Clinical Outcomes of Passive Sensors in Remote Monitoring: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
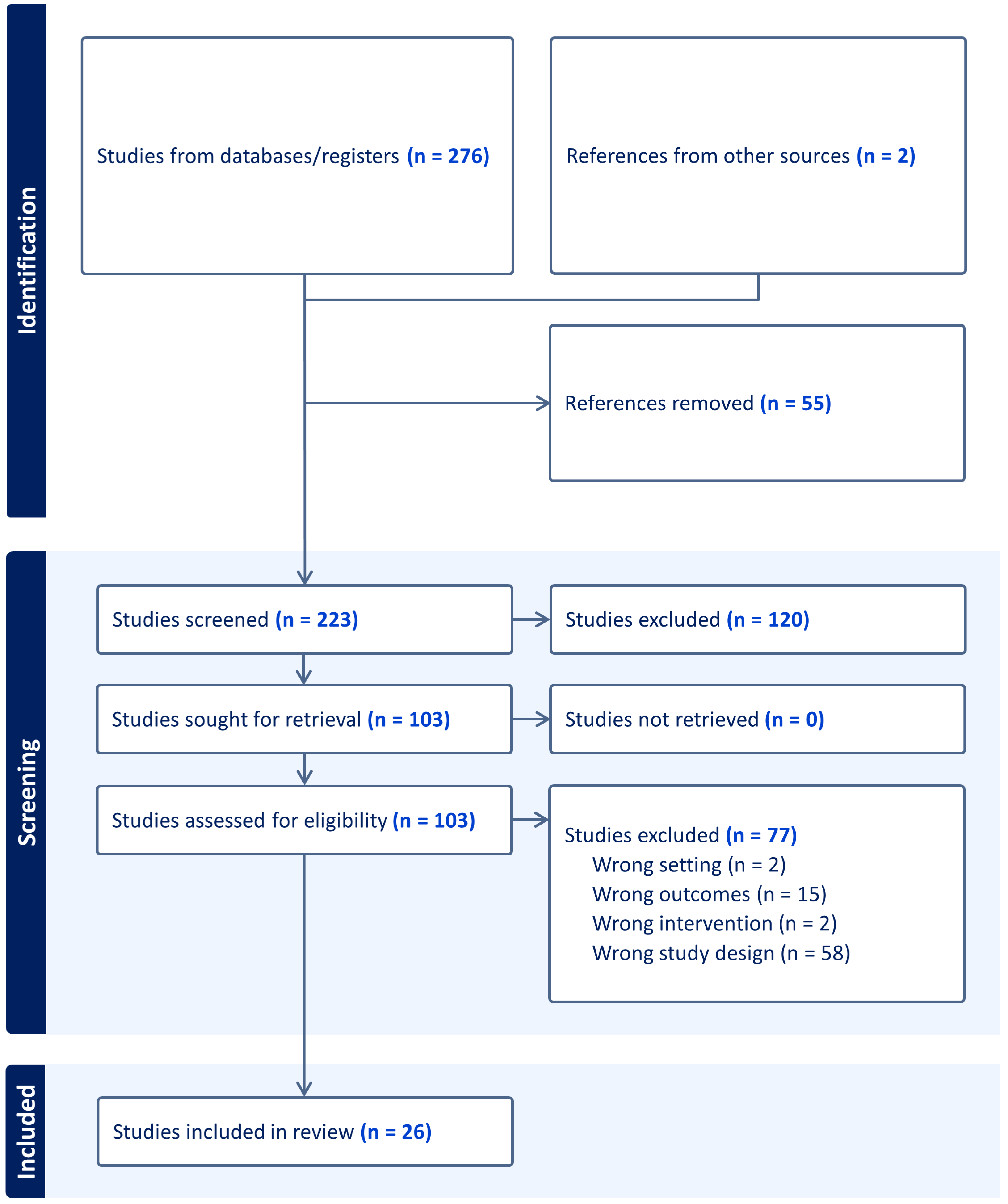
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Types of Passive Sensing Technology
3.3. Patient Populations
3.3.1. Conditions Studied
3.3.2. Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple Sclerosis
3.3.3. Dementia, Mild Cognitive Impairment, Older Adults, and Depression
3.3.4. Cancer
3.3.5. Cardiopulmonary Health
3.3.6. Musculoskeletal Health
3.4. Participant Feedback
3.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Full Search Strategy
| S1 | TI ((remote* or home*) n3 (sens* or monitor*)) OR AB ((remote* or home*) n3 (sens* or monitor*)) | 6699 |
| S2 | TI passive* OR AB passive* | 21,467 |
| S3 | S1 AND S2 | 55 |
| S6 | S1 AND S2 (Limiters—Publication Date: 1 January 2014–31 December 2024 Narrow by Subject Age:—all adult Narrow by Language:—english Search modes—Boolean/Phrase) | 21 |
| S1 | tiab((remote* or home*) near/3 (sens* or monitor*)) | 797 |
| S2 | MAINSUBJECT.EXACT(“Remote sensing”) | 29 |
| S3 | [S1] OR [S2] | 817 |
| S4 | tiab(passive*) | 1974 |
| S5 | [S3] AND [S4] | 6 |
| S6 | ([S3] AND [S4]) AND (yr(2016) OR yr(2022)) | 2 |
| S7 | ([S3] AND [S4]) AND (la.exact(“ENG”) AND (yr(2016) OR yr(2022))) | 2 |
| S8 | tiab((remote* or home*) near/3 (sens* or monitor*)) | 2309 |
| S9 | tiab(passive*) | 31,580 |
| S10 | [S9] AND [S8] | 64 |
| S11 | ([S9] AND [S8]) AND pd(1 January 2014–9 April 2024) | 48 |
| S12 | ([S9] AND [S8]) AND (la.exact(“ENG”) AND pd(1 January 2014–9 April 2024)) | 48 |
| S13 | ([S9] AND [S8]) AND (la.exact(“ENG”) AND subject.exact(“Adulthood (18 yrs & older)”) AND pd(1 January 2014–9 April 2024)) | 28 |
References
- Prince, M.J.; Wu, F.; Guo, Y.; Robledo, L.M.G.; O’Donnell, M.; Sullivan, R.; Yusuf, S. The Burden of Disease in Older People and Implications for Health Policy and Practice. Lancet 2015, 385, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, C.; Sikka, N.; Van, C.M.; Mossburg, S. Remote Patient Monitoring. Available online: https://psnet.ahrq.gov/perspective/remote-patient-monitoring (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Tan, S.Y.; Sumner, J.; Wang, Y.; Wenjun Yip, A. A Systematic Review of the Impacts of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Interventions on Safety, Adherence, Quality-of-Life and Cost-Related Outcomes. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, V.P.; Holden, R.J. Systematic Review of Smartphone-Based Passive Sensing for Health and Wellbeing. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 77, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noah, B.; Keller, M.S.; Mosadeghi, S.; Stein, L.; Johl, S.; Delshad, S.; Tashjian, V.C.; Lew, D.; Kwan, J.T.; Jusufagic, A.; et al. Impact of Remote Patient Monitoring on Clinical Outcomes: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. npj Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 20172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enshaeifar, S.; Zoha, A.; Skillman, S.; Markides, A.; Acton, S.T.; Elsaleh, T.; Kenny, M.; Rostill, H.; Nilforooshan, R.; Barnaghi, P. Machine Learning Methods for Detecting Urinary Tract Infection and Analysing Daily Living Activities in People with Dementia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, M.E.; Doherty, R.; Curtis, F.; Soreq, E.; Lai, H.H.L.; Serban, A.-I.; Dani, M.; Fertleman, M.; Barnaghi, P.; Sharp, D.J.; et al. Using Home Monitoring Technology to Study the Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury in Older Multimorbid Adults. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lach, H.W.; Lorenz, R.A.; Palmer, J.L.; Koedbangkham, J.; Noimontree, W. Home Monitoring to Track Activity and Sleep Patterns Among Older Adults: A Feasibility Study. CIN 2019, 37, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, B.; Meyer, E.; Lazar, A.; Chaudhuri, S.; Thompson, H.J.; Demiris, G. Framing the Evidence for Health Smart Homes and Home-Based Consumer Health Technologies as a Public Health Intervention for Independent Aging: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Med. Inf. 2013, 82, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, F.M.; Lam, K.; Joshi, M.; Khan, S.; Ashrafian, H.; Darzi, A. Clinical Outcomes of Digital Sensor Alerting Systems in Remote Monitoring: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. npj Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, J.A.; Maxwell, S.A.; Mattek, N.; Hayes, T.L.; Dodge, H.; Pavel, M.; Jimison, H.B.; Wild, K.; Boise, L.; Zitzelberger, T.A. Intelligent Systems for Assessing Aging Changes: Home-Based, Unobtrusive, and Continuous Assessment of Aging. J. Gerontol. Ser. B 2011, 66B, i180–i190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capstick, A.; Palermo, F.; Zakka, K.; Fletcher-Lloyd, N.; Walsh, C.; Cui, T.; Kouchaki, S.; Jackson, R.; Tran, M.; Crone, M.; et al. Digital Remote Monitoring for Screening and Early Detection of Urinary Tract Infections. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.L.; Thomas, E.E.; Snoswell, C.L.; Smith, A.C.; Caffery, L.J. Does Remote Patient Monitoring Reduce Acute Care Use? A Systematic Review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e040232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuijt, D.G.; Radanovic, I.; Kos, M.; Schoones, J.W.; Stuurman, F.E.; Exadaktylos, V.; Bins, A.D.; Bosch, J.J.; van Oijen, M.G.H. Smartphone-Based Passive Sensing in Monitoring Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2023, 7, e2300141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifan, A.; Oliveira, M.; Oliveira, J.L. Passive Sensing of Health Outcomes Through Smartphones: Systematic Review of Current Solutions and Possible Limitations. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2019, 7, e12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. PRISMA-P Group Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 Statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covidence. Veritas Health Innovation Covidence Systematic Review Software. 2019. Available online: https://app.covidence.org/sign_in (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Stang, A. Critical Evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for the Assessment of the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay-Karmon, T.; Galor, N.; Heimler, B.; Zilka, A.; Bartsch, R.P.; Plotnik, M.; Hassin-Baer, S. Home-Based Monitoring of Persons with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease Using Smartwatch-Smartphone Technology. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatsios, D.; Antonini, A.; Gentile, G.; Marcante, A.; Pellicano, C.; Macchiusi, L.; Assogna, F.; Spalletta, G.; Gage, H.; Touray, M.; et al. Feasibility and Utility of mHealth for the Remote Monitoring of Parkinson Disease: Ancillary Study of the PD_manager Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2020, 8, e16414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabelac, Z.; Tarolli, C.G.; Snyder, C.; Feldman, B.; Glidden, A.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Hristov, R.; Dorsey, E.R.; Katabi, D. Passive Monitoring at Home: A Pilot Study in Parkinson Disease. Digit. Biomark. 2019, 3, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsmeier, F.; Taylor, K.I.; Kilchenmann, T.; Wolf, D.; Scotland, A.; Schjodt-Eriksen, J.; Cheng, W.-Y.; Fernandez-Garcia, I.; Siebourg-Polster, J.; Jin, L.; et al. Evaluation of Smartphone-Based Testing to Generate Exploratory Outcome Measures in a Phase 1 Parkinson’s Disease Clinical Trial. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tarolli, C.G.; Hristov, R.; Jensen-Roberts, S.; Waddell, E.M.; Myers, T.L.; Pawlik, M.E.; Soto, J.M.; Wilson, R.M.; et al. Monitoring Gait at Home with Radio Waves in Parkinson’s Disease: A Marker of Severity, Progression, and Medication Response. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eadc9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalkamp, A.-K.; Harrison, N.A.; Peall, K.J.; Sandor, C. Digital Outcome Measures from Smartwatch Data Relate to Non-Motor Features of Parkinson’s Disease. npj Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.-H.; Twose, J.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.; Licitra, G.; Meijer, K.; Uitdehaag, B.; De Groot, V.; Killestein, J. The Use of Smartphone Keystroke Dynamics to Passively Monitor Upper Limb and Cognitive Function in Multiple Sclerosis: Longitudinal Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e37614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaugler, J.E.; Zmora, R.; Mitchell, L.L.; Finlay, J.M.; Peterson, C.M.; McCarron, H.; Jutkowitz, E. Six-Month Effectiveness of Remote Activity Monitoring for Persons Living with Dementia and Their Family Caregivers: An Experimental Mixed Methods Study. Gerontologist 2019, 59, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayashi, K.; Kodate, N.; Ishii, Y.; Masuyama, S. Assistive Technologies and Aging in Place for People with Dementia and Disabilities: A Proof-of-Concept Study with in-Home Passive Remote Monitoring with Interactive Communication Functions. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2023, 19, 2341–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muurling, M.; Au-Yeung, W.-T.M.; Beattie, Z.; Wu, C.-Y.; Dodge, H.; Rodrigues, N.K.; Gothard, S.; Silbert, L.C.; Barnes, L.L.; Steele, J.S.; et al. Differences in Life Space Activity Patterns Between Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment Living Alone or as a Couple: Cohort Study Using Passive Activity Sensing. JMIR Aging 2023, 6, e45876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawtaer, I.; Mahendran, R.; Kua, E.H.; Tan, H.P.; Tan, H.X.; Lee, T.