An Extrinsic Optical Fiber Sensor Probe with Micrometer Size via a C-Shaped Waveguide with a Core of MIP
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. MIP and NIP Preparation
2.3. Measuring Protocol
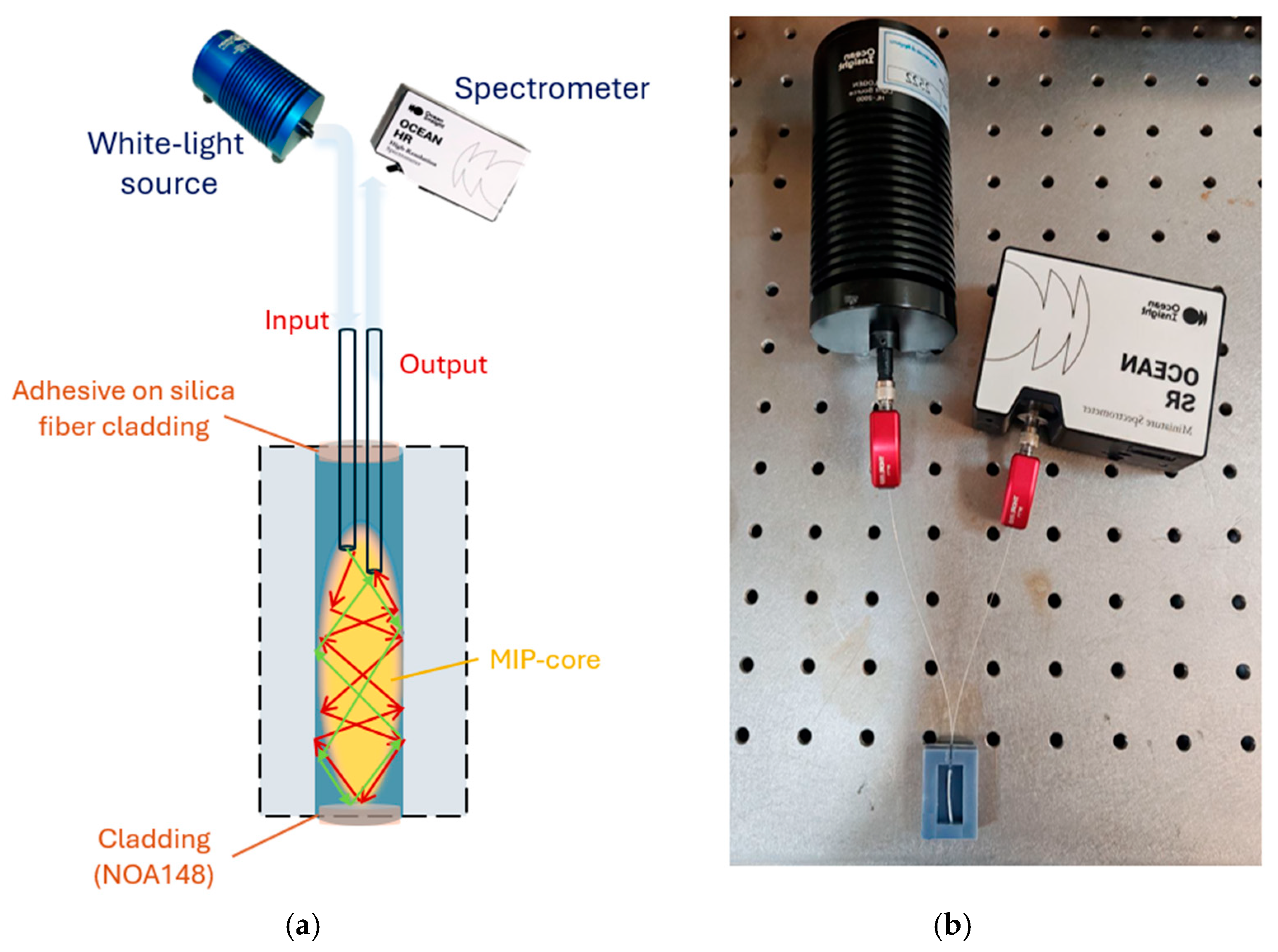
3. Sensor System Configuration
3.1. Production Steps of the Two-OFs-Based Sensor
3.2. Experimental Setup and Sensing Principle
4. Results and Discussion
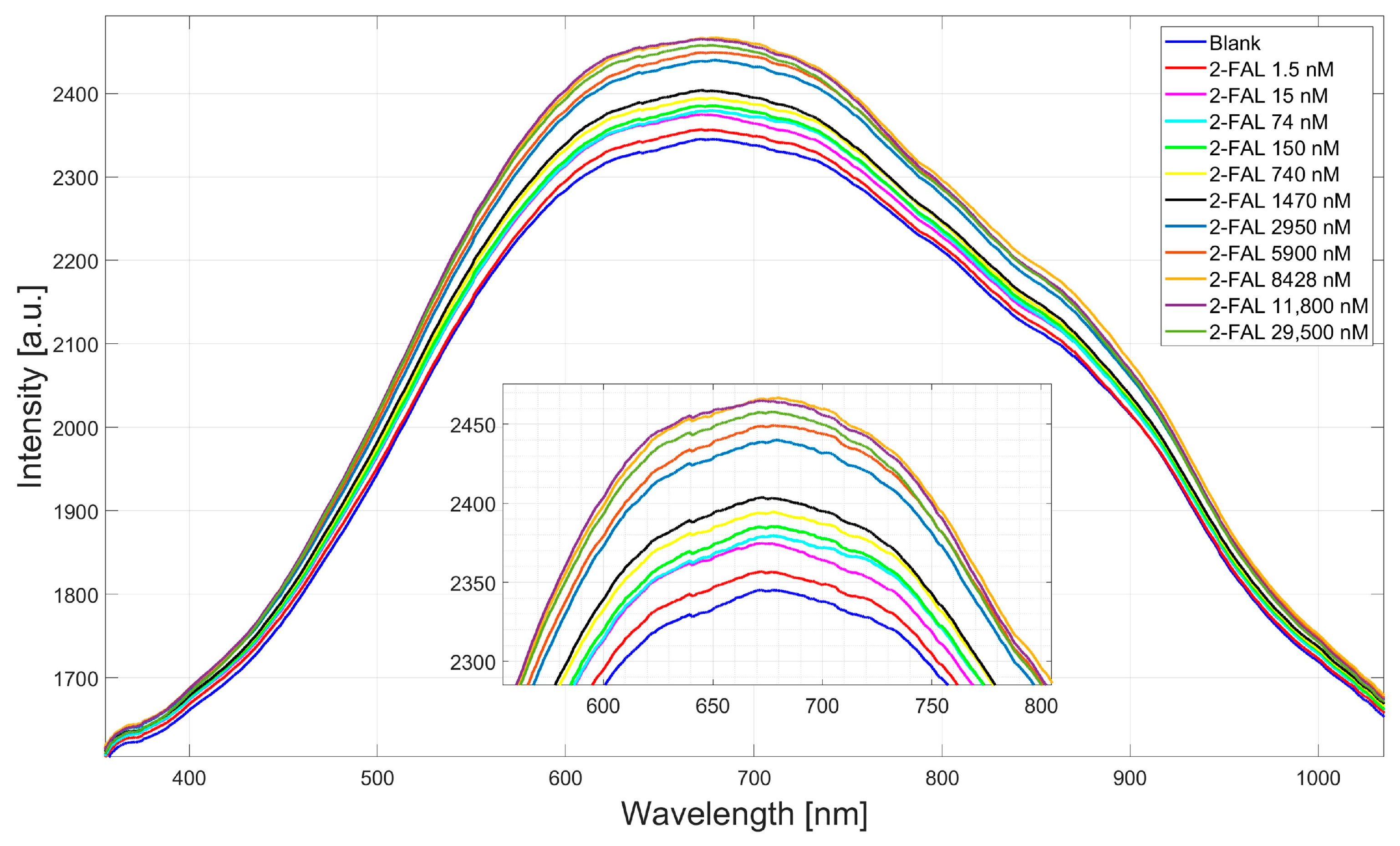
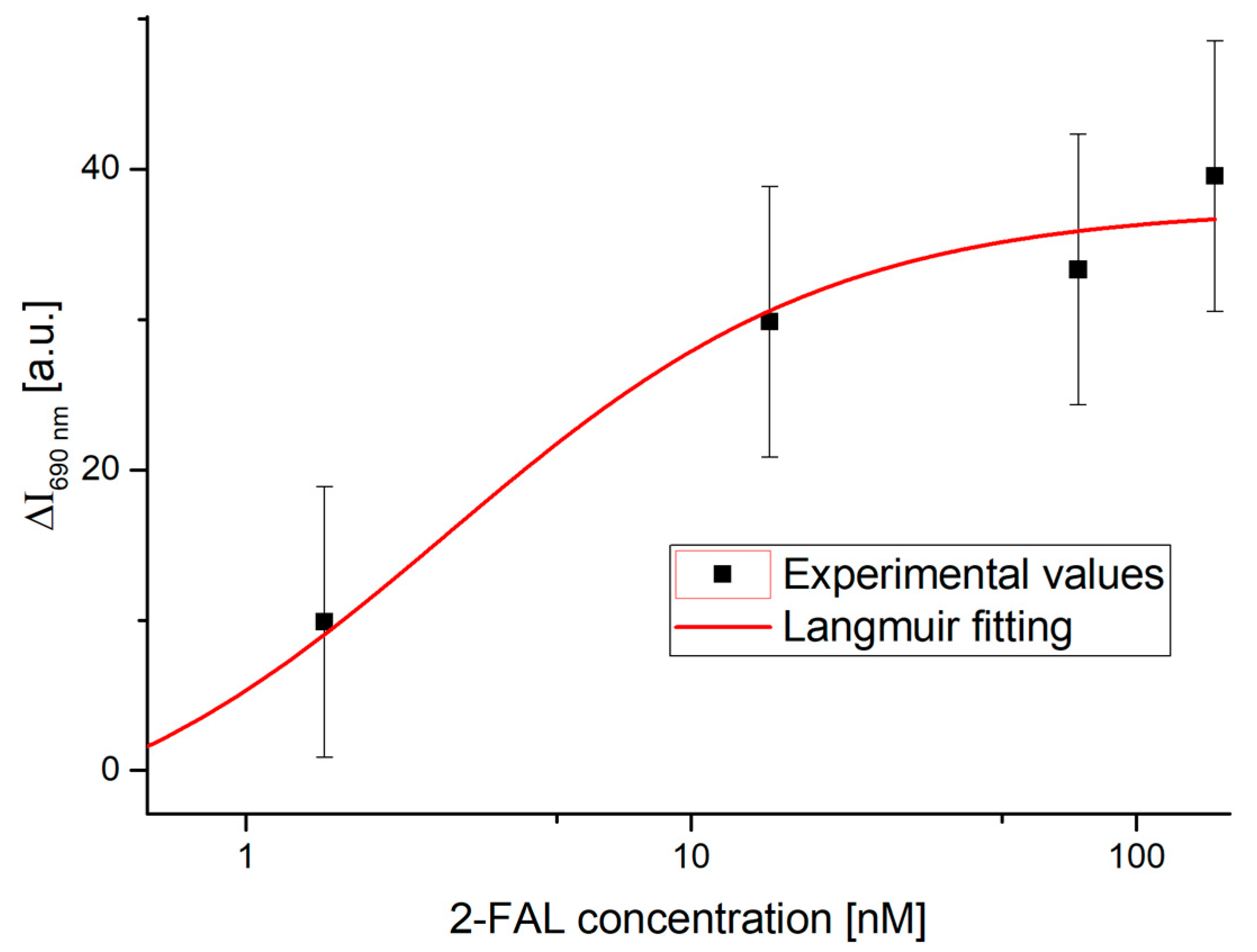
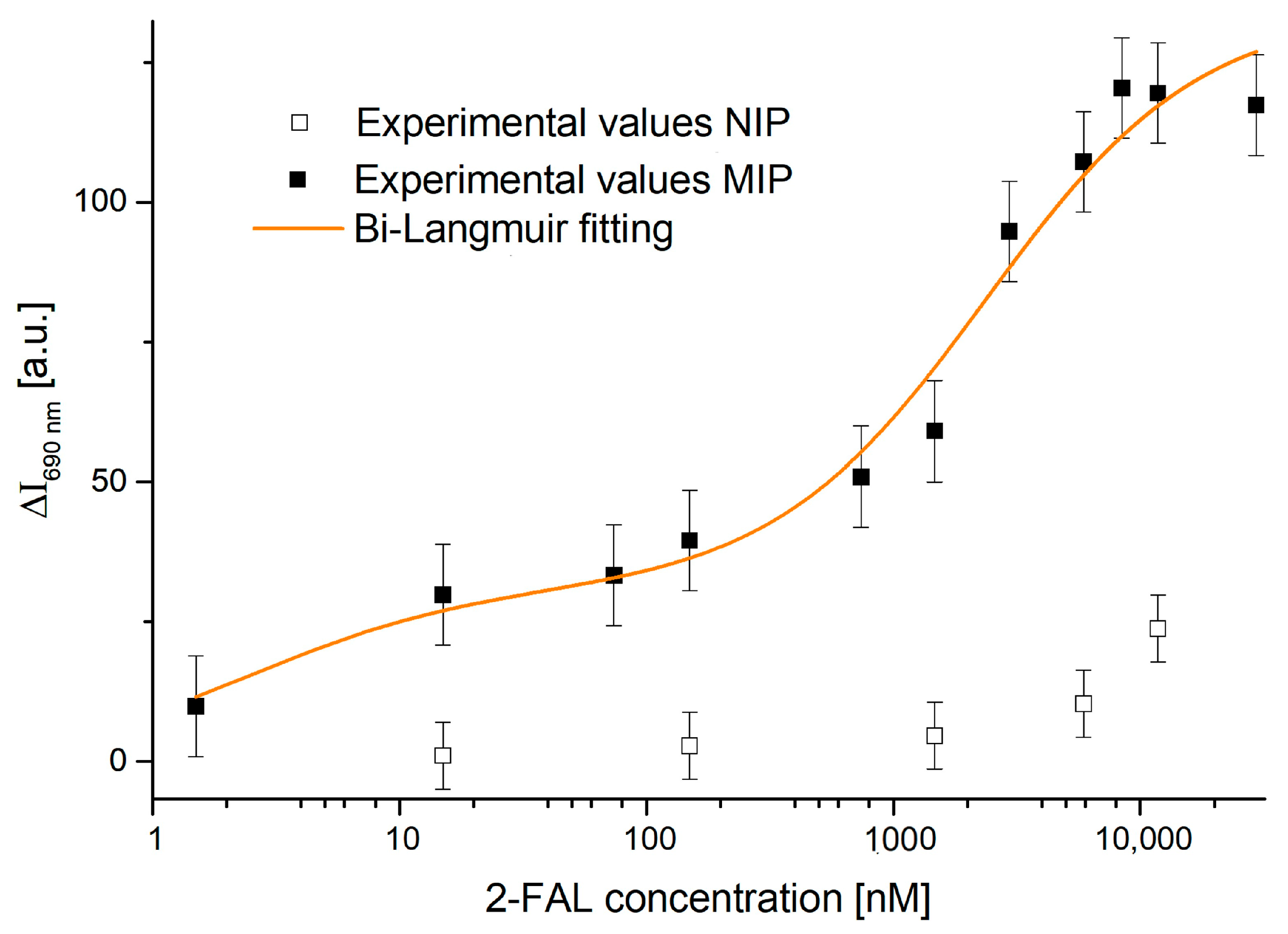
4.1. Dose–Response Curve of the Two-OFs-Based Sensor
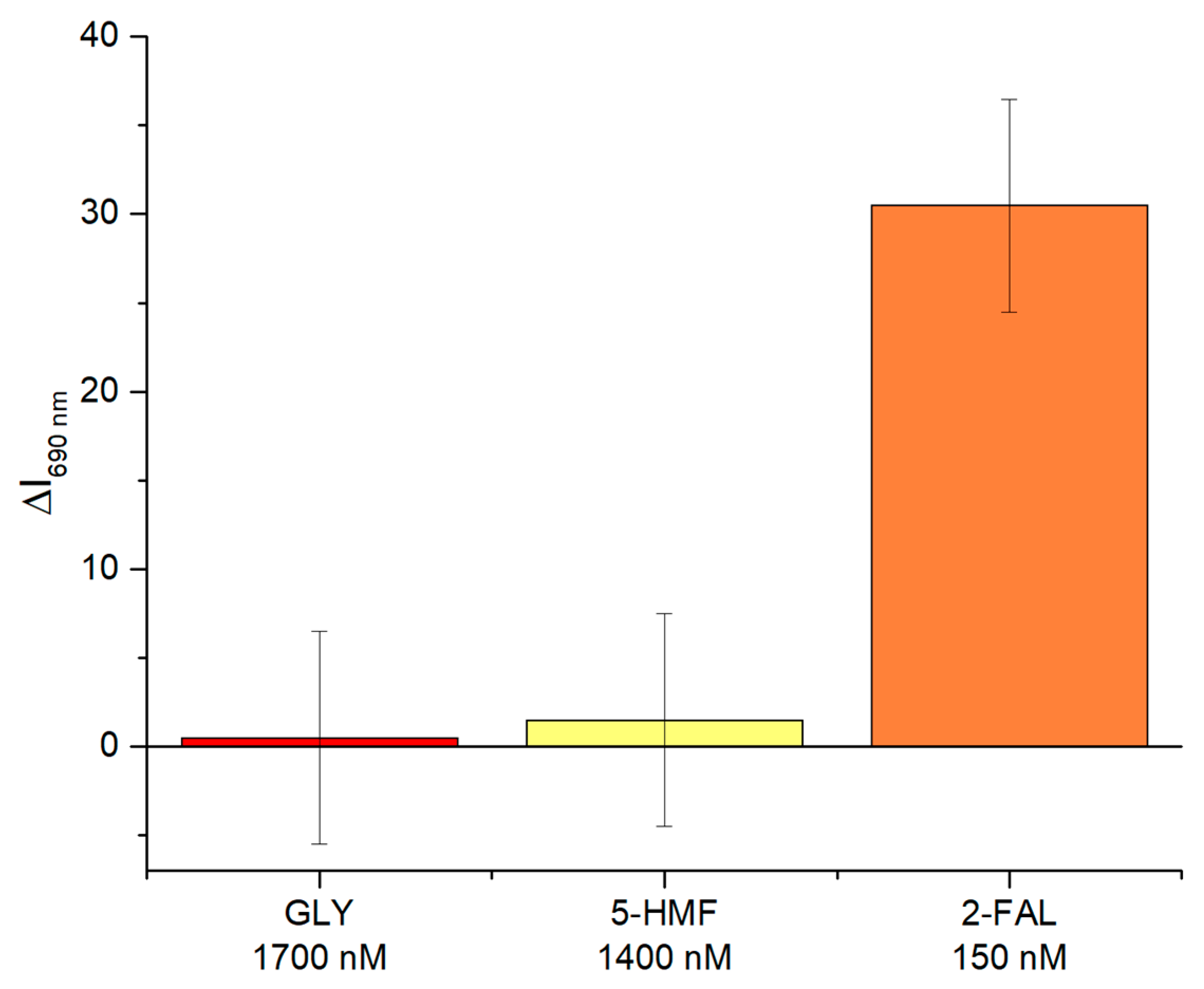
4.2. Selectivity Test of Two-OFs-Based Sensor
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors (2015–2019). Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 397–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pospíšilová, M.; Kuncová, G.; Trögl, J. Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Fiber-Optic Bio-Sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 25208–25259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Zeni, L.; Pesavento, M.; Marchetti, S.; Marletta, V.; Baglio, S.; Graziani, S.; Pistorio, A.; Ando, B. A Novel Sensing Methodology to Detect Furfural in Water, Exploiting MIPs, and Inkjet-Printed Optical Waveguides. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcadio, F.; Zeni, L.; Perri, C.; D’Agostino, G.; Chiaretti, G.; Porto, G.; Minardo, A.; Cennamo, N. Bovine Serum Albumin Protein Detection by a Removable SPR Chip Combined with a Specific MIP Receptor. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendão, C.; Silva, I. Optical Fiber Sensors and Sensing Networks: Overview of the Main Principles and Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matějec, V.; Barton, I.; Pospisilova, M.; Traplova, L. Extrinsic Fiber-Optic Sensor for Detection of Saliva pH. Chem. Afr. 2019, 2, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcadio, F.; Zeni, L.; Minardo, A.; Eramo, C.; Di Ronza, S.; Perri, C.; D’Agostino, G.; Chiaretti, G.; Porto, G.; Cennamo, N. A Nanoplasmonic-Based Biosensing Approach for Wide-Range and Highly Sensitive Detection of Chemicals. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euser, T.G.; Chen, J.S.Y.; Scharrer, M.; Russell, P.S.J.; Farrer, N.J.; Sadler, P.J. Quantitative Broadband Chemical Sensing in Air-Suspended Solid-Core Fibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 103108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.S.; Vidal, M.; Santos, N.F.; Costa, F.M.; Marques, C.; Pereira, S.O.; Leitão, C. Immunosensing Based on Optical Fiber Technology: Recent Advances. Biosensors 2021, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Córdova, G.A.; Vega-Chacón, J.; Sotomayor, M.d.P.T.; Tuesta, J.C.; Khan, S.; Picasso, G. Development of an Optical Sensor Using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as a Selective Extracting Agent for the Direct Quantification of Tartrazine in Real Water Samples. Polymers 2024, 16, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leysen, W.; Gusarov, A.; Mégret, P.; Wuilpart, M. Assessment of the Environmental Effects on the ITER FOCS Operating in Reflective Scheme with Faraday Mirror. Fusion Eng. Des. 2019, 146, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.-X.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhang, W.