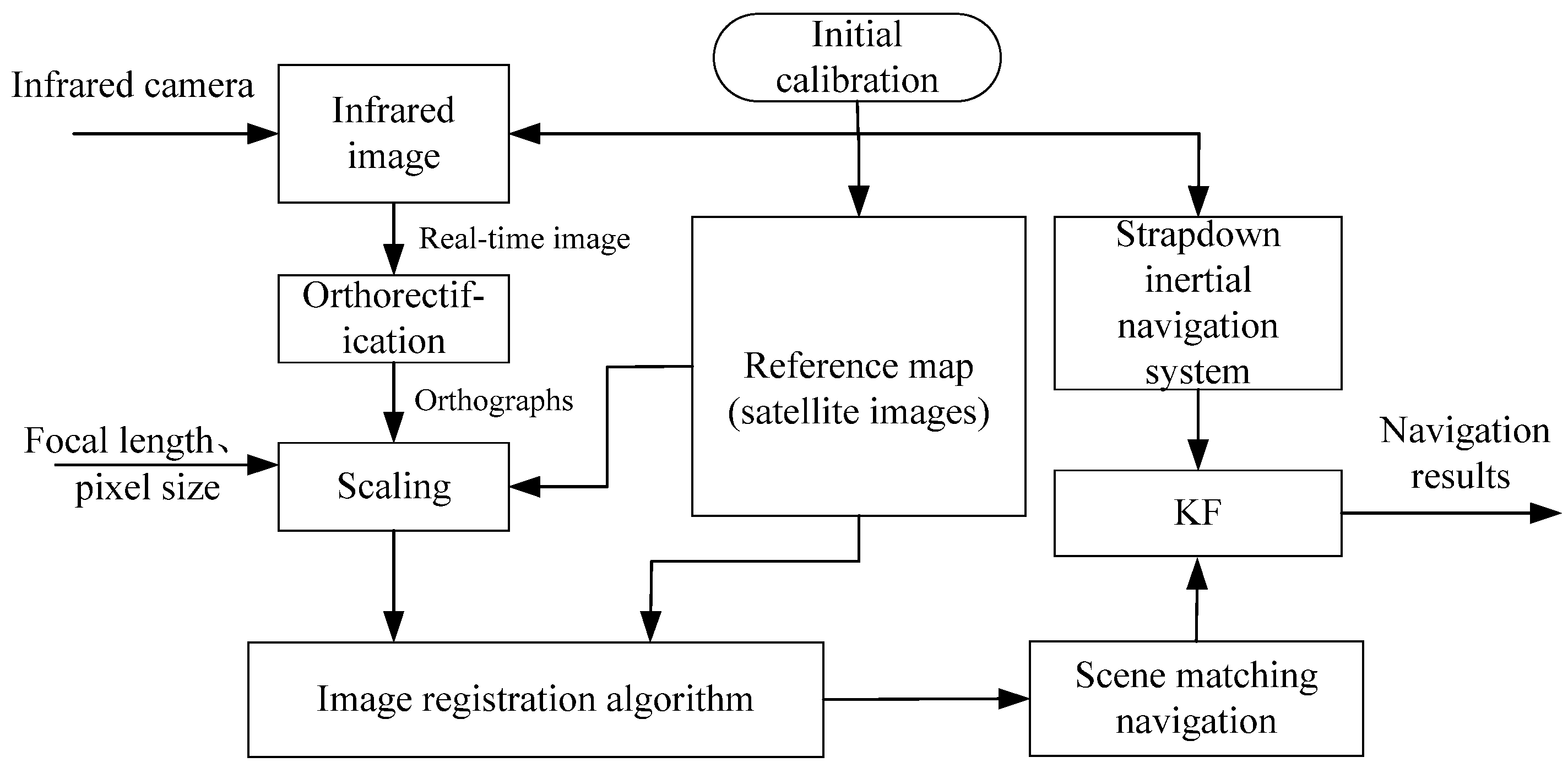
An Integrated Navigation Method Based on the Strapdown Inertial Navigation System/Scene-Matching Navigation System for UAVs
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A real-time infrared image orthorectification technique based on SINS data is introduced to reduce the impact of UAV attitude on image matching. This method features simple operation and high computational efficiency, delivering excellent real-time performance while achieving optimal processing results.
- A Log-Gabor [37] filter-based feature extraction method is proposed to extract the structural features of images, addressing the critical challenges of multi-modal image matching and achieving highly robust matching results between real-time images and reference images.
- A cascaded Kalman filtering [38] mechanism is designed to integrate high-frequency SINS measurements with SMNS positional updates. This fusion strategy reduces cumulative errors by 52.34% in latitude and 45.54% in longitude compared to standalone SMNS implementations.
