Flexible Epidermal Sensor Power Systems: Innovations in Multidimensional Materials and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Architecture and Material Considerations for Epidermal Sensor Power Systems
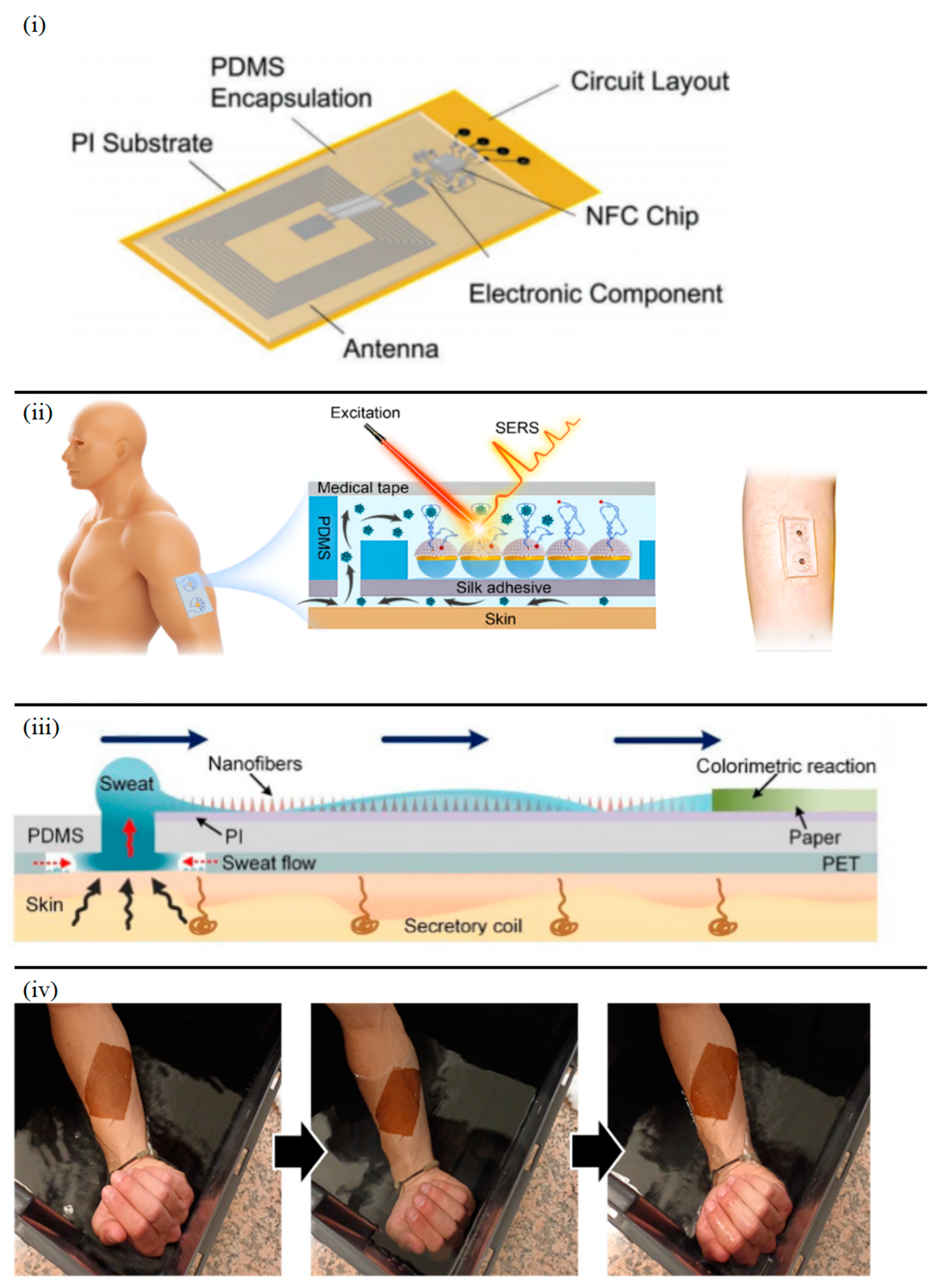
3. Power Supply Strategies for Epidermal Sensors
3.1. Chemically Powered Epidermal Sensors
3.1.1. Zinc-Based Batteries
3.1.2. Lithium-Based Batteries
3.1.3. Other Metal-Based Batteries
3.1.4. Non-Metal Batteries

3.2. Biofuel Cell-Powered Epidermal Sensors

3.3. Environmentally Powered Epidermal Sensors
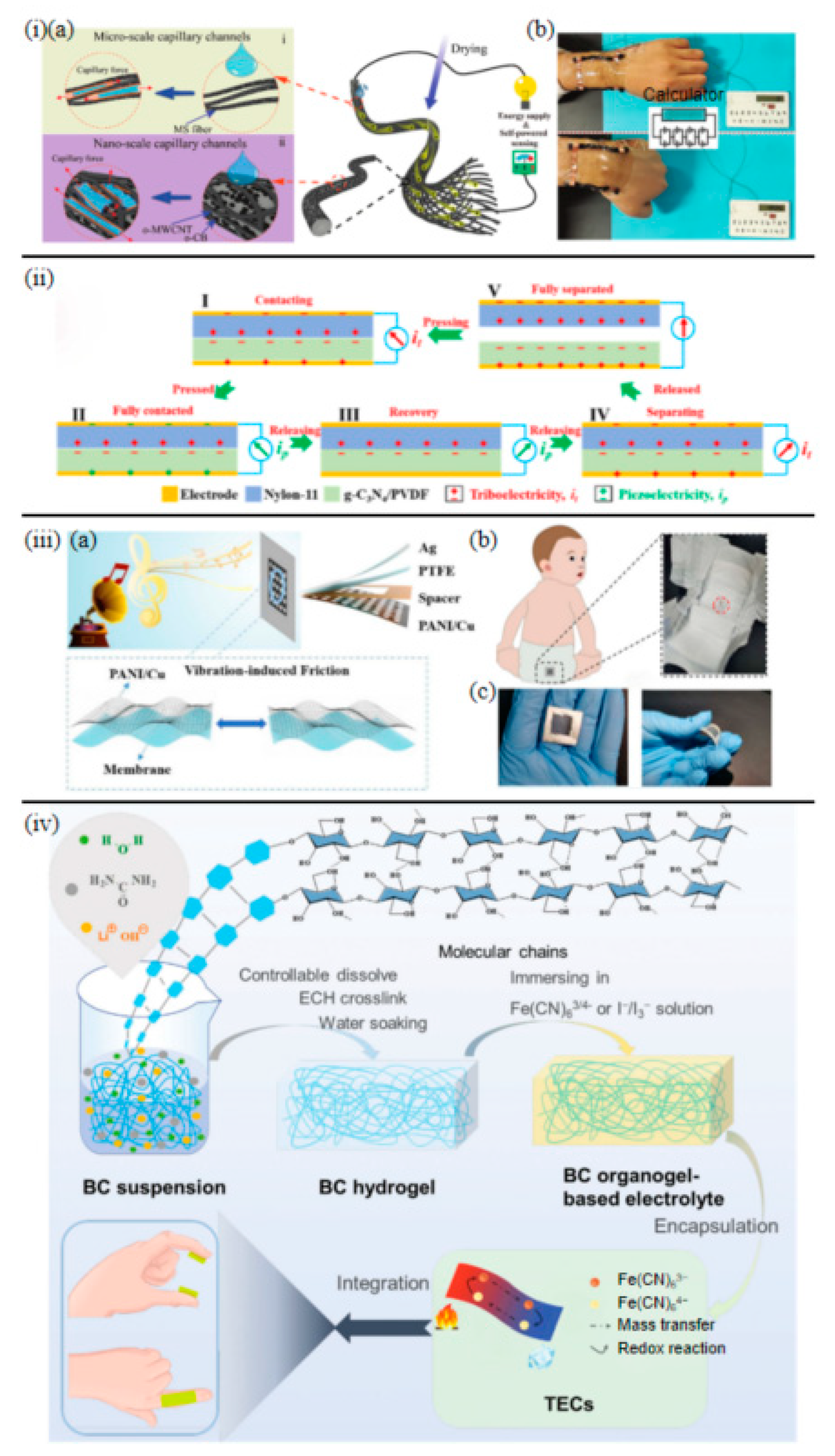
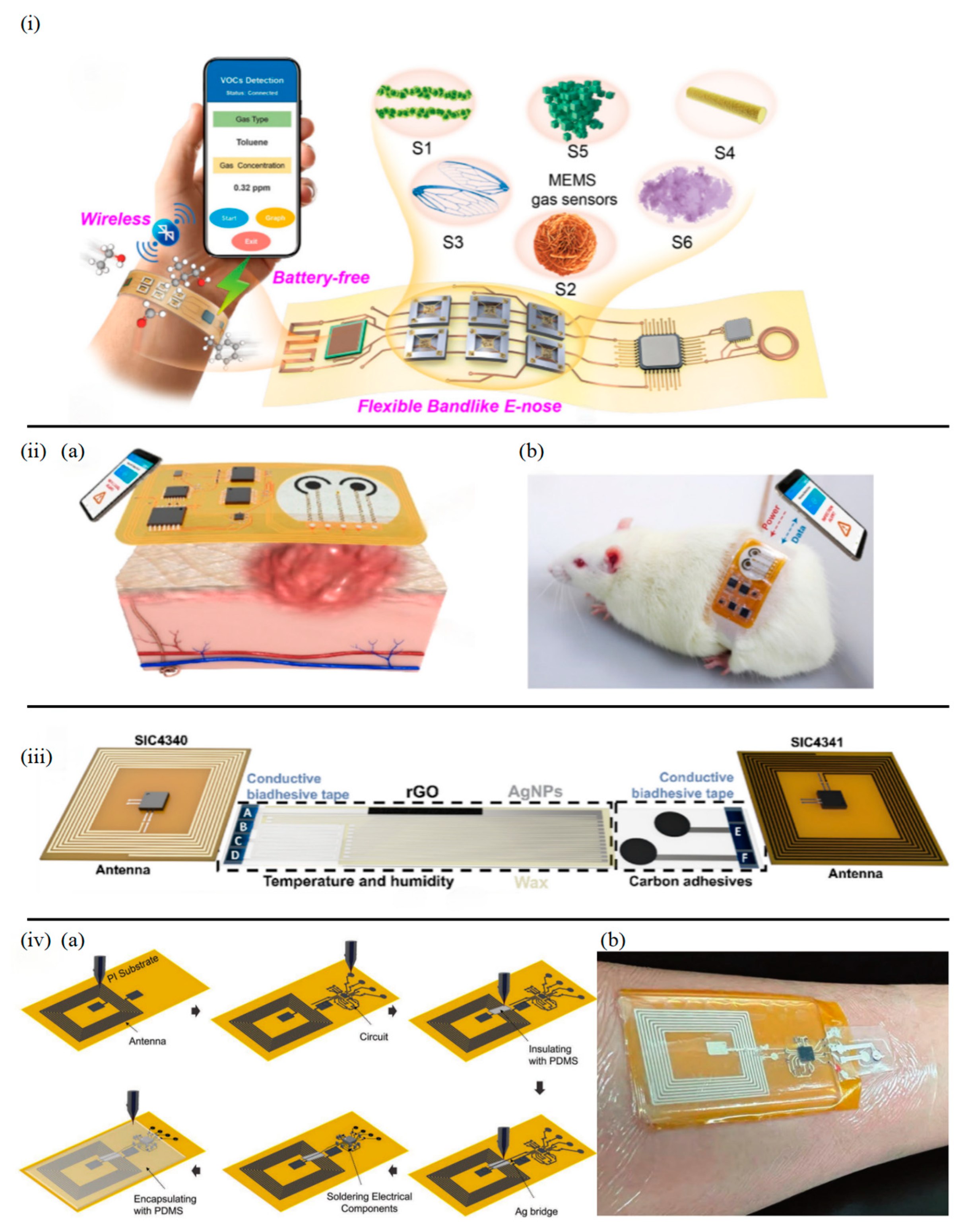
3.4. Battery-Free Epidermal Sensors with Wireless External Power Supply
4. Conclusions and Perspective
- Scenario-Specific Energy-Sensing Coupling: Future epidermal power systems will transcend simple energy provision, evolving towards intelligent scenario-specific energy-sensing coupling. This paradigm shift necessitates a dynamic alignment between energy sources and the specific demands of the sensing application, moving beyond one-size-fits-all solutions. For instance, health monitoring sensors reliant on biomolecules (e.g., glucose and lactate detection), may primarily utilize biofuel cells (BFCs) powered by target analytes supplemented by triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) harvesting motional energy and integrated with 3D porous carbon aerogel-based supercapacitors for transient energy storage and stabilization. Composite electrodes, such as MXene/carbon nanotube composite electrodes can enhance BFC catalytic stability (enzyme activity retention > 90%), while bioinspired microstructured TENGs (output density > 5 µW cm−2) improve mechanical strain sensitivity. Conversely, for motion monitoring sensors (e.g., strain and pressure detection), hybrid systems combining environmental energy (TENGs, piezoelectric materials) with miniaturized zinc-ion batteries are advantageous. Ag nanowire/PVDF composite TENGs efficiently convert mechanical energy, while fatigue-resistant 3D interlocking electrode modules (e.g., PAAM/CMC/LiCl hydrogel batteries) mitigate intermittent power supply caused by sporadic movements. In low-power wireless gas sensing scenarios (e.g., NO2 and VOCs detection) pairing near-field communication (NFC) with photothermal energy harvesting (e.g., MXene/graphene heterojunction photothermal films integrated with flexible perovskite solar cells) can enables continuous environmental. These hybrid approaches, potentially governed by intelligent power management circuits, aim not only to ensure continuous operation but also to enhance sensor sensitivity or enable new sensing modalities by leveraging the unique characteristics of each power source in synergy, marking a key direction towards truly autonomous and highly efficient epidermal devices.
