Research on Ocular Artifacts Removal from Single-Channel Electroencephalogram Signals in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients Based on Support Vector Machine, Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, and Second-Order Blind Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
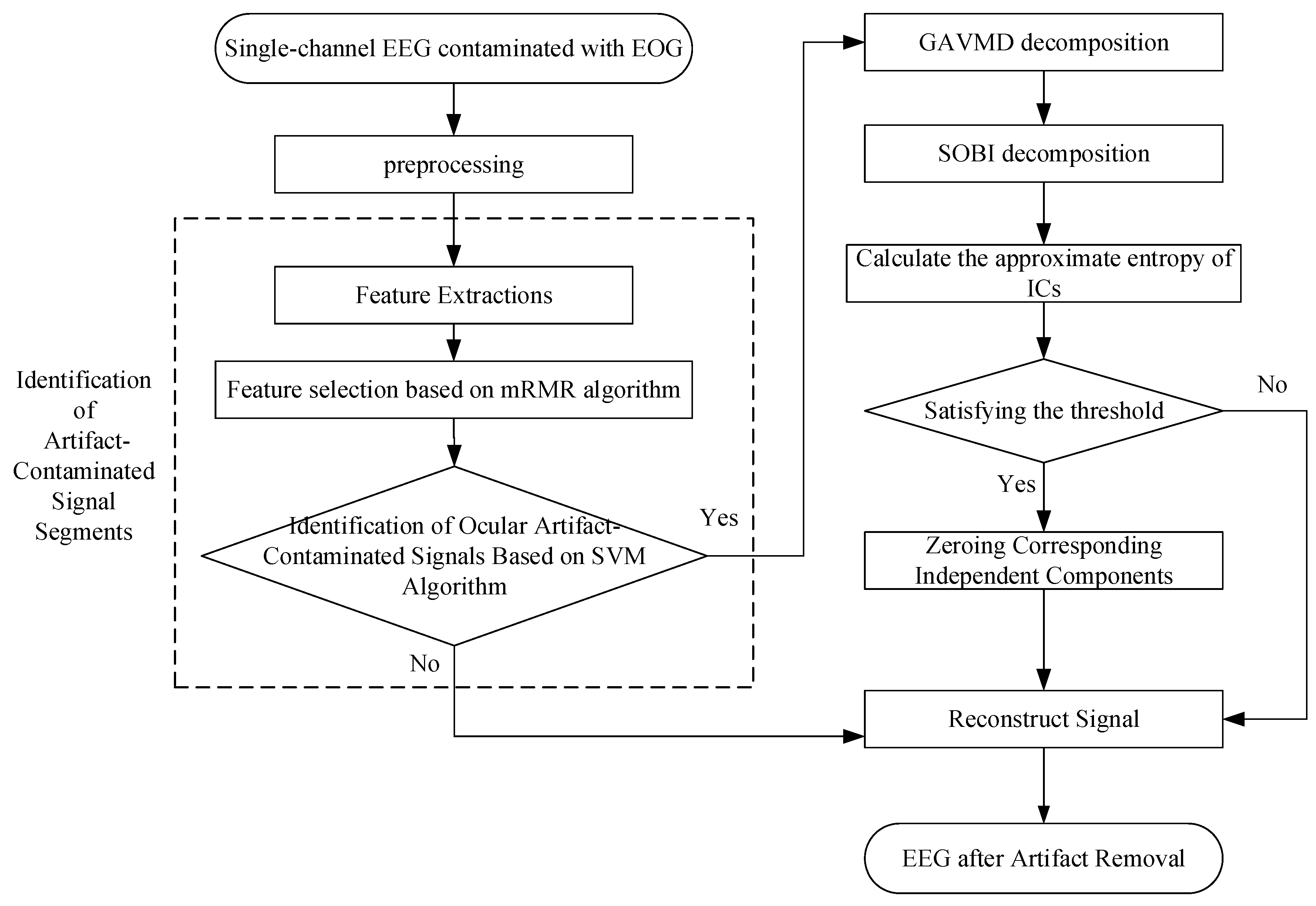
2.1. Identification of Contaminated Signals with Ocular Artifacts
2.2. Variational Modal Decomposition (VMD)
2.2.1. Fundamentals of Variational Modal Decomposition
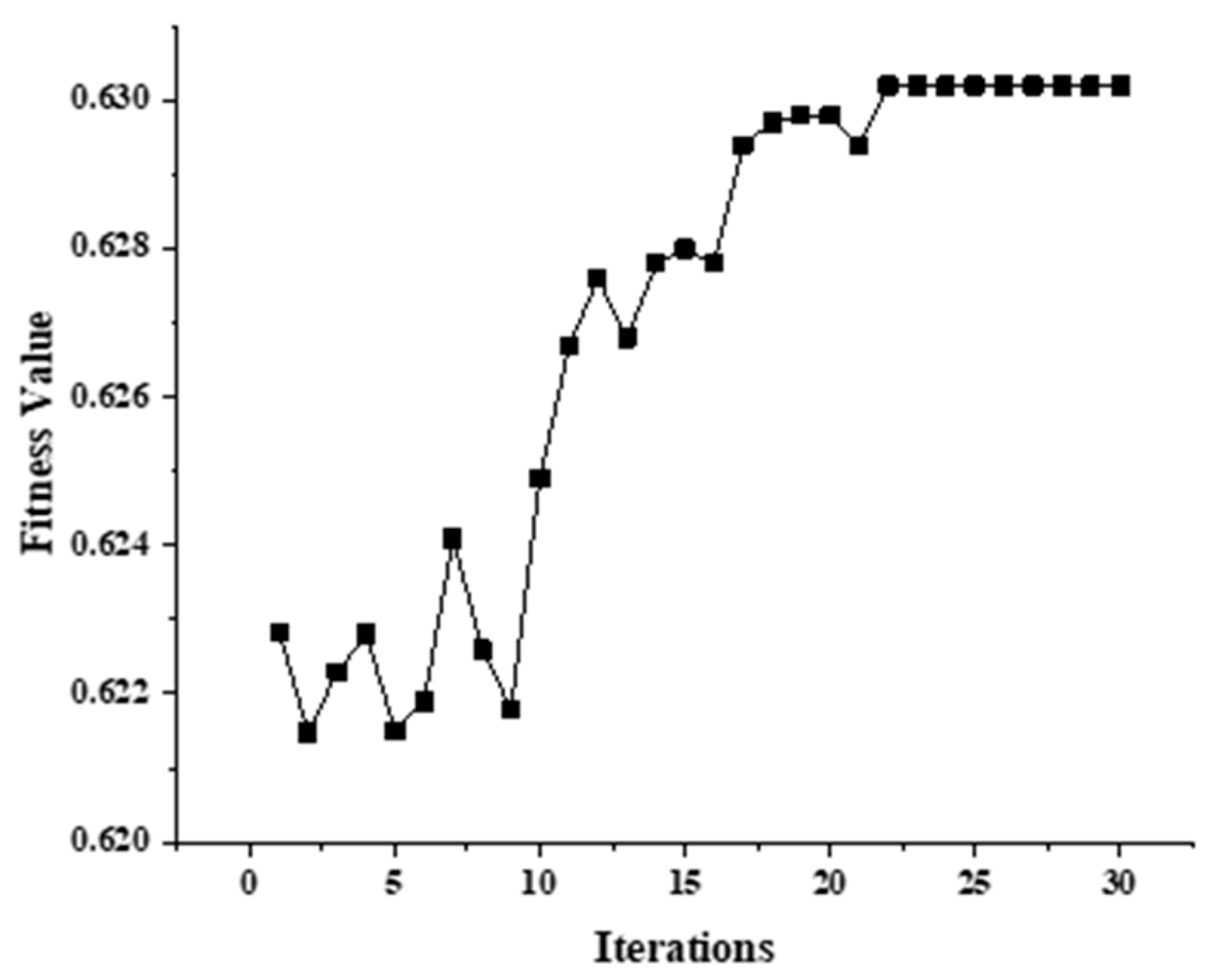
2.2.2. Optimization of VMD Parameters Based on Genetic Algorithm
2.3. Second-Order Blind Identification Algorithm (SOBI)
- Perform whitening on the original data to obtain the whitened data and whitened matrix . The covariance matrix of is a unit matrix:
- Calculate the sampling covariance matrix of with a fixed delay :
- The joint approximate diagonalization of each is performed to compute the orthogonal matrix ), satisfyingwhere is a set of diagonal arrays.
- Estimate the mixing matrix and the original signal matrix, :where is the separation matrix, the inverse matrix of . The source signals associated with the artifacts in are processed to obtain a new source signal matrix, , which in turn reconstructs the signal .
