Retrieval of Surface Soil Moisture at Field Scale Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Study Area and Dataset
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oh, Y.; Sarab, I.K.; Ulaby, F.T. An empirical model and an inversion technique for radar scattering from bare soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdhuber, T.; Hajnsek, I.; Bronstert, A.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Soil moisture estimation under low vegetation cover using a multi-angular polarimetric decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 2201–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; McCabe, M.F. Retrieval of high-resolution soil moisture through combination of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Xing, M.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Shang, J.; Huang, X.; Ni, X. Retrieving soil moisture over soybean fields during growing season through polarimetric decomposition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, P.C.; Van Zyl, J.; Engman, T. Measuring soil moisture with imaging radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.S. Backscattering from a randomly rough dielectric surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Chen, K.S.; Wu, T.D.; Lee, J.S.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.C. Extension of advanced integral equation model for calculations of fully polarimetric scattering coefficient from rough surface. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–27 July 2007; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, Y. Quantitative retrieval of soil moisture content and surface roughness from multipolarized radar observations of bare soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Saba, E.; Aubert, M.; Zribi, M.; Baup, F. Evaluation of radar backscattering models IEM, Oh, and Dubois for SAR data in X-band over bare soils. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciera, R.; Tanase, M.A.; Lowell, K.; Walker, J.P. Evaluation of IEM, Dubois, and Oh radar backscatter models using airborne L-band SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 4966–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choker, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; El