GFA-Net: Geometry-Focused Attention Network for Six Degrees of Freedom Object Pose Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The proposed GFA-Net centers on extracting the key geometric features from RGB images, thereby promoting both pose learning capacity and the efficiency of pose computation.
- Pixel-wise Feature Attention (PFA) incorporates coordinate-based positional data, enabling the network to focus on the object region and develop a robust sense of spatial relationships.
- A Geometry Feature Aggregation Module (GFAM) aggregates multi-scale features and identifies relationships among prominent geometric features.
- On the LINEMOD dataset, the proposed method attains 96.54% in the ADD metric (0.1d) on the LINEMOD dataset, and achieves 49.35% on the Occlusion LINEMOD dataset.
2. Related Work
2.1. Baseline Method
2.2. Direct Methods
2.3. PnP-Based Methods
2.4. Attention-Based Methods
3. Proposed Method
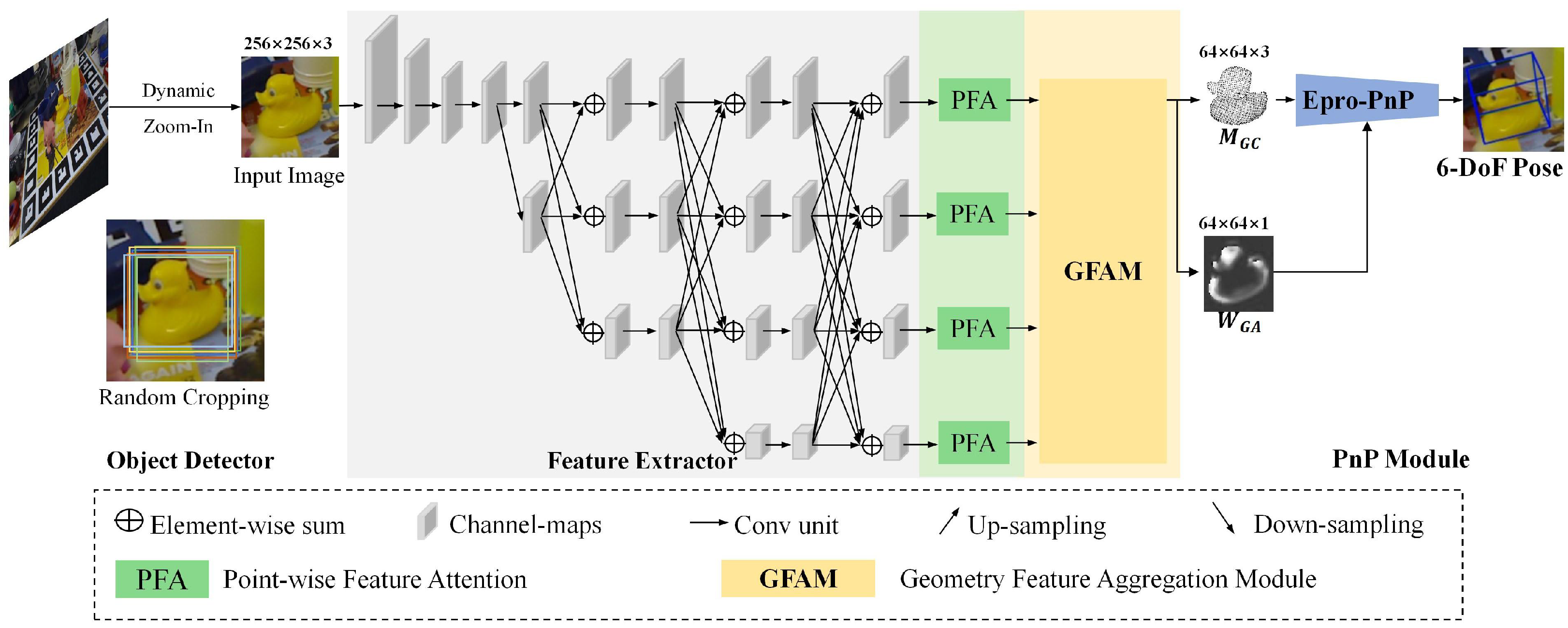
3.1. Architecture Overview
3.2. Feature Extractor
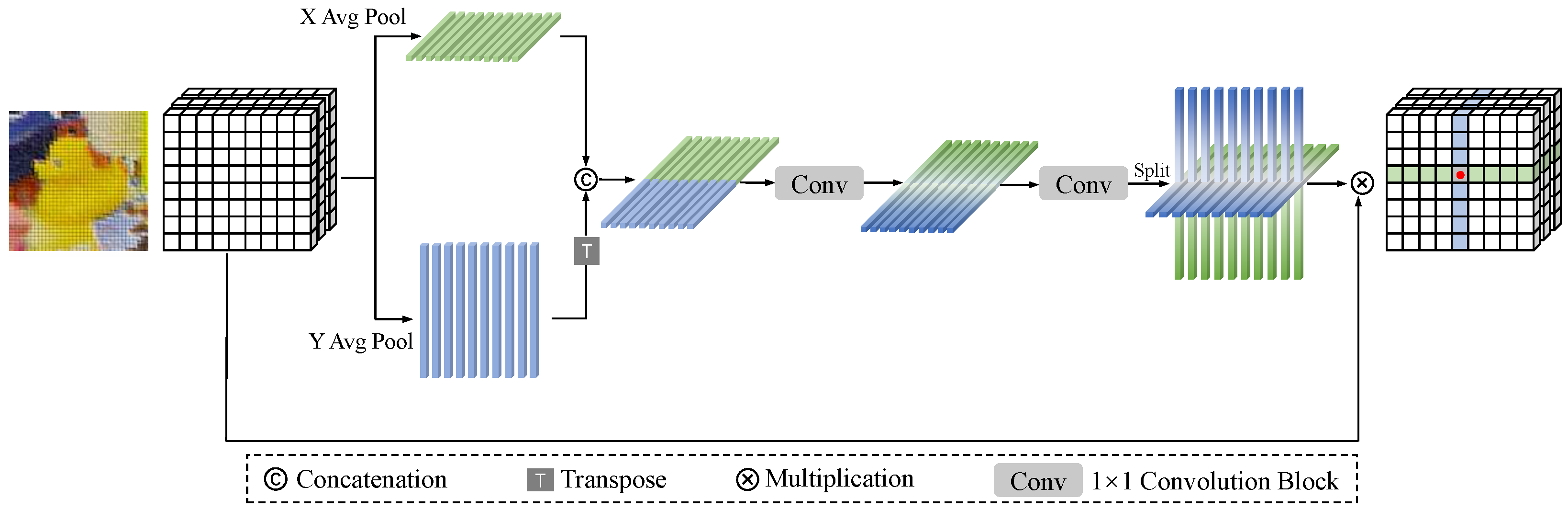
3.3. Point-Wise Feature Attention
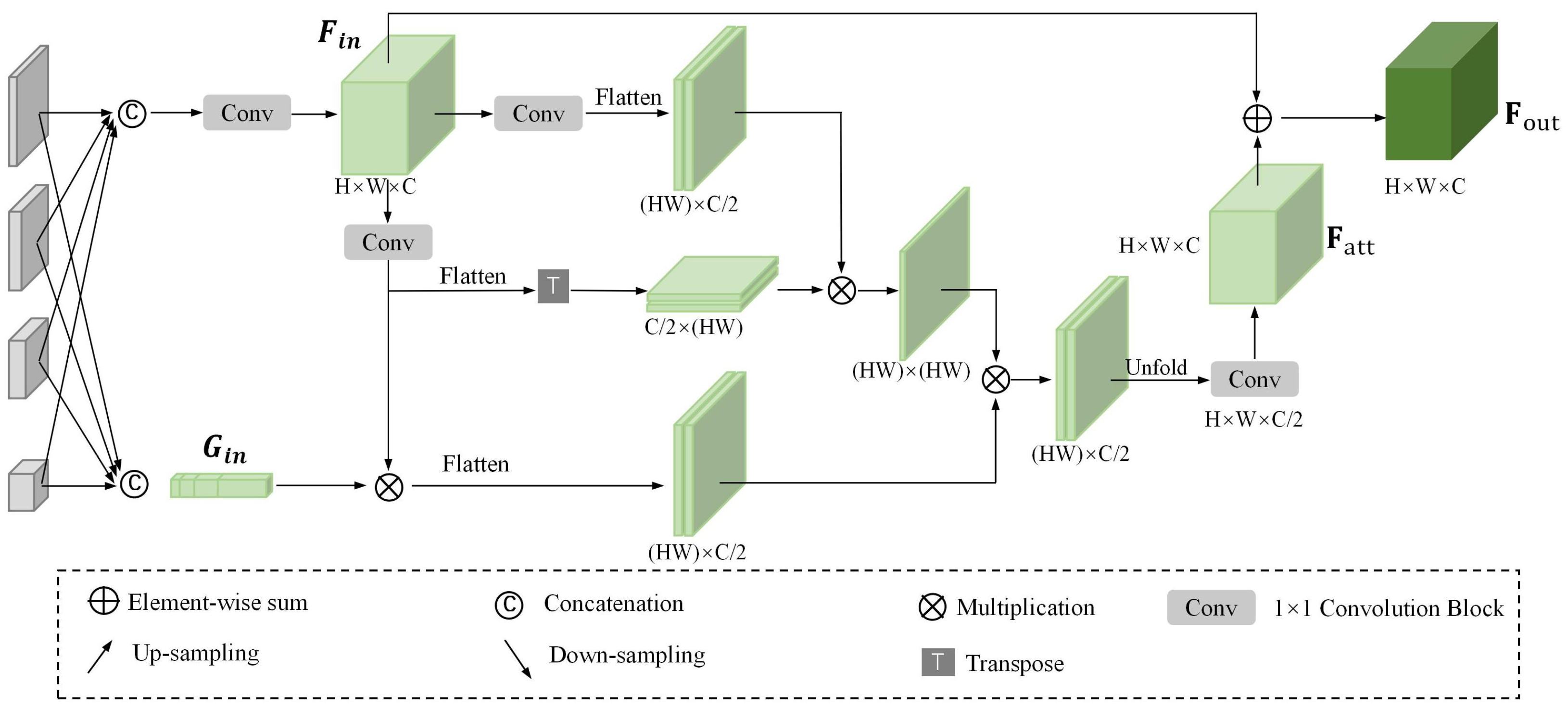
3.4. Geometry Feature Aggregation Module
3.5. Solving Dense Correspondences with Weights
3.5.1. Building Dense Correspondences
3.5.2. Dense Correspondence Resolution Through PnP
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Dataset
4.1.1. LINEMOD Dataset [10]
4.1.2. Occlusion LINEMOD Dataset [31]
4.1.3. YCB-Video Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.3.1. ADD(-s) Metric [10]
4.3.2. Two-Dimensional Projection Metric
4.3.3. The 2 cm 2° Metric [43]
4.4. Performance Comparison
4.4.1. Performance on the LINEMOD Dataset
4.4.2. Performance on the Occlusion LINEMOD Dataset
4.4.3. Performance on the YCB-Video Dataset
4.5. Ablation Study
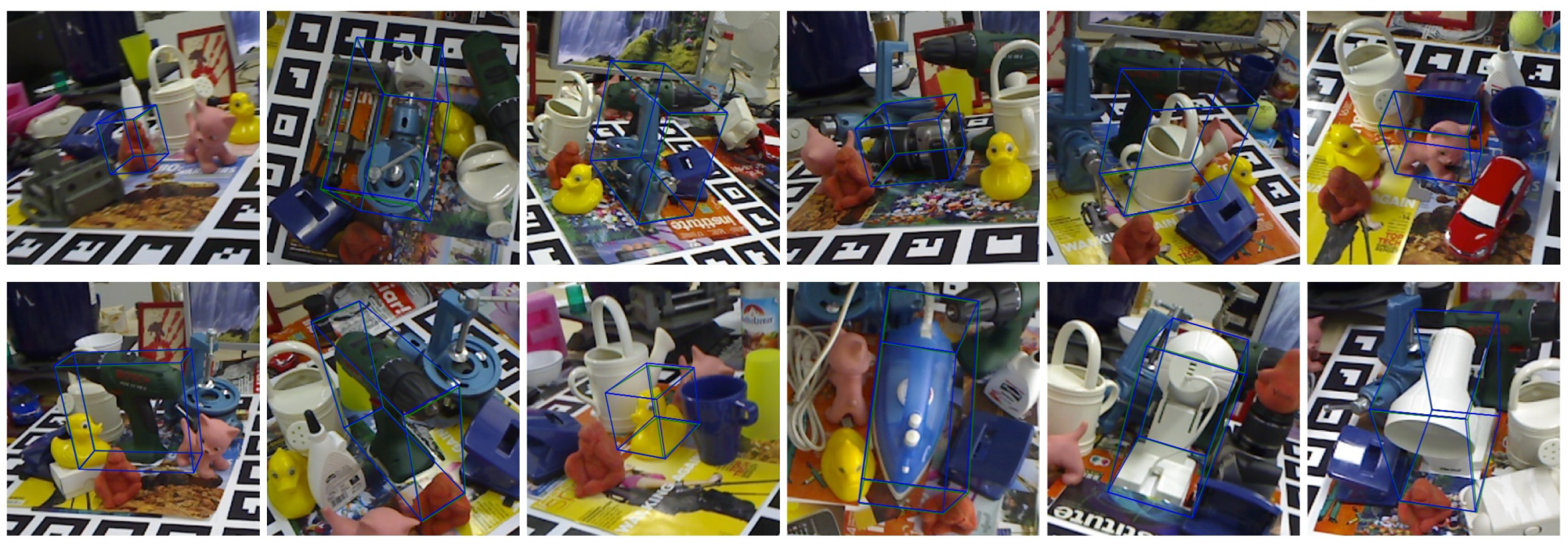
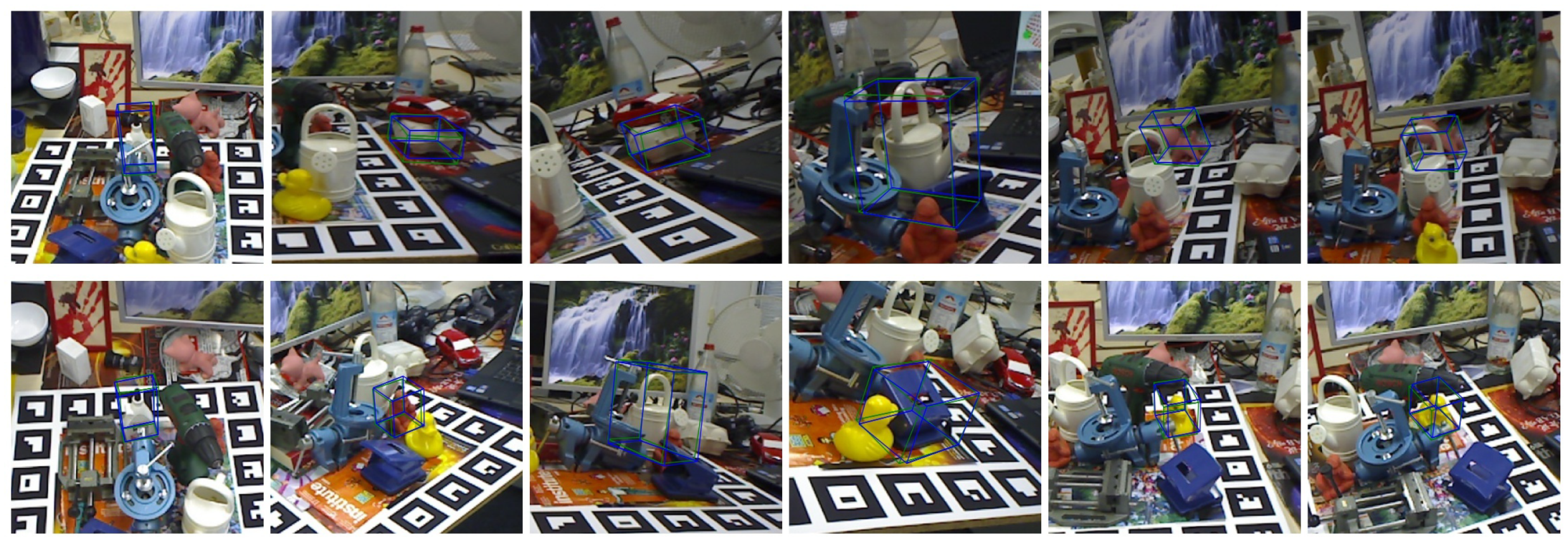
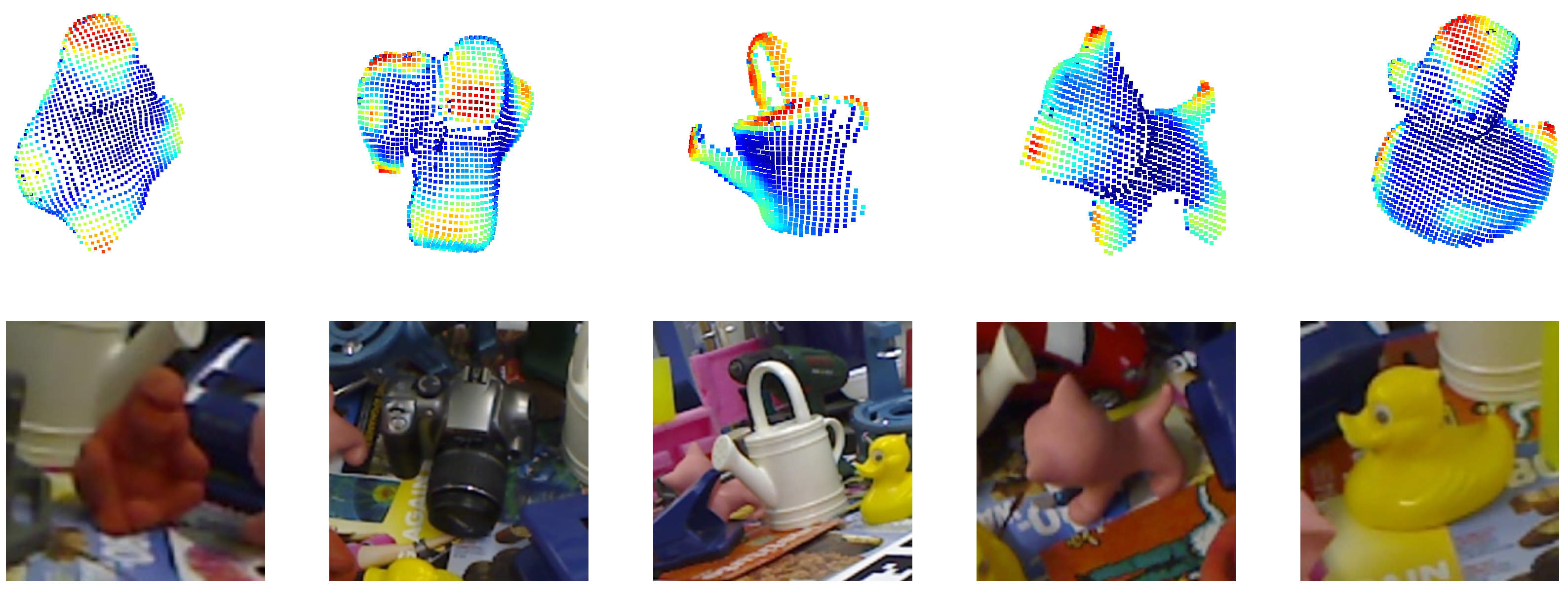
