1. Introduction
As public health awareness grows, more and more people are engaging in physical exercise. Monitoring physiological indicators is crucial for assessing individual health status and developing personalized exercise plans. Currently, smart wearable devices (such as smart clothing and smart insoles) can monitor exercise-related data, including gait and posture, thereby helping to enhance athletic performance and prevent injuries. Although a range of smart wearable devices have been developed to monitor physical activity metrics such as gait and posture, most commercial solutions do not support real-time monitoring of respiratory signals [
1]. While some advanced prototypes have demonstrated potential in detecting respiratory-related metrics, these technologies remain immature or have not been widely adopted by the general consumer market. As a result, most current devices cannot reliably monitor respiration, including both the physical process of breathing (air moving in and out of the lungs) and respiratory rate (the number of breaths per minute). While breathing describes the mechanical act of ventilation, respiratory rate quantifies its frequency, and both provide distinct yet complementary insights into exercise intensity and physiological load.
Respiration, alongside heart rate, plays a vital role in evaluating physiological states during physical activity [
2]. While heart rate reflects cardiovascular response and exercise intensity, respiratory patterns offer unique insights into ventilation efficiency, metabolic demand, and fatigue accumulation. For example, an abnormal breathing rhythm may indicate overexertion, ventilatory inefficiency, or insufficient oxygen uptake [
3]. Therefore, combining respiratory monitoring with heart rate tracking enables a more comprehensive assessment of an individual’s physical condition and supports the design of adaptive training strategies. However, accurately capturing respiratory signals during exercise remains technically challenging due to various real-world interferences.
We propose a novel physiological monitoring approach based on in-ear audio perception. By capturing subtle physiological signals from within the ear canal, this method enables real-time and non-invasive monitoring of both respiration and heart rate. The ear canal provides a structurally enclosed and stable environment, which enhances the detection of low-frequency physiological vibrations and lays a robust foundation for our audio-based monitoring system [
4].
Compared with traditional physiological monitoring methods such as photoplethysmography (PPG) or chest bands, audio-based sensing offers several notable advantages. First, it is non-invasive and does not require direct contact with the skin, avoiding signal instability caused by sweat or movement. Second, the ear canal provides a relatively enclosed and consistent structural environment, which improves the detectability of low-frequency physiological signals. Moreover, many consumer-grade earphones and headsets are already equipped with built-in microphones, making the method highly accessible and cost-effective [
5]. Taken together, these advantages make audio-based measurement especially suitable for real-time monitoring during exercise.
At present, most physiological indicator monitoring solutions still rely heavily on a quiet environment, which places high demands on device performance and usage scenarios. Therefore, when respiration and heart rate monitoring are extended to sports contexts, a series of technical challenges arise. First, because the structure of the ear canal opening varies from person to person, the wearing tightness differs between users, and even the same user may exhibit inconsistent wearing conditions over time. This fluctuation in tightness directly affects the quality of signal acquisition, leading to potential errors in the system. Second, the amplitude of physiological signals related to respiration and heart rate is small and can be easily masked by other noises. During exercise, noise sources include both motion artifacts generated by human movement and ambient environmental interference, which complicates the extraction of clear and reliable physiological signals [
6]. Finally, due to the lack of sufficient reference data, it remains technically challenging to segment and interpret the breathing process accurately.
Given the above problems, we propose an audio-based physiological monitoring method that uses an active noise-canceling headset to collect sound from the ear canal to monitor breathing and heart rate in real-time. This method not only fills the gap in existing respiratory monitoring but also proposes a brand-new heart rate detection method. Specifically, this study combines audio signal processing, an improved NMF algorithm, and a bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM)-based respiratory detection module to extract effective physiological signals from the mixed audio generated during exercise. This method is non-invasive, portable, and real-time, providing a new solution for physiological monitoring in sports scenarios. The main contributions and innovations are as follows:
An audio segment extraction method based on autocorrelation technology is proposed to select discrete audio segments with obvious periodic characteristics from long audio. The overall physiological state is measured by analyzing discrete audio segments that are continuous in time, which effectively overcomes the impact of individual differences and changes in wearing status on signal stability.
Based on an improved non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) algorithm, the audio separation method can effectively separate physiological signals from noise, significantly reducing the impact of signal aliasing and noise interference.
Based on a two-step respiratory phase detection model, it can accurately identify and classify respiratory phases, providing new ideas and solutions for developing respiratory monitoring.
The paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 reviews existing physiological monitoring methods, analyzing their strengths and limitations;
Section 3 introduces the system architecture, including data preprocessing, NMF-based audio separation, and BiLSTM-based phase detection.
Section 4 details the improved NMF algorithm, covering signal decomposition, cost function optimization, and iterative updates.
