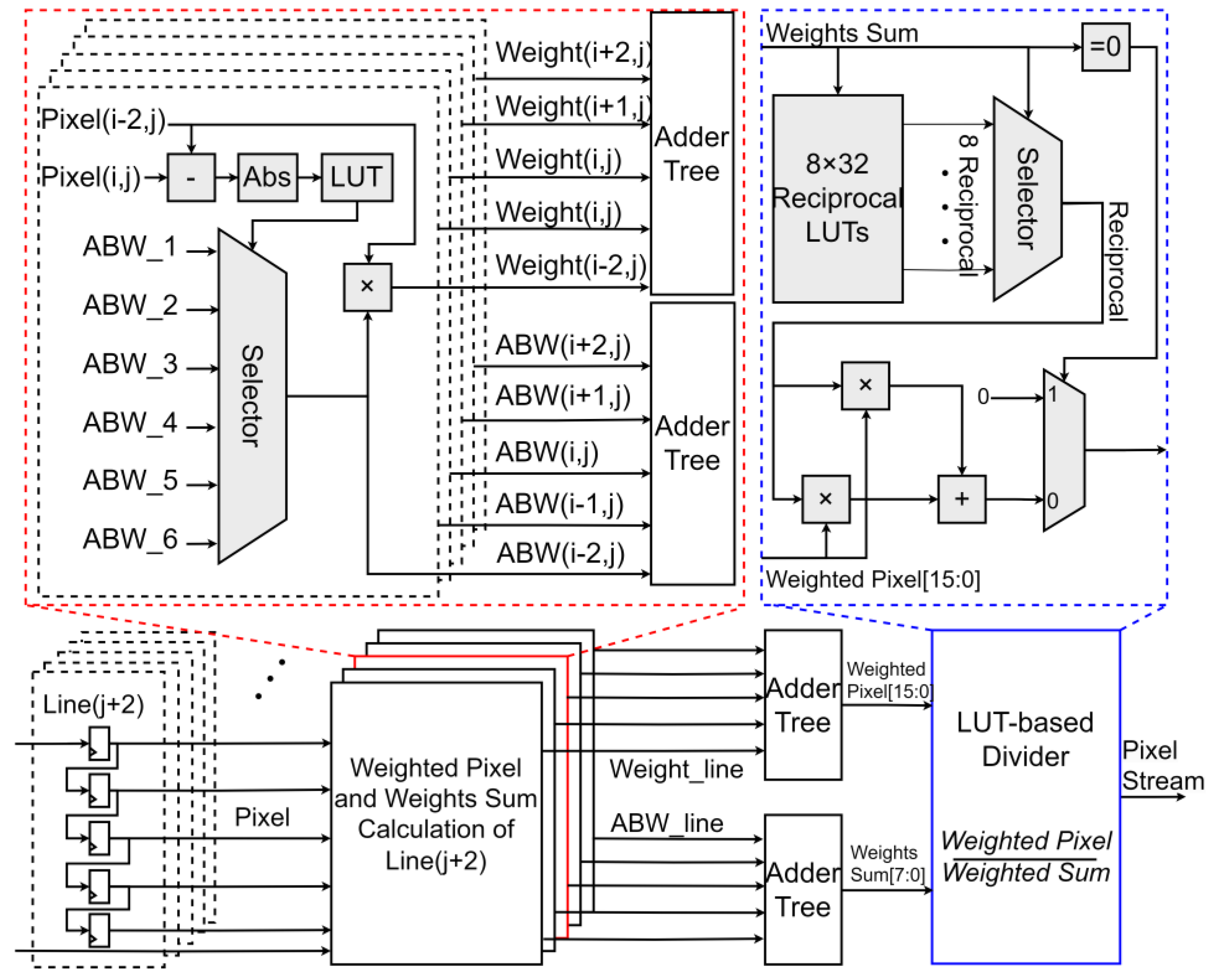
This paper proposes an overall hardware architecture for a compact bilateral filter (BF), aiming to efficiently implement image filtering processing. The architecture consists of a filter mask module with row buffers, a weighted pixel module, a weight sum computation module, and a normalization module. These modules work together to achieve efficient filtering processing. The bilateral filter architecture proposed in this paper is specifically tailored for logarithmic-domain data processing, rather than conventional image data. Moreover, to ensure precision in logarithmic data processing, the data bit-width is configurable to accommodate varying accuracy requirements across different applications.
The input pixel stream is transmitted to the filter mask module through four row buffers for a 5 × 5 mask and adopts pixel-level pipelining. The filter mask module consists of 5 × 5 shift registers, each of which is connected to the weighted pixel module and the weight sum computation module. This design ensures efficient data transfer and storage during processing, supports parallel processing, and improves system throughput as shown in
Figure 4.