4.6. Visualization
4.6.1. Visualization of
4.6.2. Visualization of Pose Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, Y.; Mottaghi, R.; Savarese, S. Beyond PASCAL: A benchmark for 3D object detection in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 24–26 March 2014; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Hao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, S.; Fang, Y. A Survey of 6DoF Object Pose Estimation Methods for Different Application Scenarios. Sensors 2024, 24, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, N.; Bekris, K.E.; Berenson, D.; Brock, O.; Causo, A.; Hauser, K.; Okada, K.; Rodriguez, A.; Romano, J.M.; Wurman, P.R. Analysis and Observations From the First Amazon Picking Challenge. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Anguelov, D.; Jain, A. PointFusion: Deep Sensor Fusion for 3D Bounding Box Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Xue, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, D. Real-Time Queue Length Estimation with Trajectory Reconstruction Using Surveillance Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 16th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Shenzhen, China, 13–15 December 2020; pp. 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Liu, L.; Xue, S.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, M.; Li, D. A Cooperation-Aware Lane Change Method for Automated Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 3236–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, E.; Uchiyama, H.; Spindler, F. Pose Estimation for Augmented Reality: A Hands-On Survey. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2016, 22, 2633–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Corfu, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinterstoisser, S.; Cagniart, C.; Ilic, S.; Sturm, P.; Navab, N.; Fua, P.; Lepetit, V. Gradient Response Maps for Real-Time Detection of Textureless Objects. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinterstoisser, S.; Lepetit, V.; Ilic, S.; Holzer, S.; Bradski, G.; Konolige, K.; Navab, N. Model Based Training, Detection and Pose Estimation of Texture-Less 3D Objects in Heavily Cluttered Scenes. In Computer Vision—ACCV 2012; Lee, K.M., Matsushita, Y., Rehg, J.M., Hu, Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 548–562. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, W.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ilic, S.; Navab, N. SSD-6D: Making RGB-Based 3D Detection and 6D Pose Estimation Great Again. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Schmidt, T.; Narayanan, V.; Fox, D. PoseCNN: A Convolutional Neural Network for 6D Object Pose Estimation in Cluttered Scenes. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.00199. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakos, G.; Zhou, X.; Chan, A.; Derpanis, K.G.; Daniilidis, K. 6-DoF object pose from semantic keypoints. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, M.; Lepetit, V. BB8: A Scalable, Accurate, Robust to Partial Occlusion Method for Predicting the 3D Poses of Challenging Objects without Using Depth. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3848–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Ji, X. CDPN: Coordinates-Based Disentangled Pose Network for Real-Time RGB-Based 6-DoF Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7677–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ji, X. GDR-Net: Geometry-Guided Direct Regression Network for Monocular 6D Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16606–16616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodaň, T.; Baráth, D.; Matas, J. EPOS: Estimating 6D Pose of Objects with Symmetries. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11700–11709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manawadu, M.; Park, S.Y. 6DoF Object Pose and Focal Length Estimation from Single RGB Images in Uncontrolled Environments. Sensors 2024, 24, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, T.; Yu, E. A dynamic keypoint selection network for 6DoF pose estimation. Image Vis. Comput. 2022, 118, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Rambach, J.; Pagani, A.; Stricker, D. SynPo-Net—Accurate and Fast CNN-Based 6DoF Object Pose Estimation Using Synthetic Training. Sensors 2021, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Wang, X.; He, M.; Wang, J. DRNet: A Depth-Based Regression Network for 6D Object Pose Estimation. Sensors 2021, 21, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H. Real-time 6D pose estimation from a single RGB image. Image Vis. Comput. 2019, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberweger, M.; Rad, M.; Lepetit, V. Making Deep Heatmaps Robust to Partial Occlusions for 3D Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Proceedings, Part XV. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Huang, Q.; Bao, H. PVNet: Pixel-Wise Voting Network for 6DoF Object Pose Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 3212–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dede, M.A.; Genc, Y. Object aspect classification and 6DoF pose estimation. Image Vis. Comput. 2022, 124, 104495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, S.; Shugurov, I.; Ilic, S. DPOD: 6D Pose Object Detector and Refiner. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Tian, W.; Xiong, L.; Li, H. Epro-pnp: Generalized end-to-end probabilistic perspective-n-points for monocular object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2781–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Tian, W.