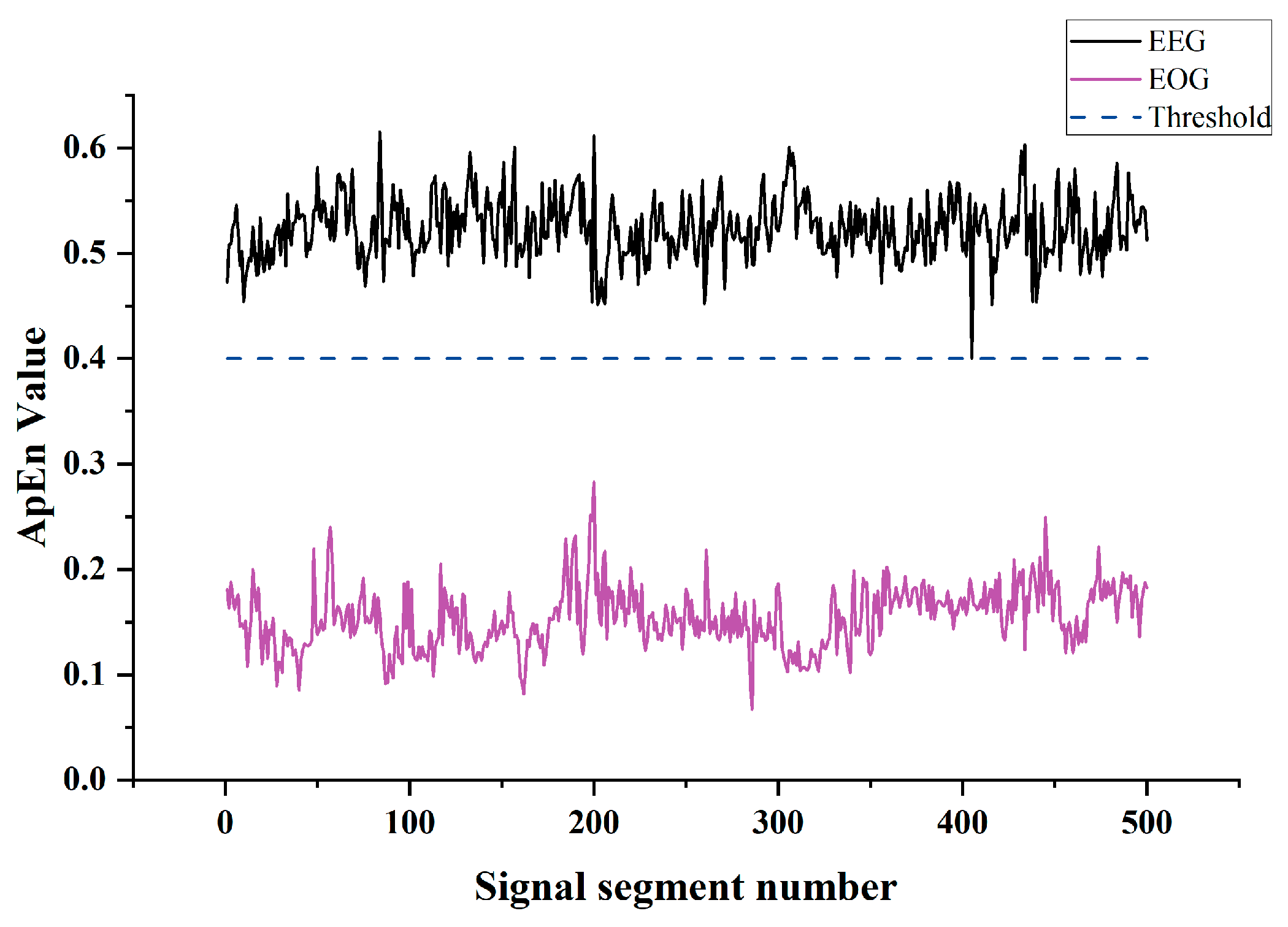
2.4. Entropy-Based Identification of Ocular Artifacts
| Algorithm 1. Approximate Entropy (ApEn) Calculation |
Input: S = [s(1), s(2), …, s(N)] // Time series data of length N m // Embedding dimension r // Similarity threshold, typically a fraction of the standard deviation of S Output: ApEn // Calculated Approximate Entropy value Begin: 1. Compute the standard deviation (SD) of the time series S. 2. Set the similarity threshold r = 0.15 ∗ SD. 3. Initialize the array of similarity counts C to zeros, of length N – m + 1. 4. For each embedding dimension m′ in {m, m + 1}: a. Construct m′-dimensional vectors X(i), i = 1 to N − m′ + 1, where each X(i) = [s(i), …, s(i + m′ − 1)]. b. For each vector X(i), i = 1 to N − m′ + 1: i. Compute the distance d[X(i), X(j)] for all vectors X(j), j = 1 to N − m′ + 1, where d[X(i), X(j)] = max(|s(i + k − 1) − s(j + k − 1)|) for k = 1 to m′. ii. If d[X(i), X(j)] < r, increment C(i) by 1. c. Compute the logarithmic frequency of similar vector pairs for X(i) as: Phi_m′(r) = (1/(N − m′ + 1)) ∗ sum(ln(C(i)/(N − m′ + 1))) over i = 1 to N − m′ + 1. 5. Calculate the Approximate Entropy ApEn as the difference between the logarithmic frequencies of the two consecutive embedding dimensions: ApEn = Phi_m(r) − Phi_m + 1(r). End |
2.5. Materials
2.5.1. Simulated EEG Dataset
2.5.2. Real EEG Dataset
3. Performance Metrics
3.1. Evaluation of the Simulated EEG Dataset
3.2. Real Data Evaluation Methodology
4. Results
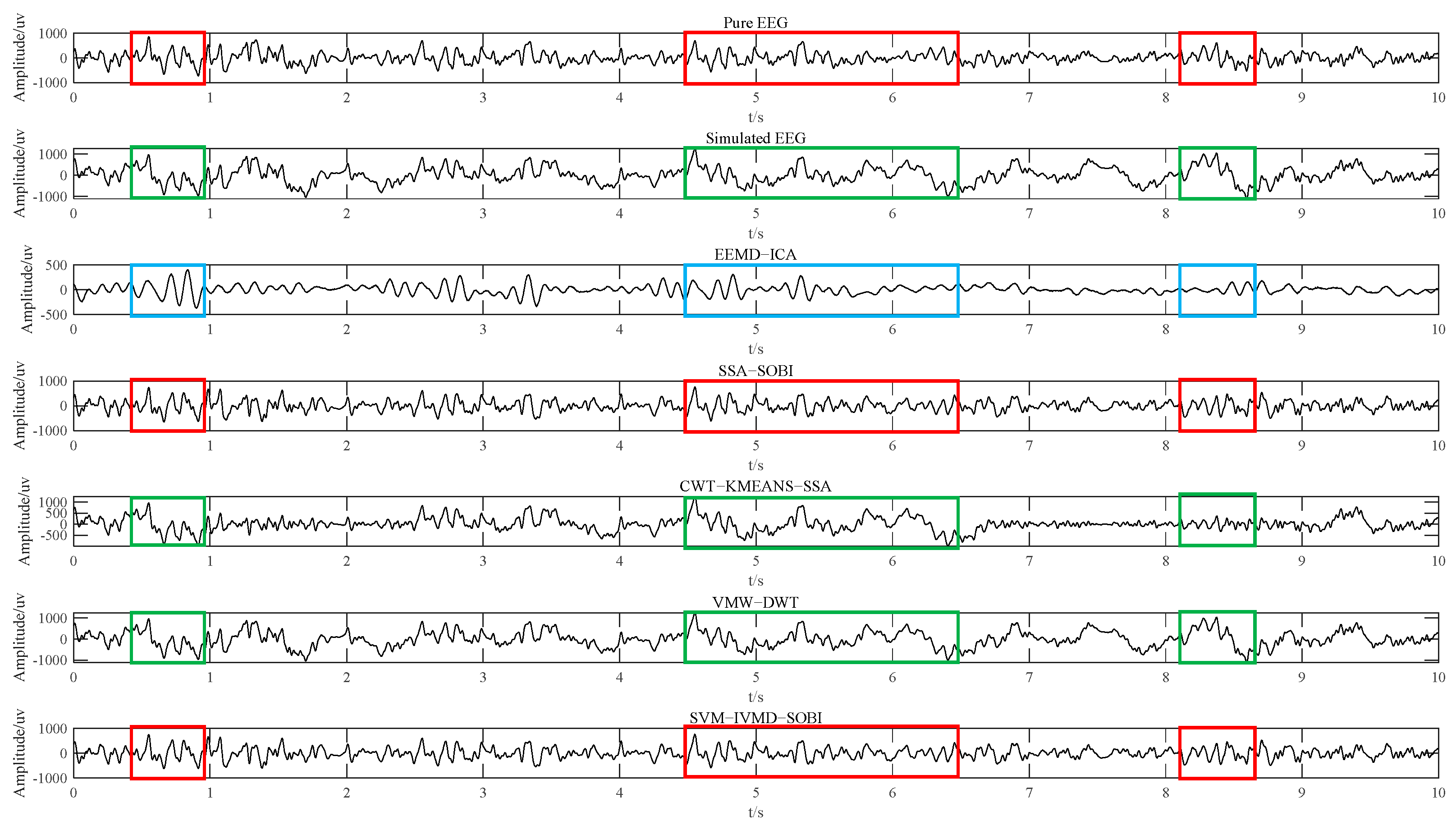
4.1. Experimental Results of Simulated EEG Data
4.2. Experiment Results of Real EEG Data
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janapati, R.; Dalal, V.; Govardhan, N.; Gupta, R.S. Review on EEG-BCI Classification Techniques Advancements. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 981, 032019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, D.; Conti, M. Brain-Computer Interface Applications: Security and Privacy Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Florence, Italy, 28–30 September 2015; pp. 663–666. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.-P.; Nie, C.; Jiang, C.-T.; Cao, S.-H.; Tian, K.-X.; Yu, S.; Gu, J.-W. Modulating Brain Activity with Invasive Brain–Computer Interface: A Narrative Review. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urigüen, J.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. EEG Artifact Removal—State-of-the-Art and Guidelines. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddirala, A.K.; Veluvolu, K.C. Eye-Blink Artifact Removal from Single Channel EEG with k-Means and SSA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egambaram, A.; Badruddin, N.; Asirvadam, V.S.; Begum, T.; Fauvet, E.; Stolz, C. FastEMD–CCA Algorithm for Unsupervised and Fast Removal of Eyeblink Artifacts from Electroencephalogram. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 57, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Li, X. AOAR: An Automatic Ocular Artifact Removal Approach for Multi-Channel Electroencephalogram Data Based on Non-Negative Matrix Factorization and Empirical Mode Decomposition. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 056012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Gao, X. EEG-based braincomputer interface technology in the medical field. Artif. Intell. 