- Multidimensional Material Engineering and Bioinspired Structural Innovations: Breakthroughs in multidimensional material engineering and bioinspired structural innovations are fundamental to overcoming the intrinsic limitations of current epidermal power systems in terms of performance, durability, and biocompatibility. For instance, meticulous 1D/2D heterojunction dynamic or 3D porous architectures (e.g., MXene-carbon composites) enhance ion/electron transport and mechanical resilience. Bioinspired dynamic interfaces, like self-healing poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) hydrogels with liquid metals, improve reliability under mechanical stress. Critically, a shift towards sustainable, biodegradable materials (e.g., silk, chitosan, and bacterial cellulose) is essential to mitigate e-waste from disposable epidermal devices, with concepts like enzymatically degradable pH-responsive batteries showing a promising path.
- Intelligent Closed-Loop Systems: The evolution towards intelligent closed-loop systems will transform epidermal electronics from passive data collectors into autonomous entities capable of real-time adaptation and optimized performance. For example, 2D g-C3N4/PANI heterojunctions can concurrently monitor sweat pH/ion concentrations and power micro-supercapacitors, forming self-sustaining energy chains. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) will be crucial for future epidermal power systems. Specifically, machine learning algorithms, such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, can enable predictive power management. This allows for dynamic optimization of energy allocation based on user activity and environmental conditions. Furthermore, technologies like flexible memristors offer pathways for adaptive energy regulation. Ultimately, these AI-driven approaches can significantly extend system runtime and enhance robustness against energy fluctuations.
- Scalable Manufacturing and Environmental Resilience: Transitioning advanced epidermal power systems from laboratory prototypes to widespread practical applications hinges on breakthroughs in scalable manufacturing and extreme-environment tolerance are imperative. Advances in printed electronics (e.g., roll-to-roll 3D printing) allow one-step fabrication of MXene/ZnO nano-ink-based microbatteries and gas sensor arrays (line width < 50 µm), drastically reducing costs. For harsh environments (e.g., high temperature/humidity), SnS2-based encapsulation combined with ionic liquid gel electrolytes ensures stable operation (>1000 h at 85 °C/95% RH), expanding applications in tropical healthcare and industrial monitoring.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, D.; Pu, Z. Electrically Inspired Flexible Electrochemical Film Power Supply for Long-Term Epidermal Sensors. Micromachines 2023, 14, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Hua, T.; Xu, M.; Yang, D.; Xiao, G.; Li, S.; Cao, X.; Shao, Y. An Energy-Autonomous Wearable Fabric Powered by High-Power Density Sweat-Activated Batteries for Health Monitoring. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2025, 7, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.K.; Wong, G.Z. Solar powered a wearable Electrocardiography (ECG) device with battery storage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 945, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Luo, J.; Pan, R.; Wu, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, D.; et al. Vanadium Dioxide Nanosheets Supported on Carbonized Cotton Fabric as Bifunctional Textiles for Flexible Pressure Sensors and Zinc-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 41577–41587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Vaghasiya, J.V.; Michalička, J.; Langer, R.; Otyepka, M.; Pumera, M. Phase Transition Driven Zn-Ion Battery With Laser-Processed V2C/V2O5 Electrodes for Wearable Temperature Monitoring. Small 2025, 21, e2409987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Sandhu, S.S.; Liu, R.; Khan, M.I.; Wicker, C.; Garcia-Gradilla, V.; Zhou, J.; Chang, A.Y.; Wu, S.; Moon, J.M.; et al. Wearable E-Skin Microgrid with Battery-Based, Self-Regulated Bioenergy Module for Epidermal Sweat Sensing. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Guo, H.; Pan, F.; Meng, F.; Jiang, H.; Ruan, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Lu, W. Breathable, durable, flexible, and battery-free full action response electronic textiles toward simply achieving the function of human skin. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, K.; Wei, J.; Ding, L.; Shao, Z.; Sha, J.; Zhou, X.; Heng, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, K. A wearable sensor device based on screen-printed chip with biofuel cell-driven electrochromic display for noninvasive monitoring of glucose concentration. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 36, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pu, Z.; Su, X.; Yu, H.; Li, D. Communication—An Epidermal Electrochemical Energy Source with a Replaceable Glucose Power Supply Membrane. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Williams, I.; Li, Y.; Qian, F.; Wang, L.; Lei, Y.; Li, B. Flat enzyme-based lactate biofuel cell integrated with power management system: Towards long term in situ power supply for wearable sensors. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xiong, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Bo, X.; Pang, D.; Sun, J.; Bian, J. Robust and flexible wearable generator driven by water evaporation for sustainable and portable self-power supply. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroli, G.; Rosati, G.; Suárez-García, S.; Bedmar-Romero, D.; Kobrin, R.; González-Laredo, Á.; Urban, M.; Alvárez-Diduk, R.; Ruiz-Molina, D.; Merkoçi, A. Wearable, battery-free, wireless multiplexed printed sensors for heat stroke prevention with mussel-inspired bio-adhesive membranes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 260, 116421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Xiang, M.; Gao, G.; Cui, D.; Li, Q. A breathable, waterproof and battery-free wearable e-nose with high flexibility based on MEMS gas sensors for accurate identification of volatile aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl. Mater. Today 2025, 42, 102527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, X. Liquid metal-polymer conductor-based wireless, battery-free epidermal patch. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvini, E.; Hajalilou, A.; Vilarinho, J.P.G.; Lopes, P.A.; Maranha, M.; Tavakoli, M. Gallium-Carbon: A Universal Composite for Sustainable 3D Printing of Integrated Sensor-Heater-Battery Systems in Wearable and Recyclable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32812–32823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.W.; Chinnamani, M.V.