-G.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Yan, T.-Y.; Geng, P.-C.; Wang, B. Lab-on-Tip: Protruding-Shaped All-Fiber Plasmonic Microtip Probe toward in-Situ Chem-Bio Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B. Optical Fiber Technologies for Nanomanipulation and Biodetection: A Review. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.P.; Langford, R.M.; Chang, S.H.; Maney, K.; Kyriacou, P.A.; Jones, D.P. Cerebral Arterial Oxygen Saturation Measurements Using a Fiber-Optic Pulse Oximeter. Neurocrit. Care 2010, 13, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, J.A.; Hou, H.; Demidenko, E.; Springett, R.J.; Khan, N.; Swartz, H.M. Simultaneous Measurement of Rat Brain Cortex PtO2Using EPR Oximetry and a Fluorescence Fiber-Optic Sensor during Normoxia and Hyperoxia. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hao, F.; Morgan, S.P.; Correia, R.; Norris, A.; Korposh, S. A Reflection-Mode Fibre-Optic Sensor for Breath Carbon Dioxide Measurement in Healthcare. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2019, 22, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, K.; Klainer, S.M.; Dandge, D.K.; Thomas, J.R. Fiber optic chemical sensors (FOCS): An answer to the need for small, specific monitors. In Biosensor Technology; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, M.; Frizera, A.; Leal-Junior, A.; Ribeiro, D.; Marques, C.; Blanc, W.; Díaz, C.A. Transmission–Reflection Analysis in High Scattering Optical Fibers: A Comparison with Single-Mode Optical Fiber. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 58, 102303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Su, H.; Li, X.; Wen, Z. Reflection and Transmission Spectra of Dynamic Optical Fiber Gratings. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2018, 50, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Their Use in Biomimetic. Sens. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, D.; Ramstrom, O.; Mosbach, K. Molecular Imprinting-New Possibilities for Sensor Technology. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdoust, S.; Arshad, U.; Mujahid, A.; Schranzhofer, L.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Development of a MIP-Based QCM Sensor for Selective Detection of Penicillins in Aqueous Media. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Akhoundian, M. A Novel Potentiometric Sensor for Promethazine Based on a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP): The Role of MIP Structure on the Sensor Performance. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse Sum Bui, B.; Haupt, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Synthetic Receptors in Bioanalysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2481–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Mahato, K. Recent Advancements in Bioreceptors and Materials for Biosensors. In Biosensors in Precision Medicine; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 163–202. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, P. Molecular Imprinting for Bio- and Pharmaceutical Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Zanoni, C.; Magnaghi, L.R.; Biesuz, R. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs). In Sensory Polymers; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 97–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.; Miao, H.; Xu, J.; Pan, G. State of the Art in Development of Molecularly Imprinted Biosensors. VIEW 2021, 3, 20200170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Pesavento, M.; Arcadio, F.; Marzano, C.; Zeni, L. Advances in Plastic Optical Fiber Bio/Chemical Sensors to Realize Point-of-Care-Tests. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 177, 117797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Liu, H.; Zhong, N.; Zhao, M.; Zhong, D.; Chang, H.; Tang, B.; He, Y.; Peng, C.; He, X. A Highly Sensitive Plastic Optic-Fiber with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coating for Selective Detection of 4-Chlorophenol in Water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 357, 131468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Pesavento, M.; Zeni, L. A Review on Simple and Highly Sensitive Plastic Optical Fiber Probes for Bio-Chemical Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 331, 129393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Feng, L.; Tan, Y.; Hu, J. An Optical Reflected Device Using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film Sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 653, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoydonckx, H.E.; Van Rhijn, W.M.; Van Rhijn, W.; De Vos, D.E.; Jacobs, P.A. Furfural and Derivatives. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Matharage, S.