Section 5 presents the BiLSTM-based breathing model with convolutional neural network (CNN)-enhanced detection.
Section 6 evaluates the NMF-based audio separation, validates the BiLSTM breathing model, and analyzes system robustness across environments, exercise intensities, body weights, and ground conditions, and
Section 7 concludes with findings, limitations, and future directions.
3. Overview
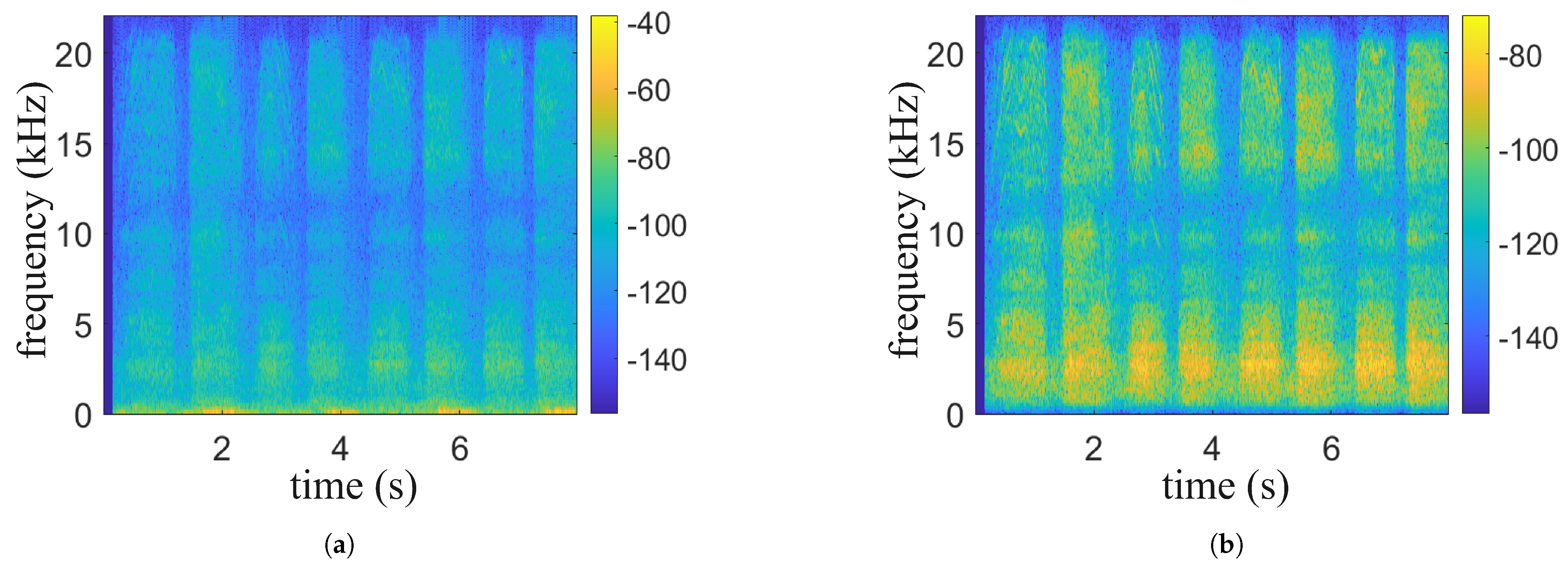
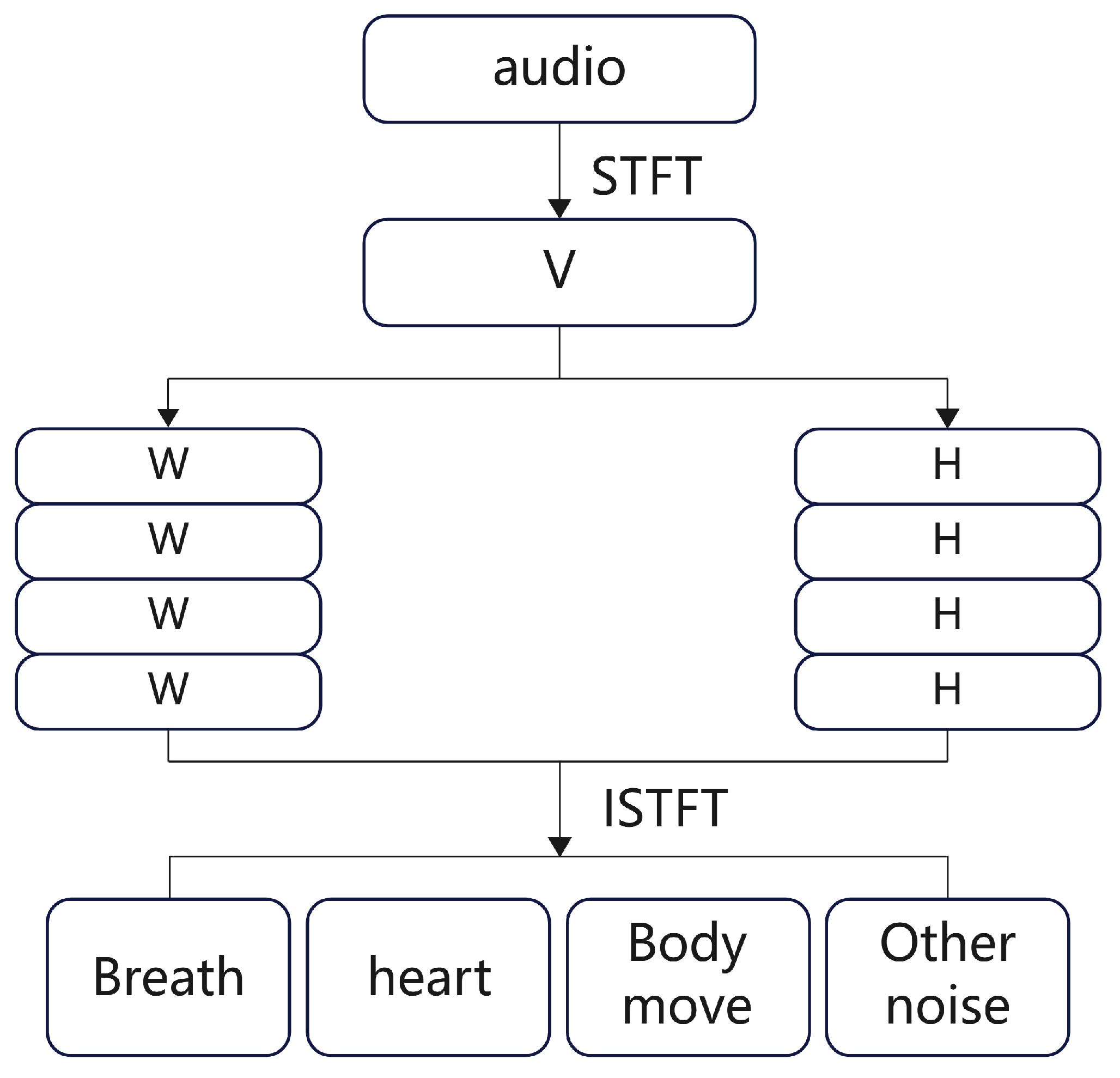
We propose a physiological signal monitoring system based on the built-in microphone of active noise-canceling headphones, which acquires physiological signals such as respiration and heartbeat as well as motion noise by collecting sound from the ear canal. The system consists of data preprocessing, an audio separation algorithm, respiratory phase detection, respiratory frequency and heart rate calculation, and experimental evaluation, as shown in
Figure 1.
The signals collected by the headset include breathing, heartbeat, and movement noise. Data preprocessing first uses bandpass filtering to remove noise and uses envelope extraction and periodicity analysis to select high-quality audio segments. In the audio separation stage, an improved NMF algorithm is combined with a standard source template matching method to separate breathing, heartbeat, and noise, and the signal is restored by inverse Fourier transform. In the signal reprocessing stage, a BiLSTM neural network is used for respiratory phase detection, which divides the respiratory signal into inhalation, exhalation, and pause, and then calculates the respiratory rate and heart rate to evaluate the intensity of exercise.
5. BiLSTM-Based Breathing Monitoring Algorithm
A complete breathing cycle can be divided into four stages: inhalation, inhalation pause, exhalation, and exhalation pause. Among these, apnoea does not need to be distinguished separately, so it is only divided into three stages: inhalation, exhalation, and pause. We propose a respiration monitoring algorithm based on a BiLSTM neural network that includes a respiration extraction module and a respiration phase detection module. It can further extract features from the audio clips with previously separated signal characteristics, accurately classify breathing phases, and thus achieve a fine-grained assessment of breathing as a physiological indicator.
5.1. Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
Respiratory parameters can measure the dynamic changes in breathing and can be used to distinguish respiratory audio from other sounds [
28]. The core task of the feature extraction module is to extract key features to effectively distinguish between respiratory and non-respiratory audio, so not all respiratory parameters are suitable.
MFCC (Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients) is inspired by the human ear’s perception of sound. The human ear does not perceive frequencies linearly, but is more sensitive to low frequencies and relatively less sensitive to high frequencies, as shown in Equation (
9). The Mel filter bank is designed to simulate this non-linear characteristic so that the MFCC is closer to the human ear’s auditory perception and thus more accurately captures the frequency distribution of the respiratory signal. Therefore, we chose MFCC and logMel as the main features to improve the representation of the respiratory signals.
