A Systematic Review of AI-Based Techniques for Automated Waste Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Planning the Review
2.1.1. Search Protocol
Data Sources, Search Strategy, and Data Extraction
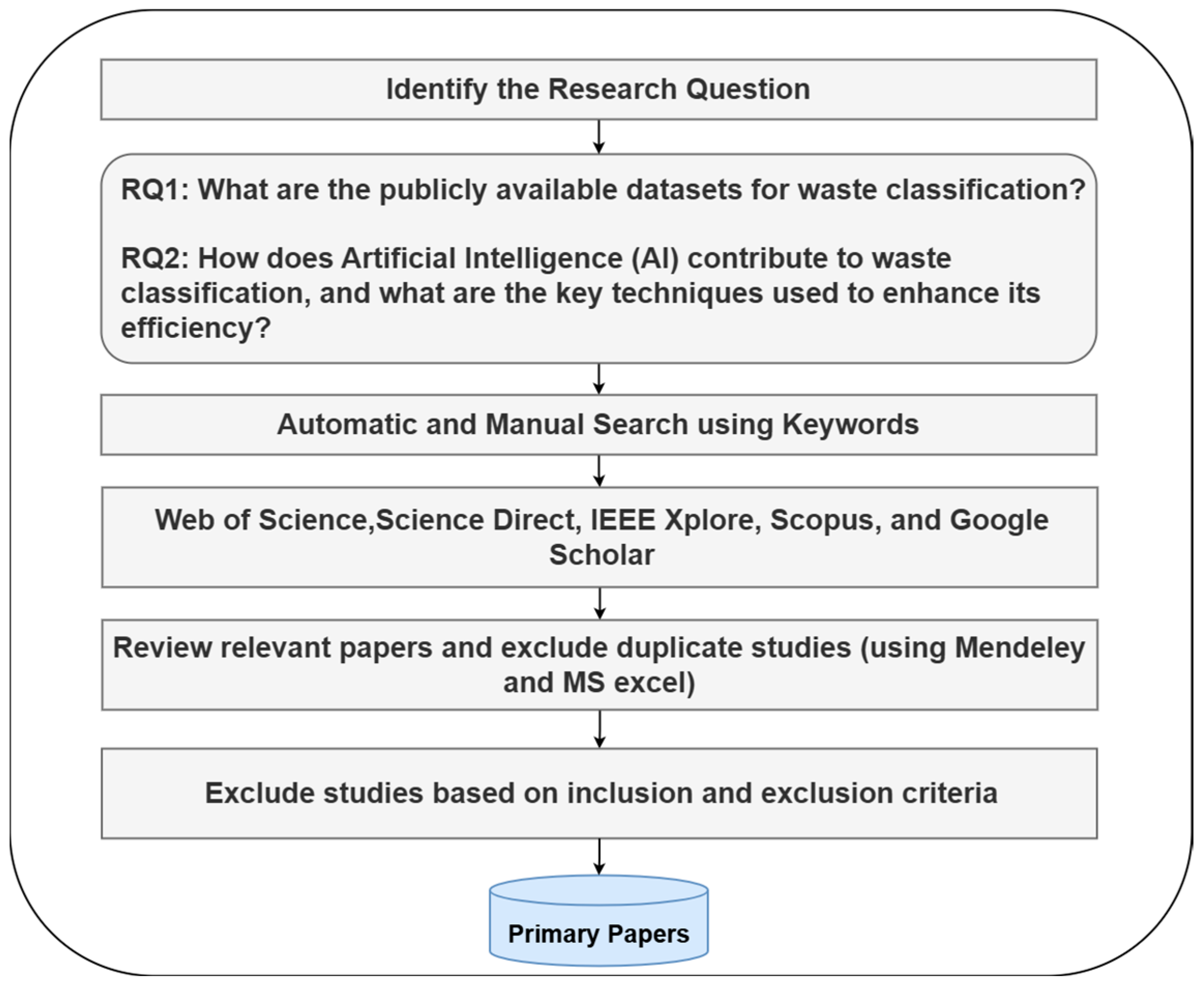
2.1.2. Research Questions
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
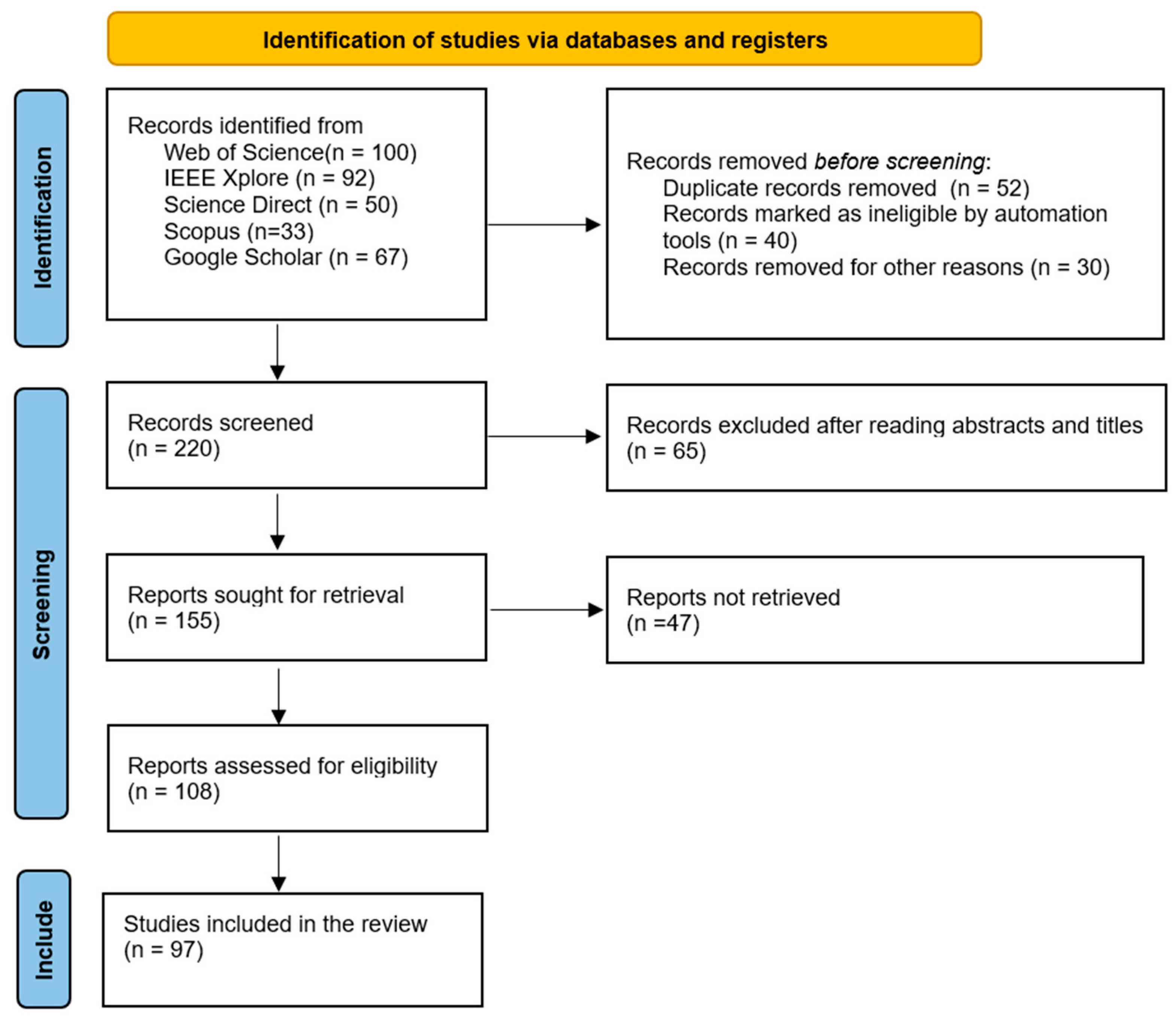
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Publicly Available Waste Dataset for Waste Classification
3.1.1. Dataset Size and Coverage
3.1.2. Platforms for Dataset Collection, Annotation, and AI Model Deployment
3.1.3. Dataset Limitations and Challenges
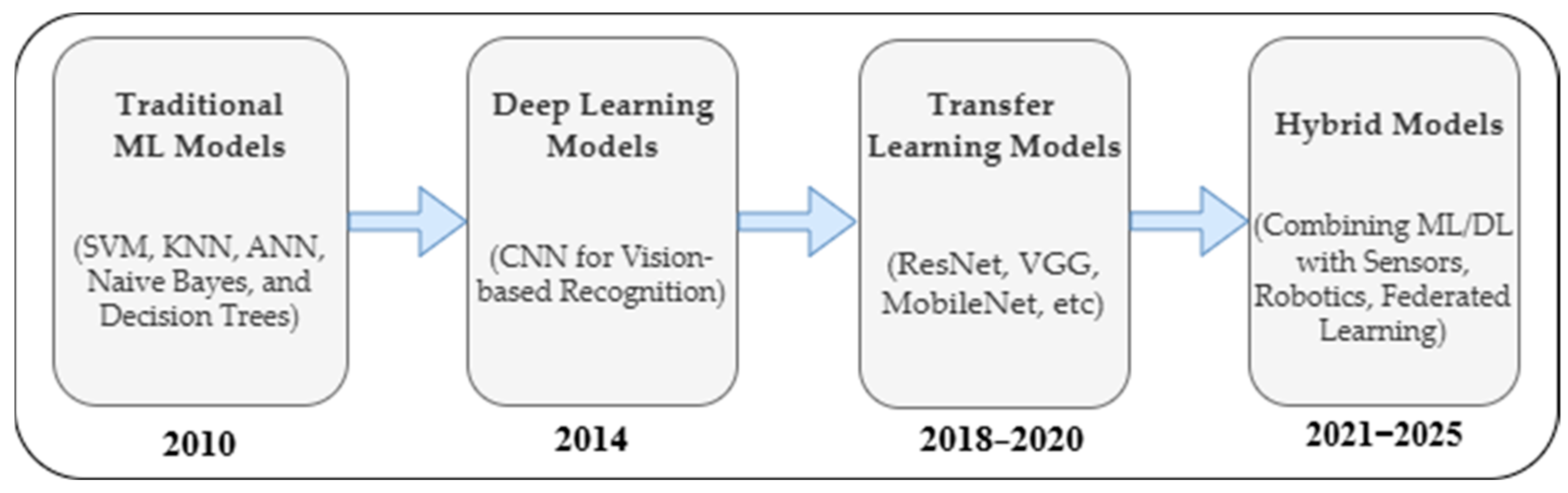
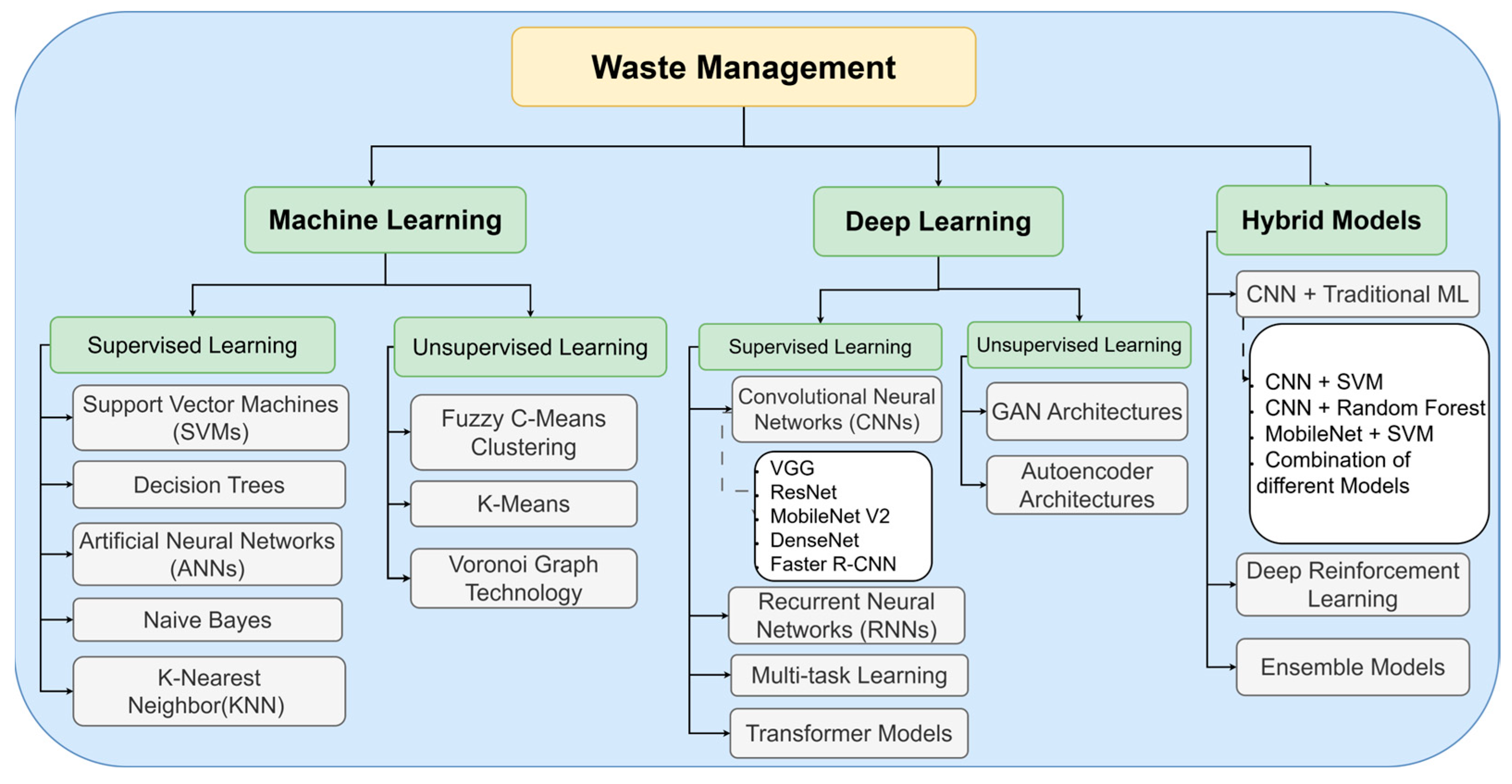
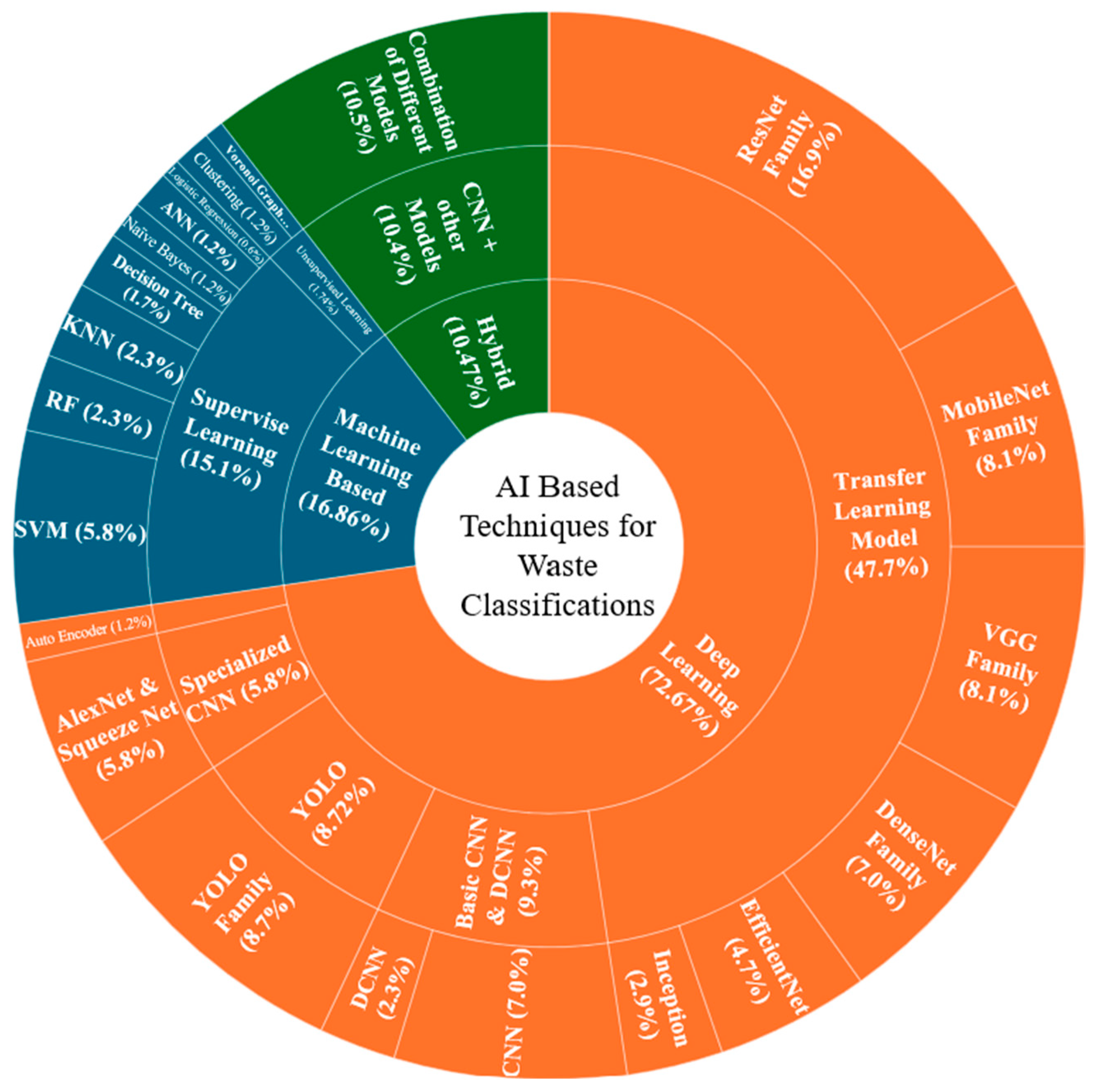
3.2. AI-Based Techniques for Waste Classification
3.2.1. Machine Learning-Based Approaches
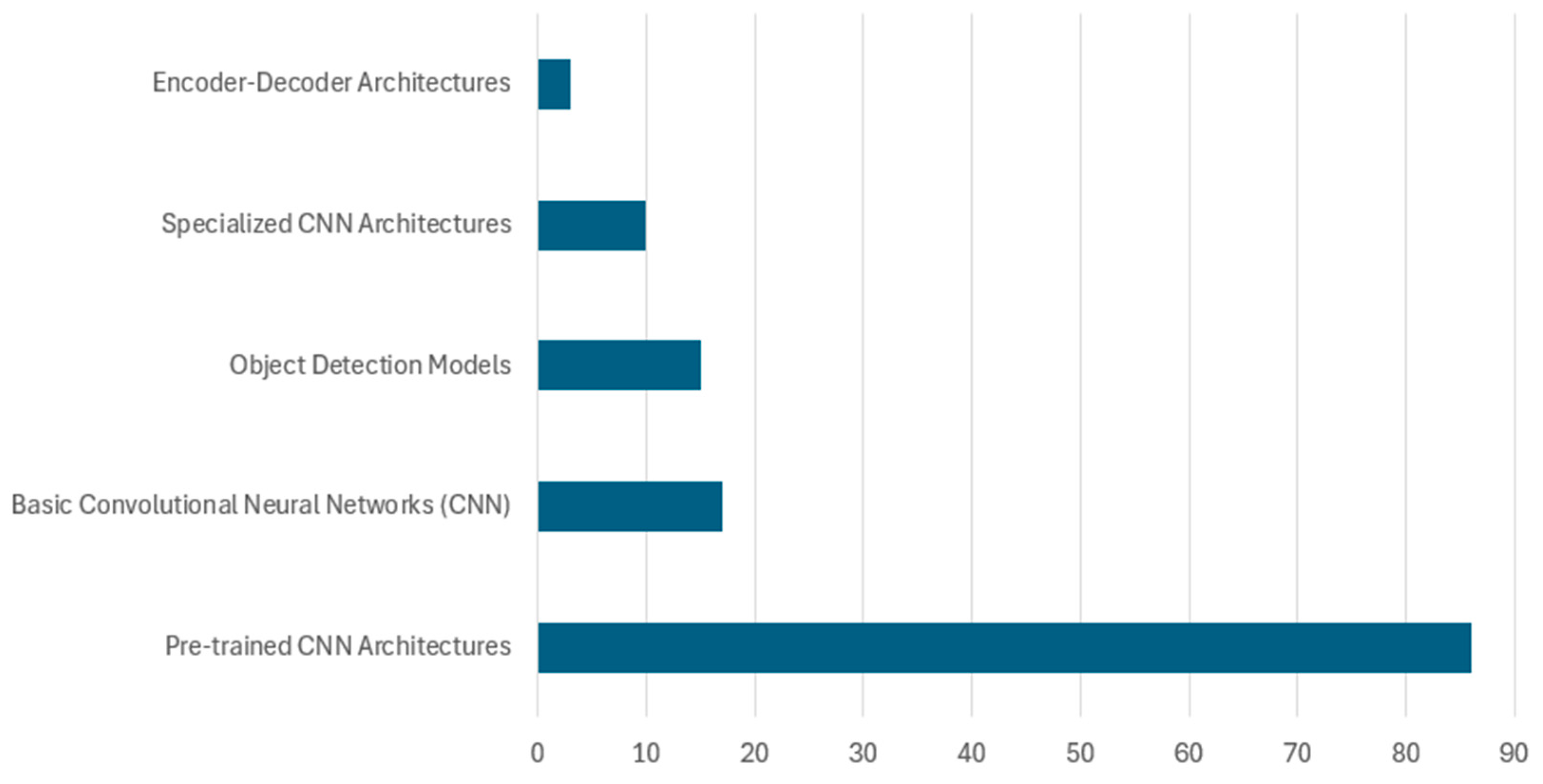
3.2.2. Deep Learning-Based Approaches
Basic CNN and DCNN Models
Pre-Trained CNN Architectures (Transfer Learning)—VGG Family
ResNet Family: Transfer Learning Using Pre-Trained CNN Architectures
Pre-Trained CNN Architectures (Transfer Learning)—DenseNet Family
Pre-Trained CNN Architectures (Transfer Learning)—MobileNet Family
Pre-Trained CNN Architectures (Transfer Learning)—Inception and EfficientNet Families
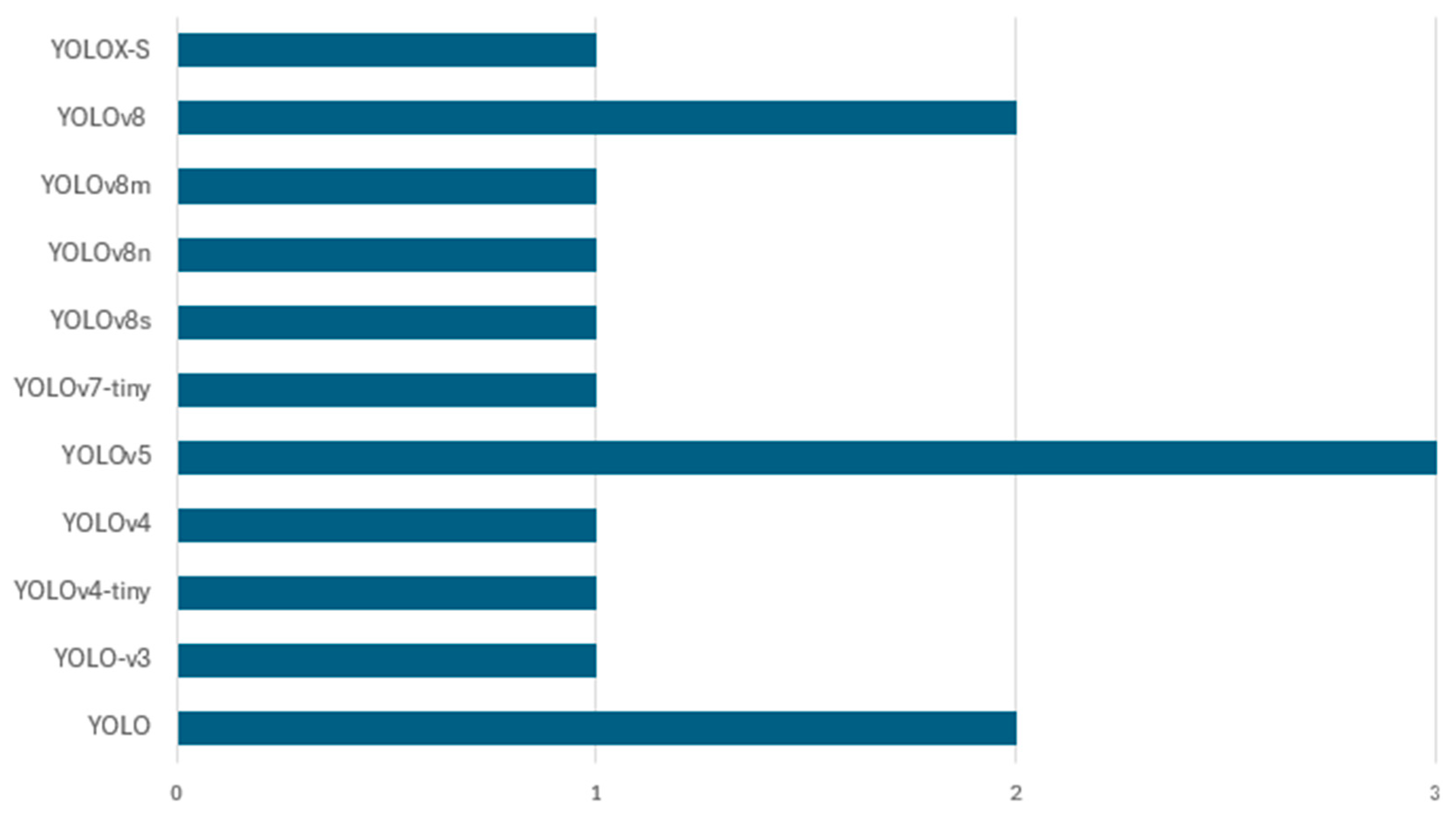
Object Detection Models for Waste Classification
Specialized CNN Architectures for Waste Classification
Waste Classification with Deep Learning (Specialized CNN Architectures for Waste Classification)
3.3. Hybrid Approaches for Waste Classification
3.4. Real-World Implementations and TRL-Level Analysis
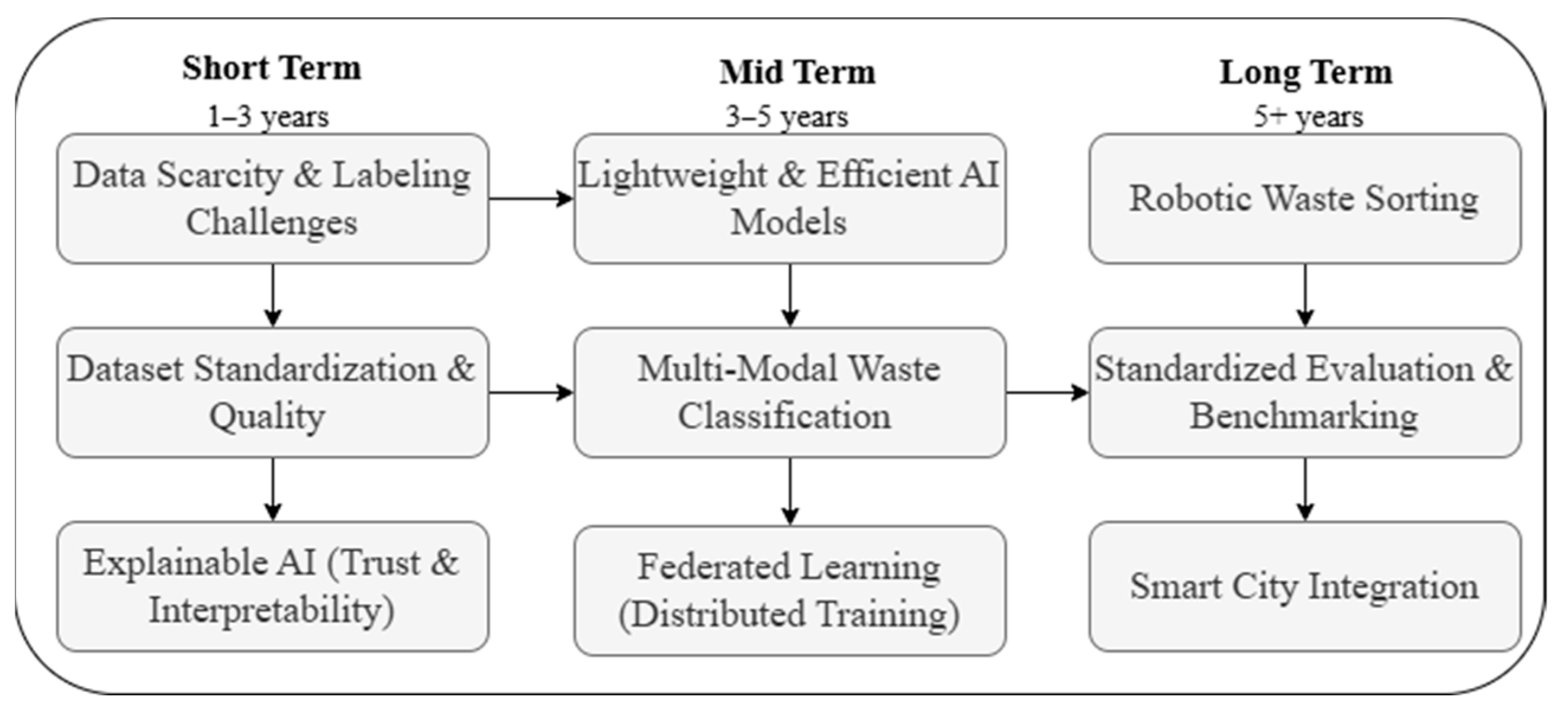
4. Challenges, Limitations, and Future Directions
4.1. Data Scarcity and Standardization Challenges
4.2. Addressing Waste Complexity in Real-World Environments
4.3. Lightweight and Efficient AI Models
4.4. Explainable AI (XAI) for Trustworthy Classification
4.5. Multi-Modal Waste Classification
4.6. Self-Supervised and Few-Shot Learning for Waste Classification
4.7. Federated Learning for Decentralized Waste Classification
4.8. AI-Driven Robotic Waste Sorting
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| RFID | Radio-Frequency Identification |
| WasteRL | Waste Reinforcement Learning |
| EDA | Exploratory Data Analysis |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbor |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| MTLA | Multi-task Learning Architecture |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| SCA | Subtractive Clustering Algorithm |
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
| MGD | Multi-Look Ground Range Detected |
| W2R | Waste Recognition-Retrieval |
| RegM | Recognition Metric |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| MHS | Multi-Hybrid System |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machine |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| KAN | Knowledge-Augmented Networks |
| GNN | Graph Neural Networks |
| MSME | Micro-, Small-, and Medium-sized Enterprise |
| SLR | Systematic Literature Review |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| GCDN | Garbage Classifier Deep Neural |
| RWC | Recyclable Waste Classification |
| RevM | Retrieval Metric |
| DQLN | Deep Q-Learning Network |
| DSCR | Deep Spatial Contextual Representation |
| HOG | Histogram of Oriented Gradients |
| SIFT | Scale-Invariant Feature Transform |
| SURF | Speeded Up Robust Features |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| LoRa | Long Range |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| mAP | Mean Average Precision |
| AR | Average Recall |
References
- Abubakar, I.R.; Maniruzzaman, K.M.; Dano, U.L.; AlShihri, F.S.; AlShammari, M.S.; Ahmed, S.M.S.; Al-Gehlani, W.A.G.; Alrawaf, T.I. Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.C.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Abu Talib, M.; Feroz, S.; Nasir, Q.; Abdalla, H.; Mahfood, B. Artificial Intelligence Applications in Solid Waste Management: A Systematic Research Review. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Solid Waste Issue: Sources, Composition, Disposal, Recycling, and Valorization. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitole, F.A.; Ojo, T.O.; Emenike, C.U.; Khumalo, N.Z.; Elhindi, K.M.; Kassem, H.S. The Impact of Poor Waste Management on Public Health Initiatives in Shanty Towns in Tanzania. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundupalli, S.P.; Hait, S.; Thakur, A. A Review on Automated Sorting of Source-Separated Municipal Solid Waste for Recycling. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pučnik, R.; Dokl, M.; Fan, Y.V.; Vujanović, A.; Novak Pintarič, Z.; Aviso, K.B.; Tan, R.R.; Pahor, B.; Kravanja, Z.; Čuček, L. A Waste Separation System Based on Sensor Technology and Deep Learning: A Simple Approach Applied to a Case Study of Plastic Packaging Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; El-Sappagh, S.; Ali, F.; Goyal, S.B.; Kumar, M. Smart Waste Management: A Systematic Review and Scientometric Analysis of Artificial Intelligence Applications. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodampegama, S.; Hou, L.; Asadi, E.; Zhang, G.; Setunge, S. Revolutionizing Construction and Demolition Waste Sorting: Insights from Artificial Intelligence and Robotic Applications. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 202, 107375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms in Municipal Solid Waste Management: A Mini Review. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.; Poudyal, P. Classification of Waste Materials Using CNN Based on Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation, Kolkata, India, 9–13 December 2022; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Bao, Q.; Su, J.; Liu, X. Waste Image Classification Based on Transfer Learning and Convolutional Neural Network. Waste Manag. 2021, 135, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, H.; Ahmed, A.; Ali, F.; Sarmad Ali, S.; Ali Khan, M. A Systematic Literature Review on Smart Waste Management Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing (MAJICC), Karachi, Pakistan, 27–28 October 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, S.; Kiruthika, B.; Lokeshvaran, R.; Midhunchakkaravarthi, B.; Dhivyasri, G. A Review on Smart Waste Collection and Disposal System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1969, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, T.; Zhao, R.; Sun, M.; Xi, B. Classification Technology of Domestic Waste from 2000 to 2019: A Bibliometrics-Based Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26313–26324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdu, H.; Mohd Noor, M.H. A Survey on Waste Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 128151–128165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serranti, S.; Carlos Arbeláez-Estrada, J.; Vallejo, P.; Aguilar, J.; Tabares-Betancur, M.S.; Ríos-Zapata, D.; Ruiz-Arenas, S.; Rendón-Vélez, E. A Systematic Literature Review of Waste Identification in Automatic Separation Systems. Recycling 2023, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Research on Service Design of Garbage Classification Driven by Artificial Intelligence. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. A Systematic Literature Review on Individuals’ Waste Separation Behavior. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 14, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.; Lopes, A.G.; Mendonça, F. Application of Machine Learning in Plastic Waste Detection and Classification: A Systematic Review. Processes 2024, 12, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; Keele University: Keele, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Shang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lyu, X.; Yang, Y. Garbage Recognition and Sorting System Based on Computer Vision. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 2023, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Thung, G. Classification of Trash for Recyclability Status. Proj. Rep. CS229 2016, 2016, 940–945. [Google Scholar]
- Ashwin, A.; Chazhoor, P.; Zhu, M.; Ho, E.S.L.; Gao, B.; Woo, W.L. Intelligent Classification of Different Types of Plastics Using Deep Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems-ROBOVIS, Virtual, 27–28 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, S.; Tor, B.; Agrawal, R.; Forbes, A.G. CompostNet: An Image Classifier for Meal Waste. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–20 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Gu, Y. A Deep Convolutional Neural Network to Simultaneously Localize and Recognize Waste Types in Images. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waste Classification Data. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/techsash/waste-classification-data (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Mittal, G.; Yagnik, K.B.; Garg, M.; Krishnan, N.C. SpotGarbage: Smartphone App to Detect Garbage Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proença, P.F.; Simões, P. TACO: Trash Annotations in Context for Litter Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.06975. [Google Scholar]
- Bobulski, J.; Piatkowski, J. PET Waste Classification Method and Plastic Waste DataBase—WaDaBa. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2018, 681, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S. OpenLitterMap.Com—Open Data on Plastic Pollution with Blockchain Rewards (Littercoin). Open Geospat. Data Softw. Stand. 2018, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub. Datacluster-Labs/Domestic-Trash-Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/datacluster-labs/Domestic-Trash-Dataset (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Kumsetty, N.V.; Bhat Nekkare, A.; Sowmya Kamath, S.; Anand Kumar, M. TrashBox: Trash Detection and Classification Using Quantum Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 31st Conference of Open Innovations Association (FRUCT), Minsk, Belarus, 3–6 October 2022; pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukel, M.; Rudinac, S.; Worring, M. GIGO, Garbage In, Garbage Out: An Urban Garbage Classification Dataset. In MultiMedia Modeling; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 13833, pp. 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkirova, D.; Abdelfattah, M.; Zhu, Z.; Akl, J.; Alladkani, F.; Hu, P.; Ablavsky, V.; Calli, B.; Bargal, S.A.; Saenko, K. ZeroWaste Dataset: Towards Deformable Object Segmentation in Cluttered Scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 21115–21125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VN Trash Classification. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/mrgetshjtdone/vn-trash-classification (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Liao, Y. A Web-Based Dataset for Garbage Classification Based on Shanghai’s Rule. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2020, 10, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, J.; Feng, J.-W.; Tang, X.-Y. Office Garbage Intelligent Classification Based on Inception-v3 Transfer Learning Model. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1487, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahiduzzaman, M.; Ahamed, M.F.; Naznine, M.; Karim, M.J.; Kibria, H.B.; Ayari, M.A.; Khandakar, A.; Ashraf, A.; Ahsan, M.; Haider, J. An Automated Waste Classification System Using Deep Learning Techniques: Toward Efficient Waste Recycling and Environmental Sustainability. Knowl. Based Syst. 2025, 310, 113028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, J.; Mehedi, S.T.; Paul, B.K.; Morshed, M. TrashNeXt: Classification of Recyclable Water Pollutants Using Deep Transfer Learning Method. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 11, 101073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Acharjee, S.; Sk, M.M.; Alharthi, S.Z.; Chaudhuri, S.S.; Akhunzada, A. DWSD: Dense Waste Segmentation Dataset. Data Brief 2025, 59, 111340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Jain, H.; Raj, H.; Gupta, P. Identification and Classification of Waste Using CNN in Waste Management. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 8th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Lonavla, India, 7–9 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, N.K.; Maheshwari, H.; Agarwal, A.K.; Tiwari, R.G.; Gautam, V. Deep Learning-Based Waste Classification: Enhancing Recycling Efficiency and Sustainability. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Emerging Research in Computational Science (ICERCS), Coimbatore, India, 7–9 December 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan Itam, D.; Chimeme Martin, E.; Taiwo Horsfall, I. Enhanced Convolutional Neural Network Methodology for Solid Waste Classification Utilizing Data Augmentation Techniques. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 2, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.; Ahmed, F.; Das, A.; Dey, A. Classification of Organic and Solid Waste Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 9th Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10-HTC), Bengaluru, India, 30 September–2 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneru, B.; Shah, K.B.; Paneru, B.; Bhattrai, N.; Alexander, V.; Pant, H.R.; Poudyal, K.N.; Nova, S. Sustainable Waste Management with AI: Waste Classification Using Deep Learning and IoT-Based Analysis of CH4 Production. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Emerging Trends in Information Technology and Engineering (ICETITE), Vellore, India, 22–23 February 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garapati, D.P.; Bhuvaneswari, K.; Kavyasri, N.; Susmita Keerthi, P.; Ayesha, S.; Dedeepya, A. Trash and Recycled Material Classification Revolutionized with Advanced Transfer Learning with Pre-Trained Models. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Networks, Multimedia and Information Technology (NMITCON), Bengaluru, India, 9–10 August 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shourie, P.; Anand, V.; Upadhyay, D.; Devliyal, S.; Gupta, S. Smart Waste Management: VGG16-Based Classification System for Organic and Recyclable Materials. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Circuit Power and Computing Technologies (ICCPCT), Kollam, India, 8–9 August 2024; pp. 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Shama, U.S.; Akash, M.D.; Karim, D.Z. Automatic Waste Classification System Using Deep Leaning Techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Communications and Mechatronics Engineering (ICECCME), Tenerife, Spain, 19–21 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Sarkar, S.; Gorai, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D. Convolutional Neural Network Based Technique for Efficient Waste Classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Machine Intelligence (CVMI), Prayagraj, India, 19–20 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, K.; Narayanan, L.K. A Deep Learning Aided Smart Waste Classification System for Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 16th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Indore, India, 22–23 December 2024; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z. An Automatic Garbage Classification System Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 140019–140029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Sultan, A.A.; Mativenga, P.T. Sustainable Location Identification Decision Protocol (SuLIDeP) for Determining the Location of Recycling Centres in a Circular Economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziouzios, D.; Baras, N.; Balafas, V.; Dasygenis, M.; Stimoniaris, A. Intelligent and Real-Time Detection and Classification Algorithm for Recycled Materials Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Recycling 2022, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Mu, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Recyclable Waste Image Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, O.; Akinlabi, S.A.; Jen, T.C.; Dunmade, I. Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Predicting the Physical Composition of Municipal Solid Waste: An Assessment of the Impact of Seasonal Variation. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, P.; Pamuła, T. Application of Deep Learning Object Classifier to Improve E-Waste Collection Planning. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alruwais, N.; Alabdulkreem, E.; Khalid, M.; Negm, N.; Marzouk, R.; Al Duhayyim, M.; Balaji, P.; Ilayaraja, M.; Gupta, D. Modified Rat Swarm Optimization with Deep Learning Model for Robust Recycling Object Detection and Classification. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 59, 103397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, A.U.; Sadiq, M.I.; Ali, T.; Irfan, M.; Shaf, A.; Aamir, M.; Shoaib, M.; Glowacz, A.; Tadeusiewicz, R.; Kantoch, E. Real Time Multipurpose Smart Waste Classification Model for Efficient Recycling in Smart Cities Using Multilayer Convolutional Neural Network and Perceptron. Sensors 2021, 21, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Joshi, R.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Sachdeva, K.; Jain, N.; Virmani, D.; Garcia-Hernandez, L. A Deep Learning Approach Based Hardware Solution to Categorise Garbage in Environment. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 1129–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallang, N.C.A.; Islam, M.T.; Islam, M.S.; Arshad, H. A CNN-Based Smart Waste Management System Using TensorFlow Lite and LoRa-GPS Shield in Internet of Things Environment. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 153560–153574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, M.; Nandhini, S.; Harine, E.; Lathika, K.M. Convolutional Neural Network Based Smart Waste Management System. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Power, Energy, Control and Transmission Systems: Harnessing Power and Energy for an Affordable Electrification of India (ICPECTS), Chennai, India, 8–9 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetarpal, D.; Khetarpal, I.; Rawat, D.; Narang, H.; Vats, S.; Sharma, V. Trash Detection: Advanced Classification of Waste Materials Using ML Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2024 OPJU International Technology Conference on Smart Computing for Innovation and Advancement in Industry 4.0, OTCON 2024, Raigarh, India, 5–7 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidharth, R.; Rohit, P.; Vishagan, S.; Karthika, R.; Ganesan, M. Deep Learning Based Smart Garbage Classifier for Effective Waste Management. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 10–12 June 2020; pp. 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafiz, M.S.; Das, S.S.; Morol, M.K.; Al Juabir, A.; Nandi, D. ConvoWaste: An Automatic Waste Segregation Machine Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 7–8 January 2023; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surender Dhiman, D.; Srivatsan, K.; Jain, A. Waste Classification Using Transfer Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 775, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adharsh, C.S.; Mammoo, J.; Afthab, P.S.; Afroos Shahana, P.A. Deep Learning Approaches for Waste Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advancements in Power, Communication and Intelligent Systems, APCI 2024, Kannur, India, 21–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.M.; Le, T.M.; Pham, H.V.; Vu, M.T.; Dao, S.V.T. An Integrated Learning Approach for Municipal Solid Waste Classification. IEEE Access 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md, Z.; Amin, A.; Sami, N.; Hassan, R. An Approach of Classifying Waste Using Transfer Learning Method. Int. J. Perceptive Cogn. Comput. 2021, 7, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ba Alawi, A.E.; Saeed, A.Y.A.; Almashhor, F.; Al-Shathely, R.; Hassan, A.N. Solid Waste Classification Using Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Congress of Advanced Technology and Engineering (ICOTEN), Virtual, 4–5 July 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, L.; Ma, L.; Sun, D.; Du, L. Application of MobileNetV2 to Waste Classification. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Yang, Z.; Królczykg, G.; Liu, X.; Gardoni, P.; Li, Z. Garbage Detection and Classification Using a New Deep Learning-Based Machine Vision System as a Tool for Sustainable Waste Recycling. Waste Manag. 2023, 162, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, W.; Akter, M.; Sultana, N.; Farjana, M.; Uddin, A.; Mazrur, M.B.; Rahman, M.M. BDWaste: A Comprehensive Image Dataset of Digestible and Indigestible Waste in Bangladesh. Data Brief 2024, 53, 110153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, S.; Wei, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tu, J. A Novel Intelligent Garbage Classification System Based on Deep Learning and an Embedded Linux System. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 131134–131146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Shetty, H.; Patil, K.; Ingawale, P.; Trivedi, M. Intelligent Waste Material Classification Using EfficientNet-B3 Convolutional Neural Network for Enhanced Waste Management. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Self Sustainable Artificial Intelligence Systems (ICSSAS), Erode, India, 18–20 October 2023; pp. 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Das, S.K. A Fusion of Three Custom-Tailored Deep Learning Architectures for Waste Classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Industry 4.0 (STI), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–18 December 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Real-Time Classification and Detection of Garbage Based on Improved Yolov5 and Embedded System. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference of Information and Communication Technology (ICTech), Wuhan, China, 14–16 April 2023; pp. 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.G.V.; Kumar, M.; Rao, K.N.; Rao, P.S.; Tirumala, A.; Patnala, E. Advanced YOLO-Based Trash Classification and Recycling Assistant for Enhanced Waste Management and Sustainability. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Cyber Physical Systems and Internet of Things (ICoICI), Coimbatore, India, 28–30 August 2024; pp. 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melinte, D.O.; Travediu, A.M.; Dumitriu, D.N. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Object Detector for Real-Time Waste Identification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawankule, R.; Gaikwad, V.; Kulkarni, I.; Kulkarni, S.; Jadhav, A.; Ranjan, N. Visual Detection of Waste Using YOLOv8. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Smart Systems (ICSCSS), Coimbatore, India, 14–16 June 2023; pp. 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Lilhore, U.; Simaiya, S.; Dalal, S.; Radulescu, M.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Intelligent Waste Sorting for Sustainable Environment: A Hybrid Deep Learning and Transfer Learning Model. Gondwana Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Lin, H. Effect of Transfer Learning on the Performance of VGGNet-16 and ResNet-50 for the Classification of Organic and Residual Waste. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1043843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gautam, J.; Rawat, S.; Gupta, V.; Kumar, G.; Verma, L.P. Evaluation of Transfer Learning Based Deep Learning Architectures for Waste Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Symposium on Advanced Electrical and Communication Technologies (ISAECT), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 19–21 November 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazhoor, A.A.P.; Ho, E.S.L.; Gao, B.; Woo, W.L. Deep Transfer Learning Benchmark for Plastic Waste Classification. Intell. Robot. 2022, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapo, J.R.; Cumbicus-Pineda, O.M. Detection of Recyclable Solid Waste Using Convolutional Neural Networks and PyTorch. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2024, 22, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandita, H.S.; Vaidya, V.; Doifode, M.; Bhavthankar, P.; Venkatesh, A. Garbage Classification Using Machine Learning to Aid Recycling. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), Belgaum, India, 27–29 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masand, A.; Chauhan, S.; Jangid, M.; Kumar, R.; Roy, S. ScrapNet: An Efficient Approach to Trash Classification. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 130947–130958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Bi, S.; Meng, C.; Guo, F. Multi-Objective Solid Waste Classification and Identification Model Based on Transfer Learning Method. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrowska, S.; Mikołajczyk, A.; Ferlin, M.; Klawikowska, Z.; Plantykow, M.A.; Kwasigroch, A.; Majek, K. Deep Learning-Based Waste Detection in Natural and Urban Environments. Waste Manag. 2022, 138, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Peng, X.; Sun, Q. DSYOLO-Trash: An Attention Mechanism-Integrated and Object Tracking Algorithm for Solid Waste Detection. Waste Manag. 2024, 178, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zeng, Q.; Zhan, L.; Chen, D. Multi-Target Detection of Waste Composition in Complex Environments Based on an Improved YOLOX-S Model. Waste Manag. 2024, 190, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.M.; Ashraf, A.; Hasan, M.; Majid, M.E.; Nashbat, M.; Kashem, S.B.A.; Kunju, A.K.A.; Khandakar, A.; Mahmud, S.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. GCDN-Net: Garbage Classifier Deep Neural Network for Recyclable Urban Waste Management. Waste Manag. 2024, 174, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.M.; Majid, M.E.; Kashem, S.B.A.; Khandakar, A.; Nashbat, M.; Ashraf, A.; Hasan-Zia, M.; Kunju, A.K.A.; Kabir, S.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. A Reliable and Robust Deep Learning Model for Effective Recyclable Waste Classification. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 13809–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaf, R.; Alegre, E.P.; Prova, T.; Aggarwal, S. Automated Waste Management Using a Customized Vision-Based Transformer Model. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 5th World AI IoT Congress (AIIoT), Seattle, WA, USA, 29–31 May 2024; pp. 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.B.; Sumon, M.S.I.; Majid, M.E.; Abul Kashem, S.B.; Nashbat, M.; Ashraf, A.; Khandakar, A.; Kunju, A.K.A.; Hasan-Zia, M.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. ECCDN-Net: A Deep Learning-Based Technique for Efficient Organic and Recyclable Waste Classification. Waste Manag. 2025, 193, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, K.N.; Amin, Z.M.A.; Hassan, R. Waste Management Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Perceptive Cogn. Comput. 2020, 6, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yang, G.; Zhao, X. An Edge-Cloud Framework Equipped with Deep Learning Model for Recyclable Garbage Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Conference on Advanced Cloud and Big Data (CBD), Taiyuan, China, 5–6 December 2020; pp. 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, A.P. Waste Object Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning Algorithm: YOLOv4 and YOLOv4-Tiny. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 2021, 12, 5583–5595. [Google Scholar]
