Light-Sheet Skew Ray-Based Microbubble Chemical Sensor for Pb2+ Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
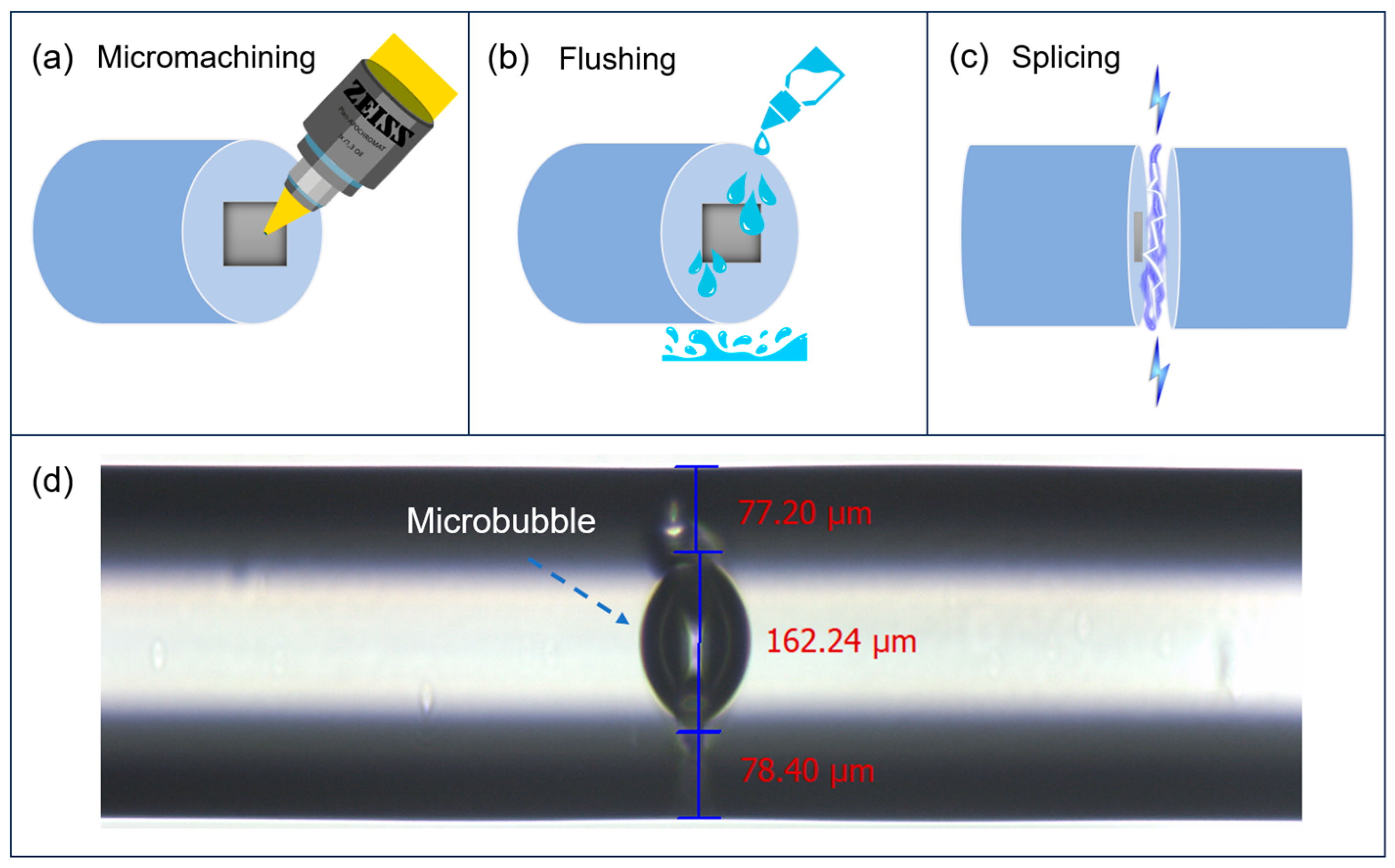
Fiber Structure Fabrication
3. Results
3.1. Principles of Skew Rays
3.2. Experiment Setup
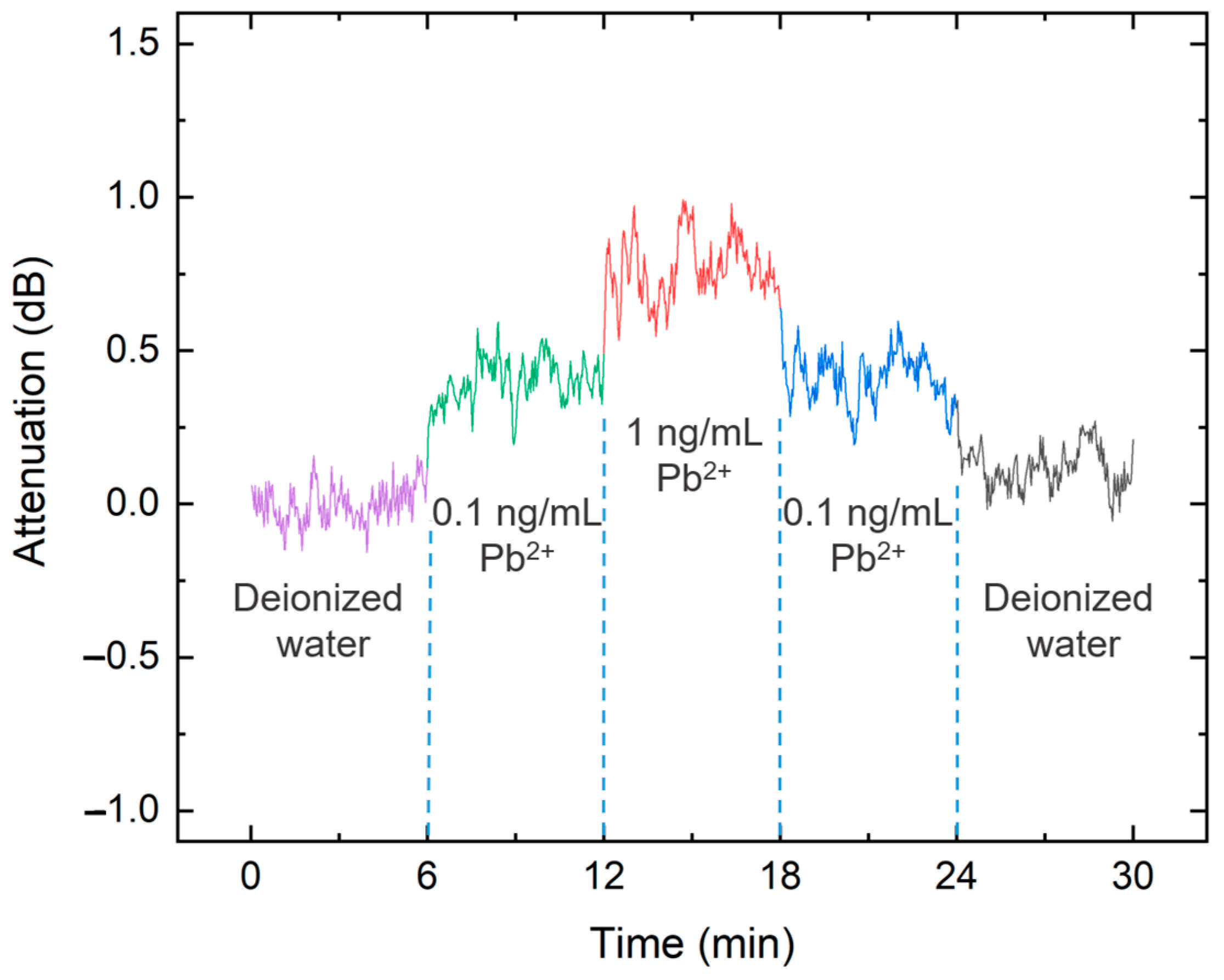
3.3. Sensitivity/Detection Limit Characterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Q. An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade. Water Res. 2018, 147, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.F.; Cinotti, L. Lead-cooled Fast Reactors (LFRs). In Handbook of Generation IV Nuclear Reactors, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2023; pp. 195–230. [Google Scholar]
- Mielcarek, K.; Nowakowski, P.; Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Gromkowska-Kępka, K.J.; Soroczyńska, J.; Markiewicz-Żukowska, R.; Naliwajko, S.K.; Grabia, M.; Bielecka, J.; Żmudzińska, A.; et al. Arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury content and health risk assessment of consuming freshwater fish with elements of chemometric analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bua, D.G.; Annuario, G.; Albergamo, A.; Cicero, N.; Dugo, G. Heavy metals in aromatic spices by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2016, 9, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, J.-F. Surface Plasmon Resonance Clinical Biosensors for Medical Diagnostics. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, X.; Hai, X.; Bi, S.; Zhang, X. Recent Progress in Sensor Arrays: From Construction Principles of Sensing Elements to Applications. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 994–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, R.; Bhalla, N.; Chu, K.; Söderström, B.; Shen, A.Q. Nanoplasmonics for Real-Time and Label-Free Monitoring of Microbial Biofilm Formation. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liao, C.; He, J.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Strain-based tunable optical microresonator with an in-fiber rectangular air bubble. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 4077–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Liao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Miniature Fabry-Perot Interferometer Strain Sensor Based on an Elliptical Air Bubble. In Proceedings of the 2017 Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC) and Photonics Global Conference (PGC), Singapore, 31 July–4 August 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ruan, Y.; Jia, P.; Gui, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Liao, C.; Yin, G.; Wang, Y. Fabrication and characterization of an egg-shaped hollow fiber microbubble. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10323, 25th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 24–28 April 2017; Volume 1032322. [Google Scholar]
- Kelani, K.M.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Ramadan, N.K.; Elzanfaly, E.S.; Eid, S.M. Comparing silver and gold nanoislands’ surface plasmon resonance for bisacodyl and its metabolite quantification in human plasma. BMC Chem. 2024, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, Z.; Cunningham, D.; Bhalla, N. Refractive Index-Modulated LSPR Sensing in 20–120 nm Gold and Silver Nanoparticles: A Simulation Study. ECS Sens. Plus 2023, 2, 043402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziai, Y.; Rinoldi, C.; Nakielski, P.; De Sio, L.; Pierini, F. Smart plasmonic hydrogels based on gold and silver nanoparticles for biosensing application. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 24, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; François, A.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.Q.; Codemard, C.A.; Xu, H.; Monro, T.M.; Lancaster, D.G. Light-Sheet Skew-Ray Enhanced Pump-Absorption for Sensing. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Monro, T.M.; Liu, T.; Lancaster, D.G. Light-sheet skew ray-enhanced localized surface plasmon resonance-based chemical sensing. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhuang, T.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Khalid, M.; Shahnia, S.; Codemard, C.A.; Bai, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Light-sheet skew rays sensing platform based on microstructuring of coreless multimode fiber. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024, 44, 100656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messica, A.; Greenstein, A.; Katzir, A. Theory of fiber-optic, evanescent-wave spectroscopy and sensors. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Uh, M.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-K. Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor using nanopatterned gold particles on the surface of an optical fiber. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 280, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, K.M.; Hafner, J.H. Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3828–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.S.; Sharma, A.K.; Gupta, B.D. Influence of skew rays on the sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio of a fiber-optic surface-plasmon-resonance sensor: A theoretical study. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 4563–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herskowitz, G.; Kobrinski, H.; Levy, U. Optical Power Distribution in Multimode Fibers with Angular-Dependent Mode Coupling. J. Lightwave Technol. 1983, 1, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Boechat, A.A.P.; Jones, J.D.C. Beam delivery by large-core fibers: Effect of launching conditions on near-field output profile. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 5816–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cottenden, A.; Jones, N.B. A theoretical evaluation of fibre-optic evanescent wave absorption in spectroscopy and sensors. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2006, 44, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archenault, M.; Gagnaire, H.; Goure, J.P.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. A simple intrinsic optical fibre refractometer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 5, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bock, W.J.; Cusano, A. Insights into tunnelling rays: Outperforming guided rays in fiber-optic sensing device. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 7630–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Rao, B.T.; Srivastava, A.K.; Patel, H.S.; Satapathy, S.; Joshi, M.P.; Sahu, V.K.; Kukreja, L.M. Studies on interdependent optical properties of Rhodamine 6G dye and gold nanoparticles at different dilutions of aqueous solutions. J. Lumin. 2014, 155, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhu, H.; Bazuin, C.G.; Peng, W.; Masson, J.