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Walker, D. Effect of Paper Type and Water Content in Paper on the Partitioning of 2-FAL between Liquid and Paper Insulations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application (ICHVE), Beijing, China, 6–10 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nezami, M.D.M.; Wani, S.A.; Khan, S.A.; Khera, N.; Sohail, S. An MIP-Based Novel Capacitive Sensor to Detect 2-FAL Concentration in Transformer Oil. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 7924–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.T.I.; Raghuwanshi, S.K.; Kumar, S. Recent Advancement in Fiber-Optic-Based SPR Biosensor for Food Adulteration Detection—A Review. IEEE Trans. Nanobioscience 2023, 22, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesavento, M.; Zeni, L.; De Maria, L.; Alberti, G.; Cennamo, N. SPR-Optical Fiber-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensor for the Detection of Furfural in Wine. Biosensors 2021, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzullo, L.P.; Tavoletta, I.; Alberti, G.; Zeni, L.; Pesavento, M.; Cennamo, N. Plasmonic Optical Fiber Sensors and Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Glyphosate Detection at an Ultra-Wide Range. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoletta, I.; Arcadio, F.; Renzullo, L.P.; Oliva, G.; Del Prete, D.; Verolla, D.; Marzano, C.; Alberti, G.; Pesavento, M.; Zeni, L.; et al. Splitter-Based Sensors Realized via POFs Coupled by a Micro-Trench Filled with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Sensors 2024, 24, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcadio, F.; Prete, D.D.; Zeni, L.; Pesavento, M.; Alberti, G.; Marletta, V.; Andò, B.; Cennamo, N. Optical Waveguides Based on a Core of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: An Efficient Approach for Chemical Sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 27411–27420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Arcadio, F.; Zeni, L.; Alberti, G.; Pesavento, M. Optical-Chemical Sensors Based on Plasmonic Phenomena Modulated via Micro-Holes in Plastic Optical Fibers Filled by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 372, 132672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitruzzella, R.; Marzano, C.; Arcadio, F.; Sequeira, F.; Cutaia, A.; Cardoso Novo, C.; Scarpellini, A.; Alberti, G. Silica Optical Fibers Connected via a Micro MIP-Core Waveguide to Build Optical-Chemical Sensors. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Ellison, S.L.R.; Wood, R. Harmonized Guidelines for Single-Laboratory Validation of Methods of Analysis (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 835–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


[a.u.] | [nM] | [a.u.] | [nM] | Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Reduced Chi-Sqr | Adj. R-Square |
| 31 | 6 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 104 | 8 | 2382 | 783 | 0.68 | 0.97 |
[a.u.] | [a.u.] | [nM] | Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Reduced Chi-Sqr | Adj. R-Square |
| −6 | 6 | 37 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0.09 | 0.97 |
| [nM] | [nM] | [a.u./nM] | [nM]−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 4.5 | 13.4 | 0.36 |
| Sensor Configuration | Scheme | Range of Detection | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPR–POF–MIP sensor | Transmission | 0.120 μM–60.4 μM | 120 nM | [37] |
| MIP-Splitter-based sensor | Transmission | 0.52 μM–52 μM | 520 nM | [39] |
