Improved RRT* Algorithm for Disinfecting Robot Path Planning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
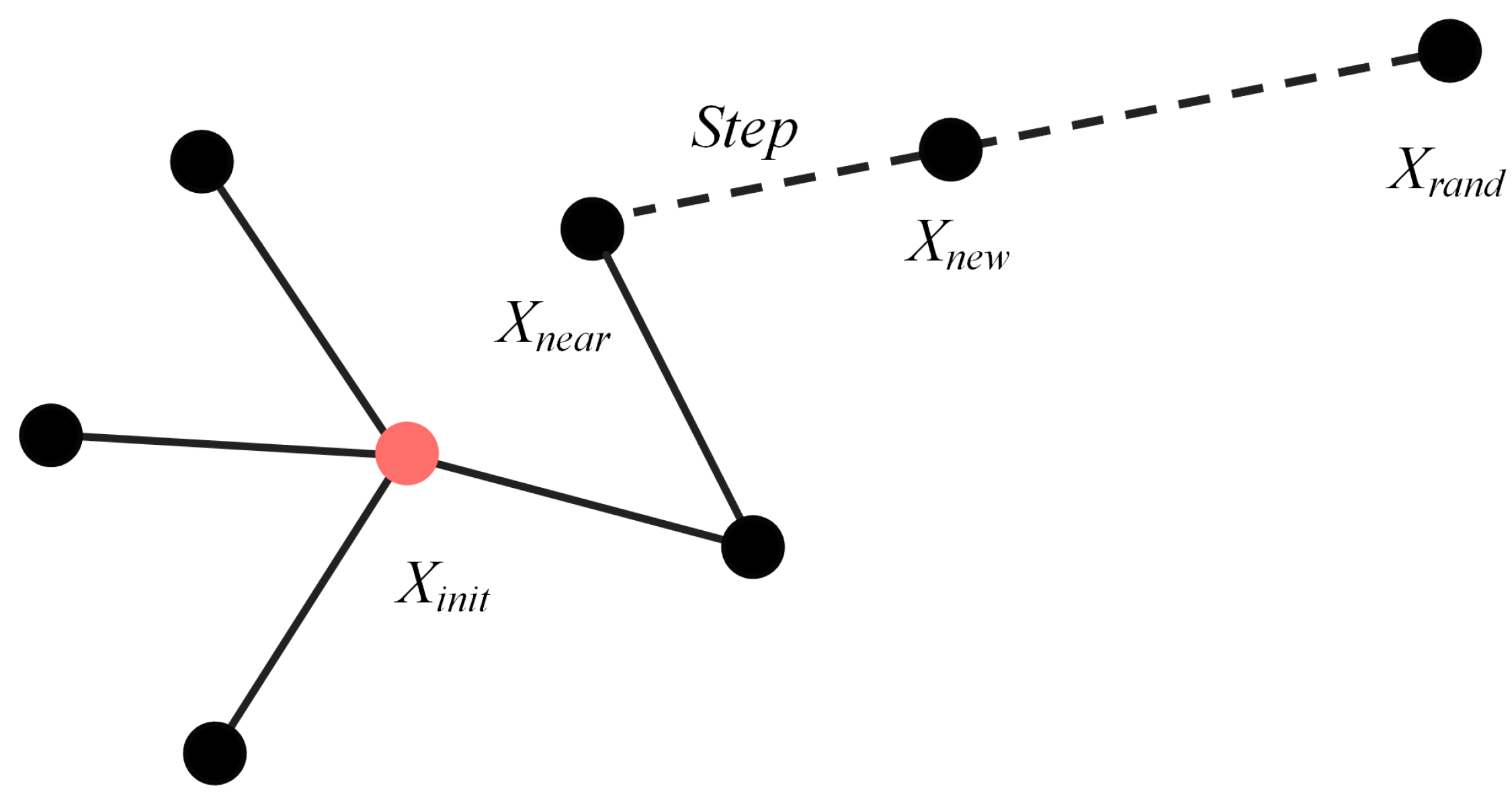
2.1. Basic RRT* Algorithm
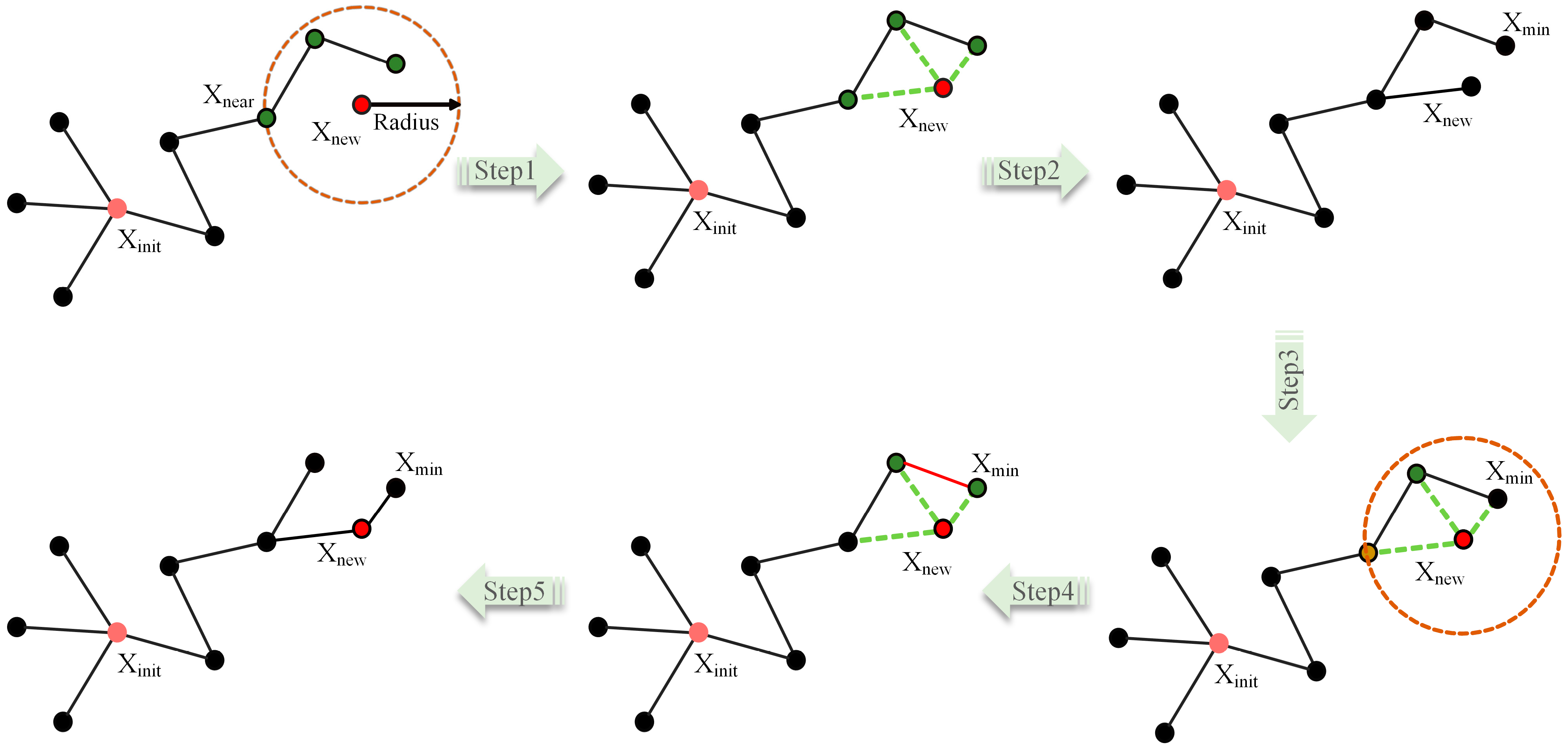
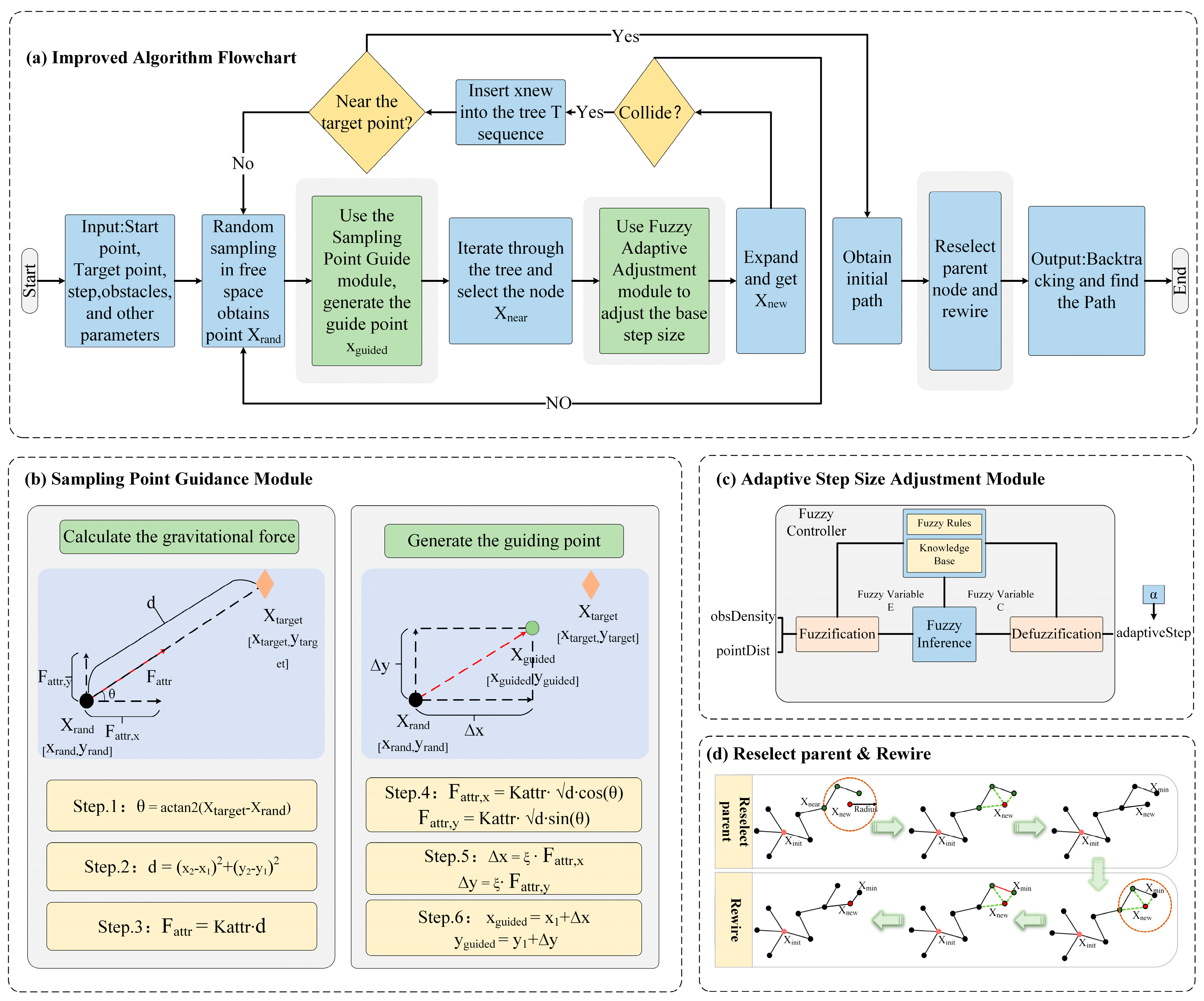
2.2. Implementation of the Improved Algorithm
2.2.1. Sampling Point Guidance Module
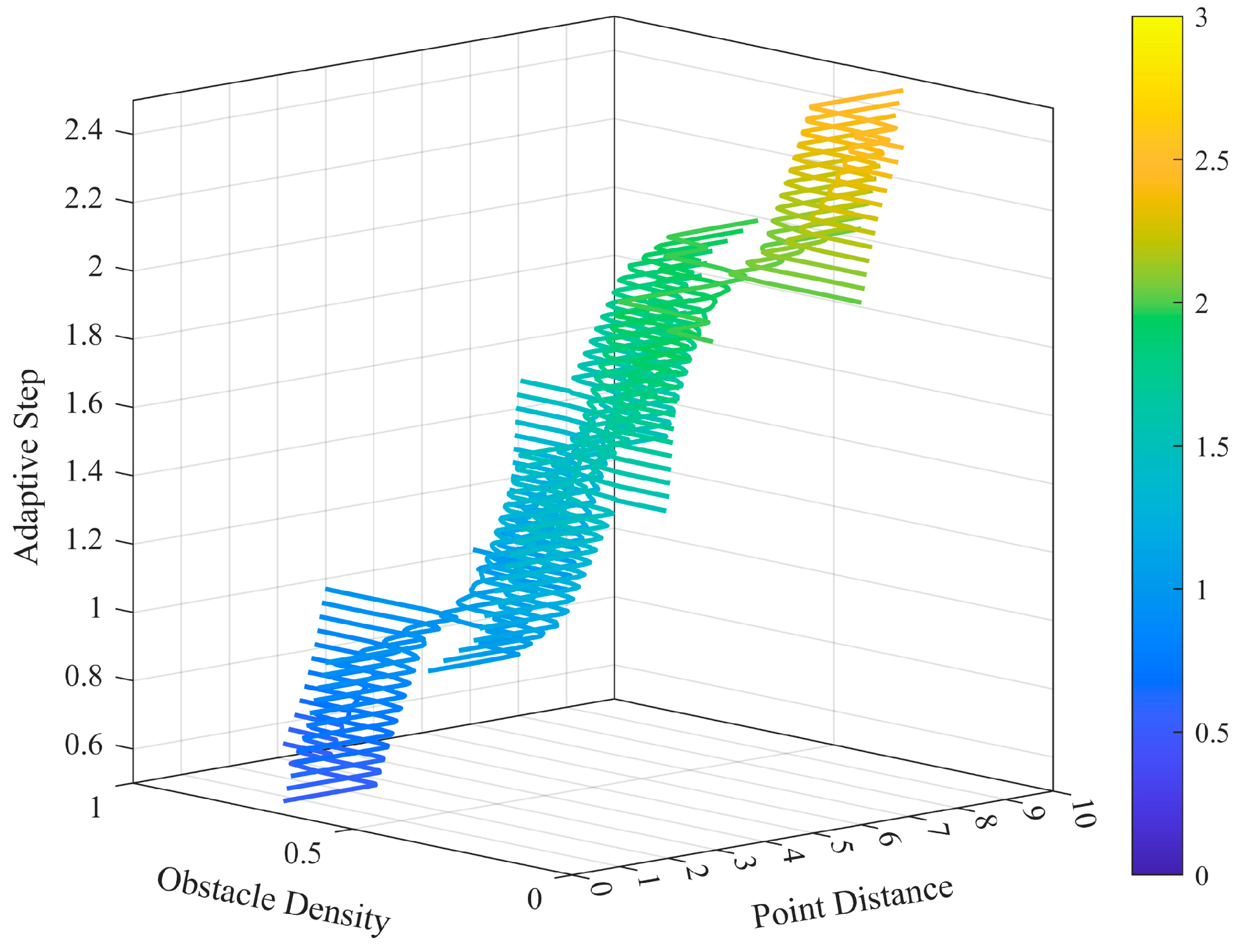
2.2.2. Adaptive Step-Size Adjustment Module
2.2.3. Implementation of the Improved Algorithm
- Initialization (lines 1–2): Initiate the whole program, set the start point , the target point , and other parameters, and create an empty tree T with as the root node.
- Main loop (iterative loop, lines 3–28):
- ➢
- Lines 4–6: Generate a random point , calculate the attraction force , and get the coordinates of the guidance point.
- ➢
- Lines 7–8: Calculate and search for node in tree T.
- ➢
- Lines 9–24: Call function to check if the line from to crosses the obstacle.
- ➢
- Line 10–11: Call the function to calculate the obstacle density level at the guided point and output according to the fuzzy rules.
- ➢
- Line 12–17: Check whether the first feasible path has been searched, if is 1, then it is currently in the path optimization stage, adjust the extended step size according to the scaling factor . Next, expand the .
- ➢
- Lines 18–23: Select the parent node and update the tree structure.
- ➢
- Lines 25–27: Check if the new node reaches the target point or nearby area, if yes, add the target point into the tree structure and backtrack the final path.
