Monitoring Long-Term Waste Volume Changes in Landfills in Developing Countries Using ASTER Time-Series Digital Surface Model Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
| Site Name | Country | Location (Lat., Long.) | Estimated Area (km2) | Start Year of Operation | Operation Status | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ghazipur | India | 28.624, 77.327 | 0.31 | 1984 | – | [51,52,53] |
| Bhalswa | India | 28.740, 77.156 | 0.27 | 1992–1994 | – | [53,54] |
| Okhla | India | 28.512, 77.284 | 0.23 | 1994–1996 | Biomining started in July 2019 | [53,55,56,57,58] |
| Deonar | India | 19.072, 72.928 | 1.31 | 1927 | – | [59,60,61] |
| Mulund | India | 19.170, 72.973 | 0.33 | 1967–1968 | Closed in October 2018 | [62,63,64] |
| Dhapa (active site) | India | 22.536, 88.425 | 0.53 | 1987 | – | [65] |
| Dhapa (closed site) | India | 22.544, 88.419 | 0.16 | 1987 | Closed in 2009 | [65,66] |
| Kodungaiyur | India | 13.136, 80.268 | 1.22 | 1987 | – | [67,68] |
| Pirana | India | 22.980, 72.567 | 0.42 | 1980 | – | [69,70] |
| Al Akaider (Al-Ekaider) | Jordan | 32.514, 36.111 | 0.42 | 1980–1981 | – | [71,72,73] |
| Al Husaineyat (Mafraq FDS) | Jordan | 32.255, 36.349 | 0.35 | 1986 | – | [71] |
| Oued Smar | Algeria | 36.698, 3.155 | 0.46 | 1978 | Closed in 2011 | [74,75] |
| Al Wafaa and Al Amal (El-wafaa and El-amal) | Egypt | 30.017, 31.362 | 2.66 | Late 1970s | Closed in 2018 or 2019 | [15,76] |
| Bishkek (BSWL) | Kyrgyzstan | 42.968, 74.590 | 0.49 | 1974–1976 | – | [77,78] |
| Jam Chakro | Pakistan | 25.030, 67.032 | 1.22 | 1996 | – | [73] |
2.2. Data Used
2.3. Method
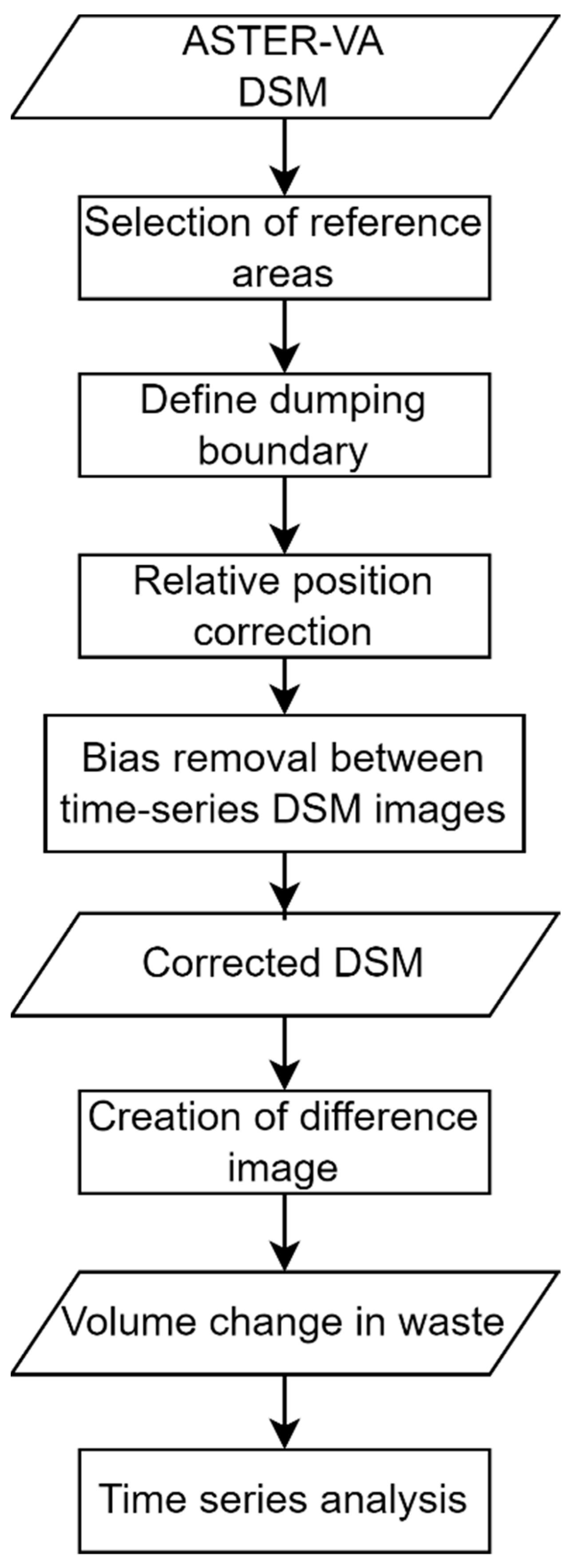
2.3.1. Estimating Amount of Waste Using ASTER DSM Images
- (1)
- Position correction
- (2)
- Height correction
- (3)
- Estimation of the relative volume of waste
- (4)
- Calculation of the absolute volume of waste
2.3.2. Evaluation of ASTER-Based Values Using Reported Values
- (1)
- Evaluation based on total amount using annual waste amount information
- (2)
- Evaluation based on total amount, assuming initial topography of the site
- (3)
- Evaluation based on the amount of change over a certain time period
2.3.3. Evaluation Based on Volume Change Between Two Time Points Using DCM Products
- In the rectangular area, including the surrounding area of each site, the height change was calculated by subtracting the DCM1 value from the DCM2 value for each pixel.
- For each pixel, if the absolute value of the height change obtained was the square root of the sum of the squares of the height accuracy indication (HAI) values or greater, included in the DCM product of DCM1 and DCM2, it was considered to be a valid pixel.
- The height change value of each valid pixel was multiplied by the pixel area, divided by the number of days between DCM1 and DCM2, and the volume change per day for each pixel was calculated.
- The volume change per day for waste at the site was calculated by taking the sum of the volume change per day of all valid pixels.
