Using Sparse Parts in Fused Information to Enhance Performance in Latent Low-Rank Representation-Based Fusion of Visible and Infrared Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based methods can be categorized into two primary methods. First, CNNs are trained on visible, infrared, and fused images to acquire the requisite weightings for fusion [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Second, it leverages pre-trained neural network models to only extract features and obtain weight maps from the images, thereby achieving the fusion objective [30,31,32,33];
- Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based methods transform the task of integrating visible and infrared images into an adversarial process, characterized by the interplay between a generator and a discriminator. Their objective is to combine visible and infrared images through the generator, at the same time tasking the discriminator with evaluating the sufficiency of visible and infrared information within the fused image [34,35,36,37,38,39,40];
- Encoder-decoder-based networks consist of two main components: an encoder and a decoder. The encoder extracts high-dimensional feature representations from the source images. The decoder’s job is to reconstruct the encoded features, gradually restoring the image’s details and structure, ultimately producing the fused image. Traditional autoencoders typically employ fully connected layers. Convolutional layers and pooling layers have also been utilized, thus improving feature extraction capabilities and robustness [41,42,43,44,45,46];
- Transformer-based methods: the Transformer was originally introduced for natural language processing and has demonstrated significant achievements in this domain [47]. Due to its remarkable long-range modeling capabilities, the Transformer has attracted the attention of researchers in the field of image fusion [48,49,50,51,52,53]. Transformer converters incorporate Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Multihead Self-Attention (MSA) blocks. Residual structures and Layer Normalization (LN) are applied before each MSA and MLP layer. The core design of these converters involves the fusion of input vectors with positional embeddings to preserve positional information for each vector.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
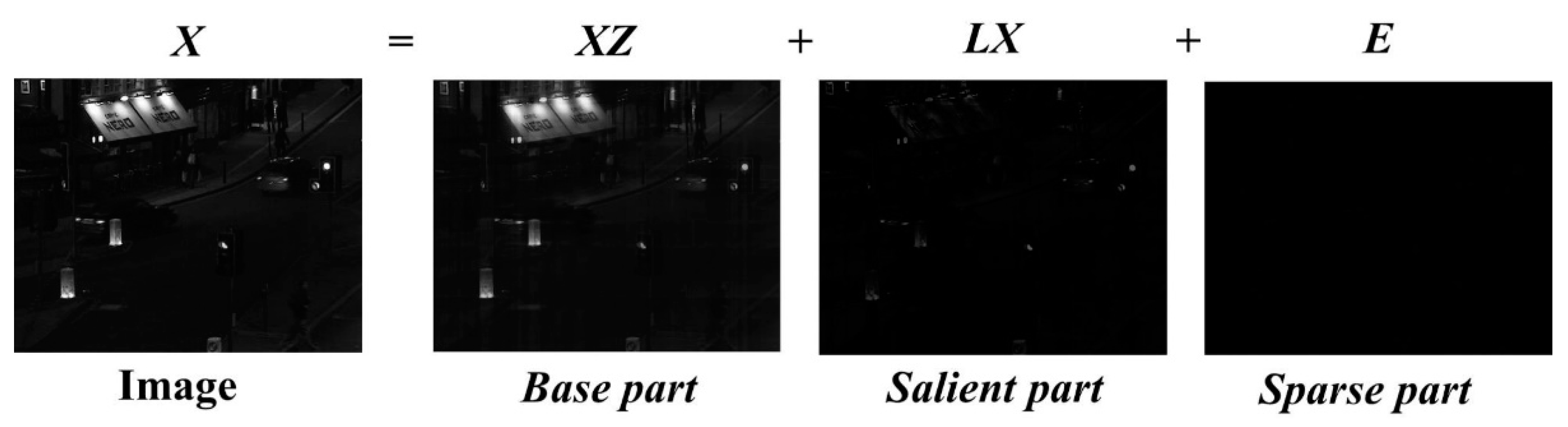
3.1. LatLRR for Image Decomposition
3.2. CNN-Based Pre-Trained Model for Weighted Maps Extraction
3.3. The Fusion Strategy
3.4. Image Dataset
4. Results
4.1. Objective Assessments
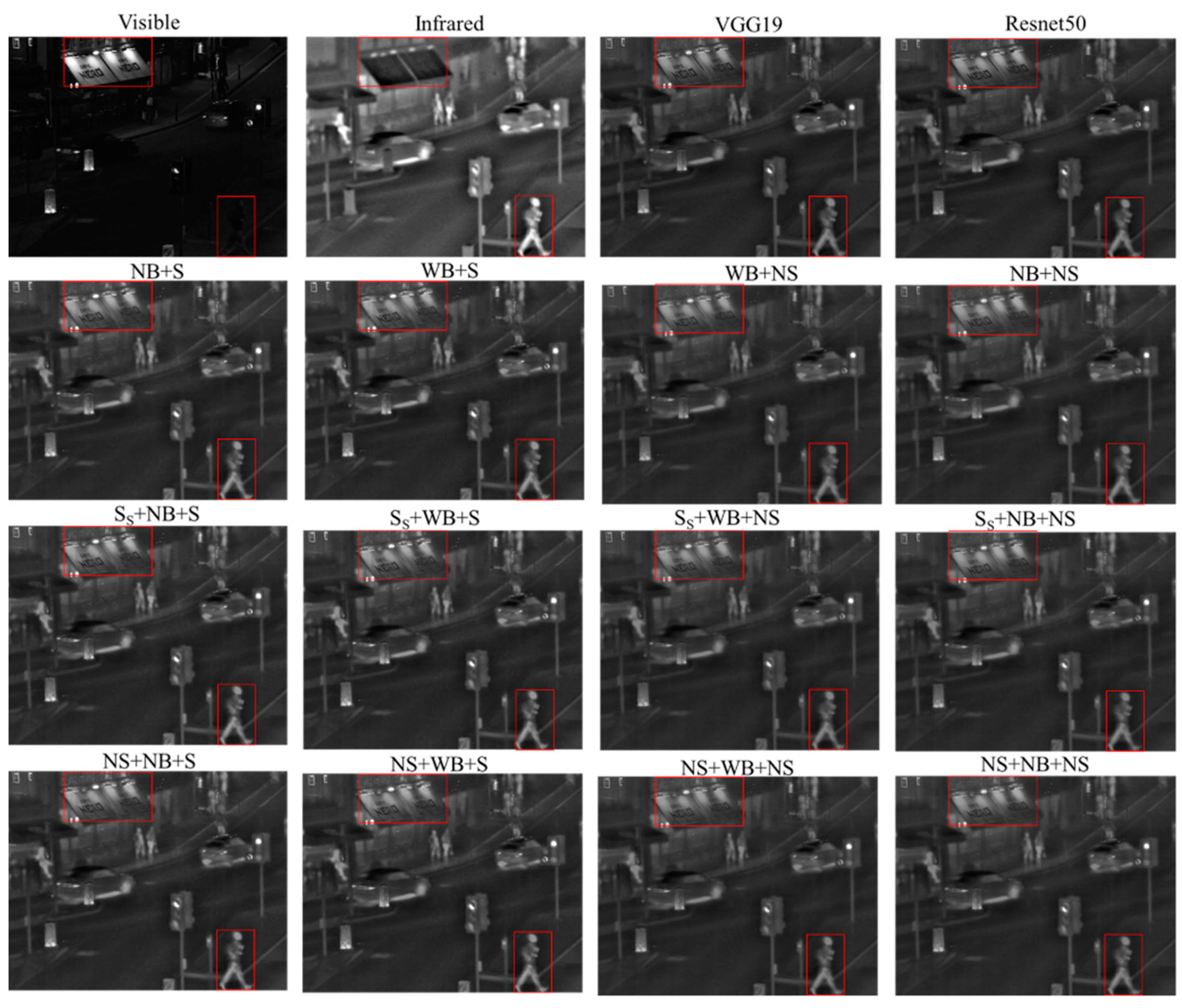
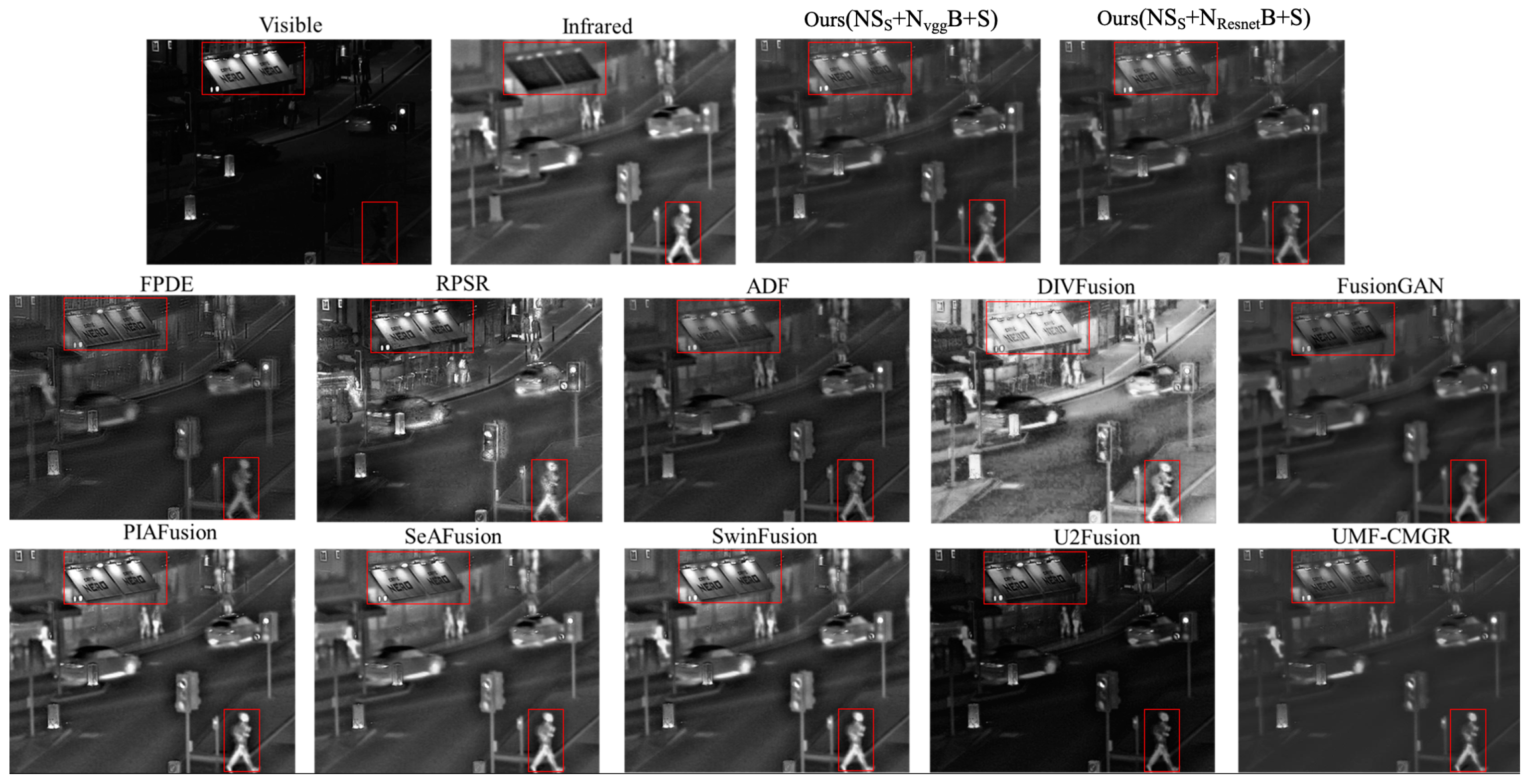
4.2. Subjective Assessments