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Xiong, L.; Li, H. EPro-PnP: Generalized End-to-End Probabilistic Perspective-N-Points for Monocular Object Pose Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachmann, E.; Krull, A.; Michel, F.; Gumhold, S.; Shotton, J.; Rother, C. Learning 6D Object Pose Estimation Using 3D Object Coordinates. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brachmann, E.; Michel, F.; Krull, A.; Yang, M.Y.; Gumhold, S.; Rother, C. Uncertainty-Driven 6D Pose Estimation of Objects and Scenes from a Single RGB Image. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3364–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, A.; Penate-Sanchez, A.; Agapito, L. Detect Globally, Label Locally: Learning Accurate 6-DOF Object Pose Estimation by Joint Segmentation and Coordinate Regression. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3960–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X. Zoom Out-and-In Network with Map Attention Decision for Region Proposal and Object Detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual Attention Network for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6450–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Proceedings, Part VII. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Gu, D. CSA6D: Channel-Spatial Attention Networks for 6D Object Pose Estimation. Cogn. Comput. 2022, 14, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, D. PAM: Point-wise Attention Module for 6D Object Pose Estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.05242. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Gong, X.; Wang, J. EANet: Edge-Attention 6D Pose Estimation Network for Texture-Less Objects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevšič, S.; Hilliges, O. Spatial Attention Improves Iterative 6D Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Fukuoka, Japan, 25–28 November 2020; pp. 