Velocity Estimation of Passive Target Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning Cross-Spectrum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sparse Bayesian Learning Mutual Spectrum Velocimetry
2.1. Modeling of Cross-Correlating Sound Fields
2.2. Joint Multi-Frequency Velocity Estimation Method
2.3. Sparse Bayesian Learning Speed Estimation Model
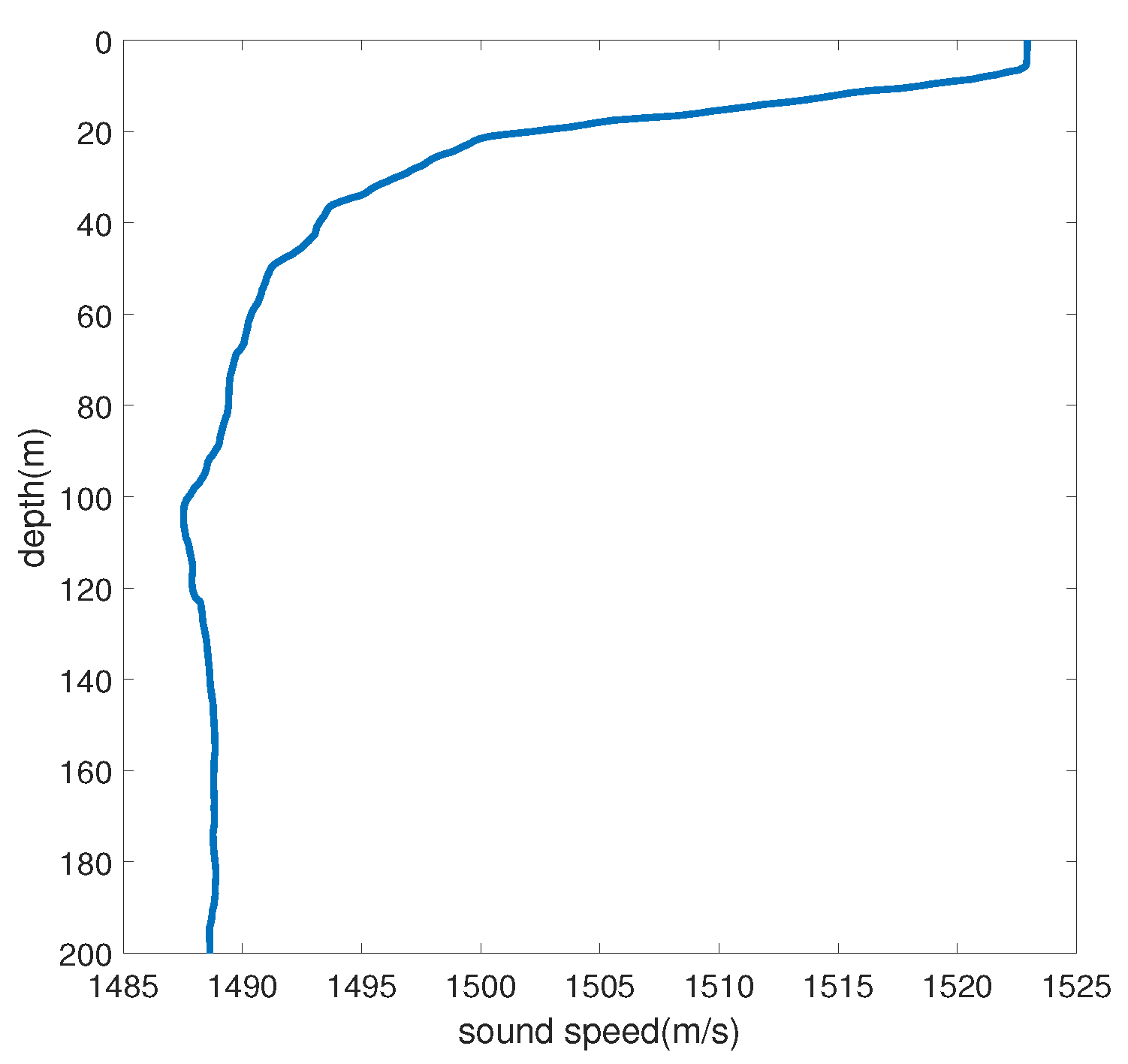
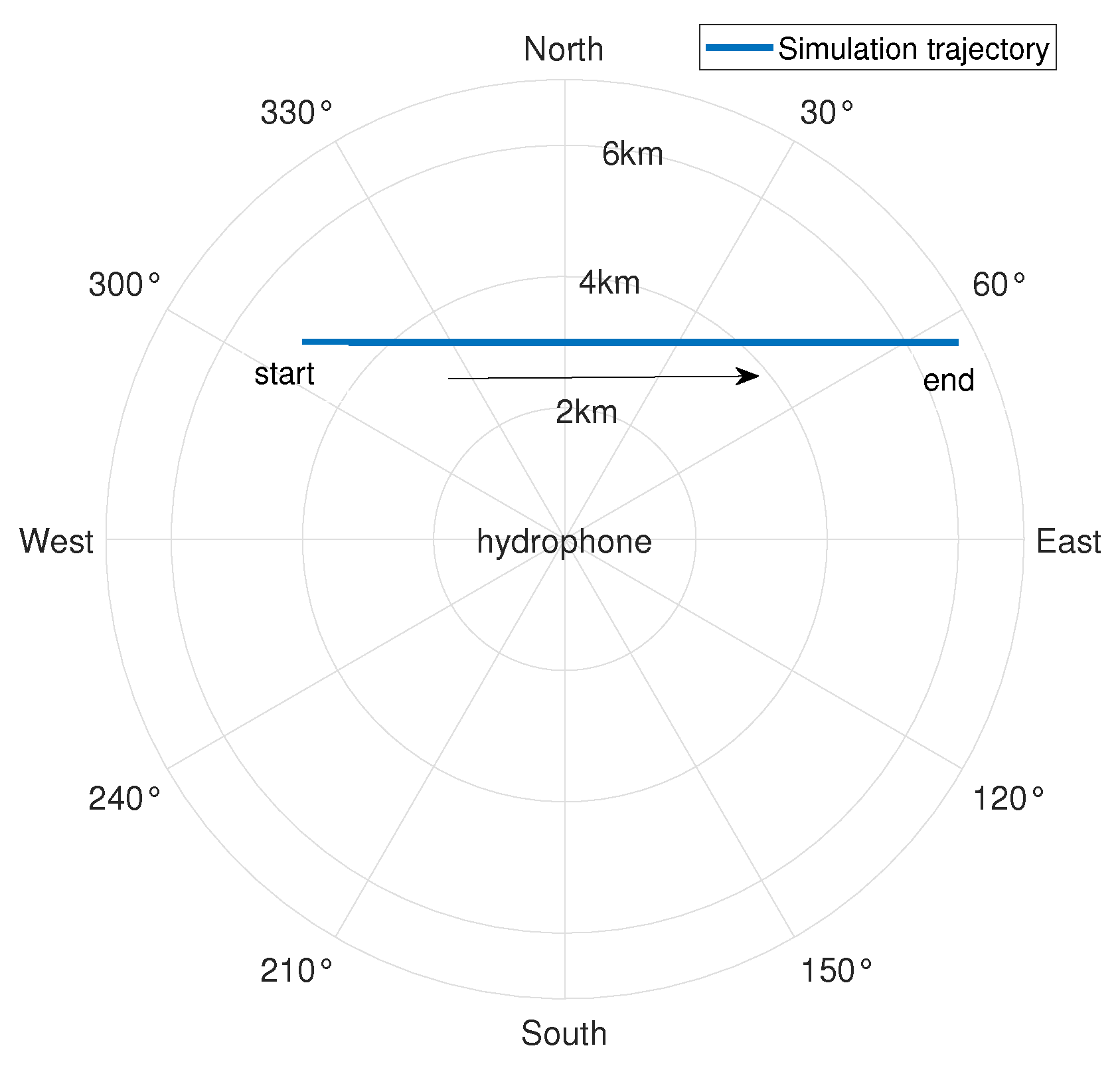
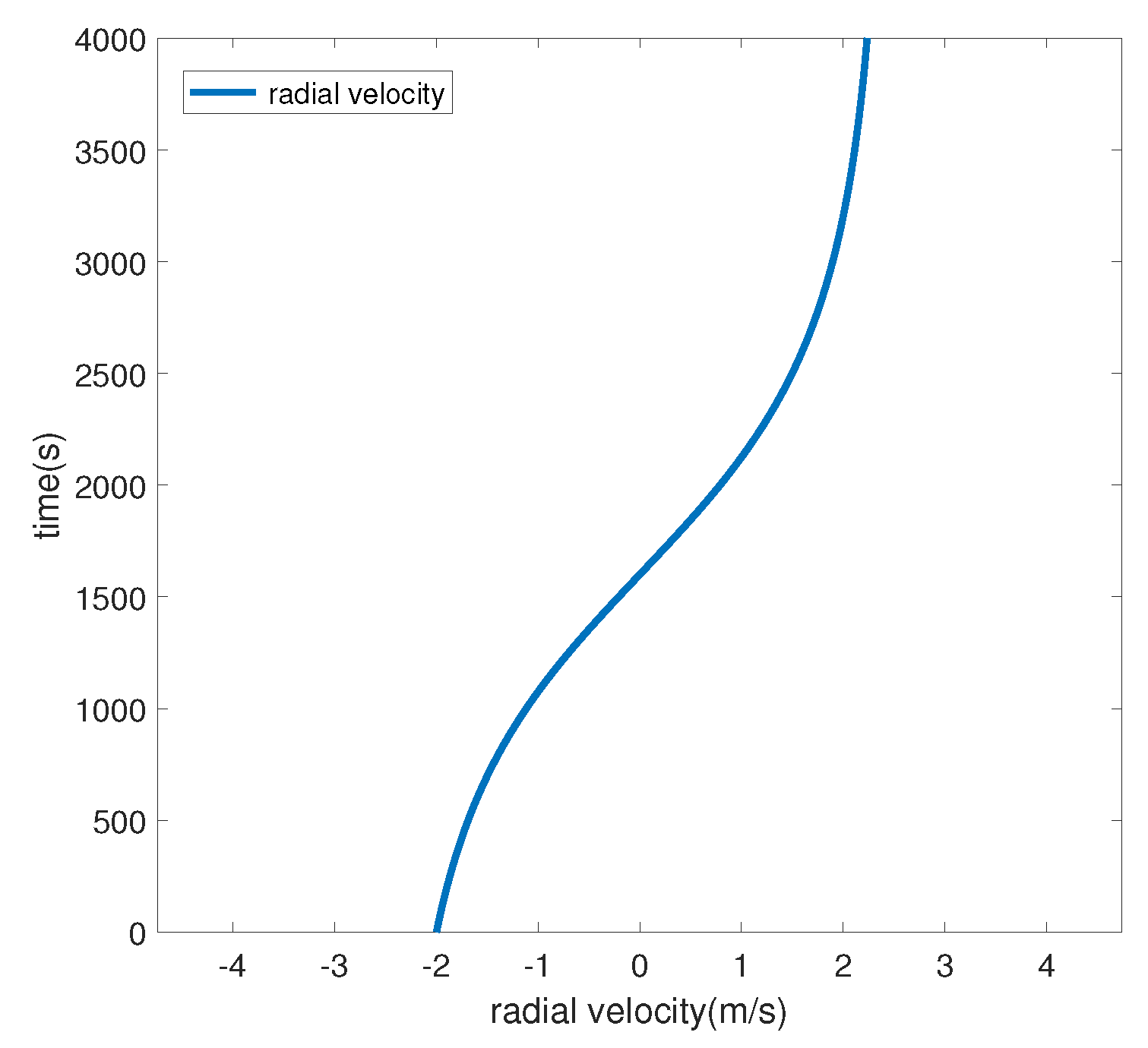
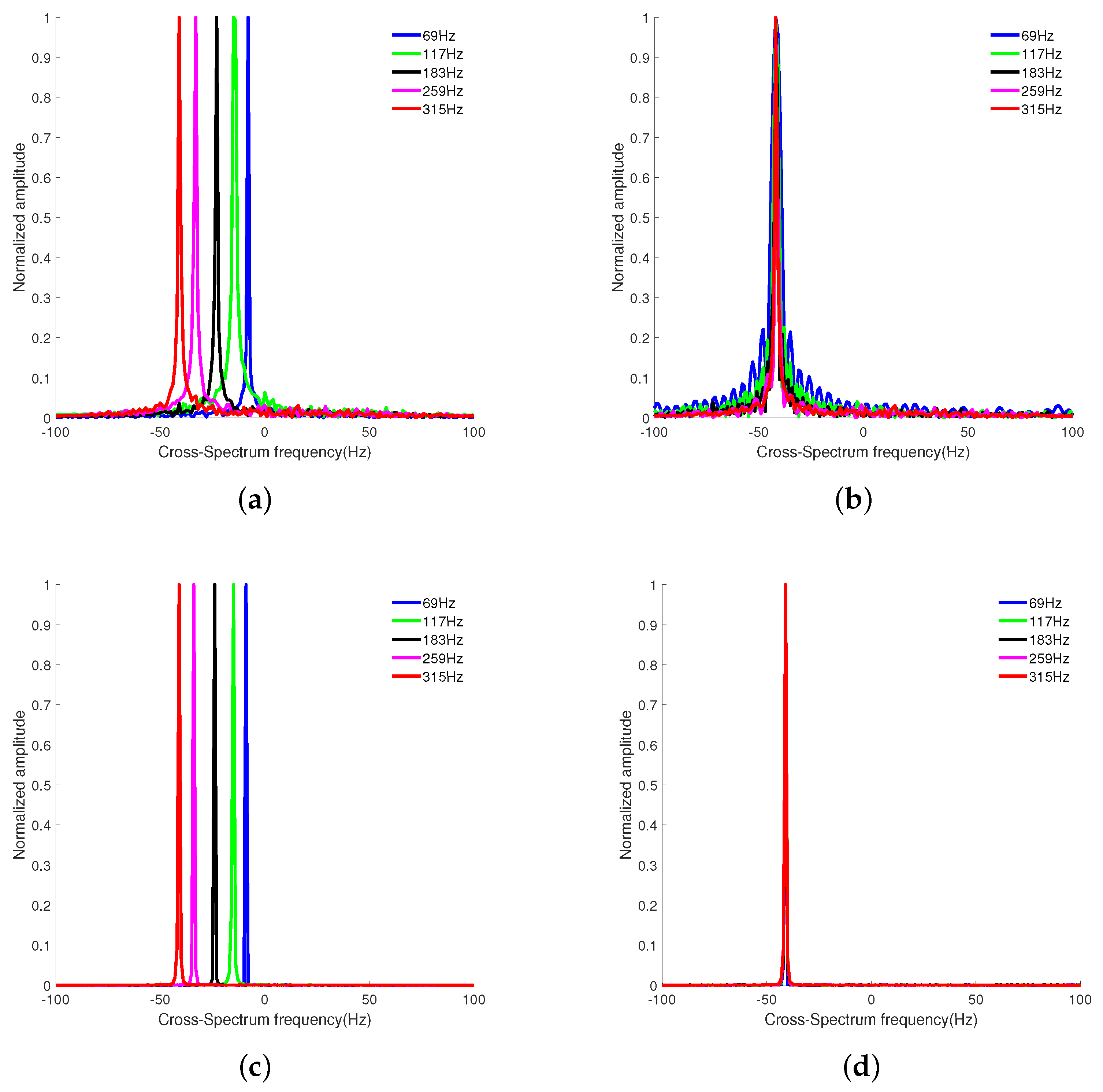
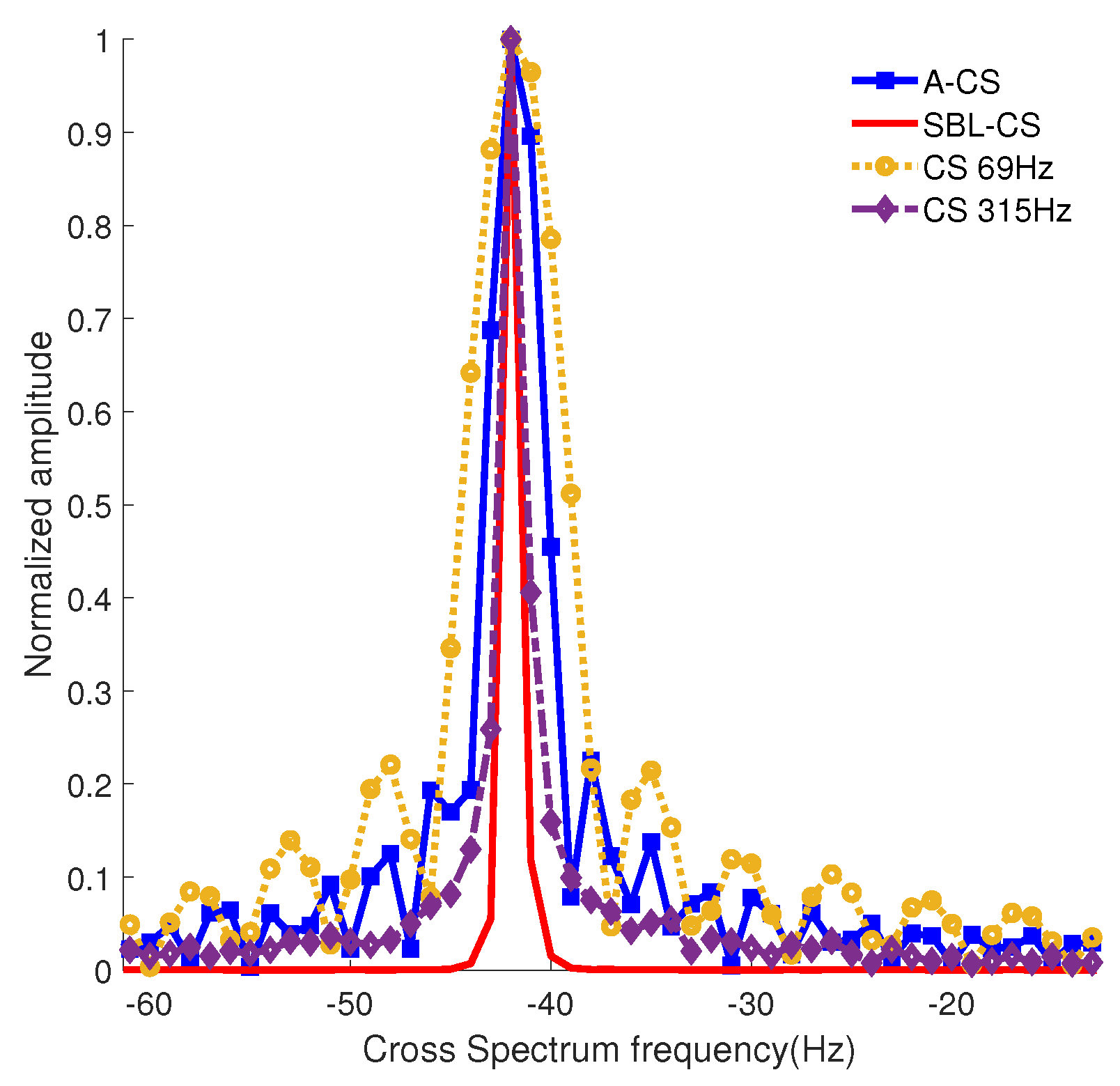
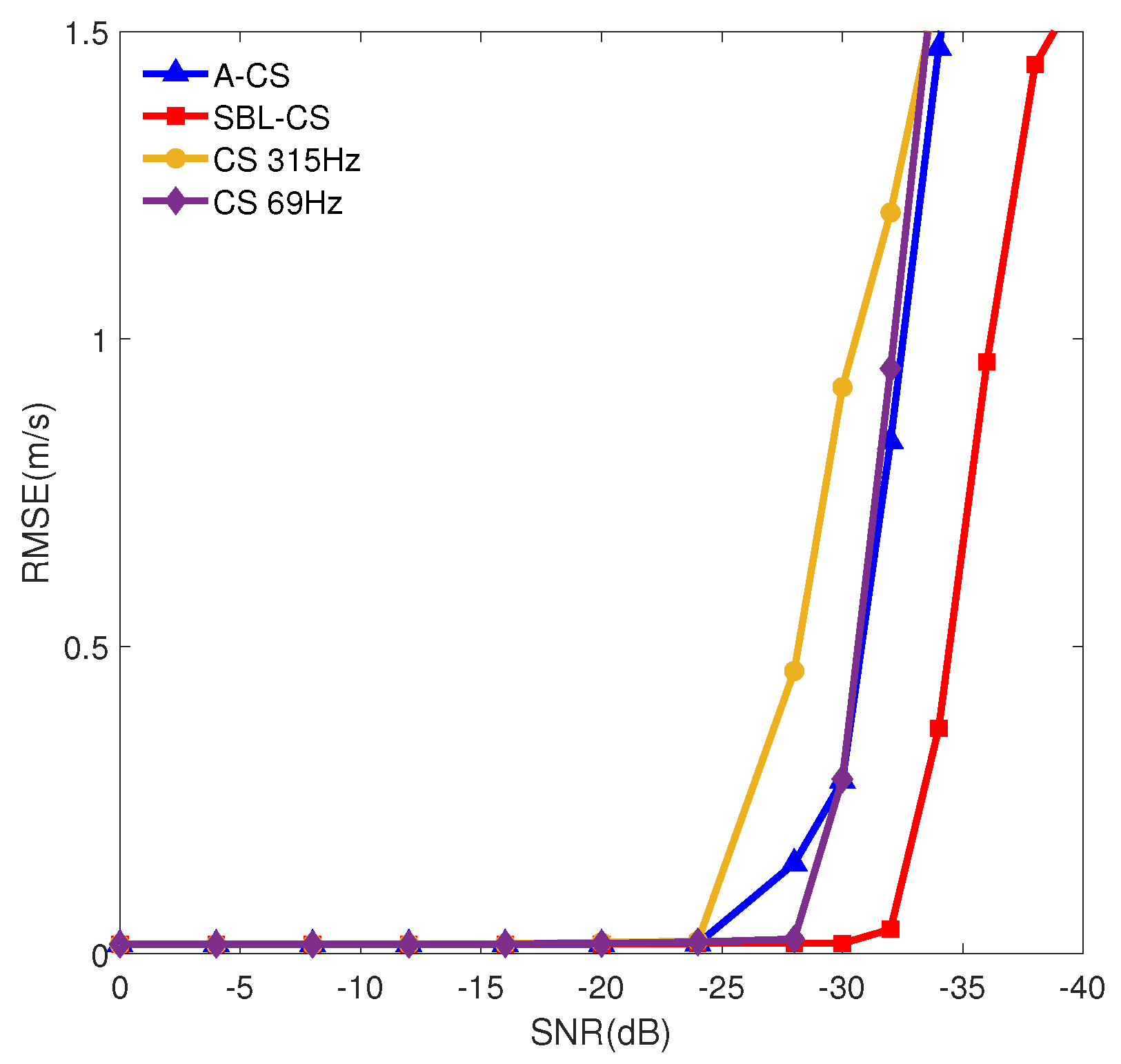
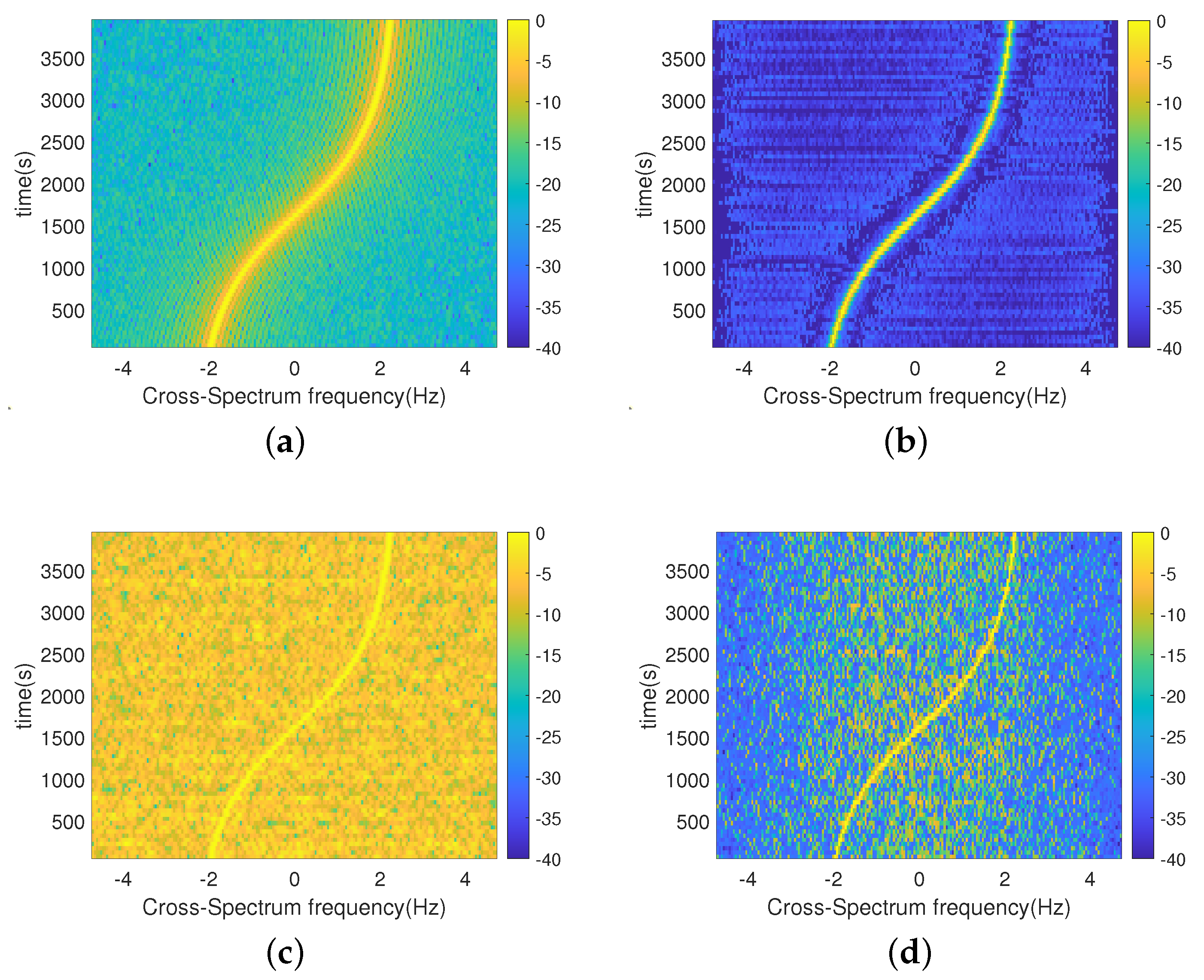
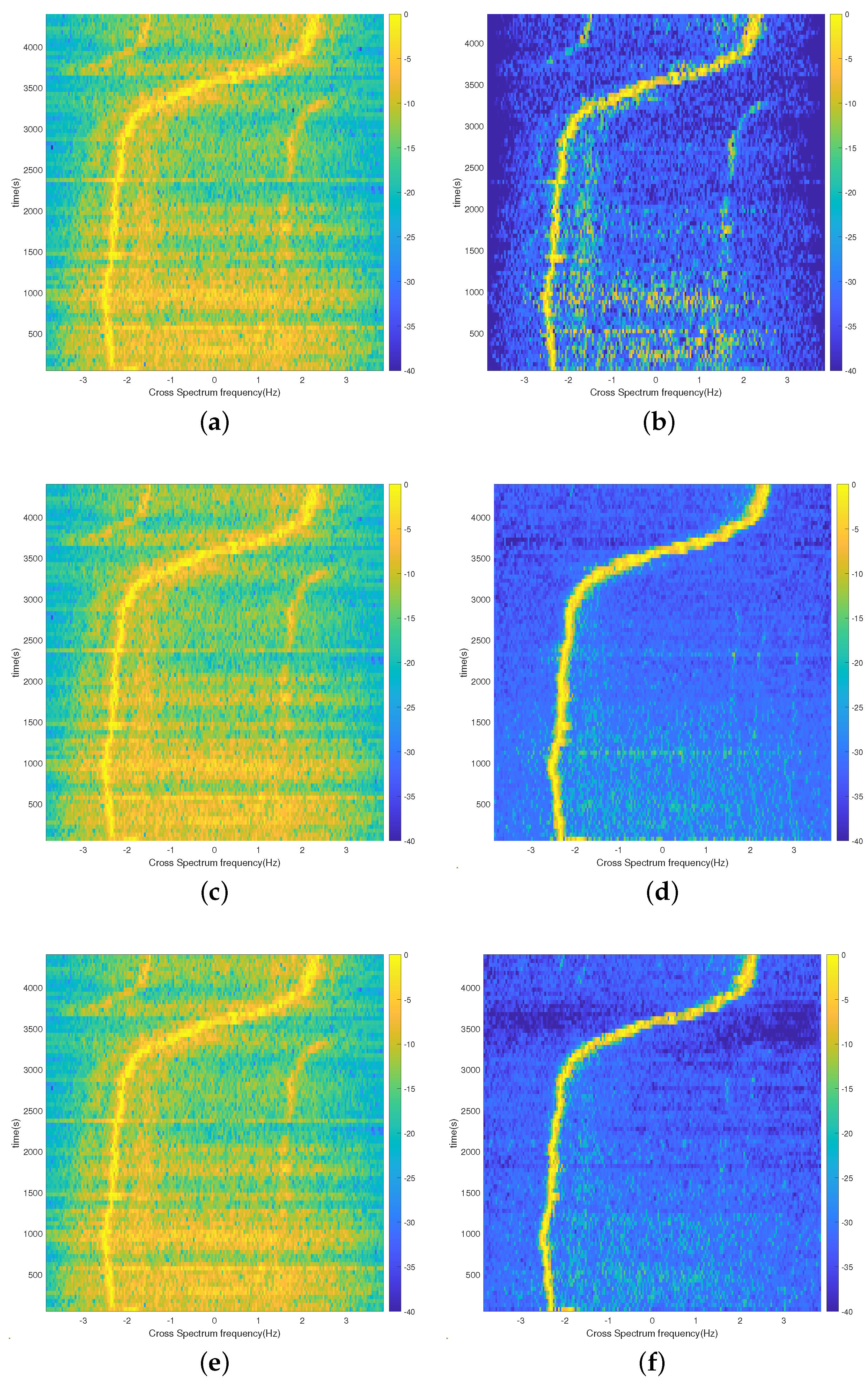
3. Simulation Analysis and Test Dataset Processing
3.1. Simulation Analysis
3.2. Experimental Dataset Processing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Da, L.; Wang, C.