Compact Waveguide Antenna Design for 77 GHz High-Resolution Radar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
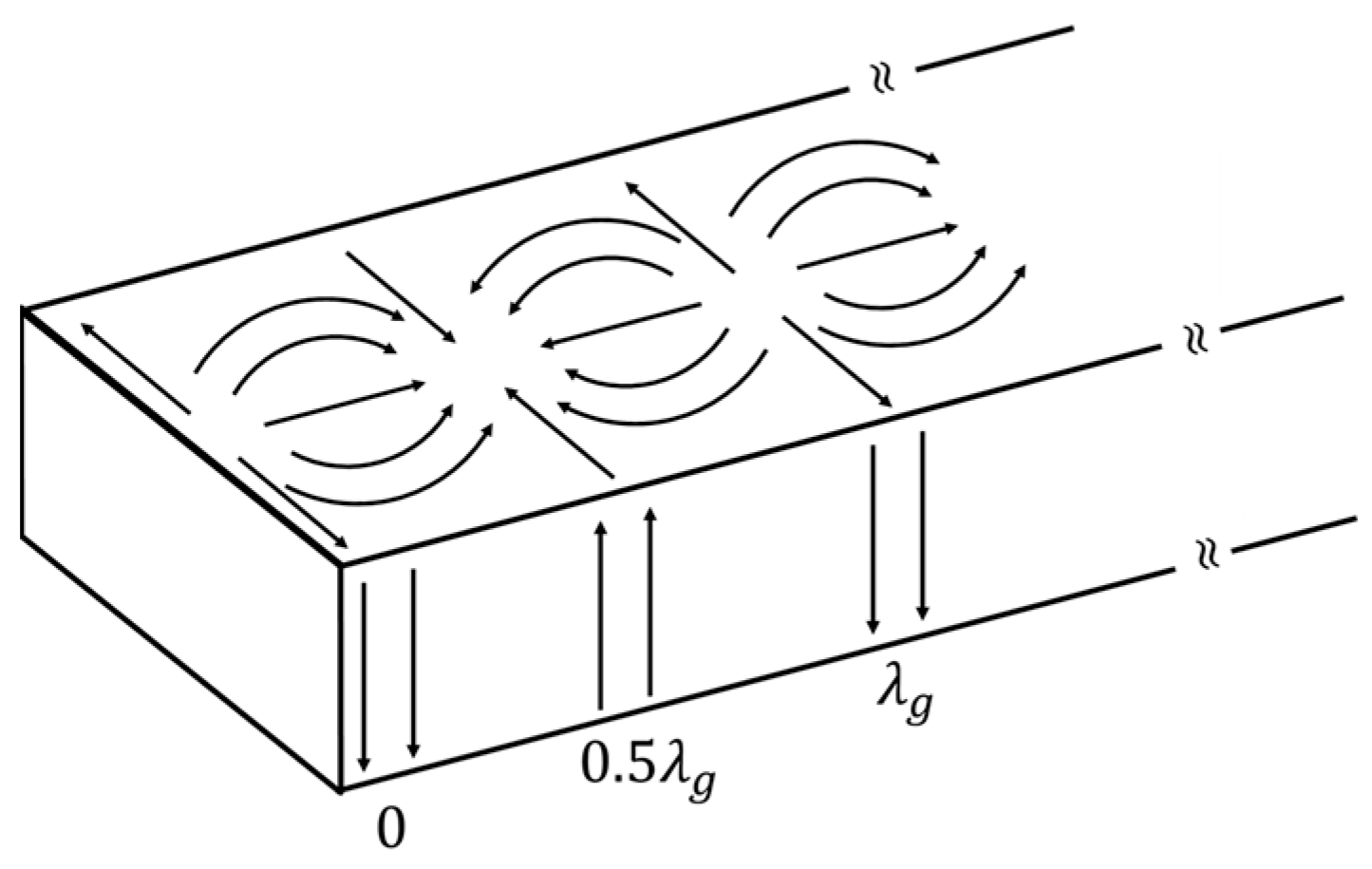
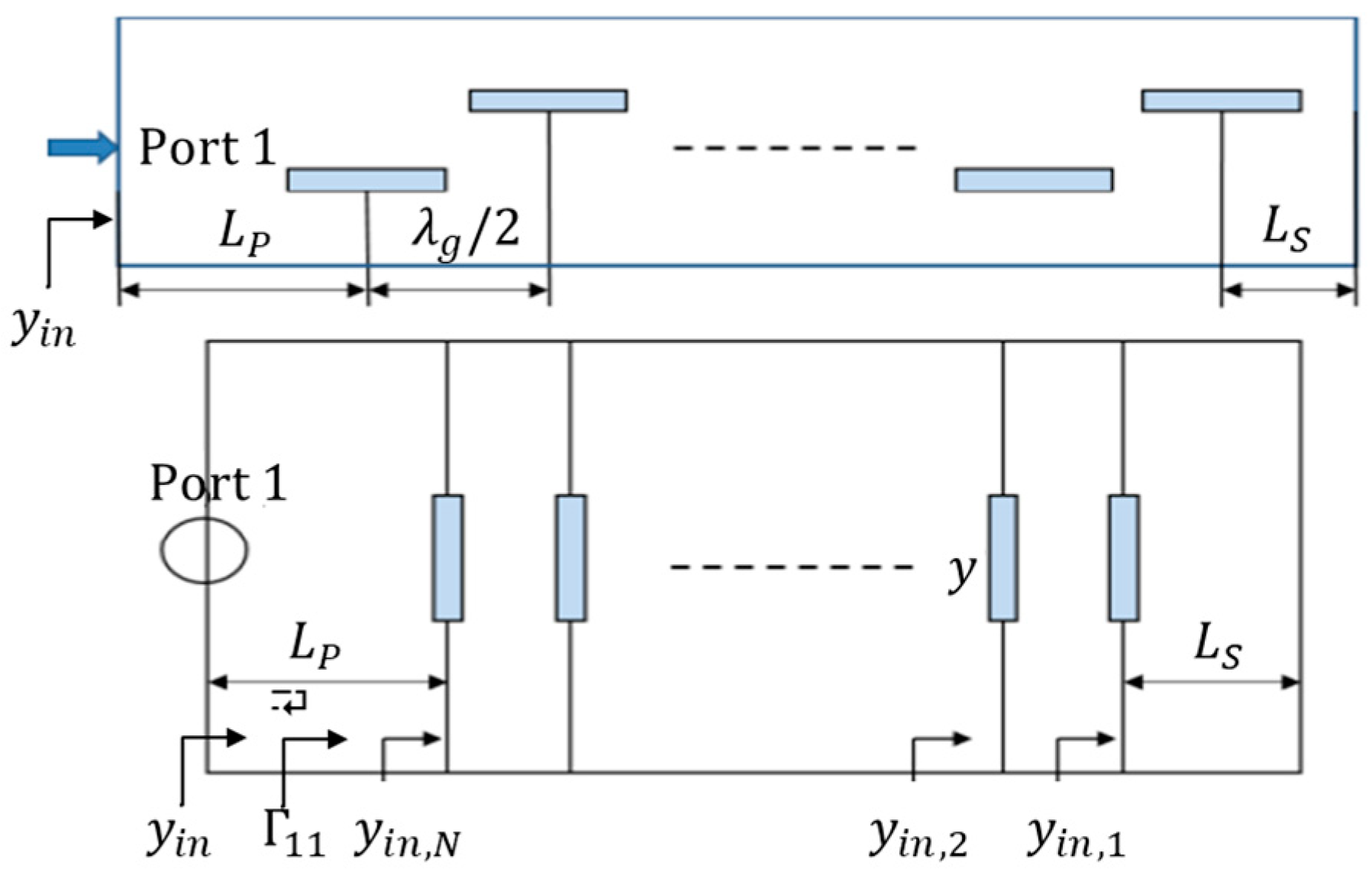
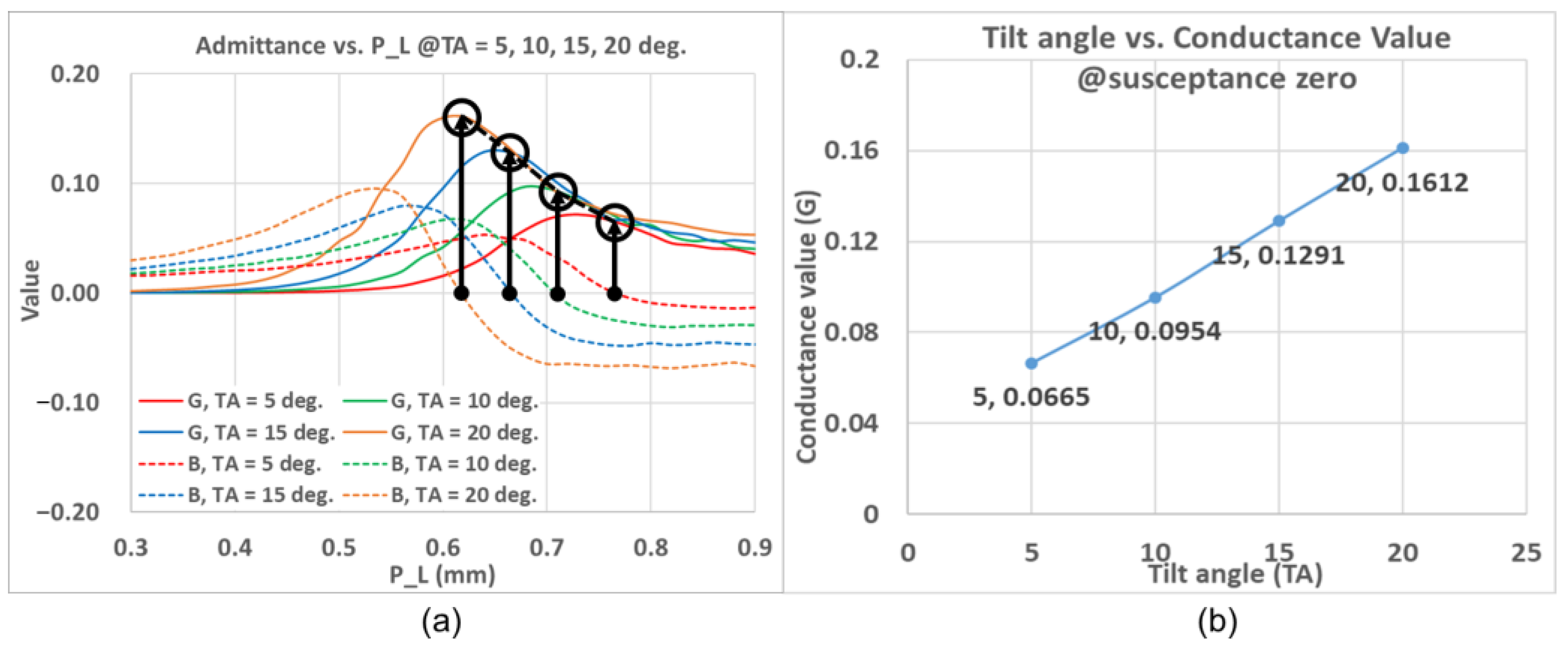
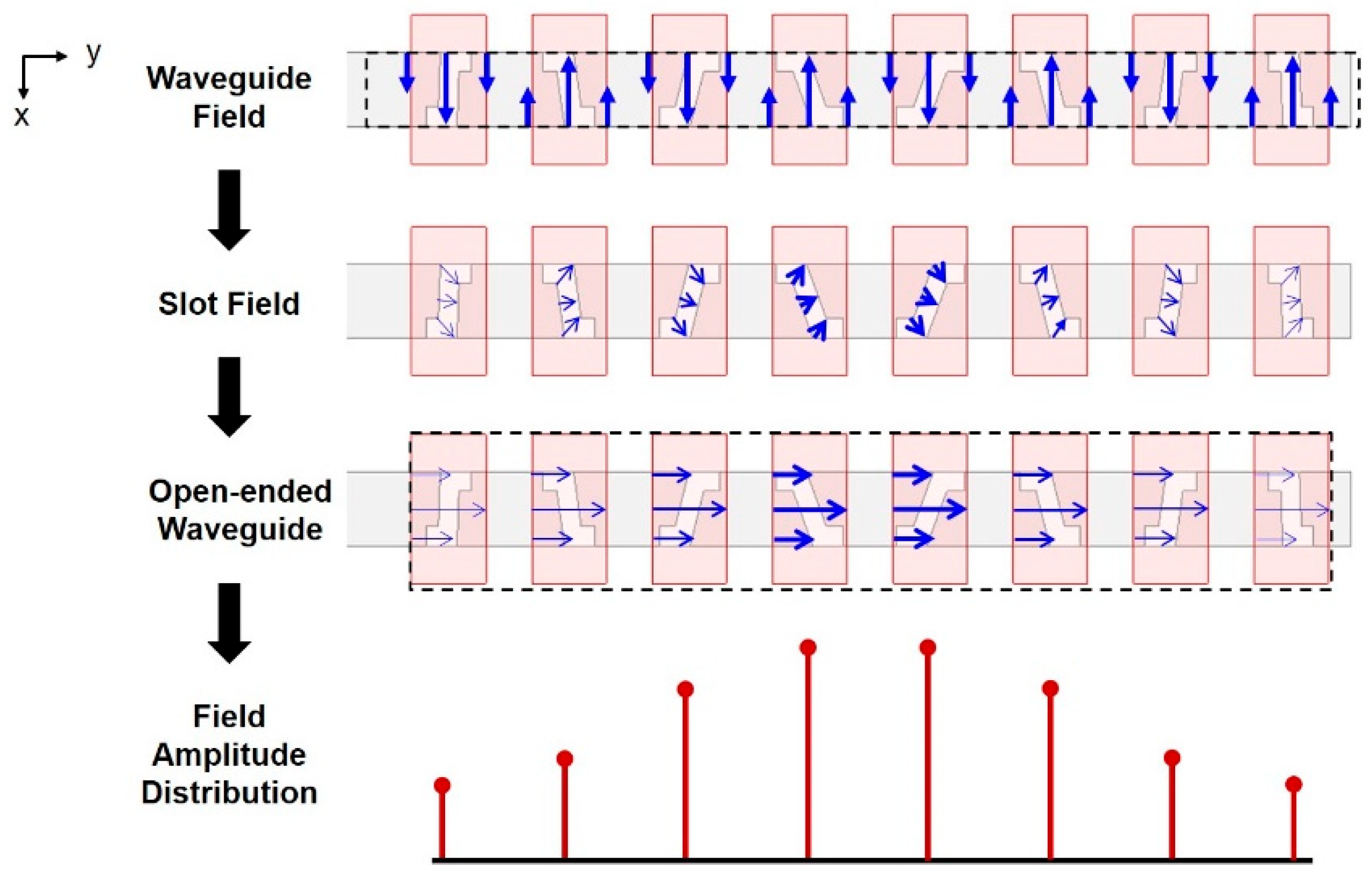
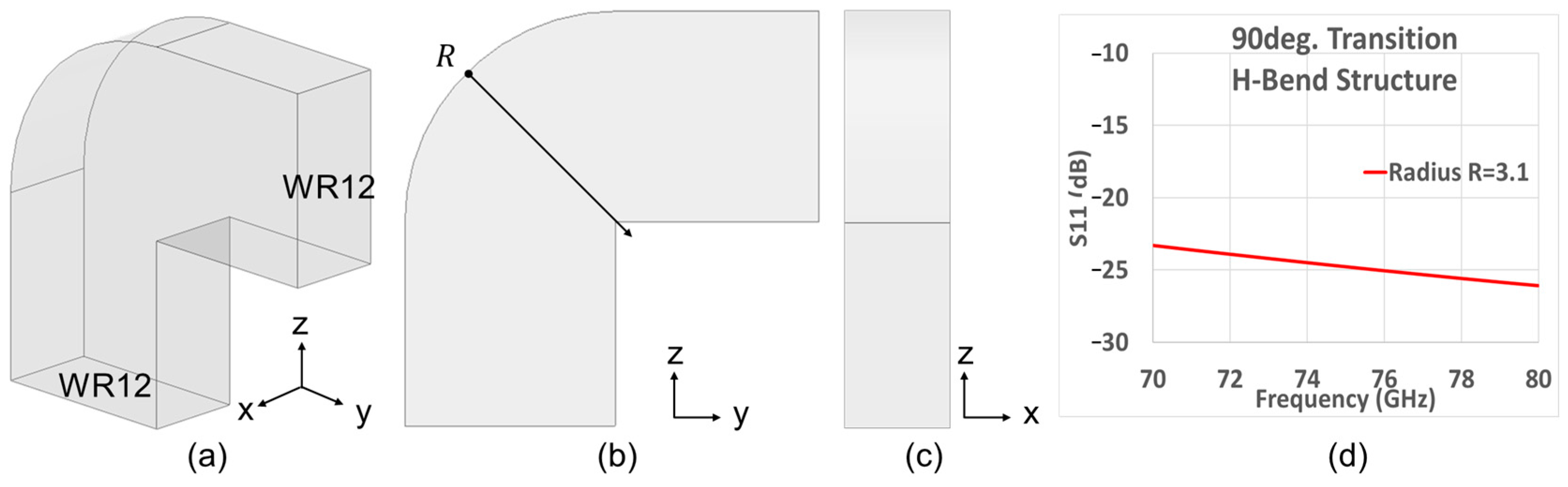
2.1. Z-Shaped Slot Coupling
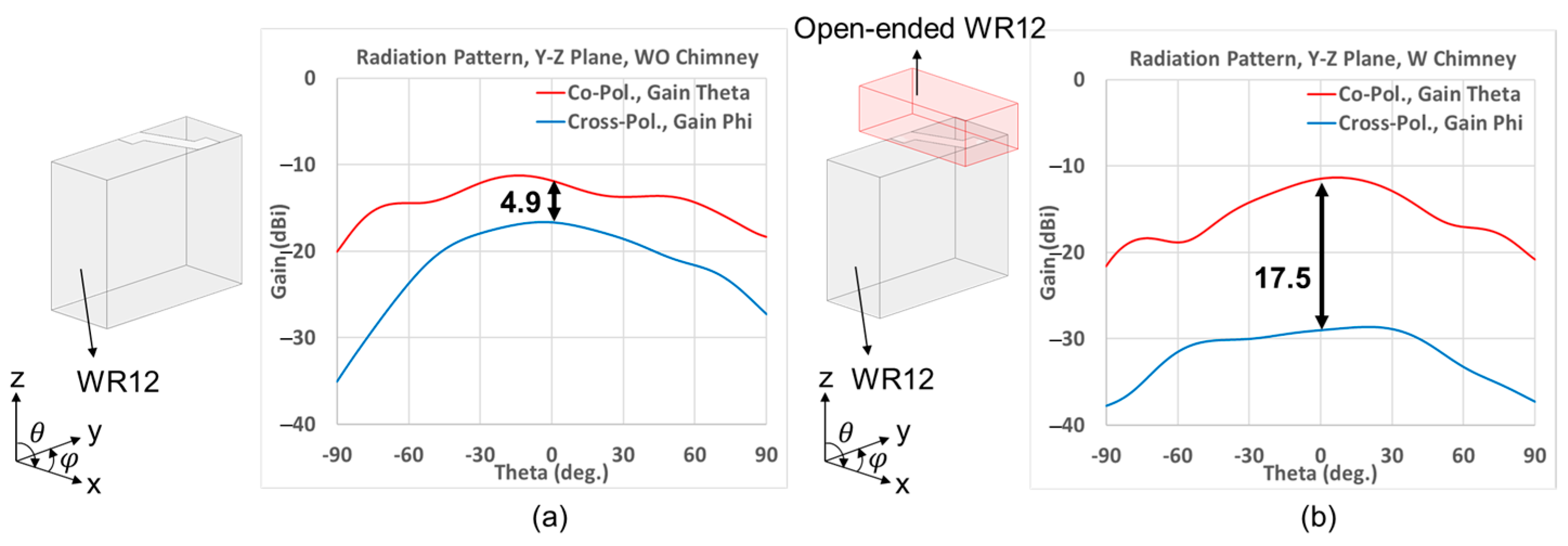
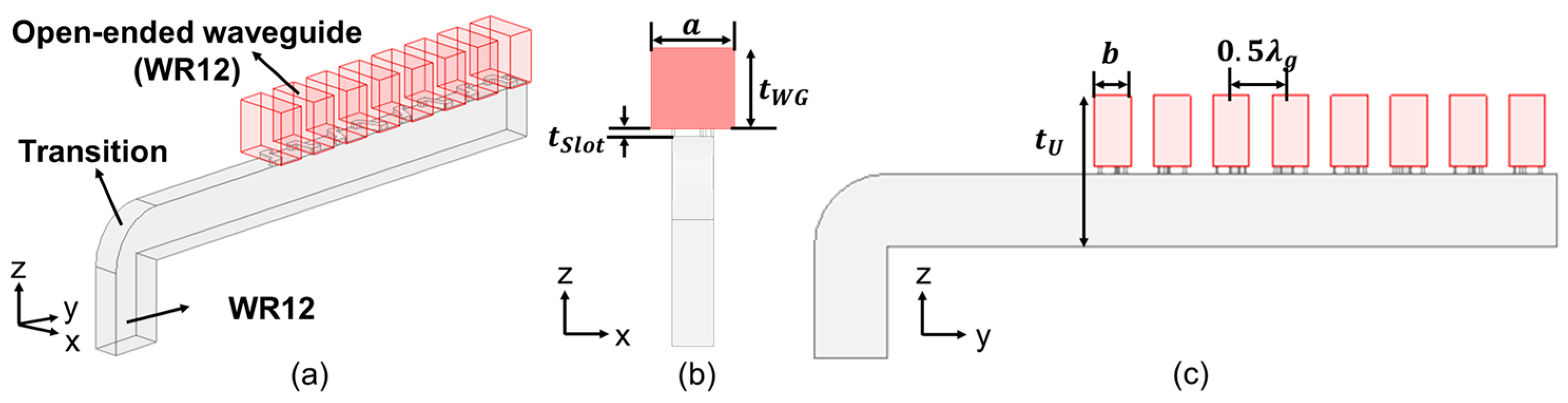
2.2. Polarization Purification by Open-Ended Waveguides
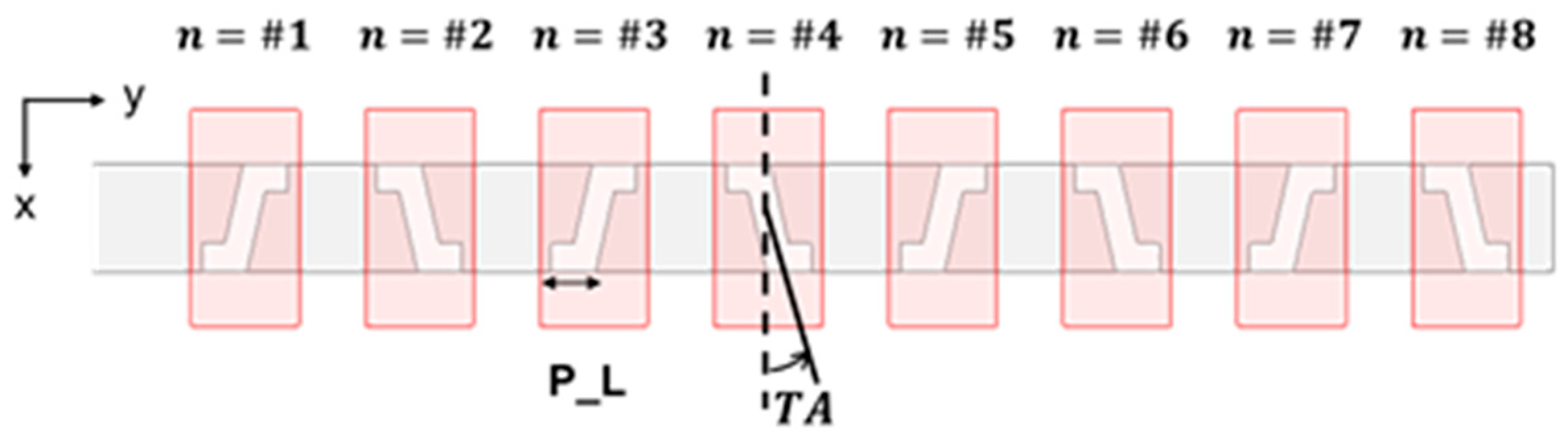
2.3. Chebyshev Distribution
3. Simulation Results
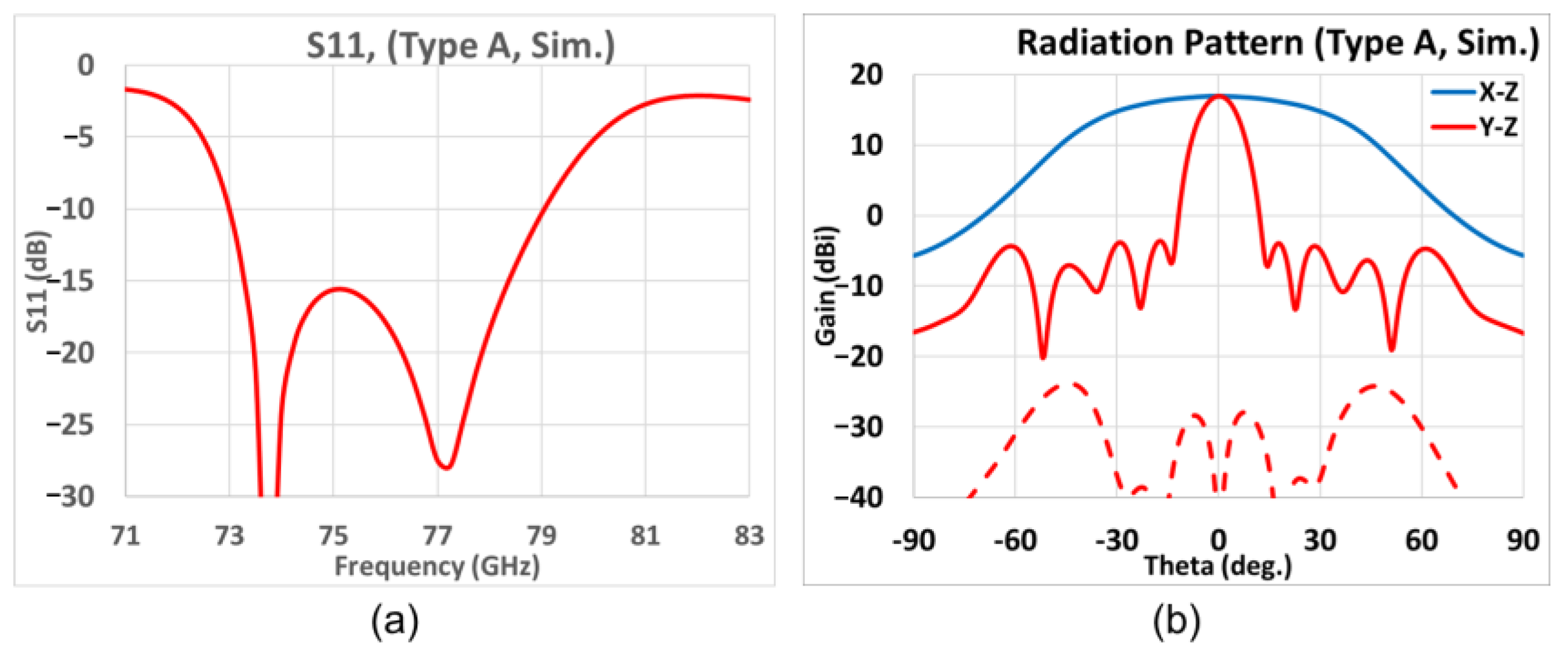
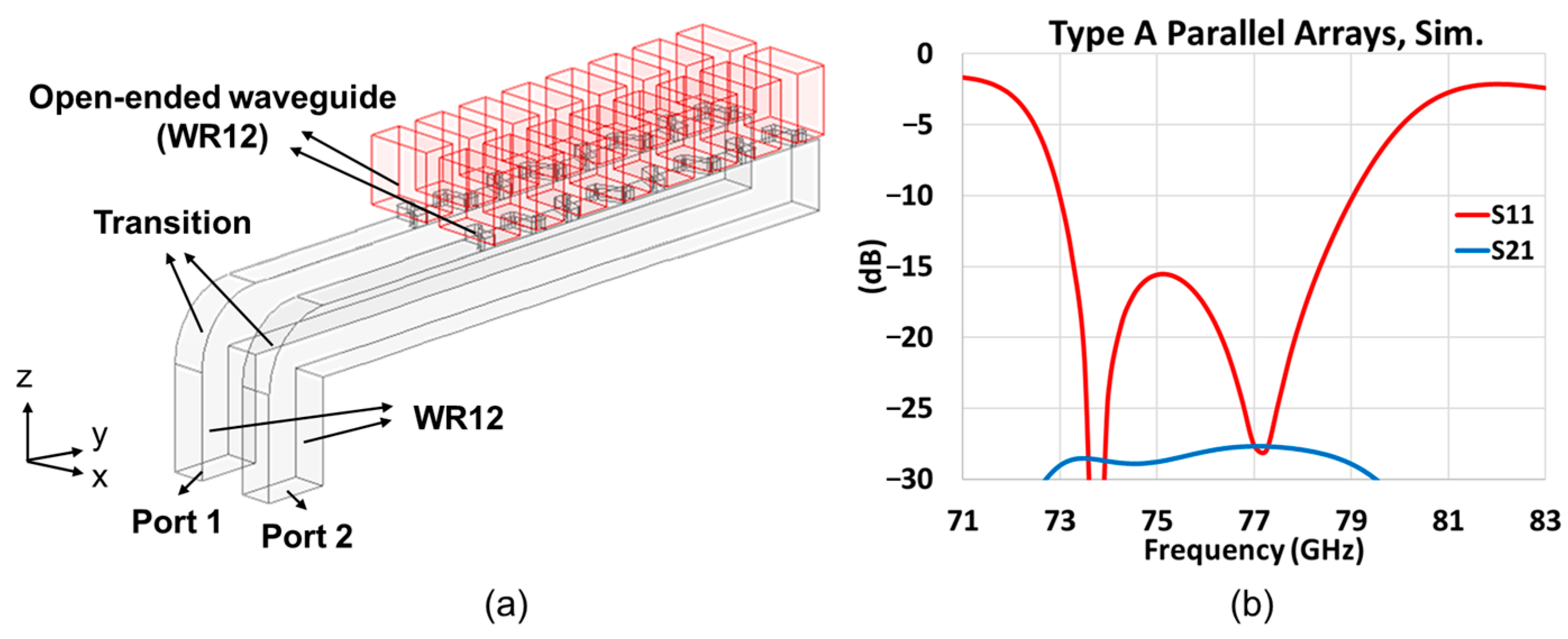
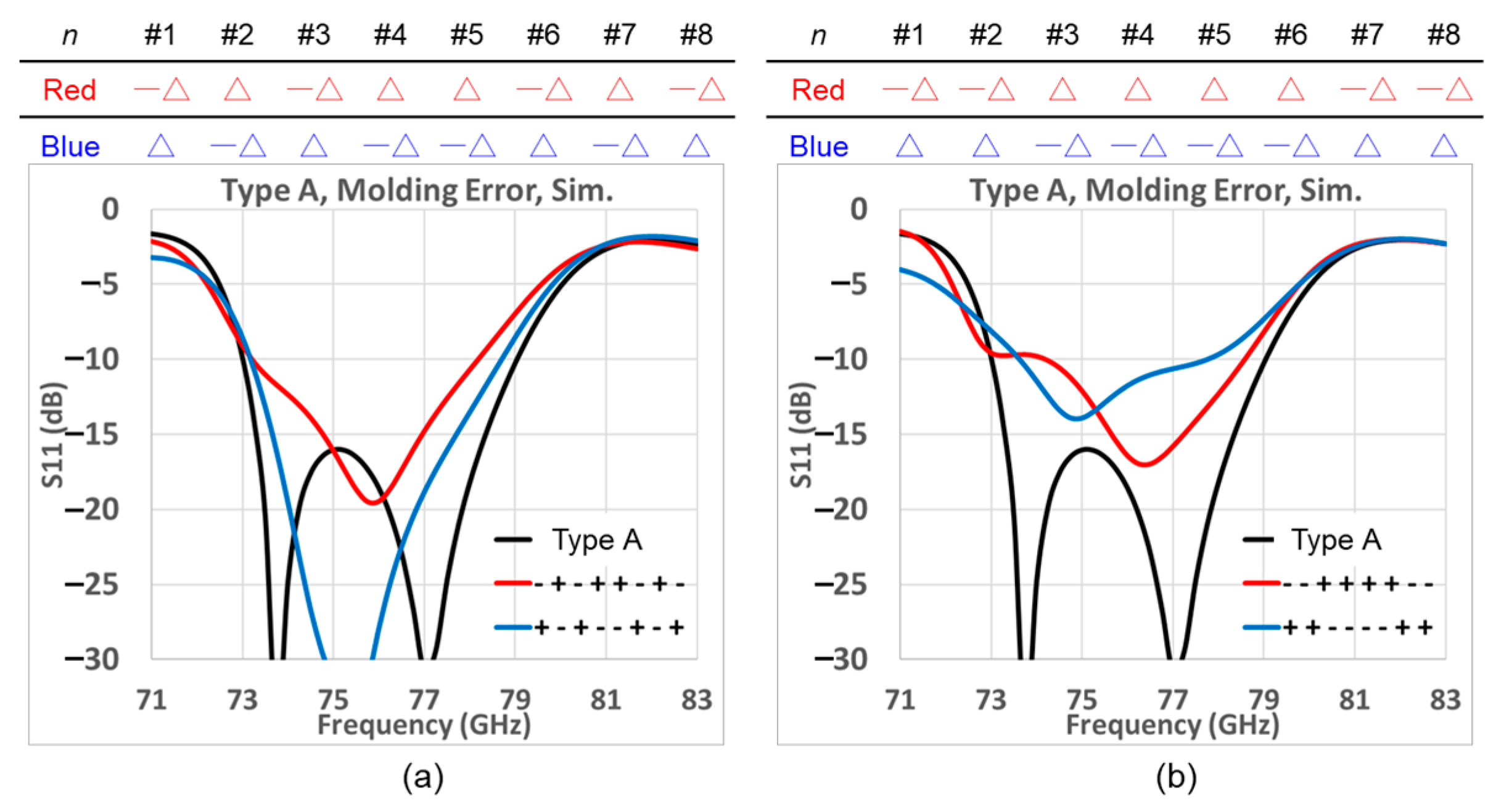
3.1. First Prototype (Type A)
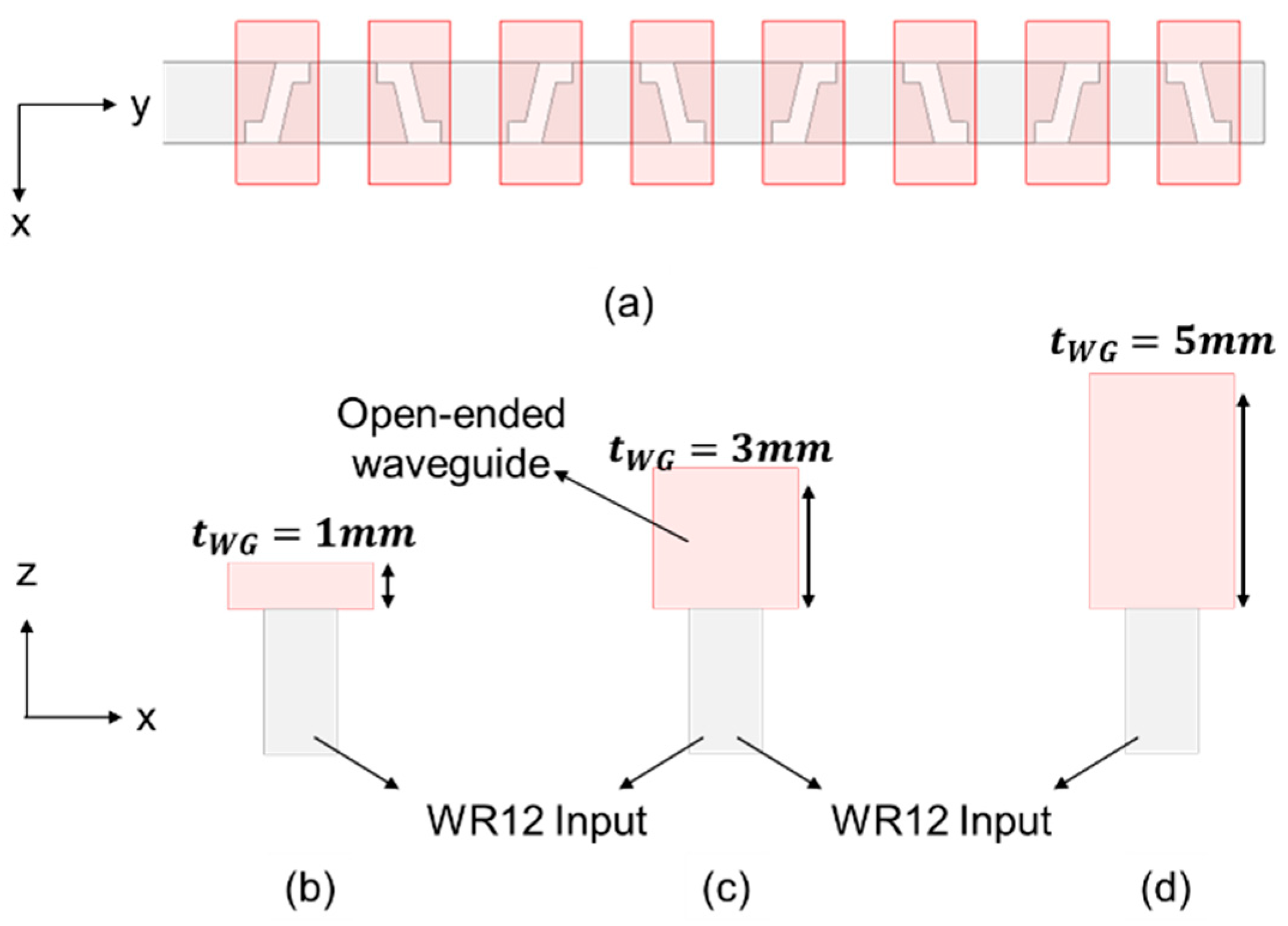
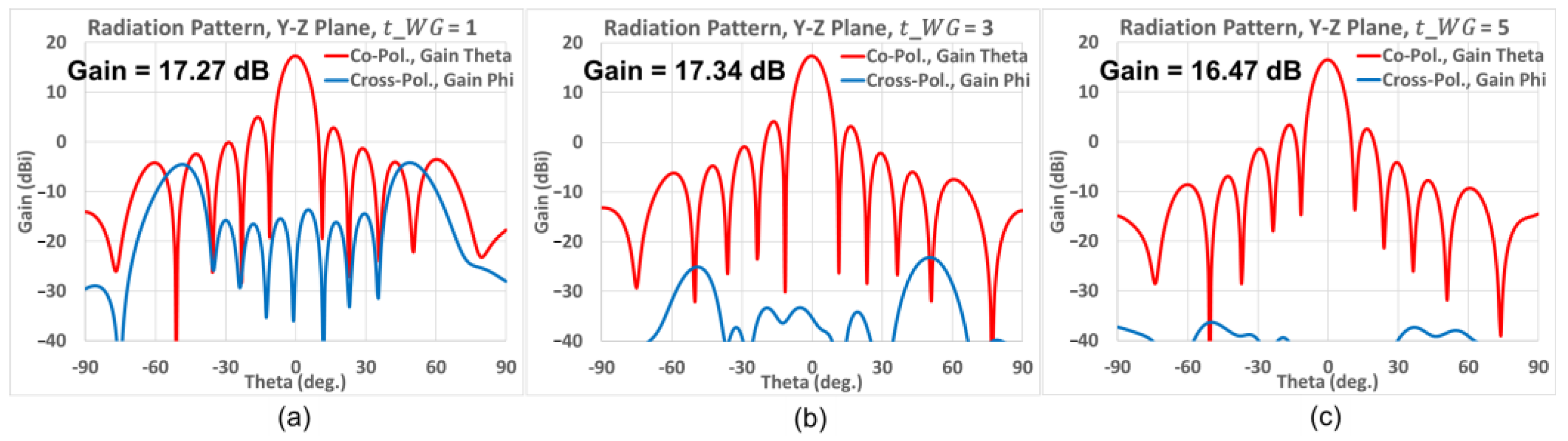
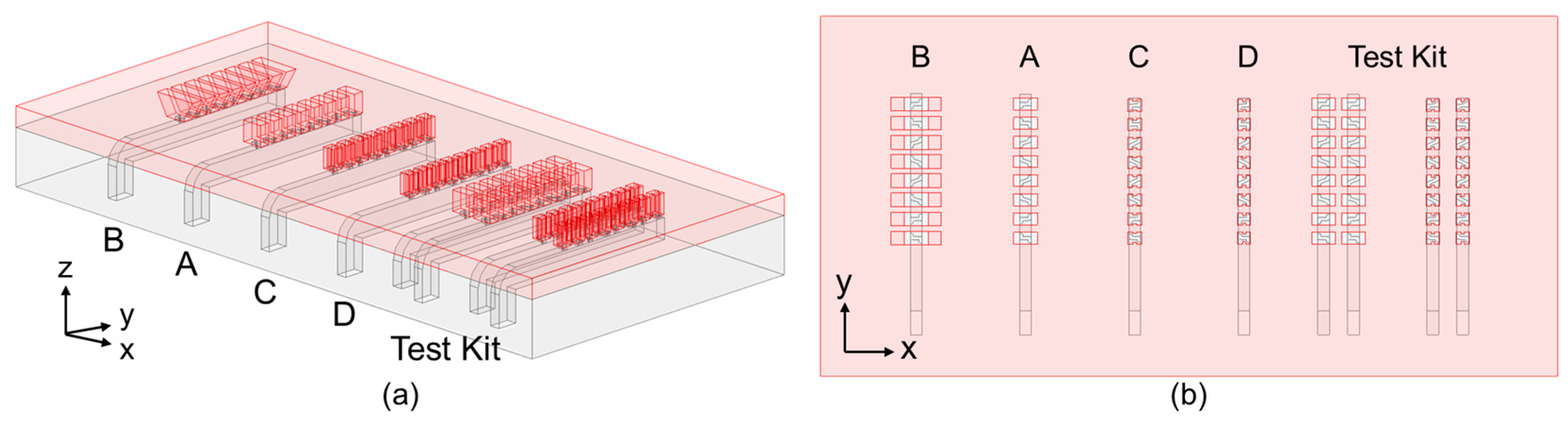
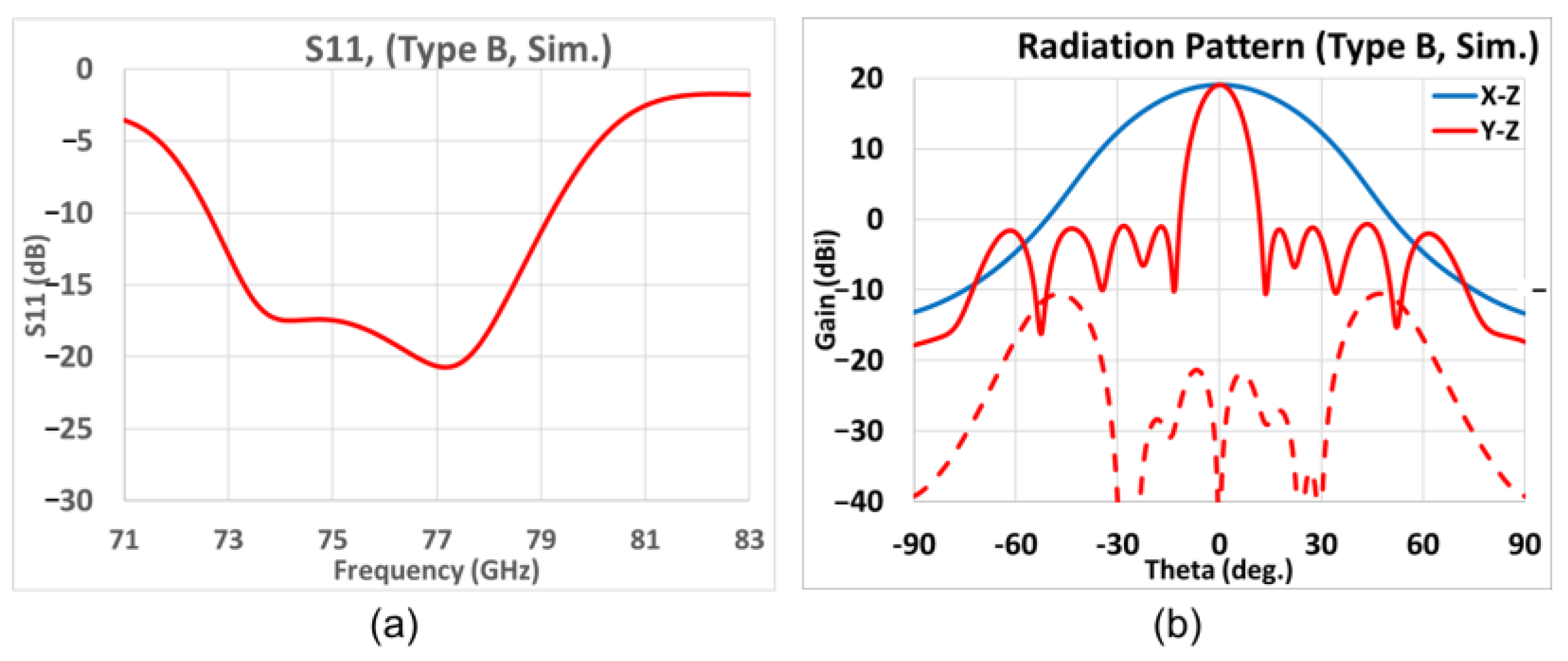
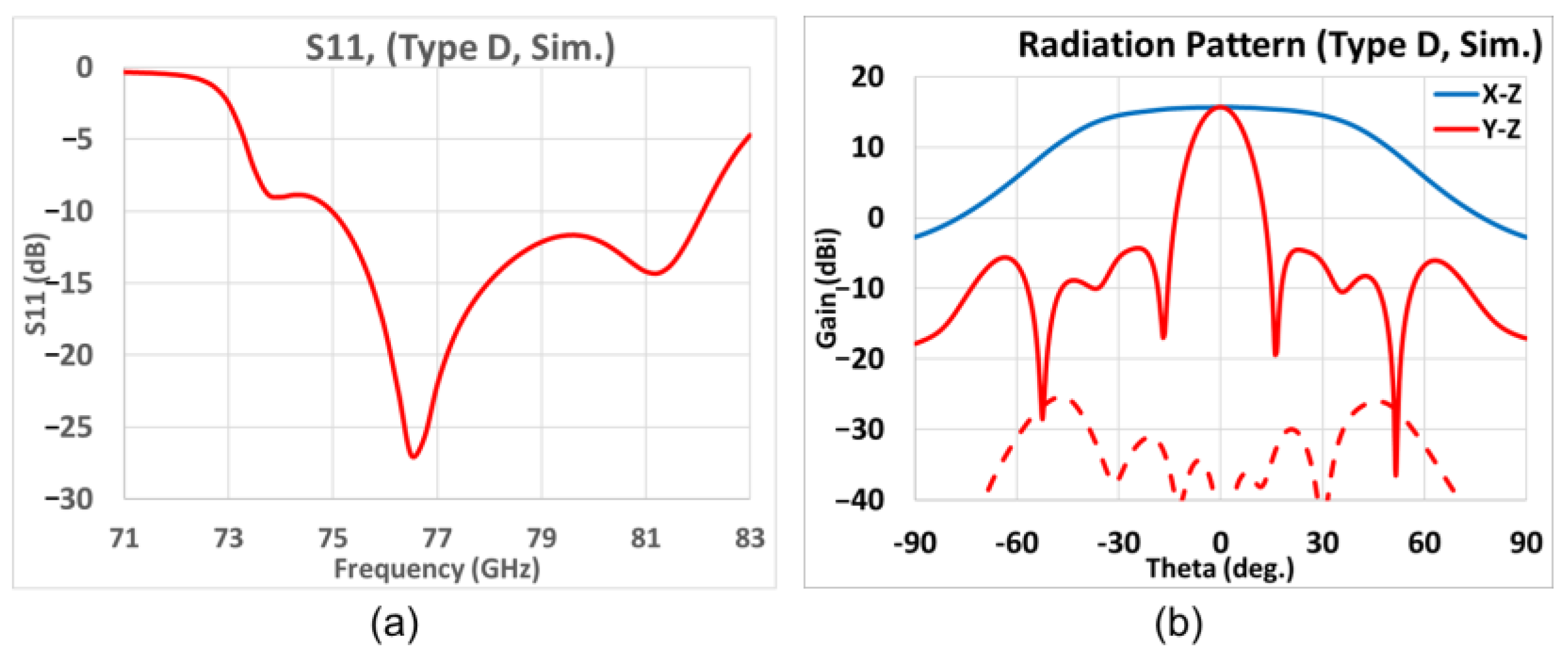
3.2. Different Antenna Types for Diverse Applications
3.3. Summary of the Proposed Antennas
4. Measurement
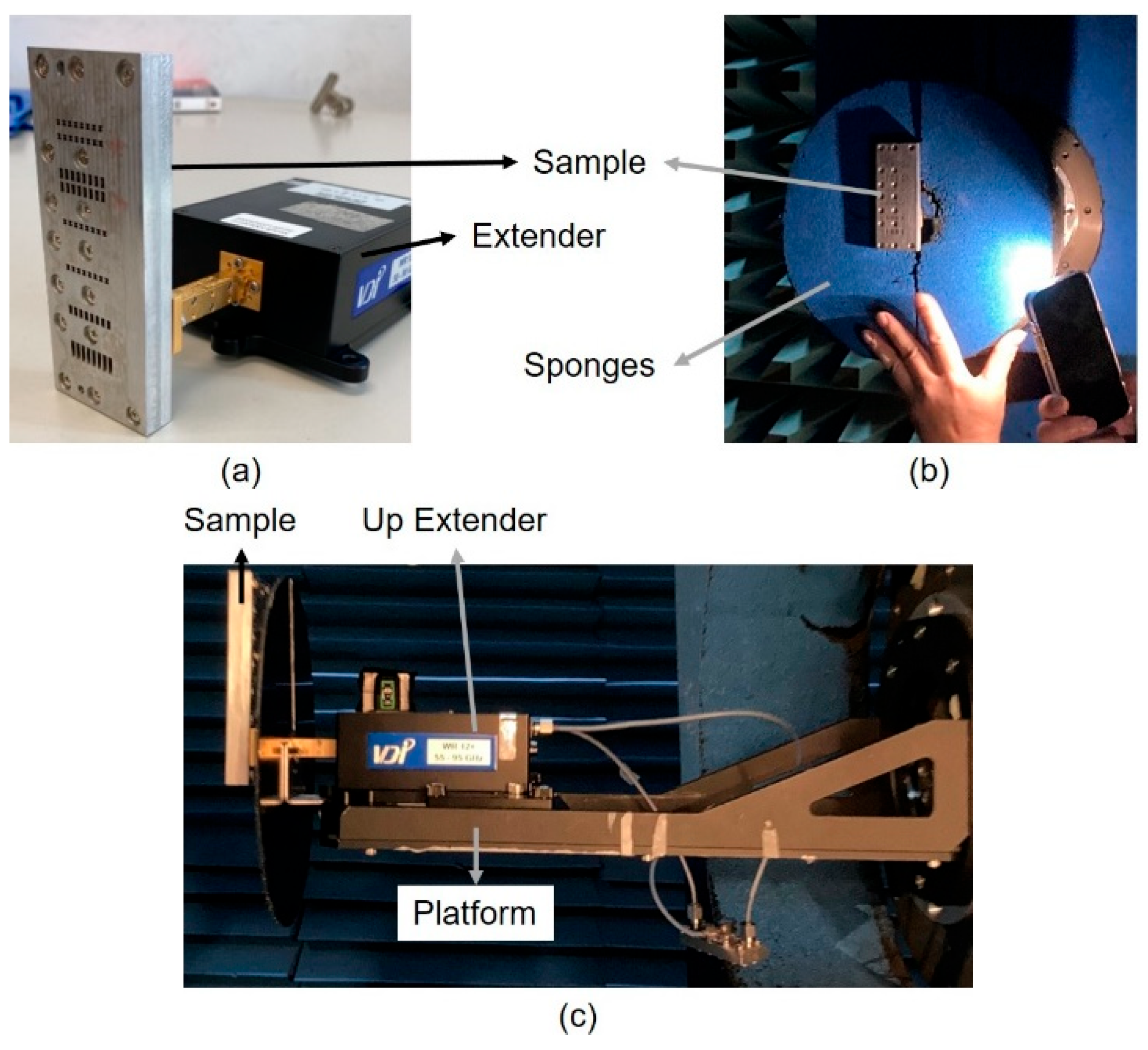
4.1. CNC Sample
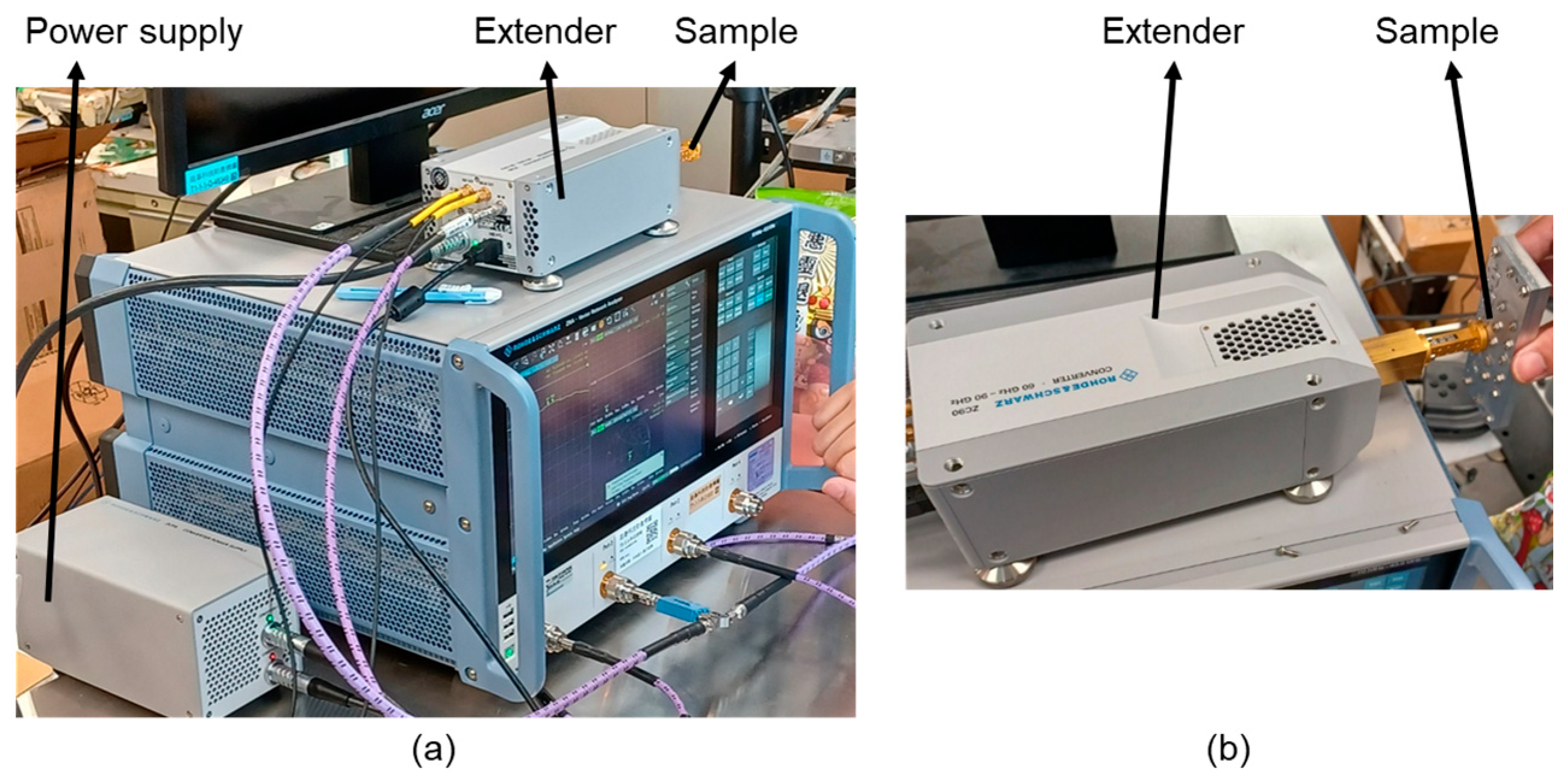
4.2. Measurement Setup
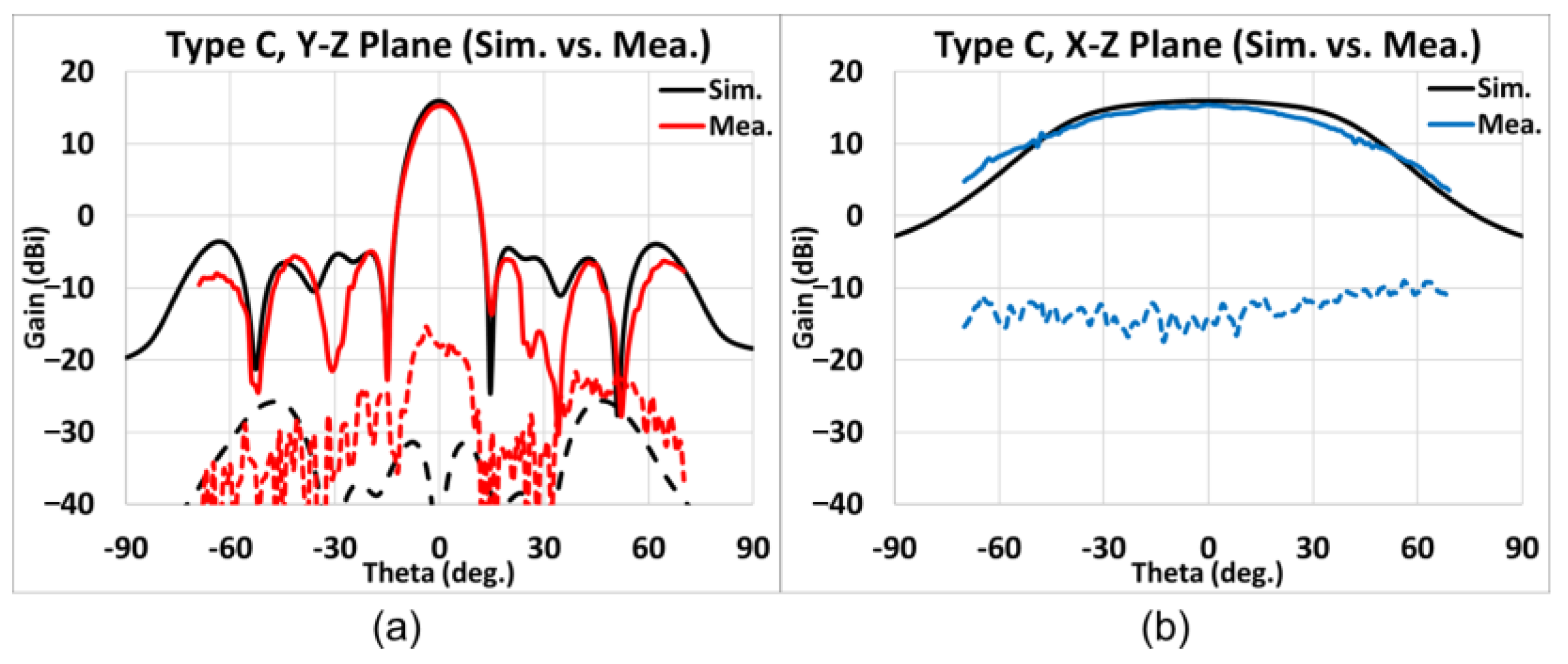
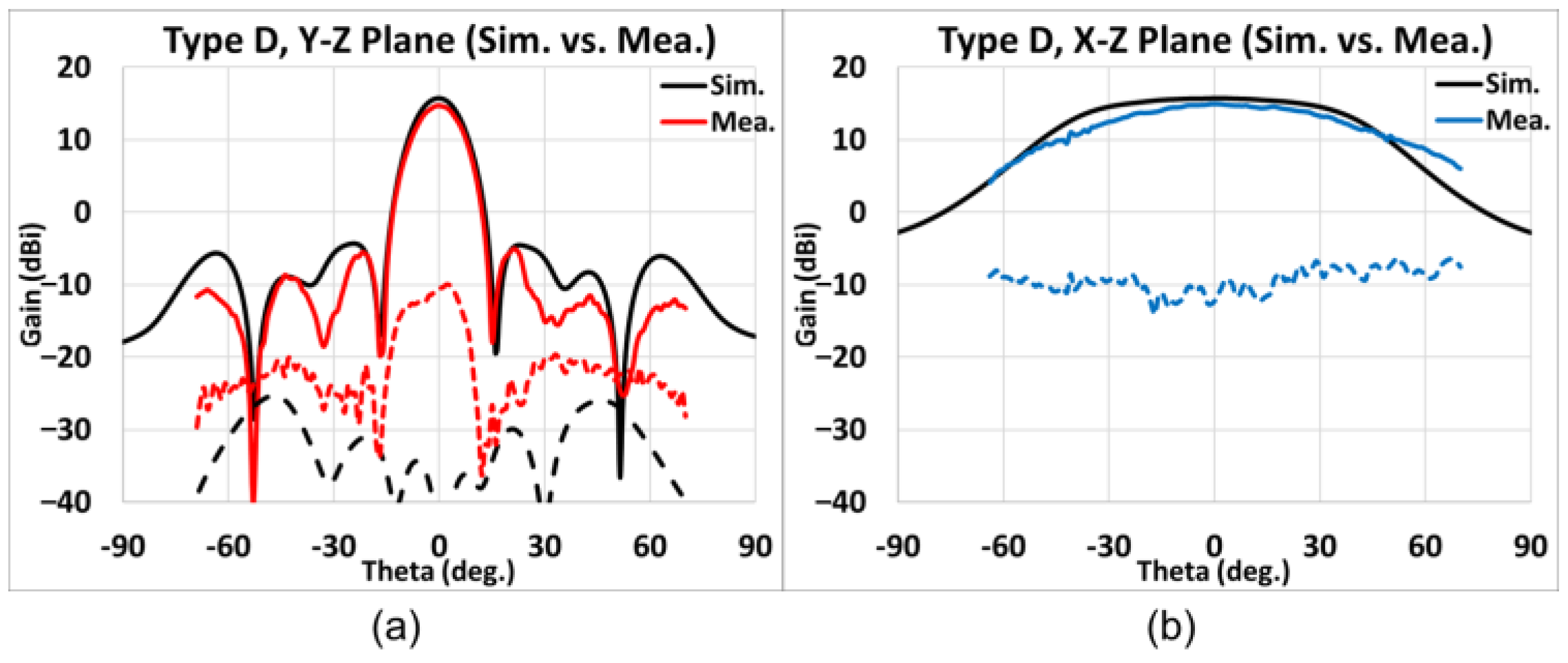
4.3. Measurement Results
4.4. Comparison of Performance with Existing Literatures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waldschmidt, C.; Hasch, J.; Menzel, W. Automotive radar—From first efforts to future systems. IEEE J. Microw. 2021, 1, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Parchin, N.O.