Mobile Robot Positioning with Wireless Fidelity Fingerprinting and Explainable Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Creation of a new Wi-Fi fingerprint dataset using Wi-Fi’s built-in hardware of a widely-used single-board computer, Raspberry Pi, for the purpose of utilizing address, channel, and signal strength.
- Implementation of the localization process in the dataset using machine learning and explainable AI techniques.
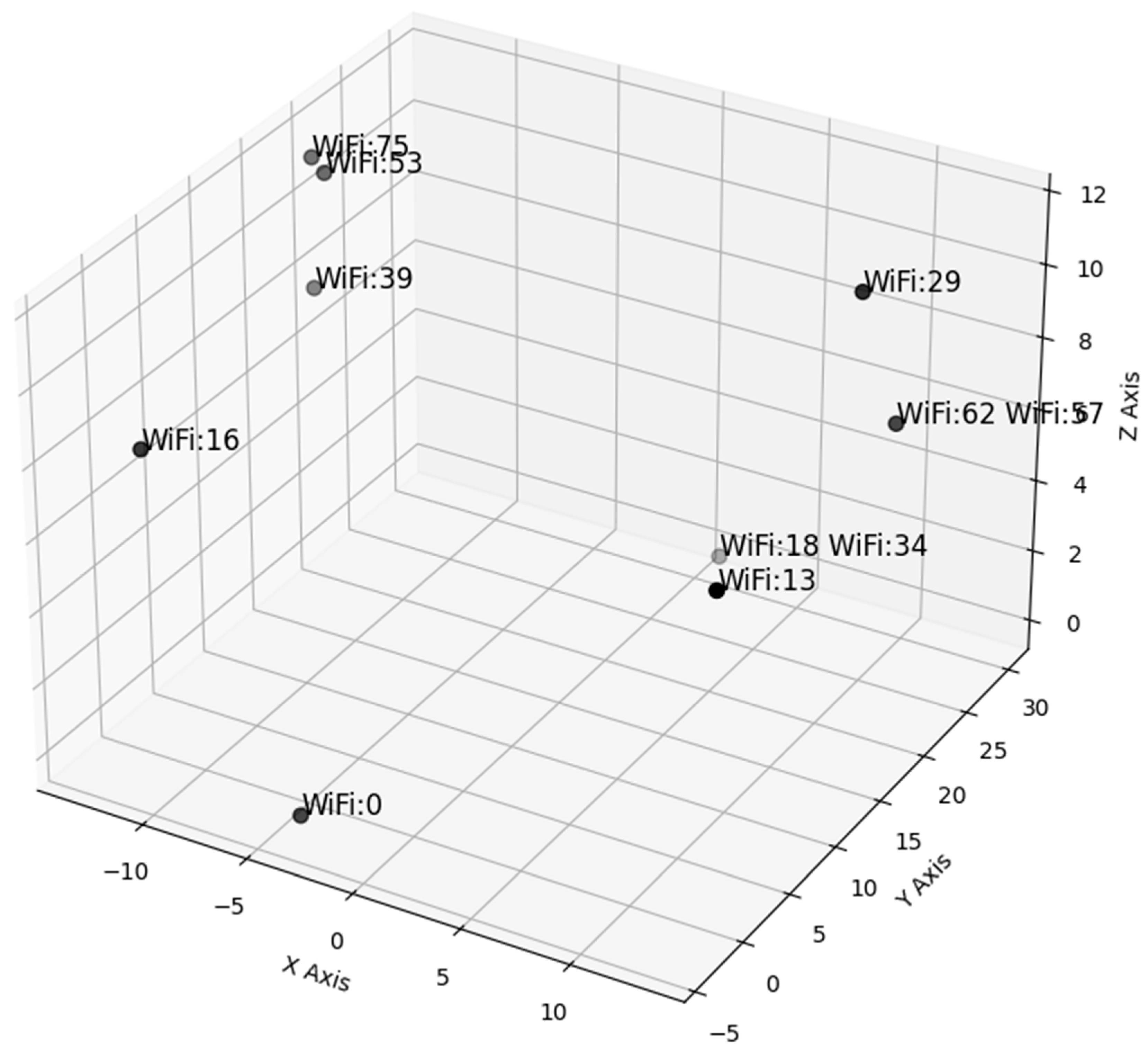
- Selection of transmitters for spatial analysis and planning purposes.
2. Materials and Methods
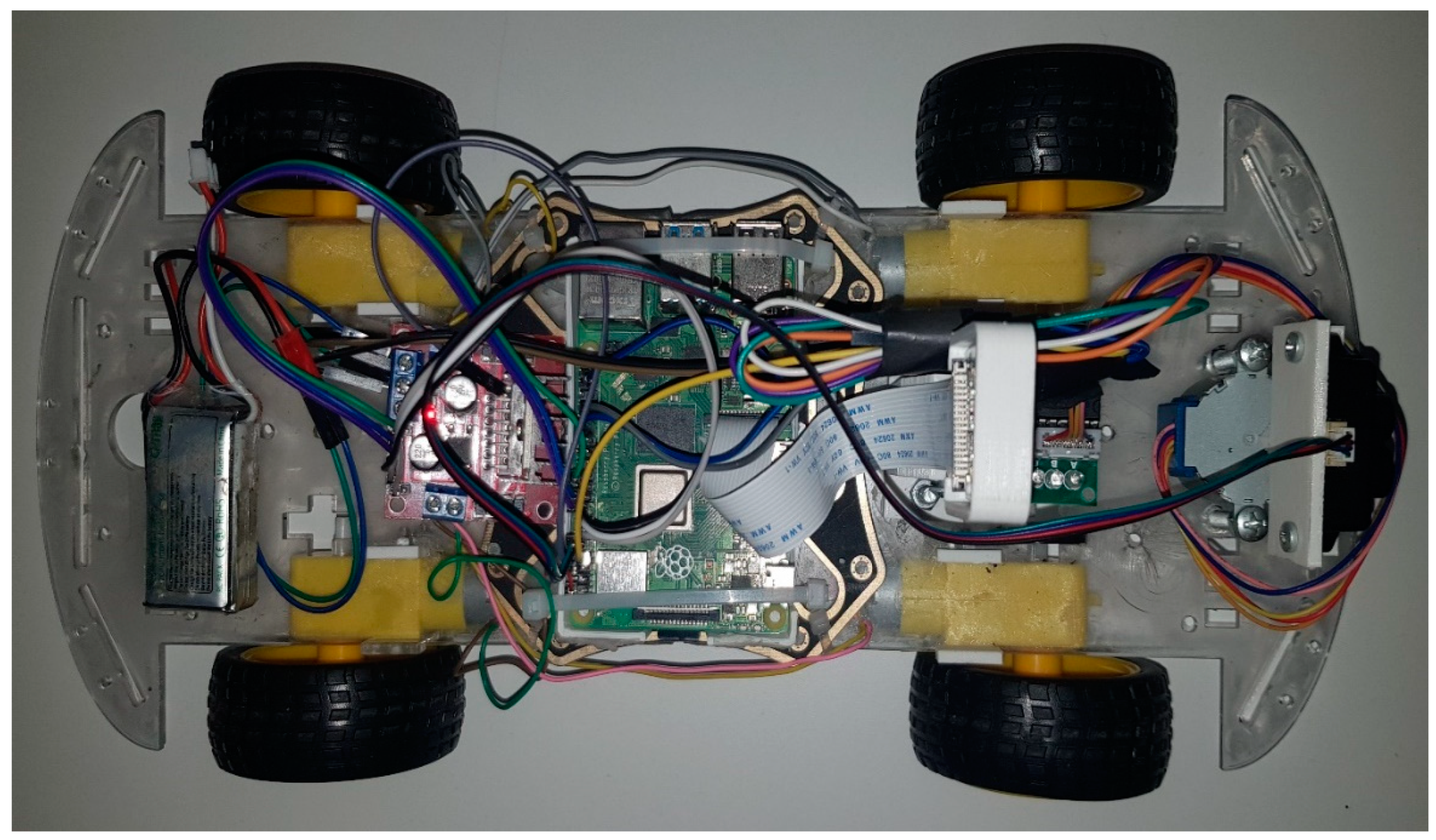
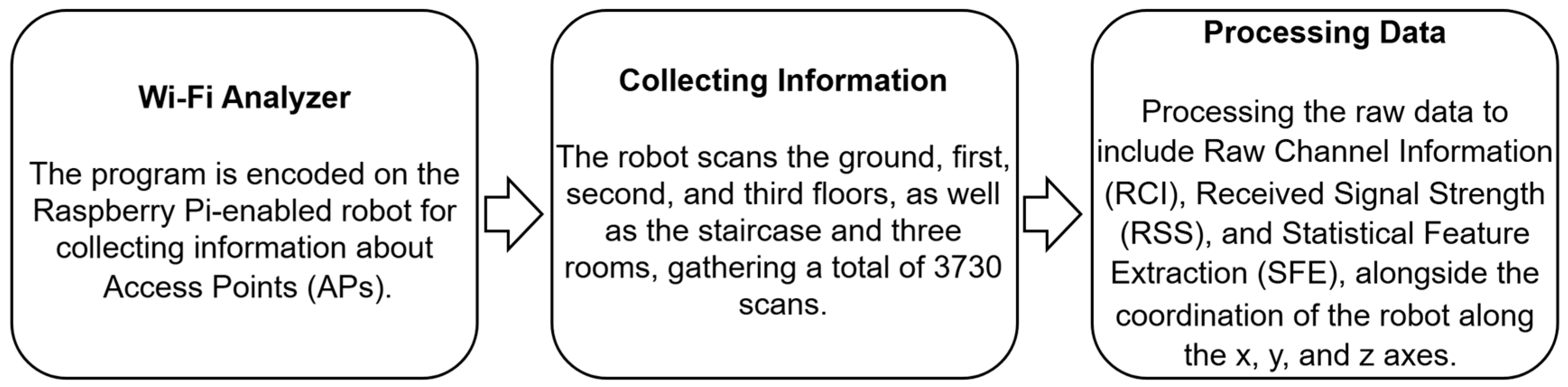
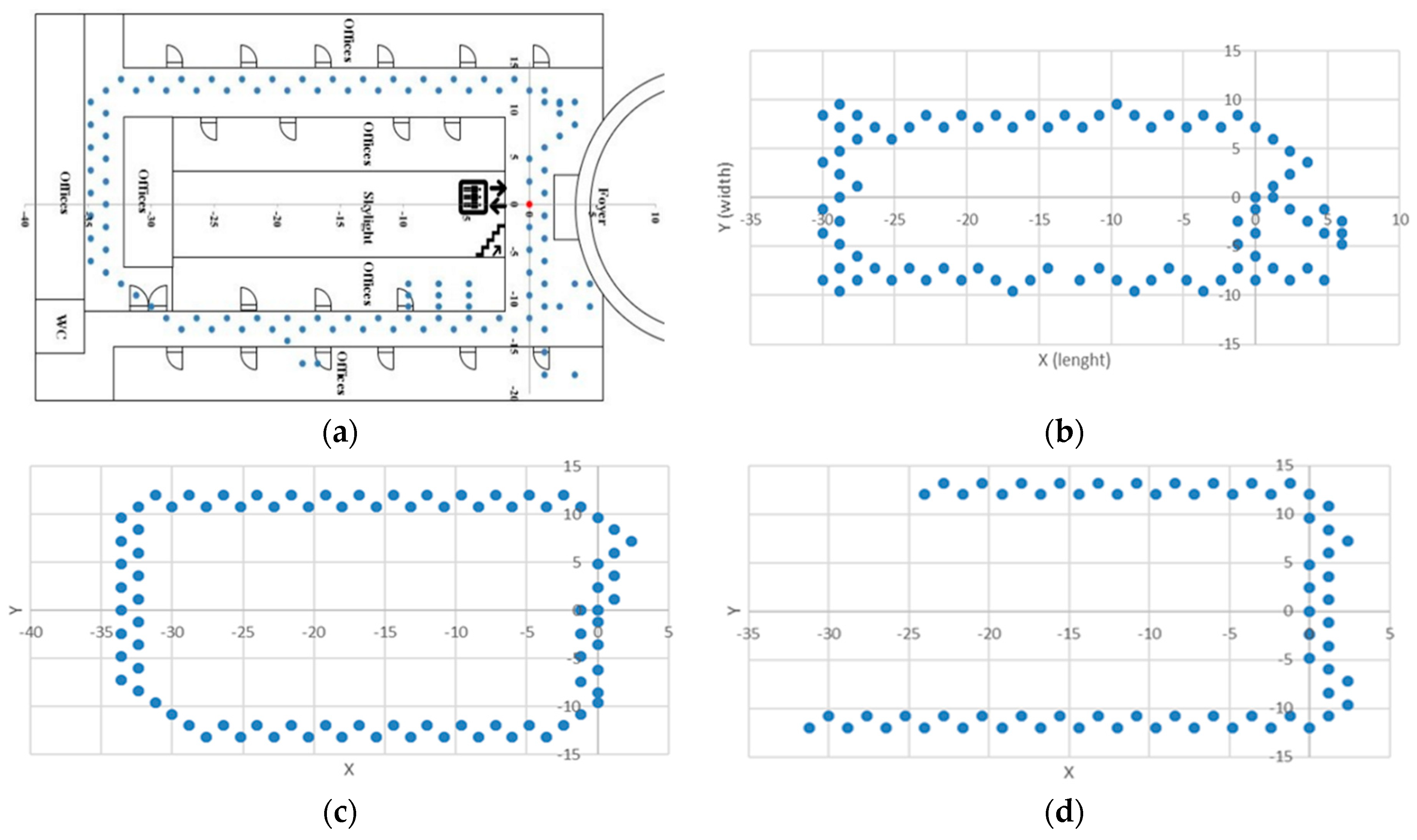
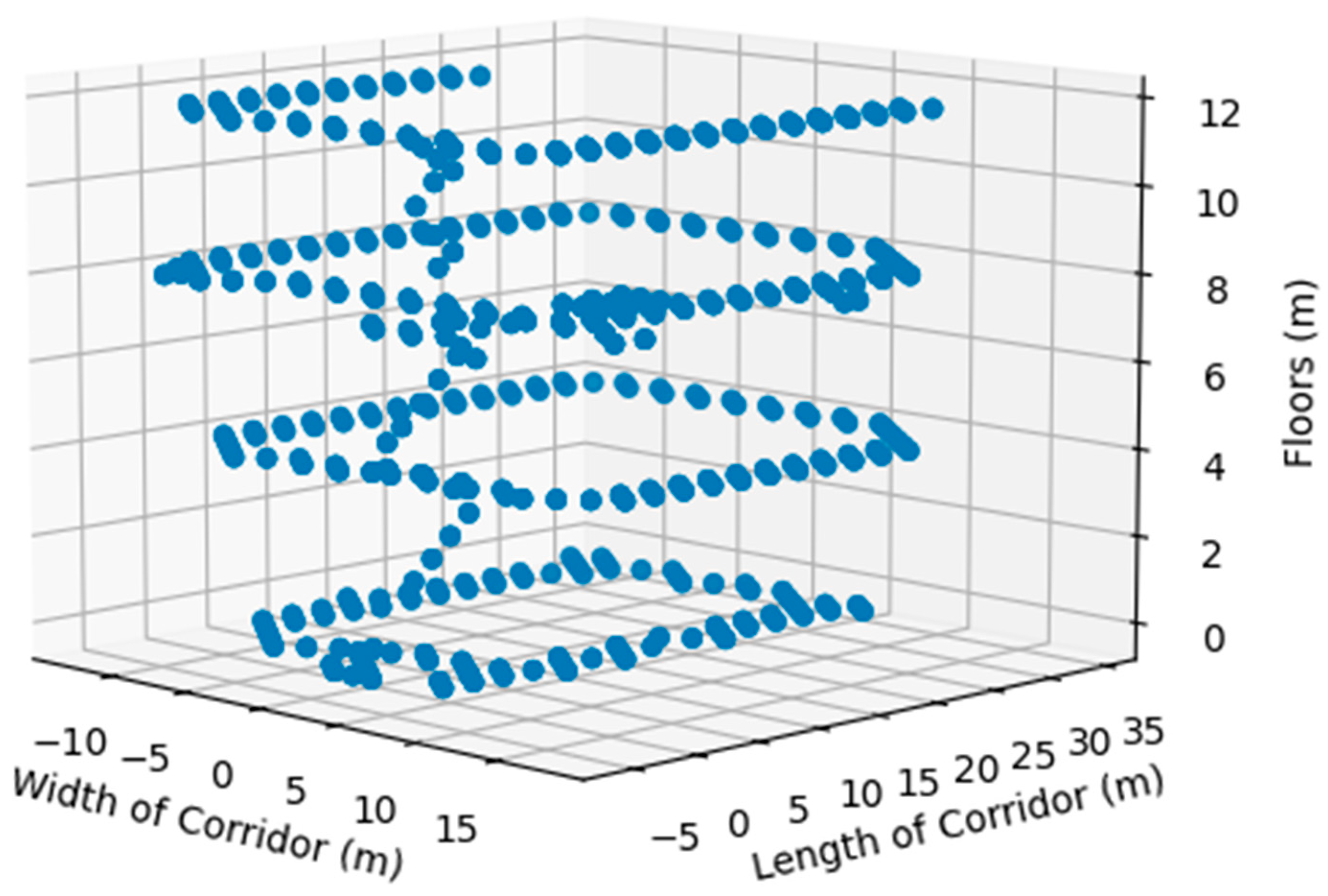
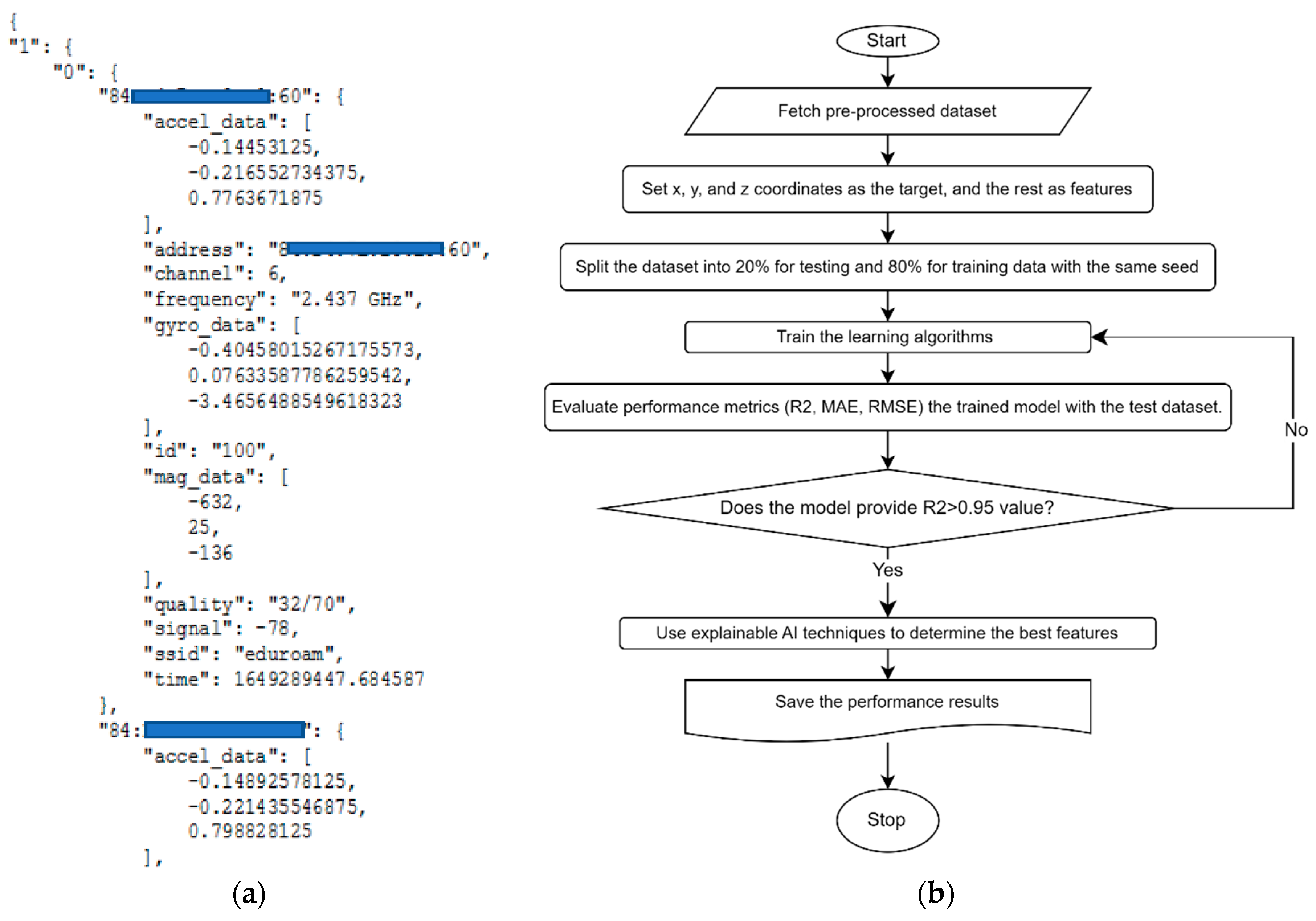
2.1. Data Collection Process and Dataset Properties
2.2. Machine Learning and Training
2.3. Explainable AI and Feature Importance
3. Results and Discussion
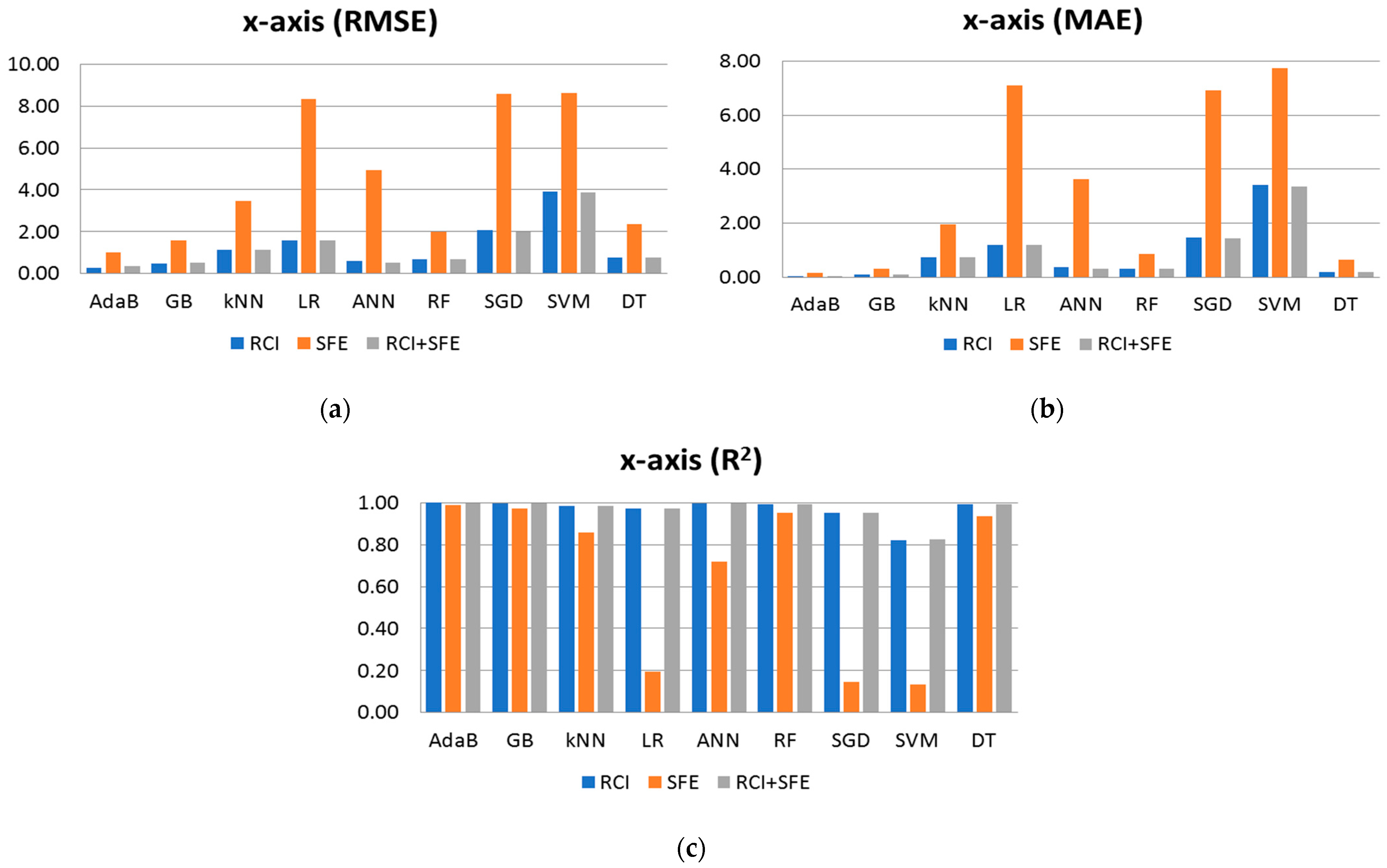
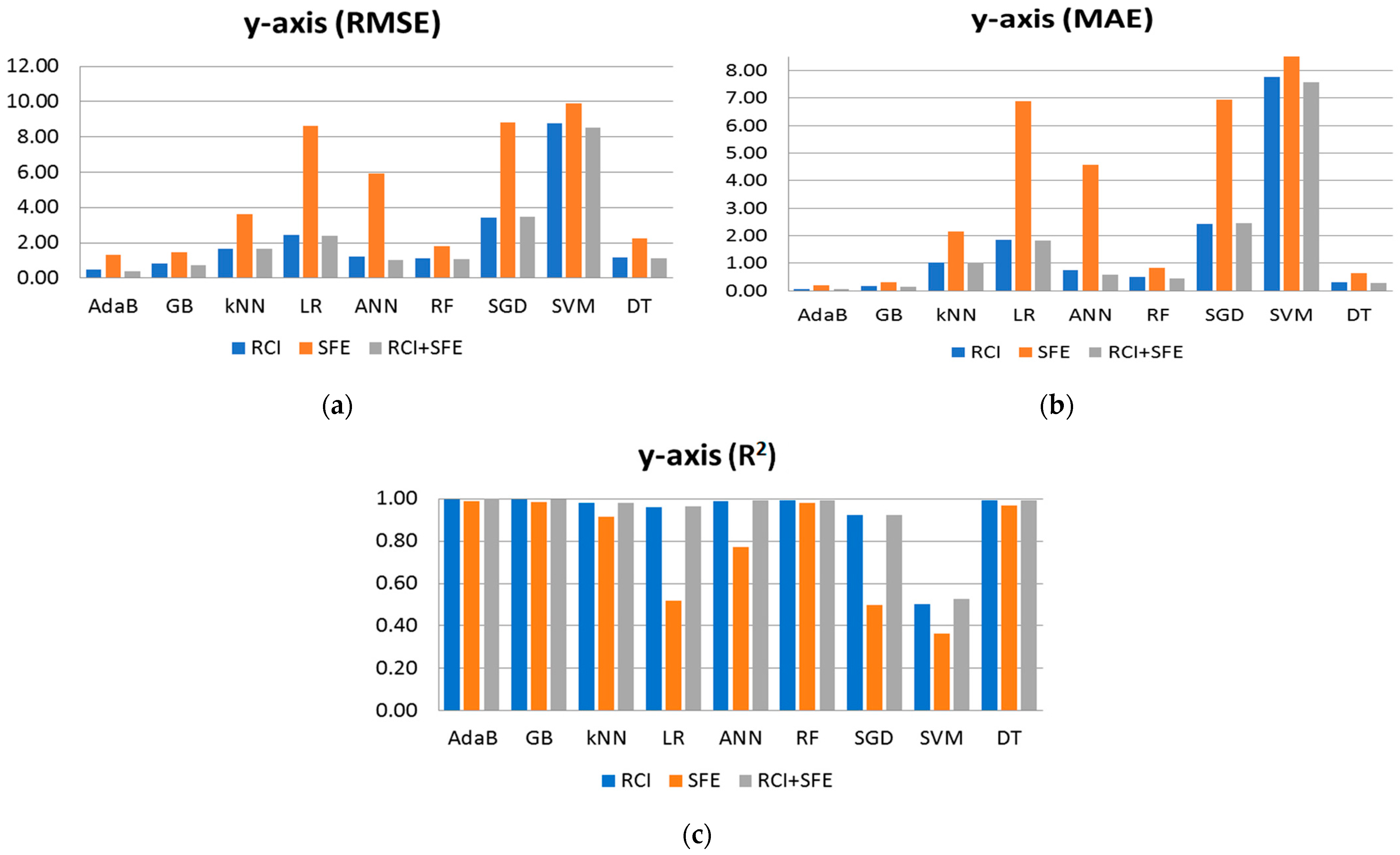
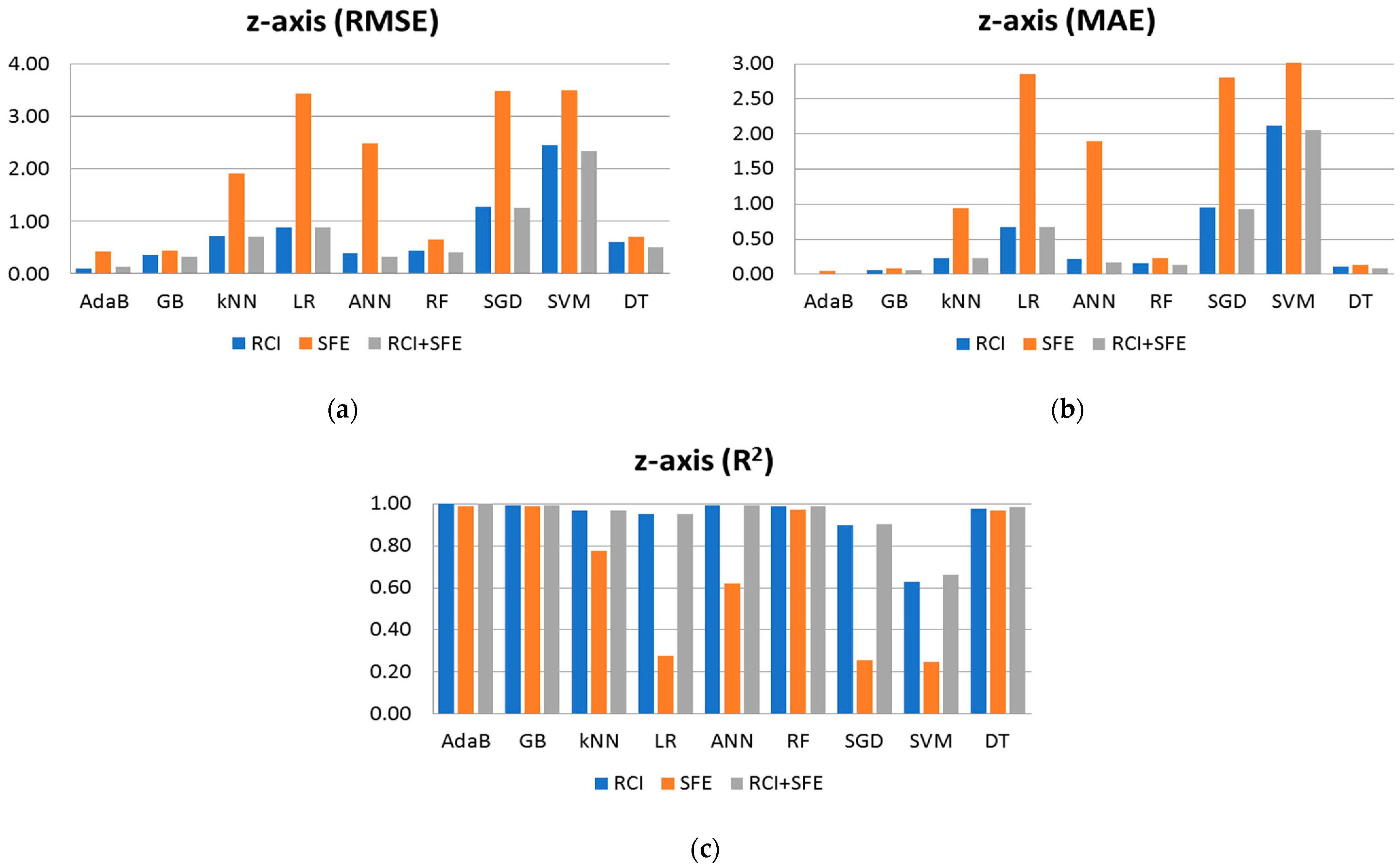
3.1. Model and Feature Selection
3.2. Explaining the Selected Model
3.3. Selecting Minimum Number of Wi-Fi AP
3.4. Comparison of Proposed Method with Existing Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borenstein, J.; Everett, H.R.; Feng, L.; Wehe, D. Mobile Robot Positioning-Sensors and Techniques. J. Robot. Syst. 1997, 14, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Darabi, H.; Banerjee, P.; Liu, J. Survey of Wireless Indoor Positioning Techniques and Systems. In Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 37, pp. 1067–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Seçkin, A.Ç.; Coşkun, A. Hierarchical Fusion of Machine Learning Algorithms in Indoor Positioning and Localization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, M.; Seçkin, A.Ç.; Özek, A.; Karpuz, C. Warehouse Drone: Indoor Positioning and Product Counter with Virtual Fiducial Markers. Drones 2023, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Ikeda, S. Visual SLAM Algorithms: A Survey from 2010 to 2016. IPSJ Trans. Comput. Vis. Appl. 2017, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manerikar, A.; Shamseldin, T.; Habib, A. SLAM-Assisted Coverage Path Planning for Indoor LiDAR Mapping Systems. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.04825. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, H.; Xia, Z.C. SLAM; Definition and Evolution. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 97, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario Barros, A.; Michel, M.; Moline, Y.; Corre, G.; Carrel, F. A Comprehensive Survey of Visual SLAM Algorithms. Robotics 2022, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, W.; Kohler, D.; Rapp, H.; Andor, D. Real-Time Loop Closure in 2D LIDAR SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1271–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Seçkin, A.