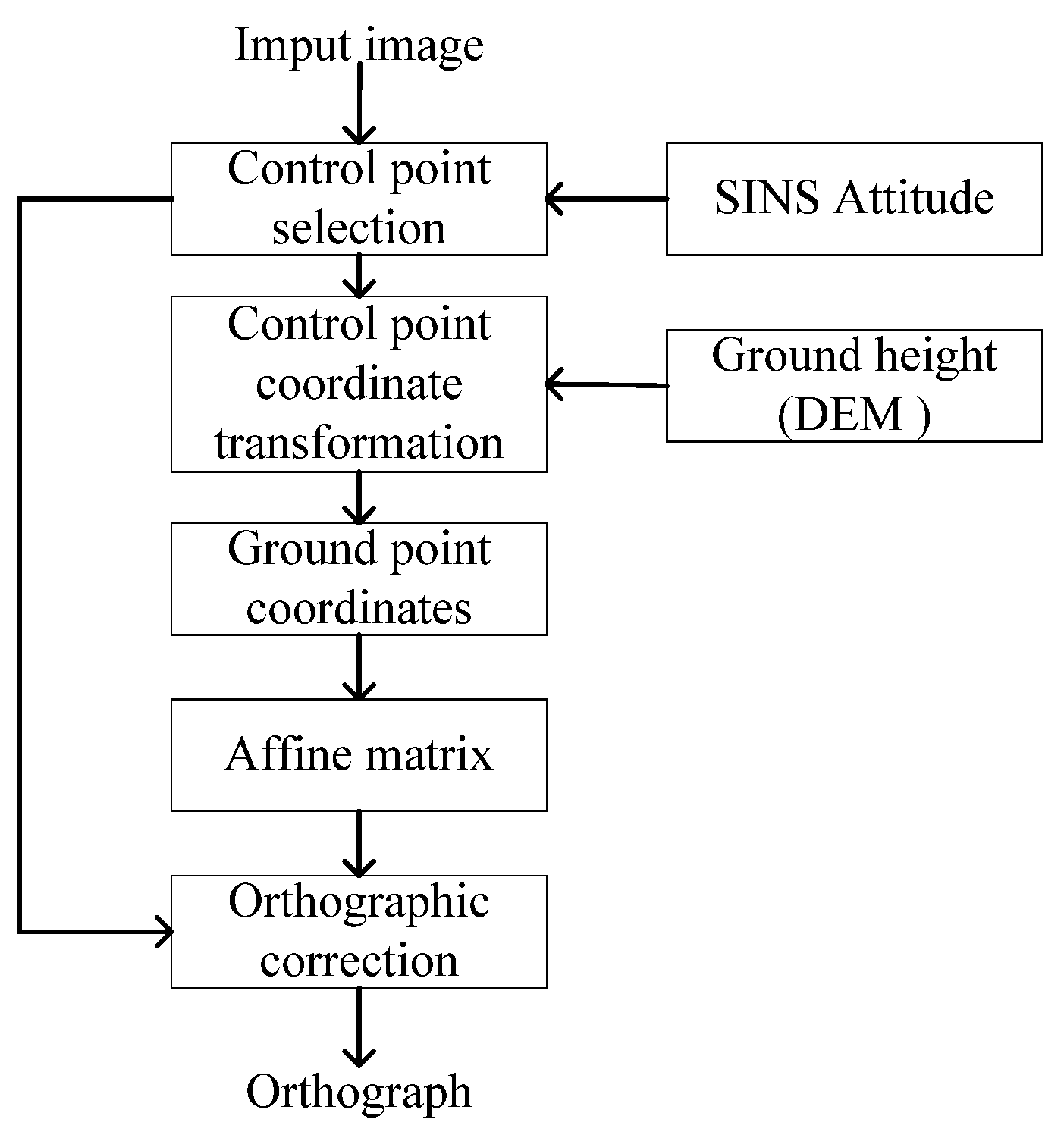
2. Orthorectification of Oblique Images Based on Inertial Attitude
- OXbYbZb: UAV body frame. The x-axis points to the right wing, the y-axis points to the front of the UAV, and the z-axis points vertically upward.
- O′XcYcZc: camera frame. O′ represents the optical center of the camera, which may not coincide with the body-frame center O. The x-axis points to the right wing, the y-axis points to the tail of the UAV, and the z-axis points vertically downward.