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Excell, P.S. Coplanar Waveguide Antenna with Defected Ground Structure for 5G Millimeter Wave Communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE MENACOMM, Manama, Bahrain, 19–21 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q.J.O.; Romero, R.A. Ground vehicle target signature identification with cognitive automotive radar using 24–25 and 76–77 GHz bands. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 1448–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasubramanian, K.; Ramaiah, K. Moving from legacy 24 GHz to state-of-the-art 77-GHz radar. ATZ Elektron. Worldw. 2018, 13, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, B. Why Are Automotive Radar Systems Moving from 24 GHz to 77 GHz? Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Riyaz, P.; Ashutosh, T. Slotted waveguide antenna design for maritime radar system. Sci.Tech. J. Inf. Technol. Mech. Opt. 2022, 22, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajo-Iglesias, E.; Kildal, P.-S. Groove gap waveguide: A rectangular waveguide between contactless metal plates enabled by parallel-plate cut-off. In Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Barcelona, Spain, 12–16 April 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rajo-Iglesias, E.; Ferrando-Rocher, M.; Zaman, A.U. Gap waveguide technology for millimeter-wave antenna systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.K. Field and Wave Electromagnetics; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.T.; Sebak, A.R. Design and modeling of a linear array of longitudinal slots on substrate integrated waveguide. In Proceedings of the National Radio Science Conference, Cairo, Egypt, 13–15 March 2007; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, C.E. Sidewall waveguide slot antenna for high power. In