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, N.E. Stretchable Non-Enzymatic Fuel Cell-Based Sensor Patch Integrated with Thread-Embedded Microfluidics for Self-Powered Wearable Glucose Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wan, X.; Li, G.; Ye, J.; Gao, J.; Wen, D. Metal Hydrogel-Based Integrated Wearable Biofuel Cell for Self-Powered Epidermal Sweat Biomarker Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2404329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Dai, C.; Deng, P.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, J.; Xiong, C.; Shuai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D.; et al. Wearable battery-free smart bandage with peptide functionalized biosensors based on MXene for bacterial wound infection detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 383, 133598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NajafiKhoshnoo, S.; Kim, T.; Tavares-Negrete, J.A.; Pei, X.; Das, P.; Lee, S.W.; Rajendran, J.; Esfandyarpour, R. A 3D Nanomaterials-Printed Wearable, Battery-Free, Biocompatible, Flexible, and Wireless pH Sensor System for Real-Time Health Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xie, F.; Wei, L.; Zheng, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, P. All-Starch-Based Hydrogel for Flexible Electronics: Strain-Sensitive Batteries and Self-Powered Sensors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 6724–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhu, K.; Wei, J.; Xu, Z.; Yang, K.; Wu, L.; Zong, S.; Wang, Z. Wearable microfluidic SERS patch based on silk fibroin for the non-invasive monitoring of sweat cortisol and pH. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 427, 137152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; He, P.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, C.; Li, X.; Jin, Q.; Peng, T.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, D.; et al. Sweat-Permeable, Microbiota-Preserving, Mechanically Antibacterial Patch for Long-Term Interfacing with Perspiring Skin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2416129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Mao, H.; Li, R.; Xiong, J. A self-driven multifunctional microfluidic sweat analysis system for efficient sweat collection and real-time monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 414, 135920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulpe, G.; Liu, G.; Oakley, S.; Pletsas, D.; Yang, G.; Dutra, R.; Guy, O.; Liu, Y.; Waldron, M.; Neary, J.; et al. Wearable technology for one health: Charting the course of dermal biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 19, 100500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Shen, J.; Lai, Y.; Hua, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, W. Freestanding MXene-Scaffolded Film Cathodes Enable High-Performance Flexible Zinc-Ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alathlawi, H.J.; Rabhi, S.; Hidouri, T.; Adawi, H.; Makin, F.A.; Alsam, A.A. Role of Ag Nanowires: MXenes in Optimizing Flexible, Semitransparent Bifacial Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells for Building-Integrated Photovoltaics: A SCAPS-1D Modeling Approach. Adv. Theory Simul. 2024, 8, 2401004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allah, A.E. Three-dimensional N-doped mesoporous carbon-MXene hybrid architecture for supercapacitor applications. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 9983–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Liao, J.; Huang, S.; Yuan, W.; Li, C.; He, J. A rigid-flexible gel polymer electrolytes with long cycle life and dendrite-free in lithium metal batteries. J. Energy Storage 2024, 75, 109591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanthappa, M.; Ahmed, S.; Chanda, D.; Soon-Yong, K.; Lee, G.S.; Hong, D.; Yang, B.L. Interfacial engineering of a MoS2–FeCoS2@NG nanocomposite: An efficient electrocatalyst for enhanced flexible zinc–air battery performance. New J. Chem. 2025, 49, 2432–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wu, C.; Ling, W.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, N. Coil-like Si-based composites prepared by encapsulating self-healing liquid metal-coated nanosilicon via flexible MXene for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes. J. Power Sources 2025, 629, 236067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanilmaz, M.; Chen, L.; Cheng, H.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, J. Flexible Centrifugally Spun N, S-Doped SnS2-Including Porous Carbon Nanofiber Electrodes for Na-Ion Batteries. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 24665–24673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Qiu, C.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Yang, G. From wood to flexible Zn-air Battery: Fe3O4 nanoparticles synergistic single iron atoms on N-doped carbon nanosheets electrocatalyst and Lignosulfonate-Functionalized gel electrolyte. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Tao, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Peng, Z.; Guo, C.; He, L.; et al. Flexible Zn-air battery for self-powered aptasensing SARS-CoV-2. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Chen, P.; Meng, F.; Han, F.; Zhu, C.; Wei, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, J. Starch-reinforced adhesive hydrogel electrolyte enables high-performance flexible zinc-air batteries. J. Energy Storage 2024, 102, 114035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Xi, Q.; Shao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Rui, Y.; Shao, Y. Recent progress in carbon nanomaterials for highly flexible fibrous aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 6109–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Qu, G.; Jin, S.; Li, X.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, H. Highly sensitive active-powering pressure sensor enabled by integration of double-rough surface hydrogel and flexible batteries. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.; Bao, Z.; Peng, Y.; Lei, H.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cao, R.; Zheng, H. A twisted carbonaceous nanotube as the air-electrode for flexible Zn-Air batteries. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, N.; Liu, Z.; Su, T.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.; Jia, P.; Lu, W.; Gao, Y. Flexible battery-type pressure sensor enhanced with locked water by calcium ion in graphene oxide solid electrolyte. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 101050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjendirane, A.C.; Sha, F.M.; Balan, B.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Vediappan, K.; Rajendra, S.P.; Alsalhi, M.S.; Angaiah, S. 3D-Polyacrylamide/Ti-MXene: A Newer Hybrid Hydrogel Electrolyte Featuring High Mechanical Strength and Durability for Flexible Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 4745–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. 