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munir, A.; Kwon, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kong, J.; Blasch, E.; Aved, A.J.; Muhammad, K. FogSurv: A fog-assisted architecture for urban surveillance using artificial intelligence and data fusion. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 111938–111959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnakian, F.; Poikonen, J.; Laurinen, M.; Makris, D.; Heikkonen, J. Visible and infrared image fusion framework based on RetinaNet for marine environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Samir, A.; Rashed, H.; Yogamani, S.; Dahyot, R. Cnn based color and thermal image fusion for object detection in automated driving. In Proceedings of the Irish Machine Vision and Image Processing, Sligo, Ireland, 31 August–2 September 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, M.A.; Khan, K.B.; Salahuddin, S.; Rehman, E.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, M.A.; Kadry, S.; Gandomi, A.H. A review on multimodal medical image fusion: Compendious analysis of medical modalities, multimodal databases, fusion techniques and quality metrics. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 144, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Q.; Lu, H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, X. GAN review: Models and medical image fusion applications. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarani, N.; Venkatakrishnan, P.; Balaji, N. Unmanned Aerial vehicle’s runway landing system with efficient target detection by using morphological fusion for military surveillance system. Comput. Commun. 2020, 151, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, S.X.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Li, Q. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Tong, G.; Li, J.; Qadir, A.; Farooq, U.; Yu, Y. Current advances and future perspectives of image fusion: A comprehensive review. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, B.S.; Jones, L.R.; Elmore, J.A.; Samiappan, S.; Evans, K.O.; Pfeiffer, M.B.; Blackwell, B.F.; Iglay, R.B. Fusion of visible and thermal images improves automated detection and classification of animals for drone surveys. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, H.; Gehlot, A.; Kaur, J.; Gagandeep. IR and visible image fusion using DWT and bilateral filter. Microsyst. Technol. 2023, 29, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qian, Y. Infrared and multi-type images fusion algorithm based on contrast pyramid transform. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 78, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Wirth, M. Visible and IR data fusion technique using the contourlet transform. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29–31 August 2009; pp. 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Adu, J.; Gan, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J. Image fusion based on nonsubsampled contourlet transform for infrared and visible light image. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2013, 61, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Xiao, G.; Liu, G. Multi-sensor image fusion based on fourth order partial differential equations. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Dhuli, R. Fusion of infrared and visible sensor images based on anisotropic diffusion and Karhunen-Loeve transform. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 16, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-F.; Luo, X.-Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-C. Image fusion based on shift invariant shearlet transform and stacked sparse autoencoder. J. Algorithms Comput. Technol. 2018, 12, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zuo, Y.; Sun, J. Infrared and visible image fusion using visual saliency sparse representation and detail injection model. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 5001715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmalraj, S.; Nagarajan, G. Fusion of visible and infrared image via compressive sensing using convolutional sparse representation. ICT Express 2021, 7, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, H.; Zhou, F.; Wang, G.; Li, X. Infrared and visible image fusion based on domain transform filtering and sparse representation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, F.; Mosavi, M.R.; Lajvardi, M.M. Image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation: An image energy approach. IET Image Process. 2017, 11, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.-B.; Wang, H.-M. Infrared and visible image fusion with supervised convolutional neural network. Optik 2020, 219, 165120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; An, W.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Zhou, D. Infrared and visible image fusion based on multi-channel convolutional neural network. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, B.; Khan, A.M.; Akram, M.U.; Batool, S. Person detection by fusion of visible and thermal images using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Communication, Computing and Digital systems (C-CODE), Islamabad, Pakistan, 6–7 March 2019; pp. 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, R. Unsupervised misaligned infrared and visible image fusion via cross-modality image generation and registration. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.11876. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Durrani, T.S. Infrared and visible image fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Kittler, J. Infrared and visible image fusion using a deep learning framework. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 2705–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Ren, K.; Wan, M.; Cheng, B.; Gu, G.; Chen, Q. An infrared and visible image fusion method based on VGG-19 network. Optik 2021, 248, 168084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, R.; Du, P. An infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on ResNet-152. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 9277–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciprián-Sánchez, J.F.; Ochoa-Ruiz, G.; Gonzalez-Mendoza, M.; Rossi, L. FIRe-GAN: A novel deep learning-based infrared-visible fusion method for wildfire imagery. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 35, 18201–18213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Tian, X.; Ma, J. GAN-FM: Infrared and visible image fusion using GAN with full-scale skip connection and dual Markovian discriminators. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, F.; Sveinsson, J.R.; Ulfarsson, M.O. Single sensor image fusion using a deep convolutional generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 23–26 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Liang, P.; Yu, W.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Learning a Generative Model for Fusing Infrared and Visible Images via Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with Dual Discriminators. In Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 3954–3960. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, M.; Fatemi, A.; Archambault, L. MedFusionGAN: Multimodal medical image fusion using an unsupervised deep generative adversarial network. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion using dual discriminators generative adversarial networks with Wasserstein distance. Inf. Sci. 2020, 529, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gong, M.; Tian, X.; Huang, J.; Ma, J. CUFD: An encoder–decoder network for visible and infrared image fusion based on common and unique feature decomposition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 218, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, G.; Bineeshia, J. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion using Enhanced Thermal Image. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Communication, IoT and Security (ICISCoIS), Coimbatore, India, 9–11 February 2023; pp. 392–397. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jeon, G.; Gao, M.; Chisholm, D. SEDRFuse: A symmetric encoder–decoder with residual block network for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 5002215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Pan, Z.; Cao, J.; Liao, J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on variational auto-encoder and infrared feature compensation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 117, 103839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataman, F.C.; Akar, G.B. Visible and infrared image fusion using encoder-decoder network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 