Sensor and Simulation Notes, Note 503; University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, T.; Sakakibara, K.; Kikuma, N.; Hirayama, H. Grating lobe Suppression of Narrow-Wall Slotted Waveguide Array Antenna Using Thin Narrow-Wall Waveguides in MilliMeter-Wave Band. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Conference Proceedings, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2–5 December 2014; pp. 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, A.; Sakakibara, K.; Seo; Kikuma, N.; Hirayama, H. Design of hollow waveguide slot antenna using quite thin narrow-wall waveguide for grating-lobe suppression. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Antenna and Propagation, ISAP2007, Niigata, Japan, 20–24 August 2007; Volume 3, p. 354. [Google Scholar]
- Herruzo, J.I.H.; Valero-Nogueira, A.; Giner, S.M.; VilaJiménez, A. Untilted narrow-wall slots excited by parasitic dipoles in groovegap waveguide technology. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 4759–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, M.A.K.S.; Apriono, C.; Zulkifli, F.Y.; Rahardjo, E.T. Design of narrow wall slotted waveguide antenna for X-band application. In Proceedings of the Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall (PIERS-FALL), Singapore, 19–22 November 2017; pp. 2625–2628. [Google Scholar]
- Chignell, R.J.; Roberts, J. Compact resonant slot for waveguide arrays. Proc. Inst. Elec. Eng. 1978, 125, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Gray, D.; Chen, Y.-T. Width effects on electromagnetic and mechanical behaviour of Z-slotted waveguide array antennas. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Gu, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, W. Beam-scanning continuous transverse stub antenna fed by a ridged waveguide slot array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, A.; Galehdar, A.; Rowe, W.; Ghorbani, K.; John, S.; Wang, C.H. A spiral shaped slot as a broad-band slotted waveguide antenna. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 139, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Geng, J.; Zhu, W.; Jin, R. Grating ridged waveguide V-shaped slot array antenna for SATCOM applications. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, K.C.; Lee, Y.; Min, B.W.; Park, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, H.J. Circularly polarized T-shaped slot waveguide array antenna for satellite communications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 19, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansha, K.K.; Abdulla, P.; Jasmine, P.M.; Kollannore, U.S. Circularly polarized split ring slotted waveguide array antenna for 6G communications. Optik 2021, 247, 167920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.-Y.; Hong, J. Design and simulation of 77GHz substrate integrated waveguide slot array antenna. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 2020, 35, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, M.-Q.; Wang, W.; Jin, M.-P. A method of calculating admittance of waveguide slot. In Proceedings of the 2005 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference Proceedings, Suzhou, China, 4–7 December 2005; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Safaai-Jazi, A. Modified chebyshev arrays. IEE Proc. Microw. Antennas Propag. 1998, 145, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.; Prashansha, P.S.S.; Vijay, S. Performance analysis of eighteen element Dolph-Chebyshev linear array at different side lobe level. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on System Modeling & Advancement in Research Trends (SMART), Moradabad, India, 23–24 November 2018; pp. 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, X. A low sidelobe 77 GHz centre-fed microstrip patch array antenna. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2023, 17, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, A.A.; Elshamy, M.A.; Ahmed, M.F. Analysis and design of 79 GHz patch antenna array for radar applications. Egypt. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. (EIJEST) 2023, 43, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Q. Procedure to Design a Series-fed Microstrip Patch Antenna Array for 77 GHz Automotive Radar. In Proceedings of the 2019 Cross Strait Quad-Regional Radio Science and Wireless Technology Conference (CSQRWC), Taiyuan, China, 18–21 July 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, H. Design of Gap Waveguide Antenna System for 77 GHz Automotive Radar. Master’s. Thesis, Department for Electrical Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, A.; Kazim, J.U.; Pang, Z.; Abbasi, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Imran, M.A.; Ur-Rehman, M. AWideband Frequency Beam-Scanning Antenna Array for Millimeter-Wave Industrial Wireless Sensing Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 13315–13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Ren, Q.; Zaman, A.U.; Yang, J. 77 GHz Fully Polarimetric Antenna System With Compact Circularly Polarized Slots in Gap Waveguide for Automotive Radar. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 5578–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Prototype (Frequency) | Simulated Loss (dB/cm) | Measured Min-Max Loss (dB/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangular waveguide (50–75 GHz) | 0.0136 | 0.0295–0.0420 |
| Microstrip (50–75 GHz) 0.127–0.200 mm substrate | Rogers 4003: 0.271 | 0.7055 |
| Ref. | Slot | Narrow/ Broad Wall | Slot Spacing | , −10 dB BW | Advantages/ Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] (2013) | Spiral | Broad wall | 35% | Wideband Stable gain Elliptical polarization Hard to fabricate | |
| [20] (2019) | V-shaped | Broad wall | 5.5% | Pure polarization Compact Narrow bandwidth Hard to fabricate | |
| [21] (2019) | T-shaped | Broad wall | 3.4% | High gain Circular polarization Compact Narrow bandwidth Hard to fabricate | |
| [22] (2021) | Split-ring | Broad wall | 30.5% | Wideband High gain Beam steering Hard to fabricate | |
| [14] (2015) | I-shaped | Narrow wall | 5% | Compact slot without tilting Hard to fabricate dipoles Lossy structure | |
| This work | Z-shaped | Narrow wall | 7.8% | Compact Easy design High gain |
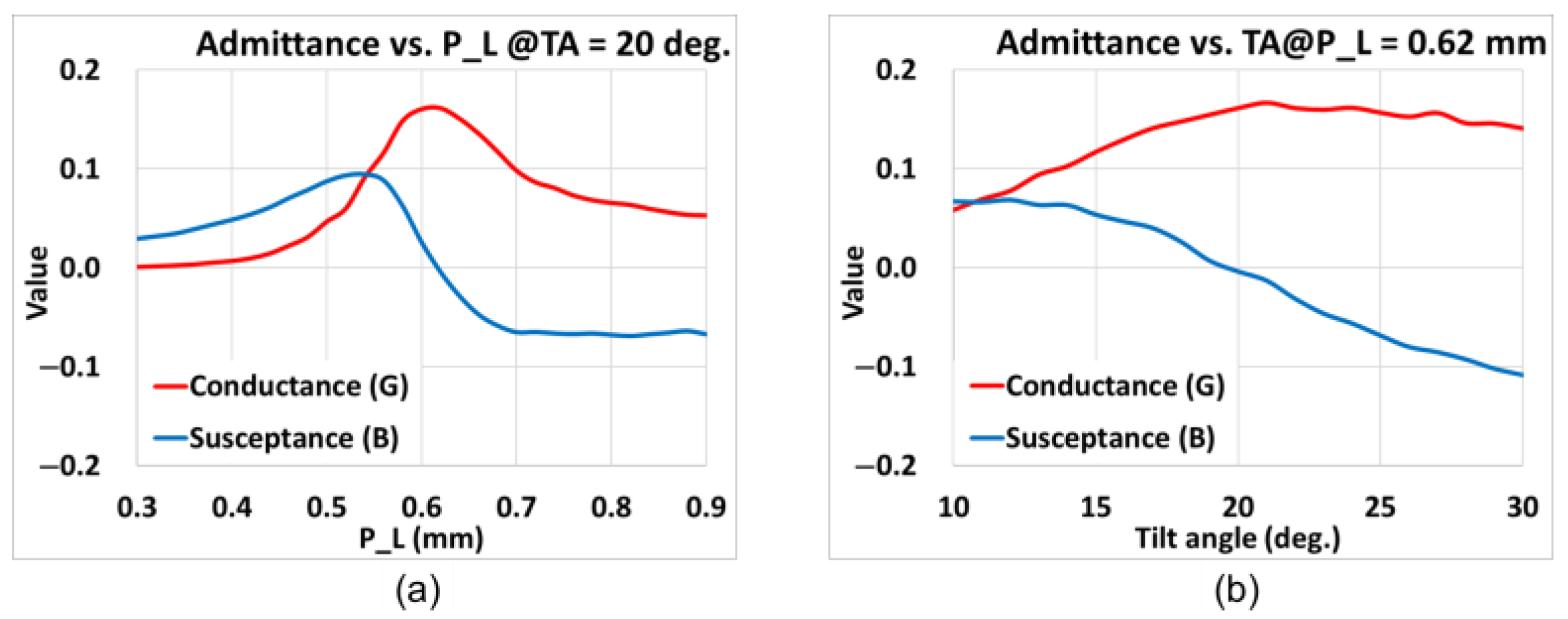
| TA (deg) | P_L (mm) | Conductance (G) | Susceptance (B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.76 | 0.0665 | 0 |
| 10 | 070 | 0.0954 | 0 |
| 15 | 0.66 | 0.1291 | 0 |
| 20 | 0.62 | 0.1612 | 0 |
| 5.01 | ~3.10 | ~1.55 | 3 | 0.5 |
| n | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 | #7 | #8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient in Power | 1.00 | 1.30 | 2.28 | 2.97 | 2.97 | 2.28 | 1.30 | 1.00 |
| n | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 | #7 | #8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA (°) | 1.1 | 3.3 | 16.7 | 20.8 | 20.8 | 16.7 | 3.3 | 1.1 |
