Lepidium virginicum Water-Soluble Chlorophyll-Binding Protein with Chlorophyll A as a Novel Contrast Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging
Abstract
Highlights
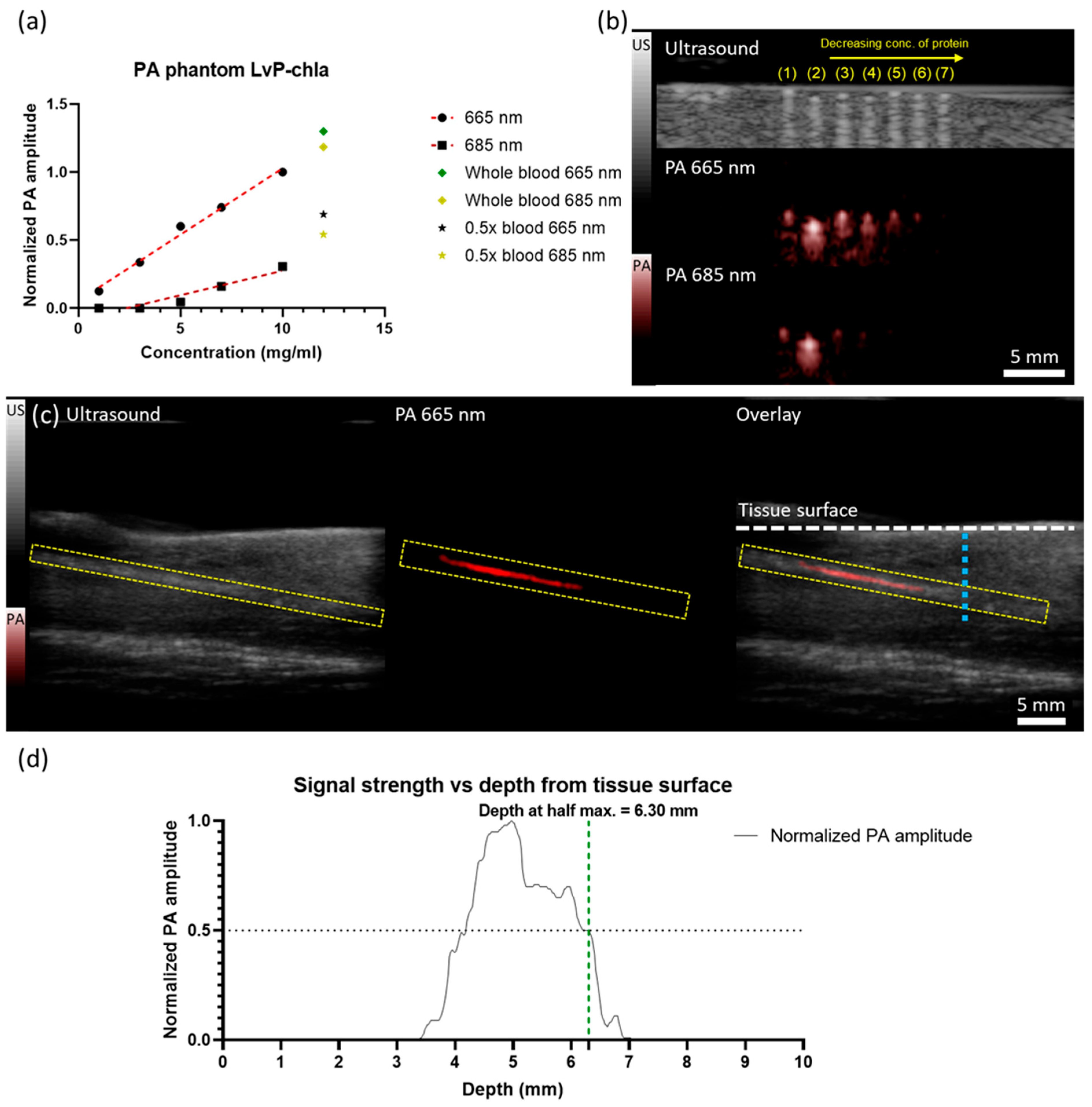