Hajj, M.; Paloscia, S.; Verhoest, N.E.; Lievens, H.; Mattia, F. Evaluation of the Oh, Dubois and IEM backscatter models using a large dataset of SAR data and experimental soil measurements. Water 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hsu, A.; Shi, J.; O’neill, P.; Engman, E. A comparison of soil moisture retrieval models using SIR-C measurements over the Little Washita River watershed. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Méric, S.; Allain, S.; Pottier, E. Adaptation of Oh Model for soil parameters retrieval using multi-angular RADARSAT-2 datasets. J. Surv. Mapp. Eng. 2014, 2, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- De Roo, R.D.; Du, Y.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C. A semi-empirical backscattering model at L-band and C-band for a soybean canopy with soil moisture inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attema, E.; Ulaby, F.T. Vegetation modeled as a water cloud. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogapurapu, N.; Dey, S.; Mandal, D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Karthikeyan, L.; McNairn, H.; Rao, Y. Soil moisture retrieval over croplands using dual-pol L-band GRD SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.; Notarnicola, C.; Campo-Bescós, M.Á.; Arregui, L.M.; Álvarez-Mozos, J. Evaluation of soil moisture estimation techniques based on Sentinel-1 observations over wheat fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; Freeman, V.; Cao, S.; Paulik, C.; Schaufler, S.; Stachl, T.; Modanesi, S.; Massari, C.; Ciabatta, L.; Brocca, L.; et al. Toward global soil moisture monitoring with Sentinel-1: Harnessing assets and overcoming obstacles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenzano, A.; Mattia, F.; Satalino, G.; Lovergine, F.P.; Palmisano, D.; Peng, J.; Marzahn, P.; Wegmüller, U.; Cartus, O.; Dąbrowska-Zielińska, K.; et al. Sentinel-1 soil moisture at 1 km resolution: A validation study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 263, 112554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogapurapu, N.; Dey, S.; Homayouni, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Rao, Y.S. Field-scale soil moisture estimation using sentinel-1 GRD SAR data. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 3845–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasolli, L.; Notarnicola, C.; Bruzzone, L. Estimating soil moisture with the support vector regression technique. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Gupta, D.K.; Kumar, P.; Prasad, R.; Pandey, D.K.; Das, A.K.; Gupta, M. Machine learning algorithms for soil moisture estimation using Sentinel-1: Model development and implementation. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 1799–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Tan, M.L.; Li, L.; Zhang, F. Comparison of three machine learning algorithms for retrieving soil moisture information from Sentinel-1A SAR data in northwest Shandong plain, China. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Cresson, R.; El Hajj, M.; Ludwig, R.; La Jeunesse, I. Estimation of soil parameters over bare agriculture areas from C-band polarimetric SAR data using neural networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogapurapu, N.; Dey, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; López-Martínez, C.; Hajnsek, I.; Rao, Y.S. Soil Permittivity Estimation Over Croplands Using Full and Compact Polarimetric SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Noll, J.; Borgeaud, M.; Rott, H. Monitoring soil moisture over the Canadian Prairies with the ERS scatterometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenzano, A.; Mattia, F.; Satalino, G.; Davidson, M.W. Dense temporal series of C-and L-band SAR data for soil moisture retrieval over agricultural crops. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynen, J.R. A Revisitation of the Phenomenological Approach with Applications to Radar Target Decomposition; University of Illinois at Chicago: Chicago, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Van Zyl, J.J. Unsupervised classification of scattering behavior using radar polarimetry data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1989, 27, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, W.A.; Barnes, R.M. On radar polarization mixed target state decomposition techniques. In Proceedings of the 1988 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 20–21 April 1988; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, A.; Durden, S.L. Three-component scattering model to describe polarimetric SAR data. In Proceedings of the Radar Polarimetry, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–24 July 1992; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 1748, pp. 