In this paper, the filter mask is divided into five columns, each containing five weight selection modules for five 13-bit pixels. Each column selects only three weights from the filter weight LUT. The weighted pixel module accumulates the product for each pixel, and the weight sum is also calculated in parallel to meet the pipeline throughput requirements. The main resource consumption and critical path of this module come from multipliers and adders. Taking a 5 × 5 filter mask as an example, addition trees are required to perform accumulation for both the weighted pixels and weight sums. The addition trees are designed as highly parallel two-stage structures, with each addition tree being a 5-to-1 adder. Larger filter masks result in increased delay in the critical path, but better smoothing effects can be achieved through spatial weights. Therefore, there is a trade-off between performance and cost. For bilateral filtering, a larger window contains more information and yields better processing results. However, in hardware implementations, a larger window requires more storage and computational resources. Therefore, a careful trade-off is necessary between these factors. In this paper, a 5 × 5 filter mask was selected to balance resource utilization and performance.
To further accelerate computational performance, an approximate weight storage strategy is adopted in the bilateral filter calculation. The bilateral filter module primarily computes the Gaussian function values of the spatial domain and the pixel intensity domain. The pixel difference (ΔIo) between the filter output and the surrounding pixel values in the filter window and the central pixel difference (ΔIin) exhibits a convex function relationship. Before the critical point, ΔIin and ΔIo are proportional, with the pixel intensity domain playing a dominant role. After the critical point, the spatial domain begins to dominate, and ΔIin and ΔIo are inversely proportional.
Based on the above relationship, fitting points are selected. Since the pixel intensity domain dominates before the critical point, the number of fitting points can be reduced accordingly. After the critical point, as the spatial domain dominates, the number of fitting points needs to be increased accordingly. Research has found that the minimum number of fitting points for range weights is six. The absolute value of the pixel difference and the pixel difference (Δx) are compared, and then six approximate bilateral weights (ABWs) are selected through a multiplexer. This weight selection mechanism reduces storage requirements while maintaining the accuracy of the filtering effect.
The divider is usually the critical path with high latency. In the architecture, an LUT-based divider is adopted, which converts the division of a 16-bit dividend and an 8-bit divisor into two multiplications, using 8-bit and 18-bit multipliers, respectively. For the weight sum, eight LUTs and an 8-input LUT are used to convert it to its reciprocal. Since the multiplier’s delay is less than that of the divider, the divisor is converted to its reciprocal, and division is replaced by multiplication. For these eight LUTs, each store 32 reciprocals, selected by the last five bits of the weight sum, and these eight LUTs correspond to the highest three bits of the weight sum. The lookup process is divided into two steps to improve path speed. The stored reciprocals are 18-bit numbers, determined by the maximum weighted pixel. After conversion, it is extended to two multipliers, with 18-bit and 8-bit inputs, respectively, to reduce latency.
Therefore, the LUT-based divider significantly reduces the delay cycle of the BF data flow. Although some clock cycles are needed for parallelization, the entire computation requires only nine clock cycles, with the divider module contributing only four delay cycles. Finally, the proposed divider in this paper significantly improves speed and reduces latency through a two-stage lookup process and extended multiplication, outperforming traditional dividers.