-S.; Ng, T.P. Early Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment with In-Home Sensors to Monitor Behavior Patterns in Community-Dwelling Senior Citizens in Singapore: Cross-Sectional Feasibility Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e16854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Dodge, H.H.; Gothard, S.; Mattek, N.; Wright, K.; Barnes, L.L.; Silbert, L.C.; Lim, M.M.; Kaye, J.A.; Beattie, Z. Unobtrusive Sensing Technology Detects Ecologically Valid Spatiotemporal Patterns of Daily Routines Distinctive to Persons with Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2022, 77, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, M.; Griffin, K.; Pacala, J.T. Reduced Healthcare Use and Apparent Savings with Passive Home Monitoring Technology: A Pilot Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saner, H.; Schütz, N.; Botros, A.; Urwyler, P.; Buluschek, P.; du Pasquier, G.; Nef, T. Potential of Ambient Sensor Systems for Early Detection of Health Problems in Older Adults. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leightley, D.; Lavelle, G.; White, K.M.; Sun, S.; Matcham, F.; Ivan, A.; Oetzmann, C.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Lamers, F.; Siddi, S.; et al. Investigating the Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Adults with a Recent History of Recurrent Major Depressive Disorder: A Multi-Centre Study Using Remote Measurement Technology. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadhania, S.; Pakzad-Shahabi, L.; Mistry, S.; Williams, M. Triaxial Accelerometer-Measured Physical Activity and Functional Behaviours among People with High Grade Glioma: The BrainWear Study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, C.A.; Li, M.; Vega, J.; Durica, K.C.; Ferreira, D.; Tam, V.; Hogg, M.; Zeh Iii, H.; Doryab, A.; Dey, A.K. Digital Biomarkers of Symptom Burden Self-Reported by Perioperative Patients Undergoing Pancreatic Surgery: Prospective Longitudinal Study. JMIR Cancer 2021, 7, e27975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, C.A.; Bartel, C.; Fedor, J.; Durica, K.C.; Marchetti, G.; Rosso, A.L.; Campbell, G. Associations between Performance-Based and Patient-Reported Physical Functioning and Real-World Mobile Sensor Metrics in Older Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2024, 15, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, N.; Bui, Q.M.; Wei, Z.; Hernandez-Pacheco, B.; DeYoung, P.N.; Wassell, A.; Duwaik, B.; Desai, A.S.; Bhatt, D.L.; Agnihotri, P.; et al. Passive Longitudinal Weight and Cardiopulmonary Monitoring in the Home Bed. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, K.; Brown, K.; Medina, M.; Alvarez, F.; Young, J.; Leadley, S.; Kim, Y.; DiCarlo, L. Medication Adherence and Activity Patterns Underlying Uncontrolled Hypertension: Assessment and Recommendations by Practicing Pharmacists Using Digital Health Care. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2016, 56, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vahia, I.V.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; May, R.; Cray, H.V.; McGrory, W.; Katabi, D. Contactless In-Home Monitoring of the Long-Term Respiratory and Behavioral Phenotypes in Older Adults with COVID-19: A Case Series. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 754169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tsai, M.-J.; Chuang, T.-Y.; Lee, O.K.-S. Wearable Motion Sensor Device to Facilitate Rehabilitation in Patients with Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis: Pilot Study to Assess Feasibility. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perraudin, C.G.M.; Illiano, V.P.; Calvo, F.; O’Hare, E.; Donnelly, S.C.; Mullan, R.H.; Sander, O.; Caulfield, B.; Dorn, J.F. Observational Study of a Wearable Sensor and Smartphone Application Supporting Unsupervised Exercises to Assess Pain and Stiffness. Digit. Biomark. 2018, 2, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Castro, A.L.; Surmacz, K.; Aguilera-Canon, M.C.; Anderson, M.B.; Van Andel, D.; Redfern, R.E.; Cook, C.E. Early Post-Operative Walking Bouts Are Associated with Improved Gait Speed and Symmetry at 90 Days. Gait Posture 2024, 107, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piau, A.; Wild, K.; Mattek, N.; Kaye, J. Current State of Digital Biomarker Technologies for Real-Life, Home-Based Monitoring of Cognitive Function for Mild Cognitive Impairment to Mild Alzheimer Disease and Implications for Clinical Care: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spira, A.P.; Kaufmann, C.N.; Kasper, J.D.; Ohayon, M.M.; Rebok, G.W.; Skidmore, E.; Parisi, J.M.; Reynolds, C.F. Association between Insomnia Symptoms and Functional Status in U.S. Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. B 2014, 69 (Suppl. S1), S35–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, G.; Bennett, P.; Vardy, E.R.L.C. Virtual Wards: A Rapid Evidence Synthesis and Implications for the Care of Older People. Age Ageing 2023, 52, afac319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Condition or Disease | Sample Size (N) | Length of Monitoring | Sensor(s)/Feedback to Participants | Outcome Measures | Algorithms/Machine Learning | Compliance and Acceptability/Feasibility | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fay-Karmon et al., 2024 [20] | Parkinson’s disease | 21 | 14 days | Smartwatch | Compliance (smartwatch usage). Smartwatch algorithm scores for tremor, dyskinesia and activity. Clinic recorded MDS-UPDRS, Daily and in-clinic motor tasks, daily symptom diary and medication intake report. | Smartwatch data as input to two algorithms: free living and motor tasks algorithm (Intel Pharma Analytics). | Compliance: 81% wearing the smartwatch for more than 12 h daily. | Validity: Significant correlation between SWA scores for tremor and both clinician assessment and MDS-UPDRS scores for tremor. Patterns: Patients categorised into four groups according to individual patterns of tremor fluctuations. |
| Gatsios et al., 2020 [21] | Parkinson’s disease | 132 | 14 days | Smartphone, wristband, insoles | Compliance (protocol completion, median usage). Measures of motor and non-motor function: NMSS, UPDRS, EQ-5D-5L, PDQ-8. | An algorithm derived from a single sensor on the wrist for detecting tremor in PD patients (PD_manager). | Compliance: 85% participants completed the protocol. Median use was 11.57 days over a 14-day period. | Validity: Significant correlation between tremor score and tremor evaluation by clinicians. Significant difference between tremor score between no-tremor (UPDRS = 0) and tremor (UPDRS > 1) groups. |
| Kabelac et al., 2019 [22] | Parkinson’s disease | 7 | 353 days | Radio-wave based in-home monitoring (Emerald device) | Activity: Gait speed, time in bed per day, circadian schedule (number and duration of nighttime awakenings, intraday rest-activity rhythms). Baseline MDS-UPDRS. | N/A | Validity: Significant correlation between device-derived gait speed and MDP-UDRS scores. | |
| Lipsmeier et al., 2018 [23] | Parkinson’s disease | 79 (35 controls) | 6 months | Smartphone based active and passive sensing | Compliance (test session completion). Activity: algorithm determined turning speed, sit to stand transitions, proportion of gait-related activity. MDP-UPDRS during screening. Active smartphone motor testing. | Machine-learning algorithm used to classify accelerometer data into labelled activities (e.g., walking, climbing stairs, standing, and sitting). | Compliance: 61% of possible test sessions over 6 months. | Validity: All active and passive monitoring features significantly discriminated PD from controls. PD participants had less time performing gait related activities, fewer sit to stand transitions and slower 90 degree turns than controls. |
| Liu et al., 2022 [24] | Parkinson’s disease | 50 (16 controls) | 1 year (only first year included) | Radio-wave based in-home monitoring | Activity: In-home gait speed. Clinical assessment at baseline, 6 months and 12 months: MDS-UPDRS, H&Y stage, TUG, Intraday ON-OFF state from Hauser diary. | Machine learning algorithms to analyse the reflected radio signals and extracted walking movements and trajectories through the home. | Validity: Significant correlation between in-home gait speed and MDS-UPDRS and H & Y stage. Individuals with PD had about 23% lower in-home gait speed than the control cohort The decline in gait speed over one year was greater for the PD group (−0.026 m/s) compared to the control group (−0.015 m/s). Patterns: intraday gait speed oscillates according to medication administration and variation in intraday gait speed is highly correlated with patient perception of disease impact on daily function. | |
| Schalkamp et al., 2024 [25] | Parkinson’s disease | 149 | 485 days | Smartwatch | Activity: Weekly averages of: sleep (total time, REM time, NREM time, WASO, awakenings, sleep efficiency), physical activity (step count, walking minutes), and vital signs (pulse rate, mean RMSSD, median RMSSD, RMSSD variance). Clinic assessments: UPDRS, MoCA, LNS, HVLT, GDS, STAI, ESS, SCOPA, RBDSQ. | N/A | Validity: Digital measures capturing weekly averages of physical measures are concordant with clinical assessments of multiple non motor symptoms (cognitive, autonomic and daily functioning). Prediction: Digital weekly averages could not predict the scores of standardised non motor symptom questionnaires. | |