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Krogager, E. Danmarks Tekniske Hojskole. In Aspects of Polarimetric Radar Imaging; Lingby, D., Establishment, D.D.R., Eds.; Danish Defence Research Establishment: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Yajima, Y.; Yamada, H. A four-component decomposition of POLSAR images based on the coherency matrix. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arii, M.; van Zyl, J.J.; Kim, Y. A general characterization for polarimetric scattering from vegetation canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Ferro-Famil, L. Extraction of particle and orientation distribution characteristics from polarimetric SAR data. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010; VDE: Offenbach am Main, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Schon, H.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Potential of estimating soil moisture under vegetation cover by means of PolSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Frery, A.C.; López-Martínez, C.; Rao, Y.S. A model-free four component scattering power decomposition for polarimetric SAR data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth. Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3887–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; Pottier, E. Quantitative comparison of classification capability: Fully polarimetric versus dual and single-polarization SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Gunn, G.; Joosse, P.; Russell, H.A. A model for downscaling SMOS soil moisture using Sentinel-1 SAR data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 72, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Entekhabi, D. On the synergy of SMAP, AMSR2 AND SENTINEL-1 for retrieving soil moisture. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 65, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, W.; Meng, L. An approach for downscaling SMAP soil moisture by combining Sentinel-1 SAR and MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornacek, M.; Wagner, W.; Sabel, D.; Truong, H.L.; Snoeij, P.; Hahmann, T.; Diedrich, E.; Doubková, M. Potential for high resolution systematic global surface soil moisture retrieval via change detection using Sentinel-1. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N. Synergetic use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data for soil moisture mapping at 100 m resolution. Sensors 2017, 17, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, S.; Deng, K.A.K.; Petropoulos, G.P. Surface soil moisture retrievals over partially vegetated areas from the synergy of Sentinel-1 and Landsat 8 data using a modified water-cloud model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 72, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Crow, W.T.; Wagner, W.; Zhao, T. Effect of vegetation index choice on soil moisture retrievals via the synergistic use of synthetic aperture radar and optical remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 80, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogapurapu, N.; Dey, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Mandal, D.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; McNairn, H.; López-Martínez, C.; Rao, Y.S. Dual-polarimetric descriptors from Sentinel-1 GRD SAR data for crop growth assessment. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Fedosejevs, G.; Tiscareño-LóPez, M.; Arnold, J.G. Assessment of MODIS-EVI, MODIS-NDVI and VEGETATION-NDVI composite data using agricultural measurements: An example at corn fields in western Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 119, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Santi, E.; Notarnicola, C.; Pasolli, L.; Reppucci, A. Soil moisture mapping using Sentinel-1 images: Algorithm and preliminary validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Jung, C.; Kim, S. Soil moisture content estimation based on Sentinel-1 SAR imagery using an artificial neural network and hydrological components. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gaurav, K. Deep learning and data fusion to estimate surface soil moisture from multi-sensor satellite images. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, J. Soil moisture retrieval in farmland areas with sentinel multi-source data based on regression convolutional neural networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep learning in remote sensing: A comprehensive review and list of resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Hu, Y.; Hu, X.; Song, W.; Wang, L. A comprehensive study of deep learning for soil moisture prediction. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2023, 2023, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, L.; Cloude, S.R.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. Model-Based Decomposition of Dual-Pol SAR Data: Application to Sentinel-1. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Bhogapurapu, N.; Hajnsek, I.; Bhattacharya, A.; Siqueira, P. Soil permittivity estimation over vegetative fields using dual polarimetric SAR data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 33, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.G.; Oh, Y.; Shoshany, M. Soil Moisture Mapping Along Climatic Gradient by Dual-Polarization Sentinel-1 C-Band Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Song, J.; Teng, Y.; Song, X.; Zeng, P.; Jia, J. Coupling model-driven and data-driven methods for estimating soil moisture over bare surfaces with Sentinel-1A dual-polarized data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 4820–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.G.; Shoshany, M.; Oh, Y. Polarimetric radar vegetation index for biomass estimation in desert fringe ecosystems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 7102–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, I.; Penuelas, J.; Llorens, L.; Estiarte, M. Reflectance assessment of seasonal and annual changes in biomass and CO2 uptake of a Mediterranean shrubland submitted to experimental warming and drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.; Hartge, K. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1, Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Klute, A., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, D. Soil Series of West Bengal; National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning: Nagpur, Maharashtra, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, S.; Debnath, S.; Das, A.; Biswas, A.; Weindorf, D.C.; Li, B.; Shukla, A.K.; Das, S.