Colorimetric Detection of Platinum (IV) Using 4-MethylSulfonylaniline-Modified Gold Nanoparticles in Lanthanum Carbonate API
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of 4-MESA-AuNPs
2.3. Pt(IV) Sensing
3. Results and Discussion
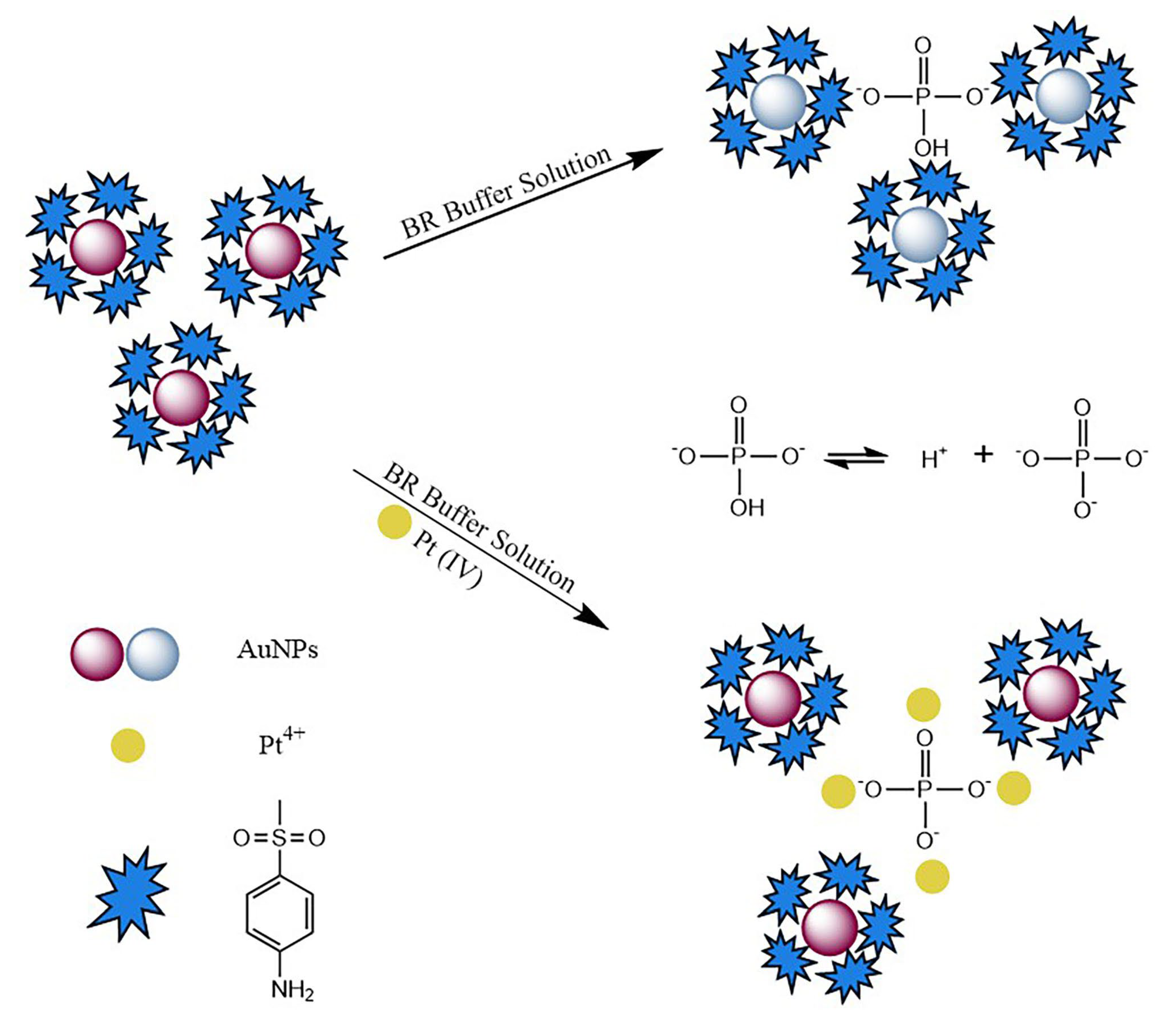
3.1. Characterization of 4-MESA-AuNPs and the Interaction Mechanism for Detecting Pt(IV)