Ç. A Natural Navigation Method for Following Path Memories from 2D Maps. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 10417–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L. Review on LiDAR-Based SLAM Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning (CONF-SPML), Stanford, CA, USA, 14 November 2021; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Seçkin, A.Ç. Pedestrian and Mobile Robot Detection with 2D LIDAR. EJOSAT 2021, 23, 583–588. [Google Scholar]
- Seçkin, A.Ç. Adaptive Positioning System Design Using AR Markers and Machine Learning for Mobile Robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), Diyarbakir, Turkey, 9–11 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Alitaleshi, A.; Jazayeriy, H.; Kazemitabar, S.J. WiFi Fingerprinting Based Floor Detection with Hierarchical Extreme Learning Machine. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 29–30 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Cao, H.; Shi, T.; Huang, L. Supplementary Open Dataset for WiFi Indoor Localization Based on Received Signal Strength. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queralta, J.P.; Martínez Almansa, C.; Schiano, F.; Floreano, D.; Westerlund, T. UWB-Based System for UAV Localization in GNSS-Denied Environments: Characterization and Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, Nevada, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 4521–4528. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa-de-Eribe-Landaberea, A.; Zamora-Cadenas, L.; Peñagaricano-Muñoa, O.; Velez, I. UWB and IMU-Based UAV’s Assistance System for Autonomous Landing on a Platform. Sensors 2022, 22, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.; Zaidi, S.A.A.; Ishtiaq, A.; Bukhari, S.U.R.; Samer, S.; Farman, A. A Comparative Survey of LiDAR-SLAM and LiDAR Based Sensor Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2021 Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing (MAJICC), Karachi, Pakistan, 15–17 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Q.; Sun, Q.; Chen, L.; Nie, B.; Li, Q. A Comparative Analysis of LiDAR SLAM-Based Indoor Navigation for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 6907–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, W.G.; Rodríguez, G.A.; Álvarez, L.; Sandoval, S.; Quisaguano, F.; Limaico, A. Visual SLAM with a RGB-D Camera on a Quadrotor UAV Using on-Board Processing. In Advances in Computational Intelligence; Rojas, I., Joya, G., Catala, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 596–606. [Google Scholar]
