Robotic Hand–Eye Calibration Method Using Arbitrary Targets Based on Refined Two-Step Registration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Hand–Eye Robot System
- Fixed binocular tracking camera (W): Used to track the robot’s end-effector;
- Tracking target (T): Mounted on the robot’s end-effector, tracked by the binocular camera;
- Structured light 3D scanner (C): Mounted on the robot’s end-effector, used to capture 3D information of the target;
- Arbitrary 3D target (B): Used as the calibration object.
2.2. Hand–Eye Calibration Algorithm
2.3. Construction of Calibration Equation
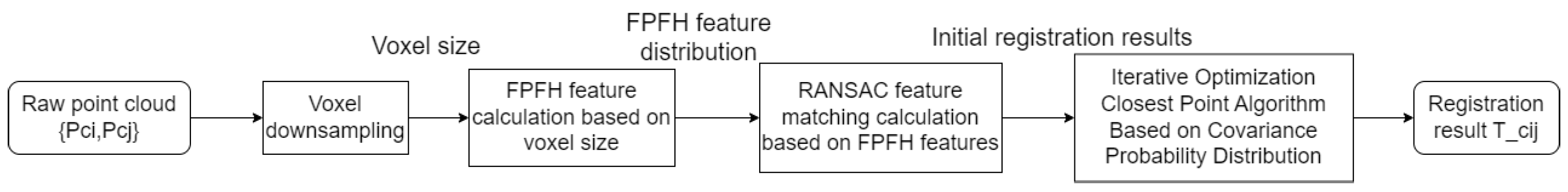
2.4. Multi-Step Registration Algorithm
3. Experiment
3.1. Experimental Platform and Evaluation Criteria
3.1.1. Experimental Platform
3.1.2. Evaluation Criteria
3.2. Experimental Procedures
3.3. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Error
3.4. Distance Measurement Error
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y. A review of applications of visual inspection technology based on image processing in the railway industry. Transp. Saf. Environ. 2019, 1, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, S.-J.; Yin, Z.-P. Hand-eye calibration in visually-guided robot grinding. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 46, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, K. Fast registration methodology for fastener assembly of large-scale structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, L.; Li, P.; Pan, Q. An ensemble fruit fly optimization algorithm for solving range image registration to improve quality inspection of free-form surface parts. Inf. Sci. 2016, 367, 953–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.W.; Tai, C.L.; Wang, G.J. A mesh reconstruction algorithm driven by an intrinsic property of a point cloud. Comput. Aided Des. 2004, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Zwicker, M. Global registration of dynamic range scans for articulated model reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2011, 30, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, X.; Luo, Q.; Li, M. An overview of hand-eye calibration. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, J.; Armangué, X.; Batlle, J. A comparative review of camera calibrating methods with accuracy evaluation. Pattern Recognit. 2002, 35, 1617–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, Y.C.; Ahmad, S. Calibration of wrist-mounted robotic sensors by solving homogeneous transform equations of the form AX=XB. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Lenz, R.K. A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3D robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, M. Comparing ARTag and ARToolkit plus Fiducial Marker Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and Their Applications, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1 October 2005; pp. 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, M. ARTag, A fiducial marker system using digital techniques. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 2, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Olson, E. AprilTag 2: Efficient and Robust Fiducial Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4193–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.X.; Zong, P.F.; Yao, P.; Ren, P. Calibration of 6-DOF industrial robots based on line structured light. Optik 2019, 183, 1166–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajal, C. A crenellated-target-based calibration method for laser triangulation sensors integration in articulated measurement arms. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2011, 27, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Reitelshofer, S.; Franke, J. Self-Calibration Method for a Robot Based 3D Scanning System. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA 2015), Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 8–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lembono, T.S.; Suarez-Ruiz, F.; Pham, Q.C. SCALAR: Simultaneous calibration of 2-D laser and robot kinematic parameters using planarity and distance constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibin, Y.; Yongjie, R.; Shenghua, Y. A vision-based self-calibration method for robotic visual inspection systems. Sensors 2013, 13, 16565–16582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, W.; Liu, H. General geometry calibration using arbitrary free-form surface in a vision-based robot system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 5994–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Yan, Y. A scene feature based eye-in-hand calibration method for industrial robot. Mechatron. Mach. Vis. Pract. 2021, 4, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Marton, Z.C.; Beetz, M. Aligning Point Cloud Views Using Persistent Feature Histograms. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, A.V.; Haehnel, D.; Thrun, S. Generalized-ICP. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, J.; Jing, F.; Deng, S.; Zheng, M.; Tan, M. An efficient calibration method of line structured light vision sensor in robotic eye-in-hand system. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 6200–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, P.K.; Sorrentino, I.; Rendiniello, A.; Fantacci, C.; Villagrossi, E.; Polo, A. In Situ Translational Hand-Eye Calibration of Laser Profile Sensors Using Arbitrary Objects. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2021), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 11067–11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Knoll, A.C. Robot self-calibration using actuated 3D sensors. J. Field Robot. 2024, 41, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Su, H. EasyHeC: Accurate and Automatic Hand-eye Calibration via Differentiable Rendering and Space Exploration. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 7234–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Zheng, K.; Chen, L. EasyHeC++: Fully Automatic Hand-Eye Calibration with Pretrained Image Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 14–18 October 2024; pp. 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Method | Camera Type | Target Type | Mean Error (mm) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-Ball System Method | Structured Light | Three Standard Spheres | (X: 2.77, Y: 1.49, Z: 1.47) 3.79 | 0.99 |
| Zhe’s Method [24] | Line Laser | 2D Calibration Board | (X: 1.334, Y: 0.511, Z: 0.925) 1.855 | - |
| Murali’s Method [25] | Laser Profiler | Arbitrary 3D Object | (X: 0.701, Y: 0.443, Z: 0.366) 0.906 | - |
| Peter’s Method [26] | Structured Light | Arbitrary 3D Object | 1.77 | - |
| Proposed Method | Structured Light | Arbitrary 3D Object | (X: 1.10, Y: 0.60, Z: 0.66) 1.53 | 0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Sun, C.; Sun, Y.; Qi, L. Robotic Hand–Eye Calibration Method Using Arbitrary Targets Based on Refined Two-Step Registration. Sensors 2025, 25, 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102976
Song Z, Sun C, Sun Y, Qi L. Robotic Hand–Eye Calibration Method Using Arbitrary Targets Based on Refined Two-Step Registration. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102976
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zining, Chenglong Sun, Yunquan Sun, and Lizhe Qi. 2025. "Robotic Hand–Eye Calibration Method Using Arbitrary Targets Based on Refined Two-Step Registration" Sensors 25, no. 10: 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102976
APA StyleSong, Z., Sun, C., Sun, Y., & Qi, L. (2025). Robotic Hand–Eye Calibration Method Using Arbitrary Targets Based on Refined Two-Step Registration. Sensors, 25(10), 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102976