- Vieri, D.; Susanto, R.; Purwanto, E.S.; Ario, M.K. Enhancing Waste Classification with YOLOv8 Models for Efficient and Accurate Sorting. Procedia Comput. Sci 2024, 245, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehadjbia, A.; Slaoui-Hasnaoui, F. Real-Time Waste Detection Based on YOLOv8. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th Interdisciplinary Conference on Electrics and Computer (INTCEC), Romeoville, IL, USA, 11–13 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.L.; Chen, W.C.; Wang, C.T.; Lin, Y.H. Recycling Waste Classification Using Optimized Convolutional Neural Network. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Varshan, S.; Ashish, M.; Binu, E.; Rajan, R.G.; Madhavan, S. Trash Image Classification Using Autoencoder. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 6–8 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqyuni, U.; Endah, S.N.; Sasongko, P.S.; Kusumaningrum, R.; Khadijah; Rismiyati; Rasyidi, H. Waste Image Segmentation Using Convolutional Neural Network Encoder-Decoder with SegNet Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Informatics and Computational Sciences (ICICoS), Semarang, Indonesia, 10–11 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulisz, M.; Kujawska, J. Prediction of Municipal Waste Generation in Poland Using Neural Network Modeling. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.L.; Liang, S.; Shen, F.W. Reconfiguration of Garbage Collection System Based on Voronoi Graph Theory: A Simulation Case of Beijing Region. J. Comb. Optim. 2022, 43, 953–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altikat, A.; Gulbe, A.; Altikat, S. Intelligent Solid Waste Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Khan, K.; Al-Fuqaha, A. Intelligent Fusion of Deep Features for Improved Waste Classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 96495–96504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobulski, J.; Kubanek, M. Deep Learning for Plastic Waste Classification System. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2021, 2021, 6626948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Singh, M.K.; Singh, P.; Aggarwal, S. Waste Management of Residential Society Using Machine Learning and IoT Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Emerging Smart Computing and Informatics (ESCI), Pune, India, 12–14 March 2020; pp. 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, M.A.; Yucel, O.; Sadikoglu, H. Optimizing Waste-to-Energy Conversion: Unveiling the Potential of Unsupervised Clustering through the New HOM Classification System. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 65, 103796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.K.; Singh, G. Automated Waste Segregation Using ResNet50 for Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Innovation and Novelty in Engineering and Technology (INNOVA), Vijayapura, India, 20–21 December 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arishi, A. Real-Time Household Waste Detection and Classification for Sustainable Recycling: A Deep Learning Approach. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspaningrum, A.P.; Endah, S.N.; Sasongko, P.S.; Kusumaningrum, R.; Khadijah; Rismiyati; Ernawan, F. Waste Classification Using Support Vector Machine with SIFT-PCA Feature Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Informatics and Computational Sciences (ICICoS), Semarang, Indonesia, 10–11 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulghane, A.; Sharma, R.L.; Borkar, P. A Formal Evaluation of KNN and Decision Tree Algorithms for Waste Generation Prediction in Residential Projects: A Comparative Approach. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 25, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghtesadifard, M.; Afkhami, P.; Bazyar, A. An Integrated Approach to the Selection of Municipal Solid Waste Landfills through GIS, K-Means and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramia, M.; Pinto, D.M.; Pizzari, E.; Stecca, G. Clustering and Routing in Waste Management: A Two-Stage Optimisation Approach. EURO J. Transp. Logist. 2023, 12, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaparthi, S.K.; Reddy, C.K.; Sharma, T.V.S.R.; Aravind Kumar Reddy, K.; Reddy, N.S.; Vishnu, A. Efficient Waste Classification in Recycling Industries. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 7–9 August 2024; pp. 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, M.; Sharan, B.; Elbarachi, M.; Kumar, M. Intelligent Waste Classification Approach Based on Improved Multi-Layered Convolutional Neural Network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 84095–84120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Qdais, H.; Shatnawi, N.; AL-Alamie, E. Intelligent System for Solid Waste Classification Using Combination of Image Processing and Machine Learning Models. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, V.; Govindaraj, M.; Kolambkar, M.L.; Mithuna, P.; Narendra Gautham, V.; Prasad, A. Classification of Plastic Waste Products Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Cognitive, Green and Ubiquitous Computing (IC-CGU), Bhubaneswar, India, 1–2 March 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, E.; Kumar, R. Harnessing Deep Learning for Sustainable Waste Classification: An Innovative Approach Using MobileNetV2 on a Diverse Bag Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Cybernation and Computation (CYBERCOM), Dehradun, India, 15–16 November 2024; pp. 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatulloh, A.; Darmawan, I.; Aldya, A.P.; Nursuwars, F.M.S. WasteInNet: Deep Learning Model for Real-time Identification of Various Types of Waste. Clean. Waste Syst. 2025, 10, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.M.; Tu, Y.H.; Li, T.; Ni, Y.; Wang, R.F.; Wang, H. Deep Learning for Sustainable Agriculture: A Systematic Review on Applications in Lettuce Cultivation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.H.; Wang, R.F.; Su, W.H. Active Disturbance Rejection Control—New Trends in Agricultural Cybernetics in the Future: A Comprehensive Review. Machines 2025, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, C.; Li, D. Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Accurate Classification of Solid Waste in the Society. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobulski, J.; Kubanek, M. Waste Classification System Using Image Processing and Convolutional Neural Networks. In Advances in Computational Intelligence; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11507, pp. 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, Y. Municipal Solid Waste Classification and Real-Time Detection Using Deep Learning Methods. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, P.; Ramya, V.; Babu Rao, M. E-Waste Management Using Hybrid Optimization-Enabled Deep Learning in IoT-Cloud Platform. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2023, 176, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Tan, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Alwaeli, M.; Pizó, J.; Gołaszewska, M. A Waste Classification Method Based on a Multilayer Hybrid Convolution Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Shi, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. Garbage Classification Algorithm Based on Improved MobileNetV3. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 44799–44807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y. Research on Image Classification Algorithm of Domestic Garbage Based on Deep Learning Method. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Power, Electronics and Computer Applications (ICPECA), Shenyang, China, 29–31 January 2023; pp. 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeyer, X.; Santos, S.C.; Liguori, E.; Walsh, S.T.; Mahto, R.V. The Ever-Evolving Relationship between Technology, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship: Current State and Future Research Needs. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 215, 124059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