- von Stumberg, L.; Usenko, V.; Engel, J.; Stückler, J.; Cremers, D. From Monocular SLAM to Autonomous Drone Exploration. In Proceedings of the 2017 European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR), Paris, France, 6–8 September 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo, J.-C.; Munguia, R.; Urzua, S.; Guerra, E.; Grau, A. Monocular Visual SLAM Based on a Cooperative UAV–Target System. Sensors 2020, 20, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krul, S.; Pantos, C.; Frangulea, M.; Valente, J. Visual SLAM for Indoor Livestock and Farming Using a Small Drone with a Monocular Camera: A Feasibility Study. Drones 2021, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipenko, M.; Afanasyev, I. Comparison of Various SLAM Systems for Mobile Robot in an Indoor Environment. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), Funchal, Portugal, 25–27 September 2018; pp. 400–407. [Google Scholar]
- Merzlyakov, A.; Macenski, S. A Comparison of Modern General-Purpose Visual SLAM Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September 2021; pp. 9190–9197. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.; Huang, J.; Yang, D.; Rao, L. Sampling Visual SLAM with a Wide-Angle Camera for Legged Mobile Robots. IET Cyber-Syst. Robot. 2022, 4, 356–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Lang, H.; Ren, J. Stereo Visual SLAM for Autonomous Vehicles: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–14 October 2020; pp. 1316–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Hu, X.; Cai, J. A Review of Visual SLAM Methods for Autonomous Driving Vehicles. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 104992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaspur Kazerouni, I.; Fitzgerald, L.; Dooly, G.; Toal, D. A Survey of State-of-the-Art on Visual SLAM. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 205, 117734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigl, T.; Janssen, G.J.M.; Dizdarevic, V.; Witrisal, K.; Irahhauten, Z. Analysis of a UWB Indoor Positioning System Based on Received Signal Strength. In Proceedings of the Navigation and Communication 2007 4th Workshop on Positioning, Hannover, Germany, 22 March 2007; pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; Ming, Y. Survey of Indoor Positioning Systems Based on Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Technology. In Wireless Communications, Networking and Applications; Zeng, Q.-A., Ed.; Springer India: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 1269–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Alarifi, A.; Al-Salman, A.; Alsaleh, M.; Alnafessah, A.; Al-Hadhrami, S.; Al-Ammar, M.A.; Al-Khalifa, H.S. Ultra Wideband Indoor Positioning Technologies: Analysis and Recent Advances. Sensors 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, S. Indoor Positioning System Using Wifi Fingerprint. Stanford University, Available Online at 2014. Available online: https://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2014/Dan%20Li,%20Le%20Wang,%20Shiqi%20Wu,%20Indoor%20Positioning%20System%20Using%20Wifi%20Fingerprint.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Hoang, T. WiFi RSSI Indoor Localization 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Cui, W.; Li, B.; Chen, C.; Cao, Z.; Gao, K. WiFi-Based Indoor Robot Positioning Using Deep Fuzzy Forests. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 10773–10781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, Z.; Shibasaki, R.; Song, X. Domain Adversarial Graph Convolutional Network Based on RSSI and Crowdsensing for Indoor Localization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 13662–13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Gao, T.; Bai, D.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Research on Multi-Sensor Assisted WiFi Signal Fingerprint Indoor Location Method Based on Extended Kalman Filter. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Cloud Computing and Mechatronic Engineering (I3CME 2022), Chendu, China, 17–19 June 2022; SPIE: Breda, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 12339, pp. 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Wu, W.; Sun, J. A Novel Fingerprint Positioning Method Applying Vision-Based Definition for WIFI-Based Localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 16092–16106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Escalona, I.; Zola, E. Improving Fingerprint-Based Positioning by Using IEEE 802.11 Mc FTM/RTT Observables. Sensors 2022, 23, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Deng, X.; Zhang, F.; Wen, Y.; Kadhim, D.J. Positioning and Guiding Educational Robots by Using Fingerprints of WiFi and RFID Array. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spachos, P. RSSI Dataset for Indoor Localization Fingerprinting. IEEE DataPort 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, S.; Spachos, P.; Plataniotis, K.N. Memoryless Techniques and Wireless Technologies for Indoor Localization With the Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 10996–11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, P.P.; Soares, E.A.; Jiang, R.; Arnold, N.I.; Atkinson, P.M. Explainable Artificial Intelligence: An Analytical Review. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2021, 11, e1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.; Wang, H.X.; Li, Y.F.; Nguyen, T.N. Explainable Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 3503–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakisim, A.G.; Turgut, Z.; Atmaca, T. XAI Empowered Dual Band Wi-Fi Based Indoor Localization via Ensemble Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 14th International Conference on Network of the Future (NoF), Izmir, Turkey, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A.H.M.; Alam, M.G.R.; Hassan, M.R.; Apon, T.S.; Hassan, M.M. Explainable Indoor Localization of BLE Devices through RSSI Using Recursive Continuous Wavelet Transformation and XGBoost Classifier. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 141, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Montoliu, R.; Martínez-Usó, A.; Avariento, J.P.; Arnau, T.J.; Benedito-Bordonau, M.; Huerta, J. UJIIndoorLoc: A New Multi-Building and Multi-Floor Database for WLAN Fingerprint-Based Indoor Localization Problems. In Proceedings of the Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), 2014 International Conference, Busan, Republic of Korea, 27–30 October 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, M.T.; Zhu, Y.; Yuen, B.; Reese, T.; Dong, X.; Lu, T.; Westendorp, R.; Xie, M. A Soft Range Limited K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm for Indoor Localization Enhancement. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 10208–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.T.; Yuen, B.; Dong, X.; Lu, T.; Westendorp, R.; Reddy, K. Recurrent Neural Networks for Accurate RSSI Indoor Localization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 10639–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.T.; Yuen, B.; Dong, X.; Lu, T.; Westendorp, R.; Reddy Tarimala, K. Semi-Sequential Probabilistic Model for Indoor Localization Enhancement. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 6160–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khullar, R.; Dong, Z. Indoor Localization Framework with WiFi Fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 2017 26th Wireless and Optical Communication Conference (WOCC), Newark, NJ, USA, 7–8 April 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Peng, J. Robot Indoor Positioning and Navigation Based on Improved WiFi Location Fingerprint Positioning Algorithm. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, e8274455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csík, D.; Odry, Á.; Sarcevic, P. Comparison of RSSI-Based Fingerprinting Methods for Indoor Localization. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 20th Jubilee International Symposium on Intelligent Systems and Informatics (SISY), Subotica, Serbia, 15–17 September 2022; pp. 000273–000278. [Google Scholar]
- Chondro, P.; Schwarz, I.; Ruan, S.-J. A Seamless Ground Truth Detection for Enhancing Localization on Mobile Robots. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 23149–23166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sier, H.; Qingqing, L.; Xianjia, Y.; Queralta, J.P.; Zou, Z.; Westerlund, T. A Benchmark for Multi-Modal Lidar SLAM with Ground Truth in GNSS-Denied Environments. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, A.; Jackson, W.; Zhang, D.; Dobie, G.; MacLeod, C.N.; Karkera, B.; Barber, T. Robotic Positioning for Quality Assurance of Feature-Sparse Components Using a Depth-Sensing Camera. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 10032–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.02754 (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Muschalik, M.; Fumagalli, F.; Hammer, B.; Hüllermeier, E. Agnostic Explanation of Model Change Based on Feature Importance. Künstl. Intell. 2022, 36, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Lucet, E.; Lenain, R. A New Neural Network Feature Importance Method: Application to Mobile Robots Controllers Gain Tuning. In Proceedings of the ICINCO 2020, 17th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Paris, France, 7 July 2020. [Google Scholar]