2021, 25, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Tang, J.; Cai, Y.; Ye, Y.; Xu, M.; Ming, D. Review on software and hardware platforms for EEG-based BCI system. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2022, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Su, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, X. A Novel End-to-End 1D-ResCNN Model to Remove Artifact from EEG Signals. Neurocomputing 2020, 404, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, H.; Whelan, R.; Reilly, R.B. FASTER: Fully Automated Statistical Thresholding for EEG Artifact Rejection. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 192, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.K.; Rastegarnia, A.; Yang, Z. Methods for Artifact Detection and Removal from Scalp EEG: A Review. Neurophysiol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 46, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatourechi, M.; Bashashati, A.; Ward, R.K.; Birch, G.E. EMG and EOG Artifacts in Brain Computer Interface Systems: A Survey. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, C.; Biswal, P.K. An Improved Algorithm for Efficient Ocular Artifact Suppression from Frontal EEG Electrodes Using VMD. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, F.; He, Y. An Electroencephalogram Artifacts Removal Algorithm for Electroencephalogram Signals Based on Sample Entropy-Complete Ensemble Empi rical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise. J. Xian Jiaotong Univ. 2020, 54, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Peh, W.Y.; Thomas, J.; Bagheri, E.; Chaudhari, R.; Karia, S.; Rathakrishnan, R.; Saini, V.; Shah, N.; Srivastava, R.; Tan, Y.-L.; et al. Multi-Center Validation Study of Automated Classification of Pathological Slowing in Adult Scalp Electroencephalograms Via Frequency Features. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2021, 31, 2150016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, N.A.M.; Velde, M.; Cluitmans, P.J.M. Clinical Evaluation of a Method for Automatic Detection and Removal of Artifacts in Auditory Evoked Potential Monitoring. J. Clin. Monit. 1995, 11, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, C.A.; Gorodnitsky, I.F.; Kutas, M. Automatic Removal of Eye Movement and Blink Artifacts from EEG Data Using Blind Component Separation. Psychophysiology 2004, 41, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.K.; Zhang, C.Z.; Abdullah, A.A.A.; Lian, S. Automatic Extraction System for Common Artifacts in EEG Signals Based on Evolutionary Stone’s BSS Algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 324750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijović, B.; De Vos, M.; Gligorijević, I.; Taelman, J.; Van Huffel, S. Source Separation from Single-Channel Recordings by Combining Empirical-Mode Decomposition and Independent Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Noise-Assisted Data Analysis Method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Bu, X. Research on ocular electroocular artifact removal algorithm for single-channel EEG signals. Acta Autom. Sin. 2017, 43, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Qian, R.; Chen, X. Remove Diverse Artifacts Simultaneously from a Single-Channel EEG Based on SSA and ICA: A Semi-Simulated Study. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 60276–60289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddirala, A.K.; Veluvolu, K.C. ICA With CWT and K−means for Eye-Blink Artifact Removal from Fewer Channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhang, C.; Lei, J.; Han, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, A.; Bai, S.; Zhang, M. Cepstral Analysis-Based Artifact Detection, Recognition, and Removal for Prefrontal EEG. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liu, A.; Li, C.; Qian, R.; Chen, X. Frequency Information Enhanced Deep EEG Denoising Network for Ocular Artifact Removal. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 21855–21865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, H.; Shafiq, U.; Sajjad, Q.; Waris, A.; Gilani, O.; Boutaayamou, M.; Brüls, O. Variational Mode Decomposition for Surface and Intramuscular EMG Signal Denoising. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 82, 104560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Yang, X.; Feng, R.; Wu, Y. Strain Signal Denoising Based on Adaptive Variation Mode Decomposition (VMD) Algorithm. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2023, 42, 1854–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Cai, K.; Zhao, J. Study of improved VMD algorithm to eliminate baseline drift of PPG. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2020, 34, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wang, J.; Niu, X. Denoising Processing of ECG Signal Myoelectricity Interference Based on VMD and Wavelet Threshold. Chin. J. Sens. Actuators 2020, 33, 867–873. [Google Scholar]
- Zangeneh Soroush, M.; Tahvilian, P.; Nasirpour, M.H.; Maghooli, K.; Sadeghniiat-Haghighi, K.; Vahid Harandi, S.; Abdollahi, Z.; Ghazizadeh, A.; Jafarnia Dabanloo, N. EEG Artifact Removal Using Sub-Space Decomposition, Nonlinear Dynamics, Stationary Wavelet Transform and Machine Learning Algorithms. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 910368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorth, B. EEG Analysis Based on Time Domain Properties. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1970, 29, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-D.; Wu, C.-W.; Lin, S.-G.; Lee, K.-Y.; Peng, C.-K. Analysis of Complex Time Series Using Refined Composite Multiscale Entropy. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostaghi, M.; Azami, H. Dispersion Entropy: A Measure for Time-Series Analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.J. Fractals and the Analysis of Waveforms. Comput. Biol. Med. 1988, 18, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitanyi, P. Three Approaches to the Quantitative Definition of Information in an Individual Pure Quantum State. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 15th Annual IEEE Conference on Computational Complexity, Florence, Italy, 4–7 July 2000; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, E.H.; Hurst, H.E.; Black, R.P.; Simaika, Y.M. Long-Term Storage: An Experimental Study. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. Gen. 1966, 129, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature Selection Based on Mutual Information Criteria of Max-Dependency, Max-Relevance, and Min-Redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Guo, Y.; Liang, Z.; Qiu, X.; Wang, F.; Sui, W. Application of Variational Mode Decomposition in Removing ECG Signal Baseline Drift. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2018, 32, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, W.; Li, M. AR Based Quadratic Feature Extraction in the VMD Domain for the Automated Seizure Detection of EEG Using Random Forest Classifier. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhen, C. Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Fuzzy C Means Clustering. Proc. CSEE 2015, 35, 3358–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Mohanty, M.N. Comparative Analysis of EMD and VMD Algorithm in Speech Enhancement. Int. J. Nat. Comput. Res. 2017, 6, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yun, W. Research progress of genetic algorithm. Appl. Res. Comput. 2012, 29, 1201–1206+1210. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, X.; Duan, L.; Yang, X.; Huang, Q. Review on the Application of Intelligent Optimization Algorithms in Mechanical Fault Diagnosis. Meas. Control Technol. 2021, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, L.; Liu, J.; Yuan, J. Denoising Analysis of Bearing Vibration Signal Based on Genetic Algorithm and Wavelet Threshold VMD. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2017, 36, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belouchrani, A.; Abed-Meraim, K.; Cardoso, J.-F.; Moulines, E. A Blind Source Separation Technique Using Second-Order Statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S. Approximate Entropy (ApEn) as a Complexity Measure. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 1995, 5, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.; Wei, C.; Mantini, D.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q. EEGdenoiseNet: A Benchmark Dataset for Deep Learning Solutions of EEG Denoising. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 056057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalighi, S.; Sousa, T.; Santos, J.M.; Nunes, U. ISRUC-Sleep: A Comprehensive Public Dataset for Sleep Researchers. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 124, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y. Research on Automatic Removal of Ocular Artifacts from Single Channel Electroencephalogram Signals Based on Wavelet Transform and Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. J. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 38, 473–482. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh-Thu, Q.; Ghanbari, M. Scope of Validity of PSNR in Image/Video Quality Assessment. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Chen, D.; Ouyang, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X. An EEMD-ICA Approach to Enhancing Artifact Rejection for Noisy Multivariate Neural Data. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddirala, A.K.; Veluvolu, K.C. SSA with CWT and K-Means for Eye-Blink Artifact Removal from Single-Channel EEG Signals. Sensors 2022, 22, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbakhti, M.; Beiramvand, M.; Nazari, M.; Broniec-Wójcik, A.; Augustyniak, P.; Marozas, V. VME-DWT: An Efficient Algorithm for Detection and Elimination of Eye Blink from Short Segments of Single EEG Channel. IEEE Trans. NEURAL Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, M.F.; Juhasz, Z. Improved EOG Artifact Removal Using Wavelet Enhanced Independent Component Analysis. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheela, P.; Puthankattil, S.D. A Hybrid Method for Artifact Removal of Visual Evoked EEG. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 336, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Gireesan, K.; Sengottuvel, S.; Janawadkar, M.P.; Radhakrishnan, T.S. Common Methodology for Cardiac and Ocular Artifact Suppression from EEG Recordings by Combining Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Regression Approach. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2017, 37, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, M.M.N.; Kamran, M.A.; Jeong, M.Y. Identification and Removal of Physiological Artifacts from Electroencephalogram Signals: A Review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 30630–30652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | F3 | C3 | O1 | F4 | C3 | O2 | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEMD_ICA [53] | 1.3362 | 1.0019 | 0.6521 | 1.3298 | 1.0479 | 1.3362 | 0.2948 | |
| 0.006 | 0.0206 | 0.0236 | 0.0134 | 0.0150 | 0.006 | 0.0064 | ||
| 0.0109 | 0.0121 | 0.0190 | 0.0117 | 0.0132 | 0.0109 | 0.0030 | ||
| 0.0068 | 0.0105 | 0.0050 | 0.0093 | 0.0097 | 0.0068 | 0.0025 | ||
| SSA_SOBI [23] | 2.5259 | 1.7836 | 1.0070 | 2.3040 | 1.7182 | 1.0555 | 1.7324 ± 0.6235 | |
| 0.0174 | 0.0206 | 0.0233 | 0.0220 | 0.0165 | 0.0247 | 0.0207 ± 0.0033 | ||
| 0.0033 | 0.0043 | 0.0076 | 0.0038 | 0.003 | 0.0082 | 0.0050 ± 0.0023 | ||
| 0.0032 | 0.0053 | 0.0095 | 0.0019 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.0060 ± 0.0031 | ||
| CWT_KMEANS_SSA [54] | 1.7120 | 1.2567 | 0.6645 | 1.6524 | 1.2114 | 0.6845 | 1.1969 ± 0.4522 | |
| 0.1651 | 0.1575 | 0.1270 | 0.1674 | 0.1451 | 0.1208 | 0.1472 ± 0.0197 | ||
| 0.0320 | 0.0325 | 0.0254 | 0.0341 | 0.0322 | 0.028 | 0.0307 ± 0.0033 | ||
| 0.0088 | 0.0050 | 0.0023 | 0.0107 | 0.0076 | 0.0029 | 0.0062 ± 0.0034 | ||
| VME_DWT [55] | 0.4991 | 0.3232 | 0.1868 | 0.4589 | 0.2884 | 0.1714 | 0.3213 ± 0.1358 | |
| 0.0091 | 0.0181 | 0.0172 | 0.0124 | 0.0069 | 0.0177 | 0.0136 ± 0.0048 | ||
| 0.0042 | 0.0028 | 0.0017 | 0.0042 | 0.0054 | 0.0067 | 0.0042 ± 0.0018 | ||
| 0.0062 | 0.0046 | 0.0015 | 0.0051 | 0.0029 | 0.0017 | 0.0037 ± 0.0019 | ||
| SVM-IVMD-SOBI | 2.5457 | 1.9539 | 1.0891 | 2.5131 | 1.8873 | 1.1672 | 1.8594 ± 0.6293 | |
| 0.0199 | 0.0291 | 0.0333 | 0.0345 | 0.0181 | 0.0376 | 0.0288 ± 0.0081 | ||
| 0.0036 | 0.0045 | 0.0037 | 0.004 | 0.0055 | 0.0033 | 0.0041 ± 0.0008 | ||
| 0.0028 | 0.0031 | 0.0054 | 0.0025 | 0.0015 | 0.0061 | 0.0036 ± 0.0018 |
| Evaluation Index | W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtering, ICA processing | Precision | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 0.84 |
| Recall | 0.92 | 0.52 | 0.78 | 0.92 | 0.75 | |
| F1 | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.77 | 0.90 | 0.79 | |