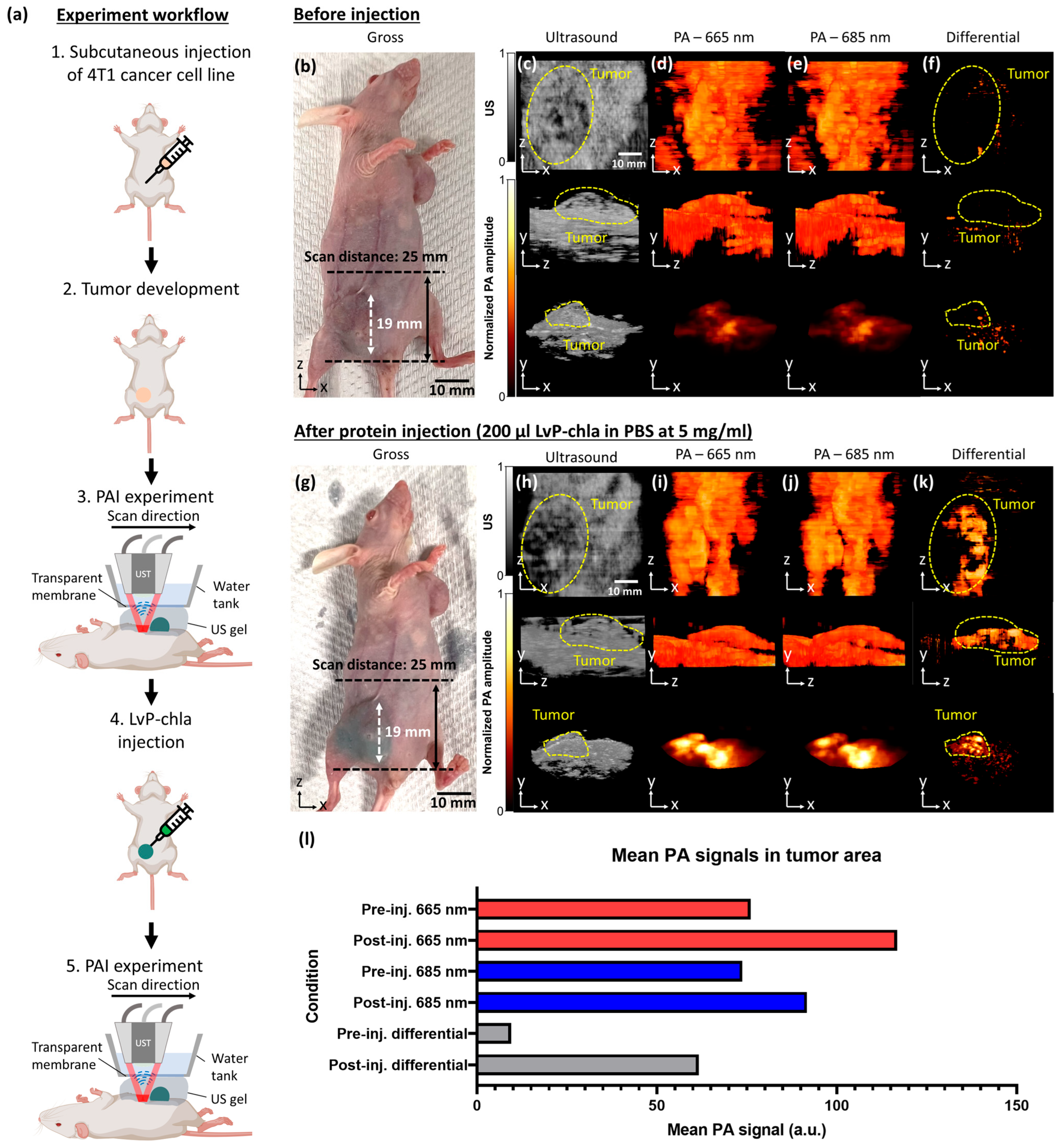
- LvP-chla exhibits a high molar extinction coefficient (59,716 M−1cm−1 at 665 nm), linear PA signal generation, and effective tumor visualization in a 4T1 mouse model with a penetration depth of 6.30 mm.
