A Novel Approach to Detect Drones Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Dataset Preparation
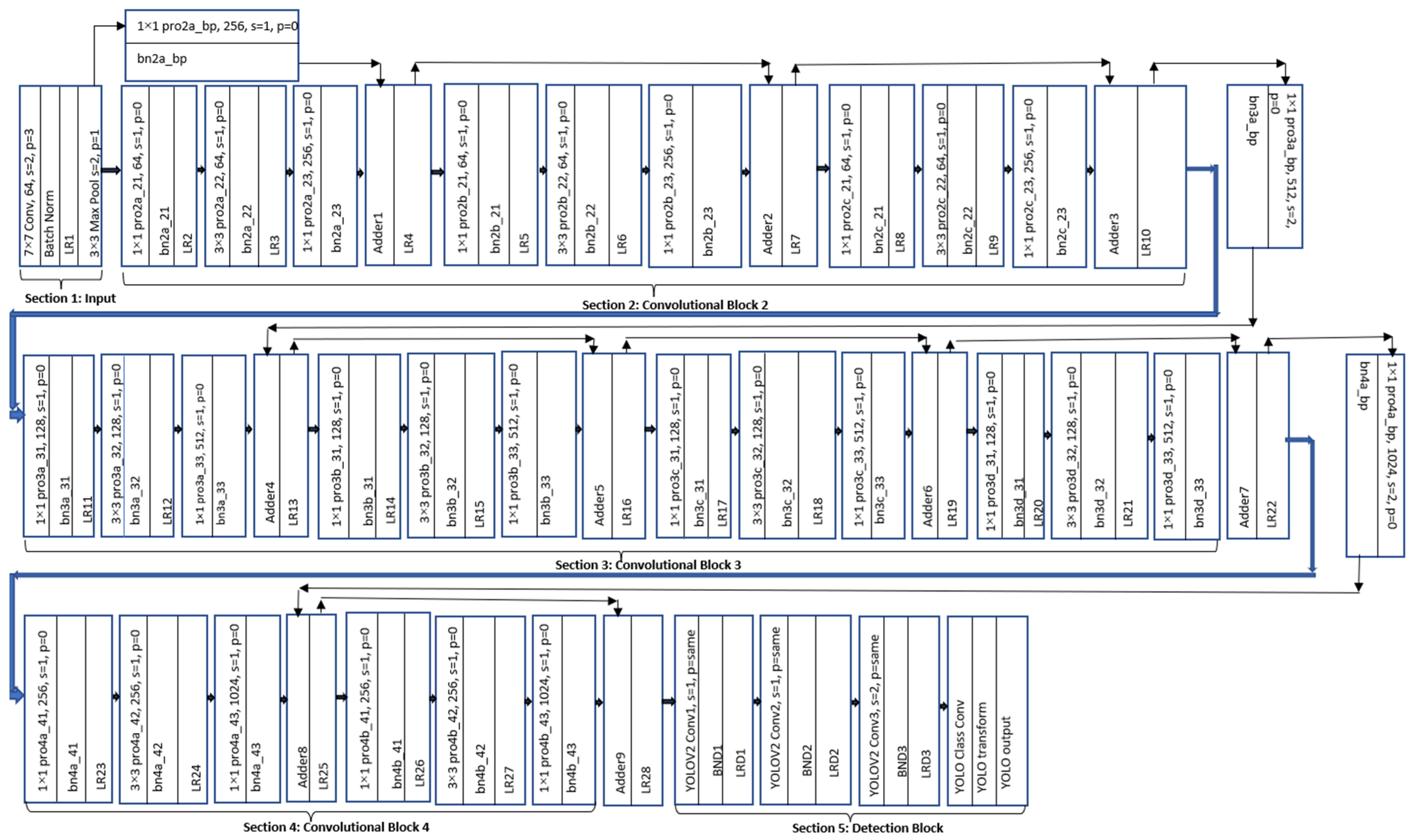
4. Proposed Algorithm
5. Experimental Results
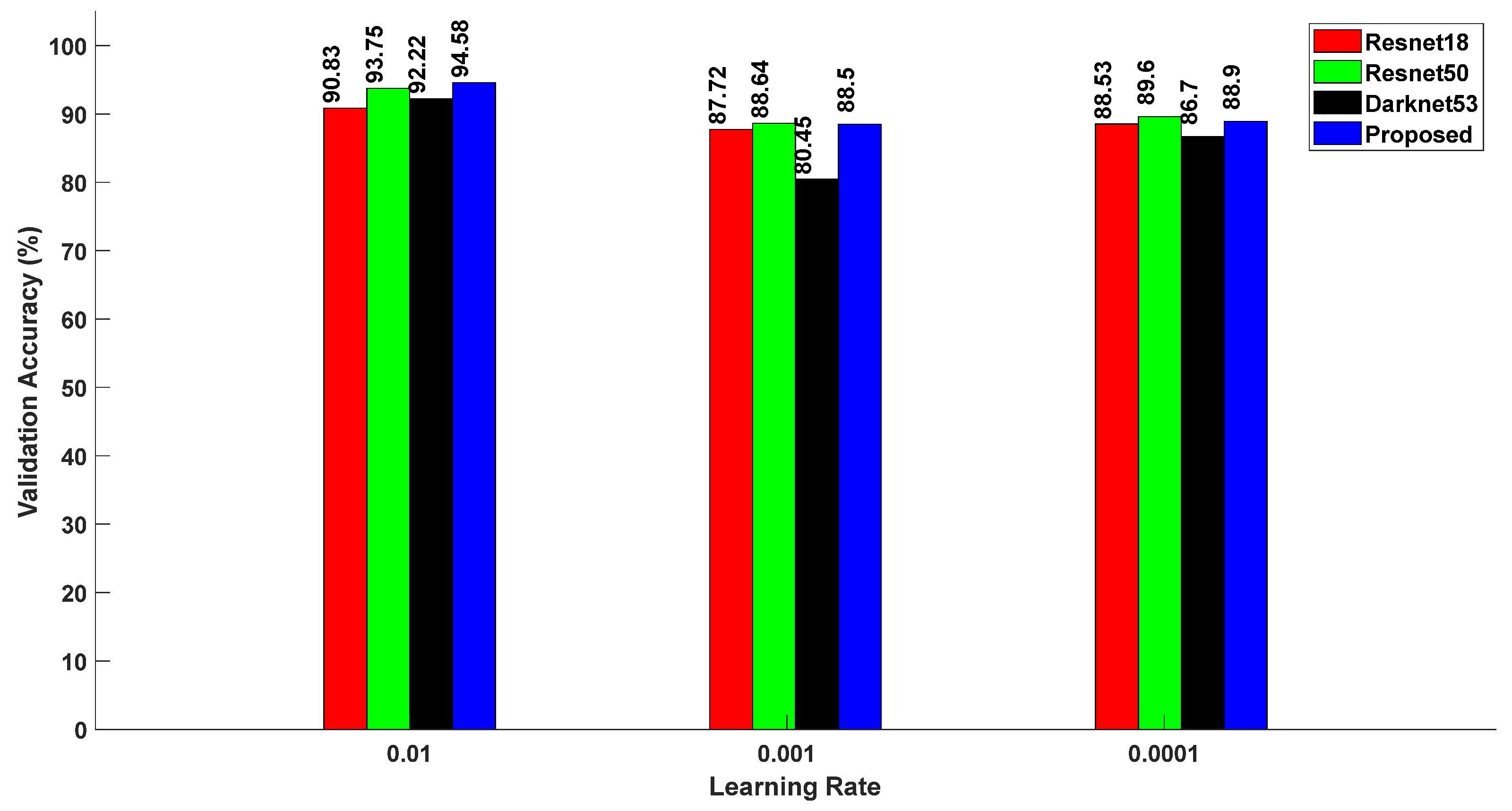
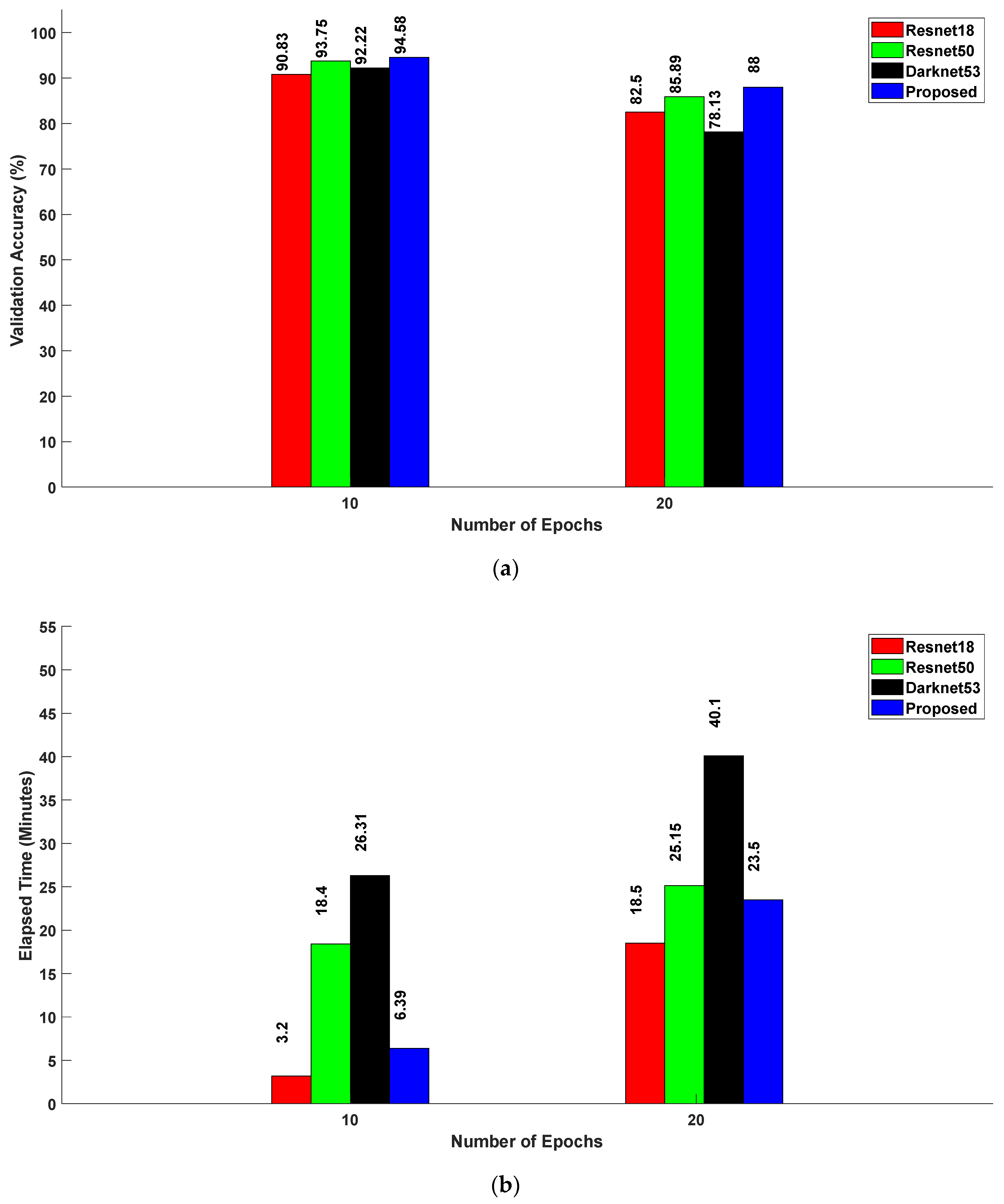
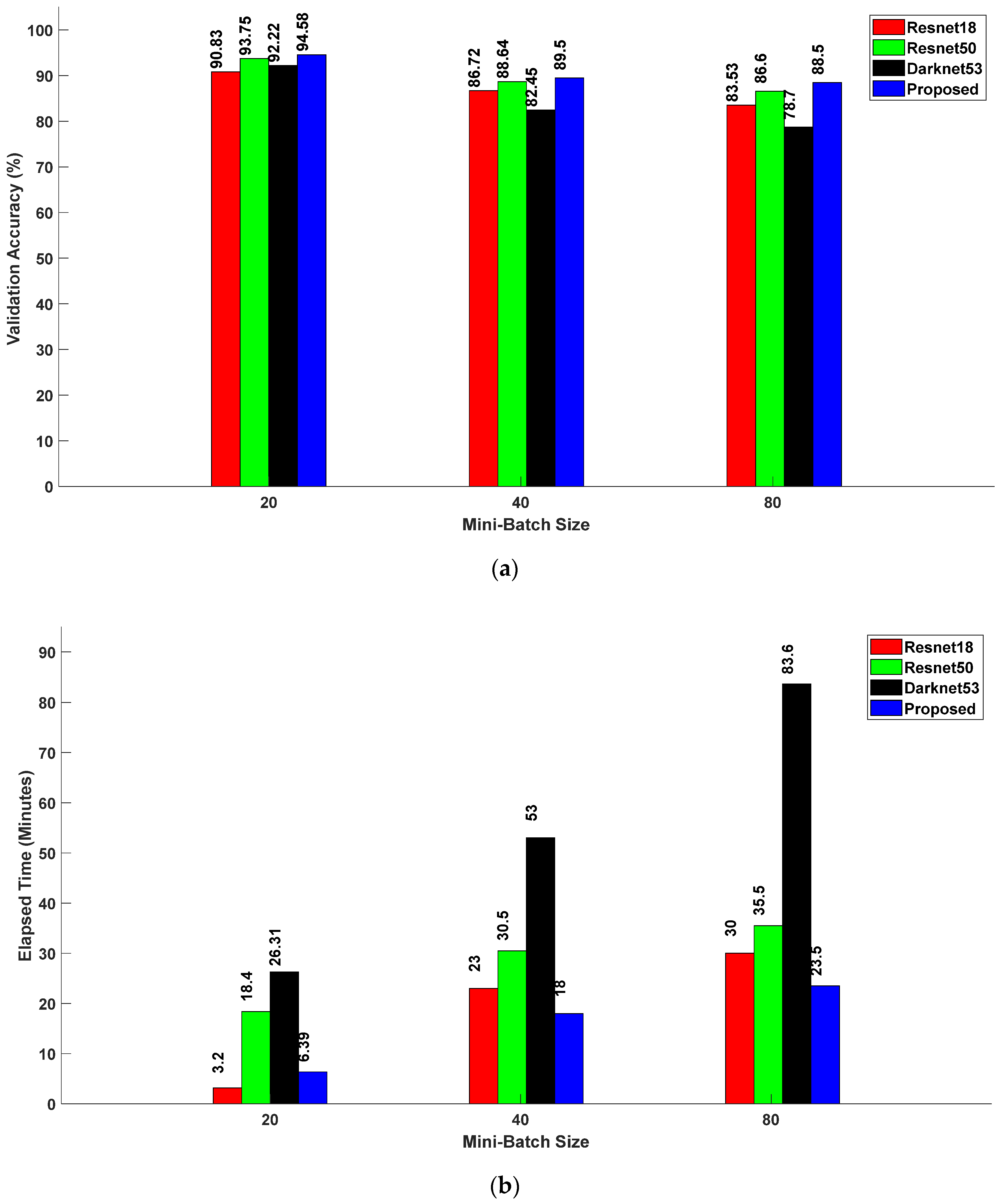
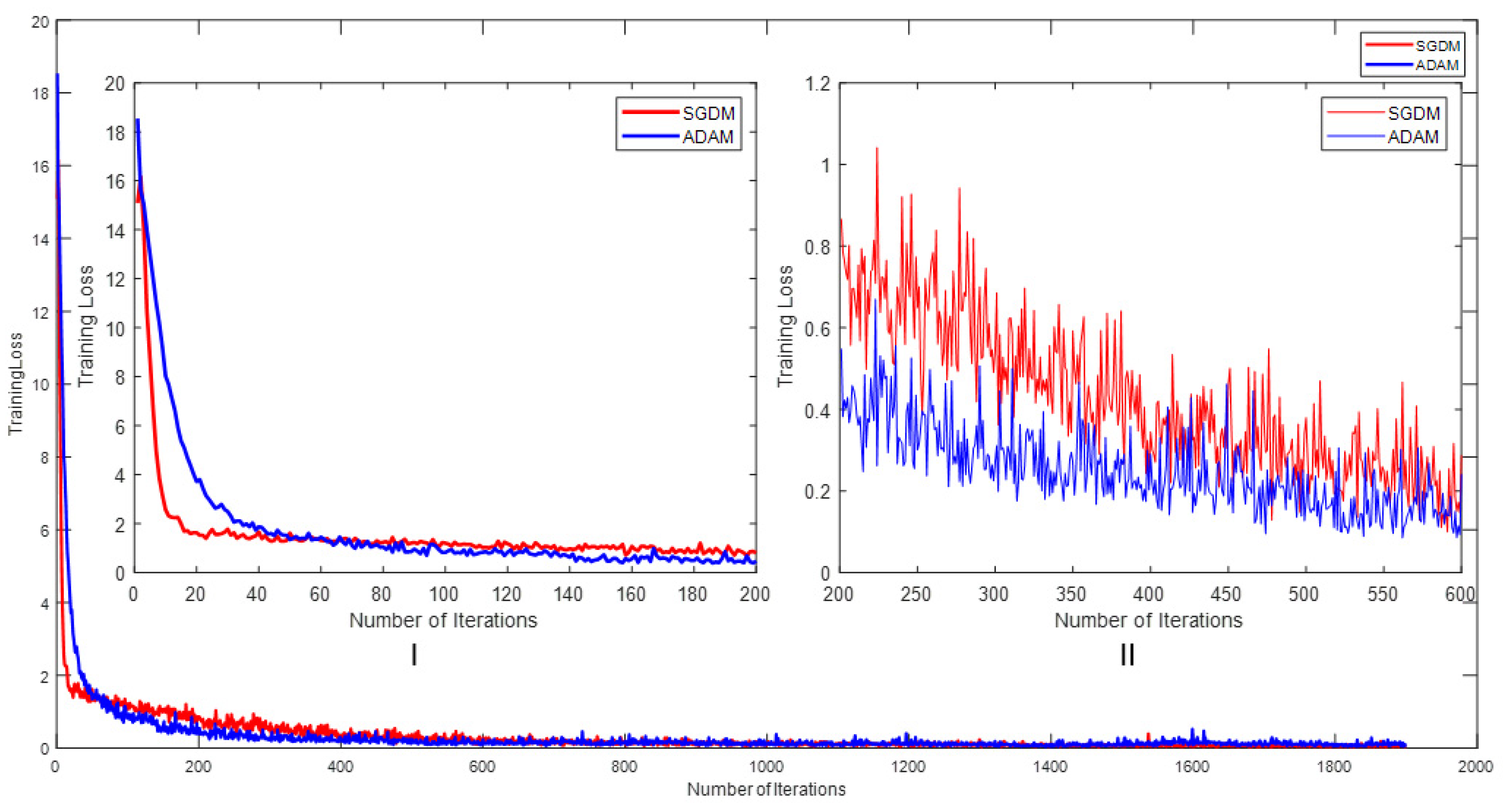
5.1. Proposed Feature Extraction Network with Different Optimizers
5.2. State-of-the-Art Feature Extraction Models vs. Proposed Model
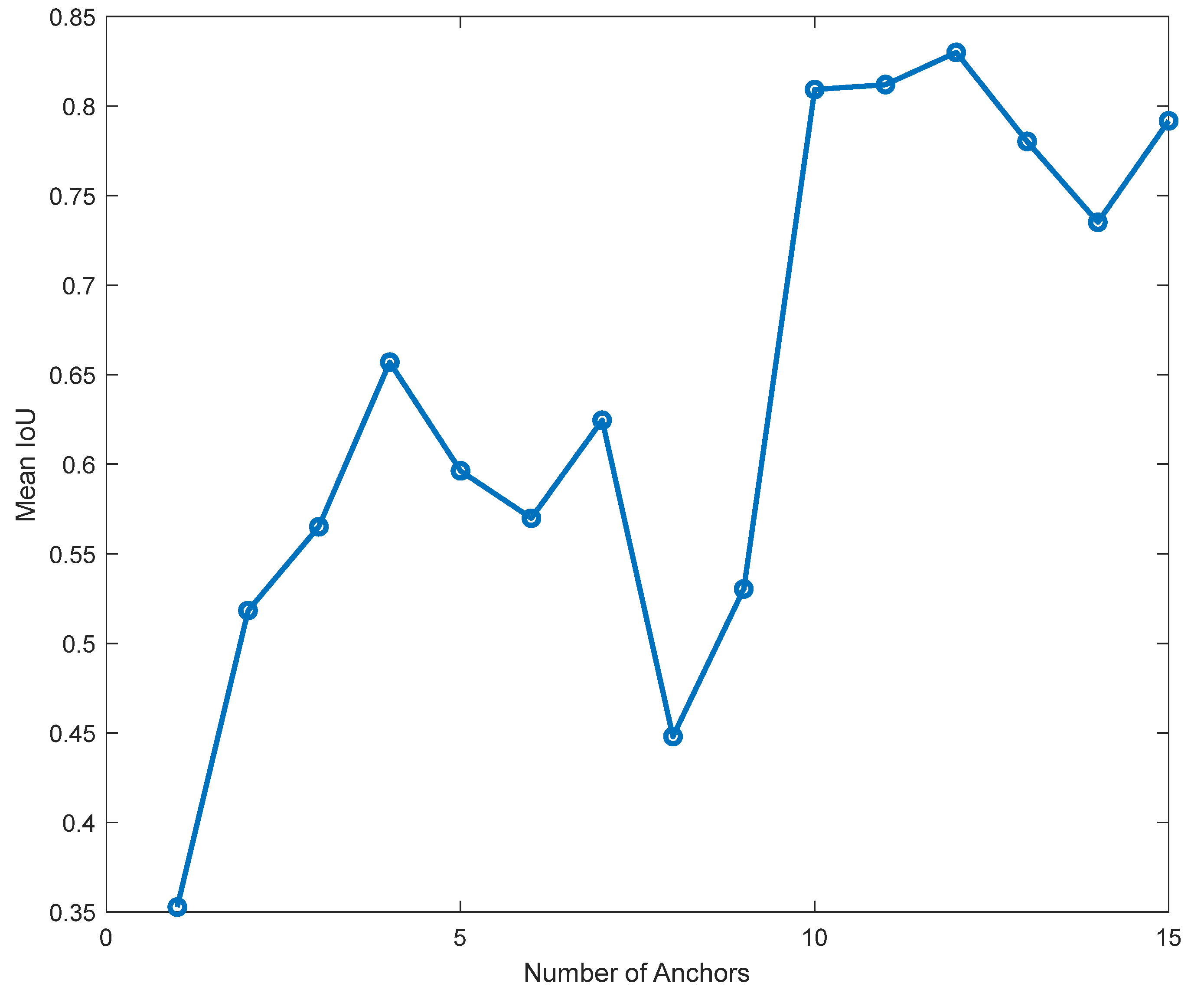
5.3. Anchor Boxes Estimation
5.4. Modified YOLOv2 Network with Different Optimizers
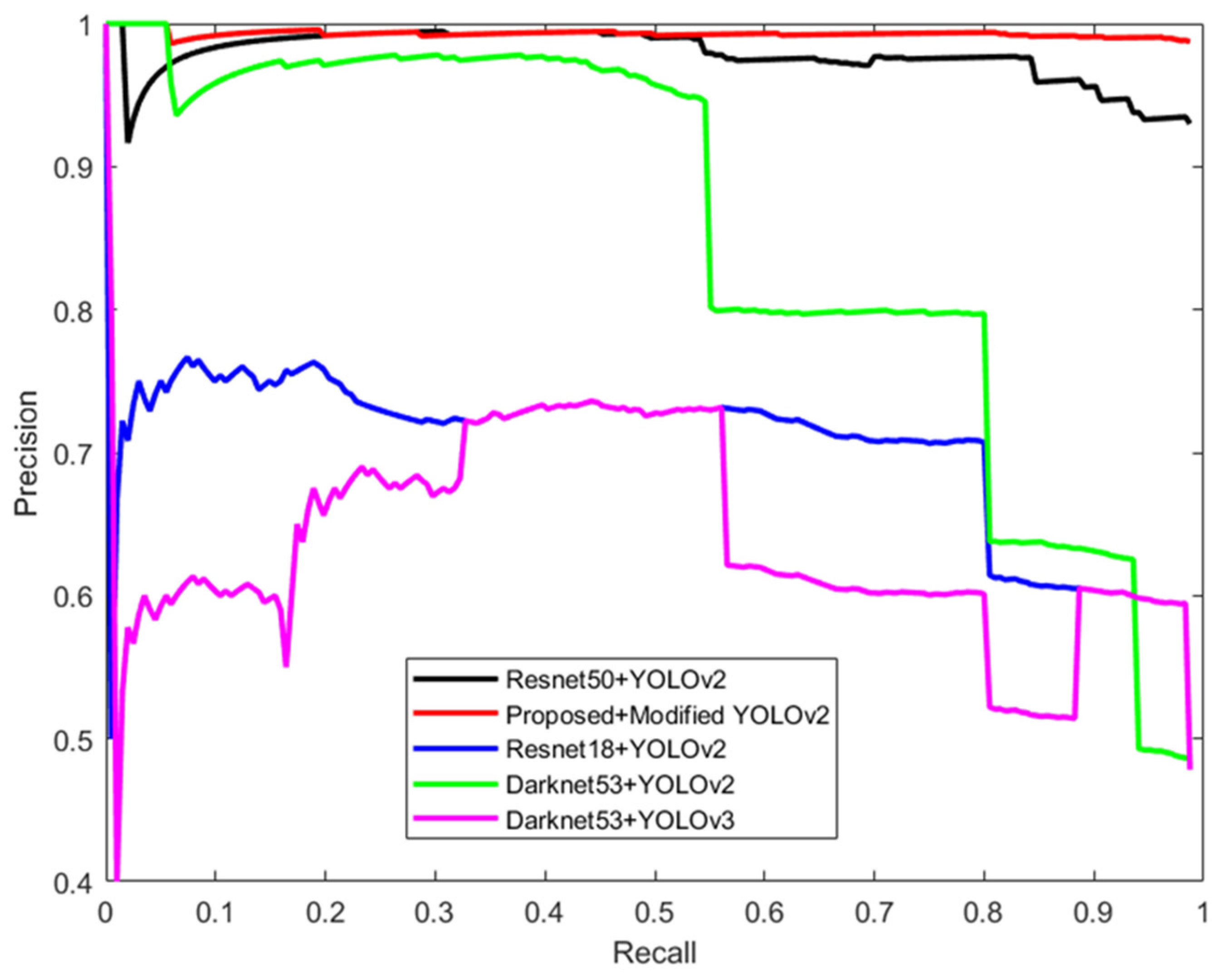
5.5. State-of-the-Art Feature Extraction Models with YOLOv2 vs. Proposed Feature Extraction Model with Modified YOLOv2
5.5.1. Resnet18 + YOLOv2
5.5.2. Resnet50 + YOLOv2
5.5.3. Darknet53 + YOLOv2
5.5.4. Darknet53 + YOLOv3
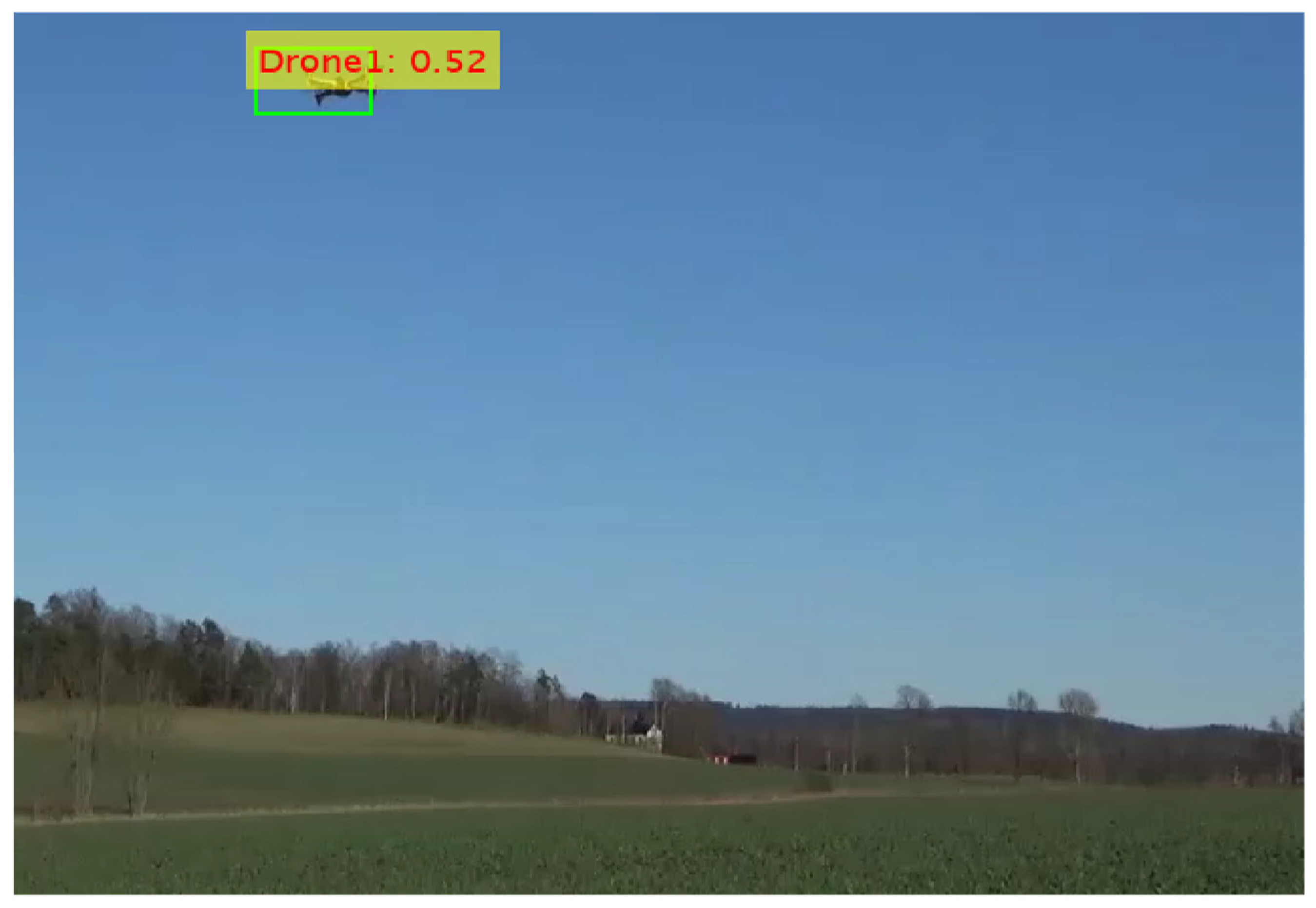
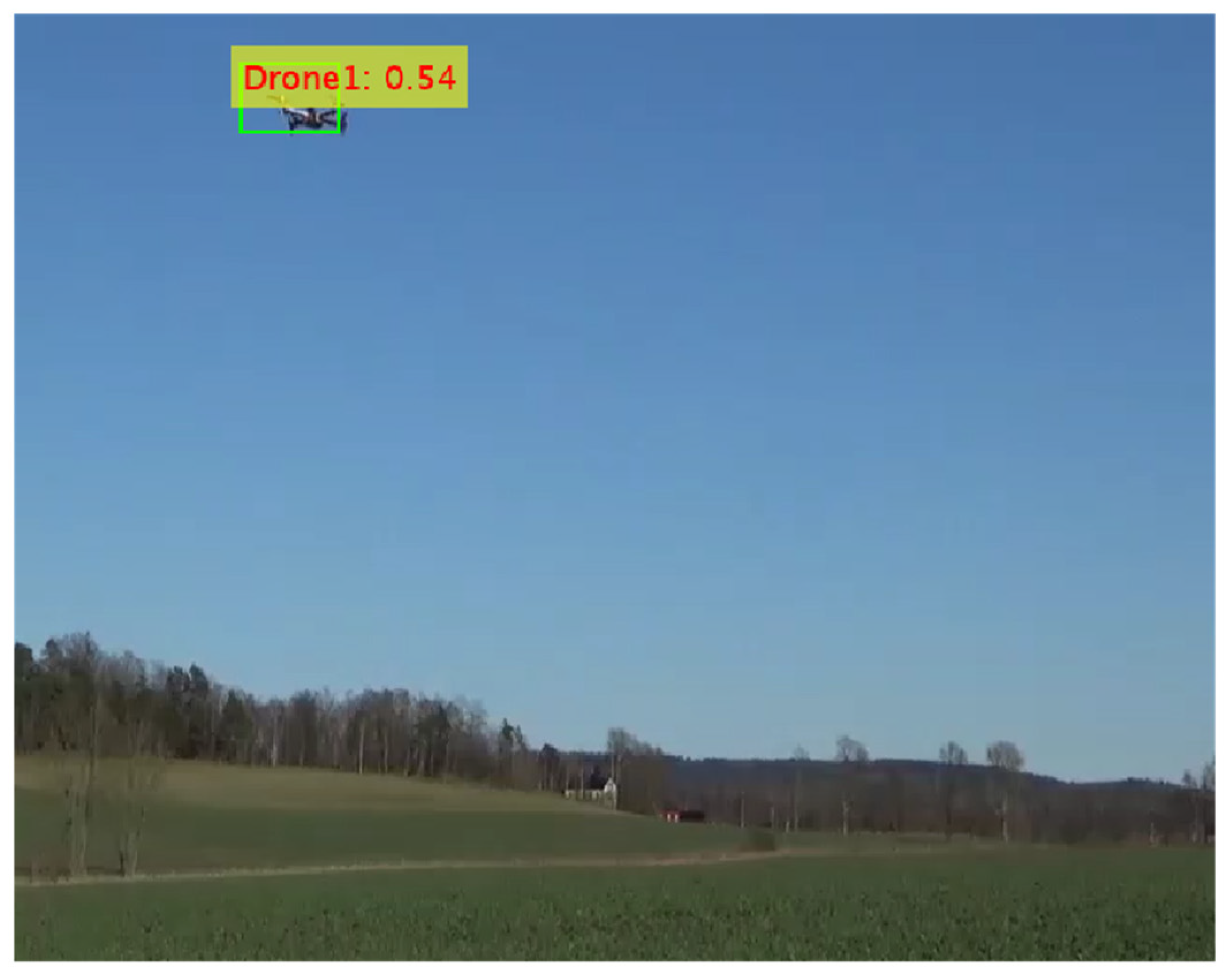
5.5.5. Proposed + Modified YOLOv2
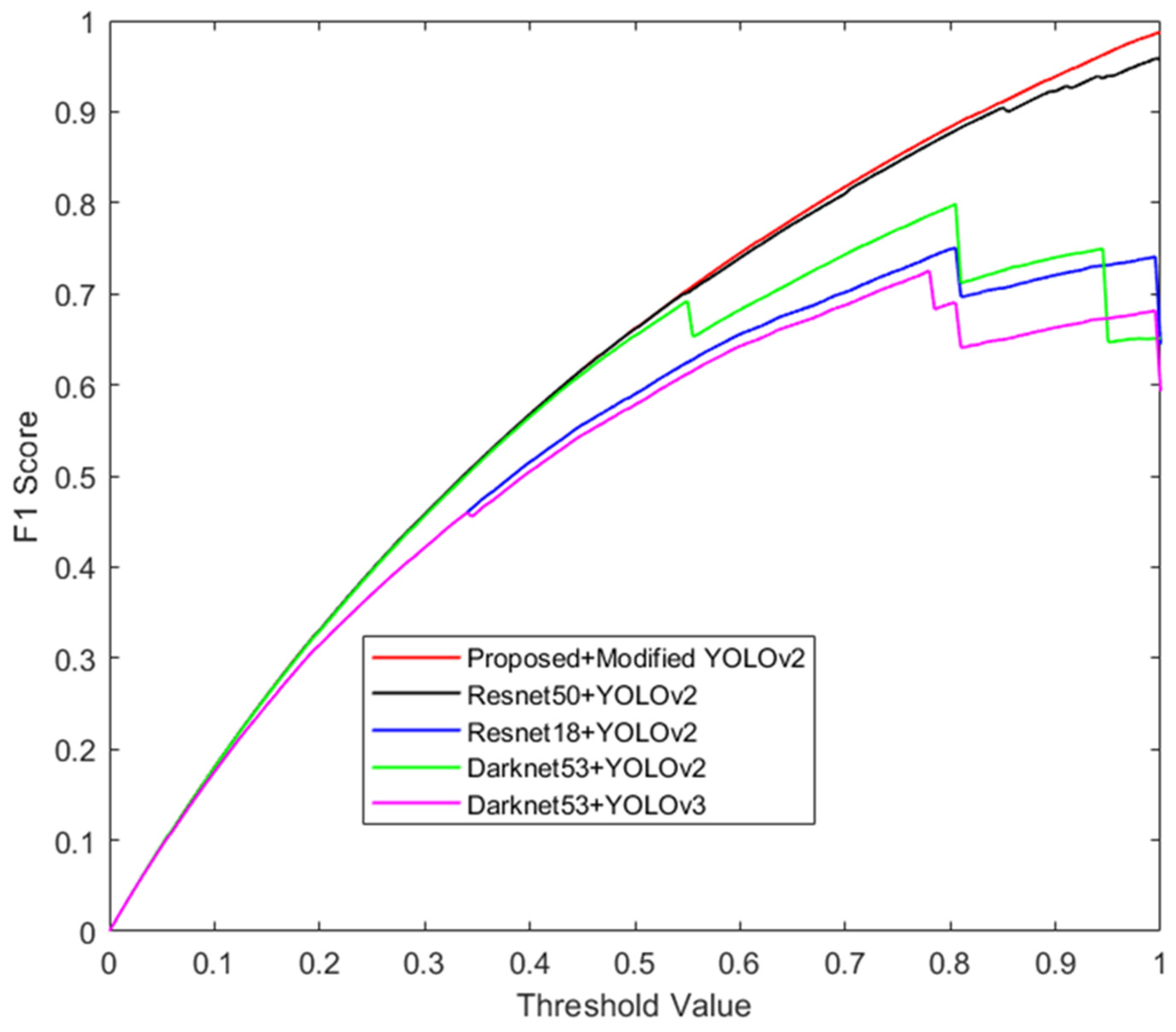
6. Performance Evaluations
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benarbia, T.; Kyamakya, K. A Literature Review of Drone-Based Package Delivery Logistics Systems and Their Implementation Feasibility. Sustainability 2022, 14, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, S.P.; Jagyasi, N. Evolution and Technological Advancements in Drone Photography. Int. J. Creat. Res. Thoughts—IJCRT 2020, 8, 2224–2227. [Google Scholar]