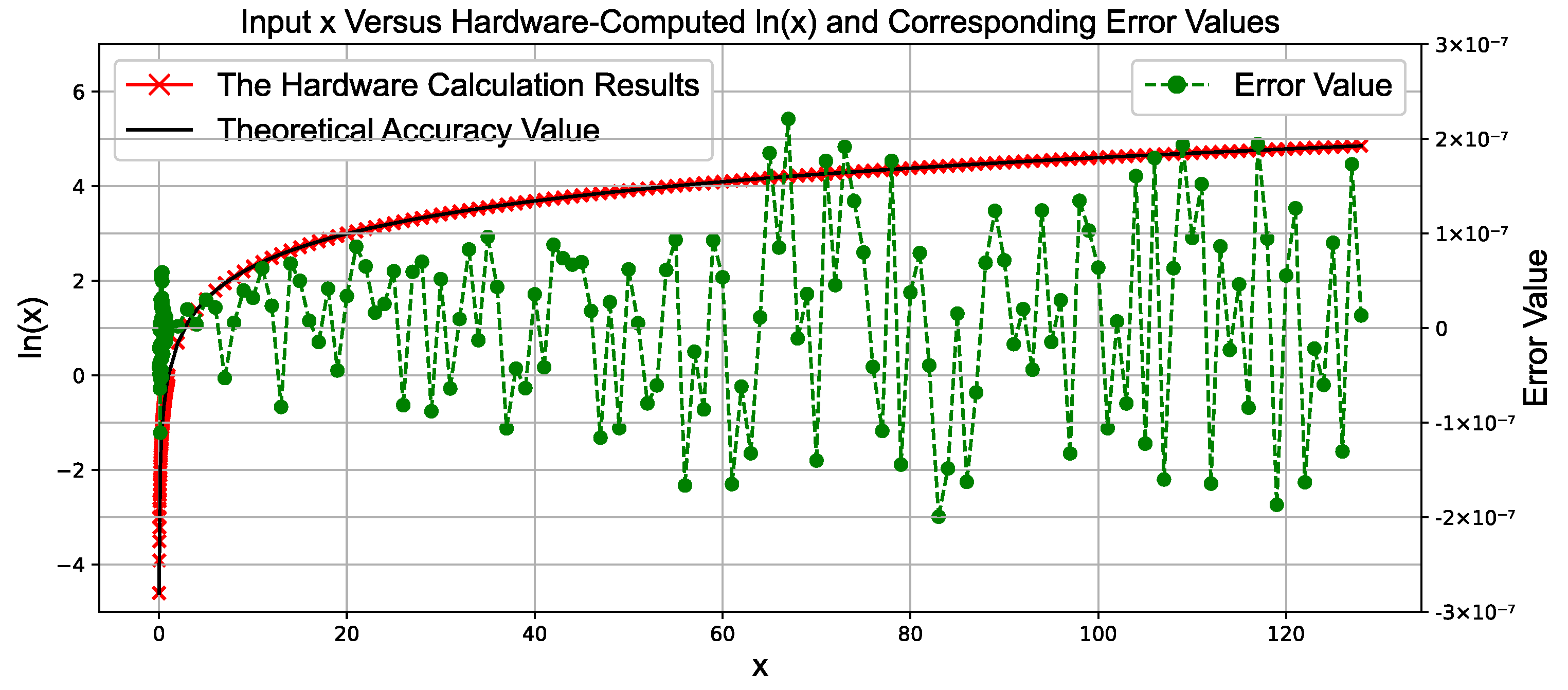
3.3. Single-Precision Floating-Point Natural Logarithm Function Module Based on High-Order Taylor Expansion
When calculating the natural logarithm of a single-precision floating-point number, the input is represented in decimal floating-point form as
where
is in the range [1, 2). The natural logarithm of
x is then calculated as
Since the input range for the natural logarithm calculation must be greater than 0, meaning (−1)
S = 1, the above formula can be simplified to
To extend the precision range of the above formula, it can be implemented using two branches, as shown below:
Thus, the above (20) can be expressed as
In this design, the first term
can be precomputed and stored in a lookup table, while the second term
can be approximated using a Taylor expansion around
x = 1.
For the Taylor expansion, a larger n results in higher precision, but in hardware implementations, this leads to increased multiplier consumption. Based on experimental testing, a cubic approximation (third-order Taylor expansion) is sufficient for the required precision, as higher-order terms provide limited improvements.
Additionally, smaller values of y yield higher precision. To reduce the range of y, the Halley iteration algorithm is used, requiring only a single iteration. This results in B = , where a is a very small value in the range [−2 − 9, 2 − 9], and b is the reciprocal of the upper 9 bits of B. Using b, a can be computed as needed.
Thus, can be expressed as . Here, is expanded using the Taylor series, and since a is a very small value, the precision of the Taylor expansion is further improved. ln(b) can be precomputed and stored in the LUT.