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuo, J. Passive ranging of a moving target in the direct-arrival zone in deep sea using a single vector hydrophone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 2426–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Liu, F.; Shao, Y. Radial source velocity estimation using multiple line spectrum signals based on compressive sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Hangzhou, China, 18–20 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, N.; Qi, B.; Li, J. AUV instantaneous velocity estimation method based on azimuth and Doppler shift. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 220, 109977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouseff, D.; Spindel, R.C. Modeling the Waveguide Invariant as a Distribution. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: Long Island, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizell, R.G.; Wales, S.C. Source localization in range and depth in an Arctic environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 78, S57–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, T.; Su, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, C.; Ma, L. High-resolution passive depth estimation for broadband sources in deep water based on orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 208, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, Y.; Bonnel, J. Passive estimation of the waveguide invariant per pair of modes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, EL230–EL236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotonarivo, S.T.; Kuperman, W.A. Model-independent range localization of a moving source in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M. Research on Passive Ranging Technology of Moving Ship Based on Vertical Hydrophone Array. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wu, F.; Hou, B. The Characteristic of Cross-Correlated Pressure Field in a Wedged Seafloor Environment. In Proceedings of the OCEANS Conference, Kobe, Japan, 28–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.D.; Li, H.; Duan, R.; Yang, Q.L. Analysis on the Characteristic of Cross-Correlated Field and Its Potential Application on Source Localization in Deep Water. J. Comput. Acoust. 2017, 25, 1750001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Song, P.; Hui, J.; Li, J.; Tang, K. Passive estimation of target velocity based on cross-spectrum histogram. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 151, 2967–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.F.; Zhao, A.B.; Hui, J.; Zeng, C.G.; Wang, K.R. Radial source velocity estimation based on cross-spectrum equalization accumulation compensation in shallow water. JASA Express Lett. 2023, 3, 056002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.; Zhang, Z. Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1993, 41, 3397–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Song, A.H.; Bilgic, B.; Ba, D. Covariance-Free Sparse Bayesian Learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 