1779–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, M.; Ma, J. DIVFusion: Darkness-free infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillioz, A.; Casas, J.; Mugellini, E.; Abou Khaled, O. Overview of the Transformer-based Models for NLP Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS), Sofia, Bulgaria, 6–9 September 2020; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Si, T. DATFuse: Infrared and visible image fusion via dual attention transformer. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 3159–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vs, V.; Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Oza, P.; Patel, V.M. Image fusion transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022; pp. 3566–3570. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.-J. Tgfuse: An infrared and visible image fusion approach based on transformer and generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y. TCCFusion: An infrared and visible image fusion method based on transformer and cross correlation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 137, 109295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shao, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. SwinFuse: A residual swin transformer fusion network for infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 5016412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, F.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, Y. SwinFusion: Cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 1200–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J. Infrared and visible image fusion using latent low-rank representation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.08992. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, C.; Ming, Z.; Guo, J.; Leopold, E.; Cheng, J.; Zuo, J.; Zhu, M. LatLRR-CNN: An infrared and visible image fusion method combining latent low-rank representation and CNN. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 36303–36323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Kittler, J. MDLatLRR: A novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prema, G.; Arivazhagan, S.; Aishwarya, C.; Dharani, S. Infrared and Visible image fusion using LatLRR and ResNet. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, X. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on LatLRR and ICA. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Systems, Bangkok, Thailand, 28–30 July 2021; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Yan, S. Latent low-rank representation for subspace segmentation and feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1615–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Lin, Z.; Yu, Y. Robust subspace segmentation by low-rank representation. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, T.; Liu, M.-X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Q. Latent low-rank representation with sparse consistency constraint for infrared and visible image fusion. Optik 2022, 261, 169102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]


