Classification of Microbial Activity and Inhibition Zones Using Neural Network Analysis of Laser Speckle Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Experimental Setup
2.2. Experiment Description
2.3. Preprocessing and Data Arrangement
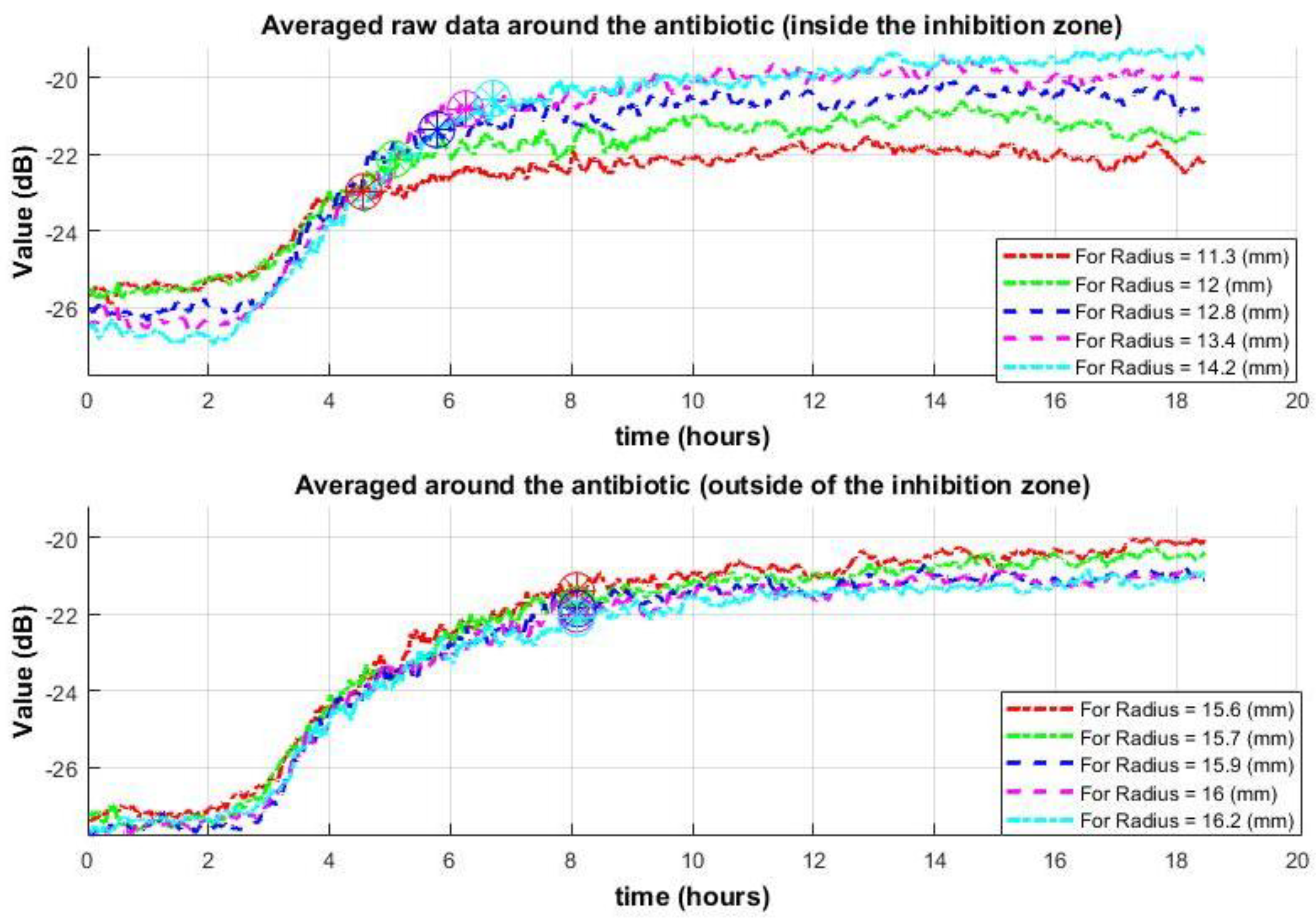
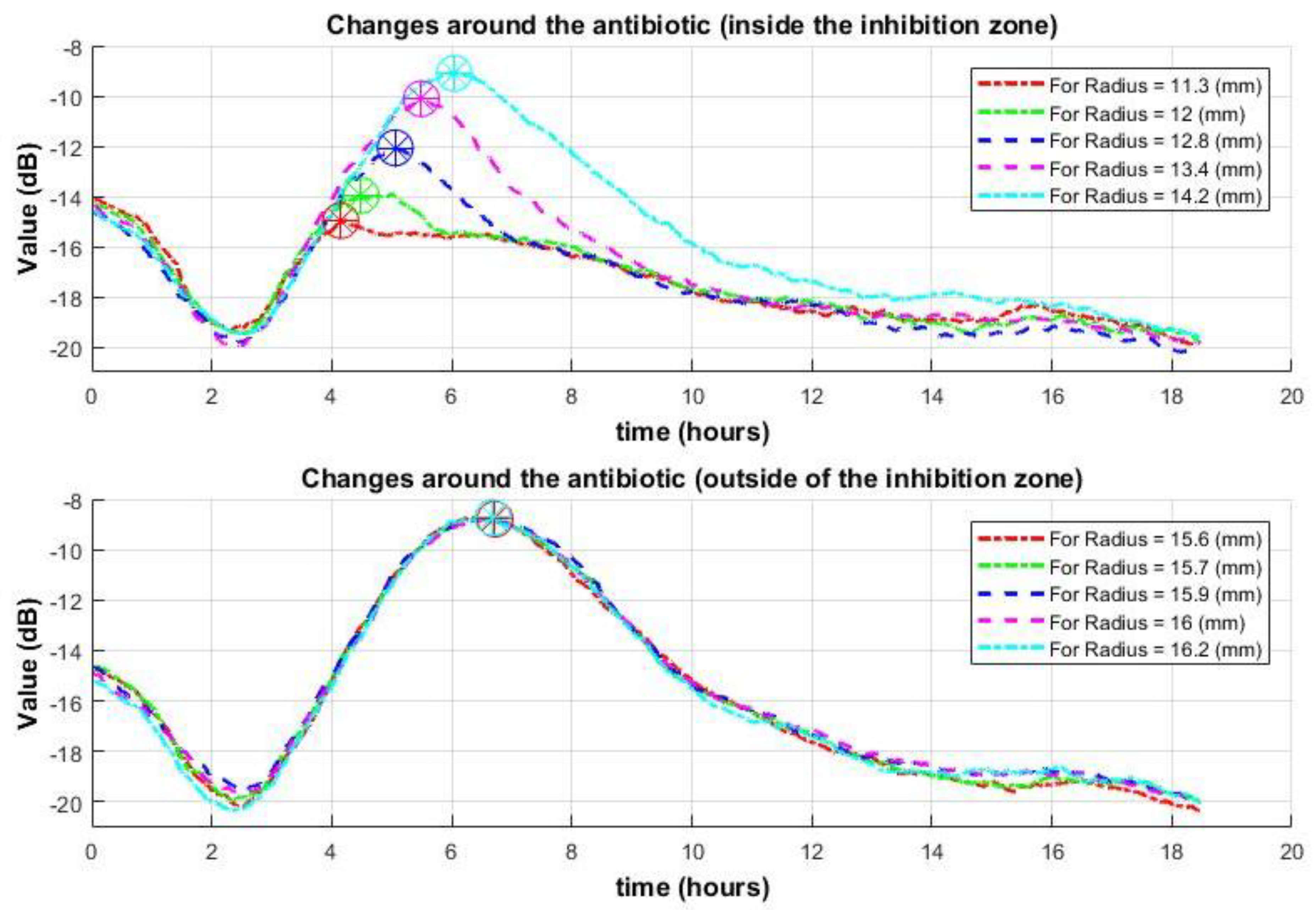
2.4. Analysis of Signal Behavior at Varying Radii from the Antibiotic Disc
- (1)