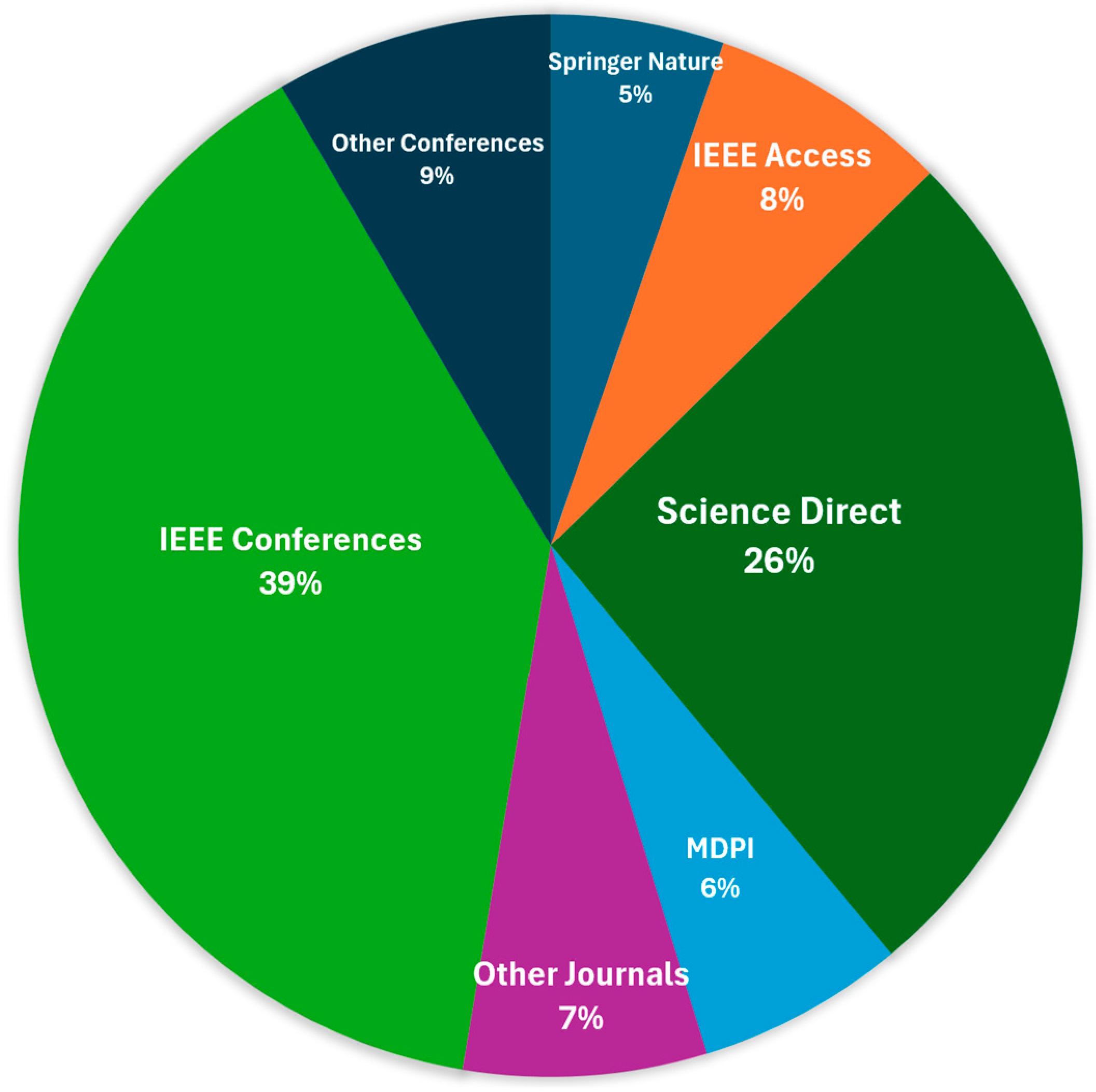


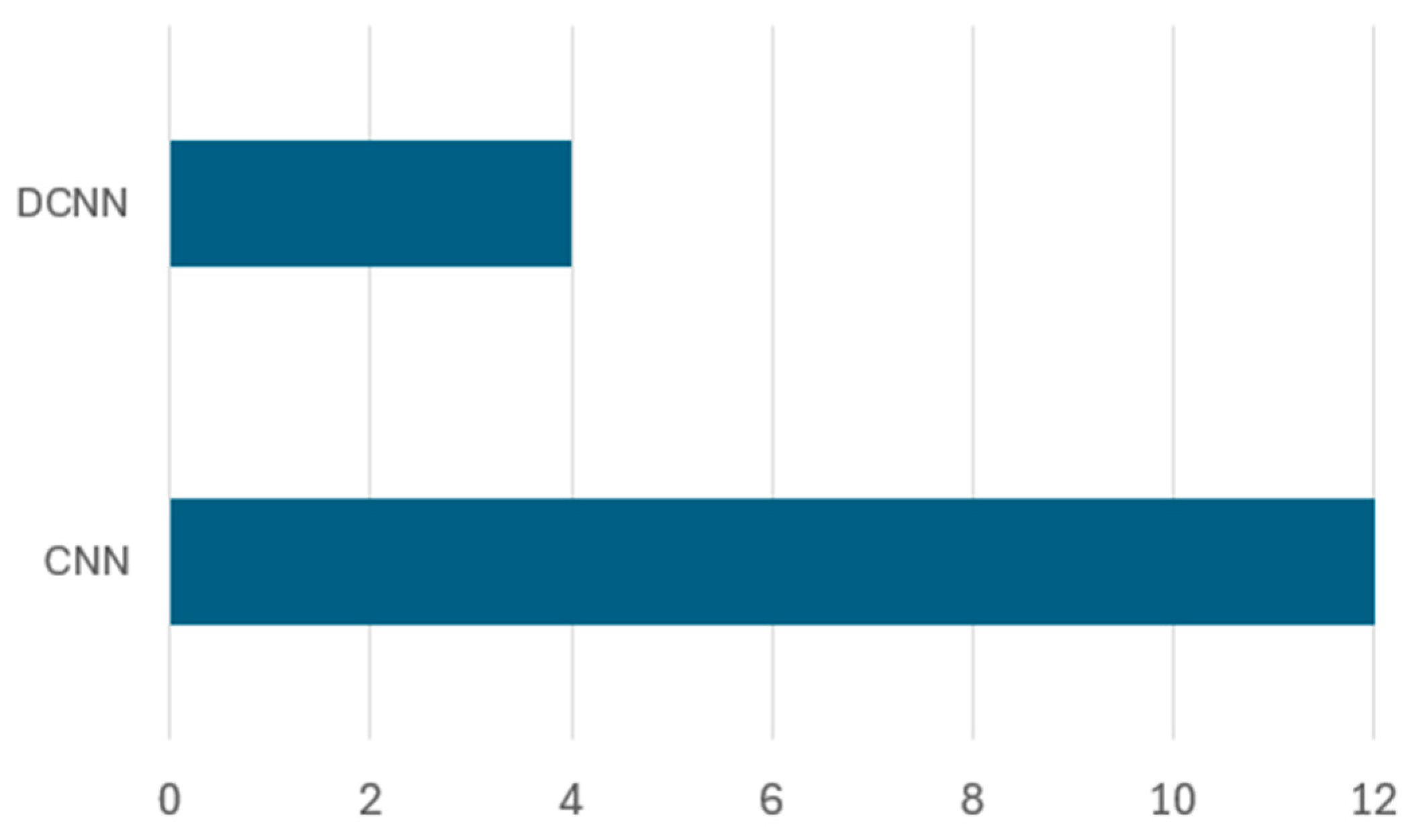


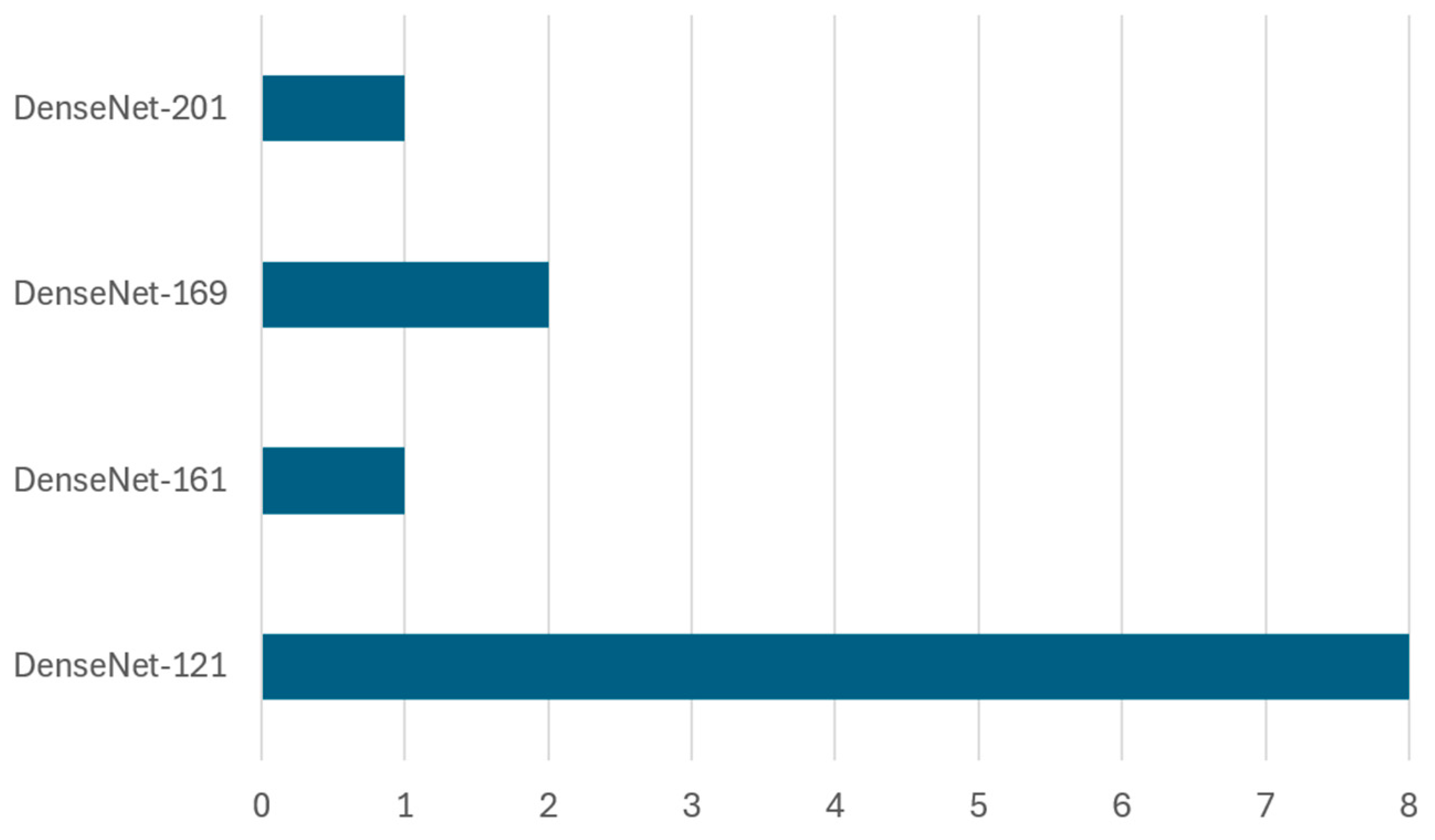




| References | Year of Publication | Covered Years | Survey Type | Waste Classification Methods | Machine Learning Methods | Deep Learning Methods | Hybrid Models | Datasets Discussed | Accuracy Comparisons | Future Directions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | 2021 | 2000–2020 | Review | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| [14] | 2021 | 2016–2021 | Review | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| [15] | 2021 | 2000–2019 | Review | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| [16] | 2022 | 2000–2022 | Survey | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| [17] | 2023 | 2017–2023 | SLR | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ |
| [18] | 2023 | 2019–2023 | Review | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| [19] | 2023 | 1965–2022 | Review | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| [20] | 2024 | 2000–2023 | SLR | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ |
| This article | 2020–2025 | SLR | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Studies specifically addressing machine learning in waste management. | Non-empirical studies like theoretical analyses, opinions, and reviews. |
| Studies have been published within the last 5 years. | Studies not focusing on machine learning in waste management. |
| Peer-reviewed articles in reputable journals or proceedings. | Publications older than ten years. |
| Studies available in full text for comprehensive evaluation. | Articles published in languages other than English. |
| Studies conducted and published in English | Studies only available in abstract form or without complete texts. |
| Strong baseline papers selected for review. | Papers with limited relevance. |
| Only reproducible papers whose works can be extended. | Papers which are general discussions. |
| Reference | Dataset Name | No. of Images | Type of Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | TrashNet Dataset | 2400 | Glass, paper, metal, plastic, cardboard, trash |
| [26] | CompostNet Dataset | 2751 | Paper, cardboard, metal, glass, plastic, trash, compost, food waste, landfill waste |
| [27] | WasteRL Dataset | 57,000 | Organic waste, recyclables, hazardous waste, other wastes (annotated with bounding boxes) |
| [28] | Kaggle Waste Classification Dataset | 22,500 | Organic waste, recyclable waste |
| [29] | GINI Dataset | 2561 | Trash (956 images directly related to garbage; remaining from Bing image search) |
| [30] | TACO Dataset | 1500 | Plastic, glass, metal, paper, cardboard, trash (plastic bags, cigarette butts, bottles, cans, other common litter) |
| [31] | WaDaBa Dataset | 4000 | Plastic waste items (photographed under different conditions of lighting and angle) |
| [32] | Open Litter Map Dataset | >100,000 | Glass, paper, metal, plastic, cardboard, trash (various types of litter in natural environments) |
| [33] | Domestic Trash Dataset | >9000 | Plastic, metal, glass, paper, cardboard, trash (plastic cups, batteries, razors, plastic bags) |
| [34] | TrashBox Dataset | 17,785 | Glass, metal, plastic, paper, cardboard, e-waste, medical waste |
| [35] | GIGO: Garbage In, Garbage Out Dataset | 25,000 | Cardboard, plastic, trash (bulky waste, garbage bags, cardboard, litter) |
| [36] | ZeroWaste Dataset | 4661 | Glass, paper, metal, plastic, cardboard, trash |
| [37] | VN Trash Dataset | >13,000 | Plastic, metal, glass, paper, cardboard, trash (aluminum cans, carton, foam box, milk box, clear plastic cup, PET bottle, other trash) |
| [38] | Baidu Garbage Classification Dataset | 17,690 | Glass, paper, metal, plastic, cardboard, trash (recyclable garbage, food waste, hazardous garbage, other garbage; 158 sub-categories) |
| [12] | NWNU-TRASH Dataset | 18,911 | Waste glass, waste fabric, waste paper, waste plastic, and waste metal |
| [39] | Custom Dataset | 2313 | Glass, paper, metal, plastic, cardboard, trash (office garbage: cans, bottles, milk boxes, paper cups, batteries) |
| [40] | TriCascade WasteImage | 35,264 | Green waste, recyclable waste, glass, metal, polymer (petroleum-based), leather and fabric, medical waste, E-waste, hazardous waste |
| [41] | TrashNeXt dataset | 23,625 | Cardboard, E-waste, foam rubber, glass, medical waste, metal, paper, plastic, organic |
| [42] | DWSD (Dense Waste Segmentation Dataset) | 784 | Plastic container, plastic bottle, Thermocol, metal bottle, plastic–cardboard, glass, Thermocol–plate, plastic, paper, plastic cup, paper cup, aluminum foil, cloth, nylon |
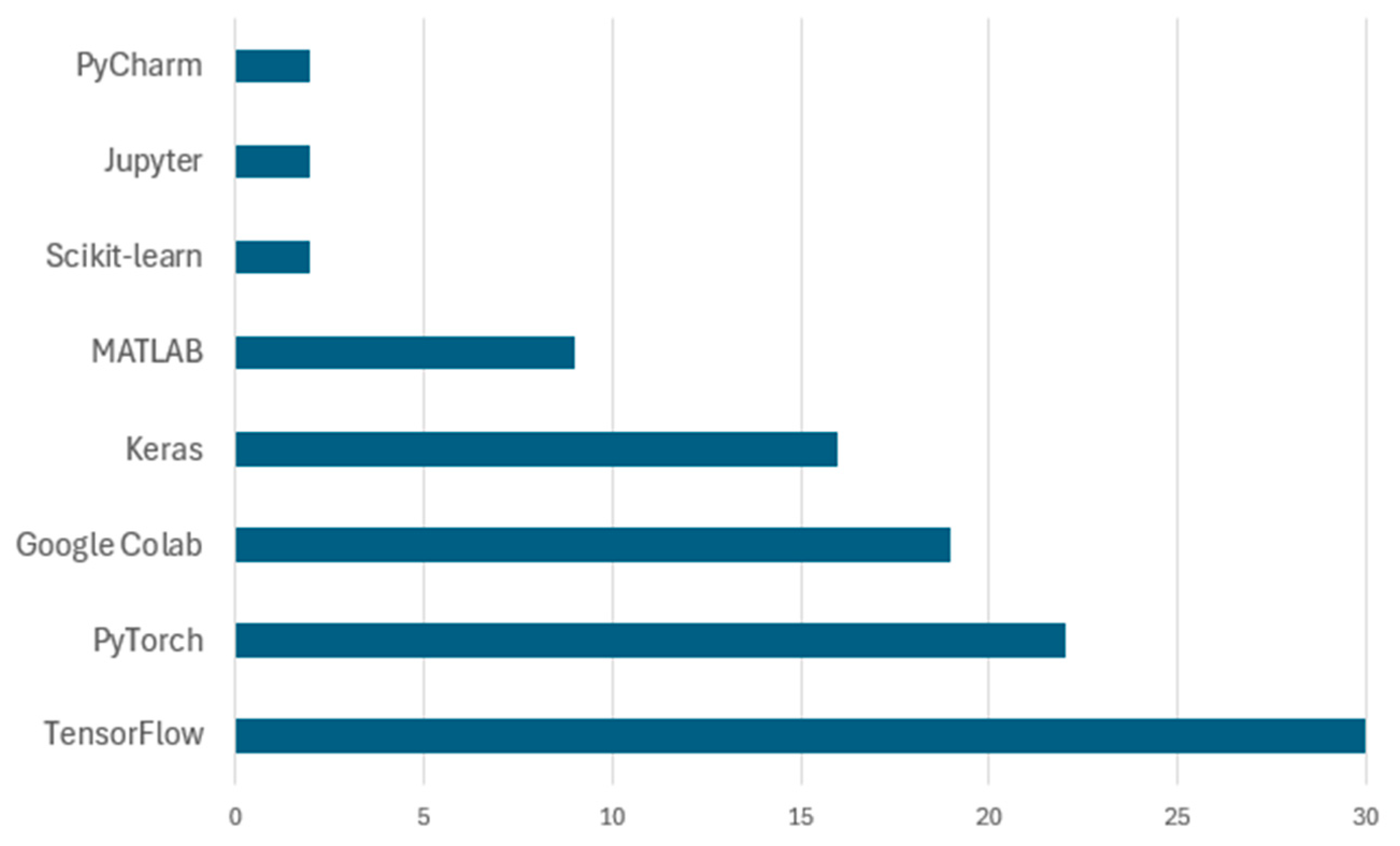
| Platform | References |
|---|---|
| TensorFlow | [39,40,41,45,46,49,51,52,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80] |
| PyTorch | [12,44,63,73,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96] |
| Google Colab | [42,44,46,51,62,63,67,70,74,76,84,86,93,94,97,98,99,100,101] |
| Keras | [40,44,46,48,49,51,53,64,66,68,70,71,82,102,103,104] |
| MATLAB | [57,58,103,104,105,106,107,108,109] |
| Scikit-learn | [110,111] |
| Jupyter | [41,45] |
| PyCharm | [40,60] |
| Technique/Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown (Train–Test or Train–Val–Test%) | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 85% | [54] |
| TrashNet dataset | 85:15 | 65% | [55] | |
| IoT sensor data from residential waste bins | 70:30 | 78% | [56] | |
| Thung Yang dataset | 70:30 | 63% | [57] | |
| Custom dataset of 15,000 images | 80:20 | 89.6% | [58] | |
| Kaggle dataset of waste photos | 80:20 | 94.8% | [59] | |
| Kaggle Trash dataset | 80:20 | 84% | [60] | |
| Waste images from Kaggle and Google | 85:15 | 80% | [61] | |
| TrashNet and local garbage datasets | 80:20 | 62.5% | [62] | |
| KNN | IoT sensor data from residential waste bins | 70:30 | 77% | [56] |
| Construction site waste dataset | 70:30 | 88.51% | [63] | |
| Custom dataset of 15,000 images | 80:20 | 87.3% | [58] | |
| Kaggle trash dataset | 80:20 | 94.1% | [60] | |
| Random forest | TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 55% | [54] |
| IoT sensor data from residential waste bins | 70:30 | 85.29% | [56] | |
| Kaggle trash dataset | 80:20 | 95.2% | [60] | |
| TrashNet and local garbage datasets | 80:20 | 72% | [62] | |
| Decision tree | TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 65% | [54] |
| IoT sensor data from residential waste bins | 70:30 | 84.1% | [56] | |
| Construction site waste dataset | 70:30 | 88.32% | [63] | |