| P_L (mm) | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 5.01 | ~3.10 | 1.80 | ~6.56 | 3 | 0.5 |
| n | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 | #7 | #8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA (°) | 1.3 | 1.4 | 17.3 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 17.3 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| P_L (mm) | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 5.01 | ~1.88 | 1.6 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.22 |
| n | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 | #7 | #8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA (°) | 2.9 | 2.0 | 24.9 | 24.8 | 24.8 | 24.9 | 2.0 | 2.9 |
| P_L (mm) | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| 5.01 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.40 | 0.30 |
| n | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 | #7 | #8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA (°) | 2.9 | 2.0 | 24.9 | 24.8 | 24.8 | 24.9 | 2.0 | 2.9 |
| P_L (mm) | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| Type | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aperture size () | 4.8 | 11.8 | 3.0 | 2.7 |
| −10 dB FBW (%) | 7.9 | 8.6 | 9.4 | 9.3 |
| Peak gain (dB) | 17.0 | 19.0 | 16.0 | 15.7 |
| SLL (dB) | −20.6 | −19.7 | −19.5 | −20.0 |
| 3-dB EL BW () | 11.4 | 11.1 | 11.9 | 12.8 |
| 3-dBAZ BW () | 68.7 | 40.1 | 80.1 | 81.2 |
| 6-dBAZ BW () | 88.9 | 56.8 | 99.1 | 100.2 |
| REF. | Antenna Type | Element Number | Aperture Dimension (λ02) | FBW (%) @ Central Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | SLL (dB) | 3 dB EL BW () | Radiation Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] (2023) | Patch | <6.5%, 77 GHz (Sim.) | 13.8 (Sim.) | −24.4 (Sim.) | 10.0 (Sim.) | N.A. | ||