- Return result (line 29): If the maximum number of iterations is reached and no path is found, then return no path.
| Algorithm 1 Algorithm |
| 01: Initialize , , and other parameters. |
| 02: Initialize an empty tree with the root node as |
| 03: for to do |
| 04: |
| 05: |
| 06: |
| 07: |
| 08: |
| 09: If then |
| 10: |
| 11: |
| 12: If then |
| 13: |
| 14: else |
| 15: |
| 16: |
| 17: end if |
| 18: |
| 19: |
| 20: |
| 21: |
| 22: |
| 23: |
| 24: end if |
| 25: if then |
| 26: return |
| 27: end if |
| 28: end for |
| 29: return |
3. Experiment and Analysis
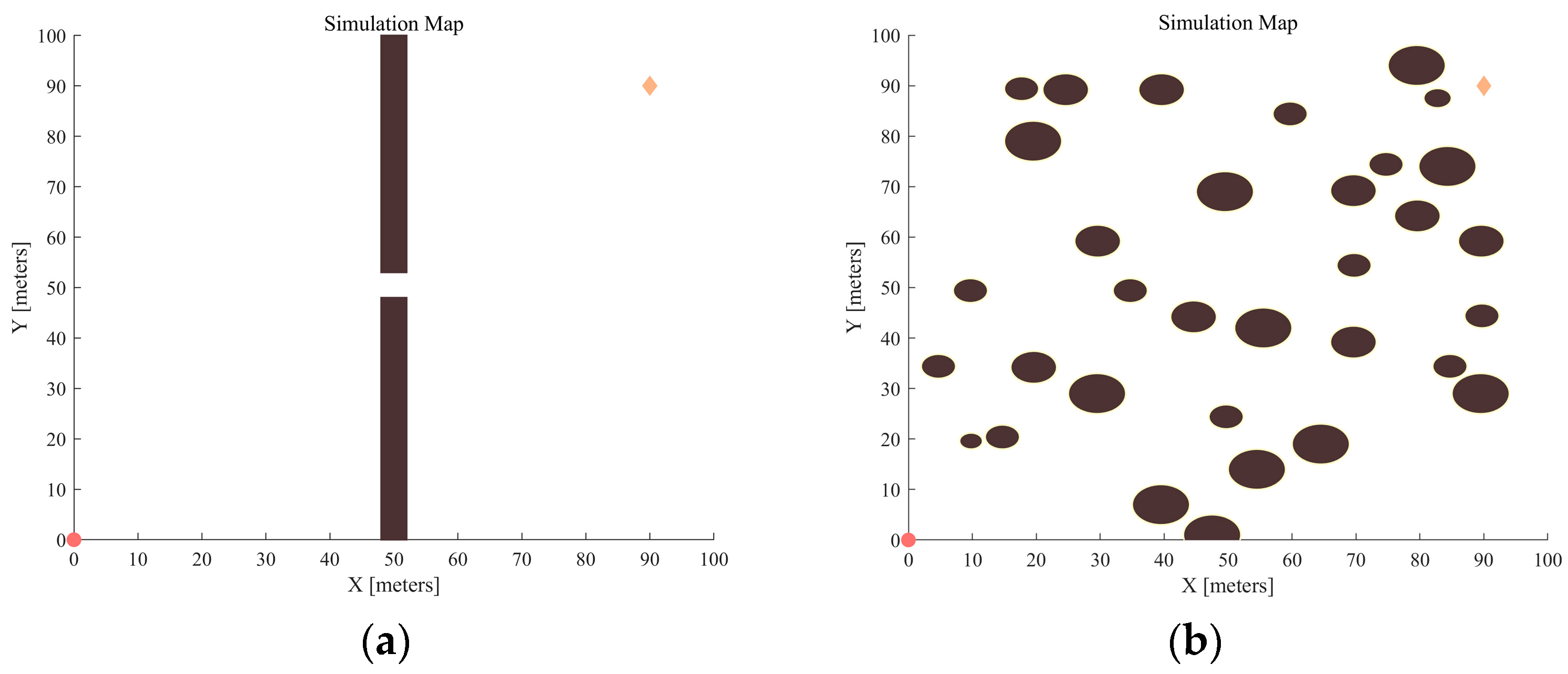
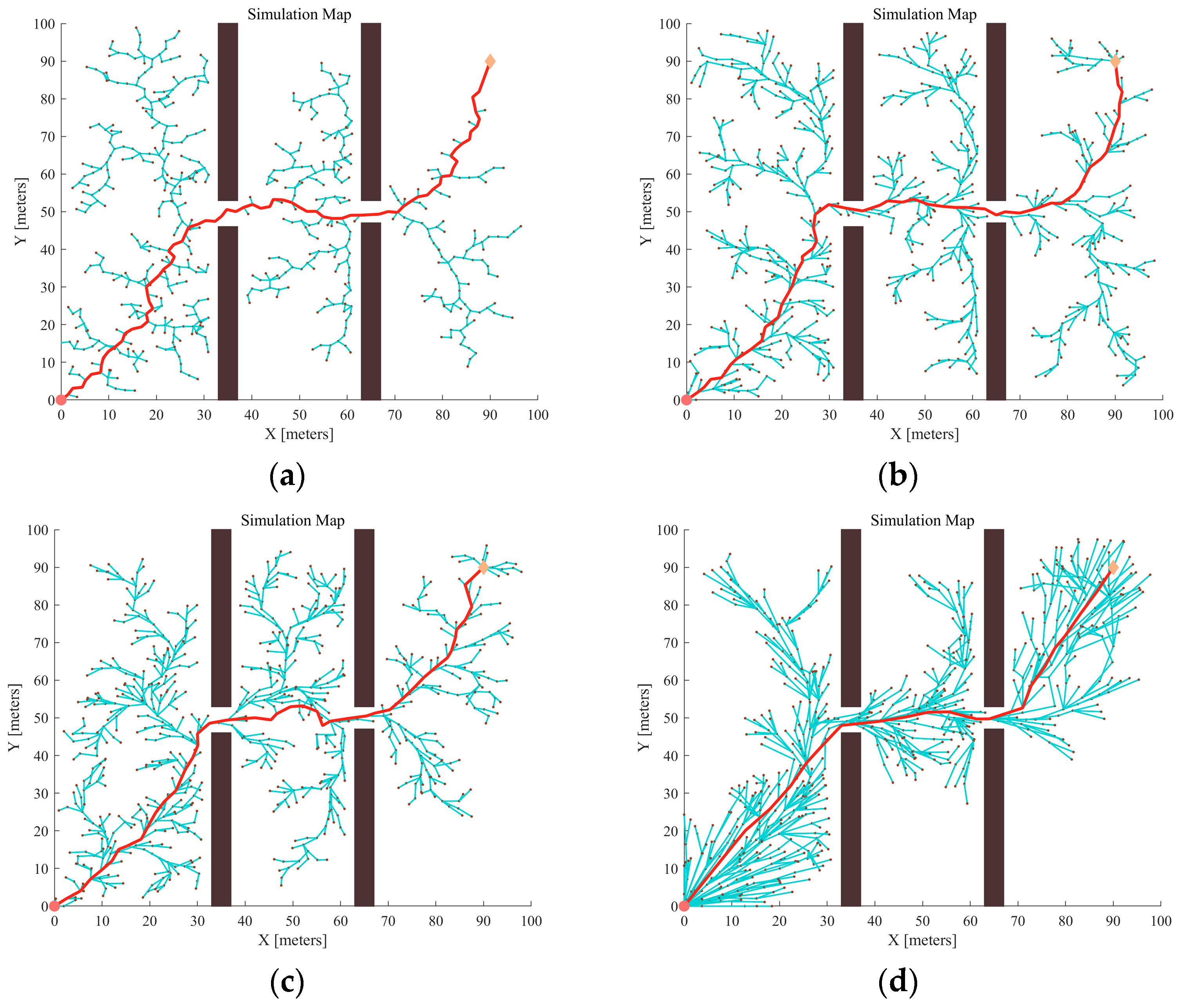
3.1. Narrow Passage Testing
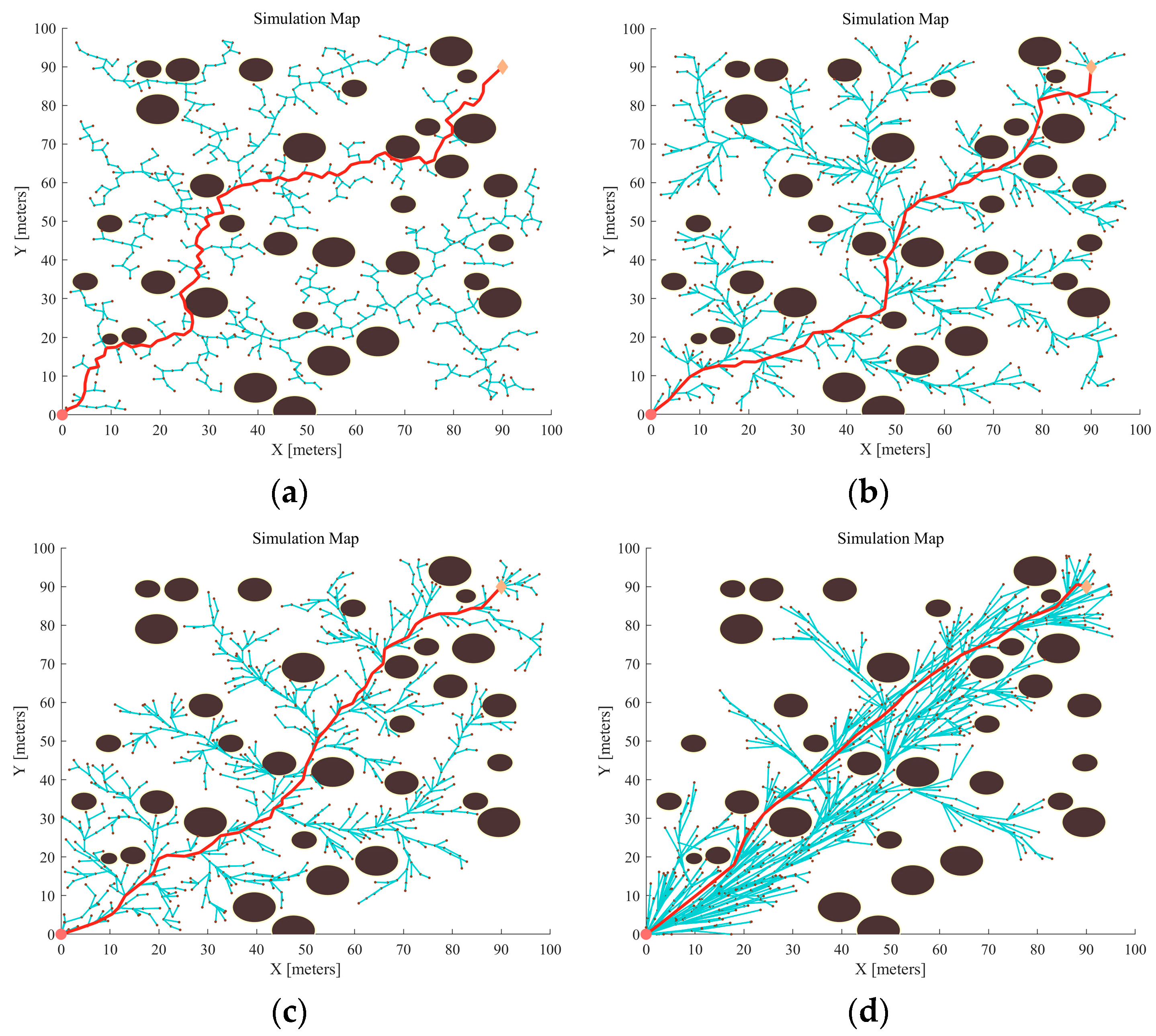
3.2. Dense Obstacle Testing
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Astrid, F.; Beata, Z.; Miriam, N.; Julia, E.; Elisabeth, P.; Magda, D.-E. The use of a UV-C disinfection robot in the routine cleaning process: A field study in an Academic hospital. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Tsai, R.-G.; Xu, C.; Chen, X.; Weng, Y.; Lai, K.; Yu, Y. UV*: A Boustrophedon Pattern-Based Path Planning and Opti-mization Strategy for an Ultraviolet Disinfection Robot. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 52603–52613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, J.; Thierauf, C.; Rule, P.; Krause, E.A.; Akitaya, H.A.; Gonczi, A.; Korman, M.; Scheutz, M. Robot Development and Path Planning for Indoor Ultraviolet Light Disinfection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 7795–7801. [Google Scholar]