| ANN | Municipal waste data | - | 98% | [64] |
| Waste characterization data from Johannesburg | 80:20 | 96.1% | [65] | |
| Naïve Bayes | IoT sensor data from residential waste bins | 70:30 | 84.1% | [56] |
| Kaggle trash dataset | 80:20 | 51.2% | [60] | |
| Logistic regression | IoT sensor data from residential waste bins | 70:30 | 80% | [56] |
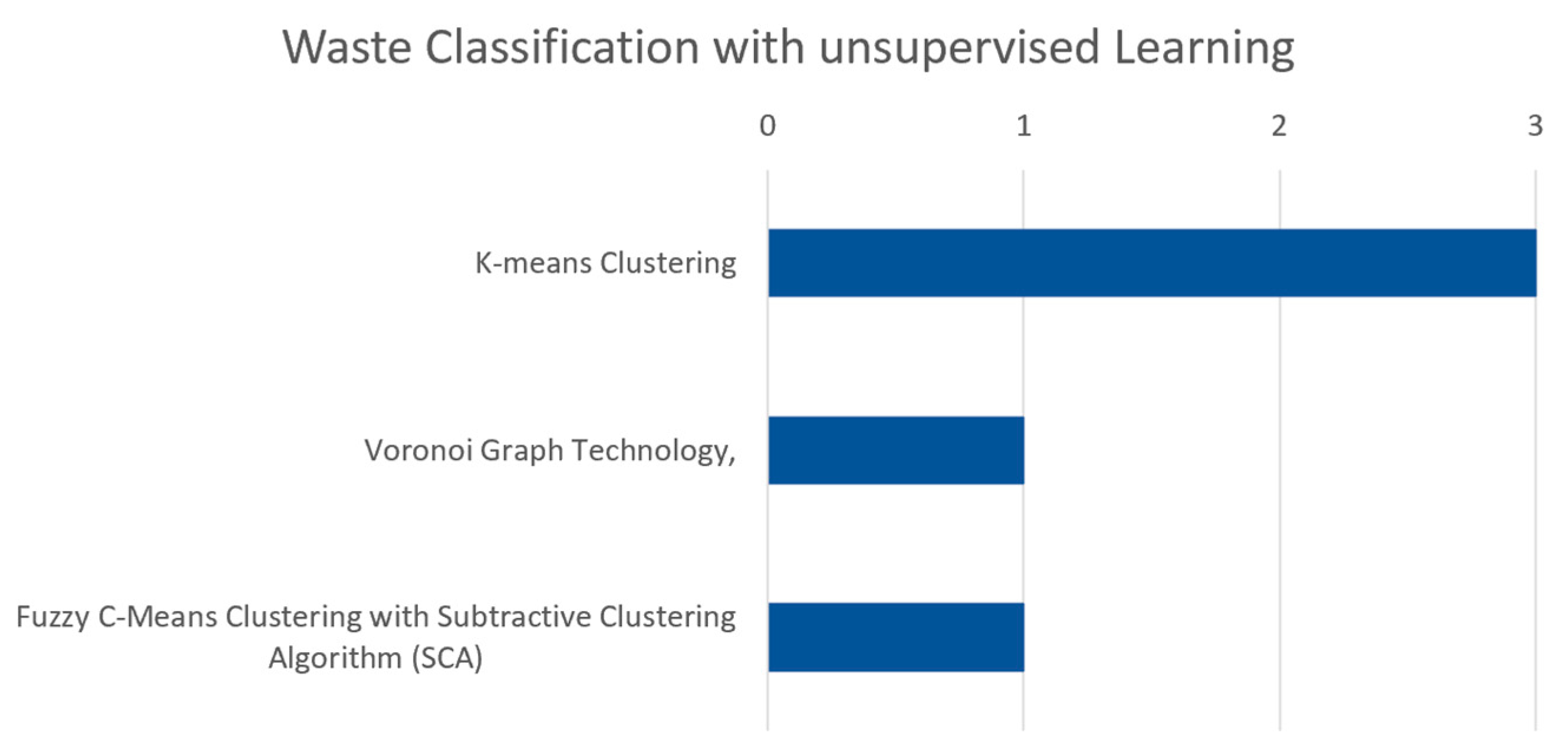
| Technique/ Model | Dataset/Usage | Key Finings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| K-means clustering | Multi-objective solid waste dataset | Employed unsupervised learning to identify patterns and classifications in solid waste without pre-labeled data. | [54] |
| GIS data for potential MSW landfill site evaluation | Effective use of GIS and clustering for evaluating and prioritizing landfill sites based on multiple criteria. | [116] | |
| Data on 1139 fuel samples including HHV | Introduced HOM CS for better fuel classification based on physical properties. Effective in optimizing fuel use for energy conversion. | [111] | |
| Voronoi graph theory | Data from Beijing’s urban garbage collection and transportation system | Efficiency improved from 74.9% to 95.6%. | [106] |
| Fuzzy C-means clustering with SCA | 1000 records of simulated waste data based on oil spill classifications | Developed a cluster-based technique to classify oily waste types from marine oil spill operations, improving waste management strategies. | [117] |
| Technique/Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown (Train–Test or Train–Val–Test) | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | Custom dataset of 15,000 images | 80:20 | 95.4% | [118] |
| Customized dataset with Kaggle trash dataset | 80:10:10 | 89.88% | [64] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:15:15 | 94.40% | [45] | |
| Thung Yang dataset | 70:13:17 | 22% | [24] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 83% | [43] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 90% | [97] | |
| Customized images augmented with TACO dataset | 80:10:10 | 92% | [55] | |
| OrgalidWaste dataset | 70:20:10 | 80.31% | [74] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 90:10 | 76% | [75] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 96% | [76] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 92.7% | [62] | |
| Custom CNN | Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 97.16% | [77] |
| DCNN | Customized images | 70:30 | 70% | [107] |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:30 | 93% | [119] | |
| Customized dataset | 75:25 | 98% | [66] | |
| Customized dataset | 85.7:14.3 | 90–97% | [58] |
| Technique/Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown (Train–Test or Train–Val–Test) | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG-16 | TrashNet dataset | 70:15:15 | 87.25 | [82] |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:20:10 | 92% | [48] | |
| Sentinel-2, Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 93% | [52] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 90:10 | 98% | [49] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 87.5% | [50] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 93.37% | [43] | |
| OrgalidWaste dataset | 70:20:10 | 88.42% | [46] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:15:15 | 93.49% | [51] | |
| Customized dataset | 70:10:20 | 95.60% | [83] | |
| Customized images from TrashNet dataset | 85.7:14.3 | 98.15% | [61] | |
| VGG-19 | Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:15:15 | 56% | [45] |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:20:10 | 91% | [48] | |
| OrgalidWaste dataset | 70:20:10 | 86.38% | [46] | |
| Customized dataset | 80:20 | 85.17% | [108] |
| Technique/Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown (Train–Test or Train–Val–Test%) | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 | TrashNet dataset | 90:10 | 95.8% | [56] |
| ResNet-34 | TrashNet dataset | 70:20:10 | 91.50% | [82] |
| TrashNet dataset | 70:30 | 94.64% | [84] | |
| VNTrash, TrashNet dataset | Not Mentioned | 96.27% | [67] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 91.8% | [43] | |
| Customized dataset | 70:20:10 | 98.5% | [53] | |
| ResNet-50 | TrashNet dataset | 70:20:10 | 92.45% | [82] |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:20:10 | 95% | [48] | |
| WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 85.34% | [109] | |
| Customized dataset | 70:30 | 50.92% | [68] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:15:15 | 66.67% | [45] | |
| Customized dataset | 80:20 | 94.3% | [50] | |
| Customized images from TrashNet dataset | 85.7:14.3 | 97.9% | [61] | |
| WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 85.5% | [85] | |
| Taco trash dataset | 95:5 | 97% | [86] | |
| Customized dataset | 70:10:20 | 96.6% | [83] | |
| Customized dataset | 80:20 | 96.8% | [87] | |
| OrgalidWaste dataset | 70:20:10 | 50.28% | [46] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:15:15 | 93.02% | [51] | |
| Customized dataset | 80:20 | 96% | [112] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 70:30 | 92.24% | [84] | |
| ScrapNet dataset | 80:20 | 83.11% | [88] | |
| Customized dataset | 80:20 | 84.1% | [89] | |
| ResNet-101 | ScrapNet dataset | 80:20 | 80.5% | [88] |
| customized | 80:20 | 87.76% | [108] | |
| ResNet-152 | TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 70.7% | [69] |
| ScrapNet dataset | 80:20 | 79.11% | [88] | |
| ResNeXt | WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 87.44% | [85,121] |
| Technique/ Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sDenseNet121 | WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 85.58% | [121] |
| WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 85.5% | [85] | |
| Customized Dataset | 70:30 | 91% | [68] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 90:10 | 94% | [102] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 70:30 | 94.4% | [84] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 85:15 | 93.3% | [70] | |
| VNTrash, TrashNet | - | 96.4% | [67] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:20:10 | 94.1% | [71] | |
| DenseNet161 | TrashBox dataset | 80:20 | 97.4% | [69] |
| DenseNet169 | TrashNet dataset | 70:30 | 95.6% | [84] |
| NWNU-TRASH dataset | 70:30 | 82.8% | [12] | |
| DenseNet201 | TrashNet and local garbage datasets | 80:20 | 96% | [120] |
| Technique/ Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV2 | Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:20:10 | 93% | [48] |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 96.9% | [50] | |
| VNTrash, TrashNet | - | 96.2% | [67] | |
| WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 87.3% | [121] | |
| Customized dataset | 80:10:10 | 90% | [68] | |
| WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 87.3% | [85] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 85:15 | 93% | [70] | |
| Customized dataset | 80:10:10 | 83% | [72] | |
| Customized dataset | 70:30 | 80% | [62] | |
| Huawei Cloud datasets | - | 90.7% | [73] | |