After framing and applying a window to the extracted audio segments that meet the signal characteristics, a Fourier transform is performed to obtain the power spectrum, given by
, where
represents the signal frame and
w is the Hamming window. Then,
is passed through a set of Mel filters to calculate the MFCC coefficients, as shown in Equation (
10):
where
represents the
i-th MFCC coefficient,
denotes the
m-th MFCC component, and
is the DCT coefficient.
logMel is used to compensate for the missing coefficients in the MFCC calculation, including the differential and acceleration coefficients, as shown in Equation (
11). Here logMel
represents the logarithmic transformation of the power spectrum mapped onto the Mel scale. The denominator “1.0” is introduced to prevent zero values in logarithmic operations, thus ensuring computational stability.
5.2. Breathing Detection Model
We have developed a two-stage breathing detection model to achieve breathing phase detection. The model consists of two modules: the Breath Extraction Module (BEM) filters out non-breathing noise, and the Breath Phase Detection Module (BPDM) identifies different breathing phases (inhalation, exhalation, pause).
5.2.1. Breath Extraction Module
The Breath Extraction Module uses a convolutional neural network to recognize segments of breath sounds and distinguish them from other sounds in the environment.
We use a single-layer CNN to extract information from the acoustic features of the entire audio clip. The convolutional layer operates on the spectrogram converted from the acoustic features and extracts local patterns by multiplying the filter over the entire image. As shown in
Figure 6, we apply 10 filters of size