- Dogru, S.; Marques, L. Path and Trajectory Planning for UV-C Disinfection Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4099–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.M.; Bibinov, N.K.; Blanco, E.V.; Pfaender, S.; Theiß, S.; Wolter, H.; Awakowicz, P. Characterization of a robot-assisted UV-C disinfection for the inactivation of surface-associated microorganisms and viruses. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 11, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinn, C.; Scott, R.; Donnelly, N.; Roberts, K.L.; Bogue, M.; Kiernan, C.; Beckett, M. Exploring the Applicability of Robot-Assisted UV Disinfection in Radiology. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 7, 590306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiseni, L.; Chiaradia, D.; Gabardi, M.; Solazzi, M.; Leonardis, D.D.; Frisoli, A. UV-C Mobile Robots with Optimized Path Planning: Algorithm Design and On-Field Measurements to Improve Surface Disinfection Against SARS-CoV-2. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2021, 28, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guettari, M.; Gharbi, I.; Hamza, S. UVC disinfection robot. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 40394–40399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Y. Research on global path planning of electric disinfection vehicle based on improved A* algorithm. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wilson, J.P.; Gupta, S. An Online Coverage Path Planning Algorithm for Curvature-Constrained AUVs. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–31 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Ferrari, S. Information-Driven Sensor Path Planning by Approximate Cell Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 2009, 39, 672–689. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, G.; Niu, X.; Xia, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y. A hybrid formation path planning based on A* and mul-ti-target improved artificial potential field algorithm in the 2D random environments. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 54, 101755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.L.; Su, B.Y.; Dong, C.Z.; Shen, D.W.; Xiang, E.Z.; Mao, F.P. A two-level dynamic obstacle avoidance algorithm for unmanned surface vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2018, 170, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Dai, J.; Jiang, B.; Karimi, H.R. Robot path planning based on artificial potential field with deterministic annealing. ISA Trans. 2023, 138, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, M.; Sushnigdha, G. A Hybrid Path planning approach combining Artificial Potential Field and Particle Swarm Op-timization for Mobile Robot. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, O. Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St. Louis, MO, USA, 25–28 March 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Q.; Wang, X. Independent travel recommendation algorithm based on analytical hierarchy process and simulated annealing for professional tourist. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 1565–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, D.V.; Sierra-García, J.E.; Santos, M. Glasius bio-inspired neural networks based UV-C disinfection path planning improved by preventive deadlock processing algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2023, 175, 103330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, B.; Yin, J.; Elara, M.R.; Tamilselvam, Y.K.; Rayguru, M.M.; Muthugala, V.J.; Gómez, B.F. A Human Support Robot for the Cleaning and Maintenance of Door Handles Using a Deep-Learning Framework. Sensors 2020, 20, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Deng, G.; Luo, C.; Lin, Q.; Yan, Q.; Ming, Z. A Hybrid Path Planning Method in Unmanned Air/Ground Vehicle (UAV/UGV) Cooperative Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 9585–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Wang, Z.; Zou, L. An improved PSO algorithm for smooth path planning of mobile robots using continuous high-degree Bezier curve. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, X. Path planning optimization of medical service robots based on PSO. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Applications (ICWCAPP), Haikou, China, 20–21 August 2022; pp. 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Nayeem, G.M.; Fan, M.; Daiyan, G.M.; Fahad, K.S. UAV Path Planning with an Adaptive Hybrid PSO. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development (ICICT4SD), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 21–23 September 2023; pp. 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- LaValle, S.M. Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees: A New Tool for Path Planning; The Annual Research Report; Department of Computer Science, Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, H.T.L.; Tapia, L. COLREG-RRT: An RRT-Based COLREGS-Compliant Motion Planner for Surface Vehicle Navigation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enevoldsen, T.T.; Galeazzi, R. Grounding-aware RRT* for Path Planning and Safe Navigation of Marine Crafts in Confined Waters. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, L. Path planning algorithm of robot arm based on improved RRT* and BP neural network algorithm. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseko, B.B.; van Daalen, C.E.; Treurnicht, J. Optimised Informed RRTs for Mobile Robot Path Planning. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. SET: Sampling-Enhanced Exploration Tree for Mobile Robot in Restricted Environments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 10467–10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, X.; He, M.; Fu, X.; Wu, X.; Shao, G. Improved Artificial Potential Field based Parallel RRT Star for Fast Path Planning. In Proceedings of the 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC), Beijing, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 5801–5806. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Duan, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, J. A probability smoothing Bi-RRT path planning algorithm for indoor robot. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 143, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffner, J.J.; LaValle, S.M. RRT-connect: An efficient approach to single-query path planning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automa-tion. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 1002, pp. 995–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, S.; Frazzoli, E. Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 846–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammell, J.D.; Srinivasa, S.S.; Barfoot, T.D. Informed RRT*: Optimal sampling-based path planning focused via direct sampling of an admissible ellipsoidal heuristic. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 2997–3004. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Wei, C.; Huang, Q.; Hu, J. APF-RRT*: An Efficient Sampling-Based Path Planning Method with the Guidance of Arti-ficial Potential Field. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Mechatronics and Robotics Engineering (ICMRE), Shenzhen, China, 10–12 February 2023; pp. 207–213. [Google Scholar]






| ObsDensity | PointDist | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NL | NS | ZE | PS | PL | |
| NL | ZE | PS | PS | PL | PL |
| NM | NS | ZE | PS | PS | PL |
| ZE | NS | NS | ZE | PS | PS |
| PM | NL | NS | NS | ZE | PS |
| PL | NL | NL | NS | NS | ZE |
| Algorithm Name | Avg Path Nodes | Avg Path Cost | Search Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| RRT | 63.4727 | 159.0696 | 75.48% |
| RRT* | 58.3754 | 145.8456 | 71.67% |
