Exploring the Utility of the Muse Headset for Capturing the N400: Dependability and Single-Trial Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli
2.3. Experimental Procedure
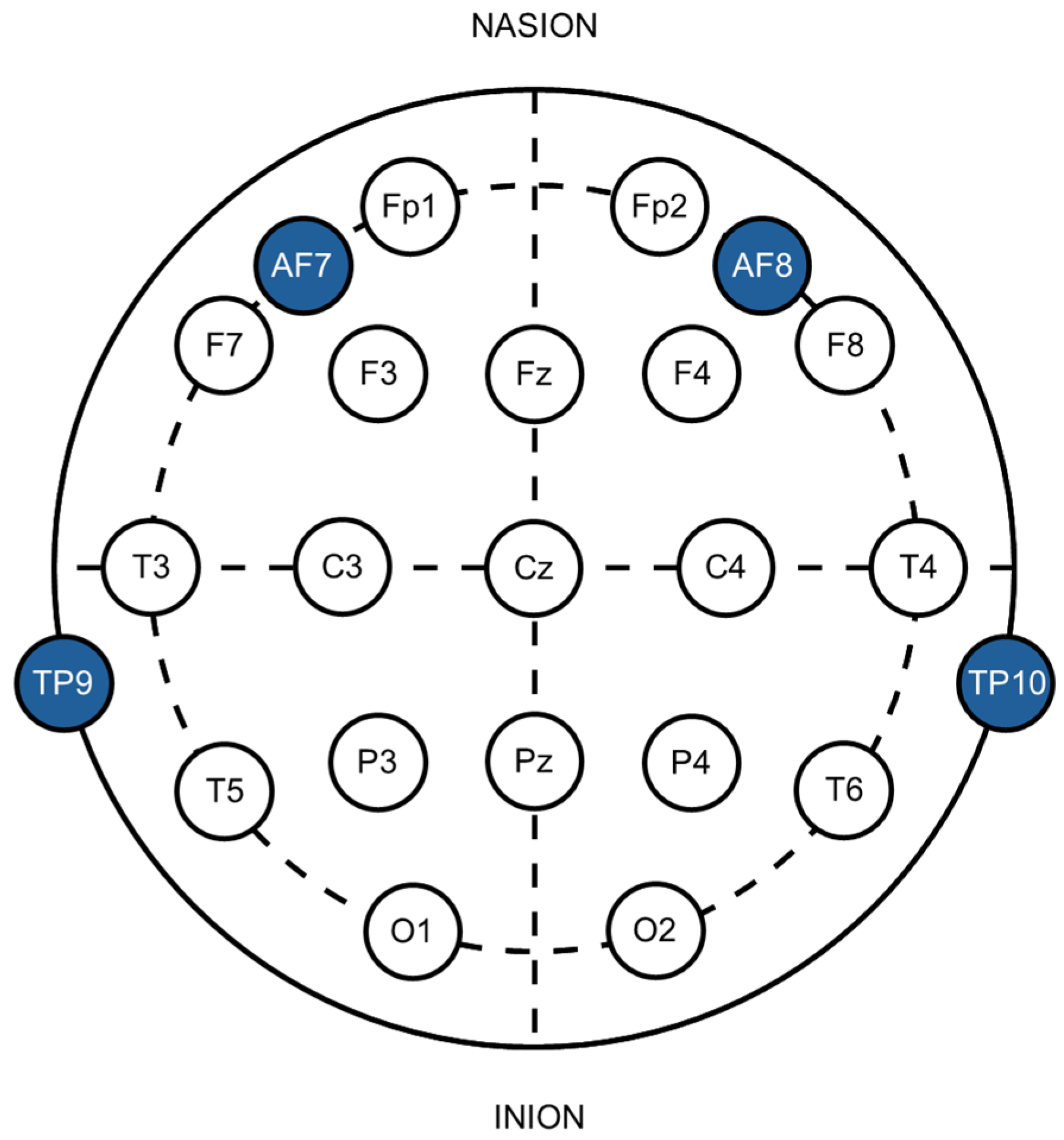
2.4. EEG Data Acquisition
2.5. EEG Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Behavioral Data Analysis
2.6.2. ERP Reliability Analysis
2.6.3. N400 Effect of Semantic Relatedness
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Data
3.2. EEG Data
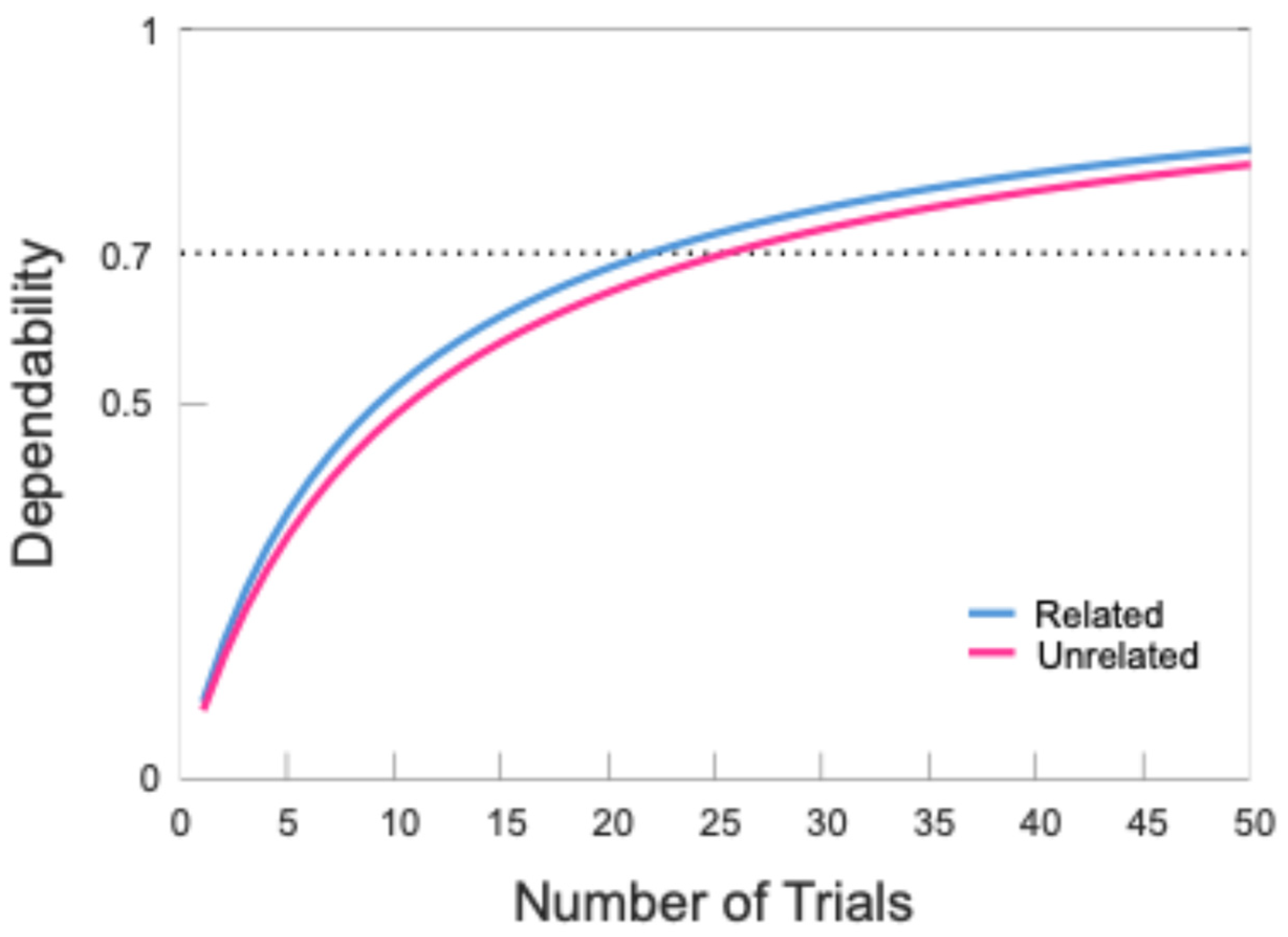
3.2.1. Internal Consistency
3.2.2. N400 Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance of the Muse 2 for N400 Research
4.2. Expanding Access and Inclusion in EEG Research
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casson, A. Wearable EEG and Beyond. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, S.J. An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique, Second Edition, 2nd ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-262-52585-5. [Google Scholar]
- Niso, G.; Romero, E.; Moreau, J.T.; Araujo, A.; Krol, L.R. Wireless EEG: A Survey of Systems and Studies. NeuroImage 2023, 269, 119774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothe, C.; Shirazi, S.Y.; Stenner, T.; Medine, D.; Boulay, C.; Grivich, M.I.; Mullen, T.; Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. The Lab Streaming Layer for Synchronized Multimodal Recording. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirce, J.; Gray, J.R.; Simpson, S.; MacAskill, M.; Höchenberger, R.; Sogo, H.; Kastman, E.; Lindeløv, J.K. PsychoPy2: Experiments in Behavior Made Easy. Behav. Res. 2019, 51, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, S.F.; Saeed, S.M.U.; Monis, Z.U.A.E.D.A.; Shabbir, Z.; Habib, F. Prediction of Perceived Stress Scores Using Low-Channel Electroencephalography Headband. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technologies (IBCAST), Islamabad, Pakistan, 12–16 January 2021; pp. 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, L.L.; Rector, N.A.; DaSilva, A.; Laposa, J.M.; Richter, M.A. Technology Supported Mindfulness for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Self-Reported Mindfulness and EEG Correlates of Mind Wandering. Behav. Res. Ther. 2021, 136, 103757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, J.J.; Manso, L.J.; Ribeiro, E.P.; Ekart, A.; Faria, D.R. A Study on Mental State Classification Using EEG-Based Brain-Machine Interface. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), Funchal, Portugal, 25–27 September 2018; pp. 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthini, K.; Pyingkodi, M.; Sivabalaselvamani, D.; Kaviya. EEG Signal Analysis for Emotional Classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 17–19 August 2022; pp. 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Lion, K.M.; Todorovic, M.; Moyle, W. Portable EEG Monitoring for Older Adults with Dementia and Chronic Pain—A Feasibility Study. Geriatr. Nurs. 2021, 42, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengmolee, W.; Chaisaen, R.; Autthasan, P.; Rungsilp, C.; Sa-Ih, N.; Cheaha, D.; Kumarnsit, E.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. Consumer-Grade Brain Measuring Sensor in People With Long-Term Kratom Consumption. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 6088–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.E.; Ouda, H.T.; Azab, M. MUSE: A Portable Cost-Efficient Lie Detector. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–3 November 2018; pp. 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krigolson, O.E.; Williams, C.C.; Norton, A.; Hassall, C.D.; Colino, F.L. Choosing MUSE: Validation of a Low-Cost, Portable EEG System for ERP Research. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krigolson, O.E.; Hammerstrom, M.R.; Abimbola, W.; Trska, R.; Wright, B.W.; Hecker, K.G.; Binsted, G. Using Muse: Rapid Mobile Assessment of Brain Performance. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 634147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, N.T.; Meshi, D.; Bente, G.; Schmälzle, R. Media Neuroscience on a Shoestring: Examining Electrocortical Responses to Visual Stimuli via Mobile EEG. J. Media Psychol. Theor. Methods Appl. 2022, 35, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocquyt, E.; Van Laeken, H.; Van Mierlo, P.; De Letter, M. Test–Retest Reliability of Electroencephalographic and Magnetoencephalographic Measures Elicited during Language Tasks: A Literature Review. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 57, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutas, M.; Federmeier, K.D. Thirty Years and Counting: Finding Meaning in the N400 Component of the Event-Related Brain Potential (ERP). Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2011, 62, 621–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holcomb, P.J.; Neville, H.J. Auditory and Visual Semantic Priming in Lexical Decision: A Comparison Using Event-Related Brain Potentials. Lang. Cogn. Process. 1990, 5, 281–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentin, S.; McCarthy, G.; Wood, C.C. Event-Related Potentials, Lexical Decision and Semantic Priming. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 60, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, E.F.; Weber, K.; Gramfort, A.; Hämäläinen, M.S.; Kuperberg, G.R. Spatiotemporal Signatures of Lexical–Semantic Prediction. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basma, B.; Savage, R.; Luk, G.; Bertone, A. Reading Disability in Children: Exploring the N400 and Its Associations with Set-For-Variability. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyal, M.; Groleau, C.; Bouchard, C.; Wilson, M.A.; Fecteau, S. Semantic Processing in Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of the N400 Differences. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Spencer, K.M.; Onitsuka, T.; Hirano, Y. Language-Related Neurophysiological Deficits in Schizophrenia. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2020, 51, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balota, D.A.; Yap, M.J.; Hutchison, K.A.; Cortese, M.J.; Kessler, B.; Loftis, B.; Neely, J.H.; Nelson, D.L.; Simpson, G.B.; Treiman, R. The English Lexicon Project. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řehůřek, R.; Sojka, P. Software Framework for Topic Modelling with Large Corpora. In Proceedings of the LREC 2010 Workshop on New Challenges for NLP Frameworks, Valletta, Malta, 22 May 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Grave, E.; Bojanowski, P.; Puhrsch, C.; Joulin, A. Advances in Pre-Training Distributed Word Representations. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.09405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milnik, V. Instruction of Electrode Placement to the International 10-20-System. Neurophysiol. Labor. 2006, 28, 113–143. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, J.; Bacon, R.; Blaizot, J.; Boissier, S.; Boselli, A.; NicolasBouché; Brinchmann, J.; Castro, N.; Ciesla, L.; Crowther, P.; et al. BlueMUSE: Project Overview and Science Cases. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.01657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soskic, A.; Jovanovic, V.; Styles, S.J.; Kappenman, E.S.; Kovic, V. How to Do Better N400 Studies: Reproducibility, Consistency and Adherence to Research Standards in the Existing Literature. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2022, 32, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project Jamovi. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Webb, N.M.; Shavelson, R.J.; Haertel, E.H. 4 Reliability Coefficients and Generalizability Theory. In Handbook of Statistics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 26, pp. 81–124. ISBN 978-0-444-52103-3. [Google Scholar]
- Clayson, P.E.; Miller, G.A. ERP Reliability Analysis (ERA) Toolbox: An Open-Source Toolbox for Analyzing the Reliability of Event-Related Brain Potentials. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2017, 111, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayson, P.E.; Miller, G.A. Psychometric Considerations in the Measurement of Event-Related Brain Potentials: Guidelines for Measurement and Reporting. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2017, 111, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, S.J.; Stewart, A.X.; Simmons, A.M.; Rhemtulla, M. Standardized Measurement Error: A Universal Metric of Data Quality for Averaged Event-related Potentials. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernet, C.R.; Chauveau, N.; Gaspar, C.; Rousselet, G.A. LIMO EEG: A Toolbox for Hierarchical LInear MOdeling of ElectroEncephaloGraphic Data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, e831409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernet, C.R.; Latinus, M.; Nichols, T.E.; Rousselet, G.A. Cluster-Based Computational Methods for Mass Univariate Analyses of Event-Related Brain Potentials/Fields: A Simulation Study. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 250, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.-M. FieldTrip: Open Source Software for Advanced Analysis of MEG, EEG, and Invasive Electrophysiological Data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 156869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, M.; Revonsuo, A. Cognitive Representations Underlying the N400 Priming Effect. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 2001, 12, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Sejnowski, T.; Makeig, S. Enhanced Detection of Artifacts in EEG Data Using Higher-Order Statistics and Independent Component Analysis. NeuroImage 2007, 34, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Martin, J.A. Automated Data Cleaning for the Muse EEG. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Houston, TX, USA, 9 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lees, T.; Ram, N.; Swingler, M.M.; Gatzke-Kopp, L.M. The Effect of Hair Type and Texture on Electroencephalography and Event-related Potential Data Quality. Psychophysiology 2024, 61, e14499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friederici, A.D. Towards a Neural Basis of Auditory Sentence Processing. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002, 6, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, C.; Besson, M.; Robert, S. Context Influences the Processing of Verb Transitivity in French Sentences: More Evidence for Semantic−syntax Interactions. Lang. Cogn. 2014, 6, 181–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, C.; Astésano, C.; Lacheret-Dujour, A.; Morel, M.; Alter, K.; Besson, M. On-Line Processing of “Pop-Out” Words in Spoken French Dialogues. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.; Osterhout, L.; Kim, A. Neural Correlates of Second-Language Word Learning: Minimal Instruction Produces Rapid Change. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| M | SD | Frequency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 19.95 | 3.81 | - | |
| Sex (female) | - | - | 51.35 | |
| Race | ||||
| Asian | - | - | 2.70 | |
| Black | - | - | 8.11 | |
| Other | - | - | 8.11 | |
| White | - | - | 81.08 | |
| Ethnicity (Hispanic) | - | - | 8.33 | |
| Handedness (Right) | - | - | 86.49 | |
| Highest Education | ||||
| High School | - | - | 48.65 | |
| Some College | - | - | 40.54 | |
| Bachelor’s Degree | - | - | 8.11 | |
| Master’s Degree | - | - | 2.70 | |
| Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Related | Unrelated | |
| Accuracy Rate (%) | M | 97.06 | 97.64 |
| SD | 16.91 | 15.20 | |
| Response Time (ms) | M | 813.71 | 984.11 |
| SD | 415.31 | 514.33 | |
| Condition | Threshold | N | Dependability | Trials | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Included | Excluded | M | SD | Min | Max | |||
| Match | 0.70 | 29 | 7 | 0.82 CI [0.71 0.90] | 43.17 | 9.04 | 24 | 55 |
| Mismatch | 0.70 | 29 | 7 | 0.80 CI [0.67 0.89] | 42.93 | 8.29 | 27 | 54 |
| Condition | Total SD | SME | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS | Min | Max | ||
| Match | 1.46 | 0.96 | 0.46 | 1.93 |
| Mismatch | 1.83 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 1.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayes, H.B.; Magne, C. Exploring the Utility of the Muse Headset for Capturing the N400: Dependability and Single-Trial Analysis. Sensors 2024, 24, 7961. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247961
Hayes HB, Magne C. Exploring the Utility of the Muse Headset for Capturing the N400: Dependability and Single-Trial Analysis. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):7961. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247961
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayes, Hannah Begue, and Cyrille Magne. 2024. "Exploring the Utility of the Muse Headset for Capturing the N400: Dependability and Single-Trial Analysis" Sensors 24, no. 24: 7961. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247961
APA StyleHayes, H. B., & Magne, C. (2024). Exploring the Utility of the Muse Headset for Capturing the N400: Dependability and Single-Trial Analysis. Sensors, 24(24), 7961. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247961