- “Long-term” approach: The signal section where the difference is clearly visible (e.g., a 5-h window) is processed as one indivisible segment.
- (2)
- “Short-term” approach: The data are divided into smaller time intervals (e.g., 1-h segments). The first approach is expected to yield better results, but this will only be apparent after the entire 5-h interval has passed.
2.5. Neural Network for Classification
- (1)
- Zones of active bacterial growth
- (2)
- Inhibition zones formed around antibiotic discs
2.5.1. Neural Network Considerations
2.5.2. Database and Neural Network Parameters
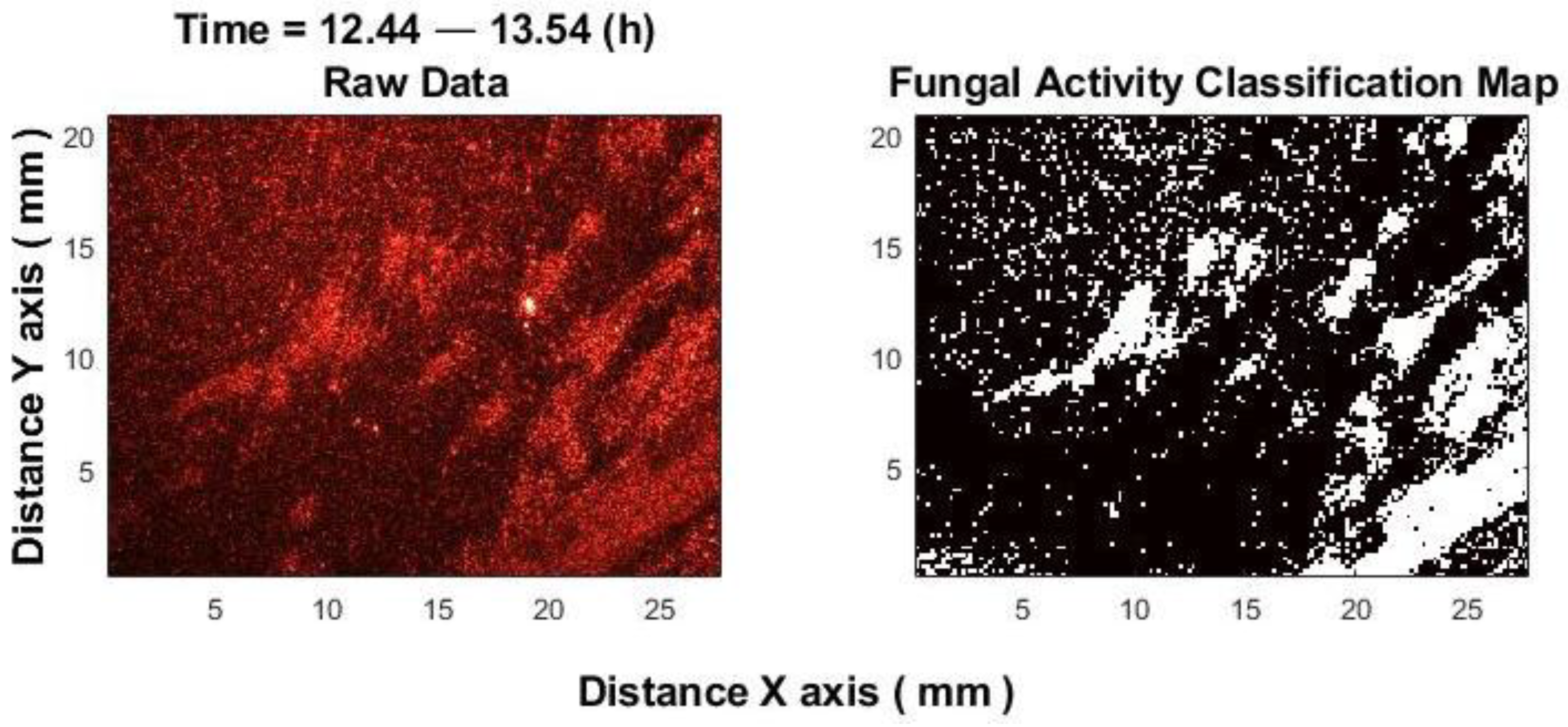
3. Results
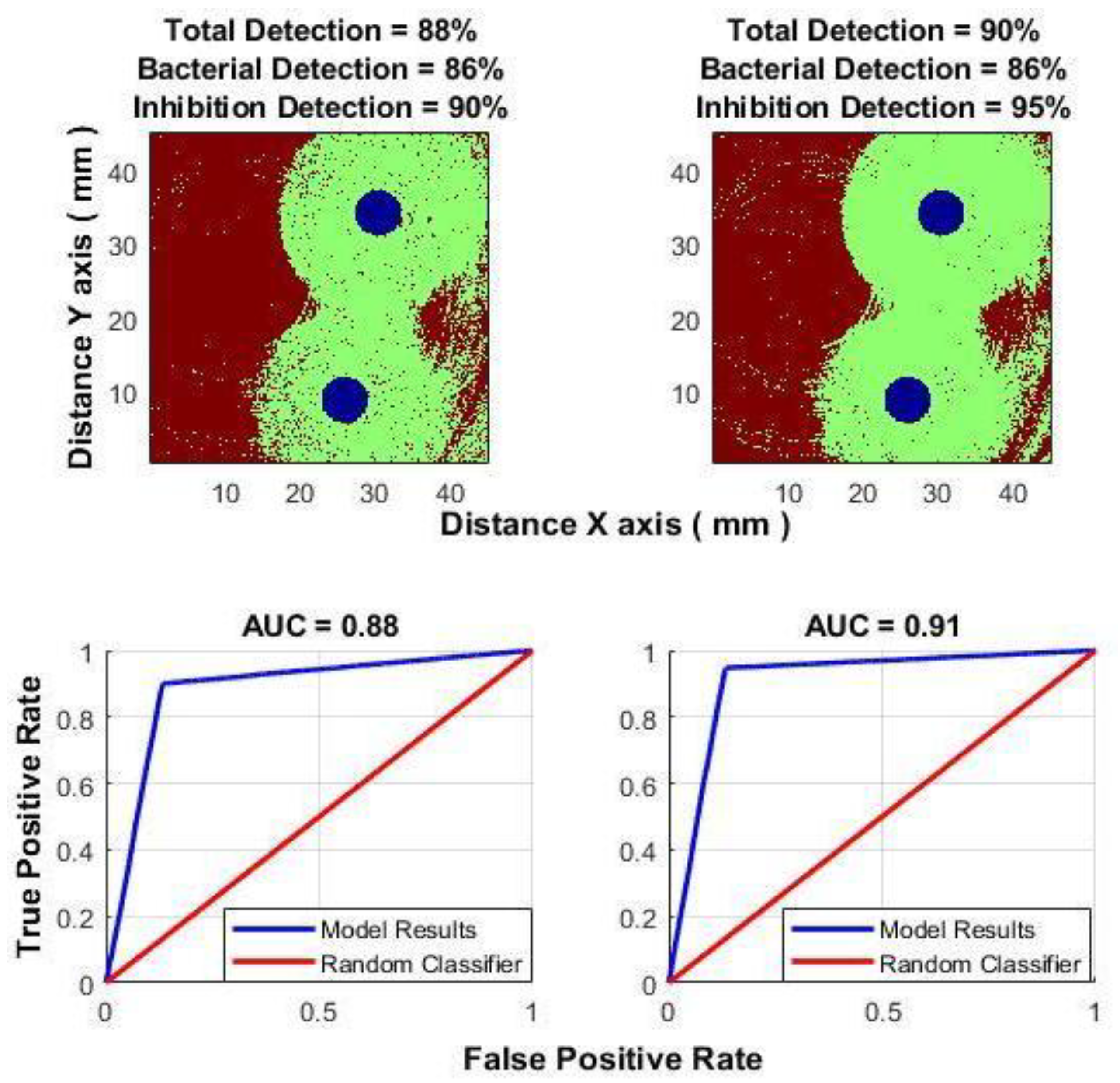
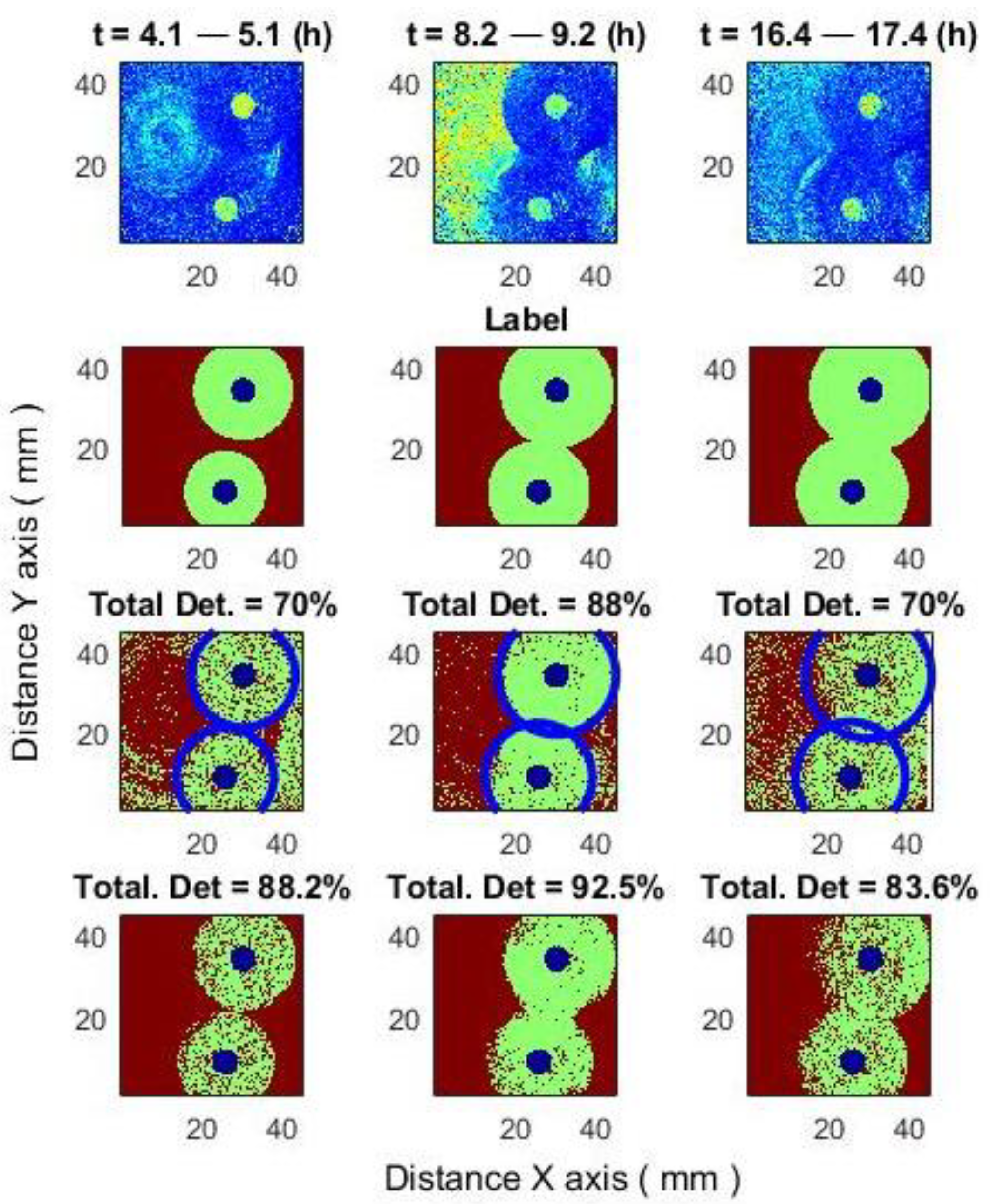
3.1. Classification Results
3.2. Improving Classification Results
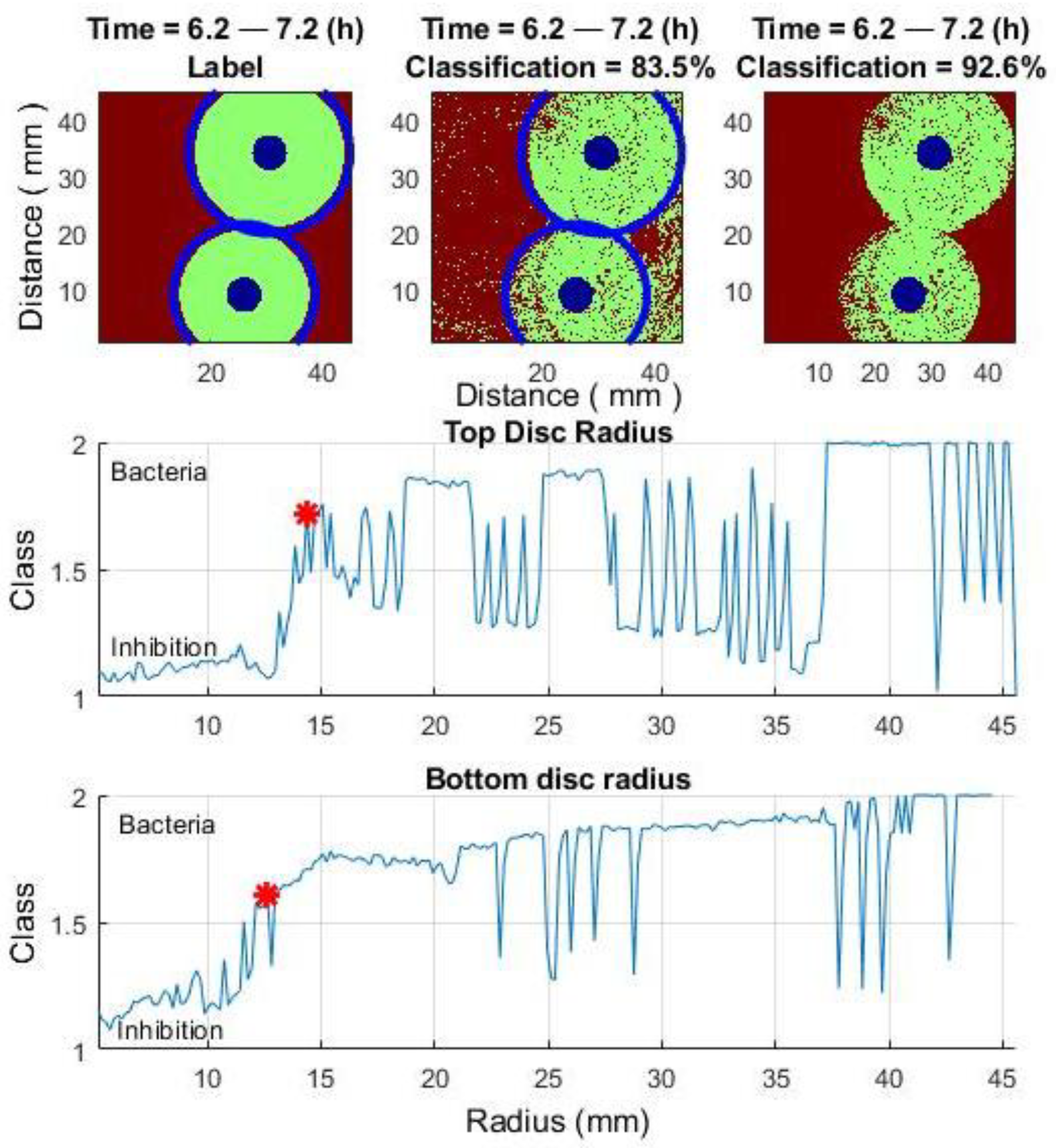
3.2.1. Improving Classification Results by Using a Class-Changing Function Based on the Distance from the Antibiotic
- (1)
- The inhibition zones occur around the antibiotic, and the location and size of the antibiotic are known. Although the exact size, shape, radius, and location of the antibiotic are known in each experiment, its position can also be reliably detected using algorithmic tools. There are several approaches to circle detections: (a) based on Hough transform [57], (b) based on random sampling [58], (c) based on edge detection technique [59], (d) based on different intelligent optimization algorithms [60], (e) based on circle properties [61], (f) and various others [62,63]. In ref. [64], we demonstrated that speckle imaging with image processing algorithms can be used not only to detect an antibiotic tablet but also to identify the imprinted name of the antibiotic.
- (2)
- The inhibition zone typically forms in a shape close to a circle; the classification result can be improved.