3. Results
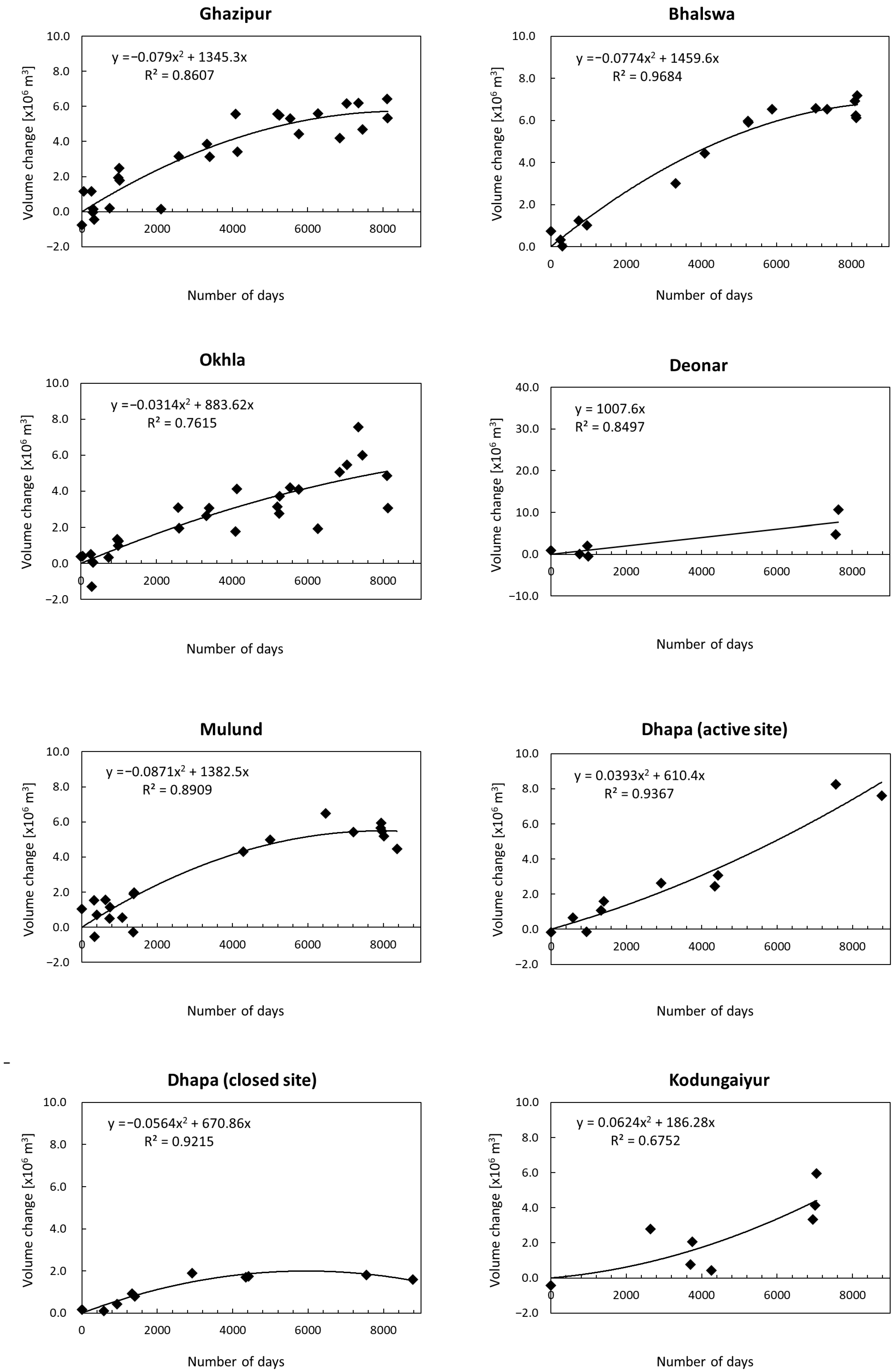
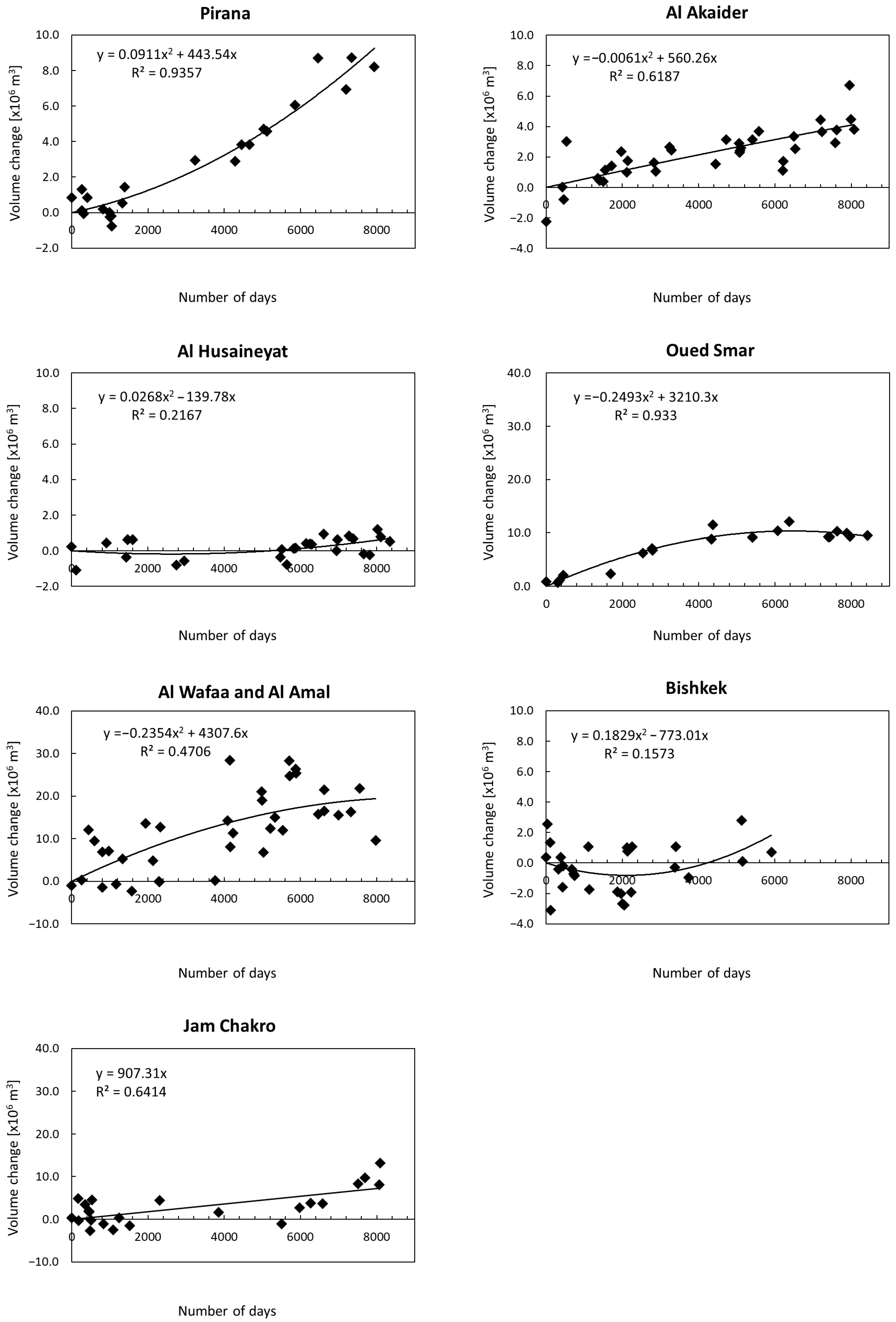
3.1. Time-Series Plot of Relative Volume of Waste Obtained from ASTER DSM Data
3.2. Comparison of ASTER-Based Values and Reported Values Based on Total Waste Volume at Certain Points in Time
3.3. Comparison Between ASTER-Based Volume Change per Day and Reported Amount of Waste Disposed of per Day
3.4. Comparison of DCM-Based and ASTER-Based Values for Volume Change Between Two Time Points
4. Discussion
4.1. Reliability of Reported Values
4.2. Comparison with Method Using DCM
4.3. Uncertainty of ASTER Estimates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.C.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; Urban Development; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10986/30317 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Daniel, H.; Perinaz, B.-T. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10986/17388 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Talyan, V.; Dahiya, R.P.; Sreekrishnan, T.R. State of municipal solid waste management in Delhi, the capital of India. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Ramanathan, A.L. Assessment of Methane Flux from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Landfill Areas of Delhi, India. J. Environ. Prot. 2011, 2, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Trash Heap 62 Meters High Shows the Scale of India’s Climate Challenge—CNN. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2022/12/10/india/india-bhalswa-landfill-pollution-climate-intl-hnk-dst/index.html (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- India’s Ghazipur Landfill Could Grow Taller Than the Taj Mahal. Available online: https://www.waste360.com/landfill/india-s-ghazipur-landfill-could-grow-taller-than-the-taj-mahal (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- South corporation finally stops dumping at saturated Okhla landfill. Hindustan Times, 11 March 2018. Available online: https://www.hindustantimes.com/delhi-news/south-corporation-finally-stops-dumping-at-saturated-okhla-landfill/story-mVJm6Al0PcPc7uUNsqlktJ.html (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Lee, U.; Han, J.; Wang, M. Evaluation of landfill gas emissions from municipal solid waste landfills for the life-cycle analysis of waste-to-energy pathways. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 166, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastev, M.; Therrien, R.; Lefebvre, R.; Gélinas, P. Gas production and migration in landfills and geological materials. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2001, 52, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, S.; Lou, Z.; Zhu, N.; Feng, L. The identification and health risk assessment of odor emissions from waste landfilling and composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, L. Health hazards and waste management. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadder, S.R.; Prabhakar, R.; Khan, D.; Kishan, D.; Chauhan, M.S. Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, B.N.; Anantharama, V. Comparative analysis of soil contamination caused by existing municipal solid waste management facilities. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donno, G.; Melegari, D.; Paoletti, V.; Piegari, E. Electrical and Electromagnetic Prospecting for the Characterization of Municipal Waste Landfills: A Review. In Technical Landfills and Waste Management; Springer Water; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–29, Part F2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Magd, I.A.; Attwa, M.; El Bastawesy, M.; Gad, A.; Henaish, A.; Zamzam, S. Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Municipal Waste in Uncontrolled Dumpsites and Landfills Using Integrated Remote Sensing, Geological and Geophysical Data: A Case Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Segura, M.A.; Vásconez-Maza, M.D.; García-Nieto, M.C. Volumetric characterisation of waste deposits generated during the production of fertiliser derived from phosphoric rock by using LiDAR and electrical resistivity tomography. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bièvre, G.; Garambois, S. Characterization of a Small Abandoned Municipal Solid Waste Scattered Landfill Combining Remote Sensing and Near-Surface Geophysical Investigations. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2023, 28, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaïri, M.; Ferchichi, M.; Ismaïl, A.; Jenayeh, M.; Hammami, H. Rehabilitation of El Yahoudia dumping site, Tunisia. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, B.N.; Valeria, C.; Anisoara, I.; Ioan, P.; Elena, P. Use of a method RTK measurement to determine the volume of waste by landfill solid danger, Ghizela town, County Timiş. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConf. SGEM 2016, 2, 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Tserng, H.P.; Russell, J.S. A 3-D graphical database system for Landfill operations using GPS. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2002, 17, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filkin, T.; Sliusar, N.; Huber-Humer, M.; Ritzkowski, M.; Korotaev, V. Estimation of dump and landfill waste volumes using unmanned aerial systems. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julge, K.; Ellmann, A.; Köök, R. Unmanned aerial vehicle surveying for monitoring road construction earthworks. Balt. J. Road Bridge Eng. 2019, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaamin, M. Volumetric Change Calculation for a Landfill Stockpile Using UAV Photogrammetry. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2019, 11, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Incekara, A.H.; Delen, A.; Seker, D.Z.; Goksel, C. Investigating the Utility Potential of Low-Cost Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in the Temporal Monitoring of a Landfill. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Mello, C.C.; Salim, D.H.C.; Simões, G.F. UAV-based landfill operation monitoring: A year of volume and topographic measurements. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbančič, T.; Grahor, V.; Koler, B. Impact of the grid cell size and interpolation methods on earthwork volume calculation. Geod. Vestn. 2015, 59, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliusar, N.; Filkin, T.; Huber-Humer, M.; Ritzkowski, M. Drone technology in municipal solid waste management and landfilling: A comprehensive review. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira da Silva, F.H.; Feitoza Lêdo, É.R.; Candido Damasceno, C.S.; Da Silva, J.A.; De Brito Alves, I.M. Evaluation of the accuracy of volume calculation obtained by UAV. Rev. Agro@Mbiente Online 2020, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, D.; Allemand, P.; Delacourt, C.; Grandjean, P. Potential and limitation of UAV for monitoring subsidence in municipal landfills. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2014, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetyuk, Y.; Mårtensson, S.G. Terrestrial laser scanning for detection of landfill gas: A pilot study. J. Appl. Geod. 2014, 8, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocchi, V.; Napoleoni, Q.; Tesei, M.; Servodio, G.; Alicandro, M.; Costantino, D. UAV for monitoring the settlement of a landfill. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fys, M.; Yurkiv, M.; Lozynskyi, V. Zodeling of 3-D objects using geodetic and cartographic data and determining their volumes with an accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. 2021, 22, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3D-Geospatial Data Using Unmanned Airborne Vehicles. Available online: https://ask-eu.de/Artikel/27107/3D-Geospatial-Data-using-Unmanned-Airborne-Vehicles.htm (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Mudura, R.; Trif, A.; Nedelcu, B.; Bara, C. Calculate the volume of landfill cristeşti, mureş using the classical method and digital terrain model using pictures from UAV. In Proceedings of the 14th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConferences SGEM2014, Albena, Bulgaria, 17–26 June 2014; pp. 113–120. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290872900_Calculate_the_volume_of_landfill_cristesti_mures_using_the_classical_method_and_digital_terrain_model_using_pictures_from_UAV (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Hajdukiewicz, M. Use of Archival Aerial Photos and Images Acquired Using UAV to Reconstruct the Changes of Annual Load of the Suburban Landfill: Case Study of Promnik, Poland. Energies 2023, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanassi, V.; Choussiafis, C.; Grammatikou, Z. Monitoring the change in volume of waste in landfill using SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the 32nd EARSeL Symposium and 36th General Assembly, Mykonos, Greece, 21–24 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Papale, L.G.; Guerrisi, G.; De Santis, D.; Schiavon, G.; Del Frate, F. Satellite Data Potentialities in Solid Waste Landfill Monitoring: Review and Case Studies. Sensors 2023, 23, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Fu, H.; Liu, L.; Feng, G.; Wen, D.; Peng, X.; Ding, H. Continued Monitoring and Modeling of Xingfeng Solid Waste Landfill Settlement, China, Based on Multiplatform SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Fielding, E.J.; Masi, S.; Lundgren, P.; Serio, C. Monitoring municipal solid waste small magnitude landfill settlement with DInSAR. EARSeL eProc. 2015, 14, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T.; Zhao, W.; Fujita, S. Analysis of Detailed Geographical Features using Shadow of Satellite Images in the Case of Illegal dumping site on the Border between Aomori and Iwate Prefectures. Int. J. Soc. Mater. Eng. Resour. 2006, 14, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, D.; Wobbe, F.J. Solid Waste and Remote Sensing. Photogramm. Eng. 1974, 40, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wezernak, C.T.; Thomson, F.J. Monitoring of Dumping by Means of Satellite Remote Sensing. AMBIO 1973, 2, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Xu, J. Ground Deformation Detection Using China’s ZY-3 Stereo Imagery in an Opencast Mining Area. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, A.S.; Avtar, R. Methodology for measuring landfill dumping statistics globally using Digital Elevation Change maps. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 107924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, H. Retrieving Surface Deformation of Mining Areas Using ZY-3 Stereo Imagery and DSMs. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lei, S.; Dai, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Sheng, Y.; Lin, H. DEM-based topographic change detection considering the spatial distribution of errors. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, I.T.; Williams, D.B.; Ramsey, M.S. Quantifying volumes of volcanic deposits using time-averaged ASTER digital elevation models. Sci. Remote Sens. 2024, 10, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Nie, W.; Chung, I.-H. Automatic Volume Calculation and Mapping of Construction and Demolition Debris Using Drones, Deep Learning, and GIS. Drones 2022, 6, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P. Process to Flatten Delhi’s Landfills Slowest at Ghazipur, Fresh Dumping Goes On. Available online: https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/delhi-news/process-to-flatten-delhi-s-landfills-slowest-at-ghazipur-fresh-dumping-goes-on-101713808464525.html (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Bhalerao, S. Mumbai’s second-largest landfill to shut in October. Hindustan Times, 8 August 2018. Available online: https://www.hindustantimes.com/mumbai-news/mumbai-s-second-largest-landfill-to-shut-in-october/story-MW6Hx1rygSNHASL6qHmVOK.html (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Chaudhary, S. Leachate characterization generated from municipal solid waste at landfill site Ghazipur New Delhi. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Khan, A.H.; Islam, R.; Sabi, E.; Khan, N.A.; Zargar, T.I. Identification of prevalent leachate percolation of municipal solid waste landfill: A case study in India. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Anunay, G.; Rohit, G.; Shivangi, G.; Vipul, V. Greenhouse gas emissions from landfills: A case of NCT of Delhi, India. J. Climatol. Weather Forecast 2016, 4, 1000157. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanfar, A.; Amirmojahedi, M.; Gharabaghi, B.; Dubey, B.; McBean, E.; Kumar, D. A novel risk assessment method for landfill slope failure: Case study application for Bhalswa Dumpsite, India. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Rajamani, P. Evaluation of the leachate composition and contamination potential of municipal solid waste landfill sites in Delhi. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Datta, M.; Nema, A.K.; Pérez, I.V. Evaluating Groundwater Contamination Hazard Rating of Municipal Solid Waste Landfills in India and Europe Using a New System. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2012, 17, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Mittal, A.K. Groundwater pollution by municipal solid waste landfill leachate: A case study of Okhla Landfill Delhi. In Proceedings of the IWRA World Water Congress, Pernambuco, Brazil, 25–29 September 2011; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P. Lagging on work at Okhla landfill: Delhi CM Kejriwal. Hindustan Times, 5 October 2023. Available online: https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/delhi-news/lagging-on-work-at-okhla-landfill-delhi-cm-101696443792198.html (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Acharya, P. Dharavi redevelopment: Clearing Deonar dumping ground could take at least 6 years, cost Rs 1000 crore. Indian Express, 29 October 2024. Available online: https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/mumbai/dharavi-redevelopment-clearing-deonar-dumping-ground-6-years-cost-rs-1000-crore-9643915/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Parab-Pandit, S. Mumbai: BMC Aims to Close Deonar Dumping Ground by October 2025 with New Waste-To-Energy Plant. Free Press Journal, 9 February 2024. Available online: https://www.freepressjournal.in/mumbai/mumbai-bmc-aims-to-close-deonar-dumping-ground-by-october-2025-with-new-waste-to-energy-plant (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Deonar Dumping Ground to Shut by 2025. Available online: https://www.mid-day.com/mumbai/mumbai-news/article/deonar-dumping-ground-to-shut-by-2025-23221170 (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Clean It Right Dumpsite Management in India. Available online: https://www.cseindia.org/content/downloadreports/10487 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Sen, S. Mulund east: Dumped, diseased, forgotten. Times of India, 14 January 2017. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/mumbai/mulund-east-dumped-diseased-forgotten/articleshow/56529342.cms (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Singh, A.; Chandel, M.K. Physicochemical and biological assessment of legacy waste for application as soil conditioner. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 29699–29710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkata Attempts to Eliminate ‘Legacy Waste’ in Landfills Through Biomining. Available online: https://india.mongabay.com/2023/06/kolkata-attempts-to-eliminate-legacy-waste-in-landfills-through-biomining/ (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Dhapa Dumpsite Environmental and Social Assessment Report. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/383421497427377147/pdf/SFG3430-V1-EA-P091031-Box402914B-PUBLIC-Disclosed-6-14-2017.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Aishwarya, R. Assessment of Spatial Distribution of Physico-Chemical Parameters of Groundwater around Kodungaiyur Dump yard. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2070, 012215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.H.; Swamy, N.K.; Krishnaiah, S.; Senthil, M.S. A Study on Physico-Chemical analysis of Ground Water and Heavy Metal Analysis of Leachate in Kodungaiyur Landfill Site, Chennai. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1112, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, H.; Shah, C. Review on Current Management Practices and Environment Status of Pirana Dump Site, Ahmedabad. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.I.; Malek, A.M.; Gajjar, H.H.; Gandhi, N.V.; Patel, D.P. Qualitative Assessment of Groundwater Around the Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Site at Pirana in Ahmedabad City. Int. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2014, 2, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Aljaradin, M. Environmental Impact of Municipal Solid Waste Landfills in Semi-Arid Climates—Case Study—Jordan. Open Waste Manag. J. 2012, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzouby, A.M.; Al-Shawabkeh, R.K.; Dweiri, A.M.M. Integrated infrastructure: A study of rehabilitation of Al-Akaider landfill. Alex. Eng. J. 2019, 58, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, H.; Shrestha, S.; Tanaka, M.; Themelis, N.J.; Juca, J.F.; Pariatamby, A.; Russo, M.; Velis, C. WASTE ATLAS The World’s 50 Biggest Dumpsites 2014 Report. Available online: http://www.atlas.d-waste.com/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Authorities in Algiers Convert the Largest Landfill into an Amusement Park (Translated from Arabic). Available online: https://www.maghrebvoices.com/varieties/2022/07/09/%D8%B3%D9%84%D8%B7%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AC%D8%B2%D8%A7%D8%A6%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A7%D8%B5%D9%85%D8%A9-%D8%AA%D8%AD%D9%88%D9%91%D9%84-%D8%A3%D9%83%D8%A8%D8%B1-%D9%85%D9%81%D8%B1%D8%BA%D8%A9-%D9%86%D9%81%D8%A7%D9%8A%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%AD%D8%AF%D9%8A%D9%82%D8%A9-%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AA%D8%B1%D9%81%D9%8A%D9%87 (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Rehabilitation of Wadi Al-Sammar Landfill (Translated from Arabic). Available online: https://gloriousalgeria.dz/Ar/Achievements/show/149/ (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Hussieny, M.A.; Morsy, M.S.; Ahmed, M.; Elagroudy, S.; Abdelrazik, M.H. Municipal Solid Waste and Leachate Characterization in the Cairo Metropolitan Area. Resources 2022, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oznobikhina, L.A. Analysis of indicators of the ecological state of the environment in the Kyrgyz Republic. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1045, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzy, V.E.; Shaikieva, N.; Kemelov, K.; Dolaz, M. Environmental pollution size of the Bishkek Solid Waste Landfill and treatment of generated leachate wastewater. MANAS J. Eng. 2021, 9, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- METI AIST Satellite Data Archive System. Available online: https://gbank.gsj.jp/madas/?lang=en (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- ERSDAC. ASTER User’s Guide Part III DEM Product (L4A01), Ver.1.1. Available online: https://unit.aist.go.jp/igg/rs-rg/ASTERSciWeb_AIST/en/documnts/users_guide/part1/pdf/Part3D_1.1E.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Lachaise, M.; Schweißhelm, B. TanDEM-X 30m DEM Change Maps Product Description. Available online: https://geoservice.dlr.de/web/dataguide/tdm30/pdfs/TD-GS-PS-0216_TanDEM-X_30m_DEM_Change_Maps_Product_Description_1.0.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Singh, P. MCD calls bids for Phase-2 of biomining at Delhi’s three landfills. Hindustan Times, 17 July 2024. Available online: https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/delhi-news/mcd-calls-bids-for-phase-2-of-biomining-at-delhi-s-three-landfills-101721153137681.html (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Stege, A.; Goldstein, R. Report of the Pump Test and Pre-Feasibility Study for Landfill Gas Recovery and Utilization at the Pirana Landfill, Ahmedabad, India. Available online: http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/Pirana.Report.EnglishApril2008.