The final formula is as follows:
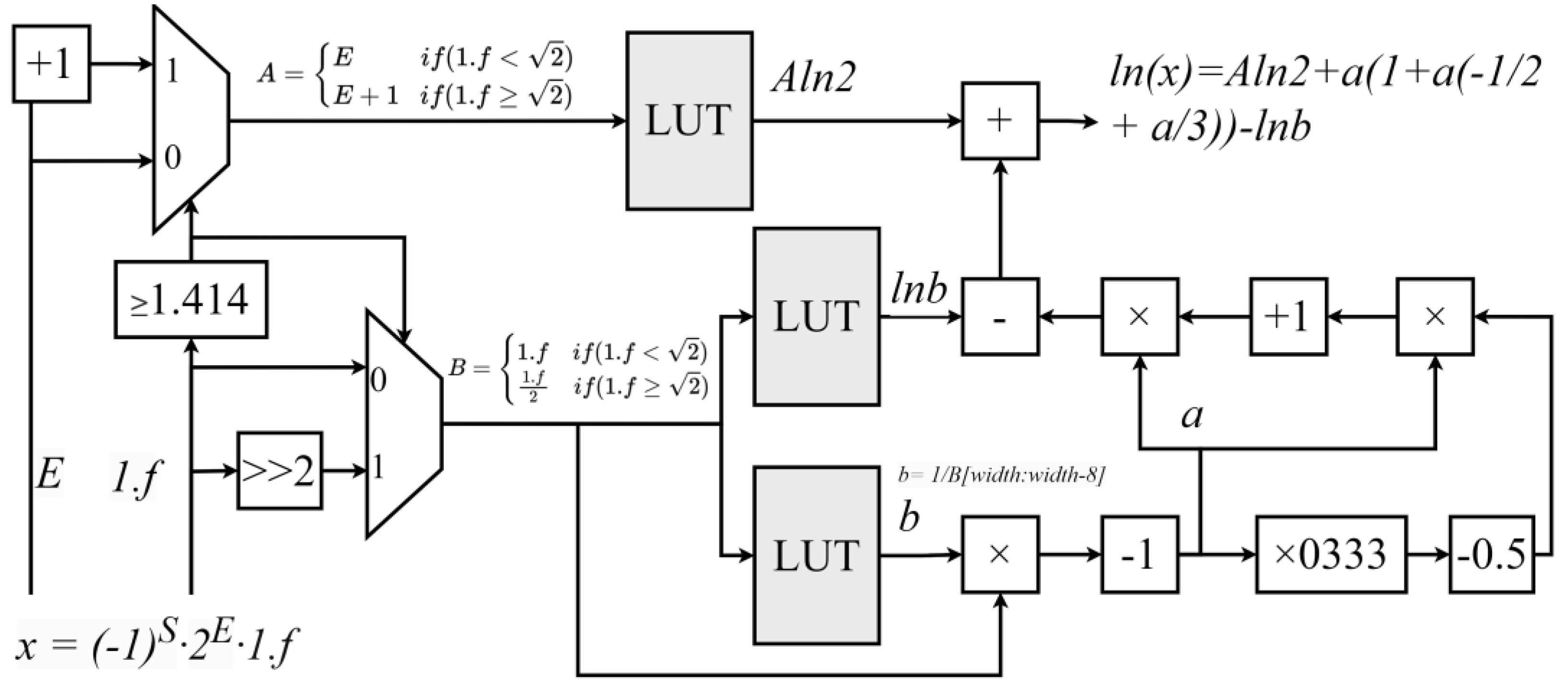
As described in (24), the design of the logarithm function module combines a lookup table with polynomial approximation. First, the input value is preprocessed to obtain A and B. Then, a single Halley iteration is performed on B to compute b. The values of and are precomputed and stored in the lookup table. Subsequently, b is used to calculate a, and the natural logarithm value is finally obtained using a Taylor expansion.
The hardware architecture of a floating-point natural logarithm calculation module consists of two key modules: the preprocessing module and the Taylor expansion module. The preprocessing module is composed of comparators and a lookup table, while the Taylor expansion module consists of multipliers and adders, as shown in
Figure 5.
Specifically, the comparator first determines whether is greater than , thereby identifying the values of A and B. Next, the value of is selected from the lookup table based on A, and the values of and a are selected based on B. Then, the Taylor expansion is used to calculate . Finally, simple addition and subtraction operations are performed to obtain the desired logarithmic value.