3.2.2. Improving Classification Results Using the Median Signal per Radius
4. Summary and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodman, J.W. Speckle Phenomena in Optics. Theory and Application; Roberts and Company: Englewood, CO, USA, 2007; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo, S.E.; Sendra, G.H.; Passoni, L.I.; Arizaga, R.; Gonzalez, J.F.; Rabal, H.; Trivi, M. Analysis of bacterial chemotactic response using dynamic laser speckle. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 064015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murialdo, S.E.; Passoni, L.I.; Guzman, M.N.; Sendra, G.H.; Rabal, H.; Trivi, M.; Gonzalez, J.F. Discrimination of motile bacteria from filamentous fungi using dynamic speckle. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 056011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Lee, K.; Park, Y. A simple and rapid method for detecting living microorganisms in food using laser speckle decorrelation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.07343. [Google Scholar]
- Loutfi, H.; Pellen, F.; Le Jeune, B.; Lteif, R.; Kallassy, M.; Le Brun, G.; Abboud, M. Real-time monitoring of bacterial growth kinetics in suspensions using laser speckle imaging. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Singh, A.K.; Bhunia, A.K.; Bae, E. Laser-induced speckle scatter patterns in Bacillus colonies. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, H.C.; García, L.C.; Lobo-Sulbarán, M.L.; Velásquez, A.; Andrades-Grassi, F.A.; Cabrera, H.; Andrades-Grassi, J.E.; Andrades, E.D.J. Quantitative Laser Biospeckle Method for the Evaluation of the Activity of Trypanosoma cruzi Using VDRL Plates and Digital Analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, H.C.; Velásquez, A.; Belandria, O.M.; Lobo-Sulbarán, M.L.; Andrades-Grassi, J.E.; Cabrera, H.; Andrades, E.D. Biospeckle laser digital image processing for quantitative and statistical evaluation of the activity of Ciprofloxacin on Escherichia coli K-12. Laser Phys. 2019, 29, 075603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piederriere, Y.; Cariou, J.; Guern, Y.; Le Jeune, B.; Le Brun, G.; Lotrian, J. Scattering through fluids: Speckle size measurement and Monte Carlo simulations close to and into the multiple scattering. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briers, J.D.; Richards, G.J.; He, X.W. Capillary blood flow monitoring using laser speckle contrast analysis (LASCA). J. Biomed. Opt. 1999, 4, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draijer, M.; Hondebrink, E.; van Leeuwen, T.; Steenbergen, W. Review of laser speckle contrast techniques for visualizing tissue perfusion. Lasers Med. Sci. 2009, 24, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfischer, L.I. Autocorrelation function and power spectral density of laser-produced speckle patterns. JOSA 1965, 55, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdunek, A.; Muravsky, L.I.; Frankevych, L.; Konstankiewicz, K. New nondestructive method based on spatial-temporal speckle correlation technique for evaluation of apples quality during shelf-life. Int. Agrophy. 2007, 21, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Vaz, P.G.; Humeau-Heurtier, A.; Figueiras, E.; Correia, C.; Cardoso, J. Effect of static scatterers in laser speckle contrast imaging: An experimental study on correlation and contrast. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 63, 015024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmages, I.; Reinis, A.; Kistkins, S.; Bliznuks, D.; Lihachev, A.; Lihacova, I. Comparison of algorithms for monitoring the behavior of microorganisms based on remote laser speckle method. In Proceedings of the SPIE Artificial Intelligence and Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXX, Edinburgh, UK, 16–19 September 2024; Volume 13196. [Google Scholar]
- Gåsvik, K.J. Optical Metrology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Balmages, I.; Liepins, J.; Zolins, S.; Bliznuks, D.; Lihacova, I.; Lihachev, A. Laser speckle imaging for early detection of microbial colony forming units. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmages, I.; Liepins, J.; Zolins, S.; Bliznuks, D.; Broks, R.; Lihacova, I.; Lihachev, A. Tools for classification of growing/non-growing bacterial colonies using laser speckle imaging. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1279667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J.A. Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Chatterjee, A.; Rajput, L.S.; Rana, S.; Kumar, S.; Nataraj, V.; Bhatia, V.; Prakash, S. Development of an intelligent laser biospeckle system for early detection and classification of soybean seeds infected with seed-borne fungal pathogen (Colletotrichum truncatum). Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 212, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larose, D.T. Data Mining Methods and Models; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bramer, M. Principles of data mining. In Undergraduate Topics in Computer Science; Springer: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, K.; Güneş, S. Classification of epileptiform EEG using a hybrid system based on decision tree classifier and fast Fourier transform. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 187, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Sharma, N. Intrusion detection using naive Bayes classifier with feature reduction. Procedia Technol. 2012, 4, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks and Learning Machines, 3rd ed.; Pearson Education, Inc., McMaster University: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubczyk, T.; Jakubczyk, D.; Stachurski, A. Assessing the properties of a colloidal suspension with the aid of deep learning. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2021, 261, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, C.; Sapre, A.; Pavlock, J.H.; Weaver, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Noble, J.; Kovac, J.; Liu, Z.; Ebrahimi, A. Dynamic Laser Speckle Imaging meets Machine Learning to enable Rapid Antibacterial Susceptibility Testing (DyRAST). ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3140–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhou, C.; Khamsi, P.S.; Voloshchuk, O.; Hernandez, L.; Kovac, J.; Ebrahimi, A.; Liu, Z. Label-free rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing with machine-learning based dynamic holographic laser speckle imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 278, 117312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, K.; Park, Y.G.; Yoo, J.W.; Yong, D. Rapid bacterial detection in urine using laser scattering and deep learning analysis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01769-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Jain, V.; Mishra, A. An analysis of convolutional neural networks for image classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliznuks, D.; Chizhov, Y.; Bondarenko, A.; Uteshev, D.; Liepins, J.; Zolins, S.; Lihachev, A.; Lihacova, I. Embedded neural network system for microorganisms growth analysis. In Proceedings of the Saratov Fall Meeting 2019: Optical and Nano-Technologies for Biology and Medicine, Saratov, Russia, 23–27 September 2019; Volume 11457, pp. 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, S.; Wang, J.; Ul Hassan, T.; Fei, Z. 3D-CNN-based fused feature maps with LSTM applied to action recognition. Future Internet 2019, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmages, I.; Reinis, A.; Kistkins, S.; Liepins, J.; Pogorielov, M.; Korniienko, V.; Diedkova, K.; Bliznuks, D.; Lihachev, A.; Lihacova, I. Determination of operating parameters of fungal [growth signals analyzed by laser speckle contrast imaging. In Proceedings of the SPIE Biomedical Spectroscopy, Microscopy, and Imaging III, Strasbourg, France, 12–16 April 2024; Volume 13006. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clinical Breakpoints—Breakpoints and Guidance. 2023. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Antifungal Susceptibility Testing (AFST). 2023. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast_of_fungi (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Tom, W.J.; Ponticorvo, A.; Dunn, A.K. Efficient processing of laser speckle contrast images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Unni, S.N.; Jayasankar, S. Spatio-temporal feature analysis of laser speckle images for simultaneous quantification of skin thickness and perfusion demonstrated using in-vitro scleroderma phantoms. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 176, 108057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Yoon, J. Accurate estimation of the inhibition zone of antibiotics based on laser speckle imaging and multiple random speckle illumination. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 174, 108417. [Google Scholar]
- Tukey, J.W. Nonlinear (nonsuperimposable) methods for smoothing data. In Proceedings of the EASCON’74: Electronics and Aerospace Systems Convention, Washington, DC, USA, 7–9 October 1974; p. 673. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, E.L. Theory of Point Estimation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Balmages, I.; Reinis, A.; Kistkins, S.; Bliznuks, D.; Plorina, E.V.; Lihachev, A.; Lihacova, I. Laser speckle imaging for visualization of hidden effects for early detection of antibacterial susceptibility in disc diffusion tests. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1221134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Torp, H. Interpolation methods for time-delay estimation using cross- correlation method for blood velocity measurement. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1999, 46, 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- Balmages, I.; Bliznuks, D.; Liepins, J.; Zolins, S.; Lihachev, A. Laser speckle time-series correlation analysis for bacteria activity detection. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Spectroscopy, Microscopy, and Imaging III, Online, 6–10 April 2020; Volume 11359. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, V.; Mandracchia, B.; Nazzaro, F.; Marchesano, V.; Gennari, O.; Paturzo, M.; Grilli, S.; Ferraro, P. Food quality inspection by speckle decorrelation properties of bacteria colonies. In Proceedings of the Optical Methods for Inspection, Characterization, and Imaging of Biomaterials III, Munich, Germany, 26–28 June 2017; Volume 10333, pp. 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, A.; Kadono, H.; Rajagopalan, U.M. Fast and reliable micro bioassay techniques based on biospeckle for swift water assessment using plankton. In Proceedings of the Biophotonics in Point-of-Care III, Strasbourg, France, 10–12 April 2024; Volume 13008, pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.X.; Qu, W. Comparison between mean filter and median filter algorithm in image denoising field. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 644, 4112–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmages, I.; Liepins, J.; Auzins, E.T.; Bliznuks, D.; Baranovics, E.; Lihacova, I.; Lihachev, A. Use of the speckle imaging sub-pixel correlation analysis in revealing a mechanism of microbial colony growth. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, A.; Mehrotra, K.; Mohan, C.K.; Ranka, S. Characterization of a class of sigmoid functions with applications to neural networks. Neural Netw. 1996, 9, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. In Parallel Distributed Processing; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985; Volume 1, pp. 318–362. [Google Scholar]