, use the ReLU activation function to accelerate the convergence of gradient descent, and use a fully connected layer with a softmax function to output a probability distribution.
5.2.2. Breathing Phases Detection Module
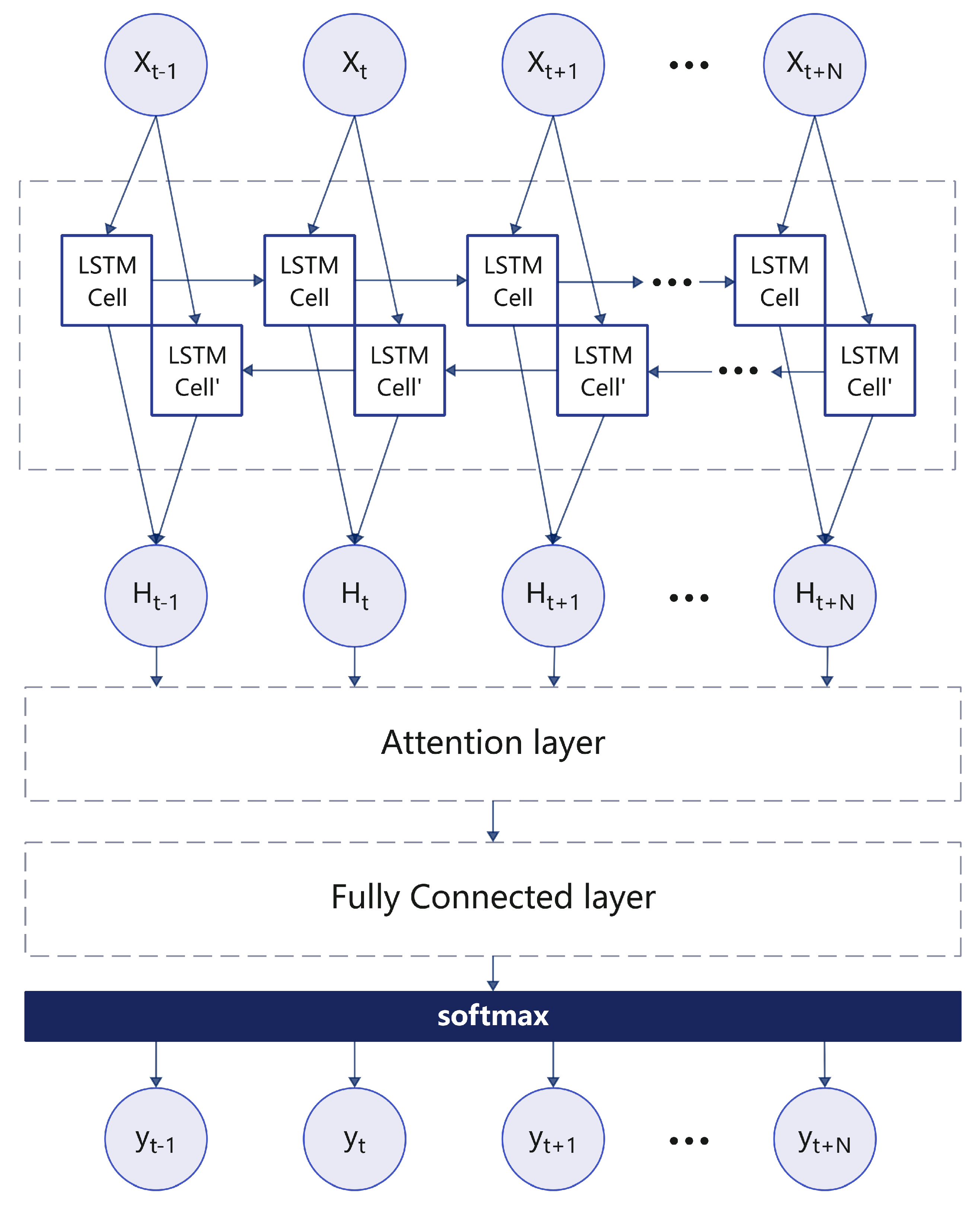
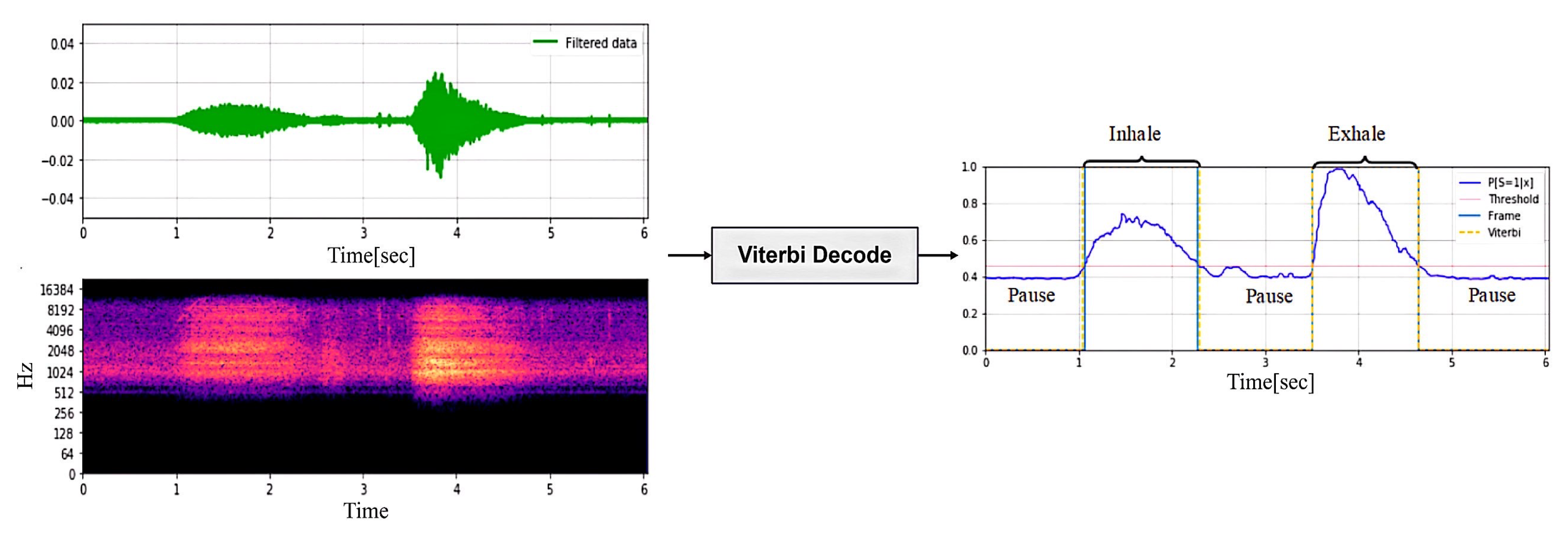
In this module, we train a real-time detection model to continuously monitor the breathing phase. The system begins to detect the respiratory phase after the respiratory signal passes through the BEM module. Since the audio characteristics of the inhalation and exhalation phases are similar, it is difficult to distinguish between the two. Therefore, this paper proposes a BiLSTM neural network based on an attention mechanism to detect and evaluate the breathing phase. First, the breathing phases (inspiration, inspiration pause, exhalation, and exhalation pause) of each breathing cycle are labeled using the Viterbi decoding algorithm in the training dataset. For indistinguishable phases, the data can be discarded directly.
We input each time step of the 44 ms respiratory signal. If the duration of an inhalation, exhalation, or pause is greater than or equal to 1 s, it is considered a complete breathing phase, which corresponds to a sequence of 87 samples, which is sufficient to characterize the complete breathing process. Therefore, the bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM) architecture combines the contribution of forward units to the current hidden state and the modelling of future information by backward units, allowing the model to take full advantage of the time dependence in the entire sequence, thereby improving the modelling and analysis of respiratory signals, as shown in
Figure 7.