3.2. Optimization of Detection Conditions
3.2.1. pH
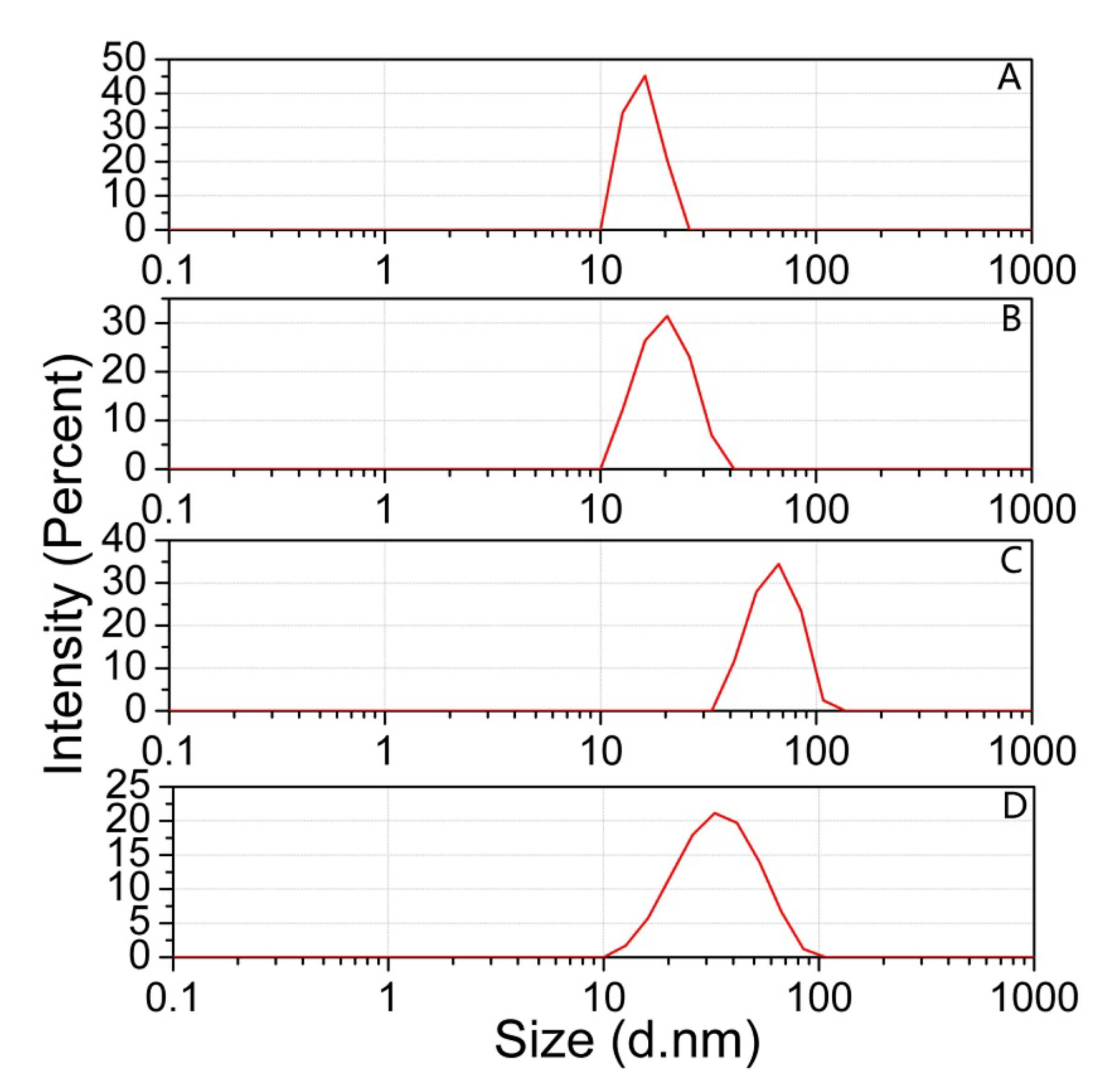
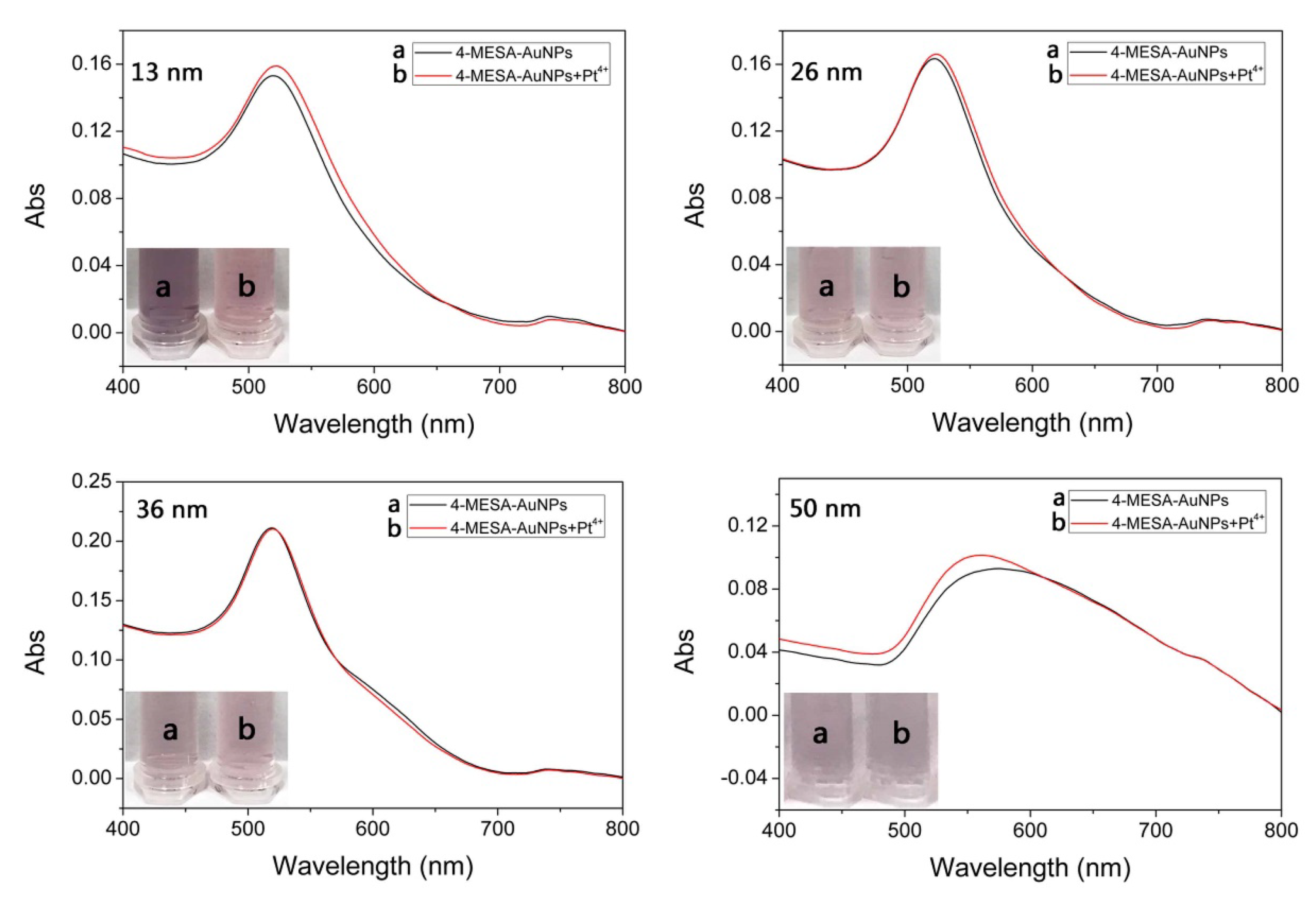
3.2.2. The Size of AuNPs
3.3. Detection of Pt(IV) Using 4-MESA-AuNPs
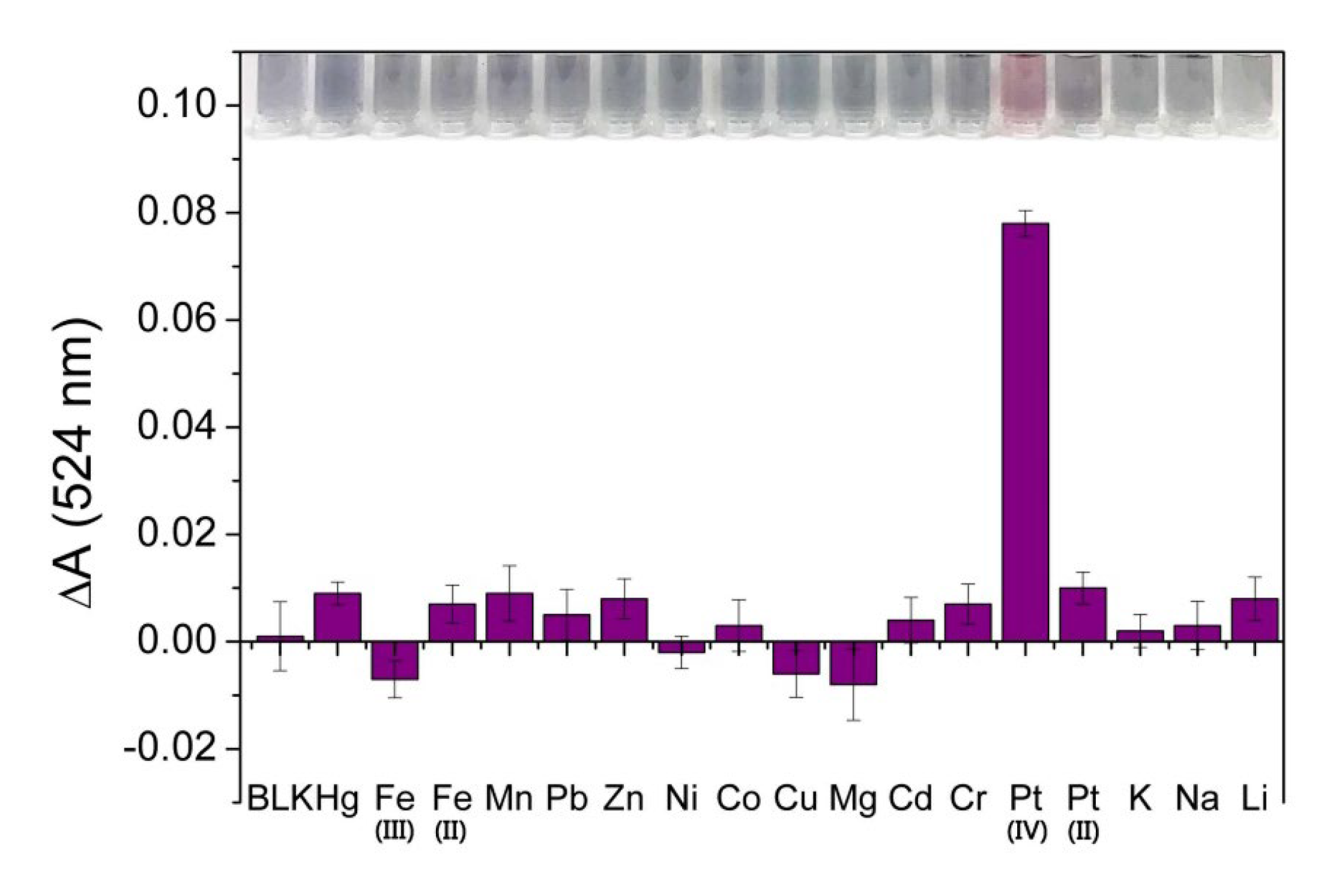
3.4. Selectivity of 4-MESA-AuNPs
3.5. Application to Lanthanum Carbonate API
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ando, R.; Kimura, H.; Sato, H.; Iwamoto, S.; Yoshizaki, Y.; Chida, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Takayama, M.; Yamada, K.; Tachibana, K.; et al. Multicenter study of long-term (two-year) efficacy of lanthanum carbonate. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2013, 17 (Suppl. S1), 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombolà, G.; Londrino, F.; Corbani, V.; Falqui, V.; Ardini, M.; Zattera, T. Lanthanum carbonate: A postmarketing observational study of efficacy and safety. J. Nephrol. 2012, 25, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH. ICH Harmonised Guideline: Guideline For Elemental Impurities Q3D(R1). Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q3D-R1EWG_Document_Step4_Guideline_2019_0322.pdf (accessed on 22 March 2019).