-F. Polymer-Templated Gold Nanoparticles on Optical Fibers for Enhanced-Sensitivity Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, B.S.; Biswas, R. Localized surface plasmon resonance based U-shaped optical fiber probe for the detection of Pb2+ in aqueous medium. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, S.P.; Toh, P.Y.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C.; Majetich, S.A.; Lim, J.J. Colloidal Stability and Magnetophoresis of Gold-Coated Iron Oxide Nanorods in Biological Media. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22561–22569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, K.; Mitsui, K. Optical fiber biosensor based on localized surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles. In Nanosensing: Materials and Devices; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5593. [Google Scholar]
- Perri, C.; Arcadio, F.; D’Agostino, G.; Cennamo, N.; Porto, G.; Zeni, L. Chemical and Biological Applications Based on Plasmonic Optical Fiber Sensors. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2021, 24, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoki, A.; Nishiyama, M.; Kumekawa, N.; Watanabe, K.; Yatabe, R.; Tahara, Y.; Onodera, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Sakurai, N. Lipid-coated hetero-core optical fiber sensor for wide-range chemical detection. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 169, 110045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.-S.; Shi, Y.-W. Optical Fiber Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Based on the Gold-Coated Hollow Fiber Structure for the Detection of Liquid With High Refractive Index. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 9447–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleneva, E.; Khaydukova, M.; Ashina, J.; Yaroshenko, I.; Jahatspanian, I.; Legin, A.; Kirsanov, D. A Simple Procedure to Assess Limit of Detection for Multisensor Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, B.; Alfè, M.; Gargiulo, V.; Polichetti, T.; Massera, E.; Miglietta, M.L.; Di Francia, G. A New Chemical Sensing Material for Ethanol Detection: Graphene-Like Film. In Proceedings of the Sensors: Third National Conference on Sensors, Rome, Italy, 23–25 February 2016; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Volume 431. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Y.; Shahnia, S.; Monro, T.M.; Lancaster, D.G. Force Sensors Using the Skew-Ray-Probed Plastic Optical Fibers. IEEE Photon. J. 2018, 10, 6802208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Xi, J.; Deng, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, H. Recent Development of Polymer Nanofibers in the Field of Optical Sensing. Polymers 2023, 15, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, H.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tong, L. Coiled Optical Nanofiber for Optofluidic Absorbance Detection. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2267–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.L.; Zhuang, J.H.; Feng, W.L. Fiber-optic lead ion sensor based on MXene film integrated Michelson interference structure. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 025708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagong, H.Y.; Son, M.H.; Park, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; Li, T.; Jung, Y.K. Dual-signal optical detection of Lead (II) ions (Pb2+) using galloyl group-functionalized polydiacetylene. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1230, 340403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dissanayake, K.; Asokan, S.; Sun, T.; Rahman, B.M.A.; Grattan, K.T.V. Lead (Pb2+) ion sensor development using optical fiber gratings and nanocomposite materials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, S.K.; Das, P.; Tripathy, S.K. Agricultural soil health monitoring using photonic crystal fiber based on combined principles of surface plasmon resonance and interferometry for lead ion detection. J. Nanophotonics 2023, 17, 036013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Noman, A.; Dash, J.N.; Cheng, X.; Tam, H.-Y.; Yu, C. PCF based modal interferometer for lead ion detection. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 4895–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Sun, D.D.; Liang, L.L.; Wang, G.J.; Ma, J. Highly sensitive detection of trace lead ions concentration based on a functional film-enhanced optical microfiber sensor. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 161, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, P.; Zhang, H.; Liao, S. Numerical modeling of transverse mode competition in strongly pumped multimode fiber lasers and amplifiers. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 3236–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Method | Functional Material | Linear Range | LoD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Michelson interferometer | MXene | ~ | 0.286 ppb | [39] |
| Colorimetric and fluorescent detection | Galloyl-PDA | 0–10 µM | 1.329 µM | [40] |
| Hybrid fiber (LPG + FBG) grating | CCS-NGO/PAA | ~ | 0.5 nM | [41] |
| PCF surface plasmon resonance interferometer | Gold layer | 0–100 ppm | 8.32 ppm | [42] |
| PCF modal interferometer | Chitosan-PVA, GSH functionalized AuNPs | ~ | 1.6 ppb | [43] |
| Film-enhanced microfiber interferometer | PDA-MA | 2 × 10−7–2.072 × 10−2 ppb | 0.1678 ppb | [44] |
| Light-sheet skew rays with inline microbubble | Au NPs-Oxalic acid | 0.1–10 ppb | 0.1305 ppb | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, T.; Xu, L.; Khalid, M.; Wu, X.; Du, L.; Shahnia, S.; Codemard, C.A.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Light-Sheet Skew Ray-Based Microbubble Chemical Sensor for Pb2+ Measurements. Sensors 2024, 24, 6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216785
Zhuang T, Xu L, Khalid M, Wu X, Du L, Shahnia S, Codemard CA, Bai Z, Wang Y, Liu S, et al. Light-Sheet Skew Ray-Based Microbubble Chemical Sensor for Pb2+ Measurements. Sensors. 2024; 24(21):6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216785
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Tingting, Lukui Xu, Mamoona Khalid, Xuan Wu, Linqiao Du, Soroush Shahnia, Christophe A. Codemard, Zhiyong Bai, Ying Wang, Shen Liu, and et al. 2024. "Light-Sheet Skew Ray-Based Microbubble Chemical Sensor for Pb2+ Measurements" Sensors 24, no. 21: 6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216785
APA StyleZhuang, T., Xu, L., Khalid, M., Wu, X., Du, L., Shahnia, S., Codemard, C. A., Bai, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, S., Chen, G. Y., & Wang, Y. (2024). Light-Sheet Skew Ray-Based Microbubble Chemical Sensor for Pb2+ Measurements. Sensors, 24(21), 6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24216785