- OXgYgZg: local gravity frame. The origin is centered at the UAV’s center of mass. The x-axis points geographically east, the y-axis points geographically north, and the z-axis points vertically upward, perpendicular to the local reference ellipsoid surface, and is almost opposite to the direction of gravity.
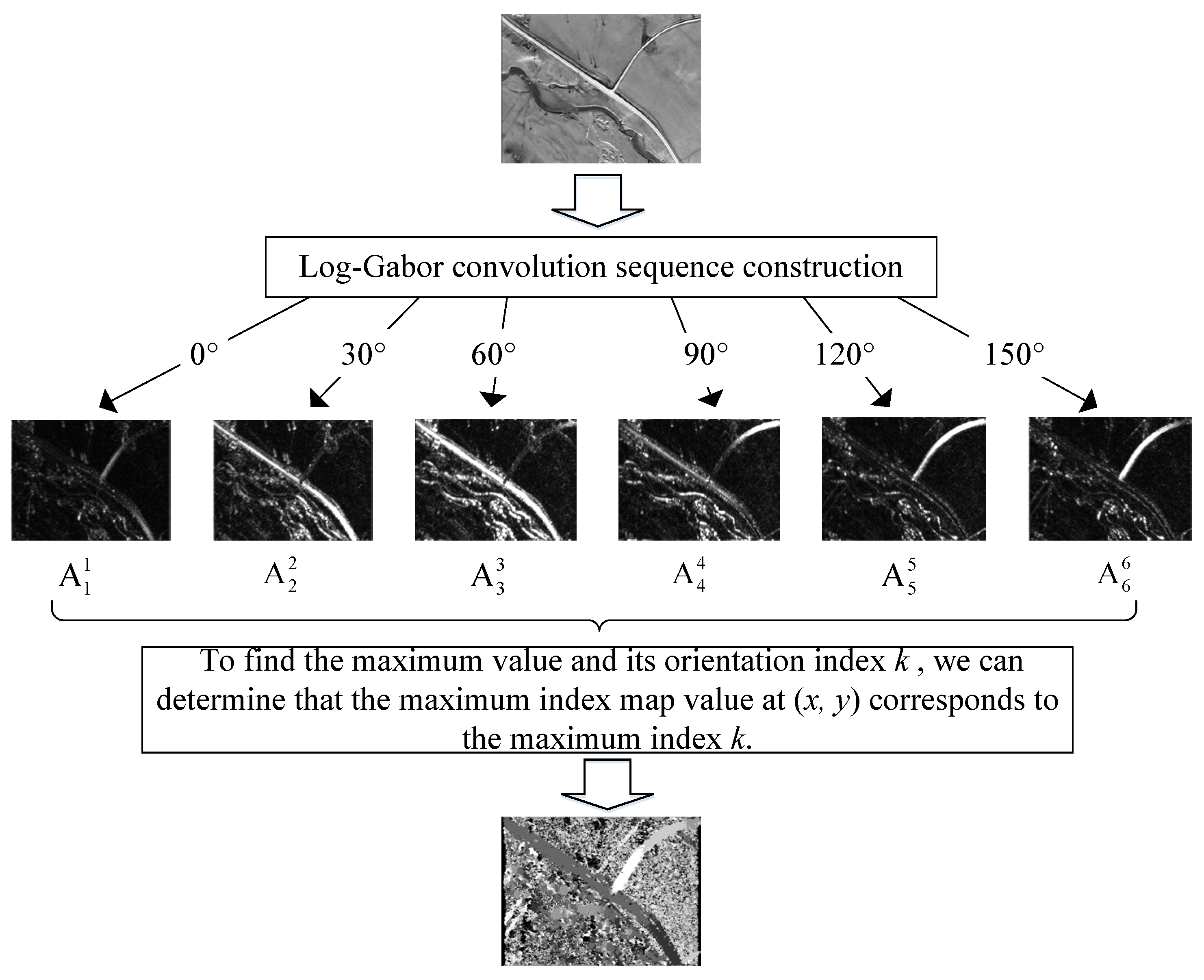
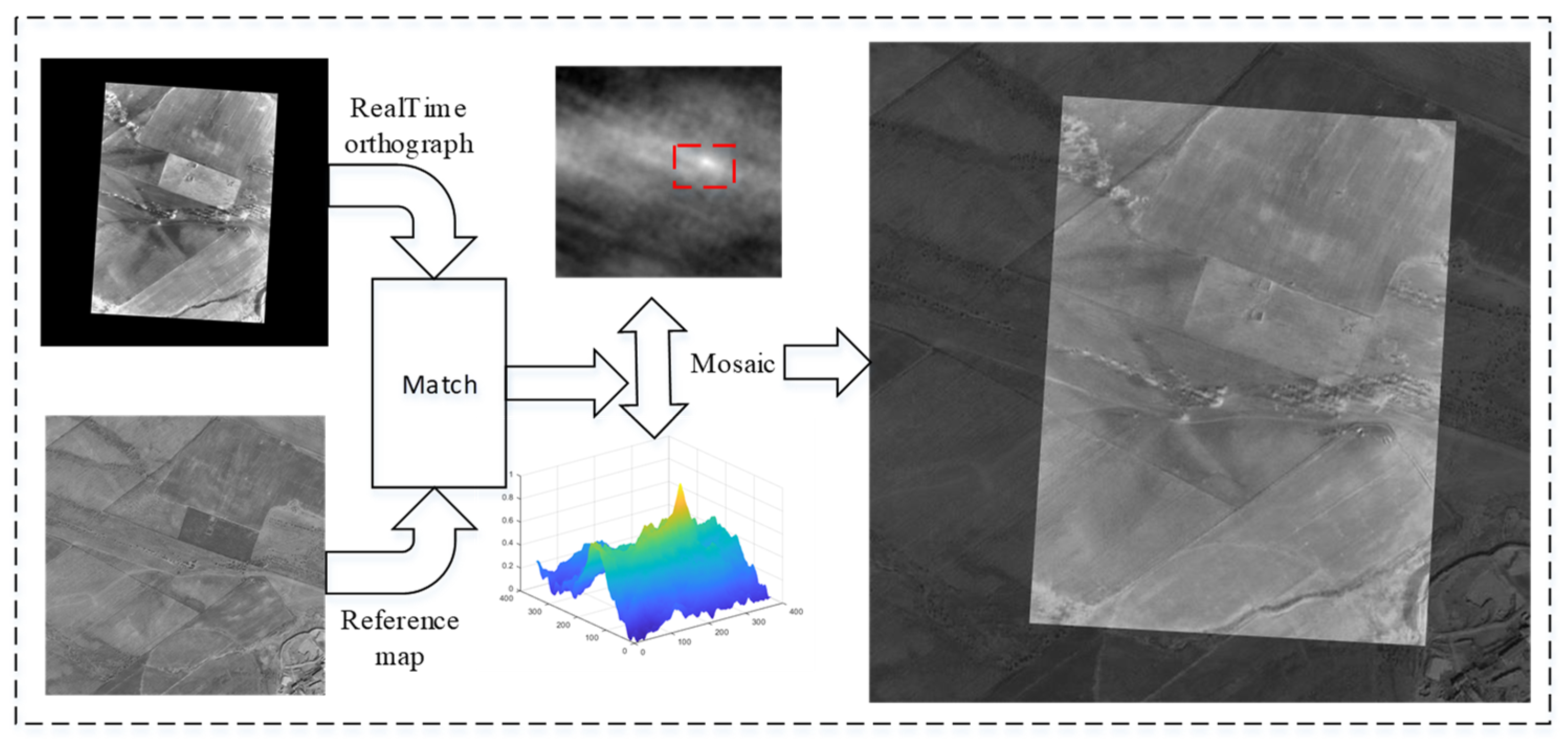
3. Image Registration Method Based on Maximum Index Map
- Calculate the structural feature maps of the infrared image and the satellite map using the Log-Gabor filter;