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, S. Developing regional soil micronutrient management strategies through ensemble learning based digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2023, 433, 116457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Digital image enhancement and noise filtering by use of local statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1980, PAMI-2, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Meyer, D. Study of high SAR backscattering caused by an increase of soil moisture over a sparsely vegetated area: Implications for characteristics of backscattering. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; He, B.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Su, Z. First assessment of Sentinel-1A data for surface soil moisture estimations using a coupled water cloud model and advanced integral equation model over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shang, J.; Vachon, P.W.; McNairn, H. Multiyear crop monitoring using polarimetric RADARSAT-2 data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 2227–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

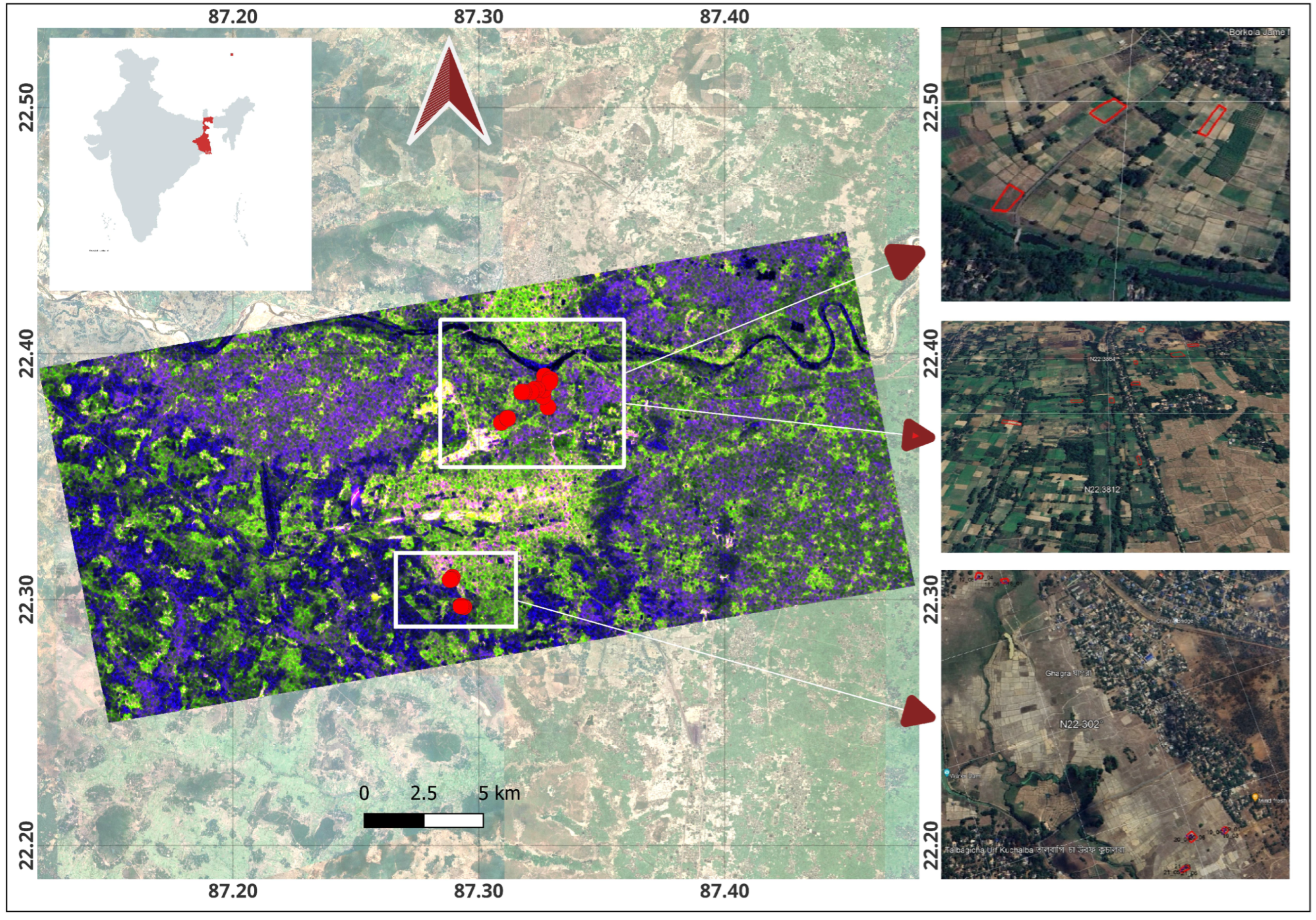


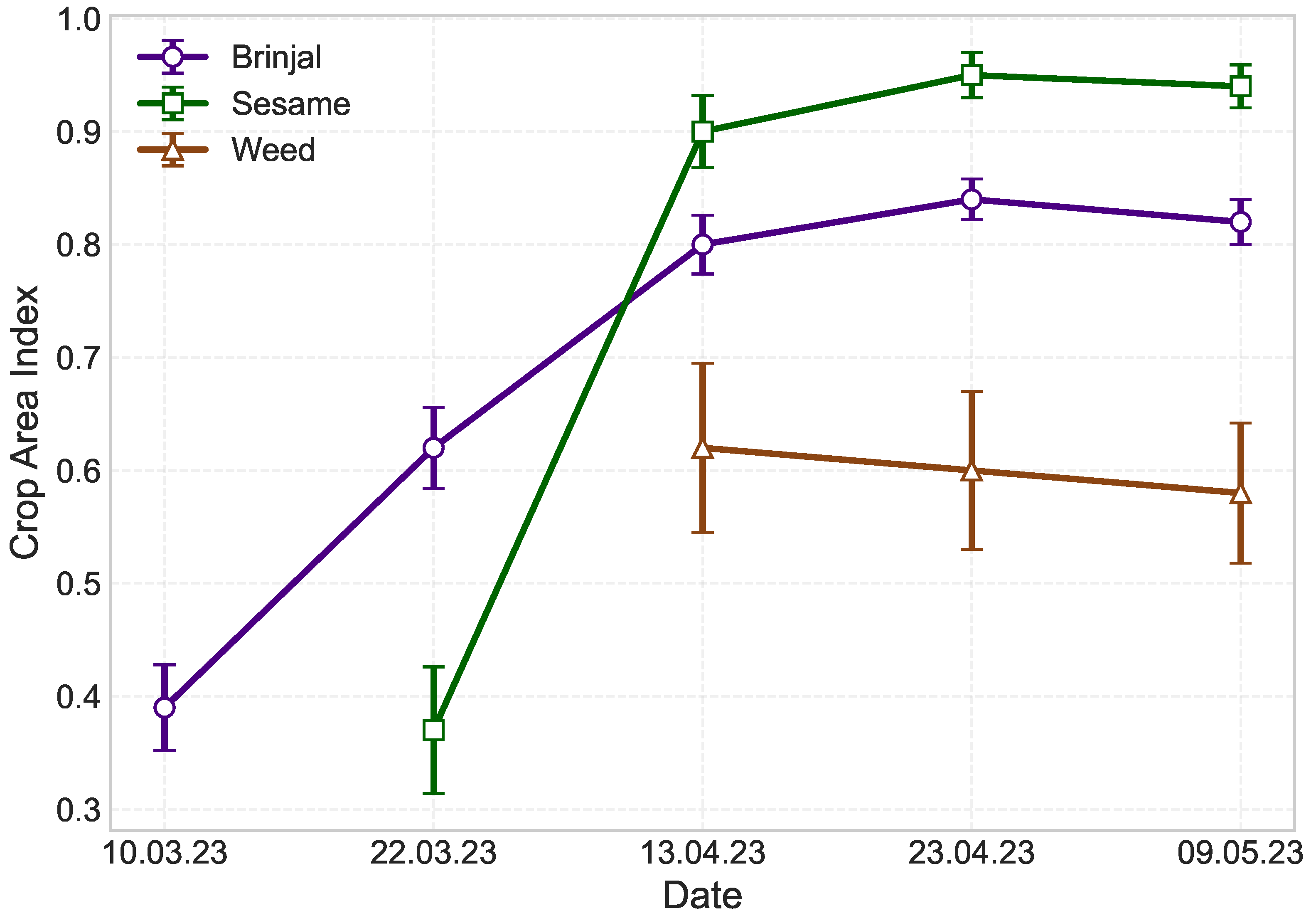
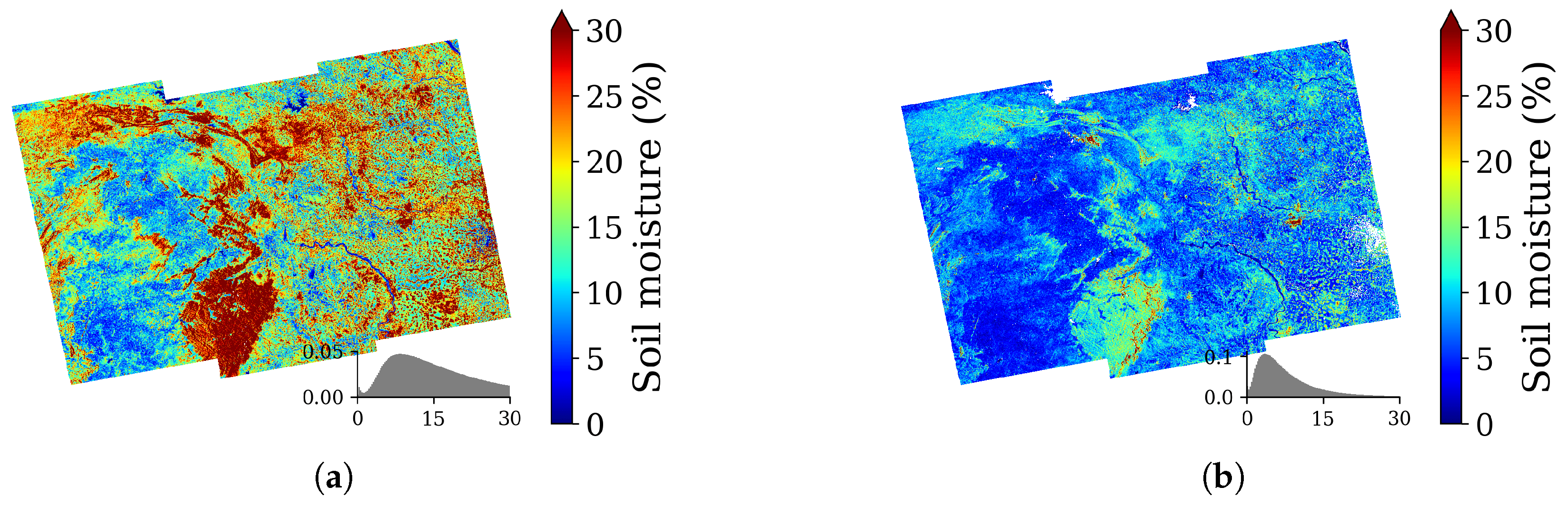
| Acquisition Date | Beam Mode | Incidence Angle Range (Deg.) | Orbit | rg (m) × az (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 March 2023 | IW | 42.2–46.1 | Ascending | 13 × 14 |
| 22 March 2023 | IW | 41.6–46.0 | Ascending | 13 × 14 |
| 03 April 2023 | IW | 41.9–46.1 | Ascending | 13 × 14 |
| 13 April 2023 | IW | 38.1–42.2 | Descending | 13 × 14 |
| 15 April 2023 | IW | 41.9–46.1 | Ascending | 13 × 14 |
| 25 April 2023 | IW | 38.1–42.3 | Descending | 13 × 14 |
| 27 April 2023 | IW | 41.7–46.1 | Ascending | 13 × 14 |
| 07 May 2023 | IW | 40.1–42.1 | Descending | 13 × 14 |
| 09 May 2023 | IW | 42.3–44.5 | Ascending | 13 × 14 |
| 19 May 2023 | IW | 38.1–41.7 | Descending | 13 × 14 |
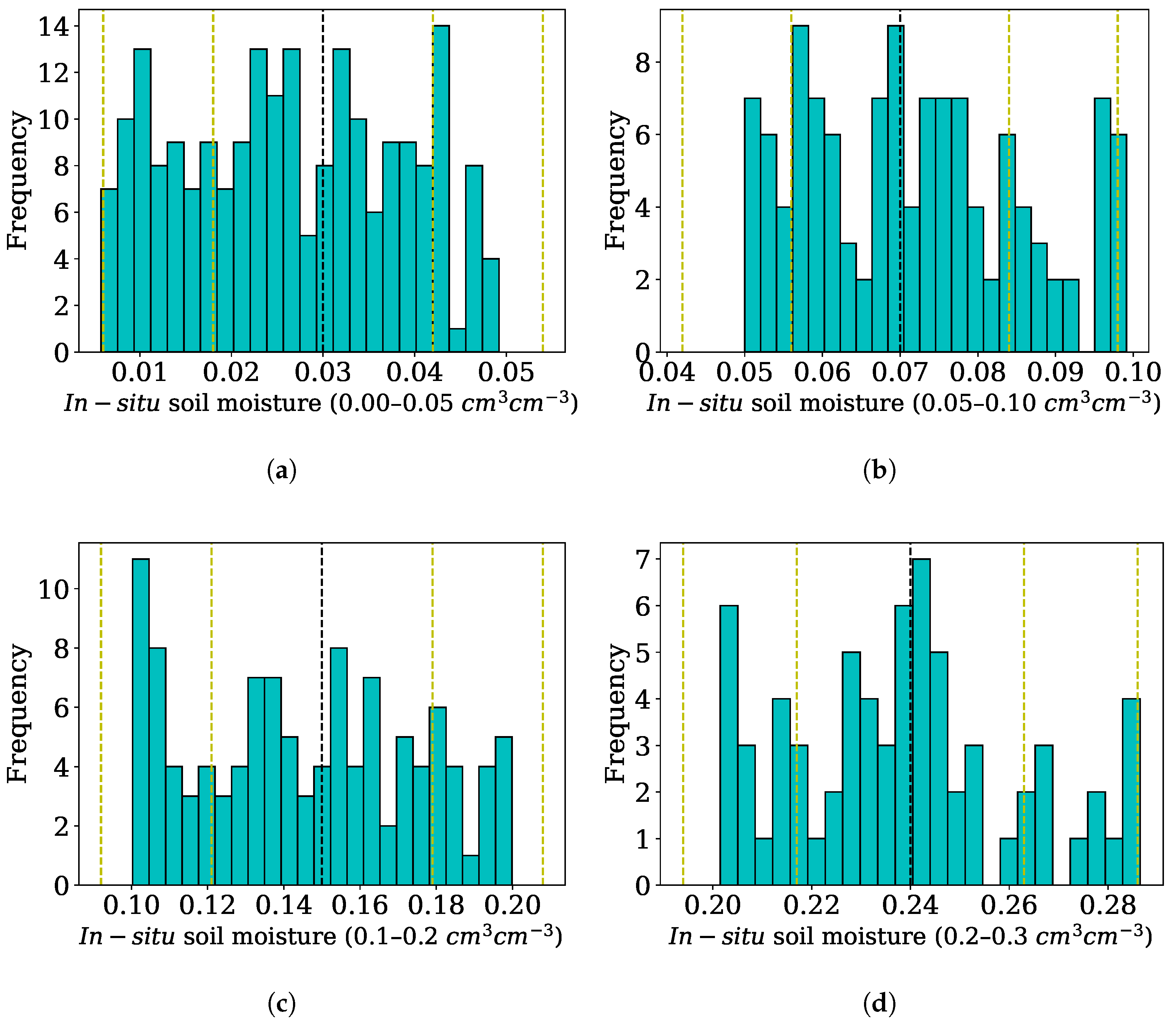
| Soil Moisture Range | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–4.9% | 0.030043 ± 0.017466 | −0.000262 ± 0.002927 | −0.000390 ± 0.002677 | 0.007928 ± 0.006652 |
| 5–9.9% | 0.038554 ± 0.016041 | 0.000319 ± 0.003465 | −0.000109 ± 0.003037 | 0.009798 ± 0.004416 |
| 10–19.9% | 0.038862 ± 0.015381 | −0.000179 ± 0.002856 | −0.000140 ± 0.003620 | 0.009453 ± 0.003810 |