- Samadzadegan, F.; Javan, F.D.; Mahini, F.A.; Gholamshahi, M. Detection and Recognition of Drones Based on a Deep Convolutional Neural Network Using Visible Imagery. Aerospace 2022, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touil, S.; Richa, A.; Fizir, M.; Argente Garcia, J.E.; Skarmeta Gomez, A.F. A review on smart irrigation management strategies and their effect on water savings and crop yield. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 71, 1396–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, P.V.; Narasayya, N.L.; Kiran, N.G.; Sekhar, A.C.; Krishna, C.N. Design and Fabrication of Agri Copter for Spraying Pesticides. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Al Shamsi, M.; Al Shamsi, M.; Al Dhaheri, R.; Al Shamsi, R.; Al Kaabi, S.; Al Younes, Y. Foggy Drone: Application to a Hexarotor UAV. In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Advances in Science and Engineering Technology, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 6 February–5 April 2018; pp. 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.; Idries, A.; Mohamed, N.; Al-Jaroodi, J.; Jawhar, I. UAVs for Smart Cities: Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski, M.; Rana, Z.A.; Petrunin, I. Drone Model Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network Trained on Synthetic Data. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamola, V.; Kotesh, P.; Agarwal, A.; Gupta, N.; Guizani, M. A Comprehensive Review of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Attacks and Neutralization Techniques. Ad Hoc Netw. 2021, 111, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmen, Z.; Kuloglu, M. A New Era for Drug Trafficking: Drones. Forensic Sci. Addict. Res. 2018, 2, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, S.R.; Kim, Y. Implementation of detection and tracking mechanism for small UAS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Arlington, VA USA, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 1254–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Gu, H.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Gui, G.; Gacanin, H. Deep Complex-Valued Convolutional Neural Network for Drone Recognition Based on RF Fingerprinting. Drones 2022, 6, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreano, D.; Wood, R.J. Science, technology and the future of small autonomous drones. Nature 2015, 521, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2005. IEEE Computer Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Corfu, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Erabati, G.K.; Gonçalves, N.; Araújo, H. Object Detection in Traffic Scenarios—A Comparison of Traditional and Deep Learning Approaches; CS & IT—CSCP 2020; Institute of Systems and Robotics, University of Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2020; pp. 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-J.; Kim, D.-W.; Hong, W.-H.; Kim, M.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Jeong, J.-H. Application of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to Recognize Ship Structures. Sensors 2022, 22, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, M.; Dash, R. A Survey on Deep Learning: Convolution Neural Network (CNN). In Intelligent and Cloud Computing; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies 153; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalagala, S.; Walgampaya, C. Application of AlexNet convolutional neural network architecture-based transfer learning for automated recognition of casting surface defects. In Proceedings of the International Research Conference on Smart Computing and Systems Engineering (SCSE), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 16 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, V.; Ganeshbabu, T.R. A Convolutional Neural Network Classifier VGG-19 Architecture for Lesion Detection and Grading in Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Deep Learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 66, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavati, P.; Mohammadi, H.M. Obstacle Detection Using GoogleNet. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 25–26 October 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767v1. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 39, 91–99. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.01497.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once:Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; Available online: https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/html/Redmon_You_Only_Look_CVPR_2016_paper.html (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolo9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/html/Redmon_YOLO9000_Better_Faster_CVPR_2017_paper.html (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.02325 (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Dadrass Javan, F.; Samadzadegan, F.; Gholamshahi, M.; Ashatari Mahini, F. A Modified YOLOv4 Deep Learning Network for Vision-Based UAV Recognition. Drones 2022, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanströma, F.; Alonso-Fernandez, F.; Englund, C. A dataset for multi-sensor drone detection. Data Brief 2021, 39, 107521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USC Drone Dataset. Available online: https://chelicynly.github.io/Drone-Project (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Dawson, H.L.; Dubrule, O.; John, C.M. Impact of dataset size and convolutional neural network architecture on transfer learning for carbonate rock classification. Comput. Geosci. 2023, 171, 105284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yin, W. An Improved Analysis of Stochastic Gradient Descent with Momentum. In Proceedings of the Conf. Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Aggarwal, P.; Choi, J.; Kuo, J.C.-C. A Deep Learning Approach to Drone Monitoring. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.00863. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J. A Review of Object Detection Based on Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 36th Chinese Control Conference, Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Tian, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Du, S.; Lan, X. A review of object detection based on deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 23729–23791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.-T.; Wu, X. Object Detection with Deep Learning: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn.Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

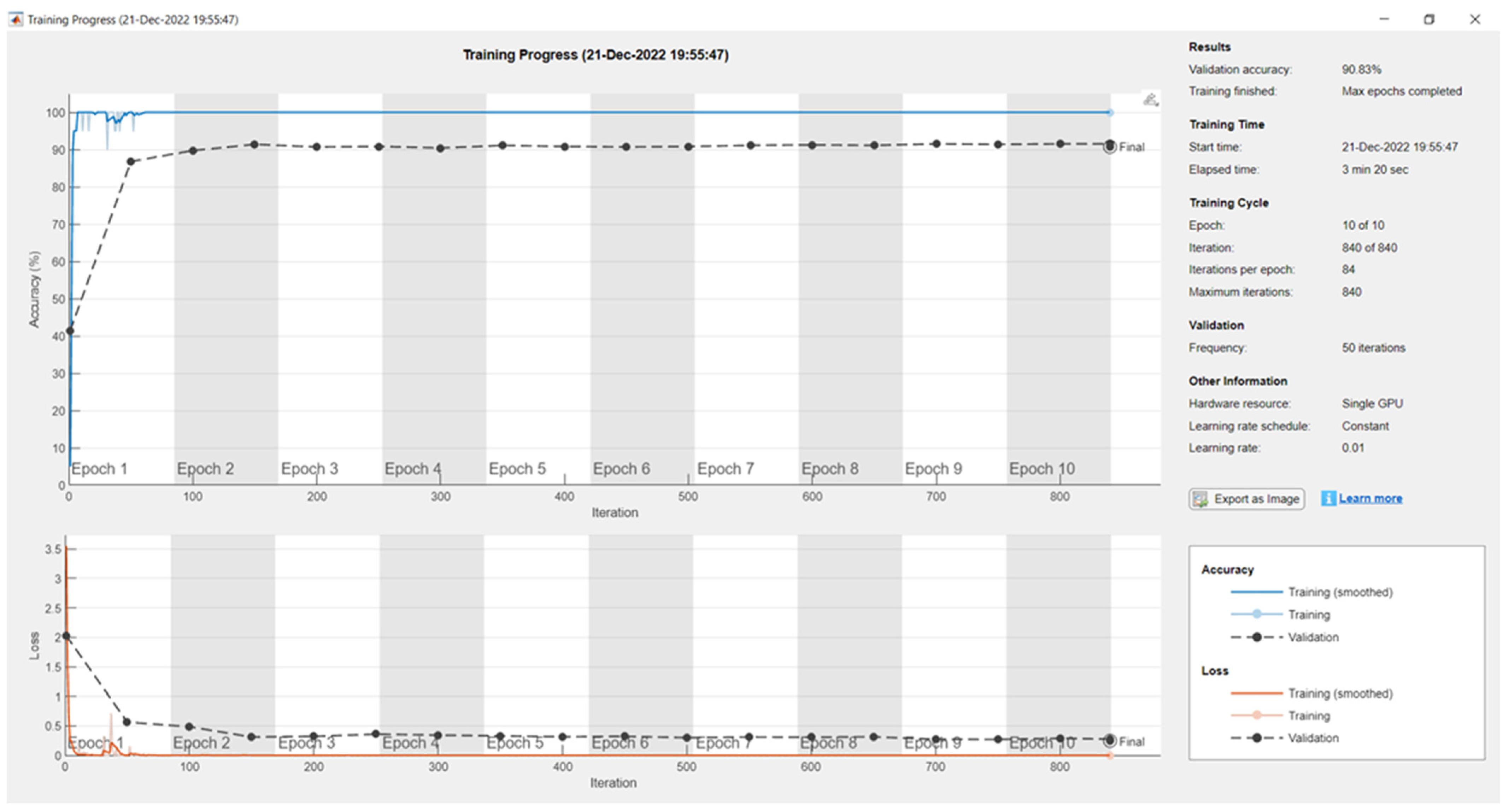
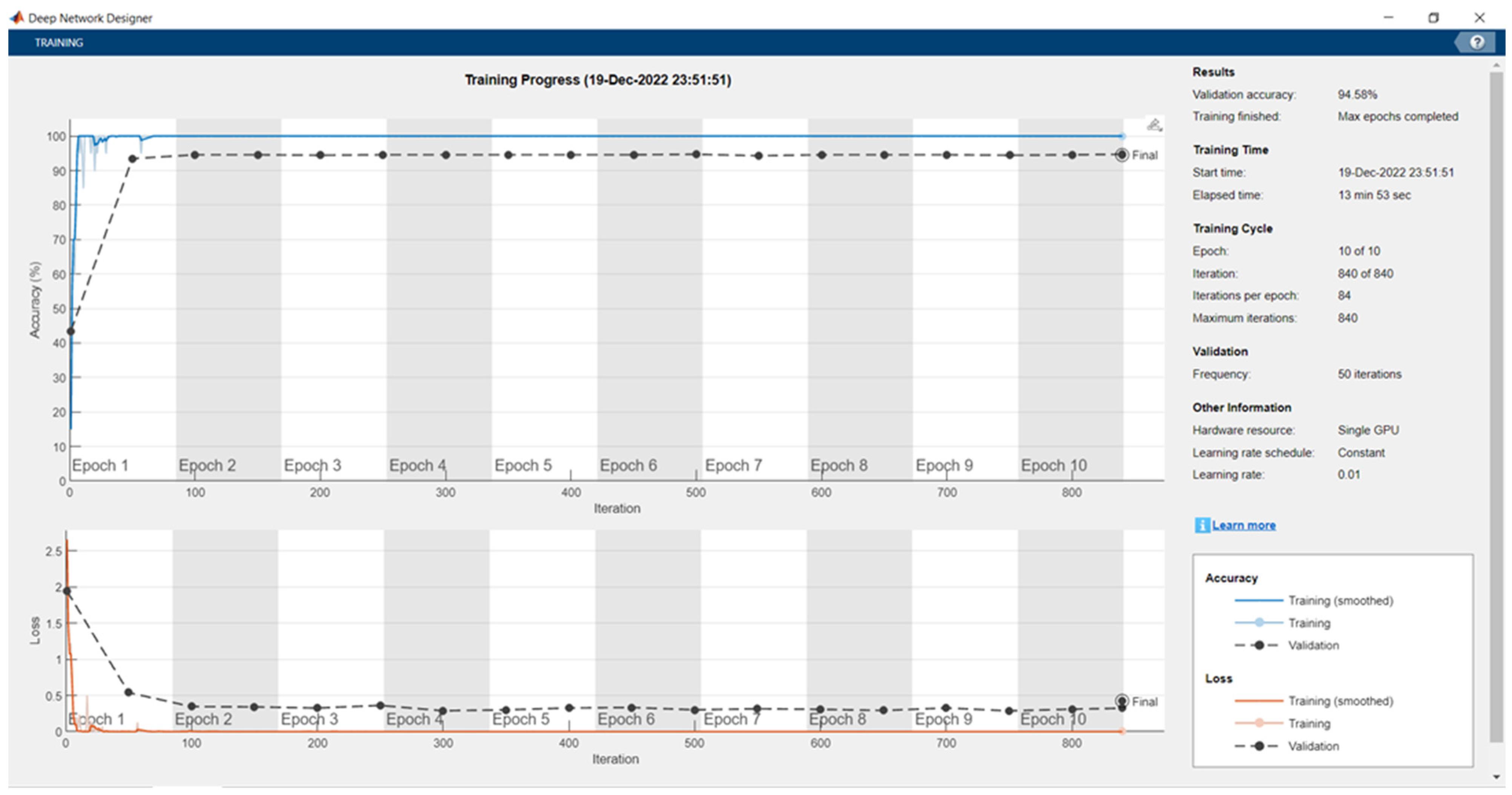

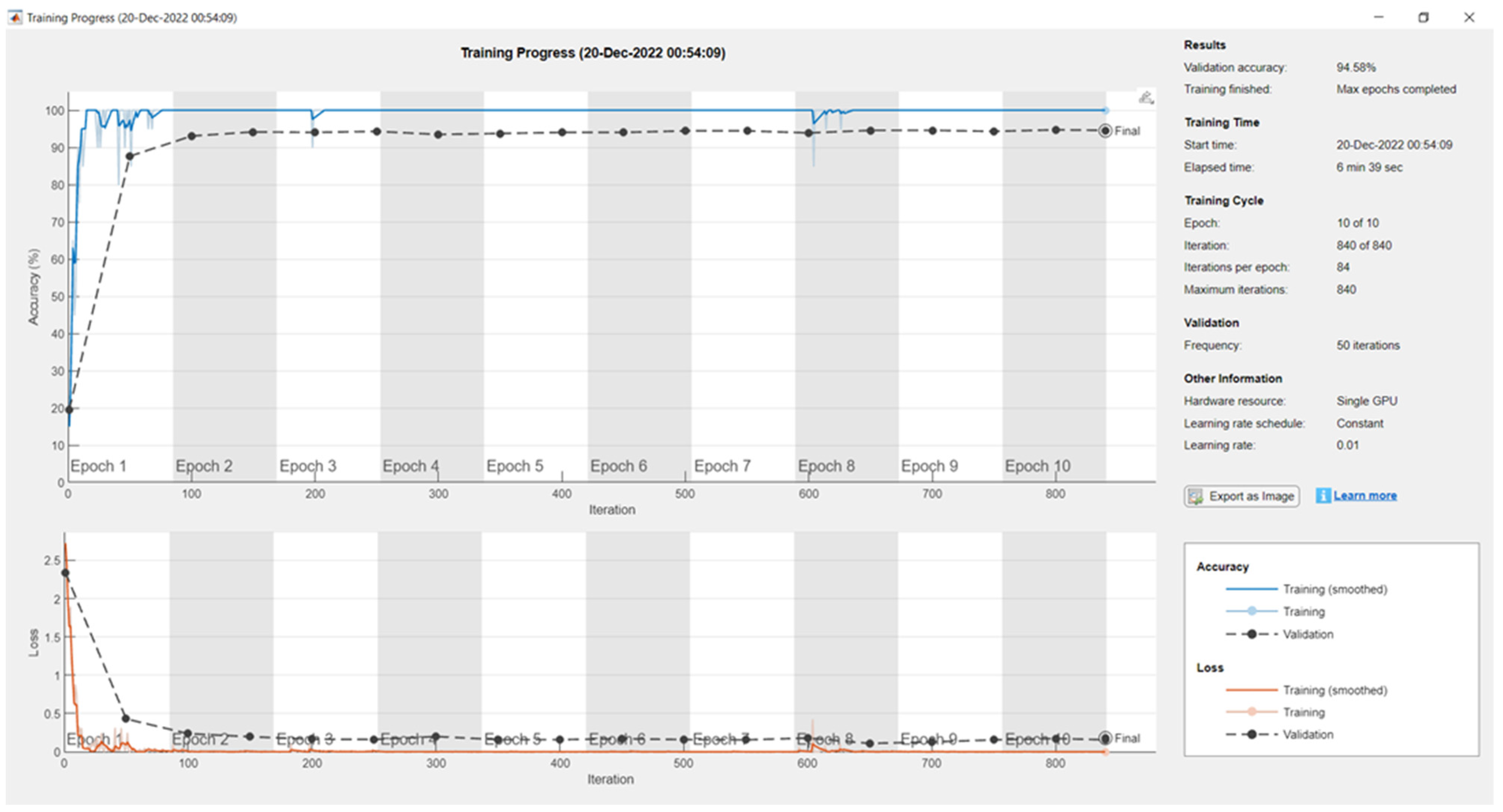







| Epoch | Iteration | Elapsed Time (hh:mm:ss) | Mini-Batch Accuracy | Validation Accuracy | Mini-Batch Loss | Validation Loss | Base Learning Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 00:00:15 | 5.00% | 25.97% | 2.7688 | 4.2363 | 0.0100 |
| 1 | 50 | 00:01:20 | 75.00% | 61.53% | 0.5686 | 1.3813 | 0.0100 |
| 2 | 100 | 00:02:26 | 95.00% | 76.53% | 0.1081 | 1.3301 | 0.0100 |
| 2 | 150 | 00:03:33 | 95.00% | 73.47% | 0.3317 | 1.1884 | 0.0100 |
| 3 | 200 | 00:04:42 | 100.00% | 74.17% | 0.04370 | 1.4640 | 0.0100 |
| 3 | 250 | 00:05:50 | 100.00% | 86.53% | 0.05330 | 1.2644 | 0.0100 |
| 4 | 300 | 00:06:58 | 95.00% | 67.92% | 0.1578 | 2.3191 | 0.0100 |
| 5 | 350 | 00:08:05 | 100.00% | 80.28% | 0.0177 | 1.1865 | 0.0100 |
| 5 | 400 | 00:09:12 | 100.00% | 81.94% | 0.0088 | 1.2314 | 0.0100 |
| 6 | 450 | 00:10:20 | 100.00% | 86.39% | 0.0029 | 1.1369 | 0.0100 |
| 6 | 500 | 00:11:27 | 100.00% | 86.39% | 0.0029 | 1.1369 | 0.0100 |
| 7 | 550 | 00:12:36 | 75.00% | 79.31% | 0.7070 | 1.5656 | 0.0100 |