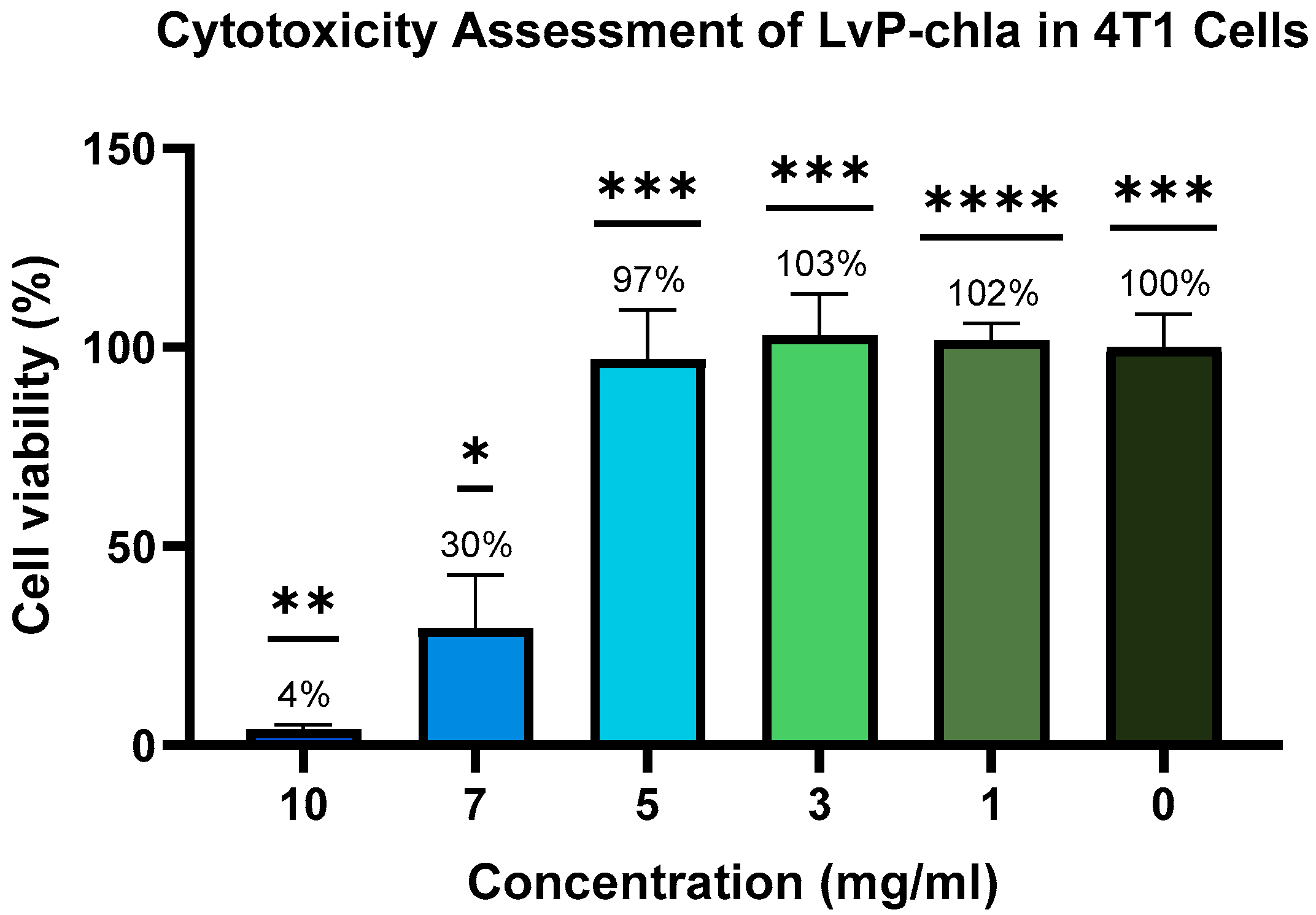
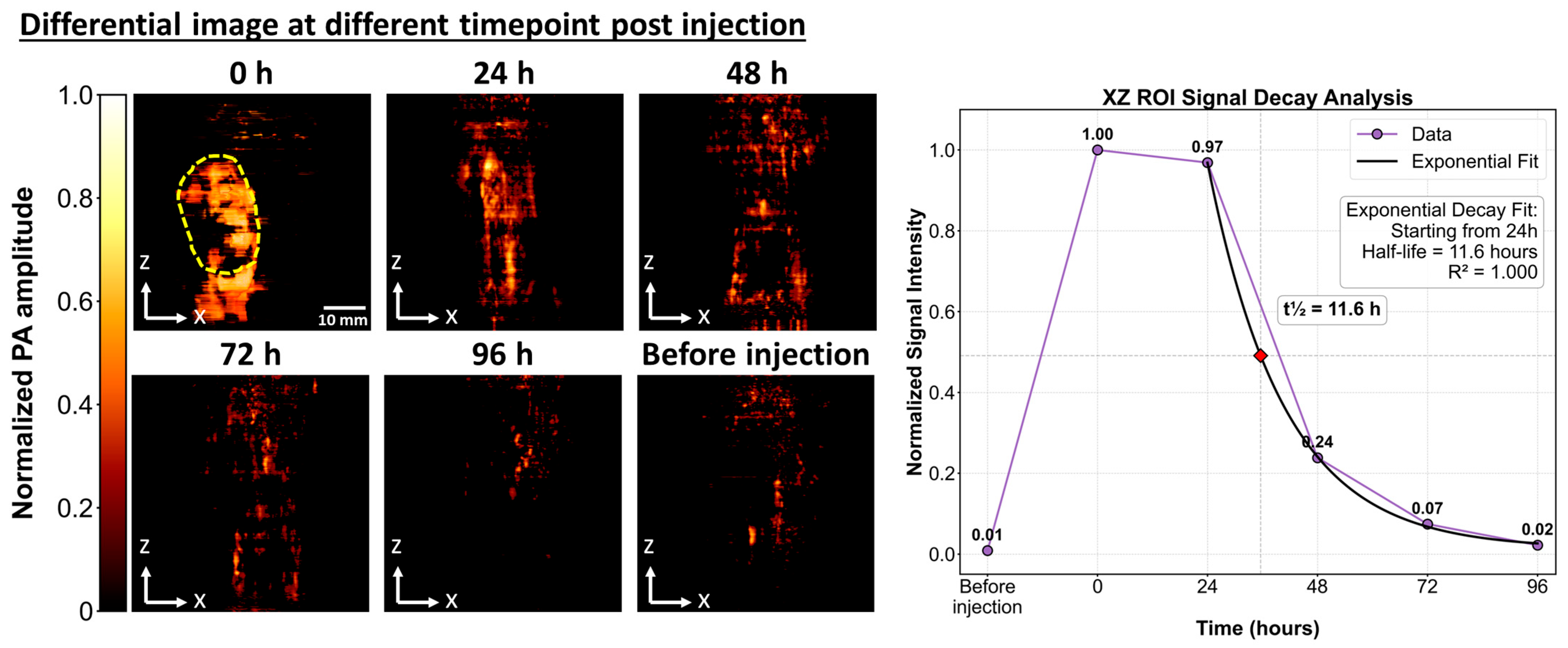
- In vitro cytotoxicity testing showed high cell viability at 5 mg/mL with no in vivo adverse effects, and clearance within 96 h, confirming biocompatibility.
- LvP-chla offers a stable and biocompatible contrast agent for PAI.