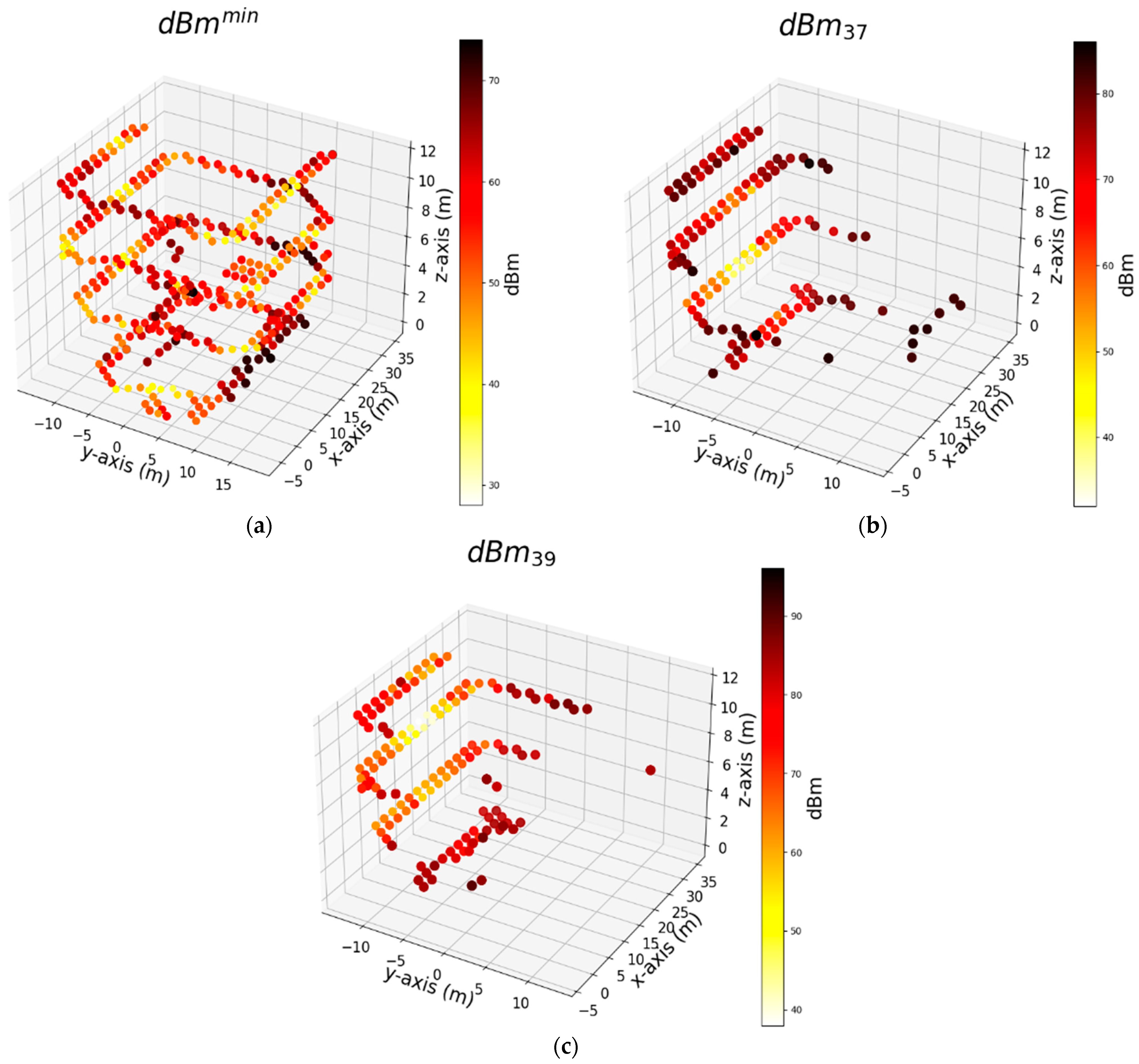
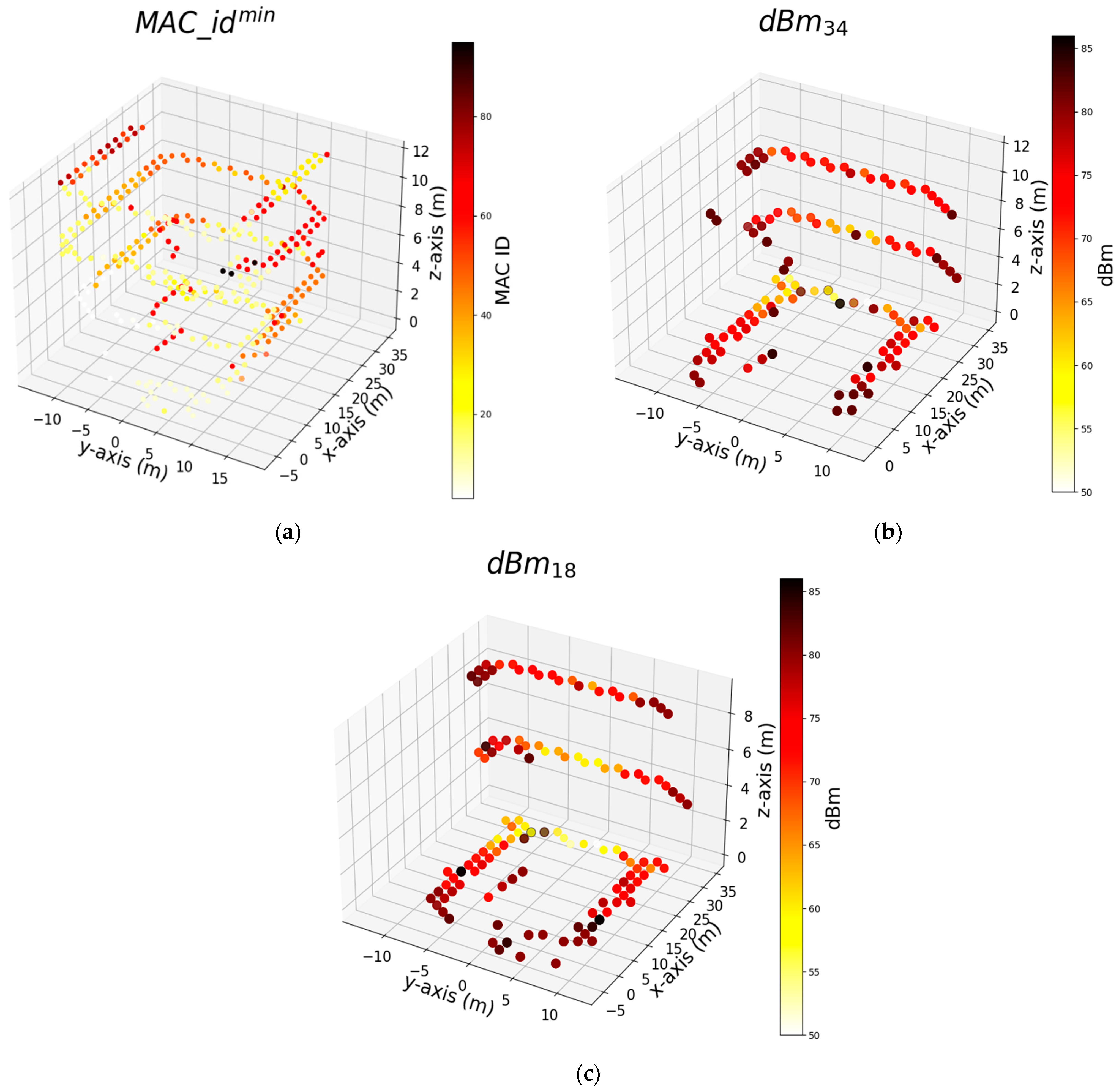
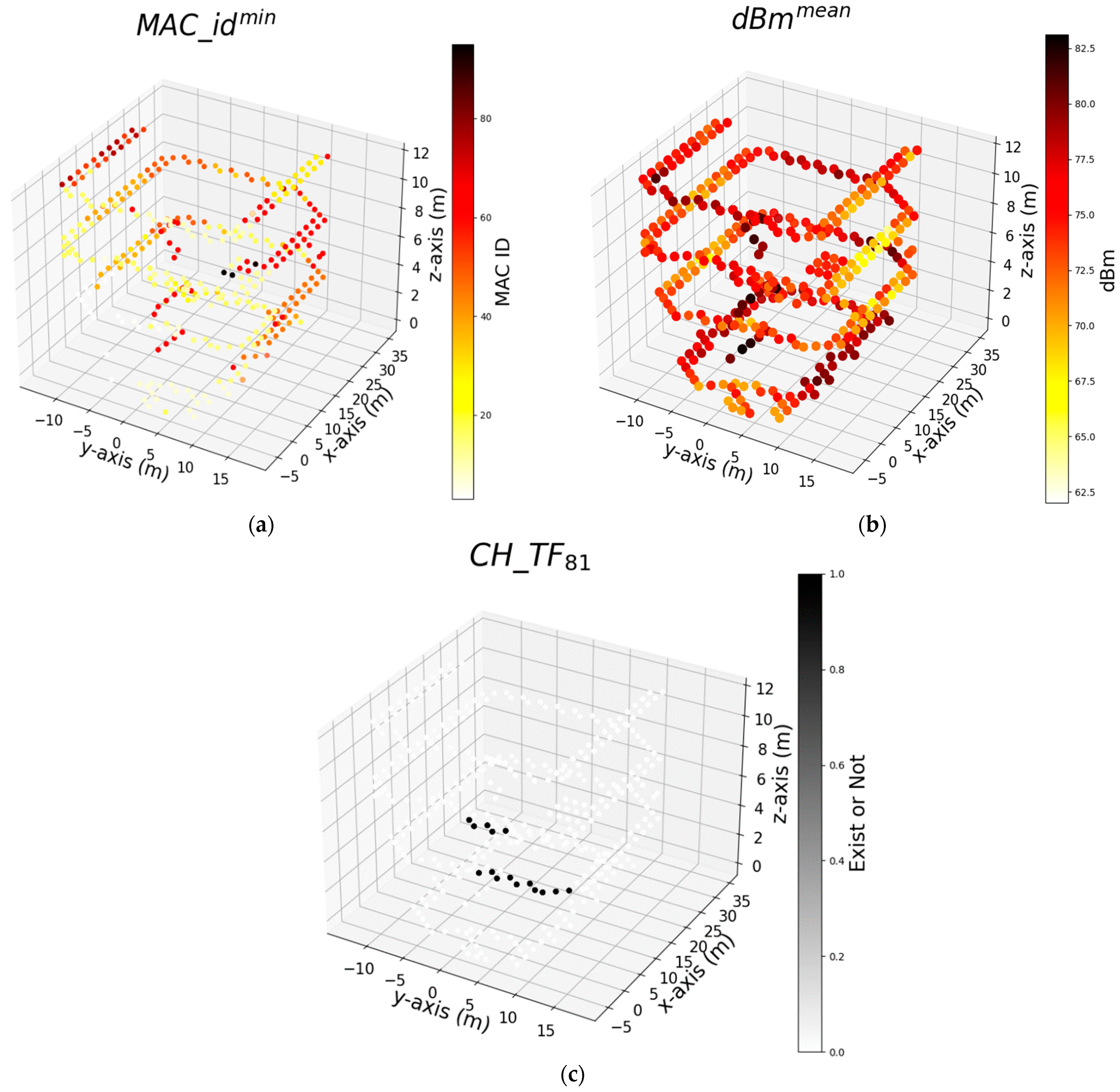

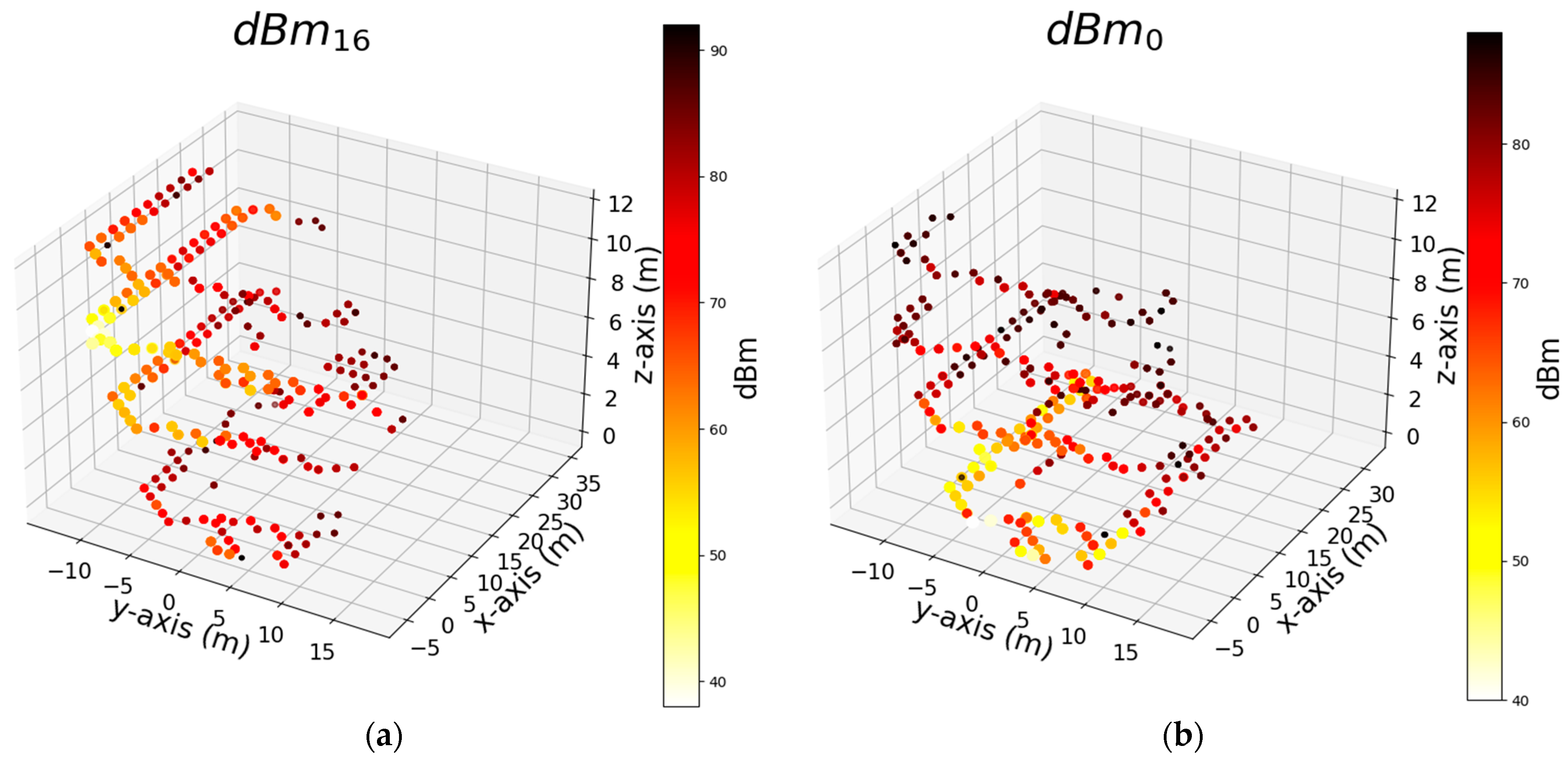
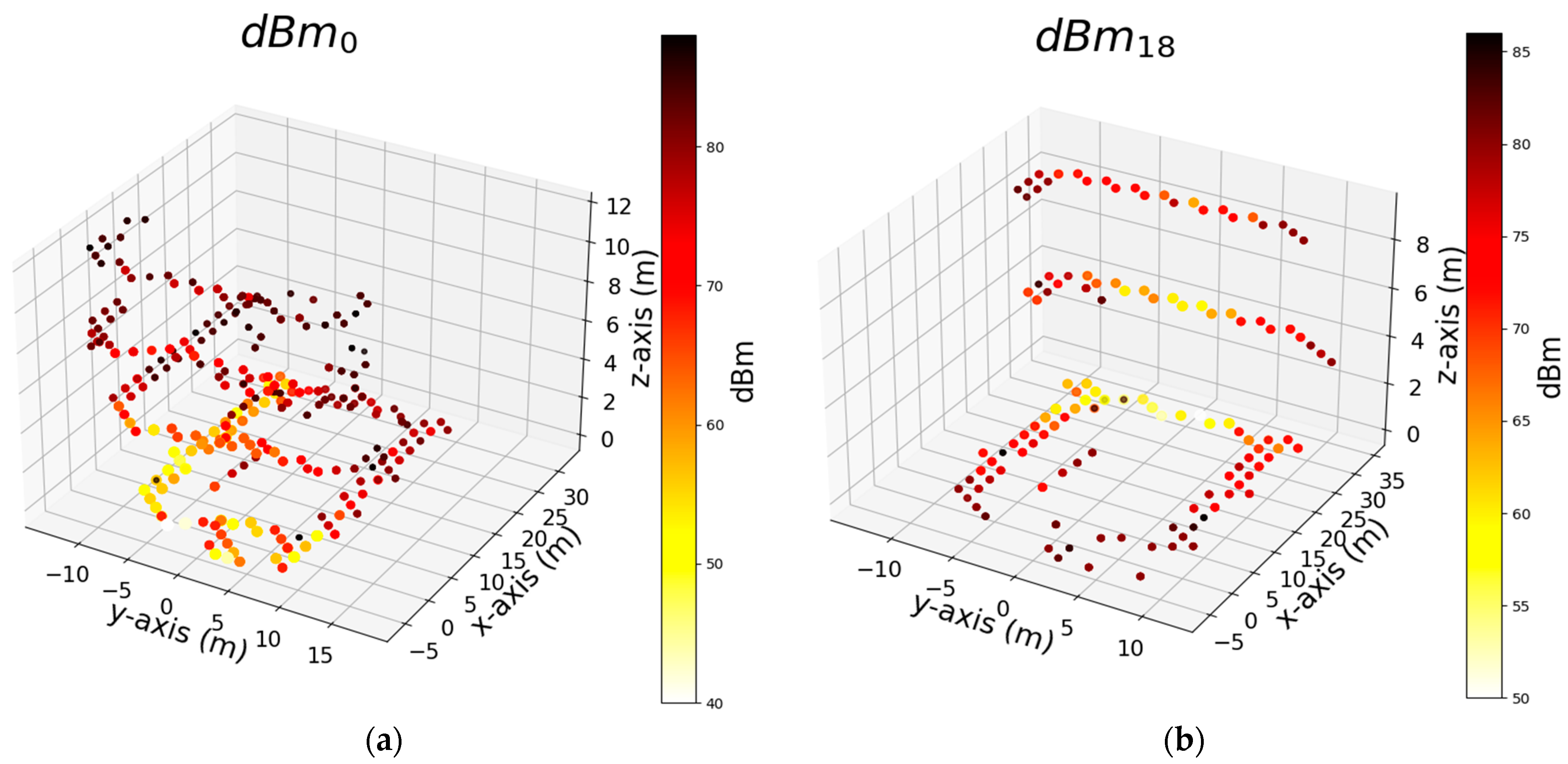
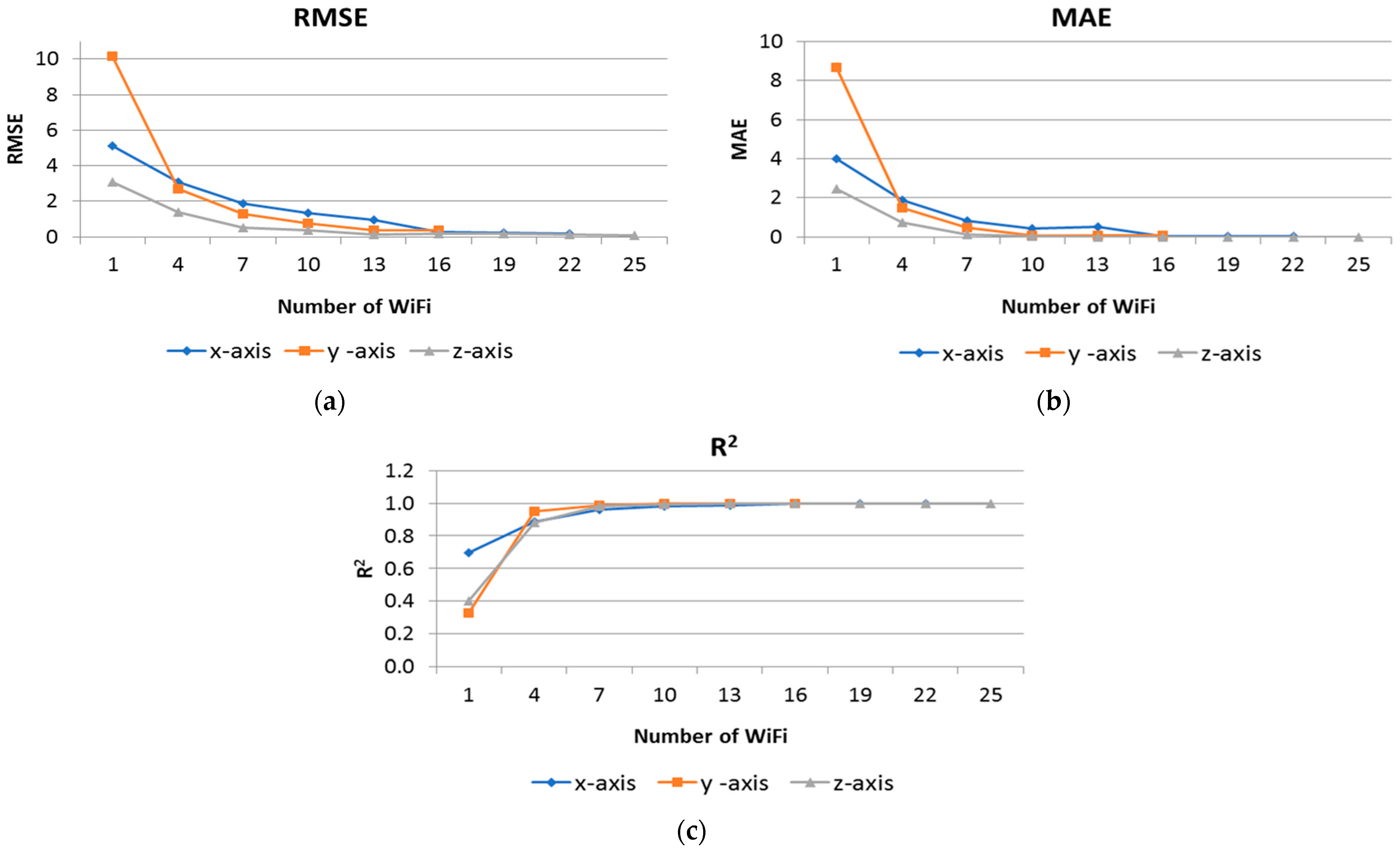
| Notation | Dataset Abbreviation | Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| x-axis | tx | Target | Robot coordination on x-axis |
| y-axis | ty | Target | Robot coordination on y-axis |
| z-axis | tz | Target | Robot coordination on z-axis |
| F_dB_min | Feature (SFE) | Minimum RSS value at a measurement point | |
| F_dB_max | Feature (SFE) | Maximum RSS value at a measurement point | |
| F_dB_mean | Feature (SFE) | Mean RSS values at a measurement point | |
| F_dB_std | Feature (SFE) | Standard deviation of RSS values at a measurement point | |
| F_dB_MAC_ID_min | Feature (SFE) | ID of the MAC with the minimum measured RSS | |
| F_dB_MAC_ID_max | Feature (SFE) | ID of the MAC with the maximum measured RSS | |
| F_dB_CH_min | Feature (SFE) | Channel of the AP with the minimum measured RSS | |
| F_dB_CH_max | Feature (SFE) | Channel of the AP with the maximum measured RSS | |
| F_nofCH | Feature (SFE) | Number of unique channels in a measurement point | |
| F_nofMAC_ID | Feature (SFE) | Number of MAC IDs in a measurement point | |
| F_CH_maxfrequent | Feature (SFE) | Most frequent Channel number in a measurement point | |
| F_CH_minfrequent | Feature (SFE) | Least frequent Channel number in a measurement point | |
| MAC_ID_X | Feature (RCI) | Whether MAC ID-X [0 to 99] exists at a measurement point or not. | |
| CH_X | Feature (RCI) | Channel number of MAC ID-X [0 to 99] (if doesn’t exist set to 0) | |
| dBm_X | Feature (RCI) | RSS of MAC ID-X [0 to 99] (if doesn’t exist set to 0) |
| Algorithm | Hyperparameters |
|---|---|
| RF | Number of trees (10), Max number of features (unlimited), Replicable training (No), Max depth (unlimited), Stop splitting subsets (5) |
| ANN | 2 Hidden layers (1st layer 100 neurons, 2nd layer 20 neuron), Activation Function: ReLu, Solver for weight optimization: Adam, Strength of the L2 regularization term (Alpha): 0.0001, Maximum number of iterations: 200, The initial learning rate: 0.001 |
| GB | Number of trees (100), Learning rate (0.1), Replicable training (Yes), Maximum depth (3), Fraction of training instances (1), Stop splitting subsets (2) |
| LR | Regularization (Ridge Regression (L2) with α = 0.0001), Fit intercept (Yes) |
| DT | Pruning (in leaves 2, internal nodes 5), Maximum depth (100), Splitting (95%), Binary trees (Yes) |
| SVM | C (1.0), ε (0.1), Kernel (RBF, exp(-auto|x-y|2)), Numerical tolerance (0.001), Iteration (100) |
| AdaB | Estimator (tree), Number of estimators (50), Algorithm (Samme.r), Loss (Linear Reg.) |