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Martín-Martín, R.; Lu, C.; Fei-Fei, L.; Savarese, S. DenseFusion: 6D Object Pose Estimation by Iterative Dense Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3338–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Ji, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fox, D. DeepIM: Deep Iterative Matching for 6D Pose Estimation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 695–711. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, T.; Dong, Q. SMOC-Net: Leveraging Camera Pose for Self-Supervised Monocular Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 21307–21316. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Song, J.; Huang, Q. HybridPose: 6D Object Pose Estimation Under Hybrid Representations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hu, Y.; Alvarez, J.M.; Salzmann, M. Knowledge distillation for 6d pose estimation by aligning distributions of local predictions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 18633–18642. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Fua, P.; Wang, W.; Salzmann, M. Single-Stage 6D Object Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Labbé, Y.; Carpentier, J.; Aubry, M.; Sivic, J. Cosypose: Consistent multi-view multi-object 6d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XVII 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 574–591. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | Ape | Benc. | Cam | Can | Cat | Dril. | Duck | Egg. | Glue | Hole. | Iron | Lamp | Phone | Ave. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ⊛ Densefusion [43] | 79.50 | 84.20 | 76.50 | 86.60 | 88.80 | 77.70 | 76.30 | 99.90 | 99.40 | 79.00 | 92.10 | 92.30 | 88.00 | 86.20 |
| ⊛ DeepIM [44] | 77.00 | 97.50 | 93.50 | 96.50 | 82.10 | 95.50 | 77.70 | 97.10 | 99.40 | 85.80 | 98.30 | 97.50 | 87.70 | 88.60 |
| ⊛ SMOC-Net [45] | 85.60 | 96.70 | 97.20 | 99.90 | 95.00 | 100.00 | 76.00 | 98.30 | 99.20 | 45.60 | 99.90 | 98.90 | 94.00 | 91.30 |