| APF-RRT* | 57.2992 | 143.2481 | 86.55% |
| APF-GFARRT* | 26.7362 | 121.0377 | 90.21% |
| Algorithm Name | Avg Path Nodes | Avg Path Cost | Search Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| RRT | 69.4068 | 187.3988 | 46.25% |
| RRT* | 64.8138 | 174.5346 | 47.23% |
| APF-RRT* | 56.3792 | 152.3845 | 65.92% |
| APF-GFARRT* | 28.2977 | 128.4178 | 85.76% |
| Algorithm Name | Avg 1st Path Time/s | Avg Path Nodes | Avg Path Cost | Search Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRT | 6.8701 | 81.1864 | 160.6656 | 73.48% |
| RRT* | 6.6804 | 46.3722 | 142.4439 | 84.98% |
| APF-RRT* | 4.74 | 45.8793 | 138.9890 | 87.16% |
| APF-GFARRT* | 3.5721 | 29.2977 | 128.184 | 97.62% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Cao, L. Improved RRT* Algorithm for Disinfecting Robot Path Planning. Sensors 2024, 24, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051520
Wang H, Zhou X, Li J, Yang Z, Cao L. Improved RRT* Algorithm for Disinfecting Robot Path Planning. Sensors. 2024; 24(5):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051520
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haotian, Xiaolong Zhou, Jianyong Li, Zhilun Yang, and Linlin Cao. 2024. "Improved RRT* Algorithm for Disinfecting Robot Path Planning" Sensors 24, no. 5: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051520
APA StyleWang, H., Zhou, X., Li, J., Yang, Z., & Cao, L. (2024). Improved RRT* Algorithm for Disinfecting Robot Path Planning. Sensors, 24(5), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051520





