Spatial–Temporal Heatmap Masked Autoencoder for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce a streamlined and effective method for masked autoencoder in skeleton-based action recognition, emphasizing the acquisition of comprehensive and adaptable representations through the masking and reconstruction of skeleton sequences.
- We present a spatial–temporal heatmap as the primary representation of skeletons, enhancing robustness in pose estimation and capitalizing on recent advancements in Visual Transformers.
- Our model underwent extensive evaluation on the NTU RGB+D 60 and NTU RGB+D 120 datasets. Experimental results indicate that STH-MAE achieves state-of-the-art performance in self-supervised settings.
2. Related Works
2.1. Self-Supervised Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
2.2. Masked Autoencoder
2.3. Pose Estimation Heatmap
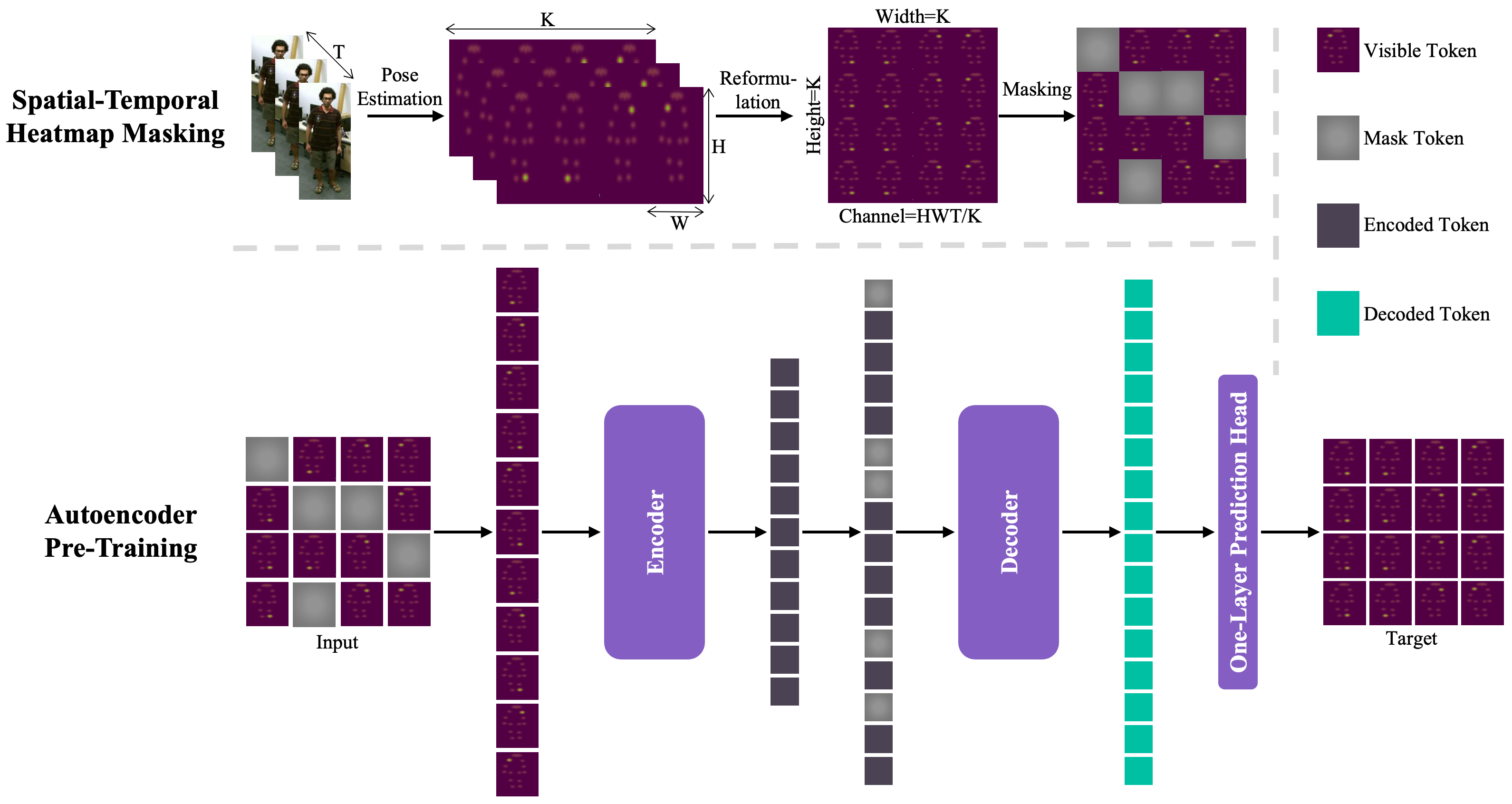
3. Proposed Method
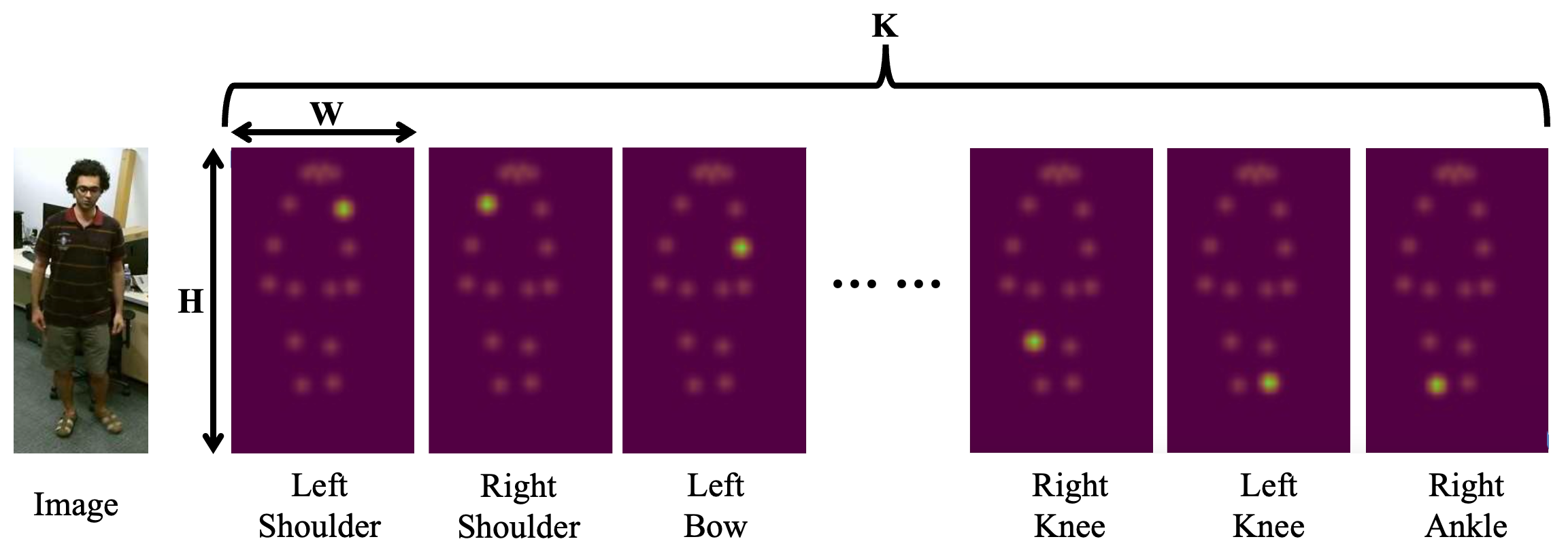
3.1. Spatial–Temporal Heatmap Masking
3.2. Autoencoder Pre-Training
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
- NTU RGB+D 60 (NTU 60) is an extensive dataset designed specifically for the recognition of human actions based on skeletal data. It consists of 56,578 video sequences covering 60 different action categories, with each human figure represented by 25 joints. This dataset includes two standard benchmark protocols: Cross-Subject (X-Sub) and Cross-View (X-View).
- NTU RGB+D 120 (NTU 120), an extension of NTU 60, provides a larger dataset with 113,945 sequences encompassing 120 action labels. It also incorporates two benchmark protocols: Cross-Subject (X-Sub) and Cross-Set (X-Set). For these datasets, the estimation of 2D heatmaps for human joints is performed using HRNet [55] on sequences of RGB frames.
4.2. Evaluation Protocol
- Linear Evaluation Protocol: The models were evaluated using a linear evaluation approach for the action recognition task. This involves training a linear classifier (comprising a fully-connected layer followed by a softmax layer) with the encoder weights fixed.
