Reverse-Bent Modular Coil Structure with Enhanced Output Stability in DWPT for Arbitrary Linear Transport Systems
Abstract
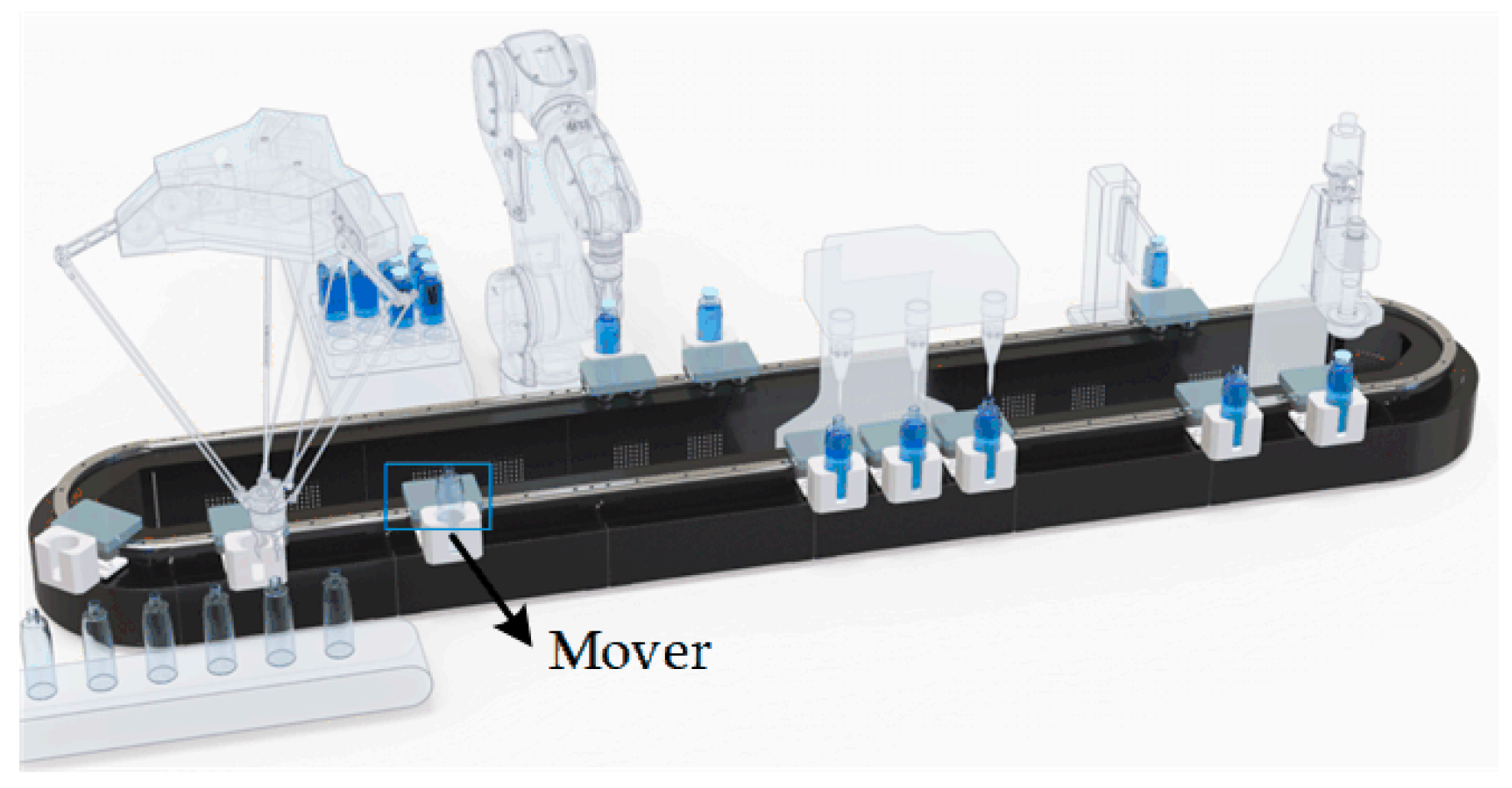
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Coil Structure for DWPT
2.1. Structure Design
2.2. Transmitter Design
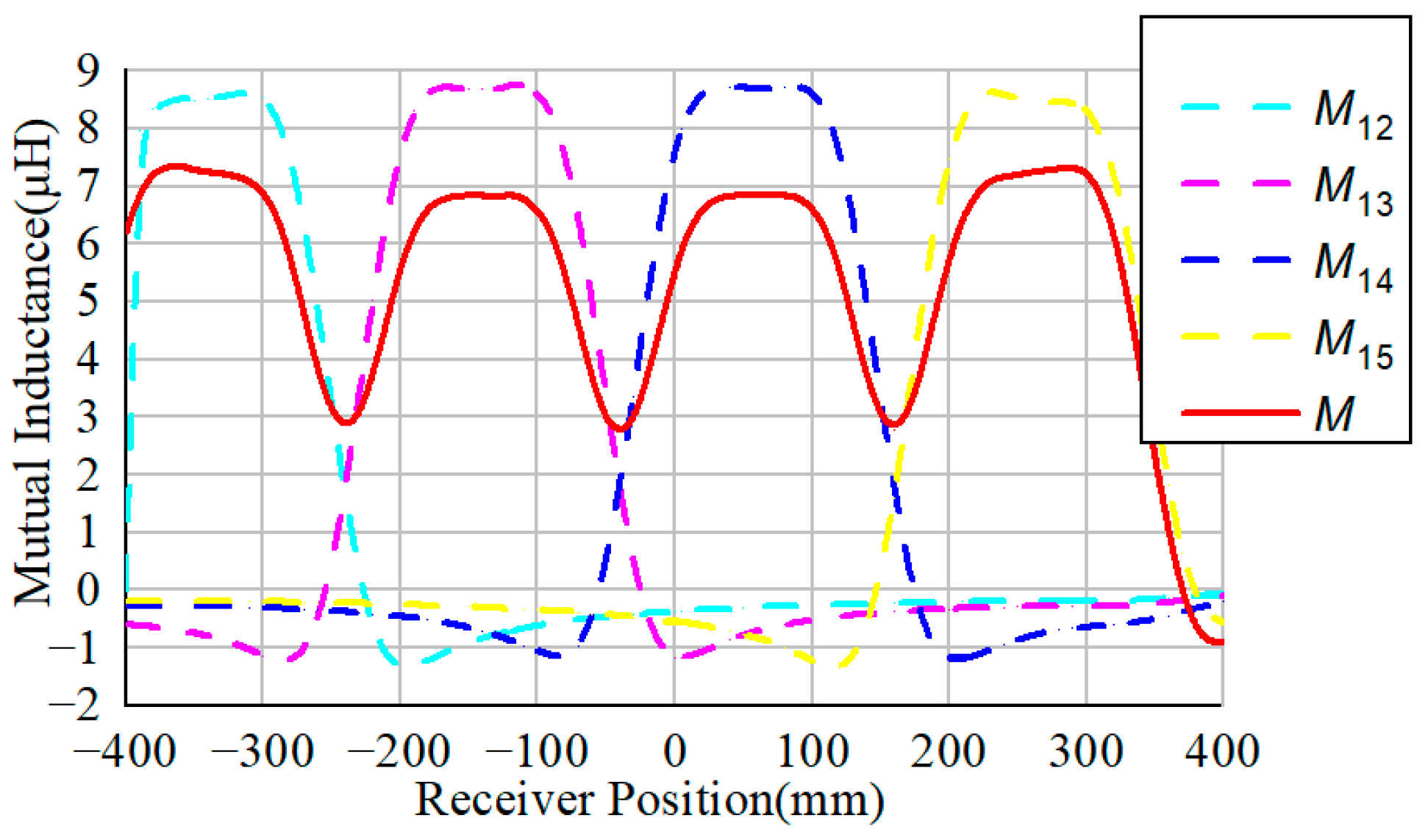
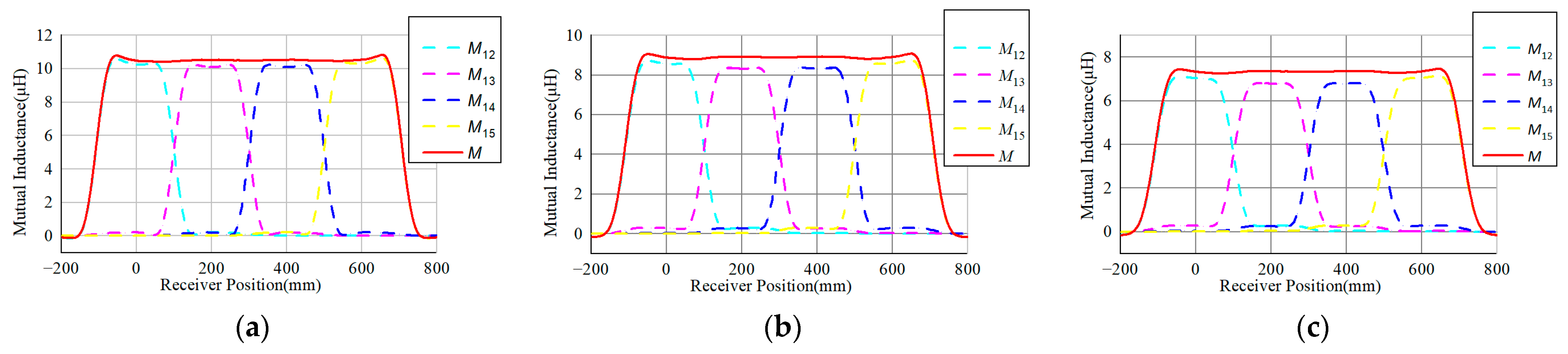
2.3. Dynamic Performance
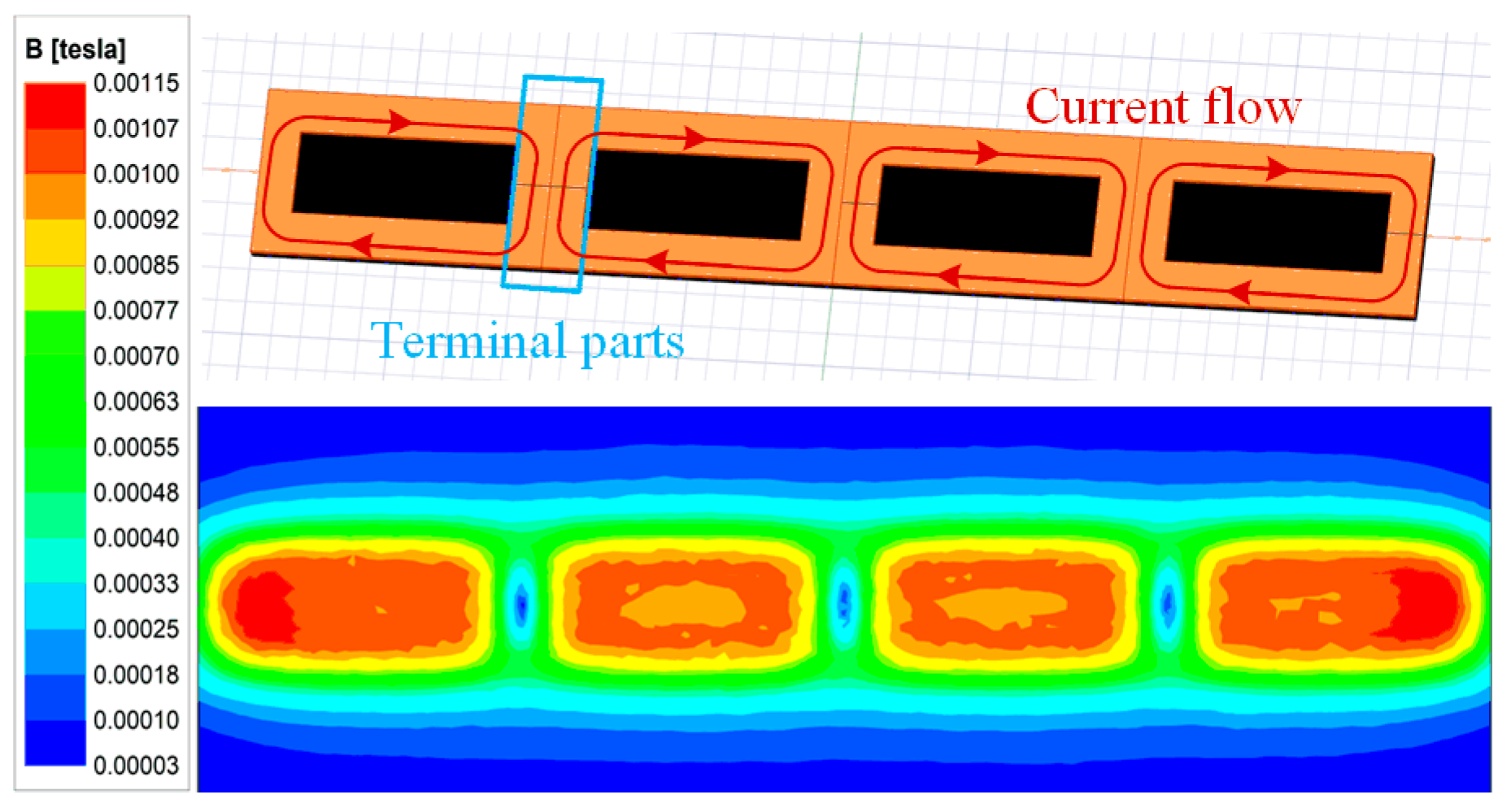
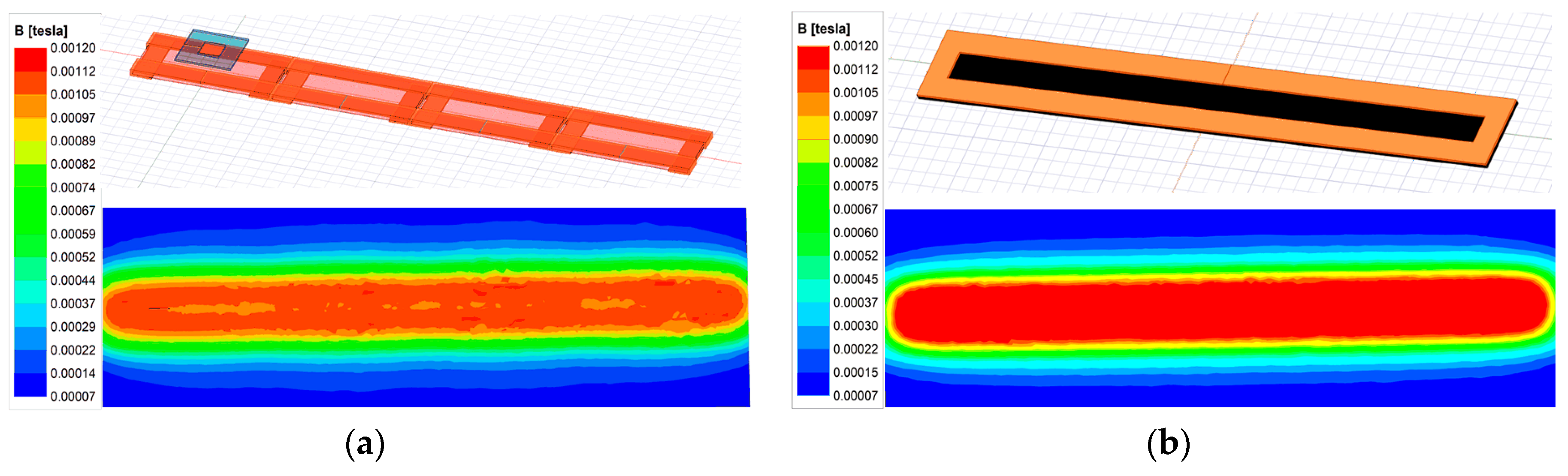
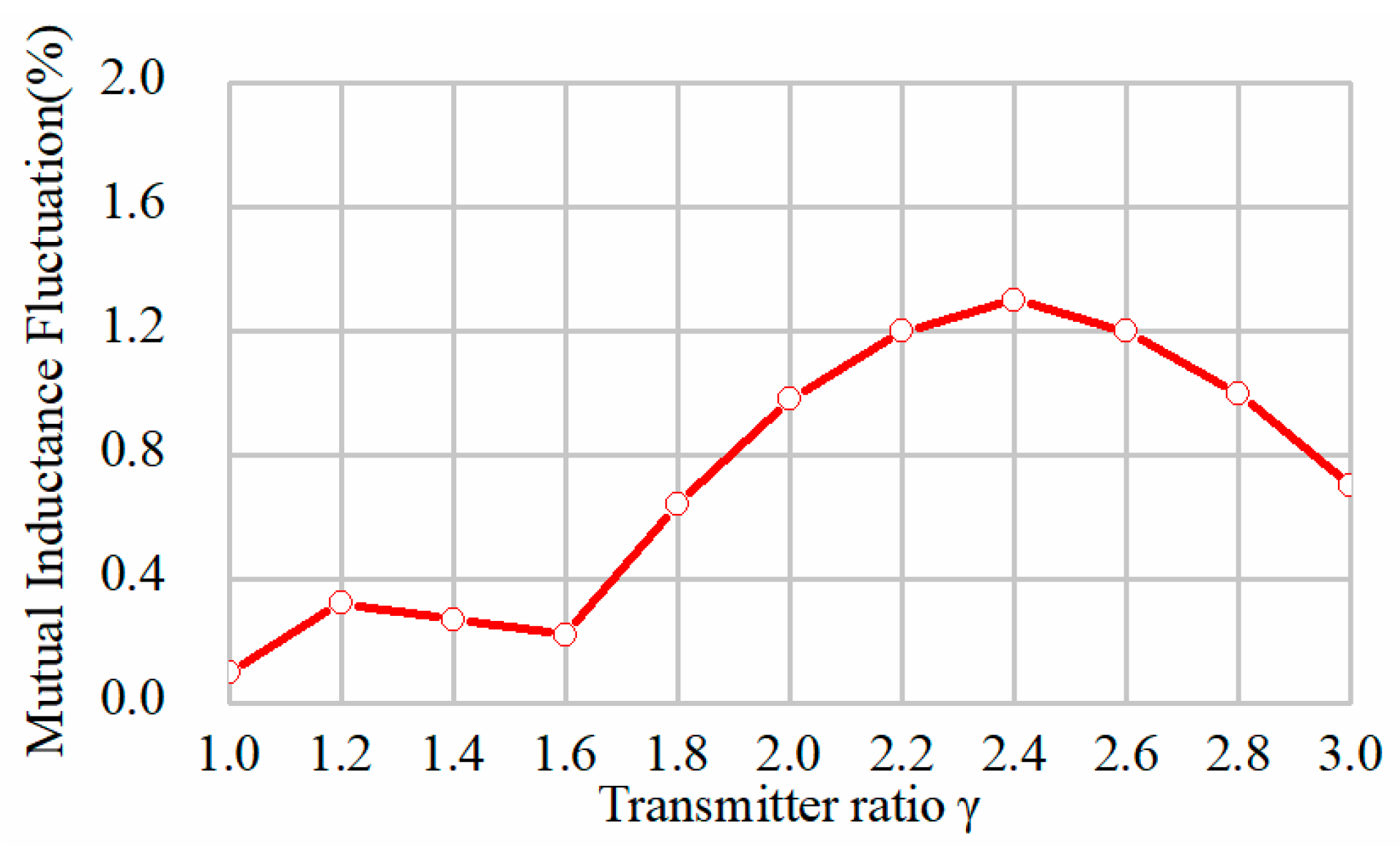
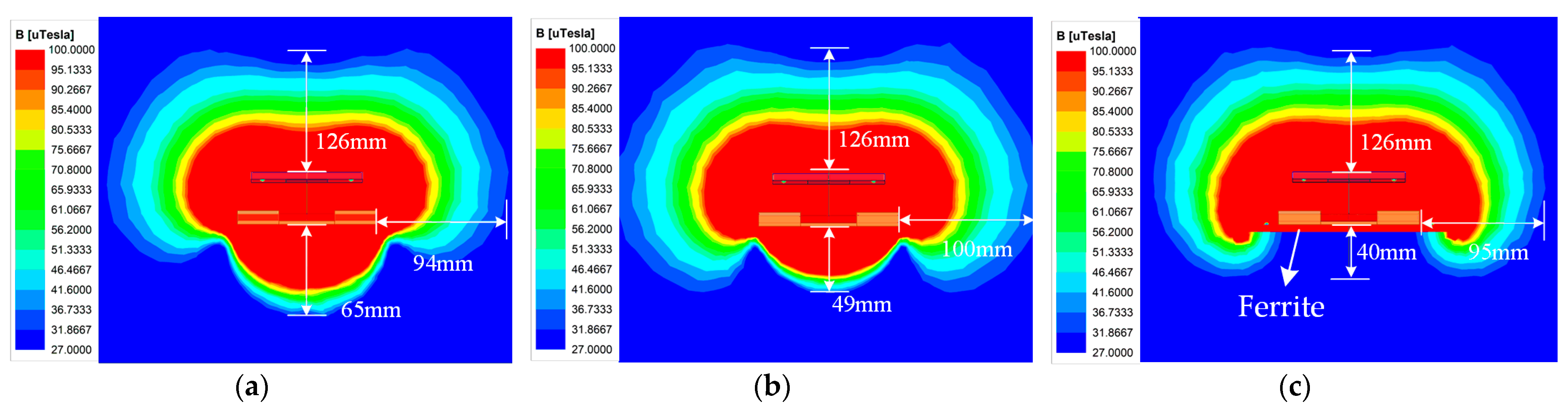
2.4. Magnetic Field Suppression Method
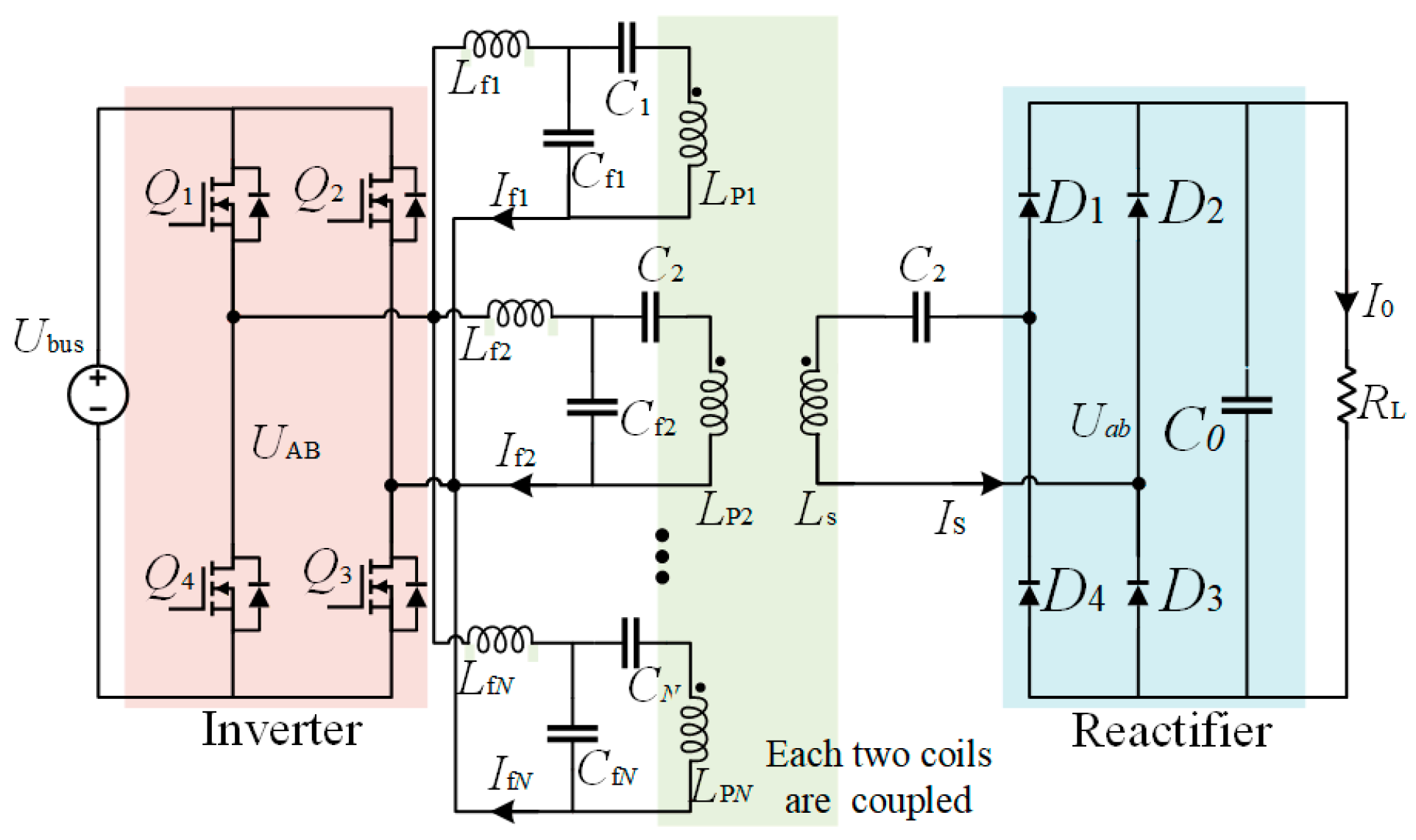
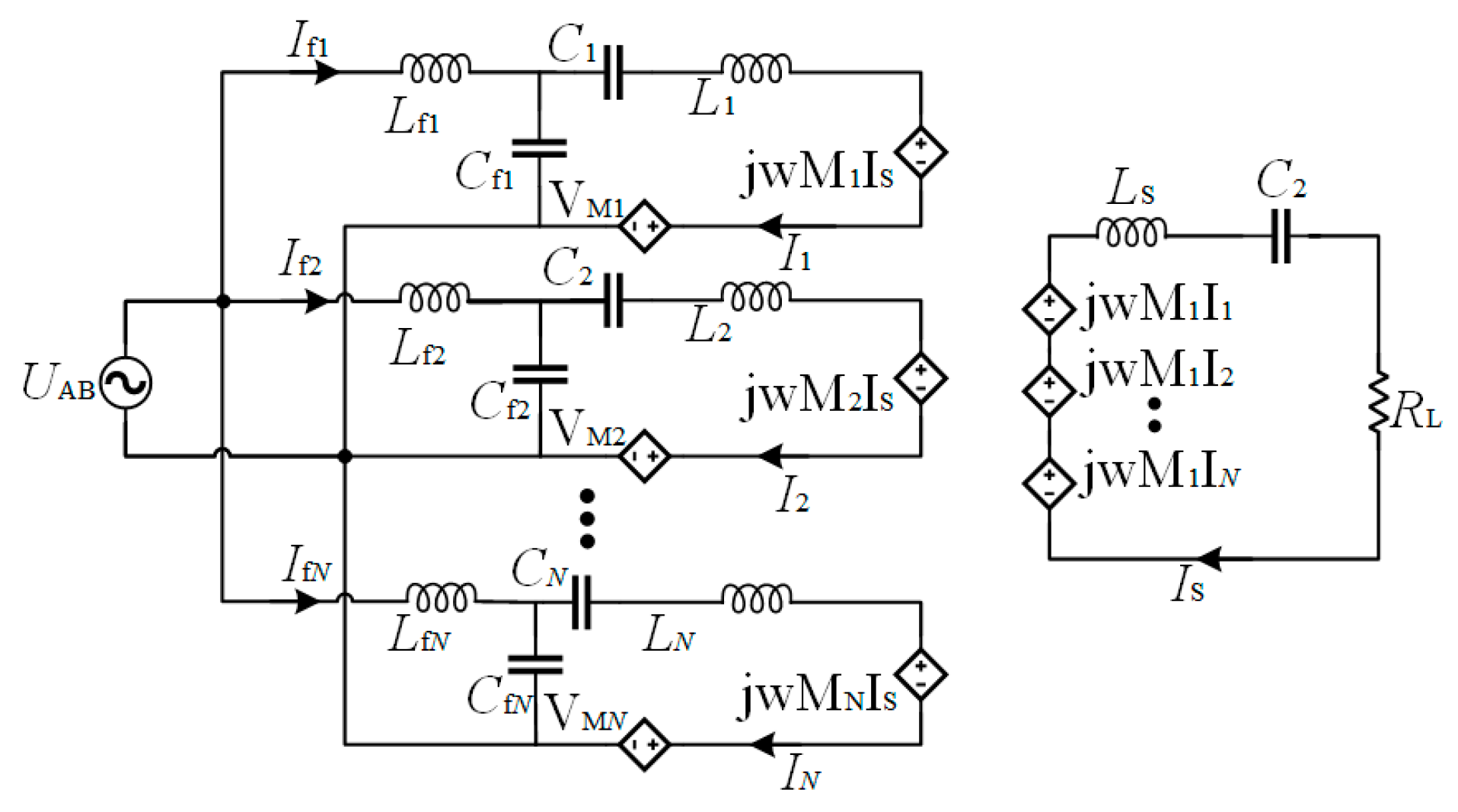
3. LCC-S Compensation Circuit Design
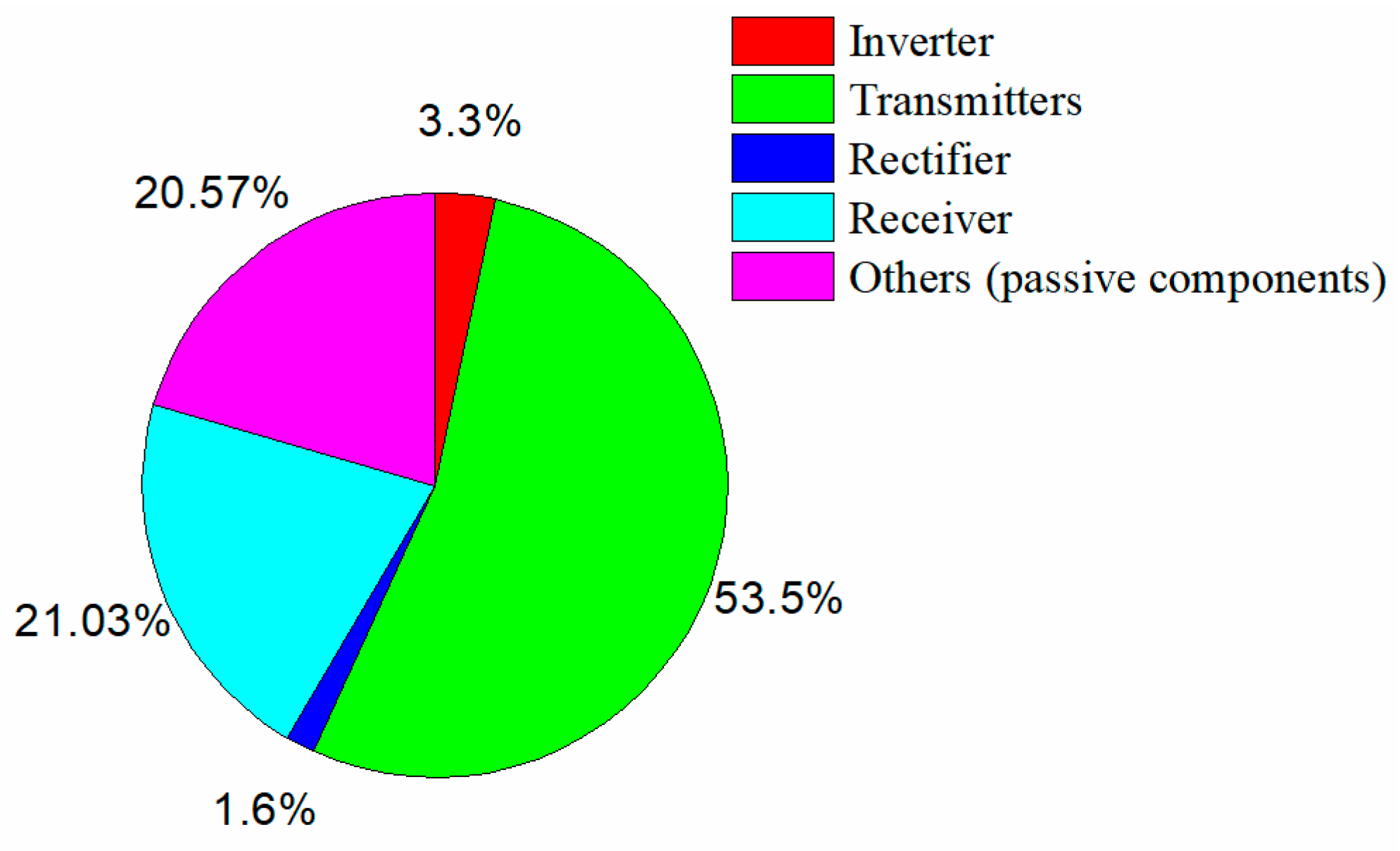
4. Experiment Setup and Validation
4.1. Prototype Setup
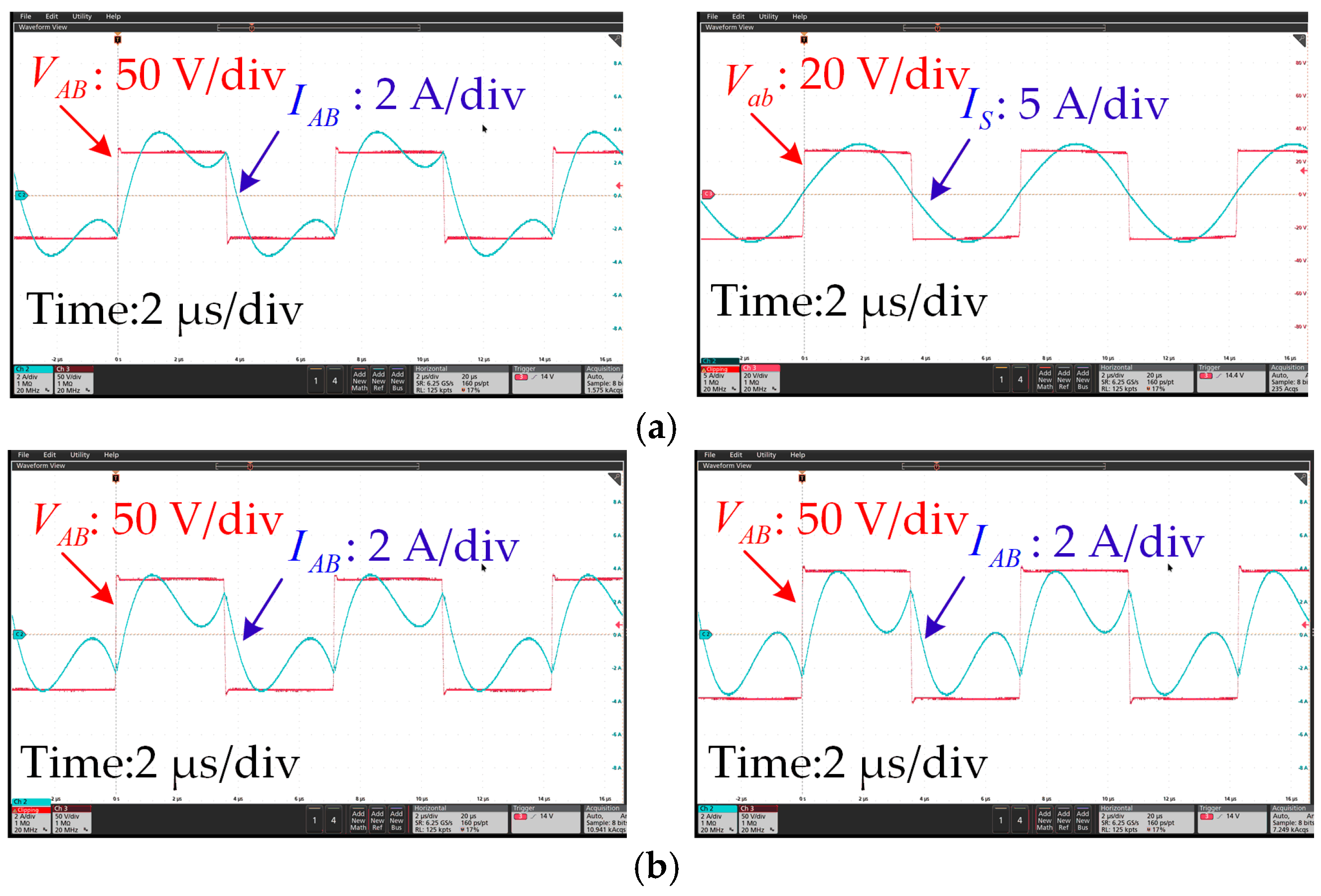
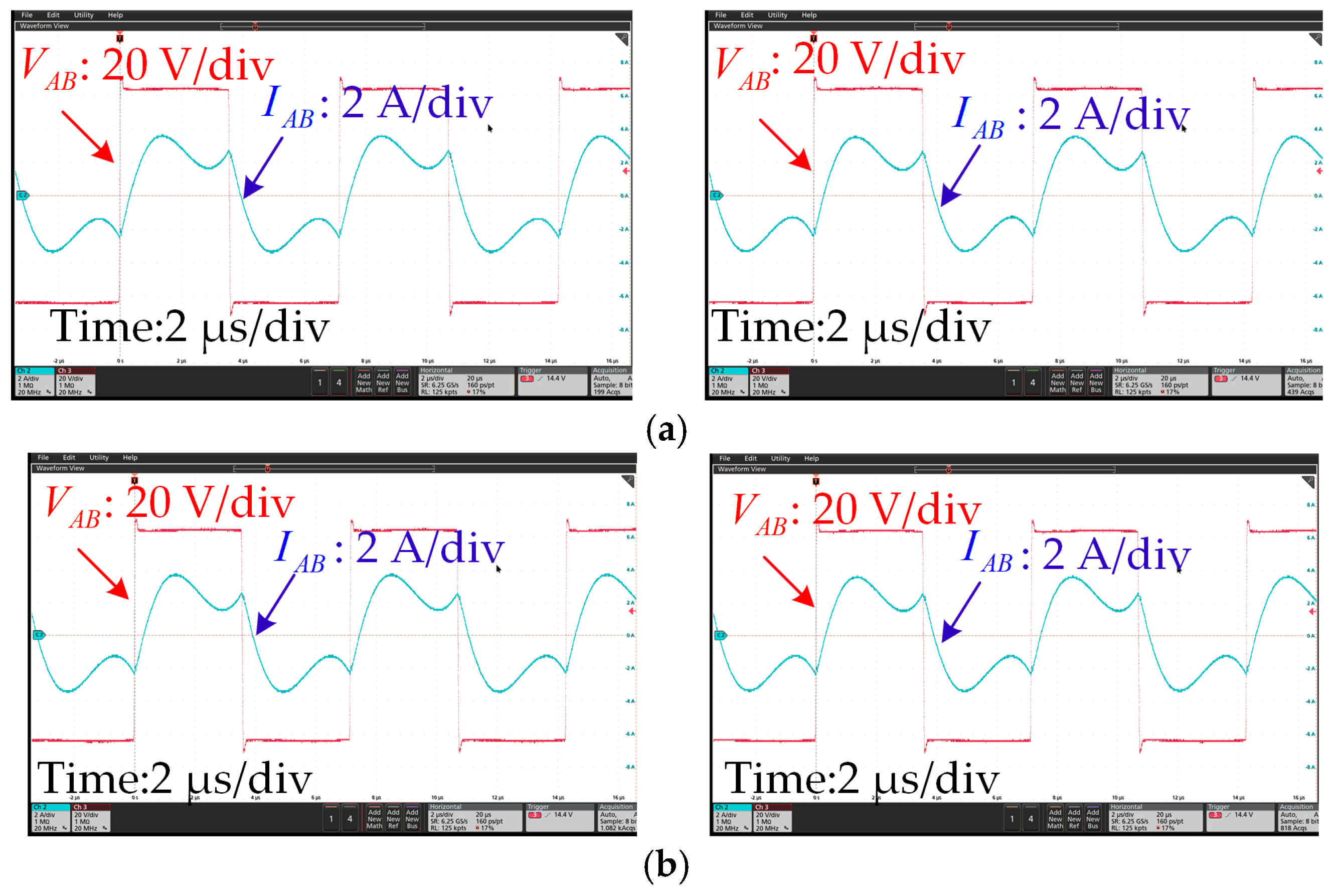
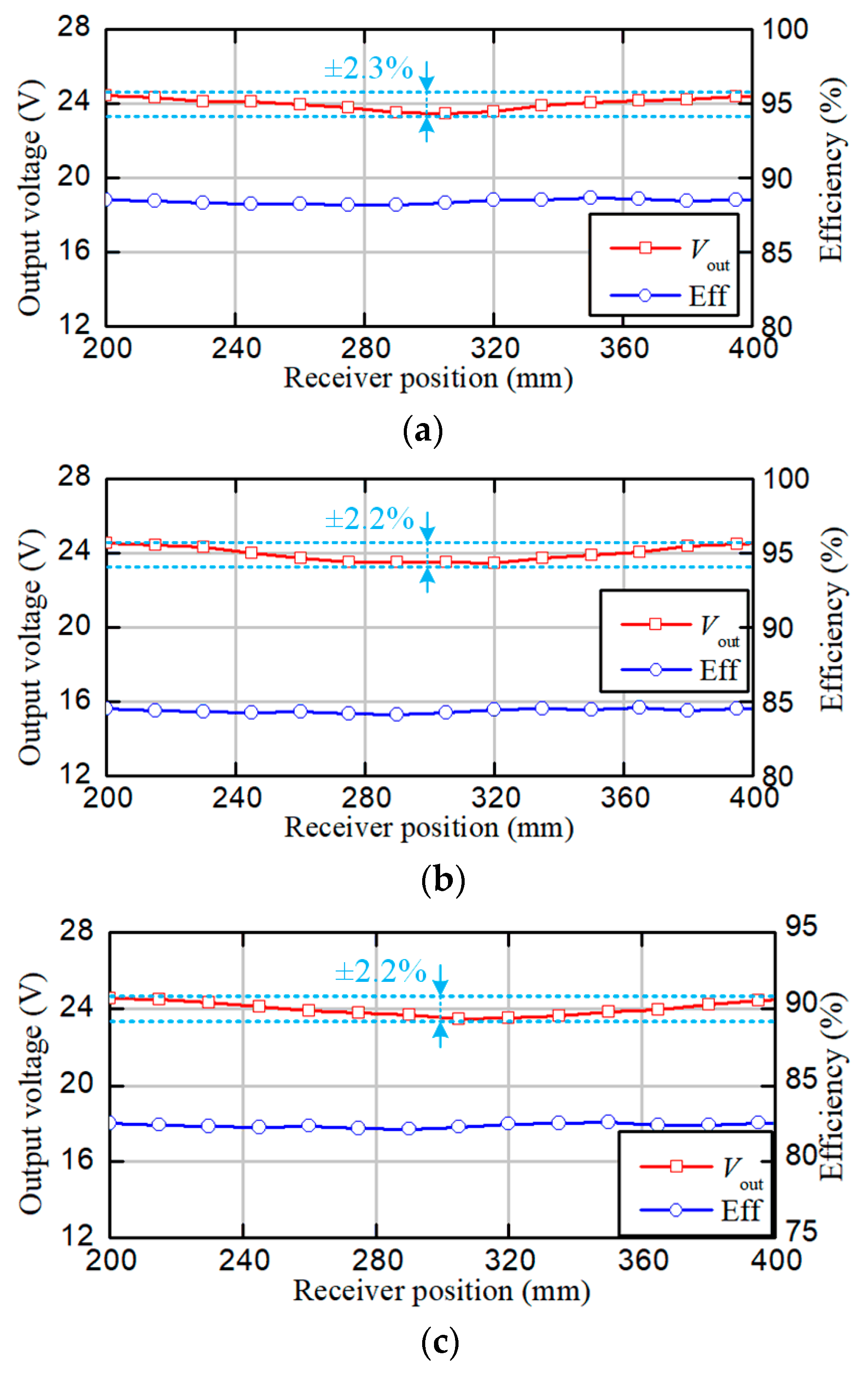
4.2. Experimental Results
4.3. Comparison with Previous Works
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cannon, B.L.; Hoburg, J.F.; Stancil, D.D.; Goldstein, S.C. Magnetic resonant coupling as a potential means for wireless power transfer to multiple small