| 20–30% | 0.039420 ± 0.017366 | −0.000501 ± 0.003349 | −0.001172 ± 0.002923 | 0.009023 ± 0.004134 |
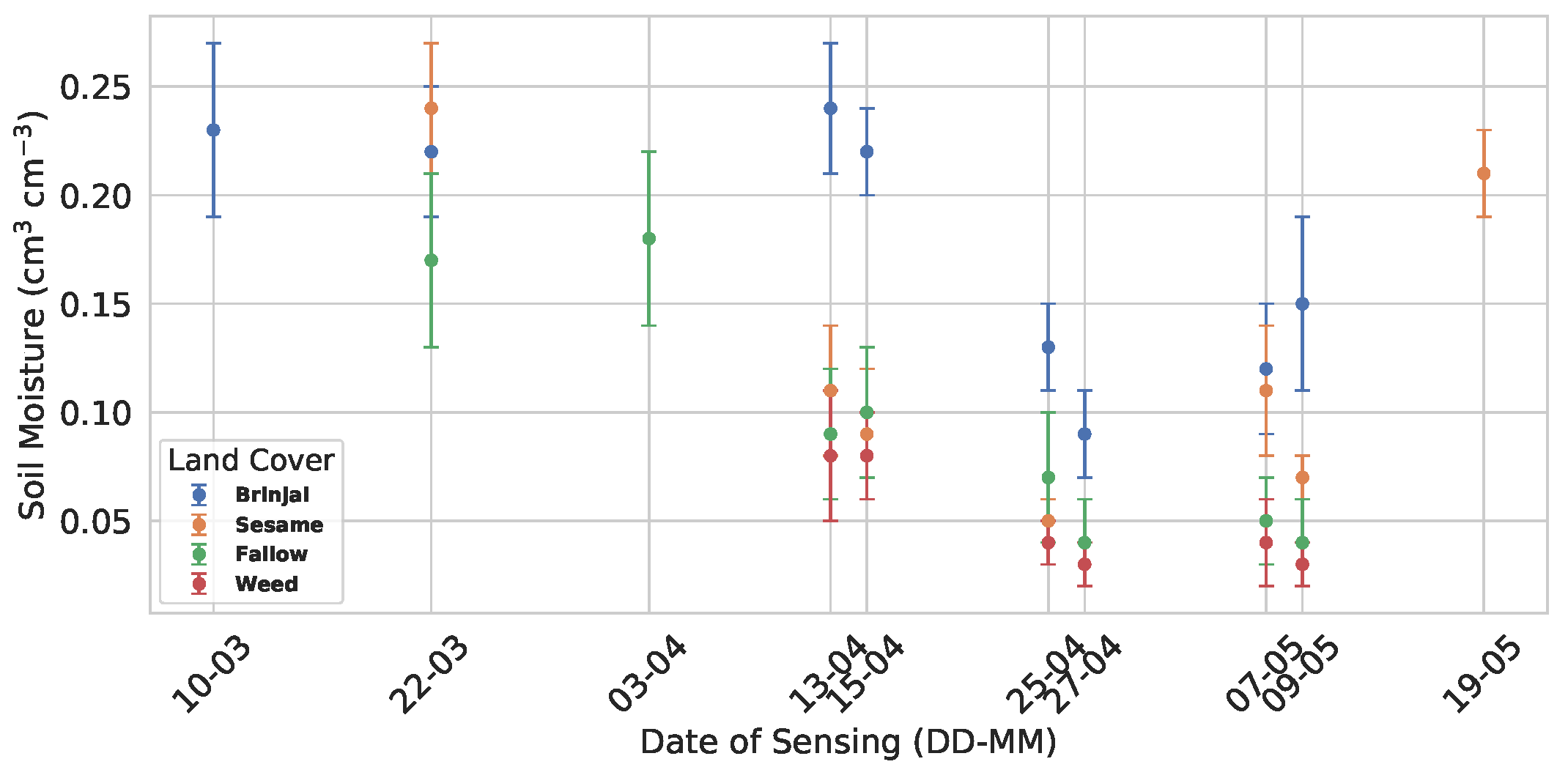
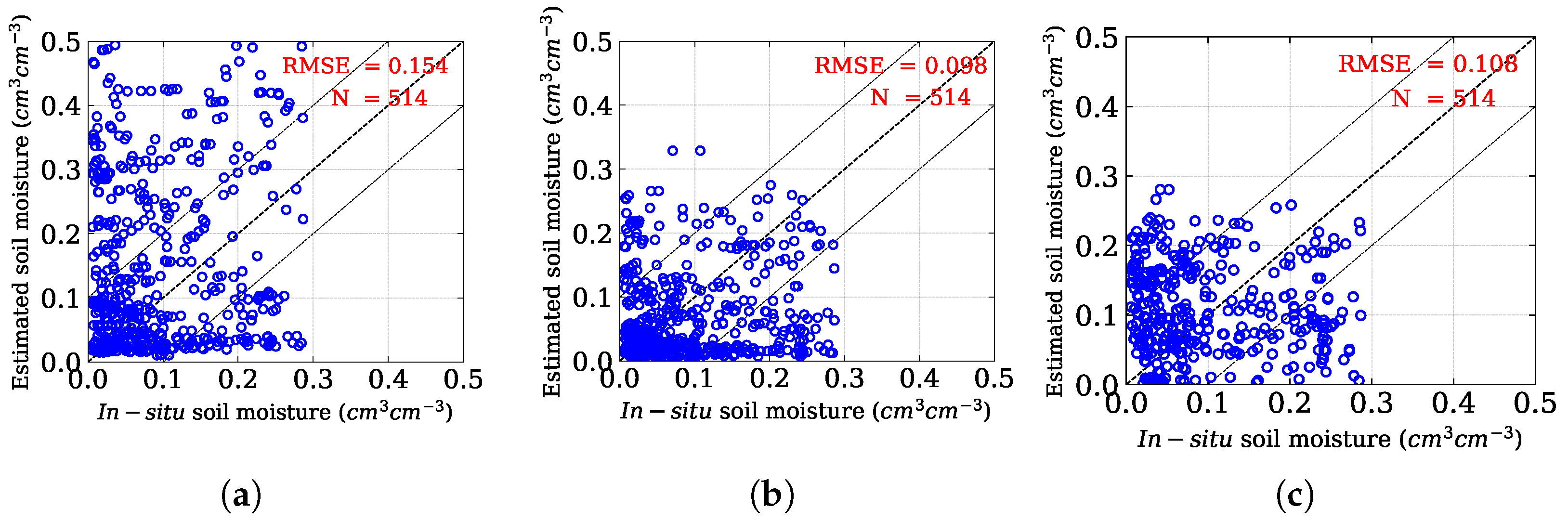
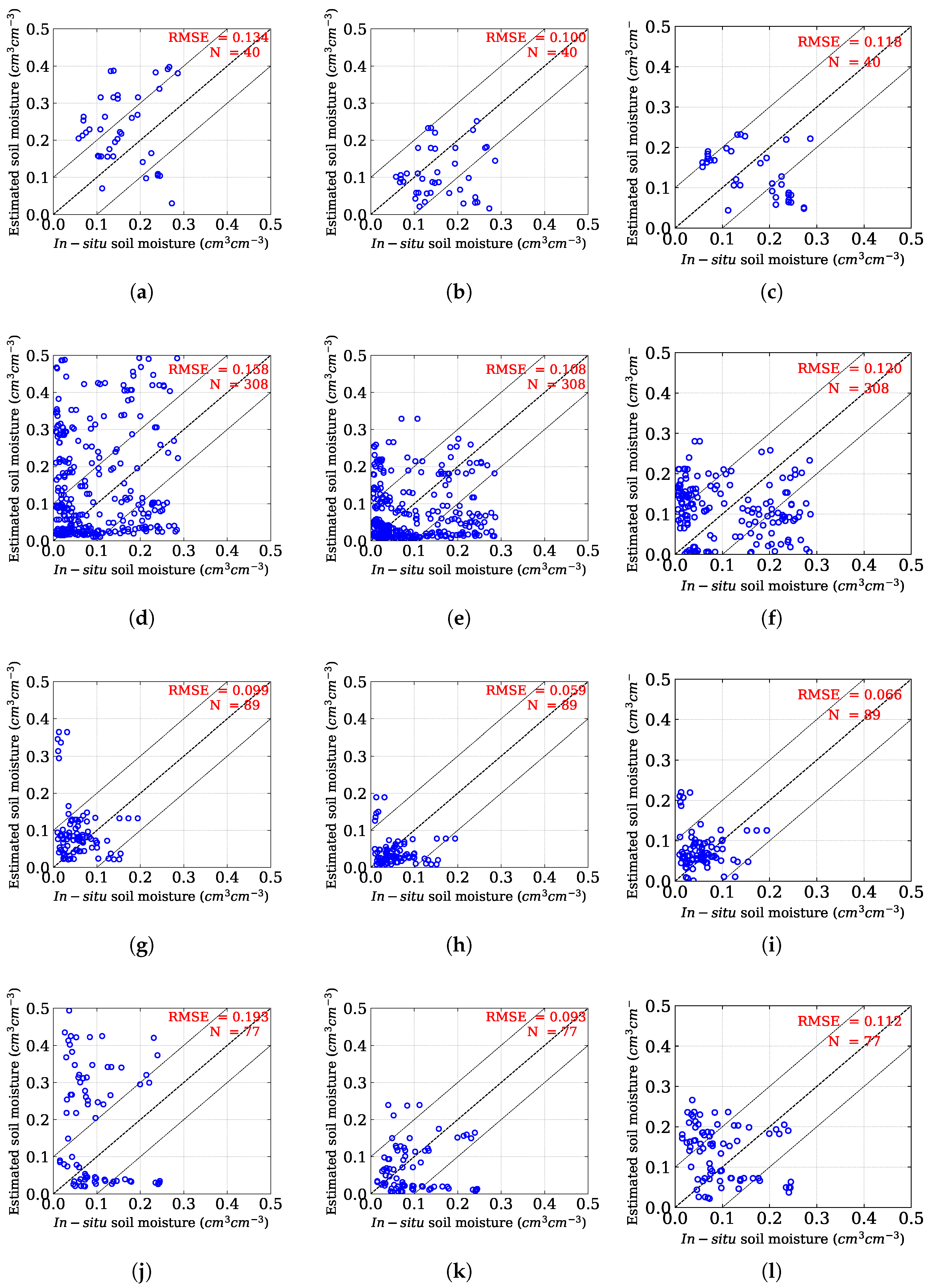
| Land-Use | Model | Evaluation Metrics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | MAPE | p | |||
| Brinjal | Oh et al. [8] | 0.134 | 0.12 | 0.93 | 0.18 | <0.001 |
| Mod. Oh | 0.100 | 0.08 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.001 | |
| Chang et al. [56] | 0.118 | 0.10 | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.02 | |
| Fallow | Oh et al. [8] | 0.158 | 0.12 | 4.12 | 0.97 | <0.001 |
| Mod. Oh | 0.108 | 0.08 | 2.22 | 1.1 | <0.001 | |
| Chang et al. [56] | 0.120 | 0.11 | 3.41 | 0.41 | 0.81 | |
| Weed | Oh et al. [8] | 0.099 | 0.06 | 2.64 | 0.59 | <0.001 |
| Mod. Oh | 0.059 | 0.04 | 1.21 | 0.79 | 0.005 | |
| Chang et al. [56] | 0.066 | 0.05 | 1.89 | 0.35 | 0.001 | |
| Sesame | Oh et al. [8] | 0.193 | 0.16 | 2.69 | 0.71 | <0.001 |
| Mod. Oh | 0.093 | 0.07 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 0.007 | |
| Chang et al. [56] | 0.112 | 0.09 | 1.78 | 0.25 | <0.001 | |
| All points | Oh et al. [8] | 0.154 | 0.12 | 3.40 | 0.84 | 0.05 |
| Mod Oh | 0.098 | 0.07 | 1.70 | 1.03 | <0.001 | |
| Chang et al. [56] | 0.108 | 0.09 | 2.42 | 0.37 | 0.06 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, P.D.; Dey, S.; Bhogapurapu, N.; Chakraborty, S. Retrieval of Surface Soil Moisture at Field Scale Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Sensors 2025, 25, 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103065
Roy PD, Dey S, Bhogapurapu N, Chakraborty S. Retrieval of Surface Soil Moisture at Field Scale Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103065
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Partha Deb, Subhadip Dey, Narayanarao Bhogapurapu, and Somsubhra Chakraborty. 2025. "Retrieval of Surface Soil Moisture at Field Scale Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103065
APA StyleRoy, P. D., Dey, S., Bhogapurapu, N., & Chakraborty, S. (2025). Retrieval of Surface Soil Moisture at Field Scale Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Sensors, 25(10), 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103065