| 8 | 600 | 00:13:43 | 100.00% | 85.14% | 0.0539 | 1.3672 | 0.0100 |
| 8 | 650 | 00:14:49 | 90.00% | 85.56% | 0.3977 | 1.0454 | 0.0100 |
| 9 | 700 | 00:15:24 | 100.00% | 87.64% | 0.0427 | 1.0036 | 0.0100 |
| 9 | 750 | 00:15:53 | 95.00% | 90.83% | 0.0540 | 0.9987 | 0.0100 |
| 10 | 800 | 00:16:21 | 100.00% | 85.14% | 0.0176 | 2.0756 | 0.0100 |
| 10 | 840 | 00:16:45 | 100.00% | 85.14% | 0.0069 | 1.6661 | 0.0100 |
| Epoch | Iteration | Elapsed Time (hh:mm:ss) | Mini- Batch Accuracy | Validation Accuracy | Mini-Batch Loss | Validation Loss | Base Learning Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 00:00:09 | 0.00% | 23.97% | 2.7197 | 2.4006 | 0.0100 |
| 1 | 50 | 00:00:46 | 100.00% | 93.19% | 0.0028 | 0.1610 | 0.0100 |
| 2 | 100 | 00:01:23 | 100.00% | 94.72% | 0.0017 | 0.1380 | 0.0100 |
| 2 | 150 | 00:02:02 | 100.00% | 93.19% | 0.0096 | 0.2071 | 0.0100 |
| 3 | 200 | 00:02:39 | 100.00% | 95.97% | 0.0054 | 0.0916 | 0.0100 |
| 3 | 250 | 00:03:17 | 100.00% | 95.97% | 0.0011 | 0.0932 | 0.0100 |
| 4 | 300 | 00:04:07 | 100.00% | 96.11% | 0.0004 | 0.0998 | 0.0100 |
| 5 | 350 | 00:05:08 | 100.00% | 95.28% | 0.0016 | 0.0908 | 0.0100 |
| 5 | 400 | 00:06:09 | 100.00% | 96.11% | 0.0002 | 0.1004 | 0.0100 |
| 6 | 450 | 00:07:11 | 100.00% | 95.28% | 0.0004 | 0.1023 | 0.0100 |
| 6 | 500 | 00:08:14 | 100.00% | 95.69% | 0.0003 | 0.1136 | 0.0100 |
| 7 | 550 | 00:09:17 | 100.00% | 95.42% | 0.0014 | 0.1045 | 0.0100 |
| 8 | 600 | 00:10:19 | 100.00% | 96.11% | 0.0001 | 0.1116 | 0.0100 |
| 8 | 650 | 00:11:24 | 90.00% | 94.72% | 0.0006 | 0.1101 | 0.0100 |