The attention-based LSTM model introduces an attention mechanism to enhance the network’s memory of sequence context. As shown in Equation (
12).
Where t represents the current time step, denotes the attention weight of input at time step t, and the align function calculates the matching degree between input and output using a single-layer feedforward network. Then, the fully connected layer aggregates the output from the attention layer, and the softmax function computes the class probabilities.
The BiLSTM neural network-based real-time respiratory monitoring algorithm can continuously identify respiratory phases. By statistically analyzing the network output, respiratory ratio and respiratory frequency can be calculated.
7. Conclusions and Future Work
We have developed an Android app called “Hearing” that can monitor breathing and heart rate in real-time during exercise through the built-in microphone of active noise-cancelling headphones, and provide post-exercise analysis. To reduce interference from environmental and exercise noise, we propose an audio separation algorithm based on improved NMF to extract breathing and heartbeat signals from the mixed audio and reconstruct them using the Fourier inverse transform. The breathing process is divided into three stages: inhalation, exhalation, and pause. The BiLSTM algorithm is used to segment and classify the audio, thereby calculating the breathing frequency and ratio. The heartbeat signal is extracted by frame segmentation and windowing to calculate the heart rate. Compared to a single exercise index, the combination of breathing and heart rate can more accurately evaluate the exercise effect.
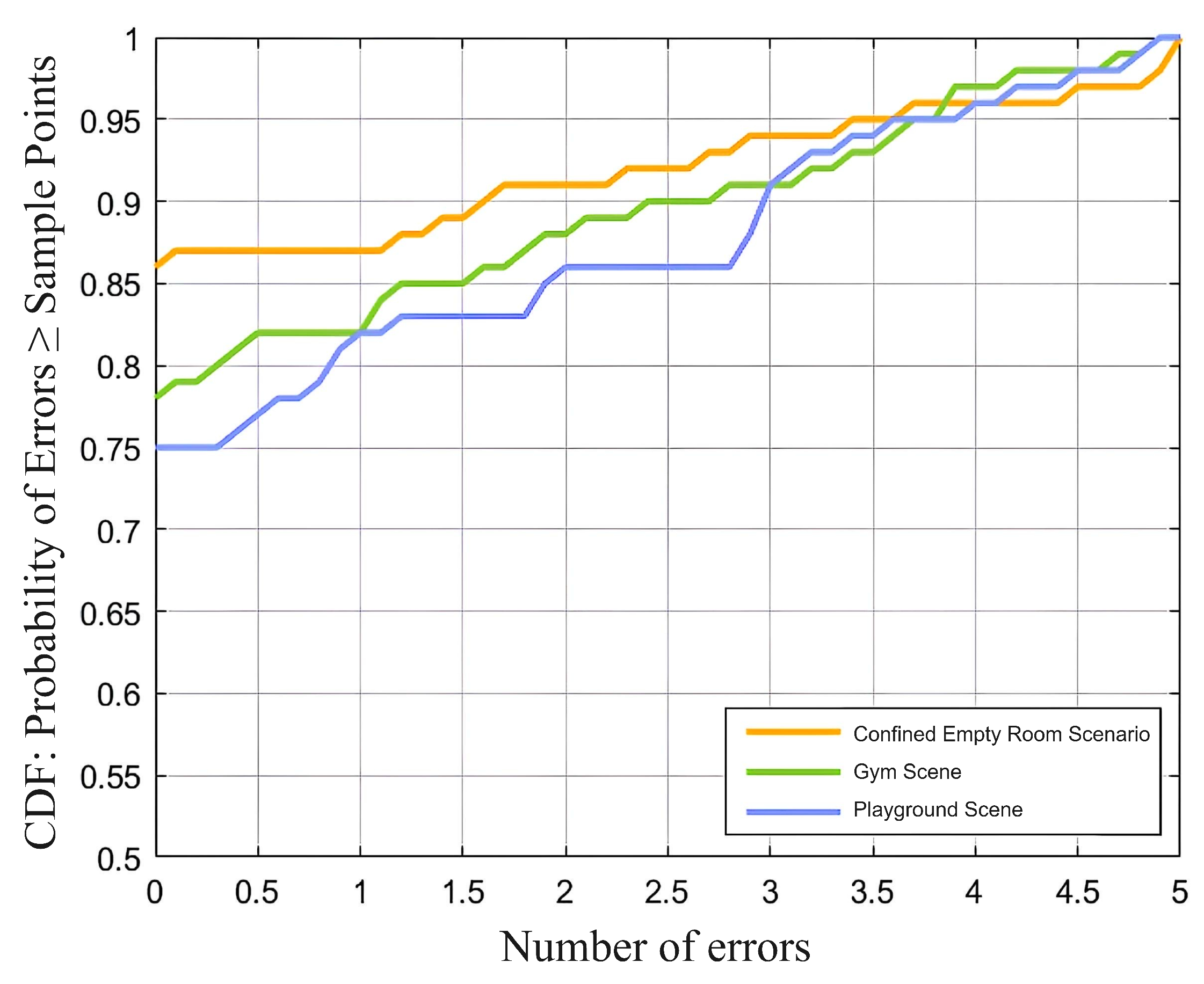
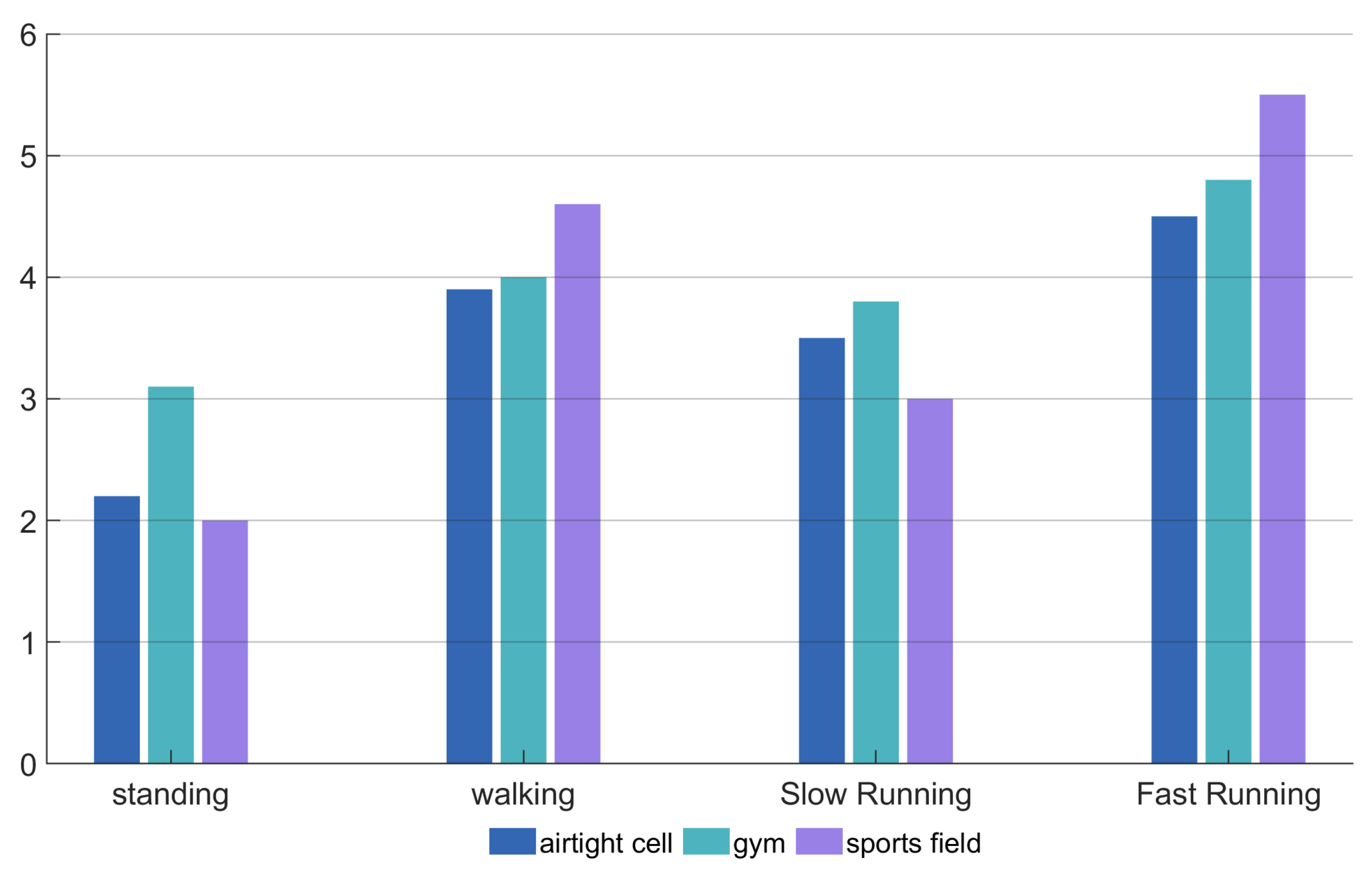
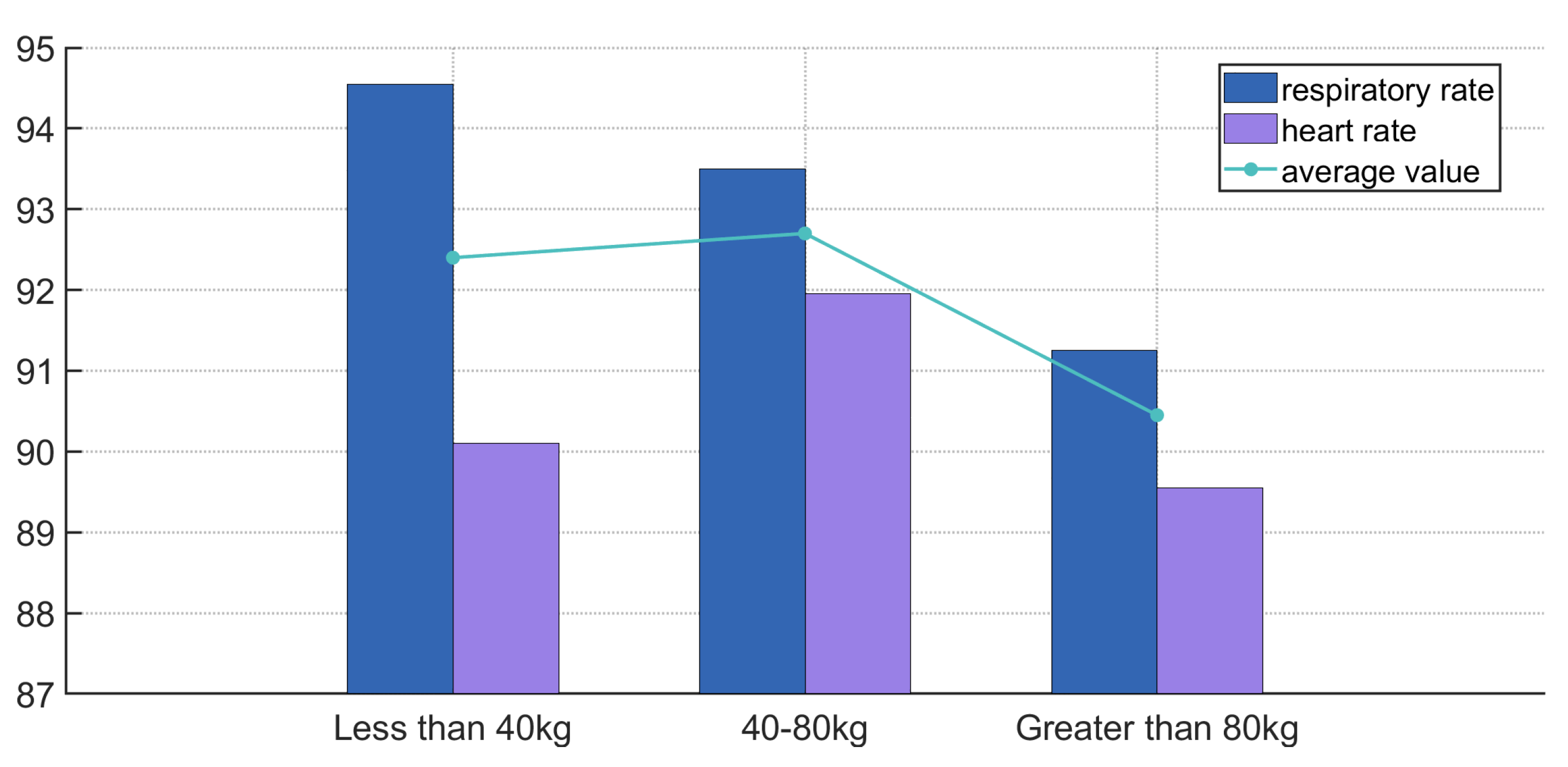
The system was tested in four exercise modes (standing, walking, jogging, and running) and three types of venues (indoor, playground, and gym), with an average accuracy of 91%, demonstrating good robustness and effectiveness. Future research will further optimize noise reduction algorithms, improve the quality of heartbeat signal separation, and explore the impact of multiple exercise types on physiological monitoring to enhance the system’s adaptability and stability in complex environments.
In future work, efforts will be directed toward addressing the accuracy fluctuations observed under varying exercise conditions. Specifically, improvements will focus on enhancing the mechanical stability of the in-ear sensor to reduce motion-induced signal distortion, refining signal processing techniques to better suppress environmental noise, and adapting the system to accommodate irregular breathing patterns. Additionally, future research will include expanding the experimental dataset to cover a broader range of activities and user profiles, thereby improving the robustness and generalizability of the system in diverse, real-world health monitoring scenarios.