| EN | MI | Qabf | FMI_Pixel | FMI_dct | FMI_w | Nabf | SCD | SSIM | MS_SSIM | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.2440 | 12.4881 | 0.3641 | 0.8985 | 0.3100 | 0.3487 | 0.0121 | 1.6506 | 0.7660 | 0.8676 | NB + S |
| 6.2541 | 12.5082 | 0.3715 | 0.8971 | 0.3467 | 0.3772 | 0.0163 | 1.6528 | 0.7671 | 0.8691 | SS + NB + S |
| 6.2475 | 12.4951 | 0.3712 | 0.8981 | 0.3411 | 0.3784 | 0.0101 | 1.6520 | 0.7680 | 0.8687 | NSS + NB + S |
| 6.1197 | 12.2395 | 0.2616 | 0.9071 | 0.3283 | 0.3531 | 0.0034 | 1.5979 | 0.7667 | 0.8300 | WB + NS |
| 6.1319 | 12.2637 | 0.2753 | 0.9040 | 0.3572 | 0.3742 | 0.0063 | 1.6004 | 0.7687 | 0.8319 | SS + WB + NS |
| 6.1241 | 12.2481 | 0.2708 | 0.9063 | 0.3634 | 0.3845 | 0.0026 | 1.5995 | 0.7693 | 0.8315 | NSS + WB + NS |
| 6.1394 | 12.2788 | 0.2652 | 0.9073 | 0.3290 | 0.3537 | 0.0034 | 1.6002 | 0.7666 | 0.8319 | NB + NS |
| 6.1512 | 12.3025 | 0.2788 | 0.9043 | 0.3578 | 0.3748 | 0.0063 | 1.6027 | 0.7686 | 0.8338 | SS + NB + NS |
| 6.1433 | 12.2867 | 0.2740 | 0.9067 | 0.3646 | 0.3858 | 0.0026 | 1.6018 | 0.7692 | 0.8331 | NSS + NB + NS |
| 6.2272 | 12.4543 | 0.3613 | 0.8982 | 0.3095 | 0.3484 | 0.0121 | 1.6483 | 0.7661 | 0.8659 | WB + S |
| 6.2373 | 12.4747 | 0.3686 | 0.8967 | 0.3462 | 0.3769 | 0.0162 | 1.6505 | 0.7671 | 0.8674 | SS + WB + S |
| 6.2307 | 12.4614 | 0.3683 | 0.8978 | 0.3407 | 0.3781 | 0.0100 | 1.6497 | 0.7681 | 0.8670 | NSS + WB + S |
| 6.1819 | 12.3639 | 0.3677 | 0.9107 | 0.4050 | 0.4168 | 0.0012 | 1.6348 | 0.7780 | 0.8746 | VGG19 |
| 6.1953 | 12.3905 | 0.3510 | 0.9092 | 0.4058 | 0.4169 | 0.0006 | 1.6336 | 0.7782 | 0.8732 | Resnet50 |
| EN | MI | Qabf | FMI_Pixel | FMI_dct | FMI_w | Nabf | SCD | SSIM | MS_SSIM | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.2878 | 12.5755 | 0.3779 | 0.9013 | 0.3097 | 0.3478 | 0.0149 | 1.6728 | 0.7651 | 0.8709 | NB + S |
| 6.2976 | 12.5952 | 0.3848 | 0.8999 | 0.3465 | 0.3763 | 0.0193 | 1.6750 | 0.7661 | 0.8724 | SS + NB + S |
| 6.2912 | 12.5824 | 0.3848 | 0.9008 | 0.3407 | 0.3772 | 0.0129 | 1.6742 | 0.7671 | 0.8720 | NSS + NB + S |
| 6.1225 | 12.2449 | 0.2655 | 0.9073 | 0.3277 | 0.3531 | 0.0034 | 1.5999 | 0.7668 | 0.8311 | WB + NS |
| 6.1345 | 12.2691 | 0.2790 | 0.9043 | 0.3570 | 0.3745 | 0.0063 | 1.6023 | 0.7688 | 0.8330 | SS + WB + NS |
| 6.1281 | 12.2561 | 0.2756 | 0.9068 | 0.3644 | 0.3862 | 0.0025 | 1.6020 | 0.7697 | 0.8333 | NSS + WB + NS |
| 6.1875 | 12.3749 | 0.2871 | 0.9092 | 0.3269 | 0.3520 | 0.0059 | 1.6262 | 0.7659 | 0.8372 | NB + NS |
| 6.1988 | 12.3976 | 0.3000 | 0.9067 | 0.3568 | 0.3735 | 0.0089 | 1.6287 | 0.7679 | 0.8391 | SS + NB + NS |