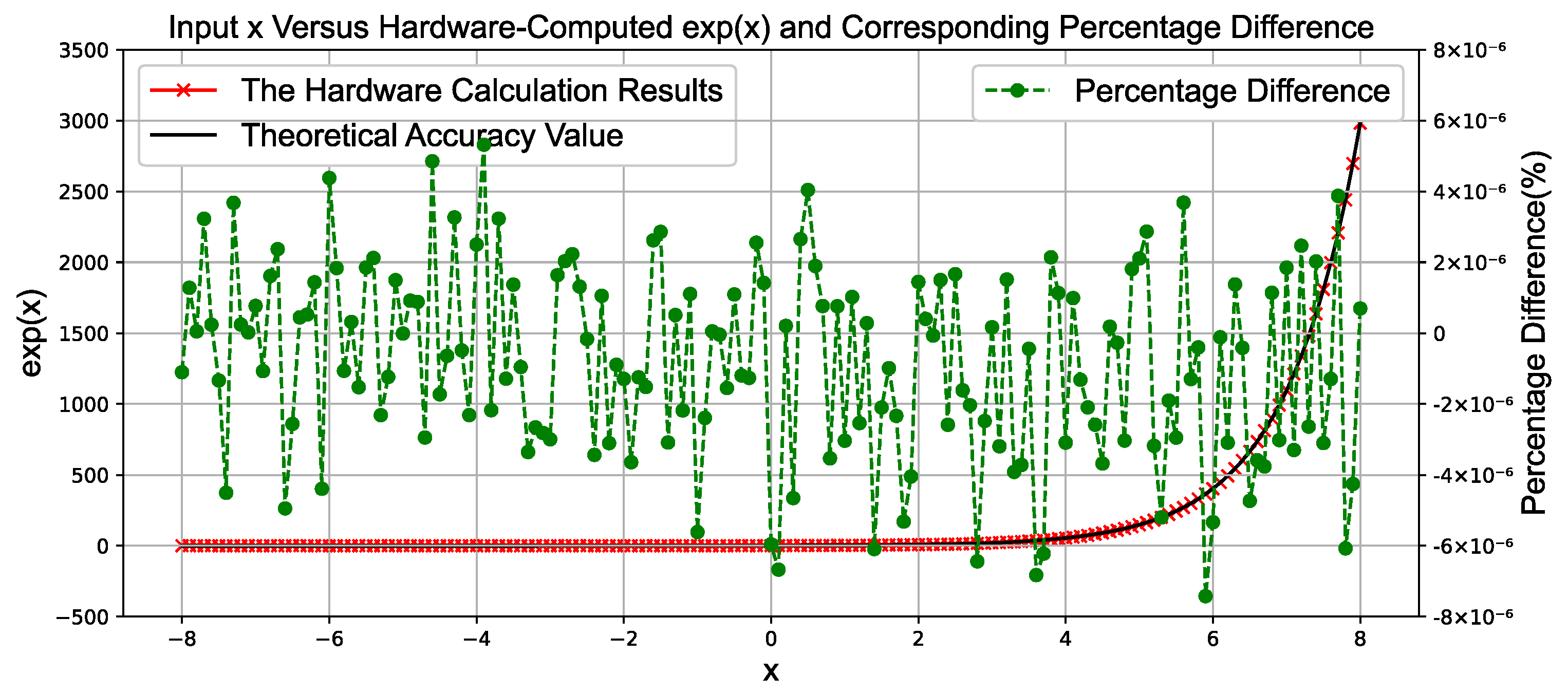
3.4. Single-Precision Floating-Point Exponential Function Module for
For the single-precision floating-point function, due to the limitations of the single-precision floating-point representation range, the input domain is not infinite but has upper and lower bounds. The domain of the single-precision floating-point function is defined as [−87.33, 88.72], with the maximum output value being and the minimum output value being .
Here, the
value is calculated using a Taylor expansion, as shown in (25):
Here, we also need to minimize the range of
x to maximize the precision of the Taylor expansion. To achieve this,
x is divided into its integer and fractional parts, as shown in (26). The integer part
i is obtained by rounding
to the nearest integer. By subtracting
from
x, we can obtain the fractional part
f, where the absolute value of f is less than ln2.
Finally, the calculation of the exponential function can be transformed into
In this way, the calculation of the exponential function can be transformed into the calculation of and The value of can be obtained in hardware through simple bit shifting, thereby saving hardware resources. The value of can be computed using a Taylor expansion. Based on the required precision, it is sufficient to expand up to the second-order term.
