Reinforcement-Learning-Based Fixed-Time Prescribed Performance Consensus Control for Stochastic Nonlinear MASs with Sensor Faults
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This paper presents an improved fixed-time prescribed performance framework. By constructing coordinate transformations, the consensus error can converge to a prescribed performance boundary in fixed time. Moreover, this framework overcomes the defect in finite-time control [20], where convergence time depends on the initial state.
- (2)
- Considering the potential impact of sensor faults in real-world systems, which leads to a poor control performance, this paper utilizes neural networks to construct a sensor fault compensation mechanism. This enables the consensus error to efficiently converge to the prescribed performance boundary, even in the presence of unknown sensor faults.
- (3)
- Compared with traditional backstepping methods [39], which do not account for system resource consumption, this paper uses RL to design an optimal control strategy, reducing the resource consumption associated with backstepping. Furthermore, compared with existing RL strategies [40], our approach uses a simpler adaptive laws form, ensuring that the RL network can be trained sufficiently and efficiently.
2. Preliminaries and Description
2.1. Graph Theory
2.2. Neural Networks (NNs)
2.3. System Description
3. Adaptive Optimal Consensus Controller Design and Stability Analysis
3.1. Adaptive Optimal Consensus Controller Design
| Algorithm 1: The Fixed-time prescribed performance optimization consensus control algorithm |
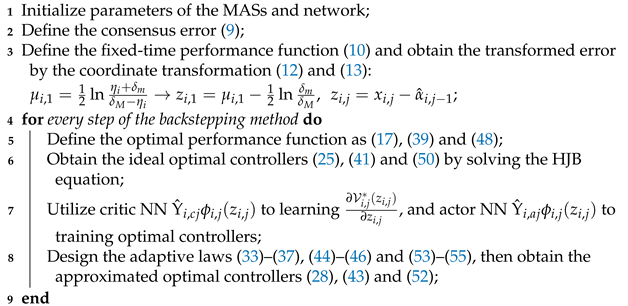 |
3.2. Stability Analysis
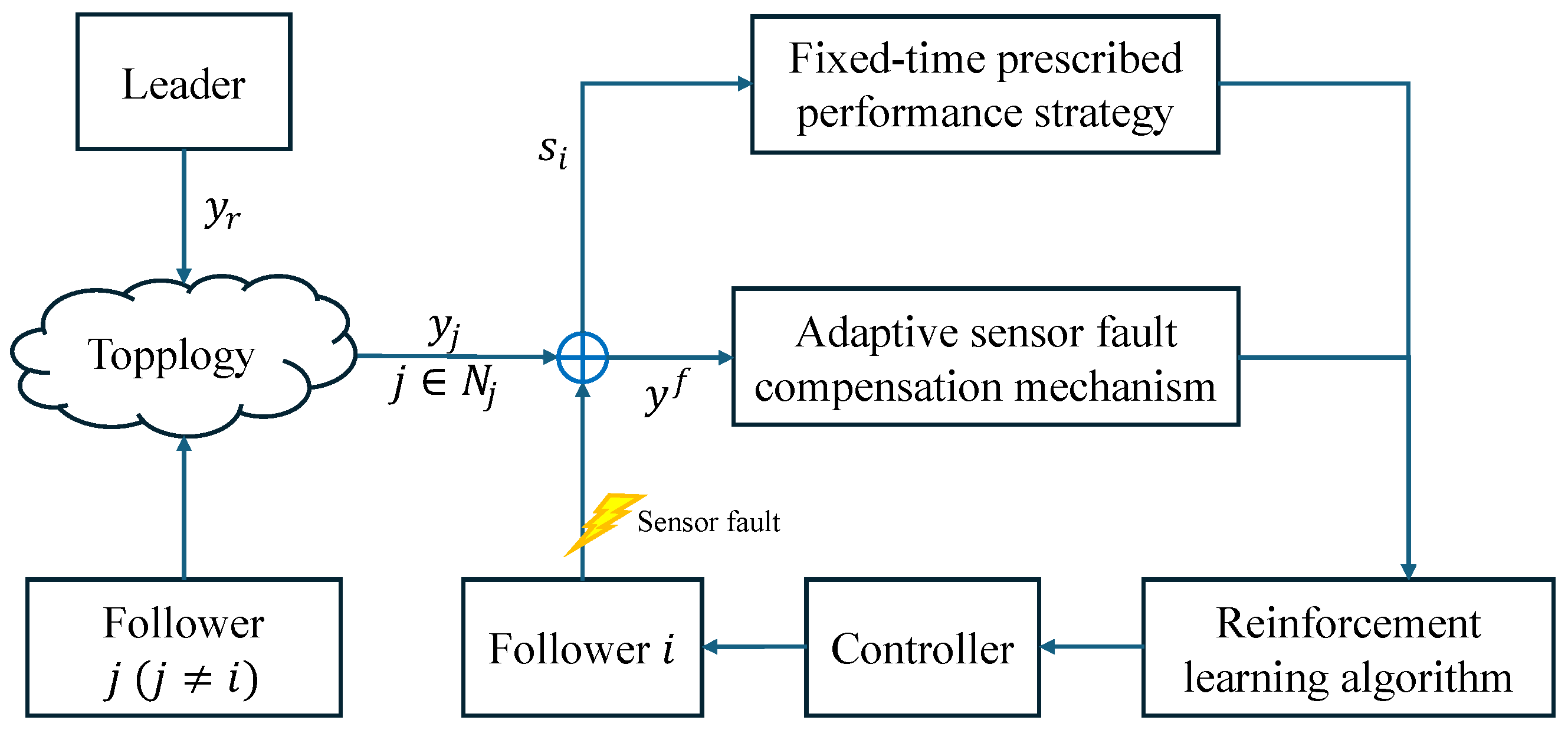
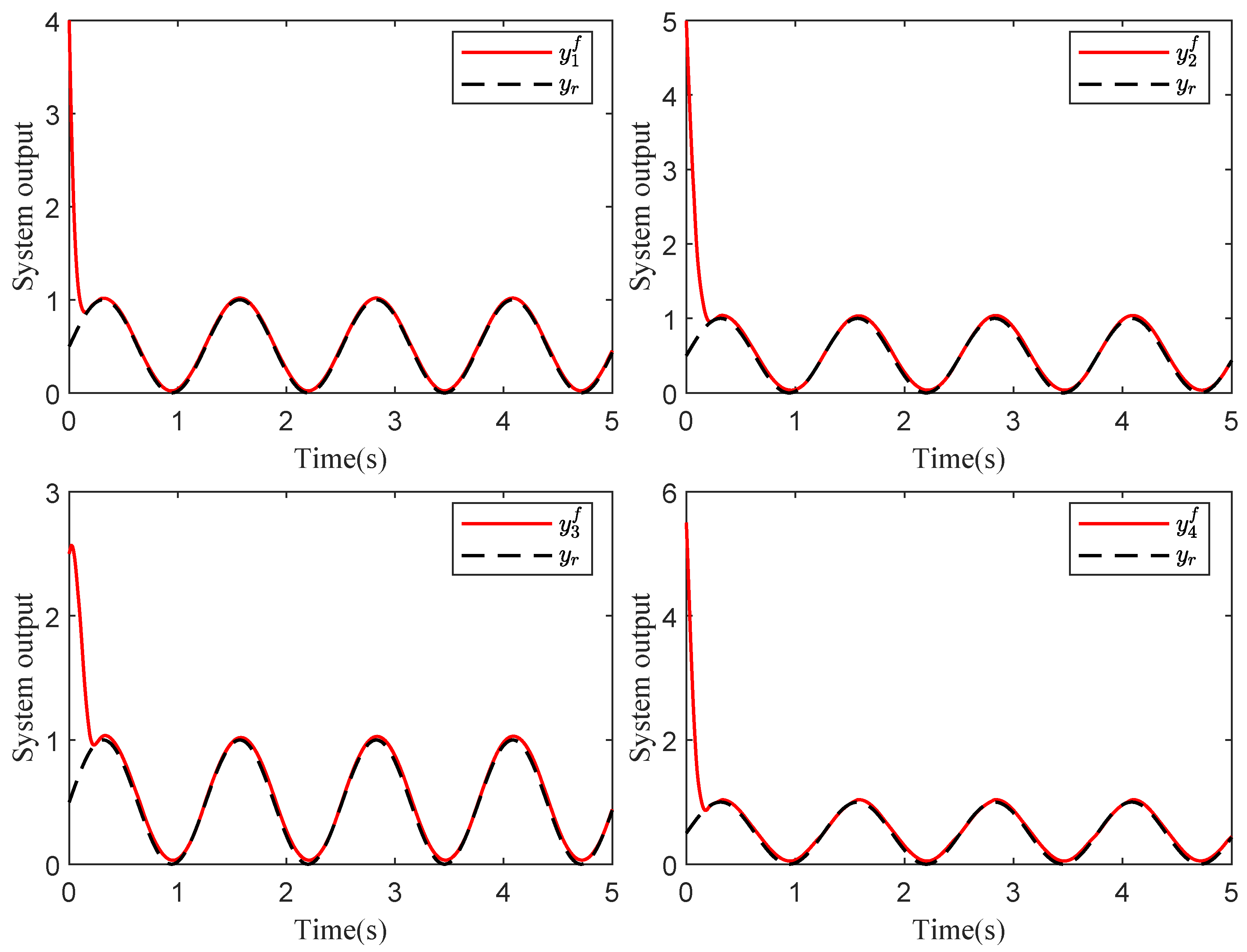
4. Simulation Example
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable | Definition |
|---|---|
| System state | |
| System output state with sensor fault | |
| t | Time |
| Consensus error | |
| Virtual controller | |
| Actual controller | |
| Network weight | |
| Optimal parameters | |
| Approximate optimal parameters |
| Abbreviation | Full Spelling |
|---|---|
| MASs | Multi-agent systems |
| SNMASs | Stochastic Nonlinear MASs |
| FTC | Fixed-time control |
| FTPPC | Fixed-time prescribed performance control |
| PPC | Prescribed performance control |
| HJB | Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman |
| RL | Reinforcement learning |
| NNs | Neural networks |
| FTPF | Fixed-time performance function |
References
- Yang, S.; Liang, H.; Pan, Y.; Li, T. Security control for air-sea heterogeneous multiagent systems with cooperative-antagonistic interactions: An intermittent privacy preservation mechanism. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2024. Available online: https://www.sciengine.com/SCTS/doi/10.1007/s11431-024-2758-6 (accessed on 21 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, Z.; Liang, H.; Li, H. Pinning-based neural control for multiagent systems with self-regulation intermediate event-triggered method. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Li, H. Bipartite consensus for quantization communication multi-agents systems with event-triggered random delayed impulse control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, C.; Ma, H.; Li, H. Cloud-based distributed group asynchronous consensus for switched nonlinear cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, J.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Q. Observer-based event-triggered iterative learning consensus for locally Lipschitz nonlinear MASs. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2024, 16, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, J. Safe consensus control of cooperative-competitive multi-agent systems via differential privacy. Kybernetika 2023, 58, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, K.; Chen, C.L.P. Fixed-time formation control for uncertain nonlinear multiagent systems with time-varying actuator failures. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Gu, P. Resilient output control of multiagent systems with DoS attacks and actuator faults: Fully distributed event-triggered approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 7681–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, B.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lin, C. Finite-time fuzzy control of stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Li, K.; Guan, X. Decentralized event-triggered control for interconnected time-delay stochastic nonlinear systems using neural networks. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.E.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y. Prescribed performance bipartite consensus control for stochastic nonlinear multiagent systems under event-triggered strategy. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Niu, B.; Shang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Distributed adaptive asymptotic consensus tracking control for stochastic nonlinear MASs with unknown control gains and output constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Hua, C.; You, X.; Ahn, C.K. Leader-following consensus control for uncertain feedforward stochastic nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Cheng, Z.; Qin, J.; Lu, R. Deception attacks on event-triggered distributed consensus estimation for nonlinear systems. Automatica 2023, 154, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xie, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.L.P.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive inverse optimal consensus control for uncertain high-order multiagent systems with actuator and sensor failures. Inf. Sci. 2022, 605, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.G.; Wang, B.Q.; Wang, J.L.; Wu, Z.G.; Guo, L. Adaptive event-triggered PIO-based anti-disturbance fault-tolerant control for MASs with process and sensor faults. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 11, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ren, Q.; Ma, H.; Chen, G.; Li, H. Model-free adaptive control for nonlinear systems under dynamic sparse attacks and measurement disturbances. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 4731–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Z. Distributed resilient tracking of multiagent systems under actuator and sensor faults. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 4653–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Peng, S.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, Z. UIF-based cooperative tracking method for multi-agent systems with sensor faults. Sci. China-Inf. Sci. 2018, 62, 10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xie, X.; Zhang, K. Finite-time stabilization of stochastic high-order nonlinear systems with FT-SISS inverse dynamics. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 64, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Chen, C.L.P.; Tong, S. Fuzzy adaptive finite-time control design for nontriangular stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G. Finite-time stability and stabilization of Itô stochastic systems with Markovian switching: Mode-dependent parameter approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 2428–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. Adaptive fixed-time control of nonlinear MASs with actuator faults. IEEE-CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B. Global fixed-time consensus tracking of nonlinear uncertain multiagent systems with high-order dynamics. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Wu, J.; Zhan, X.; Yan, H. Practical finite-time and fixed-time containment for second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems with IDAs and Markov switching topology. Neurocomputing 2023, 573, 127180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yan, Z.; Luo, M.; Hu, M. Fixed-time partial component consensus for nonlinear multi-agent systems with/without external disturbances. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2024, 130, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H. Event-triggered predefined-time control for full-state constrained nonlinear systems: A novel command filtering error compensation method. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 2867–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Deng, F. Fixed-time prescribed performance consensus control for multiagent systems with nonaffine faults. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 3433–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, B. Fixed-time fault-tolerant formation control for a cooperative heterogeneous multiagent system with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J. Fixed-time consensus control for multi-agent systems with prescribed performance under matched and mismatched disturbances. ISA Trans. 2021, 119, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Ma, H.; Ren, H.; Li, H. Practically fixed-time adaptive consensus control for multiagent systems with prescribed performance. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 3867–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Z. A fixed-time consensus control with prescribed performance for multi-agent systems under full-state constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Chen, C.L.P. Optimized backstepping consensus control using reinforcement learning for a class of nonlinear strict-feedback-dynamic multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Ma, H.; Ren, H.; Li, H. Estimator-based reinforcement learning consensus control for multiagent systems with discontinuous constraints. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, H. Observer-based consensus control for MASs with prescribed constraints via reinforcement learning algorithm. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 17281–17291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C. Event-triggered containment control for nonlinear multiagent systems via reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2023, 70, 2904–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Ge, S.S.; Chen, C.L.P.; Tu, F.; Wang, S. Adaptive tracking control of surface vessel using optimized backstepping technique. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Chen, C.L.P.; Ge, S.S. Simplified optimized backstepping control for a class of nonlinear strict-feedback systems with unknown dynamic functions. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 51, 4567–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Ge, S.S.; Tu, F. Optimized backstepping for tracking control of strict-feedback systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 3850–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Chen, C.L.P.; Li, B. Optimized formation control using simplified reinforcement learning for a class of multiagent systems with unknown dynamics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 7879–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ming, Z. Cooperative differential game-based distributed optimal synchronization control of heterogeneous nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 7933–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Pan, Y.; Liang, H.; Ahn, C.K. Event-based adaptive neural network control for large-scale systems with nonconstant control gains and unknown measurement sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 7027–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Li, H.; Dong, G.; Lu, R. Event-triggered control for multiagent systems with sensor faults and input saturation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 3855–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Y. Fuzzy adaptive optimal consensus fault-tolerant control for stochastic nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 2870–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Adaptive virotherapy strategy for organism with constrained input using medicine dosage regulation mechanism. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 2505–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Mao, Z.; Jiang, B.; Yan, X.G. Prescribed performance fault-tolerant control for synchronization of heterogeneous nonlinear MASs using reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 5451–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Li, H. Data-based optimal consensus control for multiagent systems with time delays: Using prioritized experience replay. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 3244–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Shi, P. T-S fuzzy data-driven tomfir with application to incipient fault detection and isolation for high-speed rail vehicle suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 7921–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Su, Y.; Shi, P. Data-driven ToMFIR-based incipient fault detection and estimation for high-speed rail vehicle suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Cai, X.; Luo, A.; Ma, H.; Xu, S. Reinforcement-Learning-Based Fixed-Time Prescribed Performance Consensus Control for Stochastic Nonlinear MASs with Sensor Faults. Sensors 2024, 24, 7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247906
Wang Z, Cai X, Luo A, Ma H, Xu S. Reinforcement-Learning-Based Fixed-Time Prescribed Performance Consensus Control for Stochastic Nonlinear MASs with Sensor Faults. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247906
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhenyou, Xiaoquan Cai, Ao Luo, Hui Ma, and Shengbing Xu. 2024. "Reinforcement-Learning-Based Fixed-Time Prescribed Performance Consensus Control for Stochastic Nonlinear MASs with Sensor Faults" Sensors 24, no. 24: 7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247906
APA StyleWang, Z., Cai, X., Luo, A., Ma, H., & Xu, S. (2024). Reinforcement-Learning-Based Fixed-Time Prescribed Performance Consensus Control for Stochastic Nonlinear MASs with Sensor Faults. Sensors, 24(24), 7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247906