3818–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M.E. Sparse Bayesian Learning and the Relevance Vector Machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2001, 1, 211–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipf, D.P.; Rao, B.D. An Empirical Bayesian Strategy for Solving the Simultaneous Sparse Approximation Problem. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 3704–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Duarte, M.F.; Janaswamy, R. Cramér–Rao Bounds for DoA Estimation of Sparse Bayesian Learning with the Laplace Prior. Sensors 2023, 23, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Li, C.; Qiu, L.; Shen, T.; Hao, Y. State-updating-based DOA estimation using sparse Bayesian learning. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 192, 108719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. Real-Valued Sparse Bayesian Learning for Off-Grid Direction-of-Arrival (DOA) Estimation in Ocean Acoustics. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 46, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Hong, W.; Lee, K.; Choo, Y. Passive Sonar Target Identification Using Multiple-Measurement Sparse Bayesian Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X. Non-Circular Signal DOA Estimation with Nested Array via Off-Grid Sparse Bayesian Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B.; Schmidt, H. Computational Ocean Acoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- D’Spain, G.L.; Kuperman, W.A. Application of waveguide invariants to analysis of spectrograms from shallow water environments that vary in range and azimuth. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 2454–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, C.; Niu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Passive synthetic aperture for direction-of-arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian learning. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhou, S.