3D printed dual network Cross-Linked hydrogel electrolytes for high area capacity flexible zinc ion Micro-Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Zheng, A.; He, B.; Xiong, Y.; Han, F.; Wei, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, K.; Sun, L. In situ crafting of a 3D N-doped carbon/defect-rich V2O5−x·nH2O nanosheet composite for high performance fibrous flexible Zn-ion batteries. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022, 7, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Lou, J. Carboxymethylated nanocellulose-based gel polymer electrolyte with a high lithium ion transfer number for flexible lithium-ion batteries application. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Han, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J. Flexible Ti3C2Tx/Nanocellulose Hybrid Film as a Stable Zn-free Anode for Aqueous Hybrid Zn-Li Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Han, L.; Han, Q. Flexible self-powered integrated sensing system based on a rechargeable zinc-ion battery by using a multifunctional polyacrylamide/carboxymethyl chitosan/LiCl ionic hydrogel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, R.; Liu, C.; Jiang, K. Electrospraying Si/SiO x /C and Sn/C nanosphere arrays on carbon cloth for high-performance flexible lithium-ion batteries. J. Semicond. 2025, 46, 012605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Deng, N.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, L.; Ju, J.; Zhao, C.; Kang, W. Flexible self-supporting inorganic nanofiber membrane-reinforced solid-state electrolyte for dendrite-free lithium metal batteries. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 6748–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, X.; Yuan, W.; Yu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Luan, L.; Ding, Y.; Sun, H. A Highly Stable Long-Cycle Lithium-Oxygen Battery Based on Flexible PVDF-HFP@LATP Solid-State Electrolyte. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 3484–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zheng, X.; Li, K.; Jia, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z. Surface Metallization of Carbon Nanotube Film for Flexible Lithium-ion Batteries with High Output Current. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 36, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Hao, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Ultraviolet-cured heat-resistant and stretchable gel polymer electrolytes for flexible and safe semi-solid lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2024, 613, 234944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xue, M.; Cheng, Y.; Che, L.; Liu, M.; Selabi, N.B.S.; Zhou, Y. Flexible self-supporting interconnected cobalt sulfide nanosheets enable high-loading and long-cycling Li-S batteries with high areal capacity. Mater. Des. 2024, 237, 112598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, H.; Guo, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, W.; Yao, J.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y. In Situ Growth of NiCoSe Nanoparticles/Holey Carbon Nanosheet on Carbon Cloth as an Efficient Sulfur Host for Flexible Li-S Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 060504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, G.; Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Nia, A.S.; Yu, M.; Feng, X. Facile assembly of layer-interlocked graphene heterostructures as flexible electrodes for Li-ion batteries. Faraday Discuss 2021, 227, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Tong, Z.; Wu, Z.P.; Gao, F.; Zhou, S.Y.; Pan, S.Y.; Zhang, P.F.; Zhou, Z.H.; Liao, H.G.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Disposing of excessive decomposition and destructive intercalation of solvated Li+ in CNT-based flexible 3D Si anode of flexible battery. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 51, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, C.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, X.; Bao, Y.; Lourenço, M.; Homewood, K.; Gao, Y. Synergetic Contributions from the Components of Flexible 3D Structured C/Ag/ZnO/CC Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 6, 12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Y.F.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kim, D.; Lu, X.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.I. 3D-printed topological-structured electrodes with exceptional mechanical properties for high-performance flexible Li-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 70, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xiao, S.; Cai, H.; Sun, W.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.-D.; Lai, W.-Y. Elastic Polymer Electrolytes Integrated with In Situ Polymerization-Transferred Electrodes toward Stretchable Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 3672–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetova, K.; Tatykayev, B.; Kalybekkyzy, S.; Sultanov, F.; Bakenov, Z.; Mentbayeva, A. One-step fabrication of all-in-one flexible nanofibrous lithium-ion battery. J. Energy Storage 2023, 65, 107237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Lv, S.; Yang, Q.; Lei, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J. Ionic liquid meets ZnIn2S4: Synergistically tuning coordination environment of ZnIn2S4 grown on porous carbon by N, F doping and S-vacancies to load high concentration of single-atom Sb for efficient flexible Zn-Air batteries. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 361, 124697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Liu, G.; Fu, H.; Wang, M.; Kim, J.; Yang, W.; Lee, J.K. Wearable eutectic gallium-indium liquid fuel cells. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 247, 114729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Nie, W.; Xu, S.; Gao, P.; Sun, S.; Zheng, X.; Hu, Q.; Xu, Z. A Honeycomb-like Ammonium-Ion Fiber Battery with High and Stable Performance for Wearable Energy Storage. Polymers 2022, 14, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Crum, A.N.; Wang, Y. A full metal-free flexible ammonium-ion battery with biodegradable hydrogel electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 11975–11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Tian, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Sun, G.; Qin, G.; Chen, Q. Self-powered wearable sensing devices based on a flexible ammonium-ion battery with fatigue resistance and frost resistance based on a strong and tough hydrogel. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 17675–17683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.H.P.J.; Zhu, Z. A wearable and flexible lactic-acid/O2 biofuel cell with an enhanced air-breathing biocathode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 246, 115845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithianandam, P.; Liu, T.L.; Chen, S.; Jia, Y.; Dong, Y.; Saul, M.; Tedeschi, A.; Sun, W.; Li, J. Flexible, Miniaturized Sensing Probes Inspired by Biofuel Cells for Monitoring Synaptically Released Glutamate in the Mouse Brain. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X.Y. Flexible dibutyl phthalate aptasensor based on self-powered CNTs-rGO enzymatic biofuel cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Pei, X.; Zheng, L.; Ma, C.; Liu, J.; Cao, M.; Bai, J.; Zhou, M. Flexible Biofuel Cell-In-A-Tube (iezTube): An Entirely Self-Contained Biofuel Cell for Wearable Green Bio-energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2209697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhao, X.; Ye, L.; Wang, G. Self-adhesive wearable poly (vinyl alcohol)-based hybrid biofuel cell powered by human bio-fluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 247, 115930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, E.; El-Maghraby, A.; El Nemr, A. Recent developments in the application of carbon-based nanomaterials in implantable and wearable enzyme-biofuel cells. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, A.; Zhang, W.; Kuang, W.; Yan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zhou, P.; Hou, W.; Liu, F.; et al. A 1.6 mW cm−2 lactate/O2 enzymatic biofuel cell: Enhanced power generation and energy harvesting from human sweat by 3D interpenetrating network porous structure CNT-membranes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 18, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ji, J.; Kwon, Y. Paper-type membraneless enzymatic biofuel cells using a new biocathode consisting of flexible buckypaper electrode and bilirubin oxidase based catalyst modified by electrografting. Appl. Energy 2023, 339, 120978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Zhou, S.; Ibrahim, O.O.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q. Innovative Material-Based Wearable Non-Invasive Electrochemical Sweat Sensors towards Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaduri, S.; Behera, M. Advancements in microbial fuel cell technology. In Sustainable Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Pollution Control; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Mu, W.; Tang, Y.; Bi, W.; Liu, W.; Wen, D. Controllable assembly of three-dimensional porous graphene-Au dual aerogels and its application for high-efficient bioelectrocatalytic O2 reduction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1251, 341013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, K.; Muramatsu, K.; Sumi, H.; Nishioka, Y. Miniaturized ascorbic acid fuel cells with flexible electrodes made of graphene-coated carbon fiber cloth. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55, 04EC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmathi, S.; Jayapiriya, U.S.; Sharma, P.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Goel, S. An implantable glucose enzymatic biofuel cell integrated with flexible gold-coated carbon foam and carbon thread bioelectrodes grafted inside a living rat. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2025, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchianò, V.; Tricase, A.; Ditaranto, N.; Macchia, E.; d’Ingeo, S.; Franco, C.D.; Scamarcio, G.; Torsi, L.; Bollella, P. High voltage flexible glucose/O2 fully printed hydrogel-based enzymatic fuel cell. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 135503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, M.; Rahimi, S.; Pandit, S.; Chokkiah, B.; Mijakovic, I. A flexible multifunctional electrode based on conducting PANI/Pd composite for non-enzymatic glucose sensor and direct alcohol fuel cell applications. Fuel 2023, 345, 128182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sha, J.; Di, K.; Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Long, L.; Ding, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, K. Reusable Self-Powered Electrochromic Sensor Patch Based on Enzymatic Biofuel Cells for On-Site Visualized Monitoring of Lactic Acid. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 2604–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.P.T.; Pinto, A.M.F.R.; Sales, M.G.F. Development of an innovative flexible paper-based methanol fuel cell (PB-DMFC) sensing platform–Application to sarcosine detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Q.; Xue, S.; Huang, Q.; Yu, N.; Wu, Y. Flexible All-Solid-State Direct Methanol Fuel Cells with High Specific Power Density. Small 2023, 19, e2205835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Gu, Y.; Pei, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Bai, J.; Zhou, M. A flexible and wearable epidermal ethanol biofuel cell for on-body and real-time bioenergy harvesting from human sweat. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Tao, Y.; Qian, Y.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Yang, J. Semi-Solid Thermo-Electrochemical Cell Based Wearable Power Generator for Body Heat Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2316068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaie, Z.; Omidvar, A. Human body heat-driven thermoelectric generators as a sustainable power supply for wearable electronic devices: Recent advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitra, A.; Paria, S.; Karan, S.K.; Bera, R.; Bera, A.; Das, A.K.; Si, S.K.; Halder, L.; De, A.; Khatua, B.B. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Driven Self-Charging and Self-Healing Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitor Power Cell for Direct Power Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5022–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.P. Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells: A Futuristic IoTs Powering Solar Cell Technology, Short Review. Small Methods 2025, 9, e2400624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luechar, P.; Harnchana, V.; Kaeochana, W.; Kongpet, S.; Mekbuntoon, P.; Laopeng, S.; Khamkong, P.; Mongkolthanaruk, W. Polydimethylsiloxane modified with yeast cells for wearable triboelectric nanogenerator with enhanced energy conversion performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 8973–8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K.; Maeda, R.; et al. Highly Stretchable, Knittable, Wearable Fiberform Hydrovoltaic Generators Driven by Water Transpiration for Portable Self-Power Supply and Self-Powered Strain Sensor. Small 2024, 20, e2306318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Deng, T.; Xiang, G. Nontoxic flexible TENG with robust piezoelectric enhancement through graphitic carbon nitride-incorporated PVDF for wearable sensors and power supplies. Energy 2024, 306, 132555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, D. A multi-indicator pulse monitoring system based on an ultra-sensitive and stable self-powered wearable triboelectric sensor with assistance of personalized deep learning. Nano Energy 2025, 140, 111039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safian, A.; Wu, N.; Liang, X. Development of an embedded piezoelectric transducer for bearing fault detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 188, 109987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Li, J.W.; Tsai, W.Y.; Lee, L.X.; Chiu, C.W. High-performance piezoelectric flexible nanogenerators based on GO and polydopamine-modified ZnO/P(VDF–TrFE) for human motion energy capture, shared bicycle nanoenergy harvesting, and self-powered devices. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 694, 137666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, F.; Han, Q.; Qin, Z.; Chu, F. A hybrid triboelectric-piezoelectric smart squirrel cage with self-sensing and self-powering capabilities. Nano Energy 2024, 124, 109506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Long, Z.; Liang, S.; Zhong, T.; Chen, M.; Xing, L.; Xue, X. A battery-free music-driven humidity sensor for intelligent wearable sensing system in smart diaper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 025016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Dai, X.; Ge, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, P.; Feng, Y.; Huang, L.B.; Feng, W. Self-regulating heating and self-powered flexible fiber fabrics at low temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 220, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Perspective on Flexible Organic Solar Cells for Self-Powered Wearable Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 5595–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, S.; Han, Z.; Qu, X.; Jin, M.; Deng, L.; Liang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wang, H. High Performance Bacterial Cellulose Organogel-Based Thermoelectrochemical Cells by Organic Solvent-Driven Crystallization for Body Heat Harvest and Self-Powered Wearable Strain Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Xu, G.; Ji, X.; Yang, Z.; Guan, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Yu, Y.; Feng, J. A strain-resistant flexible thermistor sensor array based on CNT/MXene hybrid materials for lithium-ion battery and human temperature monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 368, 115059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Deng, P.; Zhou, L.A.; Jin, M.; Fang, F.; Chen, T.; Liu, G.; Wen, H.; An, Z.; Liang, H.; et al. Wireless and battery-free wearable biosensing of riboflavin in sweat for precision nutrition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 251, 116136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiev, I.; Antchev, H.; Kurtev, N.; Tomchev, N.; Aleksandrova, M. Analysis and Design of Low-Power Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Circuit for Wearable Battery-Free Power Supply Devices. Electronics 2025, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zada, M.; Iman, U.R.; Basir, A.; Yoo, H. Battery-Free Digitally Embroidered Smart Textile Energy Harvester for Wearable Healthcare IoTs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 9865–9874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalajamony, H.M.; Nair, M.; Doshi, P.H.; Gandhiraman, R.P.; Fernandez, R.E. Plasma Printed Antenna for Flexible Battery-Less Smart Mask for Lung Health Monitoring. In Proceedings of the FLEPS 2023—IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems, Boston, MA, USA, 9–12 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Mu, B.; Cao, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M. Flexible battery-free wireless electronic system for food monitoring. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.H.; Su, W.; Cui, Y.; Bahr, R.; Tentzeris, M.M. Battery-less long-range wireless fluidic sensing system using flexible additive manufacturing ambient energy harvester and microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regmi, G.; Velumani, S. Radio frequency (RF) sputtered ZrO2-ZnO-TiO2 coating: An example of multifunctional benefits for thin film solar cells on the flexible substrate. Sol. Energy 2023, 249, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zahed, M.A.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Yoon, S.; Hui, X.; Barman, S.C.; Sharma, S.; Yoon, H.S.; Park, C.; Park, J.Y. A wearable battery-free wireless and skin-interfaced microfluidics integrated electrochemical sensing patch for on-site biomarkers monitoring in human perspiration. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Miao, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.; Gao, G.; Guo, Y.; Cui, D.; Li, Q. A battery-free, wireless, flexible bandlike e-nose based on MEMS gas sensors for precisely volatile organic compounds detection. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J.; Chen, K.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, C.; et al. 3D printing of flexible batteries for wearable electronics. J. Power Sources 2024, 602, 234350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Preparation and characterization of flexible self-supported electrodes for lithium-ion batteries from nanofibrillated cellulose. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 23737–23749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Power Supply Type | Material Innovation | Modification/Functionalization/Fabrication | Specialized Properties | Voltage | Capacity /Specific Capacity/Power Density | Motion Detection | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemically Powered Epidermal Sensors | Zn//MnO2 Battery | rGO; Locust bean gum | MnO2/rGO composite; LBG-based hydrogel | - | 1.4 V | 2.72 mAh | Large-range human motion | [36] |
| Zn//MnO2 Battery | PAAM/CMC/LiCl | Prepared via one-step UV radical polymerization | Anti-freezing capability; self-healing | 1.4 V | 214.2 mAh g−1 | Human motion detection | [44] | |
| Cu/GO[Ca]/Zn battery | GO | Ca2+ intercalation in GO layers | 0.77 V | 1.93 mW cm−2 | Human motion detection; Morse code generation via finger bending | [38] | ||
| LFP//Li battery | PVDF-HFP; P(BA-co-EGDMA); HNT | UV-curing enables rapid processing; 3D polymer network enhances mechanical properties | Effective lithium dendrite suppression | 3.2~3.8 V | 123.8 mAh g−1 | - | [49] | |
| LTO//LFP battery | Exfoliated graphene | EG-LiFePO4 nanocomposite; EG-Li4Ti5O12 nanocomposite | Withstand bending/folding/twisting | 2 V | 137 mAh g−1 | - | [52] | |
| LTO//LFP battery | AgNWs | AgNWs/PDMS Stretchable Current Collectors | 2 V | 108 mAh g−1 | - | [56] | ||
| LFP//C battery | PVDF-HFP; Nano-graphite; CNT | LiFePO4/C nanoparticles synthesized via solid-state method with carbon coating; sequential electrospinning | Semi-transparency | 3.35 V | 140 mAh g−1 | - | [57] | |
