A Rhodamine B-Based “Turn-On” Fluorescent Probe for Selective Fe3+ Ions Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of RhB-DCT Fluorescent Probe
2.3. Characterization and Instruments
3. Results and Discussion
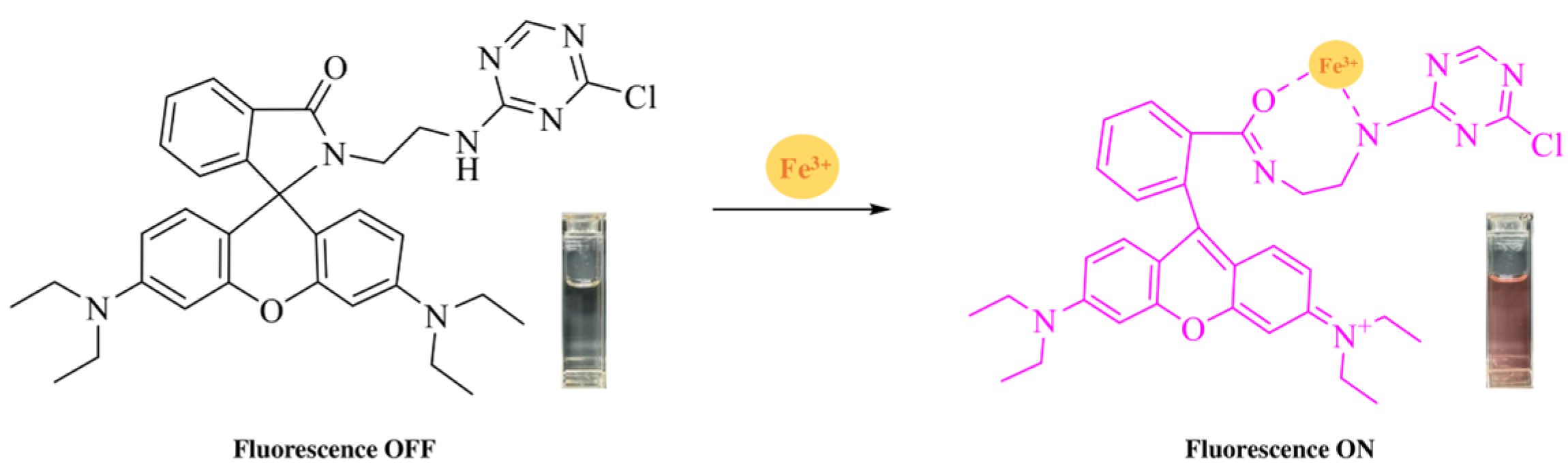
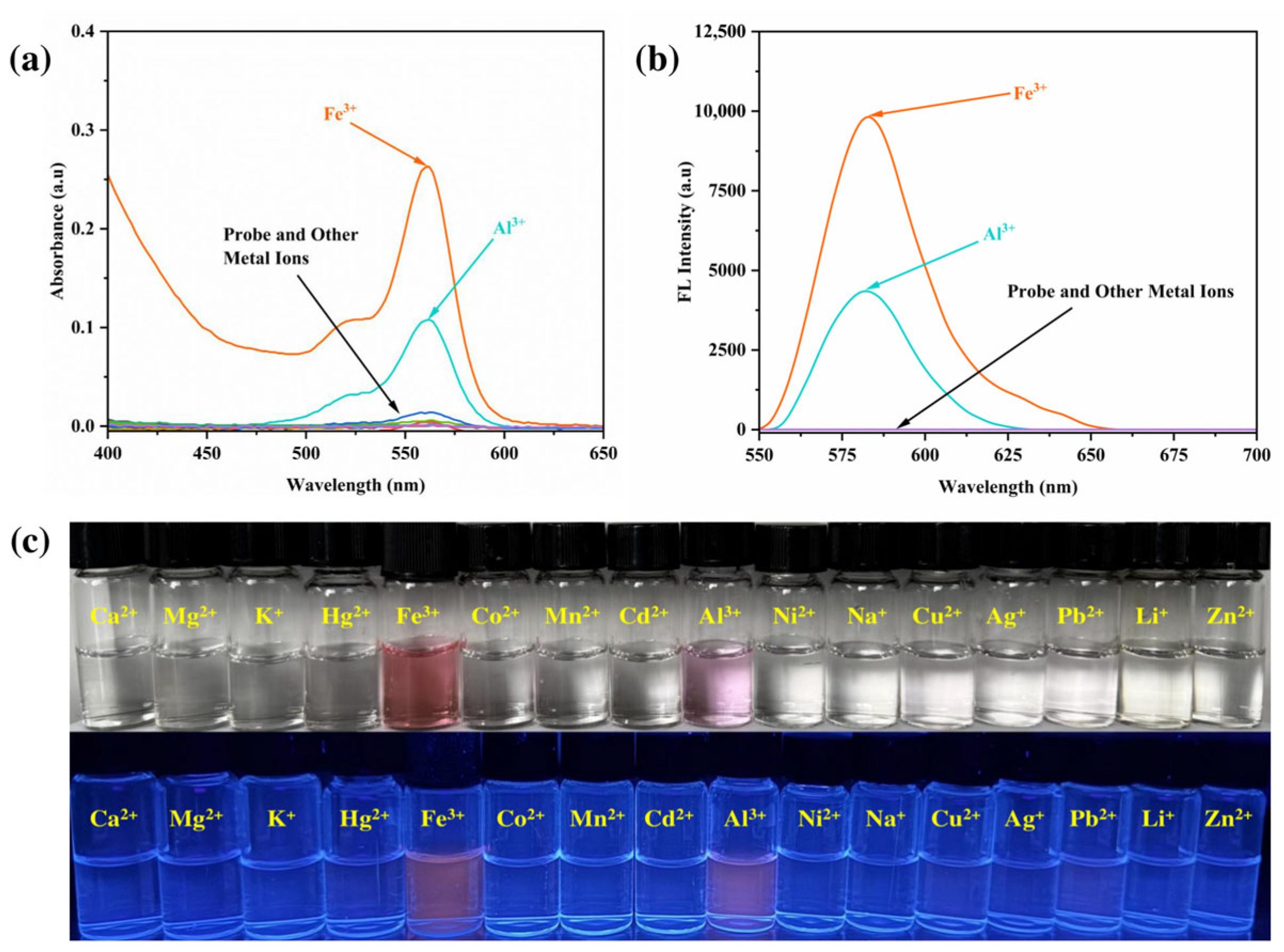
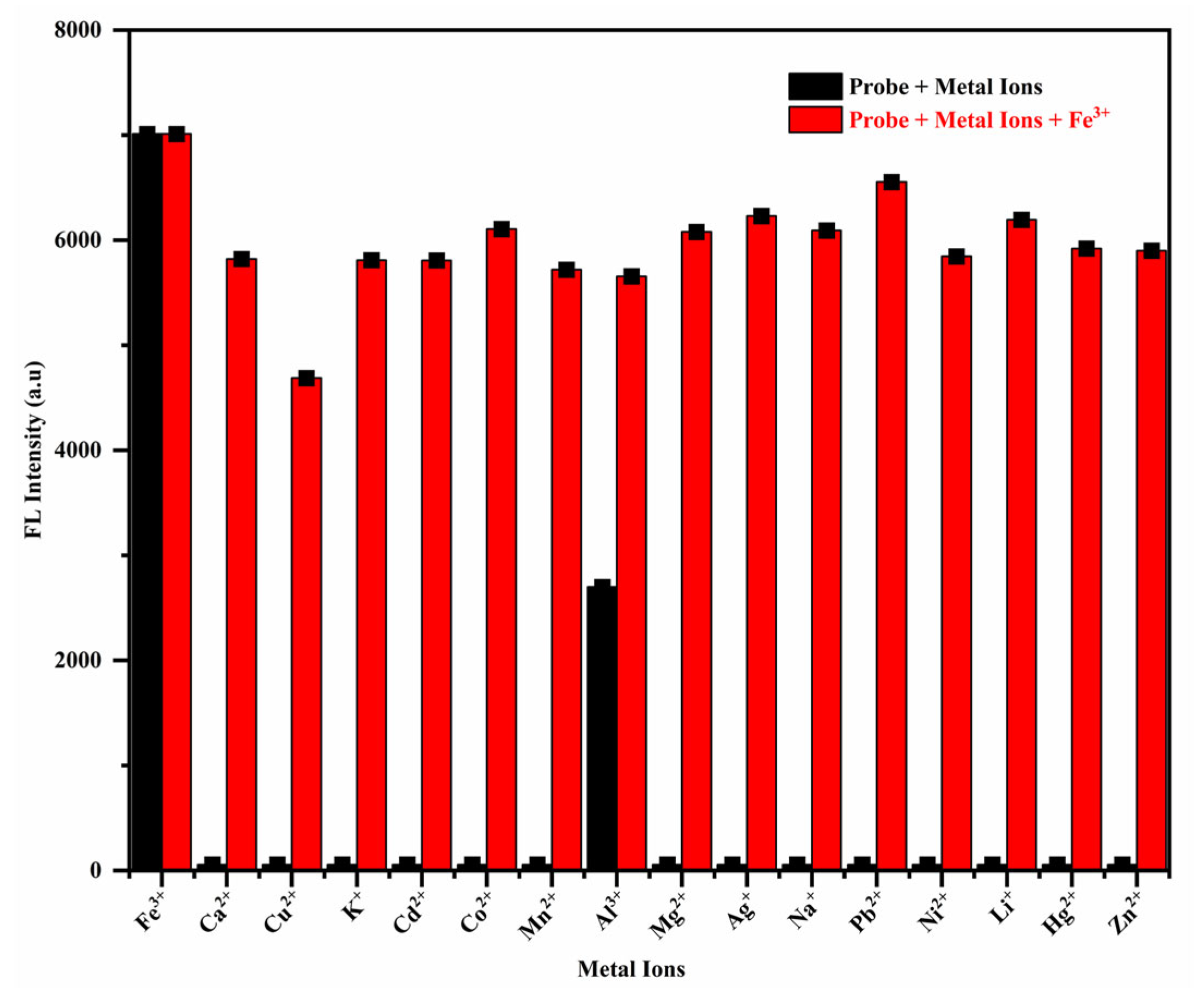
3.1. Detection of Metal Ions
3.2. Analysis of Sensing Characteristics
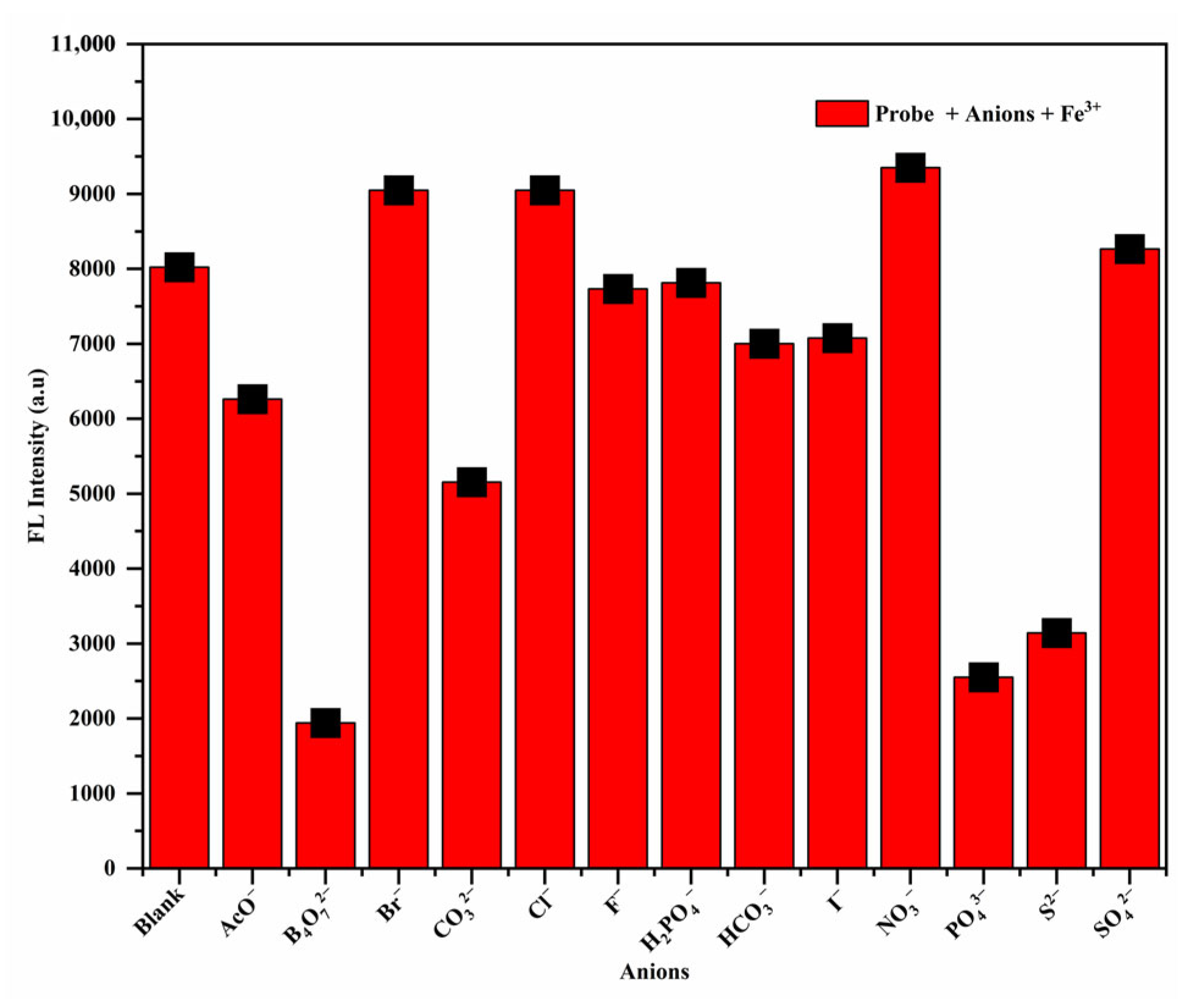
3.3. Effect of Common Anions on the Fluorescent Properties of RhB-DCT-Fe3+ Complex
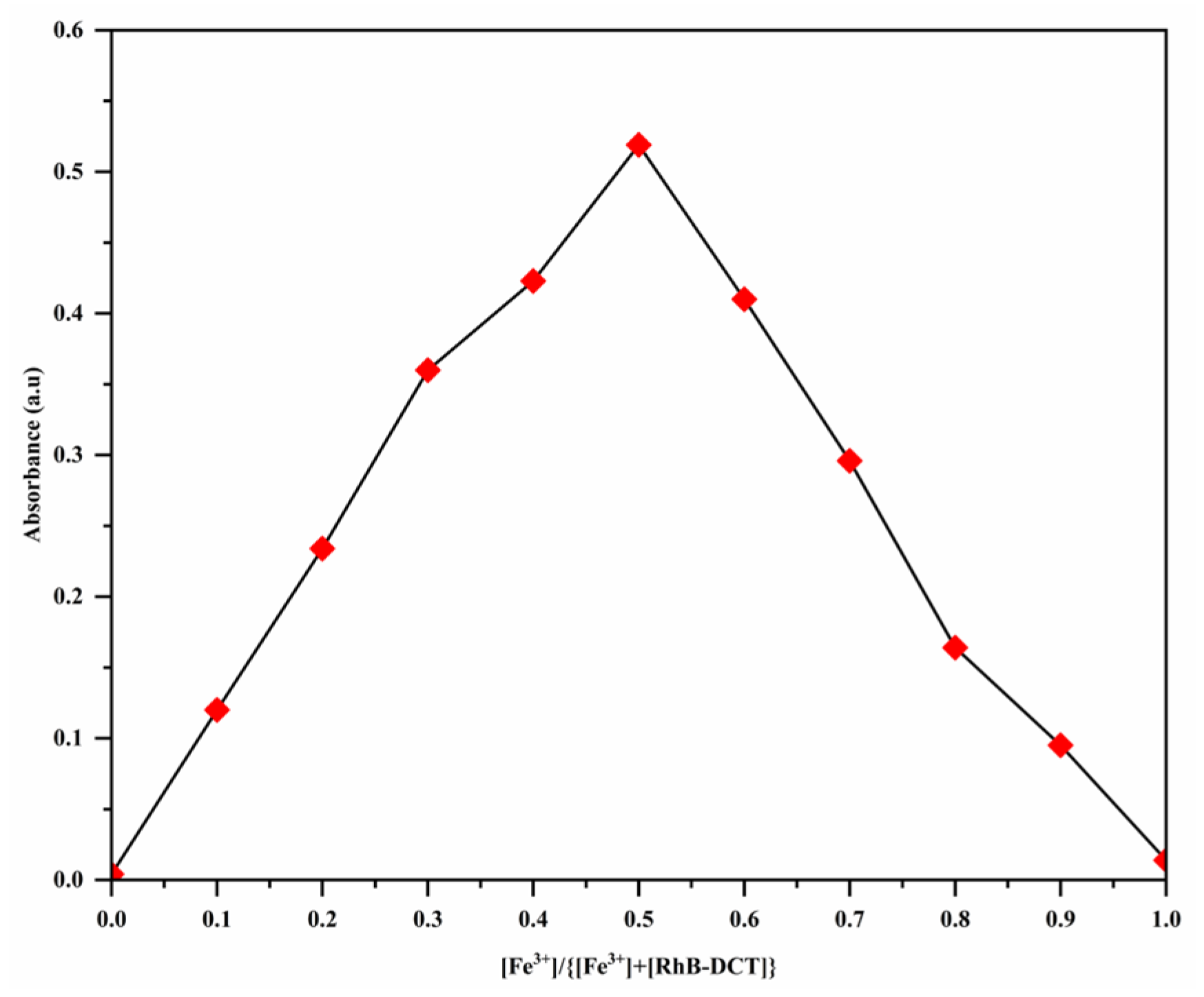
3.4. Binding Stoichiometry and the Association Constant
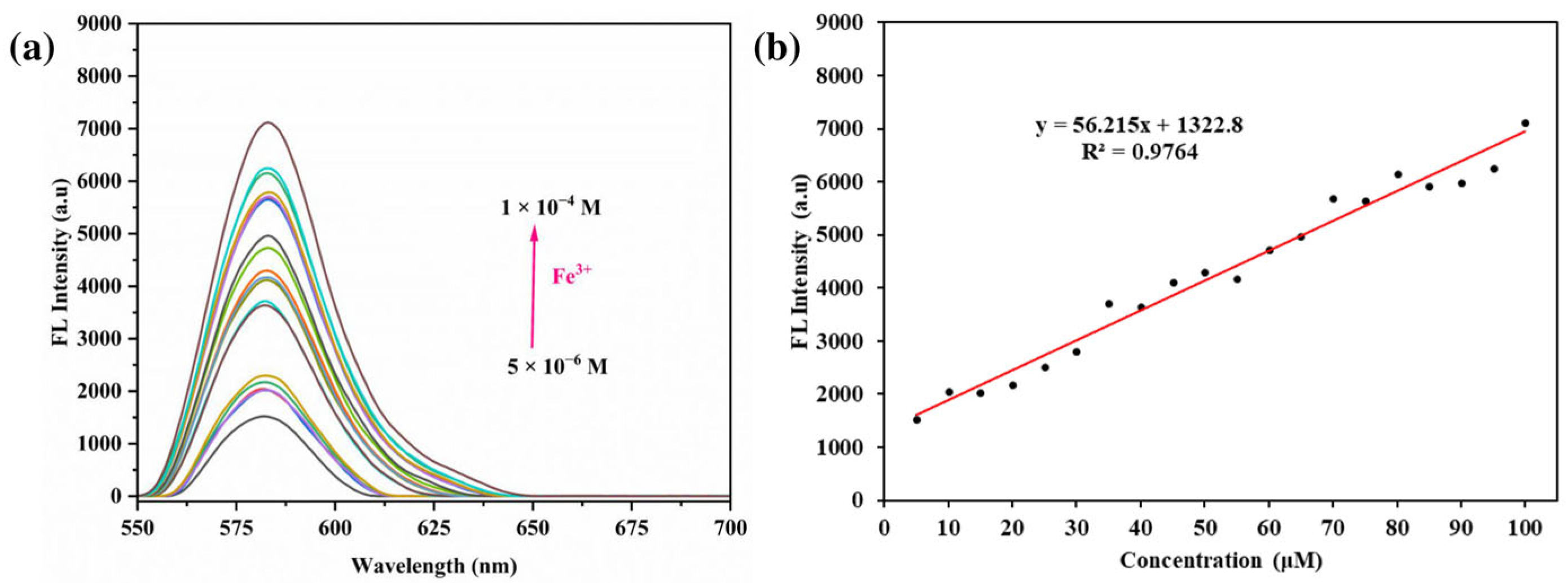
3.5. Impact of Different Concentrations
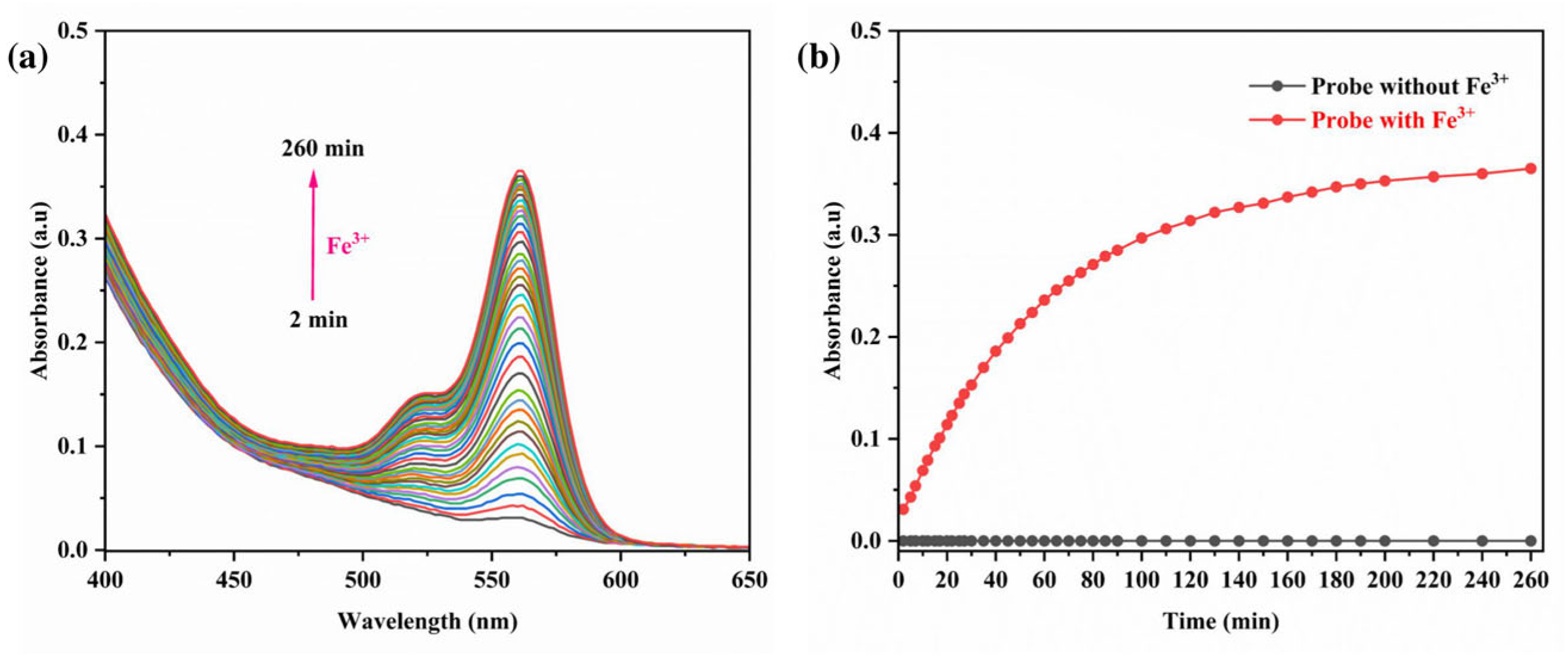
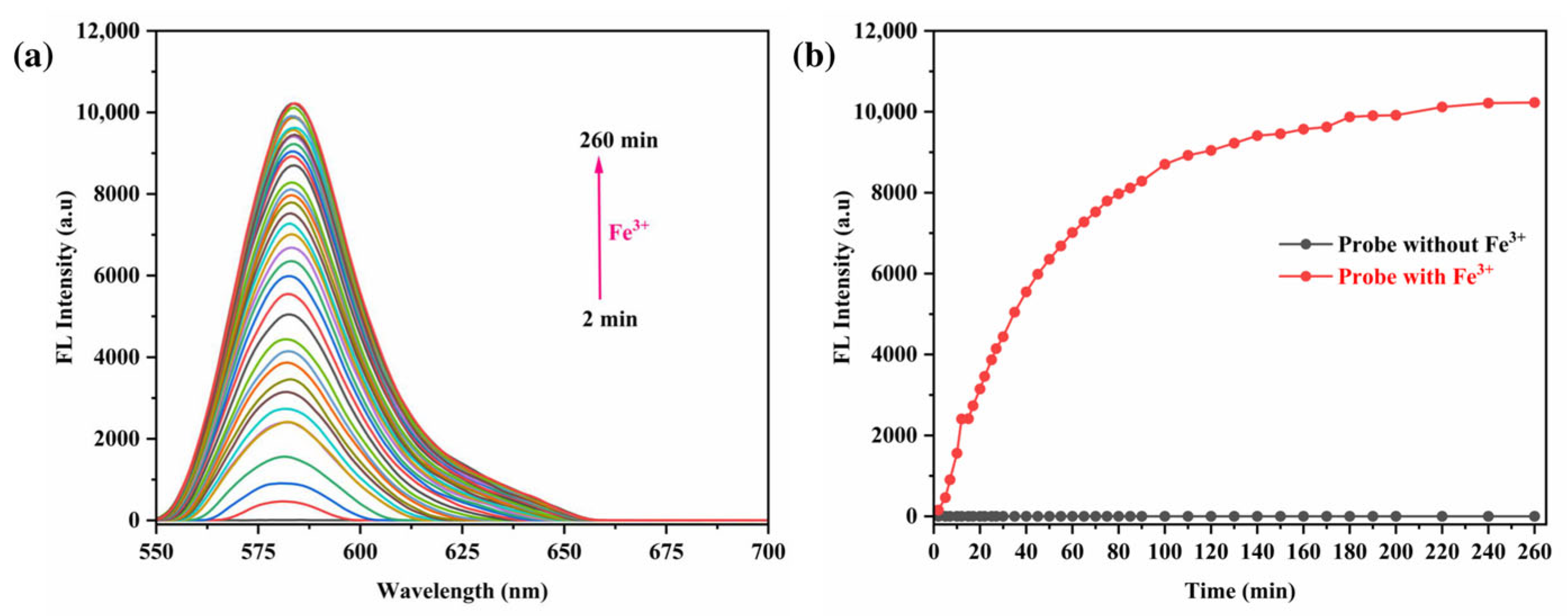
3.6. Impact of Reaction Time
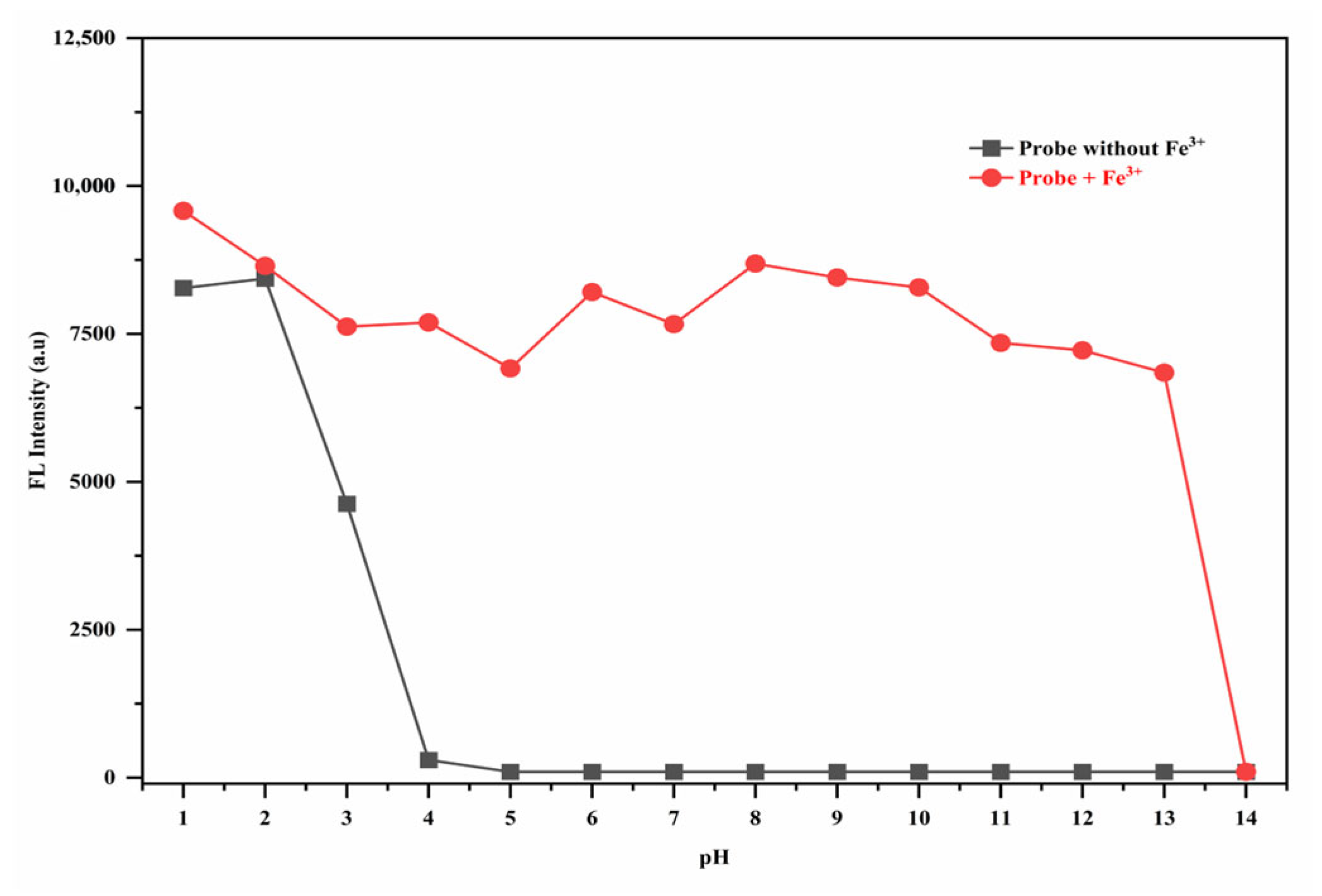
3.7. The pH Effect
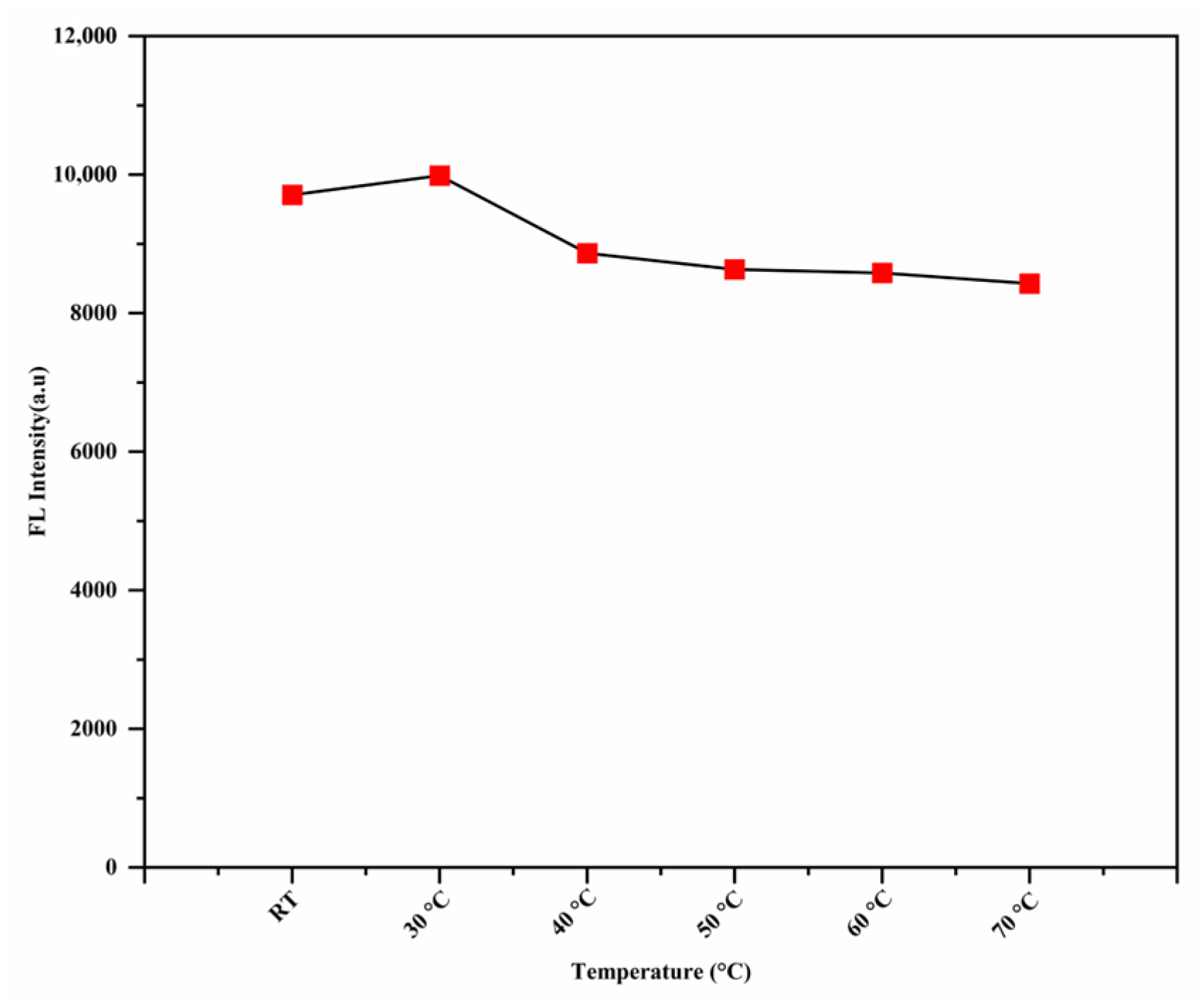
3.8. The Effect of the Temperature
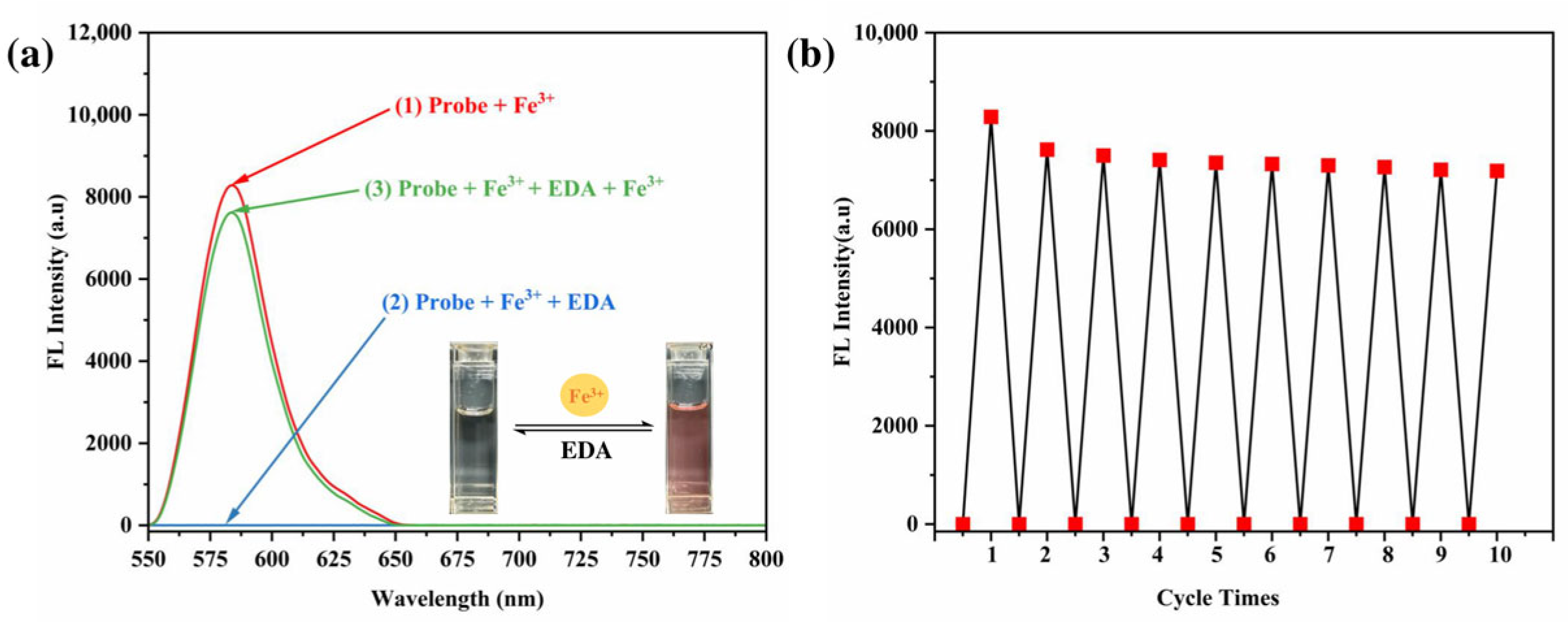
3.9. Studies on Reversibility
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saravanan, P.; Saravanan, V.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Arnica, G.; Rajasimman, M.; Gurunathan, B.; Pugazhendhi, A. Comprehensive review on toxic heavy metals in the aquatic system: Sources, identification, treatment strategies, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Affam, A.C.; Usman, A.K.; Soja, U.B.; Saleh, D.; Hussaini, A.; Noor, A.; Yaro, N.S.A. Sources of water contamination by heavy metals. In Membrane Technologies for Heavy Metal Removal from