| Lam et al., 2022 [26] | Multiple sclerosis | 102 | 1 year | Smartphone | Smartphone keystroke dynamics: fine motor cluster and cognition score clusters. Standard measures: nine-hole peg test (arm function), symbol digit modalities test (information processing speed). | Keystroke features were processed to form fine motor and cognition score clusters. | Validity: The fine motor score cluster was significantly associated with the nine-hole peg test. The cognition score cluster was significantly associated with the symbol digit modalities test. Smartphone keystroke dynamics were longitudinally associated with multiple sclerosis outcomes. | |
| Gaugler et al., 2019 [27] | Dementia | 132 (64 remote monitoring, 68 usual care control) | 6 months | Home activity monitors. Feedback: Significant and persistent deviations from baseline are communicated to family caregivers. | Mean caregiver self efficacy, sense of competence and distress. | Data are analysed using algorithms. Baseline activity pattern is established. | No difference in caregiver mean self efficacy, sense of competence and distress at 6 months with remote monitoring compared to control. | |
| Obayashi et al., 2023 [28] | Dementia | 5 | 12 weeks | Home passive infrared sensors, biometric sensors. Feedback: Alerts from the system are communicated to terminals held by care providers. | Activity: movement and sleep patterns. Weekly measures of ICF (seven measures): communication, movement, self-care, domestic activities, interpersonal activities, performing tasks (money and leisure). Weekly interRAI measurements (care measure). | N/A | Improvements in weekly measures of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) score. One participant no longer required an in-person helper at night. | |
| Muurling et al., 2023 [29] | Mild cognitive impairment | 129 homes with people living alone, 52 homes with people living as a couple | Mean of 719 days | Home passive infrared sensors, door contact sensors. | Activity: In 2-person vs. 1-person homes and MCI vs. non-MCI homes: TOOH, ILSA, kitchen, bathroom, bedroom and living room use. | Algorithms to calculate TOOH and ILSA. | Activity: People living together have a shorter TOOH, a longer ILSA, and longer room use, but only ILSA was affected by MCI status. | |
| Rawtaer et al., 2020 [30] | Mild cognitive impairment | 49 (21 controls) | 2 months | Multimodal sensor system: home passive infrared motion sensors, door contact sensor, proximity beacon tags, sensor-equipped medication box, faucet usage sensor, bed sensor, wearable sensor, smart plug. Feedback: If the system detected no movement for 8 h, an alert was sent to the caregiver. | Acceptability of sensor system Activity: Daily step count, heart rate, Sleep duration, number of sleep interruptions, time away from home daily, television use. Frequency of forgetting medication, wallet and keys. | N/A | Acceptability: Sensor system was acceptable to 80% (40/49). | Activity: MCI participants were less active, had more sleep interruptions per night and forgot their medications more frequently than their cognitively healthy counterparts, although none reached significance. |
| Wu et al., 2022 [31] | Mild cognitive impairment | 161 older adults (26 with mild cognitive impairment) | 1 month | Home passive infrared sensors, door contact sensors. | Activity: trips to bathroom, bedroom, kitchen and living room. Latent trajectory models used to identify distinct diurnal patterns of room activities. | Algorithm used to extract room activities and out-of-home activities from the motion sensors. | Activity: No difference in the total number of trips to rooms at a day level between MCI and non-MCI participants. However, MCI participants were more likely to be in the high bathroom and kitchen usage groups based on diurnal patterns of activity | |
| Finch et al., 2017 [32] | Older adults | 268 (74 with passive monitoring, 2 control groups) | 12 months | Home passive monitors. Feedback: Trending health alerts and real-time alerts and an emergency response pendant connecting the participant to an emergency call centre. | Activity: time in bed, toilet use, opening/closing of refrigerator, front door opening. Healthcare costs per member per month (inpatient, ED, LTC, SNF, ambulance, home care, outpatient, pharmacy, other, total). Healthcare use per member per month (acute hospitalisations, hospital days, ED visits, LTC admissions, LTC days, SNF admissions, SNF days, home care visits, outpatient visits). | Algorithms identified trends, which automatically trigger health alerts. | Healthcare costs: mean total per member per month costs were lower for the intervention group. Costs for inpatient services and ED visits were at least 10% lower in the intervention group. Home care and outpatient costs were not different. No differences were statistically significant for cost. Healthcare use: the intervention group had fewer acute hospitalisations, ED visits, long-term care admissions and days, and SNF admissions. | |