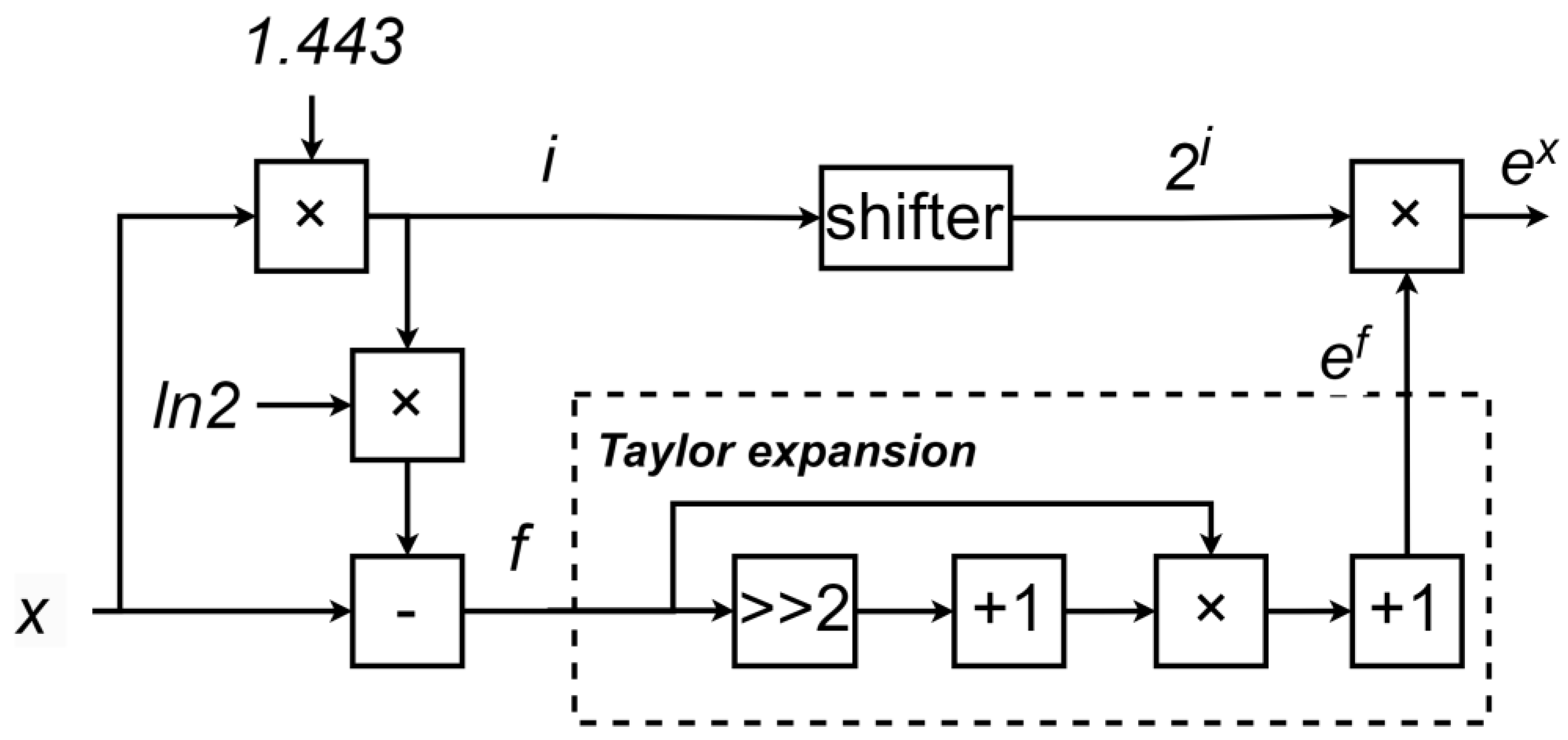
The overall hardware design is shown in
Figure 6. The architecture mainly consists of two key modules: the preprocessing module and the Taylor expansion module. The core component of the preprocessing module is a multiplier, while the Taylor expansion module primarily consists of multipliers and adders, as illustrated in
Figure 6.
Specifically, the input value x is first multiplied by the reciprocal of ln2, approximately 1.443, using a multiplier to compute (here, since will later undergo rounding, high precision is not required, and approximate computation can be used). Then, this value is rounded to obtain the integer i. Based on the value of i, the value of f is further calculated, where f represents the difference between x and .
Next, is calculated using a bit-shifting operation, while is computed using the Taylor expansion formula. Finally, and are multiplied using a multiplier to obtain the desired exponential value .
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we address the challenges associated with HDR tone mapping, with a particular focus on exposure consistency, computational complexity, and resource efficiency. To overcome these obstacles, we propose an adaptive and efficient HDR tone mapping processor designed for various exposure conditions.
Our processor introduces an adaptive computation method that dynamically adjusts processing based on the characteristics of the input image, ensuring robust image processing under different exposure levels. This approach maintains high-quality tone mapping even with exposure variations, resulting in more consistent and effective outcomes. Additionally, we developed a pixel-level pipelined architecture that optimizes critical computational modules for real-time processing of high-resolution video. This architecture enables the processor to handle 4K video at 30 FPS, meeting the demands of modern imaging applications.
To address the computational requirements of transcendental functions, we utilized a high-order Taylor expansion to accelerate floating-point natural logarithm and exponential operations. Furthermore, we employed approximate computation using LUTs for bilateral filtering, effectively balancing hardware resource utilization while maintaining computational accuracy.