Water; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Edo, G.I.; Samuel, P.O.; Oloni, G.O.; Ezekiel, G.O.; Ikpekoro, V.O.; Obasohan, P.; Ongulu, J.; Otunuya, C.F.; Opiti, A.R.; Ajakaye, R.S. Environmental persistence, bioaccumulation, and ecotoxicology of heavy metals. Chem. Ecol. 2024, 40, 322–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, S.P.; Srinivasan, P.; Madhu, D.K.; Deivasigamani, P.; Mohan, A.M. Probe-infused polymer monolithic sensor for colorimetric detection of Pb2+ in environmental water samples and tobacco extracts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, E.; Darabi, H.R.; Nazarian, R.; Zadmard, R.; Aghapoor, K.; Sayahi, H. A sensitive absorbance and “ON-OFF” fluorescence detection of Ag+ and Hg2+ ions by a multifunctional earring-shaped probe: The selective monitoring of Hg2+ and Ag+ ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116199. [Google Scholar]
- Guesmi, S.; Ali, N.H.; Missaoui, N.; Aloui, Z.; Mabrouk, C.; Martinez, C.C.; Echouchene, F.; Barhoumi, H.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Kahri, H. High-Performance ZIF-7@ PANI Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Trace Cadmium and Lead Detection in Water Samples: A Box–Behnken Design Optimization Approach. Sensors 2025, 25, 1336. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, B.; Xing, T.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Ma, S.; Sun, F.; Xing, D.; Ren, P. A chemosensing approach for the colorimetric and spectroscopic detection of Cr3+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Gd3+ metal ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krämer, R. Fluorescent chemosensors for Cu2+ ions: Fast, selective, and highly sensitive. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.