| MIP-core waveguide | Transmission | 0.01 μM–1.2 μM | 10 nM | [40] |
| Micro OF-MIP-OF sensor | Transmission | 1.5 nM–150 nM | 1.5 nM | [41] |
| Two-OFs-based sensor | Reflection | 1.5 nM–8.4 μM | 1.5 nM | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzano, C.; Pitruzzella, R.; Arcadio, F.; Sequeira, F.; Renzullo, L.P.; Cutaia, A.; Cardoso Novo, C.; Oliveira, R.; Pesavento, M.; Zeni, L.; et al. An Extrinsic Optical Fiber Sensor Probe with Micrometer Size via a C-Shaped Waveguide with a Core of MIP. Sensors 2025, 25, 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103250
Marzano C, Pitruzzella R, Arcadio F, Sequeira F, Renzullo LP, Cutaia A, Cardoso Novo C, Oliveira R, Pesavento M, Zeni L, et al. An Extrinsic Optical Fiber Sensor Probe with Micrometer Size via a C-Shaped Waveguide with a Core of MIP. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103250
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzano, Chiara, Rosalba Pitruzzella, Francesco Arcadio, Filipa Sequeira, Luca Pasquale Renzullo, Alessandra Cutaia, Catarina Cardoso Novo, Ricardo Oliveira, Maria Pesavento, Luigi Zeni, and et al. 2025. "An Extrinsic Optical Fiber Sensor Probe with Micrometer Size via a C-Shaped Waveguide with a Core of MIP" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103250
APA StyleMarzano, C., Pitruzzella, R., Arcadio, F., Sequeira, F., Renzullo, L. P., Cutaia, A., Cardoso Novo, C., Oliveira, R., Pesavento, M., Zeni, L., Alberti, G., Cennamo, N., & Nogueira, R. N. (2025). An Extrinsic Optical Fiber Sensor Probe with Micrometer Size via a C-Shaped Waveguide with a Core of MIP. Sensors, 25(10), 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103250