- The straightforward synthesis and efficient clearance of LvP-chla make it a promising candidate for clinical translation in non-invasive diagnostics.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Contrast Agent Synthesis
2.1.1. Gene Construction and Expression of LvP
2.1.2. Reconstitution of LvP with Chla
2.1.3. Protein Purification
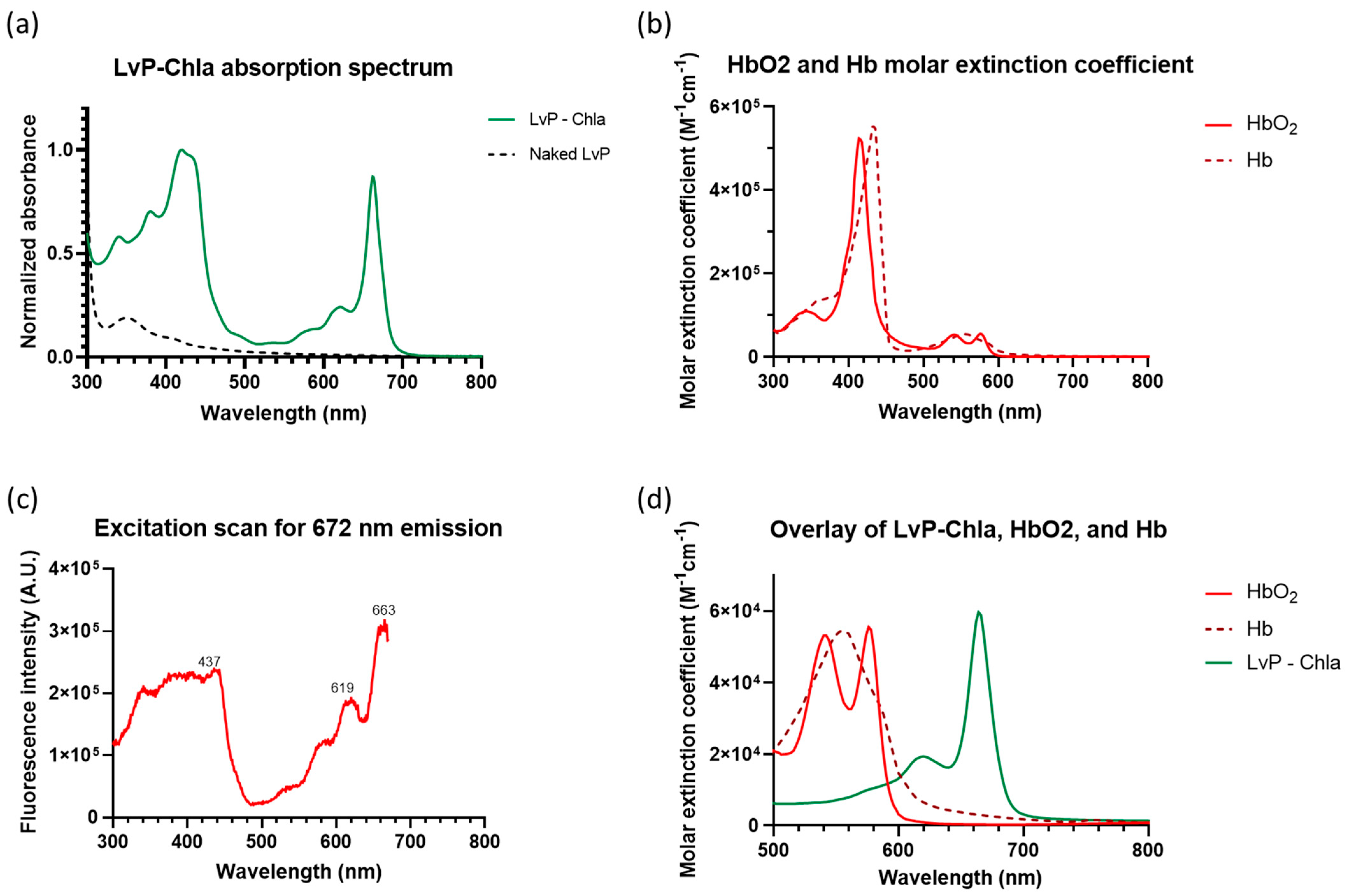
2.1.4. Spectral Measurement
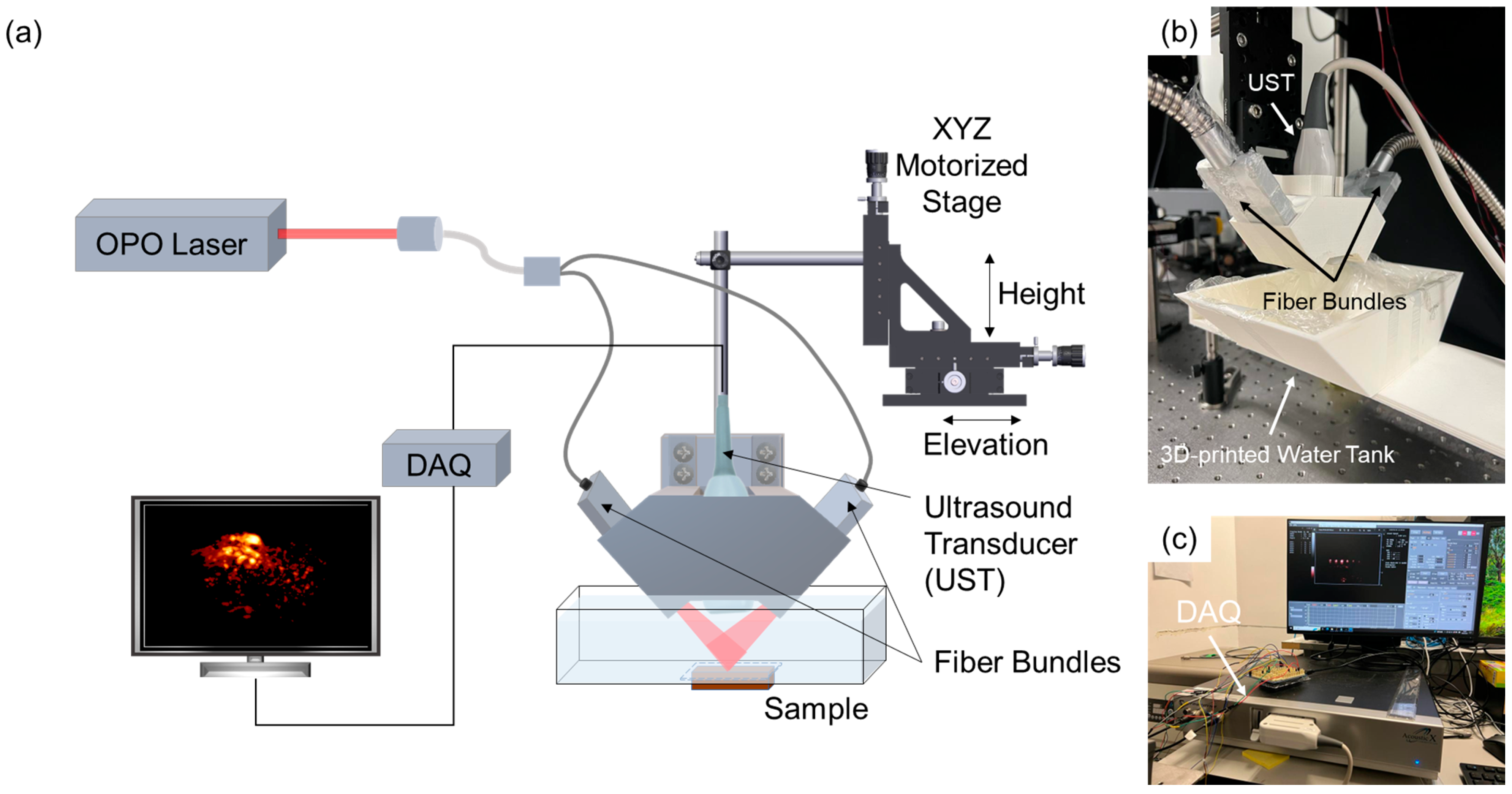
2.2. PAI Setup
2.3. Phantom Imaging
2.4. Animal Imaging
2.4.1. Tumor Mouse Model
2.4.2. Image Acquisition
2.5. Toxicity Test
2.5.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5.2. Histology Study
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PA | Photoacoustic |
| PAI | Photoacoustic imaging |
| WSCP | Water-soluble chlorophyll-binding protein |
| LvP | Lepidium virginicum Protein |
| chla | Chlorophyll a |
| LvP-chla | LvP protein reconstituted with chlorophyll a |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| PLQY | Photoluminescence quantum yield |
| FWHM | Full width at half maximum |
| EPR | Enhanced permeability and retention |
| OPO | Optical parametric oscillator |
| DAQ | Data acquisition system |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| UST | Ultrasound transducer |
| KXS | Ketamine/xylazine/saline |
References
- Xu, M.; Wang, L.V. Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 41101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.V. Photoacoustic microscopy and computed tomography. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 14, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riksen, J.J.M.; Nikolaev, A.V.; van Soest, G. Photoacoustic imaging on its way toward clinical utility: A tutorial review focusing on practical application in medicine. J. Biomed. Opt. 2023, 28, 121205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Beard, P.C.; Bohndiek, S.E. Contrast agents for molecular photoacoustic imaging. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, R.E.; Rochford, J. Molecular Photoacoustic Contrast Agents: Design Principles & Applications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 1175–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, V.T.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.T.W. A review of endogenous and exogenous contrast agents used in photoacoustic tomography with different sensing configurations. Sensors 2020, 20, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglieri, E.; Gutt, A.; Gärtner, W.; Schubert, L.; Viappiani, C.; Abbruzzetti, S.; Losi, A. Dynamics and efficiency of photoswitching in biliverdin-binding phytochromes. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 2484–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Kaberniuk, A.A.; Li, L.; Shcherbakova, D.M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Wang, L.V. Multiscale photoacoustic tomography using reversibly switchable bacterial phytochrome as a near-infrared photochromic probe. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Z.R.; Lin, Q.-F.; Liu, C.; Gao, F.; Lin, C.; Zhang, S.; Deng, H.; Mayoral, A.; Fan, W.; et al. Reversibly Photoswitchable Protein Assemblies with Collagen Affinity for In Vivo Photoacoustic Imaging of Tumors. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadn8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shemetov, A.A.; Baloban, M.; Hu, P.; Zhu, L.; Shcherbakova, D.M.; Zhang, R.; Shi, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.V.; et al. Small near-infrared photochromic protein for photoacoustic multi-contrast imaging and detection of protein interactions in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzella, F.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A.; Losi, A.; Gärtner, W.; Abbruzzetti, S.; Viappiani, C. A red-green photochromic bacterial protein as a new contrast agent for improved photoacoustic imaging. Photoacoustics 2022, 26, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Yanai, H.; Oka-Takayama, Y.; Zanma-Sohtome, A.; Fujiyama, K.; Uchida, A.; Nakayama, K.; Satoh, H. Molecular cloning, characterization and analysis of the intracellular localization of a water-soluble chlorophyll-binding protein (WSCP) from Virginia pepperweed (Lepidium virginicum), a unique WSCP that preferentially binds chlorophyll b in vitro. Planta 2013, 238, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, D.M.; Agostini, A.; Tenzer, S.; Gloeckle, B.M.; Werwie, M.; Carbonera, D.; Paulsen, H. Water-Soluble Chlorophyll Protein (WSCP) Stably Binds Two or Four Chlorophylls. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotewicz, K.; Tang, S.; Edman, L.; Wang, E. Mild and Efficient Extraction of Fluorescent Chlorophyll a from Spinach Leaves for Application as the Sustainable Emitter in Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells. ChemElectroChem 2024, 11, e202300629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, D.M.; Agostini, A.; Averesch, V.; Girr, P.; Werwie, M.; Takahashi, S.; Satoh, H.; Jaenicke, E.; Paulsen, H. Chlorophyll a/b binding-specificity in water-soluble chlorophyll protein. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, D.M.; Agostini, A.; Pohland, A.-C.; Werwie, M.; Jaenicke, E.; Paulsen, H. Stability of Water-Soluble Chlorophyll Protein (WSCP) Depends on Phytyl Conformation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7971–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Park, B.M.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, F. Controlling synthetic membraneless organelles by a red-light-dependent singlet oxygen-generating protein. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, B.; Chan, S.C.; Tsang, V.T.; Wong, T.T. Tri-modality in vivo imaging for tumor detection with combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and photoacoustic elastography. Photoacoustics 2024, 38, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanenko, O.V.; Stepanenko, O.V.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Shcherbakova, D.M.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Turoverov, K.K. Interaction of biliverdin chromophore with near-infrared fluorescent protein BphP1-FP engineered from bacterial phytochrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegiel, B.; Baty, C.J.; Gallo, D.; Csizmadia, E.; Scott, J.R.; Akhavan, A.; Chin, B.Y.; Kaczmarek, E.; Alam, J.; Bach, F.H.; et al. Cell surface biliverdin reductase mediates biliverdin-induced anti-inflammatory effects via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21369–21378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Tse, B.W.-C.; Yang, H.; Thorling, C.A.; Liu, Y.; Touraud, M.; Chouane, J.B.; Liu, X.; Roberts, M.S.; et al. Indocyanine green-incorporating nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1227–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Tang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, Z. Nano-sized indocyanine green j-aggregate as a one-component theranostic agent. Nanotheranostics 2017, 1, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleeva, Y.V.; Neverov, K.V.; Obukhov, Y.N.; Kritsky, M.S. Water Soluble Chlorophyll-Binding Proteins of Plants: Structure, Properties and Functions. Mol. Biol. 2019, 53, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girr, P.; Kilper, J.; Pohland, A.-C.; Paulsen, H. The pigment binding behaviour of water-soluble chlorophyll protein (WSCP). Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, S.; Gräslund, T.; Eriksson Karlström, A.; Frejd, F.Y.; Nygren, P.