| 6.1914 | 12.3828 | 0.2959 | 0.9086 | 0.3622 | 0.3834 | 0.0051 | 1.6278 | 0.7686 | 0.8386 | NSS + NB + NS |
| 6.2272 | 12.4543 | 0.3613 | 0.8982 | 0.3095 | 0.3484 | 0.0121 | 1.6483 | 0.7661 | 0.8659 | WB + S |
| 6.2373 | 12.4747 | 0.3686 | 0.8967 | 0.3462 | 0.3769 | 0.0162 | 1.6505 | 0.7671 | 0.8674 | SS + WB + S |
| 6.2307 | 12.4614 | 0.3684 | 0.8978 | 0.3407 | 0.3781 | 0.0100 | 1.6497 | 0.7681 | 0.8670 | NSS + WB + S |
| 6.1819 | 12.3639 | 0.3677 | 0.9107 | 0.4050 | 0.4168 | 0.0012 | 1.6348 | 0.7780 | 0.8746 | VGG19 |
| 6.1953 | 12.3905 | 0.3510 | 0.9092 | 0.4058 | 0.4169 | 0.0006 | 1.6336 | 0.7782 | 0.8732 | Resnet50 |
| EN | MI | Qabf | FMI_Pixel | FMI_dct | FMI_w | Nabf | SCD | SSIM | MS_SSIM | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | ||||||||||
| NB + S | ||||||||||
| 0.16 | 0.16 | 2.03 | −0.16 | 11.83 | 8.19 | −34.39 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.17 | SS + NB + S |
| 0.06 | 0.06 | 1.96 | −0.04 | 10.05 | 8.54 | 16.59 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.12 | NSS + NB + S |
| WB + NS | ||||||||||
| 0.20 | 0.20 | 5.23 | −0.35 | 8.80 | 6.00 | −86.37 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.23 | SS + WB + NS |
| 0.07 | 0.07 | 3.49 | −0.09 | 10.71 | 8.92 | 24.06 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.18 | NSS + WB + NS |
| NB + NS | ||||||||||
| 0.19 | 0.19 | 5.13 | −0.33 | 8.76 | 5.97 | −84.94 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.23 | SS + NB + NS |
| 0.06 | 0.06 | 3.31 | −0.07 | 10.85 | 9.08 | 24.44 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.15 | NSS + NB + NS |
| WB + S | ||||||||||
| 0.16 | 0.16 | 2.03 | −0.16 | 11.84 | 8.20 | −34.54 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.17 | SS + WB + S |
| 0.06 | 0.06 | 1.95 | −0.04 | 10.09 | 8.54 | 16.96 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.12 | NSS + WB + S |
| EN | MI | Qabf | FMI_Pixel | FMI_dct | FMI_w | Nabf | SCD | SSIM | MS_SSIM | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | ||||||||||
| NB + S | ||||||||||
| 0.16 | 0.16 | 1.81 | −0.15 | 11.87 | 8.21 | −29.23 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.17 | SS + NB + S |
| 0.05 | 0.05 | 1.83 | −0.05 | 10.00 | 8.46 | 13.19 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.12 | NSS + NB + S |
| WB + NS | ||||||||||
| 0.20 | 0.20 | 5.10 | −0.33 | 8.93 | 6.04 | −85.40 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.23 | SS + WB + NS |
| 0.09 | 0.09 | 3.83 | −0.06 | 11.19 | 9.35 | 27.87 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 0.27 | NSS + WB + NS |
| NB + NS | ||||||||||
| 0.18 | 0.18 | 4.49 | −0.27 | 9.15 | 6.11 | −51.31 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.23 | SS + NB + NS |
| 0.06 | 0.06 | 3.08 | −0.06 | 10.80 | 8.93 | 14.21 | 0.09 | 0.34 | 0.17 | NSS + NB + NS |
| WB + S | ||||||||||
| 0.16 | 0.16 | 2.03 | −0.16 | 11.84 | 8.20 | −34.54 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.17 | SS + WB + S |