- Semi-supervised Evaluation Protocol: The encoder is pre-trained using the entire dataset and then the whole model is finetuned with only 1% or 10% randomly selected labeled data.
- Finetune Evaluation Protocol: In this protocol, a linear classifier is appended to the pre-trained encoder, and the entire model is fine-tuned to compare its performance with fully supervised methods.
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Comparison with State-of-the-Art
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Kuang, Z.; Sheng, L.; Ouyang, W.; Zhang, W. Optical flow guided feature: A fast and robust motion representation for video action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Ke, Q.; Rahmani, H.; Bennamoun, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Human action recognition from various data modalities: A review. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 3200–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Learning discriminative representations for skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–22 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Koniusz, P. 3mformer: Multi-order multi-mode transformer for skeletal action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–22 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, C.; Feng, W.; Wan, L.; Wang, S. Structural knowledge distillation for efficient skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2963–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, K.; Lin, D.; Dai, B. Revisiting skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bavil, A.F.; Damirchi, H.; Taghirad, H.D. Action Capsules: Human skeleton action recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2023, 233, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Cook, C.; Zhu, C.; Gao, Y. Independently recurrent neural network (indrnn): Building a longer and deeper rnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UR, USA, 19–21 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L. Beyond joints: Learning representations from primitive geometries for skeleton-based action recognition and detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4382–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Li, B.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W. Channel-wise topology refinement graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, C.; Wang, L. Constructing stronger and faster baselines for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1474–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Bian, Y.; Jiang, M. MTT: Multi-scale temporal transformer for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Wen, J.; Liu, R.; Long, L.; Dai, J.; Gong, Z. Unsupervised representation learning with long-term dynamics for skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.; Liu, X.; Shlizerman, E. Predict & cluster: Unsupervised skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, C.; Feng, W.; Wang, S. Self-supervised representation learning for skeleton-based group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, C.; Feng, W.; Meng, F.; Wang, S. Global–local contrastive multiview representation learning for skeleton-based action recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2023, 229, 103655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Roy, A.; Shah, K.; Mishra, S.; Jacobs, D.; Cherian, A.; Chellappa, R. Halp: Hallucinating latent positives for skeleton-based self-supervised learning of actions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–22 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, B.; Sun, Q.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y. Eva: Exploring the limits of masked visual representation learning at scale. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–22 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Yu, X.; Huang, W.; Fang, G.; Lu, H. DMMG: Dual min-max games for self-supervised skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 33, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Song, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Ms2l: Multi-task self-supervised learning for skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Rao, H.; Hu, X.; Cheng, J.; Hu, B. Prototypical contrast and reverse prediction: Unsupervised skeleton based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 25, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Lu, S.; Er, M.H.; Kot, A.C. Skeleton cloud colorization for unsupervised 3d action representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, M.; Ni, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. 3d human action representation learning via cross-view consistency pursuit. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, T.; Ding, R. Contrastive learning from extremely augmented skeleton sequences for self-supervised action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22–28 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, J. Hierarchical consistent contrastive learning for skeleton-based action recognition with growing augmentations. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, C.; Lu, A.