| ACC: 0.804, MF1: 0.784, WF1: 0.802 | ||||||
| EEMD-ICA [53] | Precision | 0.85 | 0.54 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 0.73 |
| Recall | 0.90 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.68 | |
| F1 | 0.87 | 0.41 | 0.72 | 0.87 | 0.71 | |
| ACC: 0.763, MF1: 0.716, WF1: 0.754 | ||||||
| SSA-SOBI [23] | Precision | 0.90 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.86 | 0.94 |
| Recall | 0.97 | 0.49 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.84 | |
| F1 | 0.93 | 0.55 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 0.89 | |
| ACC: 0.820, MF1: 0.798, WF1: 0.816 | ||||||
| CWT-KMEANS-SSA [54] | Precision | 0.86 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.90 | 0.85 |
| Recall | 0.91 | 0.43 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.81 | |
| F1 | 0.88 | 0.51 | 0.76 | 0. 92 | 0.83 | |
| ACC: 0.815, MF1: 0.781, WF1: 0.809 | ||||||
| VME-DWT [55] | Precision | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 0.77 |
| Recall | 0.87 | 0.45 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.78 | |
| F1 | 0.86 | 0.54 | 0.81 | 0. 92 | 0.78 | |
| ACC: 0.809, MF1: 0.780, WF1: 0.803 | ||||||
| SVM-IVMD-SOBI | Precision | 0.87 | 0.68 | 0.81 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| Recall | 0.94 | 0.53 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.81 | |
| F1 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.83 | 0.94 | 0.85 | |
| ACC: 0.854, MF1: 0.824, WF1: 0.850 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; He, J. Research on Ocular Artifacts Removal from Single-Channel Electroencephalogram Signals in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients Based on Support Vector Machine, Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, and Second-Order Blind Identification. Sensors 2024, 24, 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051642
Xiong X, Sun Z, Wang A, Zhang J, Zhang J, Wang C, He J. Research on Ocular Artifacts Removal from Single-Channel Electroencephalogram Signals in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients Based on Support Vector Machine, Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, and Second-Order Blind Identification. Sensors. 2024; 24(5):1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051642
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Xin, Zhiran Sun, Aikun Wang, Jiancong Zhang, Jing Zhang, Chunwu Wang, and Jianfeng He. 2024. "Research on Ocular Artifacts Removal from Single-Channel Electroencephalogram Signals in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients Based on Support Vector Machine, Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, and Second-Order Blind Identification" Sensors 24, no. 5: 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051642
APA StyleXiong, X., Sun, Z., Wang, A., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., Wang, C., & He, J. (2024). Research on Ocular Artifacts Removal from Single-Channel Electroencephalogram Signals in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients Based on Support Vector Machine, Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, and Second-Order Blind Identification. Sensors, 24(5), 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051642