| ⊕ PVNet [25] | 43.62 | 99.90 | 86.86 | 95.47 | 79.34 | 96.43 | 52.58 | 99.15 | 95.66 | 81.92 | 98.88 | 99.33 | 92.41 | 86.27 |
| ⊕ Hybridpose [46] | 63.10 | 99.90 | 90.40 | 98.50 | 89.40 | 98.50 | 65.00 | 100.00 | 98.80 | 89.70 | 100.00 | 99.50 | 94.90 | 91.30 |
| ⊕ Guo et al. [47] | 76.20 | 96.70 | 92.00 | 94.00 | 88.60 | 94.80 | 74.70 | 99.30 | 97.70 | 82.20 | 93.20 | 96.80 | 89.60 | 90.40 |
| ⊞ CDPN [16] | 64.38 | 97.77 | 91.67 | 95.87 | 83.83 | 96.23 | 66.76 | 99.72 | 99.61 | 85.82 | 97.85 | 97.89 | 90.75 | 89.86 |
| ⊞ GDR-Net [17] | 76.29 | 97.96 | 95.29 | 98.03 | 93.21 | 97.72 | 80.28 | 99.53 | 98.94 | 91.15 | 98.06 | 99.14 | 92.35 | 93.69 |
| ⊞ Chen et al.-v1 [28] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 95.80 |
| ⊞ Chen et al.-v2 [29] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 96.36 |
| ★ GFA-Net (Ours) | 87.90 | 98.55 | 98.73 | 99.51 | 95.01 | 97.62 | 87.04 | 99.81 | 99.42 | 94.58 | 99.08 | 99.81 | 97.92 | 96.54 |
| Method | ADD(-S) | 2D Proj. | 2° 2 cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.02d | 0.05d | 0.10d | |||
| CDPN [16] | 29.10 | 69.50 | 89.86 | 98.10 | - |
| GDR-Net [17] | 35.60 | 76.00 | 93.69 | - | 67.10 |
| Chen et al.-v1 [28] | 44.81 | 81.96 | 95.80 | - | 80.99 |
| Chen et al.-v2 [29] | 43.77 | 81.73 | 96.36 | - | - |
| GFA-Net | 49.01 | 84.31 | 96.54 | 99.23 | 83.22 |
| Methods | Ape | Can | Cat | Driller | Duck | Eggbox | Glue | Hole. | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PoseCNN [13] | 9.60 | 45.20 | 0.90 | 41.40 | 19.60 | 22.00 | 38.50 | 22.10 | 24.90 |
| PVNet [25] | 15.81 | 63.30 | 16.68 | 25.24 | 65.65 | 50.17 | 49.62 | 39.67 | 40.77 |
| Hu et al. [48] | 19.20 | 65.10 | 18.90 | 69.00 | 25.30 | 52.00 | 51.40 | 45.60 | 43.30 |
| Hybridpose [46] | 20.90 | 75.30 | 24.90 | 70.20 | 27.90 | 52.40 | 53.80 | 54.20 | 47.50 |
| Guo et al. [47] | 26.90 | 54.70 | 32.90 | 52.90 | 27.00 | 50.00 | 56.90 | 54.50 | 44.50 |
| GDR-Net [17] | 41.30 | 71.10 | 18.20 | 54.60 | 41.70 | 40.20 | 59.50 | 52.60 | 47.40 |