-K.; Akogun, S.F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.-X.; Dong, X.-Y. A reversible “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for selective detection of Zn2+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 723–734. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Gao, X.; Shi, Y.; Sayyadi, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, R. Fluorescence detection of Fe3+ ions in aqueous solution and living cells based on a high selectivity and sensitivity chemosensor. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 149, 674–681. [Google Scholar]
- Jomova, K.; Makova, M.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Essential metals in health and disease. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110173. [Google Scholar]
- Wimalawansa, S.J. The role of ions, heavy metals, fluoride, and agrochemicals: Critical evaluation of potential aetiological factors of chronic kidney disease of multifactorial origin (CKDmfo/CKDu) and recommendations for its eradication. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 639–678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henle, E.S.; Luo, Y.; Linn, S. Fe2+, Fe3+, and oxygen react with DNA-derived radicals formed during iron-mediated Fenton reactions. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 12212–12219. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z. Iron and oxidizing species in oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Med. 2019, 2, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Li, R.; Rong, K.; Fang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, H.; Dong, S. A novel, environmentally friendly dual-signal water toxicity biosensor developed through the continuous release of Fe3+. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114864. [Google Scholar]
- García, R.; Báez, A. Atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS). At. Absorpt. Spectrosc. 2012, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ammann, A.A. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP MS): A versatile tool. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Ivaska, A. Electrochemical detection. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 54, pp. 441–459. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, T.; Shafi, S.; Sher, F. Smart nano-architectures as potential sensing tools for detecting heavy metal ions in aqueous matrices. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 36, e00179. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, F.; Fazal, H.; Ahmed, M.; Iqbal, A.; Ishaq, M.; Jabeen, M.; Butt, M.; Farid, S. Advances in ionic liquids as fluorescent sensors. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141434. [Google Scholar]
- Yaroshenko, I.; Kirsanov, D.; Marjanovic, M.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Korostynska, O.; Mason, A.; Frau, I.; Legin, A. Real-time water quality monitoring with chemical sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampaengsri, S.; Kaewtong, C. Immobilization of Rhodamine Derivatives on Agarose Hydrogel for Heavy Metal Detection. Ph.D. Thesis, Mahasarakham University, Maha Sarakham, Thailand, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, P.; Chaturwedi, A.K.; Patel, D.; Bai, S.; Kashyap, N.K.; Hait, M.; Patra, G.K. Rhodamine Based Chemosensors for Metal ions Detection: An Overview. J. Fluoresc. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, E.; Li, Z.; Tang, L.; Han, B.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.-J. A novel rhodamine-based colorimetric and fluorometric probe for simultaneous detection of multi-metal ions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 230, 118050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huy, B.T.; Thangadurai, D.T.; Sharipov, M.; Nghia, N.N.; Van Cuong, N.; Lee, Y.-I. Recent advances in turn off-on fluorescence sensing strategies for sensitive biochemical analysis-A mechanistic approach. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107511. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ge, H.; Tian, G.; Cao, N.; Li, Y. A fluorescent turn-off/on method based on carbon dots as fluorescent probes for the sensitive determination of Pb2+ and pyrophosphate in an aqueous solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Chai, Q.; Liang, X.-M.; Li, M.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Fu, Y. A highly selective and sensitive fluorescent turn-off probe for Cu2+ based on a guanidine derivative. Molecules 2017, 22, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Huo, F.; Cheng, F.; Zhu, X.; Mafireyi, T.; Strongin, R.M.; Yin, C. Functional synthetic probes for selective targeting and multi-analyte detection and imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4155–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.E.; Roy, B.; Ahn, K.H. “Turn-on” fluorescent sensing with “reactive” probes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7583–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, M.; Lou, X.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y. Highly sensitive and selective chip-based fluorescent sensor for mercuric ion: Development and comparison of turn-on and turn-off systems. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8060–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Su, W.; Liu, P.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, T. Facile preparation of a rhodamine B derivative-based fluorescent probe for visual detection of iron ions. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25040–25048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Ren, A.; Wu, C.; Yang, W. The solvent-dependent binding modes of a rhodamine-azacrown based fluorescent probe for Al3+ and Fe3+. Dye. Pigment. 2014, 101, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.L.; Winefordner, J.D. Limit of detection. A closer look at the IUPAC definition. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 712A–724A. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhong, H.; Tang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Ma, L.-J. A solvent-dependent fluorescent detection method for Fe3+ and Hg2+ based on a rhodamine B derivative. Talanta 2016, 154, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, C.; Song, F.; Shao, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J. Imaging of living organisms and determination of real water samples using a rhodamine-based Fe (III)-induced fluorescent probe. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104587. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, K.C.; Bag, B. Switch in ‘turn-on’signaling preferences from Fe (III) to Hg (II) as a function of solvent and structural variation in rhodamine based probes. Dye. Pigment. 