| [29] (2023) | Patch | 4.1%, 79 GHz (Sim.) 1.7%, 79 GHz (Mea.) | 15.1 (Mea.) | N.A. | 11.7 (Mea.) | N.A. | ||
| [30] (2011) | Patch | 1.9%, 77 GHz (Sim.) | 16 (Sim.) | −22 (Sim.) | 10 (Sim.) | N.A. | ||
| [31] (2018) | Slot SIW | N.A. | >4%, 76.5 GHz (Sim.) | 14.4 (Sim.) | −19.2 (Sim.) | 10.2 (Sim.) | N.A. | |
| [32] (2024) | Patch | 44.2%, 64 GHz (Sim.) 20.3%, 64 GHz (Mea.) | 13.5 (Sim.) | −10 (Sim.) | 6.4 (Sim.) | 88% (Sim.) | ||
| [33] (2024) | Slot RGW | 2.2%, 77 GHz (Sim.) 2.2%, 77 GHz (Mea.) | 16 (Sim.) 15 (Mea.) | −10 (Sim.) −10 (Mea.) | 10 (Sim.) 10 (Mea.) | 75% (Mea.) | ||
| This Work | Slot Waveguide | 7.8%, 77 GHz (Sim.) | 17.0 (Sim.) 16.4 (Mea.) | −20.6 (Sim.) −18.5 (Mea.) | 11.4 (Sim.) 11 (Mea.) | 87% (Mea.) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.-H.; Huang, T.-C.; Ng Mou Kehn, M. Compact Waveguide Antenna Design for 77 GHz High-Resolution Radar. Sensors 2025, 25, 3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113262
Wu C-H, Huang T-C, Ng Mou Kehn M. Compact Waveguide Antenna Design for 77 GHz High-Resolution Radar. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113262
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chin-Hsien, Tsun-Che Huang, and Malcolm Ng Mou Kehn. 2025. "Compact Waveguide Antenna Design for 77 GHz High-Resolution Radar" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113262
APA StyleWu, C.-H., Huang, T.-C., & Ng Mou Kehn, M. (2025). Compact Waveguide Antenna Design for 77 GHz High-Resolution Radar. Sensors, 25(11), 3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113262