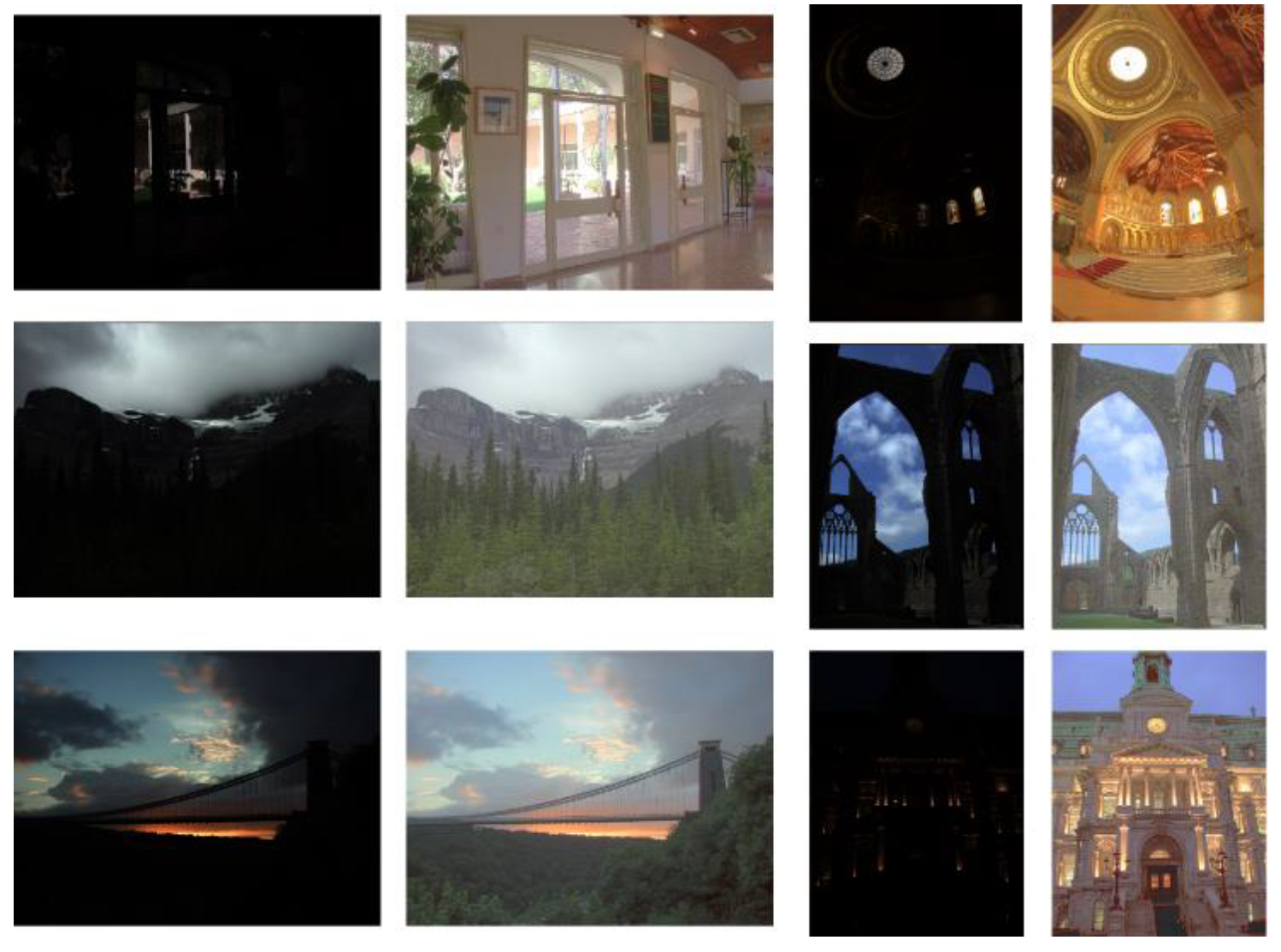
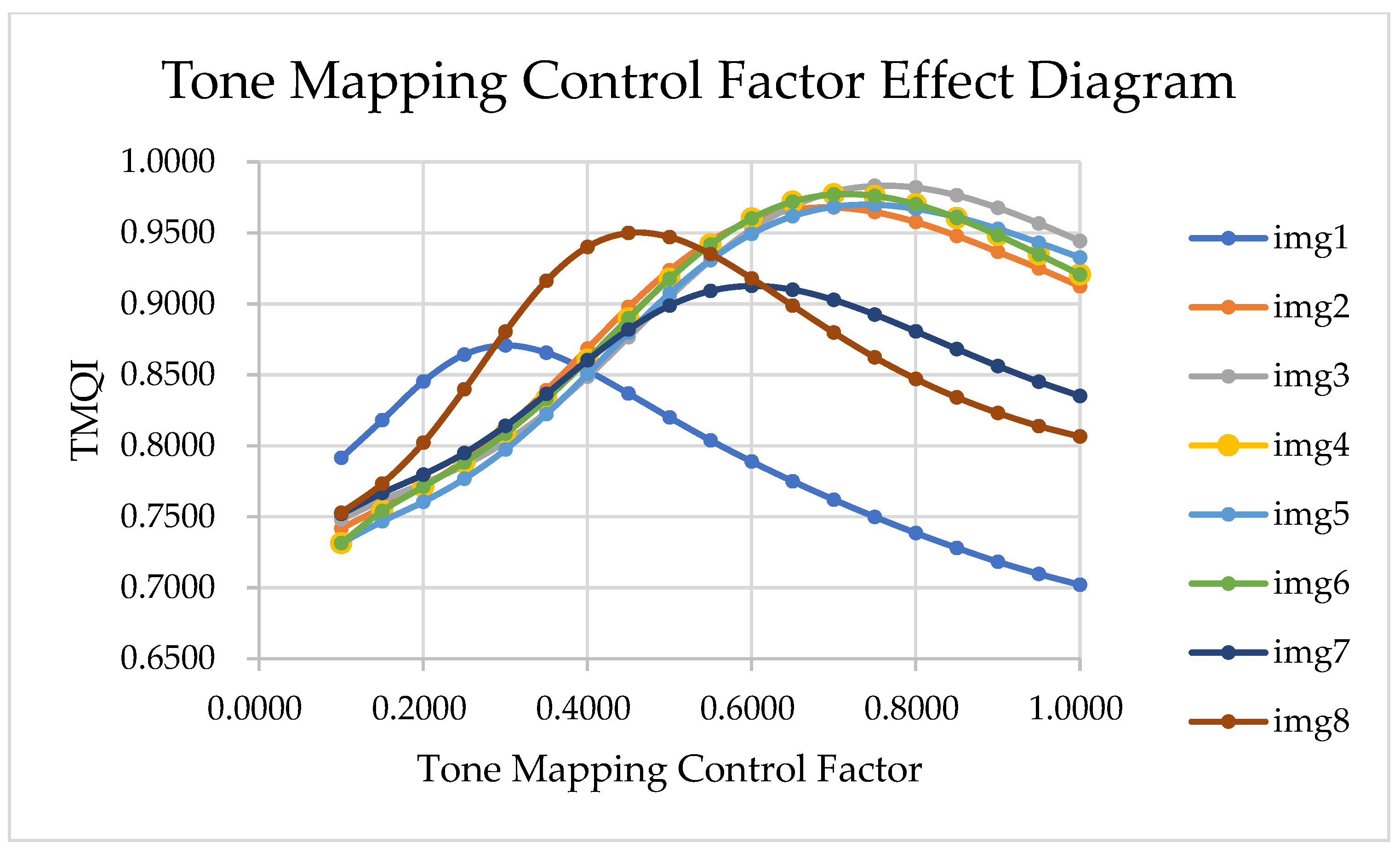
We evaluated our design using the HDR-EYE dataset and specialized HDR test datasets. Compared to other state-of-the-art methods, our work demonstrated exceptional image quality and structural similarity, as measured by metrics such as the TMQI, PSNR, and SSIM. These results validate the robustness and reliability of the proposed processor.
Finally, the hardware implementation of our processor on the Xilinx XCVU9P FPGA platform shows that it consumes fewer hardware resources, such as LUTs and registers, compared to other advanced designs. Additionally, the fully pipelined architecture operates at a high clock frequency, enabling real-time processing of high-resolution videos, offering significant performance advantages over existing solutions.
Compared to prior works in
Table 4, our method achieves superior hardware efficiency and image quality through three key innovations:
Hardware-Algorithm Co-optimization: Unlike [
13] (global–local histogram equalization) and [
16] (logarithmic number system), we unify adaptive exposure control (
Section 2.1.8) with bilateral filtering (
Section 3.2) to minimize halo artifacts while enabling fully pipelined 4K processing. This contrasts with [
14]’s WDR sensor-specific bitstream processing, which lacks exposure adaptability.
Transcendental Function Acceleration: While [
12,
15] rely on polynomial approximations, our high-radix Taylor expansions (
Section 3.3 and
Section 3.4) reduce floating-point operation latency by 40% versus traditional methods, enabling 246.9 MHz throughput.
Image Quality and Efficiency: Our TMQI (0.9314) exceeds DL-based DeepTMO [
8] (0.88) and hardware solutions [
16] (0.9527 for single-image), while using 43% fewer LUTs than [
13]. This demonstrates our balanced optimization of perceptual quality and resource efficiency.
In conclusion, our adaptive processor addresses the challenges of HDR tone mapping and demonstrates outstanding performance in image quality, computational efficiency, and resource utilization.