| Lach et al., 2019 [8] | Older adults | 5 | 3 months | Home motion sensors, bed sensor, chair sensor, door sensor, wearable sensor. | Feasibility (subjective). Activity: daily activity, sleep time and sleep efficiency, kitchen activity, bathroom activity, total activity, entry/exit, time in bed. | N/A | Validity: Sleep and activity data were similar across actigraphy and sensor measures. | |
| Saner et al., 2020 [33] | Older adults | 20 | 1 to 2 years | Multimodal sensor system: home passive infrared sensor, door sensor, bed sensor, wearable sensor. | Feasibility (completion). Activity: motion in the home, entry/exit, room use, sleep duration and disruption. Vital signs. Health deterioration: heart failure decompensation, palpitations, falls, pneumonia, urinary infection, pulmonary embolism. Health-related data collected from weekly visits: EQ-5D-3L questionnaire, information about accidents, information about lifestyle changes. | Sleep data extracted using algorithms. | Feasibility: 20/24 completed the study (2 died, 2 suffered health deterioration). 242,232 person hours were recorded. | Health deterioration: Episodes of heart failure decompensation were characterised by decreased activity, increased respiratory and heart rates and decreased sleep quality. Patient complaints of intermittent palpitations were confirmed by heart rate increases measured by the bed sensor. |
| Parkinson et al., 2023 [7] | Older adults (traumatic brain injury) | 3 | 6 months | Home passive infrared sensor, pneumatic bed mat. | Activity: bedroom, bathroom and kitchen activity, sleep patterns and disruption. Health deterioration: pneumonia, worsening sleep disturbance. | N/A | Health deterioration/recovery: an abnormally high overnight activity correlated with an episode of pneumonia in one patient, whereas consistent sleep cycles mapped a return to work for another patient recovering from traumatic brain injury. | |
| Leightley et al., 2021 [34] | Depression | 252 | 9 months | Smartphone, wearable sensor (RADAR-MDD) | Sleep duration. PHQ-8 Depressive symptom questionnaire and Rosenberg self-esteem scale questionnaire. | N/A | Mean sleep duration decreased significantly between during- and post-lockdown periods. No evidence of change in depressive symptoms or self-esteem before, during, or post lockdown. | |
| Dadhania et al., 2023 [35] | High grade glioma | 42 | Up to 14 weeks | Wearable sensor (wrist worn accelerometer) | Activity: mean daily activity, time spent performing functional activities (walking, light tasks, moderate activity, sedentary, sleep). PRO questionnaires: EORTC QLQ-C30, QLQ BN20, MoCA, MFI. Clinical data: MRI imaging, histopathology, radiotherapy and chemotherapy treatment plans. | Raw data classified into 5 accelerometer-predicted functional behaviours using a two-stage machine learning model. | Validity: Mean acceleration and time spent walking daily correlated positively with health quality of life and physical functioning scores and inversely with fatigue score. | |
| Low et al., 2021 [36] | Pancreatic cancer | 44 | At least 2 weeks prior to surgery and 60 days after postoperative discharge. | Smartphone with AWARE app, wearable sensor. | Activity: duration of exertional and nonexertional activity and sleep. Patient-reported symptoms each morning: pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, trouble concentrating, feeling sad, feeling anxious, shortness of breath, numbness, nausea, diarrhoea or constipation. | Models used sensor data to predict whether the next day would be a high or low symptom burden day. | Prediction: Models using LightGBM were able to correctly predict whether the next day would be a high symptom day with 73.5% accuracy, surpassing baseline models. LightGBM models predicting next-day diarrhoea (79.0% accuracy), fatigue (75.8% accuracy), and pain (79.6% accuracy) performed similarly. | |
| Low et al., 2024 [37] | Older cancer survivors | 40 | 4 weeks | Smartphone, wearable sensor. | Activity: daily step count, peak gait cadence, activity fragmentation, time at home, total distance travelled, geographic mobility. PRO: PROMIS-PF. Performance-based physical function: SPPB, TUG. | N/A | Validity: Wearable device features reflecting greater amount and speed and lower fragmentation of walking in daily life were significantly related to better patient-reported function and performance-based physical function. Smartphone features reflecting more geographic mobility were related to better performance-based physical function but not patient-reported function. | |