| GFA-Net(Ours) | 35.32 | 59.38 | 32.18 | 46.46 | 42.03 | 55.47 | 66.89 | 57.03 | 49.35 |
| Method | Refi. | P.E. | AUC of ADD(-S) | AUC of ADD-S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PoseCNN [13] | 1 | 61.3 | 75.9 | |
| PVNet [25] | N | 73.4 | - | |
| GDR-Net [17] | N | 84.4 | 91.6 | |
| GDR-Net [17] | 1 | 80.2 | 89.1 | |
| DeepIM [44] | ✓ | 1 | 81.9 | 88.1 |
| CosyPose [49] | ✓ | 1 | 84.5 | 89.8 |
| GFA-Net | 1 | 84.7 | 92.4 |
| Module | ADD(-S) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | PFA | GFAM | 0.10d | 0.05d | 0.02d | |
| 1 | ✓ | 95.34 | 81.07 | 44.37 | ||
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | 96.01 | 82.53 | 46.04 | |
| 3 | ✓ | ✓ | 96.16 | 83.44 | 46.80 | |
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 96.54 | 84.31 | 49.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Yu, J.; Su, P.; Xue, W.; Qin, Y.; Fu, L.; Wen, J.; Huang, H. GFA-Net: Geometry-Focused Attention Network for Six Degrees of Freedom Object Pose Estimation. Sensors 2025, 25, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010168
Lin S, Yu J, Su P, Xue W, Qin Y, Fu L, Wen J, Huang H. GFA-Net: Geometry-Focused Attention Network for Six Degrees of Freedom Object Pose Estimation. Sensors. 2025; 25(1):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010168
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shuai, Junhui Yu, Peng Su, Weitao Xue, Yang Qin, Lina Fu, Jing Wen, and Hong Huang. 2025. "GFA-Net: Geometry-Focused Attention Network for Six Degrees of Freedom Object Pose Estimation" Sensors 25, no. 1: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010168
APA StyleLin, S., Yu, J., Su, P., Xue, W., Qin, Y., Fu, L., Wen, J., & Huang, H. (2025). GFA-Net: Geometry-Focused Attention Network for Six Degrees of Freedom Object Pose Estimation. Sensors, 25(1), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010168