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Ali, S.A.; Ahmad, A. Analysis of Chemical and Heavy Metal Concentrations of Leachates and Impact on Groundwater Quality Near Dhapa Dumping Ground, Kolkata. Asian Profile 2019, 47, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Niyogi, S. Stinking Dhapa dump to turn tourist destination by 2020. Times of India, 3 August 2017. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/kolkata/stinking-dhapa-dump-to-turn-tourist-destination-by-2020/articleshow/59888917.cms (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Omjasvin, M.D. Kodungaiyur now a permanent red zone for Chennai’s waste. Times of India, 20 December 2024. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chennai/kodungaiyur-now-a-permanent-red-zone-for-chennais-waste/articleshow/116481267.cms (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Parmar, J. AMC seeks 50 days to erase Pirana dump completely. Times of India, 31 December 2023. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ahmedabad/amc-seeks-50-days-to-erase-pirana-dump-completely/articleshow/106412884.cms (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- TNN. Civic Body Says 40 Acres Freed Up at Pirana. Times of India, 4 May 2024. Available online: http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/articleshow/109828473.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Chakraborty, M.; Sharma, C.; Pandey, J.; Singh, N.; Gupta, P.K. Methane Emission Estimation from Landfills in Delhi: A comparative Assessment of Different Methodologies. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7135–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbar, P.; Verma, S.; Mehmood, G. Groundwater contamination from non-sanitary landfill sites–a case study on the Ghazipur landfill site, Delhi (India). Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 2017, 12, 1969–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhiok, J. Waste management why: Delhi’s Bhalswa could be a pointer. Times of India, 4 December 2020. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/delhi/waste-management-why-bhalswa-could-be-a-pointer/articleshow/79555697.cms (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Angmo, S.; Kharayat, Y.; Shah, S. Efficiency of Canna indica, Phragmites australis and Eichhornia crassipes in Remediation of Leachate Through a Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland. Curr. World Environ. 2024, 19, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. India—Delhi Landfills Gas Recovery Project. Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/484811468035370620/India-Delhi-Landfills-Gas-Recovery-Project (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Stege, A.; Murray, D.; Goldstein, R. Report of the Pump Test and Pre-Feasibility Study for Landfill Gas Recovery and Utilization at the Deonar Landfill Mumbai, India. Available online: http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/Deonar.Pre-feasibility.Report.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Bhalerao, S. BMC’s plan to close Mulund dump finds no takers. Hindustan Times, 25 September 2016. Available online: https://www.hindustantimes.com/mumbai-news/bmc-s-plan-to-close-mulund-dump-finds-no-takers/story-d0UwYTjxNxVrod2k0EX7dM.html (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Srivastava, A. DNA In-Depth: Solid Waste Management in City After Closure of Mulund Dumping Ground. DNA. Available online: https://www.dnaindia.com/mumbai/report-dna-in-depth-solid-waste-management-in-city-after-closure-of-mulund-dumping-ground-2672092 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Paul, K.; Dutta, A.; Krishna, A.P. A comprehensive study on landfill site selection for Kolkata City, India. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assessment Report Dhapa Disposal Site Kolkata, India. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/38197881/Dhapa_Assessment_Report (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Chennai corporation plans to reclaim Kodungaiyur dumpyard. Times of India, 1 September 2021. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chennai/chennai-corporation-plans-to-reclaim-kodungaiyur-dumpyard/articleshow/85824160.cms (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Kodungaiyur dump yard reclamation likely to be delayed further. DT NEXT, 18 October 2021. Available online: https://www.dtnext.in/city/2021/10/17/kodungaiyur-dump-yard-reclamation-likely-to-be-delayed-further (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Radhakrishnan, S. What do we do with Chennai’s legacy waste? Citizen Matters, 10 May 2022. Available online: https://citizenmatters.in/chennai-legacy-waste-bioming-perungudi-kodungaiyur-fire-source-segregation/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Patel, V. Pirana Dumping: How to Solve Mount Pirana Dumping Site? EnvCure, 6 January 2022. Available online: https://www.envcure.com/how-to-solve-mount-pirana-dumping-site/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Bishkek City Development Agency. Basic Information About Large-Scale Construction Department. Available online: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/12037495_03.