| Harrington et al., 2021 [38] | Heart failure | Feasibility in 8 patients, long term monitoring of 1 patient. | 3 months | Bed sensor (BedScales) | Overnight sleep study for validation of respiratory monitoring, heart rate monitoring and sleep study and apnoea monitoring. Long term monitoring of a heart failure patient: RR, HR, weight, presence or absence in bed. | Total body weight, respiratory waveforms, ballistocardiography quantified from force sensor data. Algorithms separate signals when the bed is shared by a partner or pet. | Validity: Close quantitative agreement of respiratory rate with measurements of belt respirometer. Heart rate monitoring showed quantitative agreement with ECG recordings. In overnight sleep studies, Bedscales could discriminate central and obstructive apneas. Health deterioration/recovery: RR and HR decreased to presurgical levels over the course of two months. | |
| Noble et al., 2016 [39] | Hypertension | 39 | 2 weeks | Ingestible sensor, wearable ‘patch’ sensor Feedback: Digital health feedback system: measurement of medication adherence using an ingestible sensor to inform tailored advice regarding medication or lifestyle modifications. | Serial blood pressure recordings | N/A | The mean change in SBP over the 2-week evaluation period was −7.9 ± 22.1; the mean change in DBP was −2.8 ± 12.9. | |
| Zhang et al., 2021 [40] | COVID-19 | 3 | 327 days | Radio-wave based in-home monitoring (Emerald device) | Activity: Gait speed, sleep patterns (sleep efficiency and total time in bed), home activity patterns. Respiratory signals (RR). COVID-19 testing. | The sensor transmits wireless signals and analyses their reflections from nearby humans and inanimate objects using machine learning to infer physiological and behavioural markers. | Health deterioration/recovery: RR of patient 1 shows a smooth recovery, whereas patient 2 had a sudden increase in RR on day of hospitalisation. Asymptomatic patient 3 had a stable RR for the whole recovery period. | |
| Chen et al., 2020 [41] | Adhesive capsulitis | 15 | 3 months | Wearable sensors (sternum, upper arm and wrist) Feedback: Physiotherapists can view the latest shoulder ROM, exercise completion rates, can assign exercises for and directly communicate with patients through the mobile app. | Sensor measured shoulder mobility. Patient reported daily exercise completion rate. Clinic measurements of shoulder active and passive ROM by two examiners PRO: qDASH (shoulder function) and VAS (pain) | Raw data from each sensor was converted into a 3-dimensional (3D) motion of the shoulder structure | Compliance: those in the motion sensor–assisted rehabilitation group had a significantly higher patient-reported exercise completion rate. | Validity: Good to excellent reliability of the motion sensor device for measuring shoulder ROM compared to measurements of two physicians. Activity: Patients in the motion sensor-assisted rehabilitation group had significantly better ROM improvement, pain reduction and higher exercise completion rates than the home-based exercise group after three months of rehabilitation |
| Perraudin et al., 2018 [42] | Arthritis | 45 (15 controls) | 4 weeks | Wearable sensor (wrist worn accelerometer) | Adherence to STS tests 5 × STS test duration (3 times weekly) PRO questionnaires: 8 items on pain and stiffness | Algorithm to detect 5 × STS tests | Compliance: 56% of tests performed. | Validity: 5 × STS test duration was significantly associated with pain and stiffness intensity reported by patient-reported outcome questionnaires. |
| Ribeiro-Castro et al., 2024 [43] | Joint arthroplasty | 2255 | 90 days | Smartphone | Activity: Gait quality metrics within 30 days of surgery. Gait speed at 90 days post surgery. | Accelerometer data from smartphone was converted into gait quality metrics | Activity: Gait speed at 90 days was significantly associated with 30-day session length in the TKA and THA cohorts Across procedure types, more evenly distributed walking bouts during the early post-operative period were positively associated with gait speed at 90 days. |
| Sensor Context | Type of Sensor | Sensor Data/Outcome Measure | Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wearable | Wrist/Arm worn sensors (smartwatch, Fitbit, AX3 accelerometer, armband sensors) | Physical activity | [20,21,25,35] |
| Step count | [25,30,36,37] | ||
| Gait speed | [37] | ||
| Functional behaviours | [35] | ||
| Tremor/Dyskinesia | [20,21] | ||
| Shoulder range of motion | [41] | ||
| Five times sit to stand test duration | [42] | ||
| Sleep duration | [8,21,25,34,36] | ||
| Sleep efficiency | [8,21,25] | ||
| Heart rate | [25,30,33,34,36] | ||
| Respiratory rate | [33] | ||
| Skin temperature/galvanic skin response | [33] | ||
| Patch sensor (torso) | Step count | [39] | |
| Sleep duration and interruption | [39] | ||
| Insoles | Weight bearing, balance and motion | [21] | |
| Gait | [21] | ||
| Ingestible | Ingestible sensor | Medication adherence | [39] |
| Portable | Smartphone | Activity recognition | [23,36] |
| Gait features | [43] | ||
| Speech patterns | [21,34] | ||
| Mood | [21,34] | ||
| Cognitive function | [21,34] | ||
| Keystroke dynamics | [26] | ||
| Application use | [36] | ||
| Location/Distance travelled | [36,37] | ||