receivers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.Y.R.; Zhong, W.; Lee, C.K. A critical review of recent progress in mid-range wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4500–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, J.; Lu, F. Design and Implementation of High-Misalignment Tolerance WPT System for Underwater Vehicles Based on a Variable Inductor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 11726–11737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madawala, U.K.; Thrimawithana, D.J. A bidirectional inductive power interface for electric vehicles in V2G systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4789–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Modern trends in inductive power transfer for transportation applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.C.; Buja, G.; Choi, S.Y.; Rim, C.T. Modern advances in wireless power transfer systems for roadway powered electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6533–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, J.P.C.; Overboom, T.T.; Jansen, J.J.; Lomonova, E.A. Comparison of position-independent contactless energy transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, A.; Costanzo, A.; Aldhaher, S.; Mitcheson, P.T. Load and position-independent moving MHz WPT system based on GaN-distributed current sources. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 5367–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakluea, C.; Worapishet, A.; Chaimool, S.; Zhao, Y. True nulls-free magnetoinductive waveguides using alternate coupling polarities for batteryless dynamic wireless power transfer applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 8835–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.W.; van Lierop, C.M.M.; Lomonova, E.A.; Vandenput, A.J.A. Magnetically levitated planar actuator with moving magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appunn, R.; Riemer, B.; Hameyer, K. Combination of a contactless power supply with an electromagnetic guiding for a vertical transportation system. Proc. Int. Symp. Linear Drives Ind. Appl. 2013, 23, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.zongweitech.com/zh-CN (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Wu, H.H.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T.; Robertson, D.T. A series-tuned inductive-power-transfer pickup with a controllable ac-voltage output. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Shin, S.; Kim, Y.; Ahn, S.; Lee, S.; Jung, G.; Jeon, S.; Cho, D. Design and implementation of shaped magnetic-resonance-based wireless power transfer system for roadway-powered moving electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, V.; Bauer, P. Distributed IPT systems for dynamic powering misalignment analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6013–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Gu, B.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Rim, C.T. Advances in wireless power transfer systems for roadway-powered electric vehicles. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M. Demonstrating dynamic wireless charging of an electric vehicle: The benefit of electrochemical capacitor smoothing. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2014, 1, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Jiang, J.; Cui, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, C.; Chan, C.C. Research on bipolar nonsalient pole transmitter for high-power EV dynamic wireless power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; He, Z.; Li, W.; Mai, R. Uniform power IPT system with three-phase transmitter and bipolar receiver for dynamic charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2013–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, Z. An output power fluctuation suppression method of DWPT systems based on dual-receiver coils and voltage doubler rectifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 10167–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A stable dynamic electric vehicle wireless charging system based on triple decoupling receiving coils and a novel triple-diode rectifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 12011–12018. [Google Scholar]
- Onar, O.C.; Miller, J.M.; Campbell, S.; Coomer, C.; White, C.; Seiber, L. A novel wireless power transfer for in-motion EV/PHEV charging. In Proceedings of the 2013 Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013; pp. 3073–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.M.; Jones, P.T.; Li, J.; Onar, O.C. ORNL experience and challenges facing dynamic wireless power charging of EV’s. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2015, 15, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, H.; Hofmann, H.; Mi, C.C. A dynamic charging system with reduced output power pulsation for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6580–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, F.; Mai, R. A new coil structure and its optimization design with constant output voltage and constant output current for electric vehicle dynamic wireless charging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 5244–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Tang, C.; Long, H.; Lv, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Power fluctuation suppression method for EV dynamic wireless charging system based on integrated magnetic coupler. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; He, X.; Yang, H.; Luo, Y.; He, Z. A magnetic field concentration enchanced I-shaped transmitter for DWPT system to achieve low power fluctuation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, A.; Neath, M.; Beh, H.Z.; Covic, G.A. A dynamic EV charging system for slow moving traffic applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 3, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Symbol | Explanation | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| lp | Transmitter length | ls | Receiver length |
| wp | Transmitter width | ws | Receiver width |
| hc | Coil thickness | hf | Ferrite thickness |
| hm | Air gap distance | lm | Receiver position |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| lp | 200 mm | ls | 80 mm |
| wp | 100 mm | ws | 80 mm |
| hc | 2.5 mm | hf | 5 mm |
| hm | 20–30 mm |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vdc | 60–100 V | Vout | 24 V |
| fs | 140 kHz | RL | 5 Ω |
| Lf1 | 20 μH | Cf1 | 64.6 nF |
| Lf2 | 20 μH | Cf2 | 64.6 nF |
| Lp1 | 59.84 μH | C1 | 36.8 nF |
| Lp2 | 60.04 μH | C2 | 36.8 nF |
| kp1p2 | −0.08 | LS | 36 μH |
| ktotal | 0.1–0.18 | Cs | 36 nF |
| References | Coupler Structure | Air Gap | Restrictions for Coupler Design | Output Stability | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This article | Tx: reversely bent Q coil; Rx: Q coil | 20–30 mm | no specific restrictions | 24 V ± 2.3% | 88.5% |
| [21] | Tx: Q coils; Rx: triple Q coils | 50 mm | matched Tx and Rx parameter design | 1000 W ± 3.49% | 93.07% |
| [24] | Tx: Q coils; Rx: Q coil | 150 mm | matched Tx and Rx parameter design | 1400 W ± 2.9% | 89.78% |
| [25] | Tx: DD + Q coils; Rx: DDQ coil | 100 mm | matched Tx and Rx parameter design | 96 V ± 2% | 90.374% |
| [27] | Tx: I-shaped coils; Rx: Q coil | 25 mm | matched Tx and Rx parameter design | 1100 W ± 1.18% | 87.98% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhu, C.; Ji, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X. Reverse-Bent Modular Coil Structure with Enhanced Output Stability in DWPT for Arbitrary Linear Transport Systems. Sensors 2024, 24, 7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24227171
Li J, Zhu C, Ji J, Ma J, Zhang X. Reverse-Bent Modular Coil Structure with Enhanced Output Stability in DWPT for Arbitrary Linear Transport Systems. Sensors. 2024; 24(22):7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24227171
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jia, Chong Zhu, Junyi Ji, Jianquan Ma, and Xi Zhang. 2024. "Reverse-Bent Modular Coil Structure with Enhanced Output Stability in DWPT for Arbitrary Linear Transport Systems" Sensors 24, no. 22: 7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24227171
APA StyleLi, J., Zhu, C., Ji, J., Ma, J., & Zhang, X. (2024). Reverse-Bent Modular Coil Structure with Enhanced Output Stability in DWPT for Arbitrary Linear Transport Systems. Sensors, 24(22), 7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24227171