| 0.06 | 0.06 | 1.95 | −0.04 | 10.08 | 8.55 | 17.01 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 0.12 | NSS + WB + S |
| EN | MI | Qabf | FMI_Pixel | FMI_dct | FMI_w | Nabf | SCD | SSIM | MS_SSIM | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.2519 | 12.5037 | 0.3870 | 0.8827 | 0.2256 | 0.2519 | 0.1460 | 1.6147 | 0.7070 | 0.8648 | FPDE [14] |
| 7.1105 | 14.2209 | 0.3848 | 0.8826 | 0.1928 | 0.2569 | 0.2448 | 1.3986 | 0.6603 | 0.8458 | RPSR [21] |
| 6.2691 | 12.5382 | 0.4127 | 0.8829 | 0.2275 | 0.2595 | 0.1451 | 1.6133 | 0.7091 | 0.8760 | ADF [15] |
| 7.5980 | 15.1960 | 0.2831 | 0.8567 | 0.1996 | 0.2399 | 0.4225 | 1.4331 | 0.5429 | 0.7264 | DIVFusion [46] |
| 6.3946 | 12.7893 | 0.1852 | 0.8863 | 0.1702 | 0.1933 | 0.0937 | 1.3831 | 0.6279 | 0.7009 | FusionGAN [40] |
| 6.7471 | 13.4943 | 0.4273 | 0.9049 | 0.2163 | 0.2628 | 0.2138 | 1.5967 | 0.6701 | 0.8233 | PIAFusion [27] |
| 7.0462 | 14.0925 | 0.4014 | 0.8958 | 0.2030 | 0.2511 | 0.3072 | 1.6298 | 0.6457 | 0.8251 | SeAFusion [26] |
| 6.7612 | 13.5225 | 0.4059 | 0.9014 | 0.2100 | 0.2544 | 0.1847 | 1.6307 | 0.6865 | 0.8292 | SwinFusion [53] |
| 6.8810 | 13.7621 | 0.3667 | 0.8869 | 0.2137 | 0.2468 | 0.3336 | 1.7128 | 0.6454 | 0.8729 | U2Fusion [29,62] |
| 6.5667 | 13.1333 | 0.3291 | 0.8898 | 0.2031 | 0.2331 | 0.1859 | 1.6164 | 0.6865 | 0.8437 | UMF-CMGR [28] |
| 6.2912 | 12.5824 | 0.3848 | 0.9008 | 0.3407 | 0.3772 | 0.0129 | 1.6742 | 0.7671 | 0.8720 | Ours(NSS + NvggB + S) |
| 6.2475 | 12.4951 | 0.3712 | 0.8981 | 0.3411 | 0.3784 | 0.0101 | 1.6520 | 0.7680 | 0.8687 | Ours(NSS + NResnetB + S) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Ning, F.-S.; Chou, T.-Y.; Chen, M.-H. Using Sparse Parts in Fused Information to Enhance Performance in Latent Low-Rank Representation-Based Fusion of Visible and Infrared Images. Sensors 2024, 24, 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051514
Hao C-Y, Chen Y-C, Ning F-S, Chou T-Y, Chen M-H. Using Sparse Parts in Fused Information to Enhance Performance in Latent Low-Rank Representation-Based Fusion of Visible and Infrared Images. Sensors. 2024; 24(5):1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051514
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Chen-Yu, Yao-Chung Chen, Fang-Shii Ning, Tien-Yin Chou, and Mei-Hsin Chen. 2024. "Using Sparse Parts in Fused Information to Enhance Performance in Latent Low-Rank Representation-Based Fusion of Visible and Infrared Images" Sensors 24, no. 5: 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051514
APA StyleHao, C.-Y., Chen, Y.-C., Ning, F.-S., Chou, T.-Y., & Chen, M.-H. (2024). Using Sparse Parts in Fused Information to Enhance Performance in Latent Low-Rank Representation-Based Fusion of Visible and Infrared Images. Sensors, 24(5), 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24051514