| Custom bag classification dataset | 64:16:14 | 98% | [122] | |
| BDWaste dataset | 80:20 | 96.8% | [74] | |
| MobileNetV3 | TrashBox dataset | 80:20 | 85.9% | [69] |
| Huawei garbage classification dataset | 83.3:16.7 | 92.6% | [75] |
| Technique/ Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inception-V3 | Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 95.7% | [50] |
| OrgalidWaste dataset | 70:20:10 | 69.9% | [64] | |
| TrashNet + custom images | 85.7:14.3 | 98.15% | [61] | |
| Kaggle’s organic and recyclable waste dataset | 70:15:15 | 52.83% | [45] | |
| Custom dataset | 80:20 | 95.33% | [39] | |
| EfficientNet | TrashNet dataset | 70:30 | 97% | [76] |
| Custom dataset | 70:20:10 | 92% | [63] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 70:30 | 98.02% | [84] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 35.92% | [50] | |
| TACO, Open Litter Map, TrashNet | 85:15 | 87% | [90] | |
| ScrapNet dataset (combination of TrashNet, OpenRecycle, TACO) | 80:20 | 92.8% | [88] | |
| TrashNet dataset | 85:15 | 87% | [70] | |
| OrgalidWaste dataset | 60:20:20 | 97% | [77] |
| Technique/ Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO | Sentinel-2, Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 93% | [52] |
| Customized dataset | 80:20 | 61% | [87] | |
| YOLO-v3 | 1000 real-life household garbage images | 90:10 | 85% | [98] |
| YOLOv4-tiny | TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 81.84% | [99] |
| YOLOv4 | TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 89.59% | [99] |
| YOLOv5 | Huawei garbage classification | 83.3:16.7 | 93% | [78] |
| TACO dataset | 70:20:10 | 73.5% | [79] | |
| MMTrash dataset | 70:30 | 97.3% | [91] | |
| YOLOv7-tiny | WasteInNet dataset | 70:30 | 86.8% | [123] |
| YOLOv8s | TrashNet dataset | 70:15:15 | 91.25% | [100] |
| YOLOv8n | TrashNet dataset | 70:15:15 | 88.86% | [100] |
| YOLOv8m | TrashNet dataset | 70:15:15 | 91.25% | [100] |
| YOLOv8 | SWAD + UAVVaste datasets | 75:15:10 | 85.9% | [101] |
| Roboflow dataset for solid waste detection | 78:9:13 | 97.7% | [81] | |
| YOLOX-S | Trash-Z dataset + public datasets (TrashNet, Kaggle, AquaTrash) | 90:10 | 85.02% | [92] |
| Technique/Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet | WaDaBa dataset | 80:20 | 80.08% | [85,121] |
| TrashNet dataset | 70:15:15 | 90.26% | [82] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:30 | 99.20% | [126] | |
| Custom dataset augmented with images from TrashNet and other sources | 85.7:14.3% | 98.27% | [61] | |
| Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:20:10 | 92.56% | [71] | |
| WaDaBa dataset | 90:10 | 99.23% | [109] | |
| Customized | 80:20 | 99.2% | [108] | |
| Customized plastic waste dataset | - | 96.41% | [127] | |
| SqueezeNet | Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:20:10 | 91.50% | [71] |
| Technique/ Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoencoder | TrashNet dataset + Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 80:20 | 81% | [103] |
| TrashNet dataset | 80:20 | 82.9% | [104] |
| Technique/Model | Dataset/Usage | Dataset Breakdown | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel lightweight depth-wise separable CNN (DP-CNN) + ensemble extreme learning machine (En-ELM) | TriCascade WasteImage dataset | 80:10:10 | Stage 1: 96% Stage 2: 91% Stage 3: 85.2% | [40] |
| Fully convolutional network (FCN) + deep belief network (DBN) + modified rat swarm optimization (MRSO) | Images of kitchen waste from Kaggle garbage classification dataset | 70:30 | 99.2% | [59] |
| Custom CNN + ANN (artificial neural network) | Kaggle trash dataset | 80:20 | 97% | [44] |
| CNN + graph-long short-term memory (GLSTM) | Customized garbage image dataset | 80:20 | 98% | [128] |
| Fractional horse herd gas optimization-based shepherd CNN (FrHHGO-based ShCNN) | Gofile E-waste dataset | 70:30 | 95% | [129] |
| EfficientNet models + Custom CNN | OrgalidWaste dataset | 60:20:20 | 97% | [77] |
| Multilayer perceptron + multilayer convolutional neural network (ML-CNN), | Real-time environment + customized images of waste | 90:10 | 99% | [60] |
| Multilayer hybrid convolution neural network (MLH-CNN) | TrashNet database | 90:10 | 93% | [130] |
| CNN (single-shot detectors (SSD) and regional proposal networks (RPNs)) | TrashNet database | 90:10 | 97.63% (SSD), 95.76% (Faster R-CNN) | [80] |
| GCDN-Net (combination of DenseNet201 + Inception-v3) | GIGO dataset | 70:10:20 | 75.01% | [93] |
| RWC-Net (combination of DenseNet201 + MobileNetV2) | TrashNet database | 70:20:10 | 95% | [94] |
| Bi-LSTM + transfer learning (CNN-based models) | TrashNet database | 70:15:15 | 96.67% | [82] |
| Parallel lightweight depth-wise separable CNN (DP-CNN) + Ensemble extreme learning machine (En-ELM) | TriCascade waste image dataset | 80:10:10 | 96% | [40] |
| GMC-MobileNetV3 (Improved MobileNetV3 with CBAM, Mish activation function, and global average pooling) | Customized dataset | 70:20:10 | 96.55% | [131] |
| ResNet and Custom CNN models | TrashNet database | 67:33 | 88.66% | [132] |
| Customized vision transformer (ViT-WM) + CNN + RNN | TrashNet dataset + Kaggle waste dataset + Google Images | 80:20 | 98.1% | [95] |
| ECCDN-Net (Densenet201 + Resnet18 + auxiliary outputs) | Customized dataset | 70:20:10 | 96.1% | [96] |
| DeepLabv3+, UNet, PSPNet, FPNet | DWSD dataset | 82:18 | DeepLabv3+: 89.39%, UNet: 88.99%, PSPNet: 83.80%, FPNet: 81.33% | [42] |
| Reference | Model Used | Reported Accuracy | Implementation Notes | Estimated TRL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [61] | VGG-16 | 98.15% | Deployed on Raspberry Pi with camera | TRL 6–7 |
| [62] | SSD MobileNetV2 Quantized | 80% | Real-time waste detection on embedded devices with TensorFlow Lite | TRL 5–6 |
| [82] | Bi-LSTM + Transfer Learning | 96.67% | Trash classification using hybrid CNN and Bi-LSTM in real-time | TRL 6 |
| [63] | EfficientNet | 92% | Deployed using Raspberry Pi, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors | TRL 6 |
| [87] | ResNet-50 + YOLO | 96.83% | Real-time object detection pipeline | TRL 6–7 |
| [81] | YOLOv8 | 97.7% | Waste detection for UAV-based system | TRL 5–6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fotovvatikhah, F.; Ahmedy, I.; Noor, R.M.; Munir, M.U. A Systematic Review of AI-Based Techniques for Automated Waste Classification. Sensors 2025, 25, 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103181
Fotovvatikhah F, Ahmedy I, Noor RM, Munir MU. A Systematic Review of AI-Based Techniques for Automated Waste Classification. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103181
Chicago/Turabian StyleFotovvatikhah, Farnaz, Ismail Ahmedy, Rafidah Md Noor, and Muhammad Umair Munir. 2025. "A Systematic Review of AI-Based Techniques for Automated Waste Classification" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103181
APA StyleFotovvatikhah, F., Ahmedy, I., Noor, R. M., & Munir, M. U. (2025). A Systematic Review of AI-Based Techniques for Automated Waste Classification. Sensors, 25(10), 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103181