| 9 | 700 | 00:12:27 | 100.00% | 94.86% | 0.0001 | 0.1153 | 0.0100 |
| 9 | 750 | 00:13:30 | 100.00% | 95.42% | 0.0015 | 0.1083 | 0.0100 |
| 10 | 800 | 00:14:32 | 100.00% | 95.69% | 0.0002 | 0.1211 | 0.0100 |
| 10 | 840 | 00:15:25 | 100.00% | 94.86% | 0.0001 | 0.1034 | 0.0100 |
| Model | Learnable Properties (In Millions) | Test Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Resnet18 + YOLOv2 | 15.90 | 52% |
| Resnet50 + YOLOv2 | 27.50 | 53% |
| Darknet53 + YOLOv2 | 41.60 | 53% |
| Darknet53 + YOLOv3 | 62.00 | 54% |
| Proposed | 5.00 | 77% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakshit, H.; Bagheri Zadeh, P. A Novel Approach to Detect Drones Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture. Sensors 2024, 24, 4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144550
Rakshit H, Bagheri Zadeh P. A Novel Approach to Detect Drones Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture. Sensors. 2024; 24(14):4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144550
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakshit, Hrishi, and Pooneh Bagheri Zadeh. 2024. "A Novel Approach to Detect Drones Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture" Sensors 24, no. 14: 4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144550
APA StyleRakshit, H., & Bagheri Zadeh, P. (2024). A Novel Approach to Detect Drones Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture. Sensors, 24(14), 4550. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144550