| kNN | Number of neighbors (5), Metric (Euclidean), Weight (Uniform) |
| SGD | Loss function (Huber), ε (0.1), Regularization (elastic net), Mixing (0.15), Learning rate (constant), Iteration (1000) |
| Model | RCI | SFE | RCI + SFE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | |
| AdaB | 0.290 | 0.044 | 0.999 | 1.018 | 0.156 | 0.988 | 0.344 | 0.055 | 0.999 |
| GB | 0.484 | 0.100 | 0.997 | 1.575 | 0.323 | 0.971 | 0.526 | 0.109 | 0.997 |
| kNN | 1.137 | 0.750 | 0.985 | 3.482 | 1.968 | 0.859 | 1.141 | 0.753 | 0.985 |
| LR | 1.600 | 1.200 | 0.970 | 8.320 | 7.108 | 0.196 | 1.577 | 1.192 | 0.971 |
| ANN | 0.627 | 0.383 | 0.995 | 4.926 | 3.631 | 0.718 | 0.528 | 0.313 | 0.997 |
| RF | 0.687 | 0.324 | 0.995 | 1.998 | 0.857 | 0.954 | 0.693 | 0.311 | 0.994 |
| SGD | 2.061 | 1.464 | 0.951 | 8.577 | 6.898 | 0.146 | 2.015 | 1.433 | 0.953 |
| SVM | 3.918 | 3.423 | 0.822 | 8.633 | 7.737 | 0.135 | 3.867 | 3.368 | 0.826 |
| DT | 0.777 | 0.190 | 0.993 | 2.361 | 0.643 | 0.935 | 0.769 | 0.196 | 0.993 |
| Model | RCI | SFE | RCI + SFE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | |
| AdaB | 0.470 | 0.063 | 0.999 | 1.311 | 0.207 | 0.989 | 0.369 | 0.058 | 0.999 |
| GB | 0.842 | 0.163 | 0.995 | 1.445 | 0.318 | 0.986 | 0.715 | 0.156 | 0.997 |
| kNN | 1.666 | 1.012 | 0.982 | 3.626 | 2.150 | 0.915 | 1.653 | 1.020 | 0.982 |
| LR | 2.433 | 1.837 | 0.962 | 8.648 | 6.888 | 0.517 | 2.412 | 1.817 | 0.962 |
| ANN | 1.213 | 0.750 | 0.990 | 5.939 | 4.575 | 0.772 | 1.027 | 0.590 | 0.993 |
| RF | 1.097 | 0.511 | 0.992 | 1.803 | 0.830 | 0.979 | 1.056 | 0.458 | 0.993 |
| SGD | 3.427 | 2.437 | 0.924 | 8.802 | 6.931 | 0.499 | 3.468 | 2.450 | 0.922 |
| SVM | 8.770 | 7.770 | 0.503 | 9.916 | 8.921 | 0.364 | 8.547 | 7.577 | 0.528 |
| DT | 1.153 | 0.299 | 0.991 | 2.261 | 0.644 | 0.967 | 1.125 | 0.288 | 0.992 |
| Model | RCI | SFE | RCI + SFE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | |
| AdaB | 0.091 | 0.003 | 0.999 | 0.418 | 0.043 | 0.989 | 0.121 | 0.004 | 0.999 |
| GB | 0.356 | 0.059 | 0.992 | 0.442 | 0.084 | 0.988 | 0.320 | 0.058 | 0.994 |
| kNN | 0.711 | 0.228 | 0.969 | 1.905 | 0.941 | 0.777 | 0.700 | 0.229 | 0.970 |
| LR | 0.882 | 0.671 | 0.952 | 3.423 | 2.860 | 0.279 | 0.881 | 0.671 | 0.952 |
| ANN | 0.383 | 0.214 | 0.991 | 2.482 | 1.895 | 0.621 | 0.332 | 0.166 | 0.993 |
| RF | 0.432 | 0.152 | 0.989 | 0.652 | 0.237 | 0.974 | 0.412 | 0.139 | 0.990 |
| SGD | 1.272 | 0.959 | 0.900 | 3.476 | 2.810 | 0.257 | 1.257 | 0.925 | 0.903 |
| SVM | 2.457 | 2.119 | 0.629 | 3.493 | 3.114 | 0.249 | 2.341 | 2.061 | 0.663 |
| DT | 0.601 | 0.103 | 0.978 | 0.697 | 0.130 | 0.970 | 0.506 | 0.085 | 0.984 |
| Feature Rank | x-Axis | y-Axis | z-Axis | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | R2 | MAE | R2 | MAE | R2 | |||||||
| 1 | 1.983 | 0.173 | 0.912 | 0.058 | 0.455 | 0.112 | ||||||
| 2 | 1.061 | 0.078 | 0.825 | 0.038 | 0.077 | 0.016 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.190 | 0.004 | 0.487 | 0.019 | 0.058 | 0.012 | ||||||