| AIB/NH4+ | PHEA/AS/Gly | Anti-freezing capability | 0.8–1.2 V | 42.5 mAh g−1 | Human motion detection | [62] | ||
| Ag-Ga battery | Ga-CB-SIS | 3D-printed | self-healing; recyclability | 1.6–1.8 V | 26.86 mAh cm−2 | Monitor finger bending gestures | [15] |
| Metabolite | Material Innovation | Modification/Functionalization/Fabrication | Voltage | Capacity /Specific Capacity/Power Density | Biomarker Detection | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biofuel Cell-Powered Epidermal Sensors | Lactic acid | Pt-deposited CP; BOD/CNT | Pt electrodeposition creating triphase interface; BOD/CNT/Nafion membrane casting | 0.75 V | 1.78 mW cm−2 | Heart rate sensing integration | [63] |
| Lactic acid | CNT-membrane (3D porous) | 3D interpenetrating network porous CNT-membrane bioanode (via NIPS); Air cathode | OCV > 0.84 V (in 20 mM lactate) | 1.6 mW cm−2 (at 20 mM lactate) | Energy harvesting from sweat; powering bluetooth | [69] | |
| Lactic acid | PVA/SAA-DA hydrogel | Self-adhesive PVA/SAA-DA hydrogel electrolyte based hybrid BFC (HBFC) | OCV 0.57 V | 85.34 µW cm−2 | Powered by human sweat; can power a watch | [67] | |
| Ascorbic acid | PtCu NPs; Au-rGO | PtCu bimetallic hydrogel; Au-rGO dual hydrogel | 0.4 V | 35 µW cm−2 | Ascorbic acid detection | [17] | |
| Glucose | NPG | PtNPs@NPG | 62.33 mV M−1 | 2.512 µW cm−2 M−1 | Glucose detection | [16] | |
| Glucose | PtNPs | Drop-casting enzyme/PtNPs/chitosan mixtures | 0.151 V | 1.9 μW | Glucose detection | [1] | |
| Glucose | Screen-printed chip; Agarose gel; PDA-CNTs | BFC-driven electrochromic display; PDA-CNTs doped agarose gel electrolyte; reverse iontophoresis for glucose extraction | —— | —— | Glucose detection (visualized by color change/RGB) | [8] | |
| Lactic acid | Agarose hydrogel; SiO2 hydrophobic film | Hydrophilic agarose hydrogel and SiO2 hydrophobic film for sweat management | OCV 0.3 V | 5.2 µW cm−2 | On-site visualized monitoring of lactic acid | [78] | |
| Glucose | CNTs-rGO; Bi3Ti2O8F; AuNPs | Bi3Ti2O8F immobilized on CNTs-rGO via chitosan; AuNPs modified CNTs-rGO activated by EDC/NHS for aptamer binding, blocked with BSA | 0.3 V | 300 µW cm−2 | DBP | [65] | |
| Ethanol | 3D-NHCAs | Developed 3D coral-like nitrogen-doped hierarchical micro-mesoporous carbon aerogel (3D-NHCAs) | 0.39 V | 1.9 µW cm−2 | Ethanol | [81] |
| Power Supply Type | Material Innovation | Modification/Functionalization/Fabrication | Voltage/OCV | Capacity/Specific Capacity/Power Density | Detection Type | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmentally Powered Epidermal Sensors | HPG | Mask straps | Dip-coating method | 0.43 V | 5.833 mWh cm−3 | Strain detection | [87] |
| TENG | g-C3N4 | Composite of two-dimensional graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and PVDF | 339 V | 0.94 W m−2 | Human motion and complex gestures detection | [88] | |
| TENG | Ripple-shaped Ag electrodes; Electro-spun PVA fiber | Single-electrode mode flexible sensor with 3D interconnected porous PVA fiber membrane | —— | —— | Pulse wave monitoring; cardiovascular health | [89] | |
| PENG | GO; Polydopamine-modified ZnO; P(VDF-TrFE) | GO-PDA@ZnO/P(VDF-TrFE) piezoelectric nanohybrid films | Up to 48.8 V (4 units in series from bicycle) | —— | Human motion energy capture; bicycle nanoenergy harvesting | [91] | |
| TENG | PTEF; PANI | Oxygen plasma treatment | - | 23.7 mW | Humidity detection | [93] | |
| TENG and photothermal | Azopolymer (PAzo9:1-co-PS); | PAzo9:1-co-PS@NF composite for self-regulating heating and TENG power generation | 170 V (−20 °C to 25 °C) | 70.6 kJ kg−1 | self-regulating heating; self-powered flexible fiber fabrics for low temp | [94] | |
| Solar–battery | 1D poly-Si PV arrays; 3D Li-ion stack | 1D nanowire-structured solar cells | 5.5–6.2 V | 2400 mAh | ECG monitoring | [3] | |
| TECs | Bacterial Cellulose; K4Fe(CN)6/K3Fe(CN)6 | Bacterial cellulose organogel; propylene glycol modification | 0.076 mV (40 °C) | 104.2 mW m−2 (40 °C) | Strain detection | [96] | |
| TECs | CNT; MXene; Si3N4 | Hybrid material of CNTs and MXene; flexible paper/PDMS/Si3N4 composite substrate | - | - | Temperature detection | [97] |
| Power Supply Type | Advantages | Limitations | Applicable Sensor Types | Power Continuity | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemically Powered | High energy density (e.g., Zn-ion: 214.2 mAh g−1), long-term stability, wide temperature tolerance (−20 °C to 200 °C) | Risk of electrolyte leakage, dendrite formation (limited cycle life), insufficient mechanical flexibility | ECG, SpO2 sensing, motion monitoring | Continuous (finite lifespan) | [36,44,52,56] |
| Biofuel Cell-Powered | Self-powered (metabolite-driven), ultra-thin (<0.5 mm), integrated sensing-power generation | Output dependent on metabolite fluctuations (e.g., glucose), enzyme activity degradation (requires enzyme-free catalysts) | Glucose, lactate, ascorbic acid detection, heart rate sensing integration | Continuous (dynamic fluctuations) | [1,17,63,65,81] |
| Environmentally Powered | Maintenance-free (e.g., TENGs), suitable for low-power intermittent sensing | Unstable output (environment dependent), low energy density (e.g., TENG: 0.94 W m−2) | Motion, temperature, humidity, pressure sensing | Intermittent (environment dependent) | [87,88,93,96,97] |
| Battery-Free Wireless | Ultra-thin wearables, no energy storage (ideal for disposable patches) | Short transmission distance (≤5 cm), antenna deformation sensitivity, efficiency limitations organogel; propylene glycol modifica-tion | Gas (VOCs), short-term wound monitoring | On-demand (requires external transmitter) | [12,18,19,106,108] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhou, S.; He, Z.; Ibrahim, O.O.; Liu, C.; Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q. Flexible Epidermal Sensor Power Systems: Innovations in Multidimensional Materials and Biomedical Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103177
Zhang S, Zhou S, He Z, Ibrahim OO, Liu C, Wu M, Wang C, Wang Q. Flexible Epidermal Sensor Power Systems: Innovations in Multidimensional Materials and Biomedical Applications. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103177
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sheng, Shulan Zhou, Zhaotao He, Oresegun Olakunle Ibrahim, Chen Liu, Mengwei Wu, Chunge Wang, and Qianqian Wang. 2025. "Flexible Epidermal Sensor Power Systems: Innovations in Multidimensional Materials and Biomedical Applications" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103177
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhou, S., He, Z., Ibrahim, O. O., Liu, C., Wu, M., Wang, C., & Wang, Q. (2025). Flexible Epidermal Sensor Power Systems: Innovations in Multidimensional Materials and Biomedical Applications. Sensors, 25(10), 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103177