- Utilize template matching to achieve automatic image matching.
3.1. Log-Gabor Filter
3.2. Maximum Index Map (MIM)
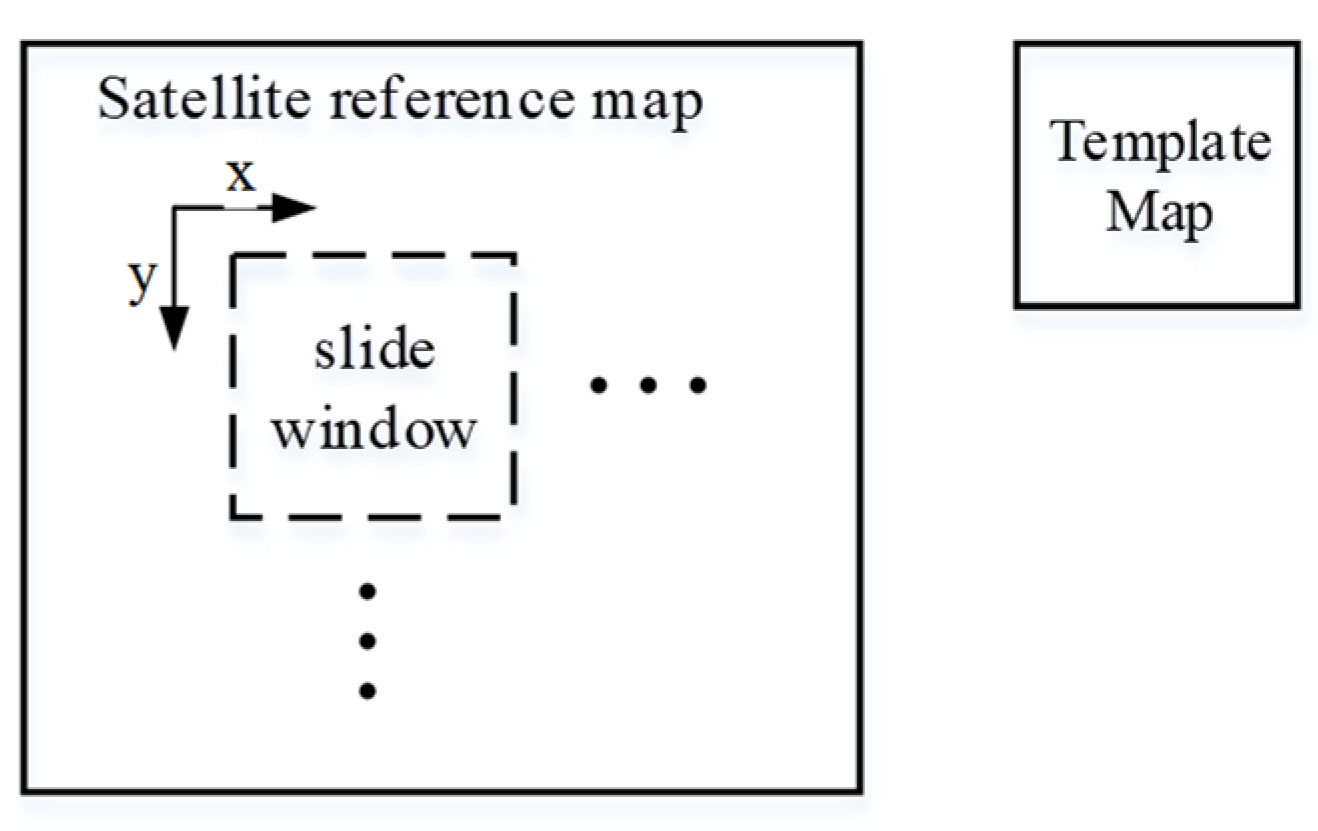
3.3. Template Matching
4. Integrated Navigation Method Based on SINS/SMNS
4.1. State Equation Design
4.2. Measurement Equation Design
4.3. Scene-Matching Position Error Compensation
4.4. Design and Implementation of KF
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
5.1. Integrated Navigation System Verification Platform
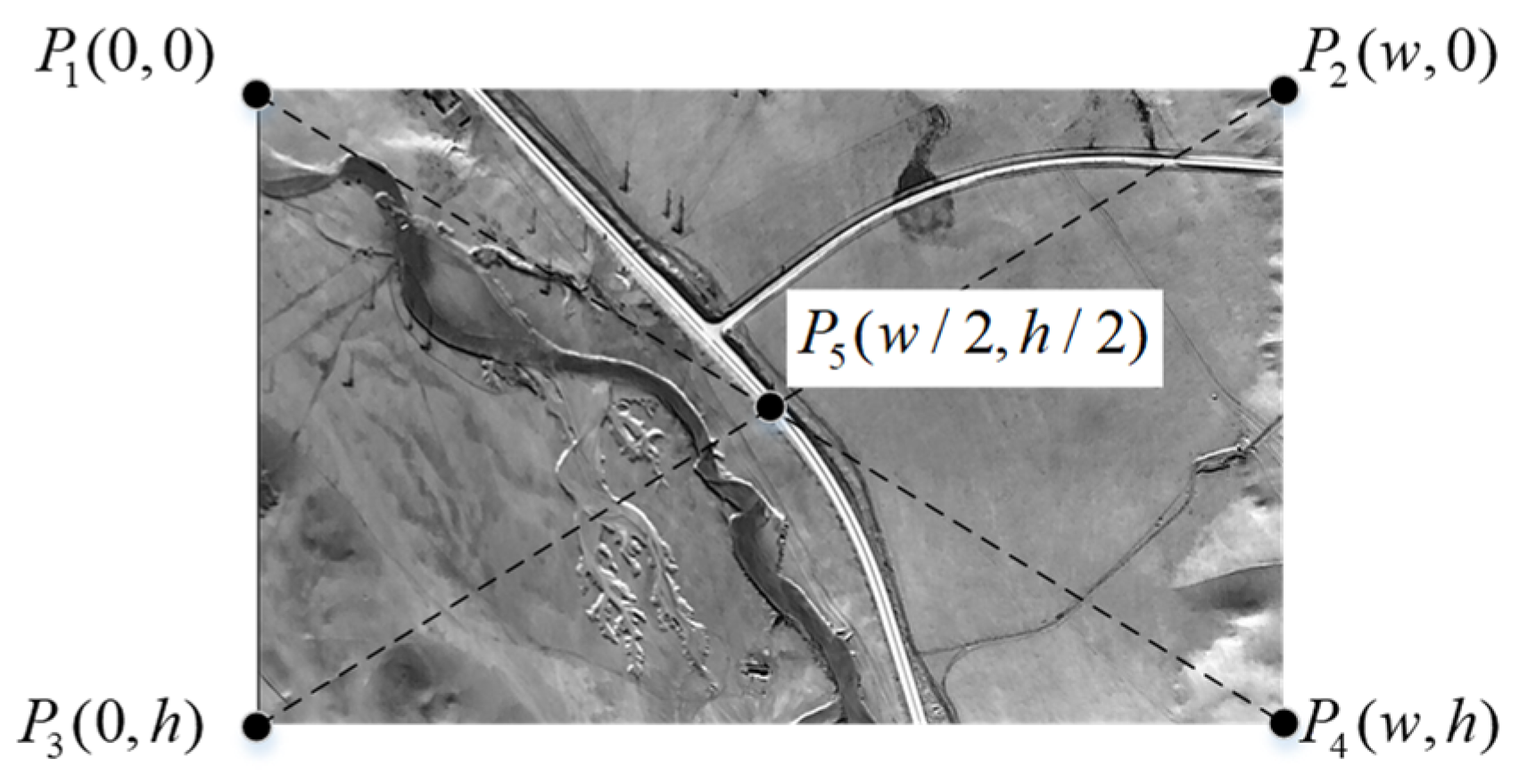
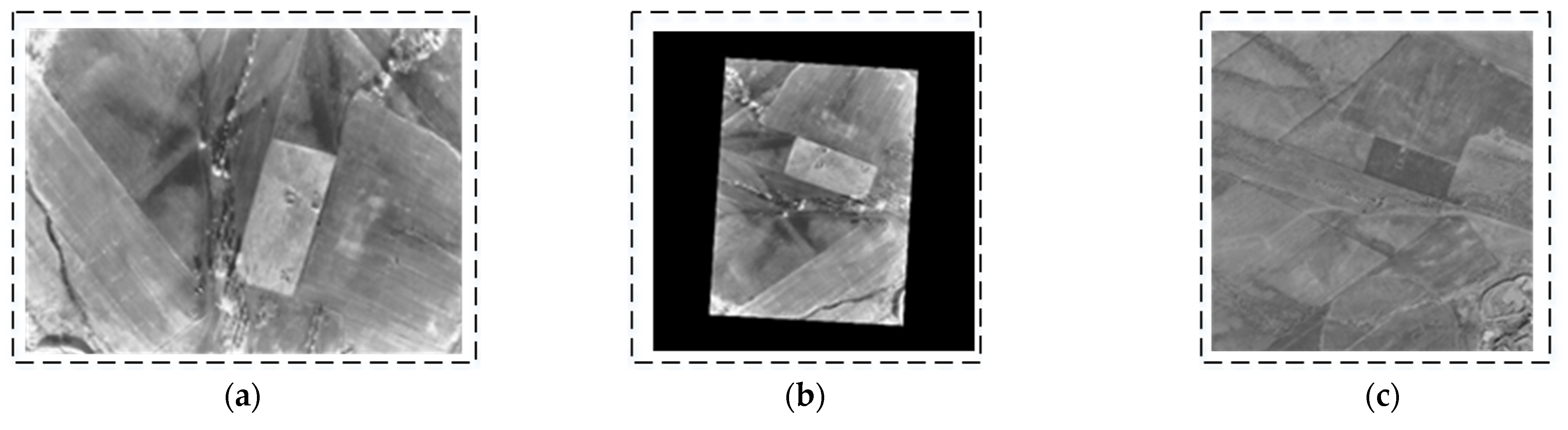