-Å.; Löfblom, J. Affibody Molecules in Biotechnological and Medical Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 691–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfblom, J.; Feldwisch, J.; Tolmachev, V.; Carlsson, J.; Ståhl, S.; Frejd, F.Y. Affibody molecules: Engineered proteins for therapeutic, diagnostic and biotechnological applications. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2670–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Fufezan, C.; Krieger-Liszkay, A.; Satoh, H.; Paulsen, H. Recombinant water-soluble chlorophyll protein from Brassica oleracea var. Botrys binds various chlorophyll derivatives. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 7427–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.-I.; Tamiaki, H. Synthesis and optical properties of bacteriochlorophyll-a derivatives having various C3 substituents on the bacteriochlorin π-system. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 2648–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anda, A.; Hansen, T.; De Vico, L. Qy and Qx Absorption Bands for Bacteriochlorophyll a Molecules from LH2 and LH3. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 5283–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, B.; Porra, R.J.; Scheer, H. Chlorophylls and Bacteriochlorophylls; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsang, V.T.C.; Kim, H.H.; Huang, B.; Chan, S.C.K.; Wong, T.T.W. Lepidium virginicum Water-Soluble Chlorophyll-Binding Protein with Chlorophyll A as a Novel Contrast Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging. Sensors 2025, 25, 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113492
Tsang VTC, Kim HH, Huang B, Chan SCK, Wong TTW. Lepidium virginicum Water-Soluble Chlorophyll-Binding Protein with Chlorophyll A as a Novel Contrast Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113492
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsang, Victor T. C., Hannah H. Kim, Bingxin Huang, Simon C. K. Chan, and Terence T. W. Wong. 2025. "Lepidium virginicum Water-Soluble Chlorophyll-Binding Protein with Chlorophyll A as a Novel Contrast Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113492
APA StyleTsang, V. T. C., Kim, H. H., Huang, B., Chan, S. C. K., & Wong, T. T. W. (2025). Lepidium virginicum Water-Soluble Chlorophyll-Binding Protein with Chlorophyll A as a Novel Contrast Agent for Photoacoustic Imaging. Sensors, 25(11), 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113492