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Srivastava, A.N.; Chakma, S. Quantification of landfill gas generation and energy recovery estimation from the municipal solid waste landfill sites of Delhi, India. Energy Sources A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2024, 46, 7453–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharholy, M.; Ahmad, K.; Mahmood, G.; Trivedi, R.C. Analysis of municipal solid waste management systems in Delhi—A review. In Proceedings of the Second International Congress of Chemistry and Environment, Indore, India, 24–26 December 2005; pp. 773–777. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303254724_Analysis_of_municipal_solid_waste_management_systems_in_Delhi_-_A_review (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Joshi, M.P.; Patil, S.B.; Mourya, K. Solid waste management on dumping ground in Mumbai region–a study. Int. J. Comp. Appl. 2013, 975, 8887. [Google Scholar]
- Sprague, S.; Zietsman, J.; Ramani, T.; Kumar, R.; Sil, A.; Wakadikar, K. Pre-Feasibility Analysis for the Conversion of Landfill Gas to Liquefied Natural Gas to Fuel Refuse Trucks in India; Project Report Prepared for U.S. EPA Methane to Markets Partnership; Texas Transportation Institute: Bryan, TX, USA, 2009; Available online: https://tti.tamu.edu/tti-publication/pre-feasibility-analysis-for-the-conversion-of-landfill-gas-to-liquefied-natural-gas-to-fuel-refuse-trucks-in-india/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- TNN. Brimming with garbage, Mulund dump yard. Times of India, 2 October 2018. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/mumbai/brimming-with-garbage-mulund-dump-yard-shut/articleshow/66035643.cms (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Singh, A.; Chandel, M.K. Effect of ageing on waste characteristics excavated from an Indian dumpsite and its potential valorisation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 134, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D.; Ray, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Rao, P.S.; Akolkar, A.B.; Chowdhury, M.; Srivastava, A. Emission, speciation, and evaluation of impacts of non-methane volatile organic compounds from open dump site. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, T.; Goel, S. Solid waste management in Kolkata, India: Practices and challenges. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, K.; Nagendran, R.; Palanivelu, K. Open dumps to sustainble landfills. CES Envis. 2014, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, D.P.; Nagar, V.R. Methane Gas Generation from Pirana Landfill Site, Ahmedabad. Int. J. Adv. Res. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Pandit, P.; Kumar, D.; Patel, Z.; Pandya, L.; Kumar, M.; Joshi, C.; Joshi, M. Landfill microbiome harbour plastic degrading genes: A metagenomic study of solid waste dumping site of Gujarat, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgyz Republic. Bishkek Solid Waste—Feasibility Study. Available online: https://www.ebrd.com/english/pages/project/eia/41712nts.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Consultancy for Up Stream Poverty and Social Impact Analysis (PSIA) for Egypt’s Solid Waste Management Reform. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/migration/eg/08_PSIA-Report_29122010-r.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Mumbai: Another fire at Deonar dumping ground, no casualties reported. The Indian Express, 27 March 2018. Available online: https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/mumbai/mumbai-another-fire-at-deonar-dumping-ground-no-casualties-reported-5112406/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Kruse, C.; Boyda, E.; Chen, S.; Karra, K.; Bou-Nahra, T.; Hammer, D.; Mathis, J.; Maddalene, T.; Jambeck, J.; Laurier, F. Satellite monitoring of terrestrial plastic waste. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0278997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


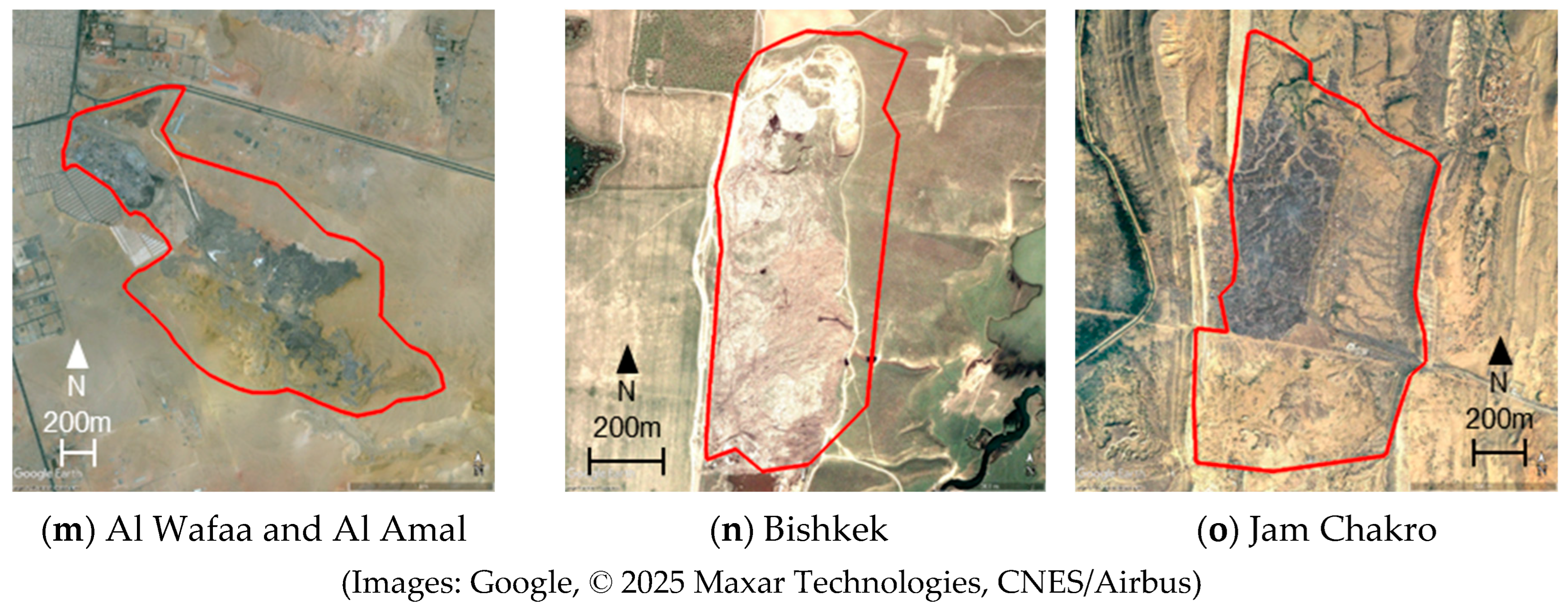





| Site Name | Observation Date and Time | |
|---|---|---|
| Oldest Image | Newest Image | |
| Ghazipur | 4 February 2001 05:54:02 | 5 May 2023 05:13:05 |
| Bhalswa | 4 February 2001 05:54:02 | 29 May 2023 05:13:02 |
| Okhla | 4 February 2001 05:54:02 | 5 May 2023 05:13:05 |
| Deonar | 27 March 2002 05:46:04 | 13 February 2023 05:34:04 |
| Mulund | 27 February 2001 06:02:04 | 25 January 2024 05:18:02 |
| Dhapa (active site) | 29 March 2000 05:10:02 | 5 April 2024 04:09:00 |
| Dhapa (closed site) | 29 March 2000 05:10:02 | 5 April 2024 04:09:00 |
| Kodungaiyur | 10 February 2004 05:16:03 | 26 May 2023 04:53:00 |
| Pirana | 6 March 2001 06:07:03 | 24 November 2022 05:39:04 |
| Al Akaider (Al-Ekaider) | 11 July 2001 08:36:02 | 18 August 2023 07:59:04 |
| Al Husaineyat (Mafraq FDS) | 1 May 2001 08:32:01 | 10 March 2024 07:50:04 |