- Ian, G.; Yoshua, B.; Aaron, C. Chapter 6—Deep Feedforward Networks. In Deep Learning: Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann, R. An introduction to computing with neural nets. IEEE ASSP Mag. 1987, 4, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, D.L. Why two hidden layers are better than one. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–21 June 1990; Caudhill, M., Ed.; Laurence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1990; Volume 1, pp. 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.J.; Petridis, M.; Walters, S.D.; Gheytassi, S.M.; Morgan, R.E. Two hidden layers are usually better than one. In Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, EANN 2017, Athens, Greece, 25–27 August 2017; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jeff, H.T. Chapter 5—Understanding Backpropagation. In Introduction to Neural Networks with Java; Heaton Research Inc.: Chesterfield, MO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yotov, K.; Hadzhikolev, E.; Hadzhikoleva, S.; Cheresharov, S. Finding the optimal topology of an approximating neural network. Mathematics 2023, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Yi, W. Curvature aided Hough transform for circle detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 51, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L. A fast and accurate circle detection algorithm based on random sampling. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 123, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamees, M.; Al-karawi, M. A Proposed Algorithm for Circle Detection Using Prewitt Edge Detection Technique. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2014, 4, 310–312. [Google Scholar]
- López, A.; Cuevas, F.J. Automatic multi-circle detection on images using the teaching learning based optimisation algorithm. IET Comput. Vis. 2018, 12, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, F.; Du, Z.; Liu, R. Circle detection using scan lines and histograms. Opt. Rev. 2013, 20, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zou, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, H. A fast circle detection method based on a tri-class thresholding for high detail FPC images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martinez, A.; Cuevas, F.J. Automatic circle detection on images using the teaching learning based optimization algorithm and gradient analysis. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 2001–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suponenkovs, A.; Bliznuks, D.; Lihacova, I. Noncontact automatic inhibition zones measurement in the disk-diffusion susceptibility test. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Spectroscopy, Microscopy, and Imaging III, Strasbourg, France, 12–16 April 2024; Volume 13006, pp. 298–305. [Google Scholar]






| Time (h) | Acc | Acc Cr | TPR | TPR Cr | FNR | FNR Cr | TNR | TNR Cr | FPR | FRP Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4–5 | 70 | 88 | 74 | 72 | 26 | 28 | 68 | 98 | 32 | 2 |
| 5–6 | 82 | 92 | 82 | 82 | 18 | 18 | 82 | 99 | 18 | 1 |
| 6–7 | 84 | 93 | 92 | 91 | 8 | 9 | 78 | 97 | 22 | 3 |
| 7–8 | 87 | 93 | 89 | 89 | 11 | 11 | 85 | 98 | 15 | 2 |
| 8–9 | 88 | 93 | 90 | 88 | 10 | 12 | 86 | 98 | 14 | 2 |
| 9–10 | 87 | 93 | 90 | 88 | 10 | 12 | 83 | 98 | 17 | 2 |
| 10–11 | 83 | 95 | 91 | 90 | 9 | 10 | 74 | 100 | 26 | 0 |
| 11–12 | 74 | 78 | 61 | 61 | 39 | 39 | 89 | 99 | 11 | 1 |
| 12–13 | 72 | 79 | 63 | 63 | 37 | 37 | 83 | 99 | 17 | 1 |
| 13–14 | 69 | 80 | 65 | 65 | 35 | 35 | 75 | 99 | 25 | 1 |
| 14–15 | 69 | 81 | 67 | 67 | 33 | 33 | 71 | 99 | 29 | 1 |
| 15–16 | 69 | 82 | 68 | 68 | 32 | 32 | 70 | 99 | 30 | 1 |
| 16–17 | 70 | 83 | 70 | 70 | 30 | 30 | 69 | 99 | 31 | 1 |
| Time (h) | Acc | TPR | FNR | TNR | FPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.5–6 | 99 | 99 | 1 | 99 | 1 |
| 6–7.5 | 98 | 95 | 5 | 100 | 0 |
| 7.5–9 | 96 | 93 | 7 | 100 | 0 |
| 9–10.5 | 94 | 89 | 11 | 100 | 0 |
| 10.5–12 | 94 | 90 | 10 | 100 | 0 |
| 12–13.5 | 96 | 93 | 7 | 100 | 0 |
| 13.5–15 | 97 | 95 | 5 | 100 | 0 |
| 15–16.5 | 96 | 99 | 1 | 91 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balmages, I.; Bļizņuks, D.; Polaka, I.; Lihachev, A.; Lihacova, I. Classification of Microbial Activity and Inhibition Zones Using Neural Network Analysis of Laser Speckle Images. Sensors 2025, 25, 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113462
Balmages I, Bļizņuks D, Polaka I, Lihachev A, Lihacova I. Classification of Microbial Activity and Inhibition Zones Using Neural Network Analysis of Laser Speckle Images. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113462
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalmages, Ilya, Dmitrijs Bļizņuks, Inese Polaka, Alexey Lihachev, and Ilze Lihacova. 2025. "Classification of Microbial Activity and Inhibition Zones Using Neural Network Analysis of Laser Speckle Images" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113462
APA StyleBalmages, I., Bļizņuks, D., Polaka, I., Lihachev, A., & Lihacova, I. (2025). Classification of Microbial Activity and Inhibition Zones Using Neural Network Analysis of Laser Speckle Images. Sensors, 25(11), 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113462