5.2. Experiments on Orthorectification
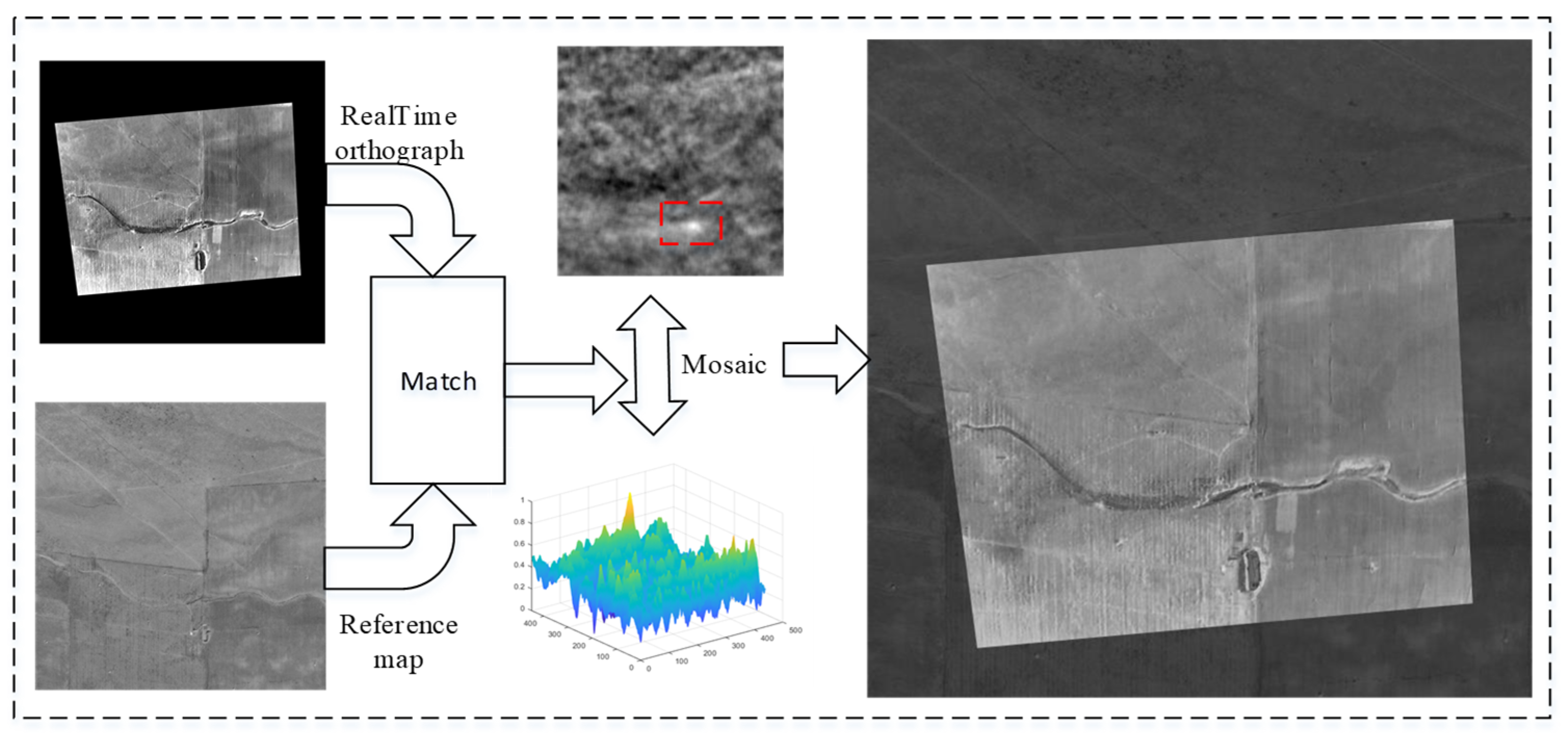
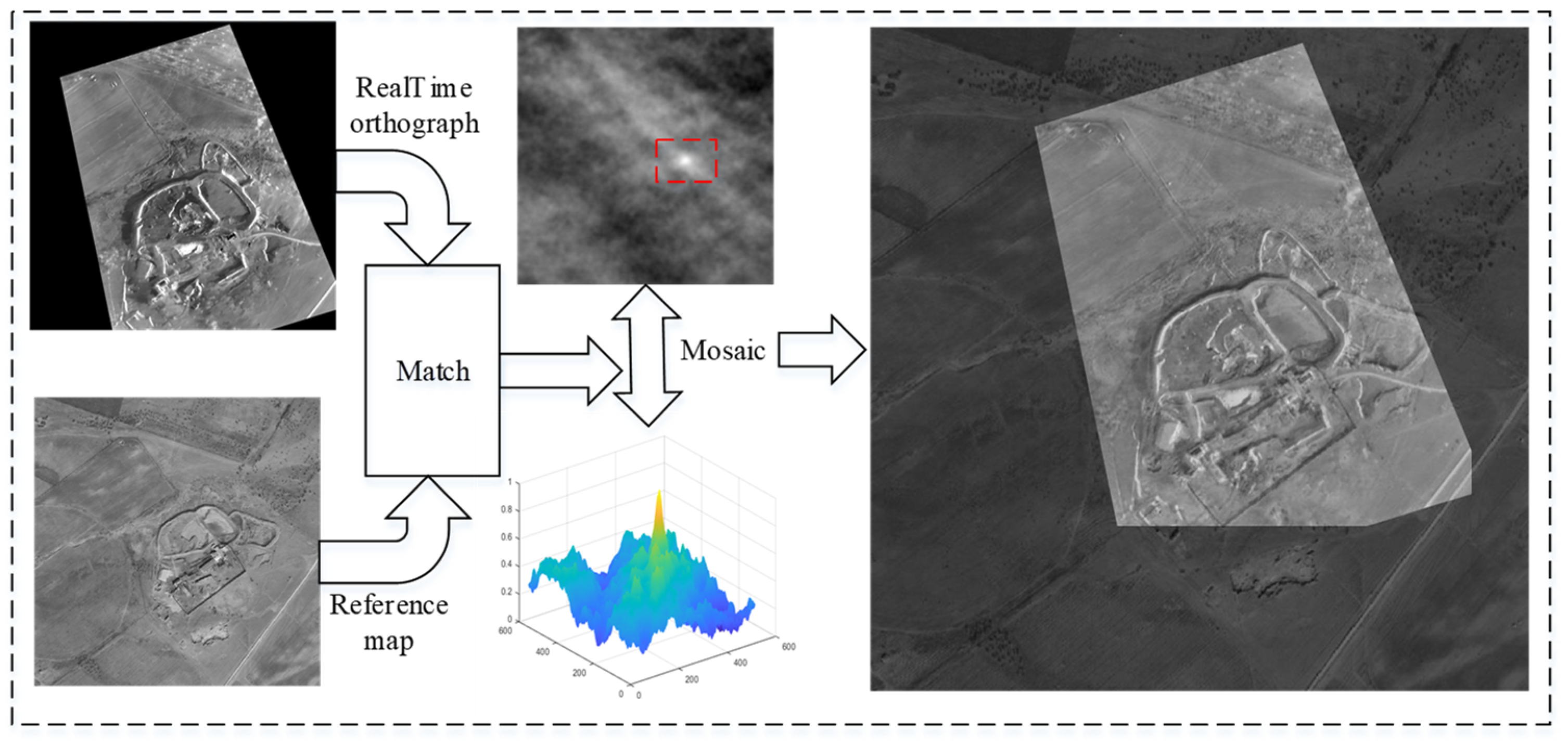
5.3. Experiments on Image Matching
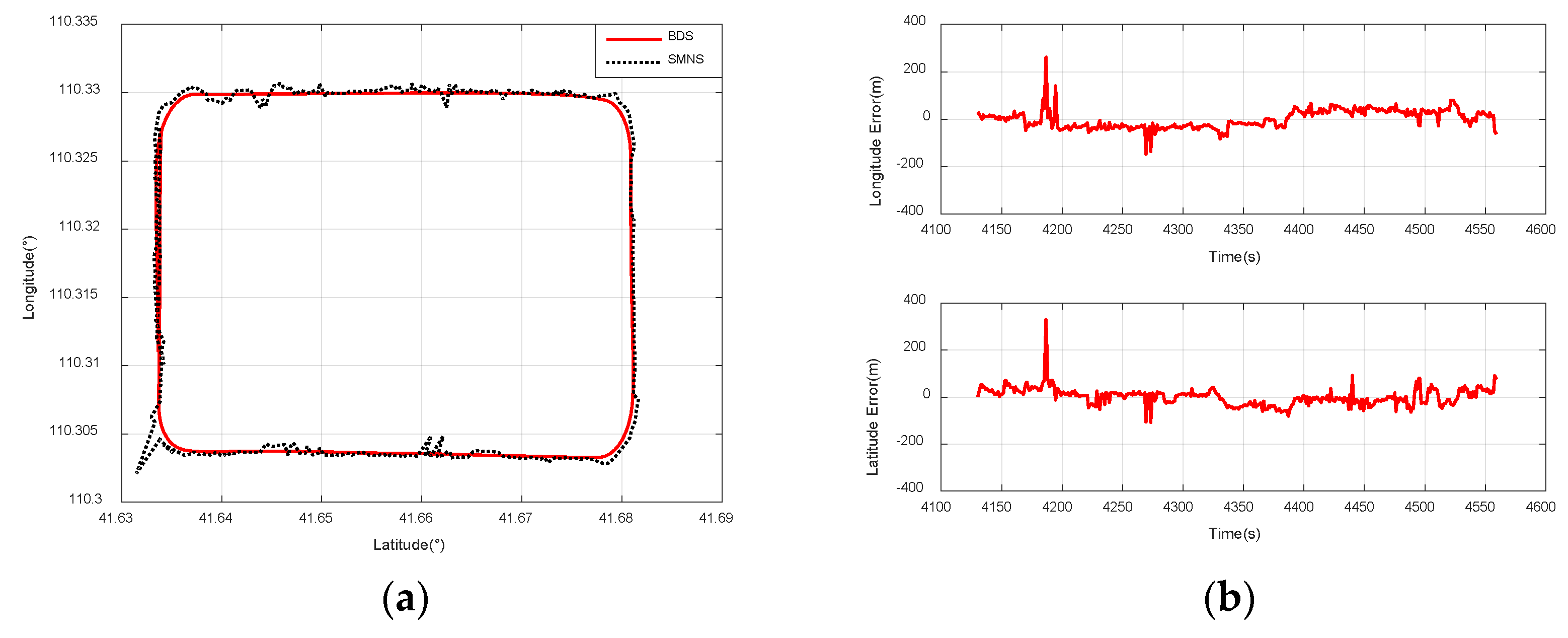
5.4. Experiments on Integrated Navigation
- When the UAV is flying at a relative altitude of 1500 m, the positioning accuracy of the SMNS is superior to that when the UAV is flying at a relative altitude of 3000 m;
- Regardless of the flight path of the UAV, the SMNS exhibits significant errors in positioning results. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced when the UAV undergoes changes in its maneuvering state, where the positioning errors become even more noticeable.
| Name | Conditions | Mean (m) | Standard Deviation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longitude error | Condition I | −3.63 | 61.96 |
| Latitude error | 31.80 | 48.57 | |
| Longitude error | Condition II | 7.49 | 50.61 |
| Latitude error | 16.08 | 40.99 | |
| Longitude error | Condition III | −0.83 | 38.00 |
| Latitude error | 1.34 | 35.78 |
- Latitude error: mean = −10.41 m; std = 26.11 m.