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Wu, S. Part aware contrastive learning for self-supervised action recognition. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 19–25 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, T.; Chen, Z.; Song, P.; Tang, H. Contrastive learning from spatio-temporal mixed skeleton sequences for self-supervised skeleton-based action recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.03065. [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti, G.; Cavazza, J.; Beyan, C.; Del Bue, A. Unsupervised human action recognition with skeletal graph laplacian and self-supervised viewpoints invariance. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Virtual, 22–15 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, M.; Gregor, K.; Murray, I.; Larochelle, H. Made: Masked autoencoder for distribution estimation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Bae, J.; He, J.; Samaras, D.; Prasanna, P. Self pre-training with masked autoencoders for medical image analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05573. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.; Liu, H.; Lee, L.; Schuurmans, D.; Levine, S.; Abbeel, P. Multimodal masked autoencoders learn transferable Representations. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Pre-Training: Perspectives, Pitfalls, and Paths Forward at ICML, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Song, J.; Yi, J.S.K.; Zhang, K.; Kweon, I.S. A survey on masked autoencoder for self-supervised learning in vision and beyond. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.00173. [Google Scholar]
- Radosavovic, I.; Xiao, T.; James, S.; Abbeel, P.; Malik, J.; Darrell, T. Real-world robot learning with masked visual pre-training. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Tang, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Bai, L.; Zhao, R.; Ouyang, W. Domain invariant masked autoencoders for self-supervised learning from multi-domains. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Grover, A.; Abbeel, P. Masked autoencoding for scalable and generalizable decision making. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, C.J.; Gupta, R.; Li, S.; Brockman, S.; Funk, C.; Clipp, B.; Keutzer, K.; Candido, S.; Uyttendaele, M.; Darrell, T. Scale-mae: A scale-aware masked autoencoder for multiscale geospatial representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Videomae v2: Scaling video masked autoencoders with dual masking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Hua, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, C.; Lu, A. Skeletonmae: Spatial-temporal masked autoencoders for self-supervised skeleton action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops, Brisbane, Australia, 10–14 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Feng, J.; Jiang, M. SSA Net: Small scale-aware enhancement network for human pose estimation. Sensors 2023, 23, 7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Dai, H.; Ye, M.; Zhu, C. Distribution-aware coordinate representation for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Song, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Mo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, B.; Jin, W. Error compensation heatmap decoding for human pose estimation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 114514–114522. [Google Scholar]
- McNally, W.; Vats, K.; Wong, A.; McPhee, J. Rethinking keypoint representations: Modeling keypoints and poses as objects for multi-person human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.; Yang, L.; Yao, A. Removing the bias of integral pose regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Wang, K.; Saenko, K.; Betke, M.; Sclaroff, S. A unified framework for domain adaptive pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Hong, C.; Han, Y.; Huang, P.; Zhuang, Y. Mh pose: 3d human pose estimation based on high-quality heatmap. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Virtual, 15–18 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Chen, H.; Ding, Y. Spatial-temporal characteristics of drought detected from meteorological data with high resolution in Shaanxi Province, China. J. Arid Land 2020, 12, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, H.; Wang, G.; Tang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. Monitoring industrial control systems via spatio-temporal graph neural networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, K.; Liang, P.; Qian, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shao, W.; Ding, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, Q. Imitation with spatial-temporal heatmap: 2nd place solution for nuplan challenge. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.15700. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 26 April–1 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, H.; Xu, S.; Hu, X.; Cheng, J.; Hu, B. Augmented skeleton based contrastive action learning with momentum lstm for unsupervised action recognition. Inf. Sci. 2021, 569, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Unsupervised 3d human pose representation with viewpoint and pose disentanglement. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, H. Cmd: Self-supervised 3d action representation learning with cross-modal mutual distillation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Duan, H.; Rao, A.; Su, B.; Wang, J. Self-supervised action representation learning from partial spatio-temporal skeleton sequences. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, L.; Mandica, P.; Munjal, B.; Galasso, F. HYperbolic self-paced learning for self-supervised skeleton-based action representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Actionlet-dependent contrastive learning for unsupervised skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Hou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Gao, J. Global and local contrastive learning for self-supervised skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 10578–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, C.; Nie, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Tan, T.; Feng, J. Adversarial self-supervised learning for semi-supervised 3d action recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Lin, G.; Wu, Q. Self-supervised 3d skeleton action representation learning with motion consistency and continuity. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Thoker, F.M.; Doughty, H.; Snoek, C.G. Skeleton-contrastive 3D action representation learning. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 20–24 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, J.; Tian, Y.; Xia, Z.; Geng, S.; Han, L.; Metaxas, D.N. Hierarchically self-supervised transformer for human skeleton representation learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
| Masking Ratio | 0.55 | 0.75 | 0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top1 | 82.84 | 84.31 | 78.65 |
| Top5 | 96.08 | 98.33 | 95.24 |
| Resolution | 4 × 4 | 8 × 8 | 16 × 16 | 32 × 32 | 48 × 48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top1 | 82.68 | 84.31 | 81.98 | 78.42 | 71.03 |
| Top5 | 97.97 | 98.33 | 97.85 | 96.97 | 94.60 |
| Depth | 4 | 8 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top1 | 82.90 | 84.31 | 83.47 |
| Top5 | 98.23 | 98.33 | 98.19 |
| Pre-Training Epoch | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top1 | 70.01 | 79.82 | 83.22 | 84.21 | 84.31 |
| Top5 | 94.45 | 97.53 | 98.15 | 98.36 | 98.33 |
| Method | Year | NTU 60 | NTU120 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | CV | X-Sub | X-Set | ||
| LongT GAN [16] | AAAI18 | 39.1 | 48.1 | - | - |
| MS2L [24] | ACM MM20 | 52.6 | - | - | - |
| AS-CAL [56] | IS21 | 58.5 | 64.8 | 48.6 | 49.2 |
| P&C [17] | CVPR20 | 50.7 | 76.3 | 42.7 | 41.7 |
| SeBiReNet [57] | ECCV20 | - | 79.7 | - | - |
| SkeletonCLR [27] | CVPR21 | 75.0 | 79.8 | 60.7 | 62.6 |
| Colorization [26] | ICCV21 | 75.2 | 83.1 | - | - |
| CrossSCLR [27] | CVPR21 | 77.8 | 83.4 | 67.9 | 67.1 |
| AimCLR [28] | AAAI22 | 78.9 | 83.8 | 68.2 | 68.8 |
| CMD [58] | ECCV22 | 79.8 | 86.9 | 70.3 | 71.5 |
| PSTL [59] | AAAI23 | 79.1 | 83.8 | 69.2 | 70.3 |
| HiCRL [29] | AAAI23 | 80.4 | 85.5 | 70.0 | 70.4 |
| HaLP [20] | CVPR23 | 79.7 | 86.8 | 71.1 | 72.2 |
| HYSP [60] | ICLR23 | 78.2 | 82.6 | 61.8 | 64.6 |
| ActCLR [61] | CVPR23 | 80.9 | 86.7 | 69.0 | 70.5 |
| skeleton-logoCLR [62] | TSCVT24 | 82.4 | 87.2 | 72.8 | 73.5 |
| STH-MAE (Ours) | - | 84.3 | 87.0 | 74.3 | 75.6 |
| Method | Year | NTU 60 | NTU120 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | CV | X-Sub | X-Set | ||
| SkeletonCLR [27] | CVPR21 | 82.2 | 88.9 | 73.6 | 75.3 |
| AimCLR [28] | AAAI22 | 83.0 | 89.2 | 76.4 | 76.7 |
| SkeletonMAE [43] | ICMEW23 | 86.6 | 92.9 | 76.8 | 79.1 |
| HYSP [60] | ICLR23 | 86.5 | 93.5 | 81.4 | 82.0 |
| ActCLR [61] | CVPR23 | 85.8 | 91.2 | 79.4 | 80.9 |
| skeleton-logoCLR [62] | TSCVT24 | 86.1 | 93.6 | 79.2 | 80.0 |
| STH-MAE (Ours) | - | 89.8 | 94.9 | 80.1 | 83.5 |
| Method | Year | 1% Data | 10% Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | CV | CS | CV | ||
| LongT GAN [16] | AAAI 2018 | 35.2 | - | 62.0 | - |
| ASSL [63] | ECCV 2020 | - | - | 64.3 | 69.8 |
| MS2L [24] | ACM MM 2020 | 31.1 | - | 65.2 | - |
| MCC [64] | ICCV 2021 | - | - | 60.8 | 65.8 |
| Skeleton-Contrastive [65] | ACM MM 2021 | 35.7 | 38.1 | 65.9 | 72.5 |
| Hi-TRS [66] | ECCV 2022 | 39.1 | 42.9 | 70.7 | 74.8 |
| STH-MAE (Ours) | - | 39.8 | 39.4 | 74.5 | 77.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Lu, W. Spatial–Temporal Heatmap Masked Autoencoder for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Sensors 2025, 25, 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103146
Bian C, Yang Y, Wang T, Lu W. Spatial–Temporal Heatmap Masked Autoencoder for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103146
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Cunling, Yang Yang, Tao Wang, and Weigang Lu. 2025. "Spatial–Temporal Heatmap Masked Autoencoder for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103146
APA StyleBian, C., Yang, Y., Wang, T., & Lu, W. (2025). Spatial–Temporal Heatmap Masked Autoencoder for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Sensors, 25(10), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103146