| Oued Smar | 27 July 2000 10:51:04 | 19 August 2023 10:18:02 |
| Al Wafaa and Al Amal (El-wafaa and El-amal) | 10 August 2001 08:49:01 | 12 June 2023 08:13:03 |
| Bishkek (BSWL) | 26 May 2002 06:04:05 | 3 August 2018 05:58:04 |
| Jam Chakro | 28 October 2001 06:25:02 | 18 December 2023 05:45:01 |
| Site Name | RMS of Residuals (×106 m3) | Maximum Relative Change (×106 m3) | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghazipur | 0.861 | 5.715 | 0.15 |
| Bhalswa | 0.468 | 6.754 | 0.07 |
| Okhla | 1.009 | 5.107 | 0.20 |
| Deonar | 1.877 | 7.686 | 0.24 |
| Mulund | 0.764 | 5.486 | 0.14 |
| Dhapa (active site) | 3.890 | 8.380 | 0.46 |
| Dhapa (closed site) | 0.190 | 1.995 | 0.10 |
| Kodungaiyur | 1.129 | 4.409 | 0.26 |
| Pirana | 0.772 | 9.252 | 0.08 |
| Al Akaider | 1.015 | 4.125 | 0.25 |
| Al Husaineyat | 0.507 | 0.701 | 0.72 |
| Oued Smar | 0.967 | 10.34 | 0.09 |
| Al Wafaa and Al Amal | 6.509 | 19.38 | 0.34 |
| Bishkek | 1.406 | 1.824 | 0.77 |
| Jam Chakro | 2.906 | 7.337 | 0.40 |
| Site Name | Specified Date | Reported Value (×106 m3) | ASTER-Based Value (×106 m3) and Discrepancy with the Reported Value (%) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section 2.3.2. (1) | Section 2.3.2. (2) | ||||
| Ghazipur | 1 January 2008 | 5.00 | 5.75 (+15.0%) | 4.30 (−14.1%) | [89,90] |
| Bhalswa | 1 January 2019 | 8.80 | 9.22 (+4.8%) | 6.54 (−25.7%) | [89,91] |
| Okhla | 31 December 2003 | 2.36 | 2.38 (+0.8%) | 1.67 (−29.4%) | [89,92] |
| 31 December 2008 | 5.12 | 3.76 (−26.4%) | 3.05 (−40.3%) | [89,92,93] | |
| Deonar | 1 January 2014 | 18.9–11.9 | 7.06 (−62.6 to −40.6%) | 6.98 (−63.1 to −41.4%) | [73,94] |
| 1 January 2020 | 13.3–12.0 | 6.54 (−51.0 to −45.5%) | 9.19 (−31.1 to −23.5%) | [62,94] | |
| Mulund | 1 January 2015 | 5.35 | - | 4.79 (−10.5%) | [95] |
| 6 October 2018 | 7.00 | - | 5.31 (−24.1%) | [96] | |
| Dhapa (active site) | 1 October 2009 | 3.54 | - | 2.62 (−25.9%) | [97] |
| 1 January 2014 | 62.7 | - | 4.05 (−93.5%) | [98] | |
| Dhapa (closed site) | 1 January 2009 | 2.00 | - | 1.80 (−10.1%) | [66] |
| 1 October 2009 | 2.28 | - | 1.89 (−17.2%) | [97] | |
| Dhapa (active + closed sites) | 1 October 2009 | 5.79 | 5.51 (−4.8%) | 4.90 (−15.3%) | [97] |
| Kodungaiyur | 1 September 2021 | 6.40 | - | 6.31 (−1.4%) | [99] |
| 18 October 2021 | 6.40 | - | 6.36 (−0.7%) | [100] | |
| 10 May 2022 | 6.40 | - | 6.56 (+2.5%) | [101] | |
| Pirana | 1 January 2017 | 5.83–7.78 | 9.11 (+17.1 to +56.1%) | 6.00 (−22.9 to +2.9%) | [83,102] |
| Al Wafaa and Al Amal | 1 January 2021 | 42.3 | - | 24.3 (−42.6%) | [15] |
| Bishkek | 28 August 2009 | 26.0 | - | 1.40 (−94.6%) | [103] |
| Site Name | Reported Value (×103 m3/day) | ASTER-Based Value (×103 m3/day) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Day | Most Recent Day | |||
| Ghazipur | 1.67–2.08 | 1.35 | 0.0616 | [62,90,104] |
| Bhalswa | 1.25–2.67 | 1.46 | 0.198 | [53,104,105] |
| Okhla | 1.00–1.67 | 0.884 | 0.373 | [53,92] |
| Deonar | 3.00–7.58 | 1.01 | 1.01 | [62,94,106] |
| Mulund | 0.385–1.76 | 1.38 | −0.0751 | [107,108,109] |
| Dhapa (active site) | 2.33–7.50 | 0.610 | 1.30 | [84,96,98,110,111] |
| Dhapa (closed site) | 2.92–16.1 | 0.671 | −0.319 | [97,98,111] |
| Kodungaiyur | 1.82–5.14 | 0.186 | 1.07 | [67,100,112] |
| Pirana | 2.50–5.22 | 0.444 | 1.89 | [83,113,114] |
| Bishkek | 3.01–5.17 | 0.560 | 0.462 | [103,115] |
| Site Name | DCM Dates | DCM Valid Pixel Rate (%) | Daily Volume Change (×103 m3/day) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCM1 | DCM2 | Period (Days) | DCM | ASTER | Difference | ||
| Bhalswa | 10 April 2019 | 30 July 2021 | 842 | 76.9 | 0.570 | 0.367 | 0.203 |
| Okhla | 16 December 2018 | 30 July 2021 | 957 | 94.5 | −3.13 | 0.444 | −3.57 |
| Deonar | 4 April 2019 | 7 July 2021 | 825 | 51.1 | 0.418 | 1.01 | −0.589 |
| Mulund | 4 April 2019 | 7 July 2021 | 825 | 68.0 | −0.465 | 0.159 | −0.624 |
| Kodungaiyur | 4 March 2019 | 28 June 2021 | 847 | 56.8 | 0.858 | 0.926 | −0.0681 |
| Bishkek | 19 July 2018 | 4 November 2019 | 473 | 65.0 | 0.855 | 1.47 | −0.616 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muto, M.; Tonooka, H. Monitoring Long-Term Waste Volume Changes in Landfills in Developing Countries Using ASTER Time-Series Digital Surface Model Data. Sensors 2025, 25, 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103173
Muto M, Tonooka H. Monitoring Long-Term Waste Volume Changes in Landfills in Developing Countries Using ASTER Time-Series Digital Surface Model Data. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103173
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuto, Miyuki, and Hideyuki Tonooka. 2025. "Monitoring Long-Term Waste Volume Changes in Landfills in Developing Countries Using ASTER Time-Series Digital Surface Model Data" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103173
APA StyleMuto, M., & Tonooka, H. (2025). Monitoring Long-Term Waste Volume Changes in Landfills in Developing Countries Using ASTER Time-Series Digital Surface Model Data. Sensors, 25(10), 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103173