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Du, S.; Dun, J.; Zhou, L. Passive source localization based on multipath arrival angles with a vertical line array using sparse Bayesian learning. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Hao, Y.; Zou, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wan, G. Sparse Bayesian learning-based spatial spectrum estimation for mobile sonar platforms during turning. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 198, 108937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Algorithm | Frequency (Hz) | RMSE (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| CS | 385 | 0.5217 |
| A-CS | 127, 145, 232, 280, 385 | 0.518 |
| 109, 127, 145, 164, 198, 232, 280, 335, 385 | 0.518 | |
| SBL-CS | 385 | 0.4549 |
| 127, 145, 232, 280, 385 | 0.3819 | |
| 109, 127, 145, 164, 198, 232, 280, 335, 385 | 0.3545 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liang, G.; Shen, T.; Luo, Z. Velocity Estimation of Passive Target Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning Cross-Spectrum. Sensors 2024, 24, 6989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216989
Li X, Liang G, Shen T, Luo Z. Velocity Estimation of Passive Target Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning Cross-Spectrum. Sensors. 2024; 24(21):6989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216989
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xionghui, Guolong Liang, Tongsheng Shen, and Zailei Luo. 2024. "Velocity Estimation of Passive Target Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning Cross-Spectrum" Sensors 24, no. 21: 6989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216989
APA StyleLi, X., Liang, G., Shen, T., & Luo, Z. (2024). Velocity Estimation of Passive Target Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning Cross-Spectrum. Sensors, 24(21), 6989. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216989