| 4 | 0.169 | 0.003 | 0.452 | 0.014 | 0.046 | 0.009 | ||||||
| 5 | 0.166 | 0.003 | 0.235 | 0.006 | 0.026 | 0.003 | ||||||
| 6 | 0.124 | 0.004 | 0.176 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.003 | ||||||
| 7 | 0.073 | 0.003 | 0.094 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.001 | ||||||
| dBm (All) | RCI | dBm (7 Wi-Fi) | dBm (10 Wi-Fi) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 |
| x | 0.294 | 0.047 | 0.999 | 0.290 | 0.044 | 0.999 | 1.888 | 0.811 | 0.959 | 1.324 | 0.438 | 0.979 |
| y | 0.472 | 0.063 | 0.999 | 0.470 | 0.063 | 0.999 | 1.306 | 0.492 | 0.988 | 0.760 | 0.096 | 0.996 |
| z | 0.122 | 0.005 | 0.999 | 0.091 | 0.003 | 0.999 | 0.528 | 0.134 | 0.982 | 0.362 | 0.048 | 0.991 |
| Axis | dBm (8 Wi-Fi) Wi-Fi: 0, 16, 18, 34, 39, 53, 57, 75 | dBm (11 Wi-Fi) Wi-Fi: 0, 13, 16, 18, 29, 34, 39, 53, 57, 62, 75 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | |
| x | 1.05 | 0.52 | 0.987 | 0.58 | 0.17 | 0.996 |
| y | 2.55 | 1.27 | 0.957 | 0.68 | 0.1 | 0.997 |
| z | 1.29 | 0.5 | 0.898 | 0.4 | 0.041 | 0.99 |
| Refs. | No. Sample (Feature) | No. Locations | No. Access Points | Device Type(s) | Localization Area in m2 | Performance in Meters | Assistive Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [47] | 21,048 (529) | 933 | 520 | Smartphones | 3 different building total: 108,703 m2 | 3D MAE: 6.05 | No |
| [41,42] | ~300 (NA) | 32 | NA | Raspberry Pi 3 and Arduino | Room 1: 6.0 × 5.5 m2 Room 2: 5.8 × 5.3 m2 Room 3: 10.8 × 7.3 m2 | 2D RMSE: 1.356 2D RMSE: 1.166 2D RMSE: 1.266 | ZigBee and Bluetooth |
| [34,48,49,50] | 365,000 (117) | 345 | 6 | Smartphone | 21 × 16 m2 | 2D MAE: 0.75 m | No |
| [15] | 23,925 (945) | 1802 | 105 | Smartphones | 3 buildings 8000 m2 | 2D MAE: 2.3 m | No |
| Proposed Method | 36,568 (312) | 398 | 100 | Raspberry Pi 4 | 1 building 3500 m2 | 2D RMSE: 0.552 3D MAE: 0.077 | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abacı, H.; Seçkin, A.Ç. Mobile Robot Positioning with Wireless Fidelity Fingerprinting and Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Sensors 2024, 24, 7943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247943
Abacı H, Seçkin AÇ. Mobile Robot Positioning with Wireless Fidelity Fingerprinting and Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):7943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247943
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbacı, Hüseyin, and Ahmet Çağdaş Seçkin. 2024. "Mobile Robot Positioning with Wireless Fidelity Fingerprinting and Explainable Artificial Intelligence" Sensors 24, no. 24: 7943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247943
APA StyleAbacı, H., & Seçkin, A. Ç. (2024). Mobile Robot Positioning with Wireless Fidelity Fingerprinting and Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Sensors, 24(24), 7943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247943