2016, 135, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, N.; Wu, S.P.; Velmathi, S. Turn on fluorescent chemosensor containing rhodamine B fluorophore for selective sensing and in vivo fluorescent imaging of Fe3+ ions in HeLa cell line and zebrafish. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 384, 112060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-R.; Wu, S.-P. New water-soluble highly selective fluorescent chemosensor for Fe (III) ions and its application to living cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Chantarasunthon, K.; Promkatkaew, M.; Waranwongcharoen, P.; Sueksachat, A.; Prasop, N.; Norasi, T.; Sonsiri, N.; Sansern, S.; Chomngam, S.; Wechakorn, K. A novel highly selective FRET sensor for Fe (III) and DFT mechanistic evaluation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 286, 122031. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Kan, C.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Bao, X. A highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for Fe3+ containing two rhodamine B and thiocarbonyl moieties and its application to live cell imaging. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Leng, T.-H.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Shi, P.; Zhu, W.-H. Water-soluble rhodamine-based chemosensor for Fe3+ with high sensitivity, selectivity and anti-interference capacity and its imaging application in living cells. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 142, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağırlı, A.; Bozkurt, E. Rhodamine-based arylpropenone azo dyes as dual chemosensor for Cu2+/Fe3+ detection. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 403, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Detectable Ions | Ex.λ (nm) | Em.λ (nm) | LOD (μM) | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3+, Hg2+ | 468 | 580 | 0.1 | Water Samples | [34] |
| Fe3+ | 520 | 582 | 0.157 | Cell Imaging | [35] |
| Fe3+ | 500 | 584 | 0.39 | Water Samples | [36] |
| Fe3+ | 520 | 580 | 0.16 | Cell Imaging | [37] |
| Fe3+ | 564 | 588 | 2.2 | Cell Imaging | [38] |
| Fe3+ | 520 | 580 | 0.083 | Water Samples | [39] |
| Fe3+ | 558 | 582 | 0.205 | Cell Imaging | [40] |
| Fe3+ | 520 | 589 | 0.27 | Water Samples | [41] |
| Fe3+, Cu2+ | 540 | 589 | 0.91 | - | [42] |
| Fe3+ | 562 | 584 | 0.0521 | Water Samples | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.F.; Abdulkadir, A.Z.; Elbayomi, S.M.; Zhang, P. A Rhodamine B-Based “Turn-On” Fluorescent Probe for Selective Fe3+ Ions Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113477
Islam MF, Abdulkadir AZ, Elbayomi SM, Zhang P. A Rhodamine B-Based “Turn-On” Fluorescent Probe for Selective Fe3+ Ions Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113477
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md Foridul, Abdulkadir Zakari Abdulkadir, Smaher M. Elbayomi, and Pengfei Zhang. 2025. "A Rhodamine B-Based “Turn-On” Fluorescent Probe for Selective Fe3+ Ions Detection" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113477
APA StyleIslam, M. F., Abdulkadir, A. Z., Elbayomi, S. M., & Zhang, P. (2025). A Rhodamine B-Based “Turn-On” Fluorescent Probe for Selective Fe3+ Ions Detection. Sensors, 25(11), 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113477