- Chancerel, P.; Rotter, V.S.; Ueberschaar, M.; Marwede, M.; Nissen, N.F.; Lang, K.-D. Data availability and the need for research to localize, quantify and recycle critical metals in information technology, telecommunication and consumer equipment. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, A.P.J.; Jarvis, K.E.; Grimes, R.W.; Marsden, O.J. Development of an iridium dissolution method for the evaluation of potential radiological device materials. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 307, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Tölg, G.; Beinrohr, E.; Tschöpel, P. Preconcentration of palladium, platinum and rhodium by on-line sorbent extraction for graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 272, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Warmerdam, L.J.C.; van Tellingen, O.; Maes, R.A.A.; Beijnen, J.H. Validated method for the determination of carboplatin in biological fluids by Zeeman atomic absorption spectrometry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1995, 351, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Shimbo, S.H.; Qu, J.B.; Liu, Z.M.; Cai, X.C.; Wang, L.Q.; Watanabe, T.; Nakatsuka, H.; Matsuda-Inoguchi, N.; Higashikawa, K.; et al. Hepatitis B and C virus infection among adult women in Jilin Province, China: An urban-rural comparison in prevalence of infection markers. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2000, 31, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, G.; Radziuk, B. Patience Clever’s exciting voyage through the world of matrices and challenging analyses. In Analytical Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 221–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerzak, M. Sample digestion methods for the determination of traces of precious metals by spectrometric techniques. Anal. Sci. 2002, 18, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard, L.P.; Barnes, S.J. A comparison of the capacity of FA-ICP-MS and FA-INAA. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2002, 254, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durani, S.; Krishnakumar, M.; Satyanarayana, K. Solid phase separation and ICP-OES/ICP-MS determination of rare earth impurities in nuclear grade uranium oxide. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 294, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; Alimonti, A.; Petrucci, F.; Irgolic, K.J.; Forastiere, F.; Caroli, S. Analytical problems in the determination of platinum-group metals in urine by quadrupole and magnetic sector field inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 363, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmers, E.; Mergel, N. Platinum and rhodium in a polluted environment: Studying the emissions of automobile catalysts with emphasis on the application of CSV rhodium analysis. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1998, 362, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M.M.; Gómez, M.M.; Palacios, M.A. Trace enrichment and measurement of platinum by flow injection inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 1996, 354, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivadinov, R.; Tekwe, C.; Bergsland, N.; Dolezal, O.; Havrdova, E.; Krasensky, J.; Dwyer, M.G.; Seidl, Z.; Ramasamy, D.P.; Vaneckova, M.; et al. Bimonthly evolution of cortical atrophy in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis over 2 years: A longitudinal study. Mult. Scler. Int. 2012, 2013, 231345–231352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Palacios, M.; Gómez, M.; Moldovan, M.; Gómez, B. Assessment of environmental contamination risk by Pt, Rh and Pd from automobile catalyst. Microchem. J. 2000, 1, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, T.; Moser, J.; Fellner, N.; Wegscheider, W.; Schoenberg, R. Simplified method for the determination of Ru, Pd, Re, Os, Ir and Pt in chromitites and other geological materials by isotope dilution ICP-MS and acid digestion. Analyst 2001, 126, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elci, L.; Soylak, M.; Buyuksekerci, E.B. Separation of gold, palladium and platinum from metallurgical samples using an amberlite XAD-7 resin column prior to their atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. Anal. Sci. 2003, 19, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwastowska, J.; Skwara, W.; Sterlińska, E.; Pszonicki, L. Determination of platinum and palladium in environmental samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after separation on dithizone sorbent. Talanta 2004, 64, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. Determination of impurities in highly pure platinum by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Talanta 1995, 42, 1959–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, S.J. The role of neutron activation with radiochemistry in geoanalysis. J. Geochem. Explor. 1992, 44, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietz, B.; Heydorn, K. Determination of gold and platinum in biological materials by radiochemical neutron activation analysis using electrolytic separation of gold. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1993, 174, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildhagen, D.; Krivan, V. Determination of platinum in enviromental and geological samples by radiochemical neutron activation analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 274, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaveri, G.; Rizzio, E.; Gallorini, M. Preconcentration and preseparation procedure for platinum determination at trace levels by neutron activation analysis. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 3488–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerzak, M.; Swiecicka, E.; Balukiewicz, E. Determination of platinum and ruthenium in Pt and Pt-Ru catalysts with carbon support by direct and derivative spectrophotometry. Talanta 1999, 48, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitrus, R.K.; Amin, S.A. Determination of trace concentration of boron in ADU by the nuclear track technique. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1988, 120, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietz, B.; Krarup-Hansen, A.; Rorth, M. Determination of platinum by radiochemical neutron activation analysis in neural tissues from rats, monkeys and patients treated with cisplatin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 426, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbin, R.; Bazel, Y.; Ružičková, S. Speciation of platinum by GFAAS using various possibilities of analytical signal enhancement. Talanta 2017, 175, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritsotakis, K.; Tobschall, H.J. Bestimmung der edelmetalle Au, Pd, Pt, Rh und Ir in gesteinen und erzen mit der elektrothermalen atomabsorptions-spektrometrie. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 1985, 320, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholkin, A.; Belova, V.; Pashkov, G.; Fleitlikh, I.; Sergeev, V. Solvent binary extraction. J. Mol. Liq. 1999, 82, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, V.; Kholkin, A.I. Binary extraction of platinum metals. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 1998, 16, 1233–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, V.V.; Khol’Kin, A.I.; Zhidkova, T.I. Extraction of platinum-group metals from chloride solutions by salts of quaternary ammonium bases and binary extractants. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2007, 41, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.M.C.; Reddi, S.G. Platinum group metals (PGM) occurrence, use and recent trends in their determination. Trends Anal. Chem. 2000, 19, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencs, L.; Ravindra, K.; Grieken, R.V. Methods for the determination of platinum group elements originating from the abrasion of automotive catalytic converters. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2003, 58, 1723–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barefoot, R.R.; Loon, J.C.V. Recent advances in the determination of the platinum group elements and gold. Talanta 1999, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, X. Ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of manganese(II) ions based on anti-aggregation of unmodified silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, Y. An ultrasensitive chemiluminescence sensor for sub-nanomolar detection of manganese(II) ions in mineral water using modified gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.Q.; Ye, B.C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric visualization of phthalates using UTP-modified gold nanoparticles cross-linked by copper(II). Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11849–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.Q.; Ye, B.C. Mononucleotide-modified metal nanoparticles: An efficient colorimetric probe for selective and sensitive detection of aluminum(III) on living cellular surfaces. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Edraki, N.; Miri, R.; Hemmateenejad, B. Exploring QSAR for substituted 2-sulfonyl-phenyl-indol derivatives as potent and selective COX-2 inhibitors using different chemometrics tools. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 72, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E. The duodecet rule: Part 2. C-H hydrogen bonding by sulfonyl compounds. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem. 1989, 186, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lásztity, A.; Kelkó-Lévai, Á.; Zih-Perényi, K.; Varga, I. Flow-injection preconcentration and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination of platinum. Talanta 2003, 59, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, C.B.; Rojas, F.S.; Pavón, J.M.C. Determination of platinum by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry in foods and beverages using an automated on-line separation-preconcentration system. Food Control 2006, 17, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, W.I.; Hassanien, M.M.; El-Asmy, A.A. Speciation of platinum in blood plasma and urine by micelle-mediated extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2013, 27, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; Ding, N.; Cao, Q. Colorimetric detection of Cu2+ using 4-mercaptobenzoic acid modified silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 391, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Yu, H. A synergistic coordination strategy for colorimetric sensing of chromium(III) ions using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8551–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, F.; Zarei, K.; Karami, C. Naked eye detection of Cr3+ and Ni2+ ions by gold nanoparticles modified with ribavirin. Silicon 2018, 10, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisen, S.; Cheewasedtham, W.; Rujiralai, T. Robust colorimetric detection based on the anti-aggregation of gold nanoparticles for bromide in rice samples. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21566–21576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C. Hydrogen-bonding-induced colorimetric detection of melamine by nonaggregation-based Au-NPs as a probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 12, 2680–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wang, P.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H.; Su, X.; Yang, J.; He, Y. Antibody-free colorimetric determination of total aflatoxins by mercury(II)-mediated aggregation of lysine-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Pan, L.; Gong, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Wu, L.; He, Y. Colorimetric and visual determination of Au(III) ions using PEGylated gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Yang, W.; Peng, X. Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: The third role of citrate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13939–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Shen, P. Multicolumn solid phase extraction with hybrid adsorbent and rapid determination of Au, Pd and Pt in geological samples by GF-AAS. Miner. Eng. 2015, 81, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, R.; Mróz, A.; Otto, M.; Kuryło, M. Development of sensitive determination method for platinum in geological materials by carbon slurry sampling graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2015, 121, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Liu, S.; Tian, M.; Li, W.; Hu, B.; Zhou, W.; Jia, Q. Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles for the on-line determination of gold, palladium, and platinum in mine samples based on flow injection micro-column preconcentration coupled with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2014, 118, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.B.; Oliva, M.M.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Rodriguez-Castellón, E.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; da Silva, J.C.E.; Algarra, M. Carbon dots on based folic acid coated with PAMAM dendrimer as platform for Pt(IV) detection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 465, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Methods | Detection | Linear Range (μM) | LOD (μM) | LOQ (μM) | Detection Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAS | GFAAS | 1.50 × 103 to 3.55 × 104 | 1.50 | 4.55 | 60 | [29] |
| AAS | GFAAS | - | 70.00 | 2.12 × 102 | 180 | [56] |
| AAS | GFAAS | - | 4.80 × 103 | 1.45 × 104 | 3600 | [57] |
| AAS | FI-column-GFAAS | - | 5.05 × 103 | 1.53 × 104 | 3600 | [58] |
| Fluorescent | CQDs | 6.00 to 96.00 | 6.57 × 10−1 | 0.24 | Not given | [59] |
| Colorimetry | AuNPs, 4-(Methylsulfonyl)aniline | 1.00 × 10−2 to 5.00 × 102 | 10.00 × 10−3 | 3.03 × 10−2 | 2 | This work |
| Lot No. | Sample No. | Added (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 240501 | 1 | 10.00 | 9.68 ± 0.02 | 96.80 | 1.10 |
| 2 | 50.00 | 48.30 ± 0.04 | 96.60 | 1.17 | |
| 3 | 100.00 | 99.00 ± 0.03 | 99.00 | 3.37 | |
| 240603 | 1 | 10.00 | 9.95 ± 0.06 | 99.50 | 3.36 |
| 2 | 50.00 | 51.20 ± 0.04 | 102.40 | 1.78 | |
| 3 | 100.00 | 99.56 ± 0.07 | 99.56 | 2.47 | |
| 240706 | 1 | 10.00 | 10.86 ± 0.02 | 108.6 | 1.50 |
| 2 | 50.00 | 49.98 ± 0.06 | 99.96 | 2.20 | |
| 3 | 100.00 | 99.97 ± 0.02 | 99.97 | 1.68 |
| Element | ICH PDE (μg·d−1) | Control Threshold (μg·d−1) | Maximum Possible Daily Intake (μg·d−1) | Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 240501 | 240603 | 240706 | ||||
| Pt | 100 | 30 | ˂0.18 | ˂0.20 | ˂0.18 | Below limit |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Duan, M.; Li, Z.; Sun, S. Colorimetric Detection of Platinum (IV) Using 4-MethylSulfonylaniline-Modified Gold Nanoparticles in Lanthanum Carbonate API. Sensors 2025, 25, 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113274
Li Z, Li L, Yang X, Duan M, Li Z, Sun S. Colorimetric Detection of Platinum (IV) Using 4-MethylSulfonylaniline-Modified Gold Nanoparticles in Lanthanum Carbonate API. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhongqiu, Longwei Li, Xiaotian Yang, Mengtao Duan, Zhiwei Li, and Shiguo Sun. 2025. "Colorimetric Detection of Platinum (IV) Using 4-MethylSulfonylaniline-Modified Gold Nanoparticles in Lanthanum Carbonate API" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113274
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, L., Yang, X., Duan, M., Li, Z., & Sun, S. (2025). Colorimetric Detection of Platinum (IV) Using 4-MethylSulfonylaniline-Modified Gold Nanoparticles in Lanthanum Carbonate API. Sensors, 25(11), 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113274