- Longitude error: mean = −2.33 m; std = 34.59 m.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gura, D.; Rukhlinskiy, V.; Sharov, V.; Bogoyavlenskiy, A. Automated system for dispatching the movement of unmanned aerial vehicles with a distributed survey of flight tasks. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 30, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.P.; Rodrigues, V.B.; Pinto, A.B.; Damas, B. Automatic detection of civilian and military personnel in reconnaissance missions using a UAV. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Autonomous Robot Systems and Com-petitions (ICARSC), Tomar, Portugal, 26–27 April 2023; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Wu, J. Tightly coupled GNSS/INS integration with robust sequential Kalman filter for accurate vehicular navigation. Sensors 2020, 20, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Akhtar, F.; Khand, Z.H.; Rajput, A.; Shaukat, Z. Complexity and limitations of GNSS signal reception in highly obstructed enviroments. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 6864–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, F.; Garraffa, G.; Sferlazza, A.; Zaccarian, L. A hybrid observer for localization from noisy inertial data and sporadic position measurements. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2023, 49, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnari, J.; Verdoja, F.; Kyrki, V. GNSS-denied geolocalization of UAVs by visual matching of onboard camera images with orthophotos. In Proceedings of the 2021 20th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 6–10 December 2021; pp. 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, F.; Lin, X. Vision-based localization methods under GPS-denied conditions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.11988. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, P.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, P. Multi-UAV collaborative absolute vision positioning and navigation: A survey and discussion. Drones 2023, 7, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, P.; Hou, Z.; Jin, H. A Novel scene matching navigation system for UAVs based on vision/inertial fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 6192–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Lu, X.; Shen, S. GVINS: Tightly coupled GNSS–visual–inertial fusion for smooth and consistent state estimation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedelbadawi, H.; Żugaj, M. Multi-modal Image Matching for GNSS-denied UAV Localization. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Drones and Unmanned Systems (DAUS‘ 2025), Granada, Spain, 19–21 February 2025; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Velesaca, H.O.; Bastidas, G.; Rouhani, M.; Sappa, A.D. Multimodal image registration techniques: A comprehensive survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 63919–63947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yang, X.; Lu, R.; Li, W.; Huang, Y. Long-term visual tracking algorithm for UAVs based on kernel correlation filtering and SURF features. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, G.; Xiao, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, S. A real-time registration algorithm of UAV aerial images based on feature matching. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wei, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, P.; Wei, X.; Zhou, W. Fast automatic registration of UAV images via bidirectional matching. Sensors 2023, 23, 8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, H.M.; El-Sheimy, N. Feature matching enhancement of uav images using geometric con-straints. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y. An improved SIFT algorithm for registration between SAR and optical images. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Deng, Y. Two-step matching approach to obtain more control points for SIFT-like very-high-resolution SAR image registration. Sensors 2023, 23, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Combination of SIFT and Canny Edge Detection for Registration Between SAR and Optical Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhou, Z. An improved ORB feature extraction and matching algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Kunming, China, 22–24 May 2021; pp. 7289–7292. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Robust optical and SAR image registration based on OS-SIFT and cascaded sample consensus. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4007205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, E.; Ferdman, B.; Weiss, L.E.; Naor, T.; Freedman, D.; Michaeli, T.; Shechtman, Y. Learning optimal wavefront shaping for multi-channel imaging. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2179–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhan, J.-P.; Rau, J.-Y. A generalized tool for accurate and efficient image registration of UAV multi-lens multispectral cameras by N-SURF matching. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 6353–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Ai, M. RIFT: Multi-Modal Image Matching Based on Radiation-Variation Insensitive Feature Transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 3296–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zheng, X.; Duan, Y.; Fang, B.; An, P.; Ma, J. NCFT: Automatic Matching of Multimodal Image Based on Nonlinear Consistent Feature Transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8014105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, X.; Yan, X.; Li, J. Multi-Modal Remote Sensing Image Matching Considering Co-Occurrence Filter. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 2584–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, D.M.; Hemami, S.S. Understanding and simplifying the structural similarity metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Interna-tional Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Motif: Multi-orientation tensor index feature descriptor for sar-optical image registration. ISPRS-Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, XLIII-B2-2, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. Heterologous images matching considering anisotropic weighted moment and absolute phase orientation. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, W.; Zheng, Z.; Xiao, R. Histogram of the orientation of the weighted phase descriptor for multi-modal remote sensing image matching. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 196, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Pati, U.C. A comprehensive review on remote sensing image registration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 5396–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoudh, K.; Knani, R.; Hamdaoui, F.; Mtibaa, A. A survey on deep multimodal learning for computer vision: Advances, trends, applications, and datasets. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 2939–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shen, L. Hopc: A novel similarity metric based on geometric structural properties for mul-ti-modal remote sensing image matching. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, III-1, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Ye, Y.; Tang, T.; Nan, K.; Qin, Y. Robust matching for SAR and optical images using multiscale convolutional gradient features. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4017605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadirov, R.; Lyakhov, P.; Butusov, D.; Nagornov, N.; Reznikov, D.; Bobrov, A.; Kalita, D. Enhancing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Object Detection via Tensor Decompositions and Positive–Negative Momentum Optimizers. Mathematics 2025, 13, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranitsyna, E.V.; Sokolov, A.I. Strapdown Inertial Navigation System Accuracy Improvement Methods Based on Inertial Measuring Unit Rotation: Analytical Review. Gyroscopy Navig. 2024, 14, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrospide, J.; Salgado, L. Log-Gabor filters for image-based vehicle verification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeong, D.J.; Velasco-Hernandez, G.; Barry, J.; Walsh, J. Sensor and sensor fusion technology in autonomous vehicles: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X. Fast template matching in multi-modal image under pixel distribution mapping. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 127, 104454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.-B.; Pan, J.-S. Feature point matching based on distinct wavelength phase congruency and log-gabor filters in infrared and visible images. Sensors 2019, 19, 4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisham, M.; Yaakob, S.N.; Raof, R.; Nazren, A.A.; Wafi, N. Template matching using sum of squared difference and normalized cross correlation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE student conference on research and development (SCOReD), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 December 2015; pp. 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Po, L.M.; Guo, K. Transform-Domain Fast Sum of the Squared Difference Computation for H.264/AVC Rate-Distortion Opti-mization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2007, 17, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, Q.; Gao, W. Image matching by normalized cross-correlation. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE international conference on acoustics speech and signal processing proceedings, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006; p. II-II. [Google Scholar]
- Barrera, F.; Lumbreras, F.; Sappa, A.D. Multimodal template matching based on gradient and mutual information using scale-space. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 2749–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.X. A review of solutions for perspective-n-point problem in camera pose estimation. Proc. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1087, 052009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
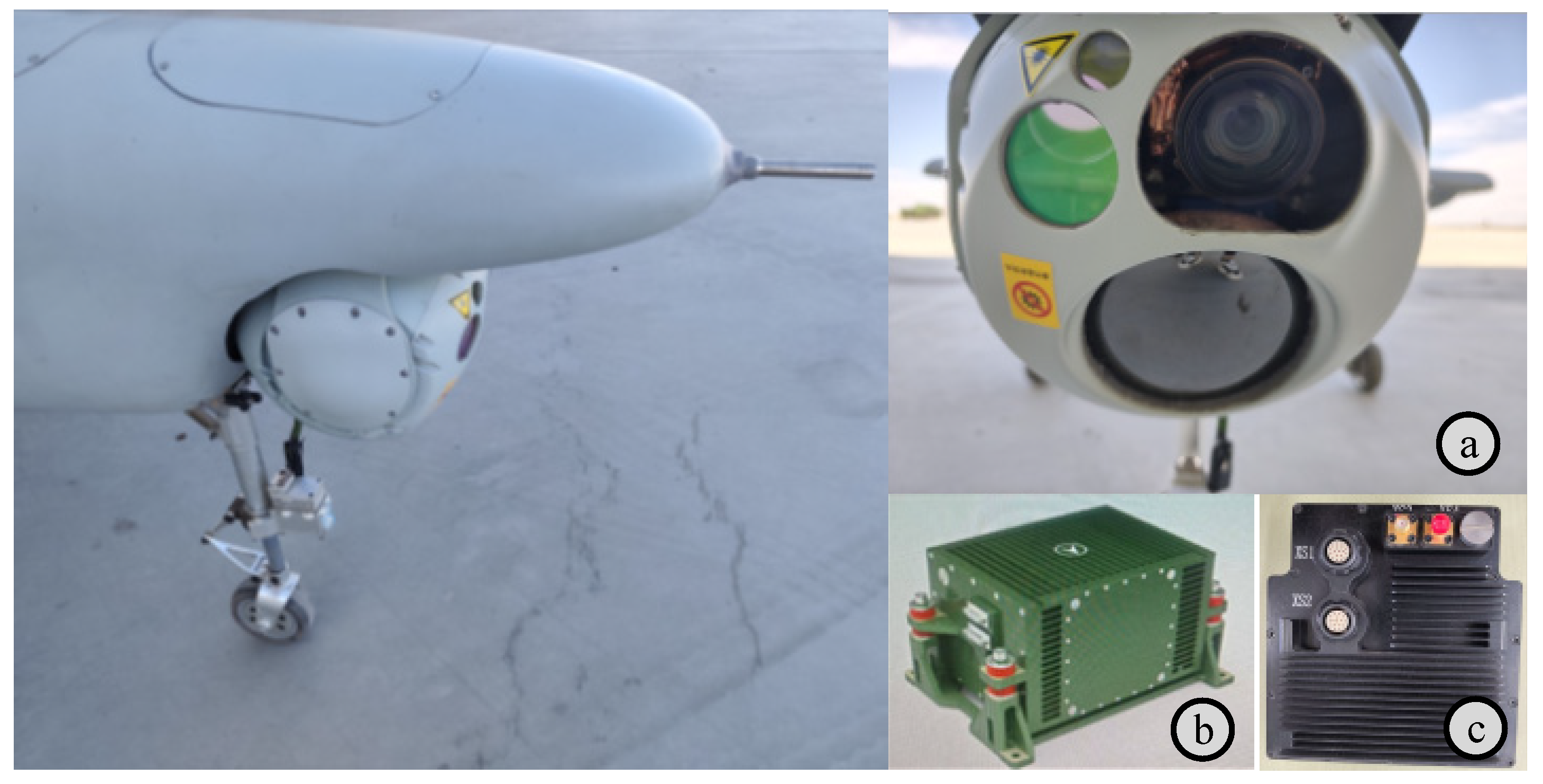









| Device Name | Metric Name | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Laser inertial navigation system | Gyroscope bias stability | ≤0.05°/h |
| Accelerometer bias stability | ≤100 μg | |
| Beidou navigation receiver | Velocity accuracy | ≤0.05 m/s |
| Position accuracy | ≤0.1 m | |
| Atmospheric data sensor system | Airspeed | ≤1 m/s |
| Barometric altitude | ≤10 m | |
| Day–night electro-optical reconnaissance payload | Visible light resolution | 1920 × 1080 |
| Infrared resolution | 1280 × 1024 | |
| Laser ranging accuracy | 5 m | |
| High-performance processor module | GPU | Volta architecture with 512 CUDA cores |
| CPU | 8-core Carmel Armv8.2 64-bit CPU 32 GB | |
| RAM | 256-bit LPDDR4 | |
| External storage | 1 TB SSD |
| ROI Size (Pixel) | Template Matching (ms) | Log-Gabor Filtering (ms) | Orthorectification (ms) | KF (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 × 2000 | 67.33 | 34.62 | 3.96 | 0.02638 |
| 3000 × 3000 | 126.53 | 54.26 | 4.06 | 0.02624 |
| 3800 × 3800 | 209.6123 | 83.51 | 4.07 | 0.02736 |
| 5400 × 5400 | 472.39 | 207.88 | 4.08 | 0.02675 |
| Methods | Error Name | Mean (m) | Standard Deviation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMNS | Latitude error | −9.48 | 54.79 |
| Longitude error | −1.87 | 63.52 | |
| SINS/SMNS | Latitude error | −10.41 | 26.11 |
| Longitude error | −2.33 | 34.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hao, Z.; Chen, P. An Integrated Navigation Method Based on the Strapdown Inertial Navigation System/Scene-Matching Navigation System for UAVs. Sensors 2025, 25, 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113379
Wang Y, Wang Q, Hao Z, Chen P. An Integrated Navigation Method Based on the Strapdown Inertial Navigation System/Scene-Matching Navigation System for UAVs. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113379
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yukun, Qiang Wang, Zhonghu Hao, and Puhua Chen. 2025. "An Integrated Navigation Method Based on the Strapdown Inertial Navigation System/Scene-Matching Navigation System for UAVs" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113379
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, Q., Hao, Z., & Chen, P. (2025). An Integrated Navigation Method Based on the Strapdown Inertial Navigation System/Scene-Matching Navigation System for UAVs. Sensors, 25(11), 3379. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113379