| Light | [36] | ||
| Screen features | [36] | ||
| In-home | Home activity monitor | Activity patterns | [8,27,32] |
| Infrared camera | Activity patterns | [28] | |
| Sleep patterns | [28] | ||
| Living conditions | [28] | ||
| Infrared sensor | Room use/activity | [7,29,31,33] | |
| Time out of home | [29,30] | ||
| Independent life space activity | [29] | ||
| Radio-signals sensor | Room use/activity | [40] | |
| Sleep patterns | [22] | ||
| Sleep efficiency | [40] | ||
| Gait speed | [22,24,40] | ||
| Respiratory rate | [40] | ||
| Biometric sensor | Body temperature | [28] | |
| Heart rate | [28] | ||
| Respiratory rate | [28] | ||
| Door contact sensor | Time out of home | [29,30] | |
| Entry/exit to home | [30,33] | ||
| Room use | [31] | ||
| Refrigerator use | [33] | ||
| Bed sensor | Sleep duration | [7,8,30,33] | |
| Sleep interruption | [7,30] | ||
| Sleep onset delay | [33] | ||
| Movements in bed | [7,33] | ||
| Body weight | [38] | ||
| Heart rate | [7,33,38] | ||
| Respiratory rate | [7,33] | ||
| Sleep apneas | [38] | ||
| Chair sensor | Time on chair | [8] | |
| Proximity beacon | Frequency of forgetting wallet/keys | [30] | |
| Medication box | Frequency of forgetting medication | [30] | |
| Smart plug | Television use | [30] |
| Study | Patient Selection | Comparability | Outcome | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representativeness of the Exposed Cohort | Selection of the Non-Exposed Cohort | Ascertainment of Exposure | Outcome of Interest Was Not Present at Start of the Study | Controls for Most Important Factor | Controls for Any Additional Factor | Assessment of Outcome | Follow-Up Length | Adequacy of Follow-Up Cohorts | ||
| Chen et al., 2020 [41] | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 4 |
| Dadhania et al., 2023 [35] | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | 5 |
| Fay-Karmon et al., 2024 [20] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | 4 |
| Finch et al., 2017 [32] | ★ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 6 |
| Harrington et al., 2021 [38] | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 3 |
| Kabelac et al., 2019 [22] | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 4 |
| Lach et al., 2019 [8] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 4 |
| Lam et al., 2022 [26] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 5 |
| Leightley et al., 2021 [34] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 4 |
| Lipsmeier et al., 2018 [23] | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 6 |
| Liu et al., 2022 [24] | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 4 |
| Low et al., 2021 [36] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 5 |
| Low et al., 2024 [37] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 5 |
| Muurling et al., 2023 [29] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | 4 |
| Noble et al., 2016 [39] | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | 3 |
| Obayashi et al., 2023 [28] | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 4 |
| Parkinson et al., 2023 [7] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | 3 |
| Perraudin et al., 2018 [42] | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 4 |
| Rawtaer et al., 2020 [30] | ★ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 |
| Ribeiro-Castro et al., 2024 [43] | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 3 |
| Saner et al., 2020 [33] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 5 |
| Schalkamp et al., 2024 [25] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | 4 |
| Wu et al., 2022 [31] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | 5 |
| Zhang et al., 2021 [40] | ★ | ☆ | ★ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ★ | ★ | ★ | 5 |
| Study | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gatsios et al., 2020 [21] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Gaugler et al., 2019 [27] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rama, E.; Zuberi, S.; Aly, M.; Askari, A.; Iqbal, F.M. Clinical Outcomes of Passive Sensors in Remote Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2025, 25, 3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113285
Rama E, Zuberi S, Aly M, Askari A, Iqbal FM. Clinical Outcomes of Passive Sensors in Remote Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113285
Chicago/Turabian StyleRama, Essam, Sharukh Zuberi, Mohamed Aly, Alan Askari, and Fahad M. Iqbal. 2025. "Clinical Outcomes of Passive Sensors in Remote Monitoring: A Systematic Review" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113285
APA StyleRama, E., Zuberi, S., Aly, M., Askari, A., & Iqbal, F. M. (2025). Clinical Outcomes of Passive Sensors in Remote Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Sensors, 25(11), 3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113285






