Tai Chi Movement Recognition and Precise Intervention for the Elderly Based on Inertial Measurement Units and Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Participants and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Method
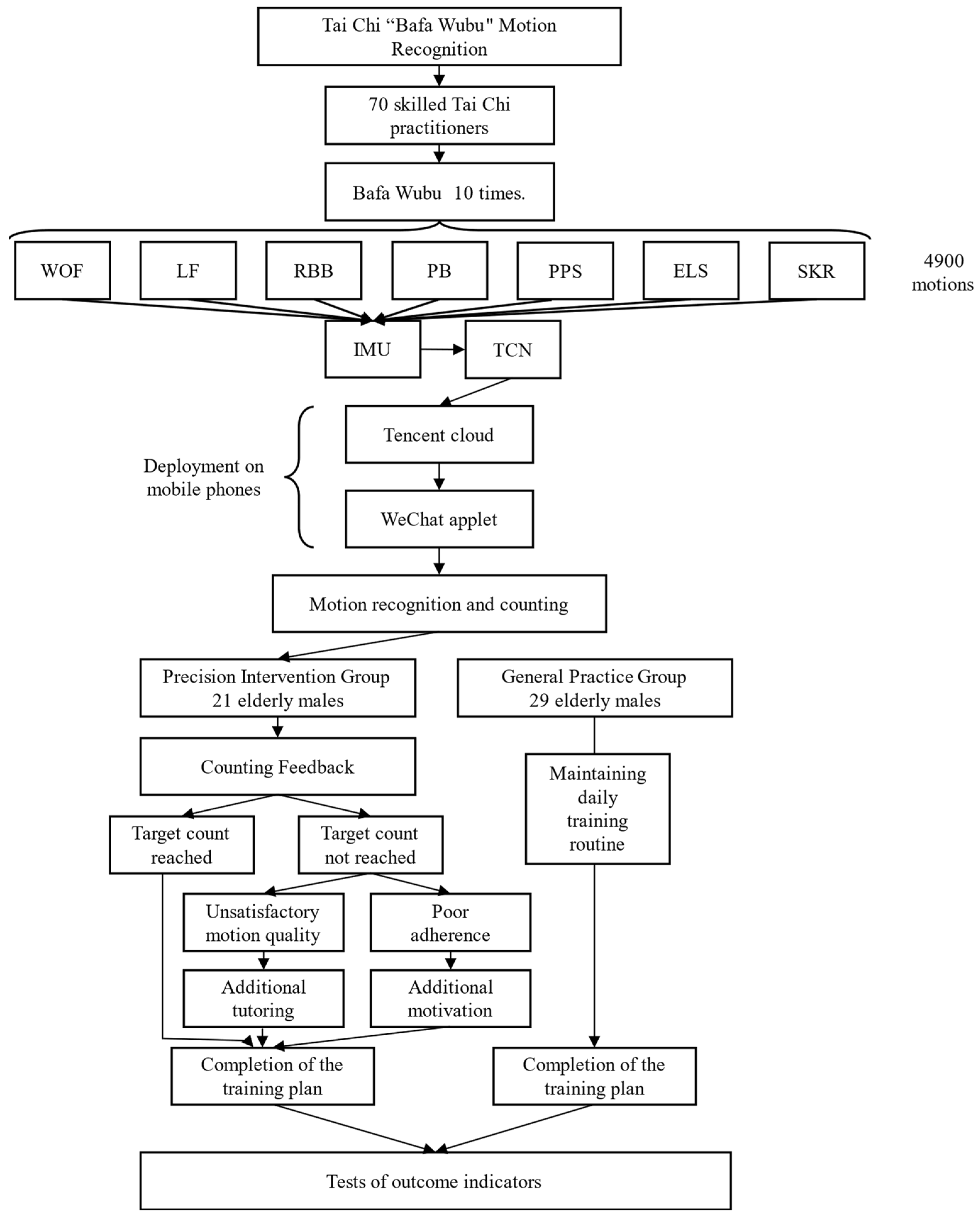
2.2.1. Study Design
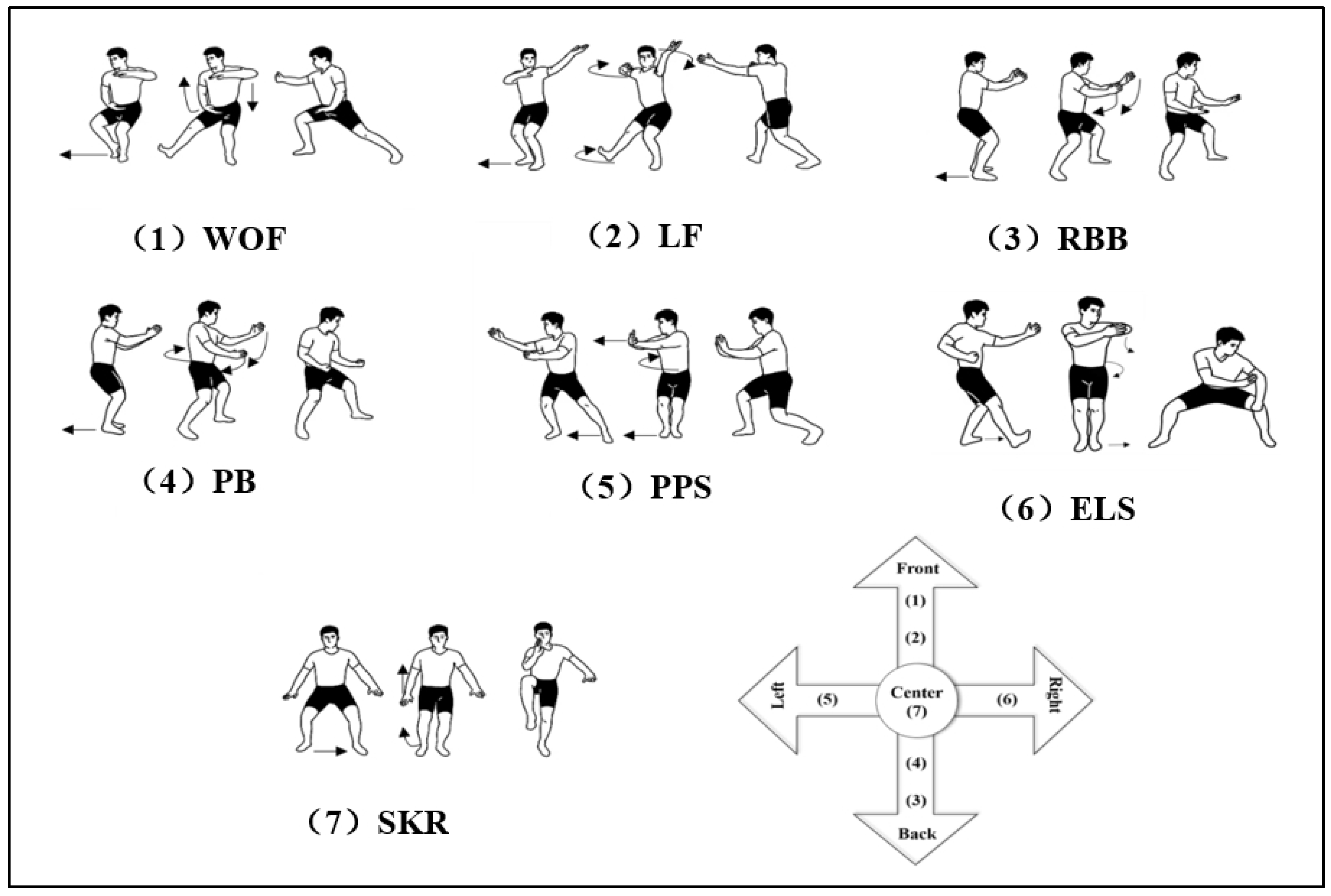
2.2.2. Bafa Wubu Formulation in Tai Chi Exercise
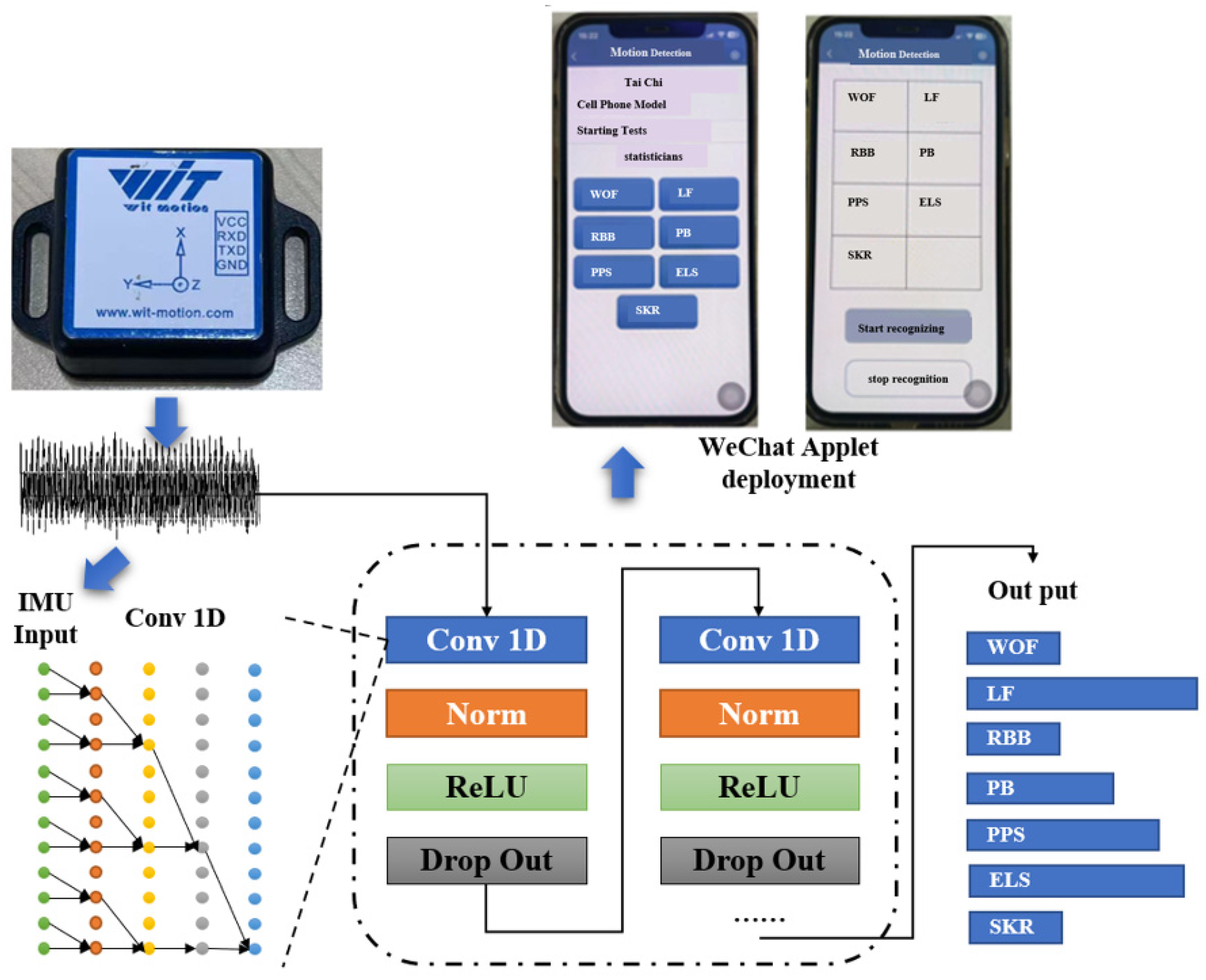
2.2.3. IMU Data Acquisition and Processing
2.2.4. Neural Network Construction
2.3. Deployment on Mobile Devices
2.3.1. WeChat Applet Deployment
2.3.2. Server-Side Deployment
2.3.3. Exercise Intervention Program
2.3.4. Health Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantage
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Wei, G. Effects of Sports Public Goods on the Health of the Elderly: Empirical Evidence from China. Soc. Work Public Health 2022, 37, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsurasako, T.; Murata, S.; Goda, A.; Nakano, H.; Shiraiwa, K.; Horie, J.; Nonaka, K. Comparison of Physical Function among Elderly Japanese Women with and without Low Bone Mass and Low Muscle Mass: A Cross-Sectional Study of Older Women Who Engage in Regular Physical Activity. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussault-Picard, C.; Havashinezhadian, S.; Turpin, N.A.; Moissenet, F.; Turcot, K.; Cherni, Y. Age-related modifications of muscle synergies during daily-living tasks: A scoping review. Clin. Biomech. 2024, 113, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formiga, F. Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Disease in the Elderly. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-G. Age score for assessing motor function in Chinese older men. J. Men’s Health 2020, 17, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musculus, L.; Kinrade, N.; Laborde, S.; Gleißert, M.; Streich, M.; Lobinger, B.H. Movement-Specific Reinvestment in Older People Explains Past Falls and Predicts Future Error-Prone Movements. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Vidal, J.L.; Teulings, H.; Stelmach, G. Elderly subjects are impaired in spatial coordination in fine motor control. Acta Psychol. 1998, 100, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Newly compiled Tai Chi (Bafa Wubu) promotes lower extremity exercise: A preliminary cross sectional study. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Du, Z.; Shen, S.; Du, W.; Kang, J.; Gong, D. An RCT-reticulated meta-analysis of six MBE therapies affecting college students’ negative psychology. iScience 2023, 26, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, L.C.; Machado, J.P.; Monteiro, F.J.; Greten, H.J. Understanding Traditional Chinese Medicine Therapeutics: An Overview of the Basics and Clinical Applications. Healthcare 2021, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M. Effectiveness of Tai Chi exercise on fear of falling and balance in older adults: A meta-analysis. Geriatr. Nurs. 2023, 51, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallinen, M.; Alen, M. Sports-related injuries in elderly men still active in sports. Br. J. Sports Med. 1994, 28, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammerlander, C. The epidemiology of sports-related injuries in older adults: A central European epidemiologic study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 24, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roell, M.; Roecker, K.; Gehring, D.; Mahler, H.; Gollhofer, A. Player Monitoring in Indoor Team Sports: Concurrent Validity of Inertial Measurement Units to Quantify Average and Peak Acceleration Values. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimstra, M.; Geneau, D.; Lacroix, M.; Jensen, M.; Greenshields, J.; Cormier, P.; Brodie, R.; Commandeur, D.; Tsai, M.-C. Wheelchair Rugby Sprint Force-Velocity Modeling Using Inertial Measurement Units and Sport Specific Parameters: A Proof of Concept. Sensors 2023, 23, 7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, M.; Beato, M.; McErlain-Naylor, S.A. Inter-unit reliability of IMU Step metrics using IMeasureU Blue Trident inertial measurement units for running-based team sport tasks. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 39, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashi, F.; Crettenand, F.; Millet, G.P.; Aminian, K. Front-Crawl Instantaneous Velocity Estimation Using a Wearable Inertial Measurement Unit. Sensors 2012, 12, 12927–12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, L.K.; Outerleys, J.; Johnson, C.D. The Effect of Sensor Placement on Measured Distal Tibial Accelerations During Running. J. Appl. Biomech. 2023, 39, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.; Yoon, S.; Perkins, N.; Najafi, K. Wireless MEMS inertial sensor system for golf swing dynamics. Sens. Actuators 2008, 141, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Yasumoto, K. Inertial Measurement Unit-sensor-based Short Stick Exercise Tracking to Improve Health of Elderly People. Sens. Mater. 2022, 34, 2911–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lladós, J.; Lopresti, D.; Uchida, S. Online Spatio-temporal 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Early Recognition of Handwritten Gestures. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 12821, pp. 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fan, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gao, P. Coupling video vision transformer (ViVit) into land change simulation: A comparison with three-dimensional convolutional neural network (3DCNN). J. Spat. Sci. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanambathina, S.D.; Burra, M.; Edupalli, B.; Vallem, E.R.; Nellore, V.S. Real time speech enhancement using densely connected neural networks and Squeezed temporal convolutional modules. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 50289–50305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gong, H.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Cen, H.; Fan, Y. Biomechanical effects of typical lower limb movements of Chen-style Tai Chi on knee joint. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2023, 61, 3087–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, B.; Ning, X. Biomechanical Analysis of Arm Manipulation in Tai Chi. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2586716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Rajakani, K. Object Extraction of Tennis Video Based on Deep Learning. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 5402410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadalinezhad, M.; Makrehchi, M. Basketball lineup performance prediction using edge-centric multi-view network analysis. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2020, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarakonda, H.; Mukherjee, S. Early Prediction of Human Action by Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 National Conference on Communications (NCC), Kanpur, India, 27–30 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, A.; Collett, J.; Cribb, L.; Zheng, Z.; Podugu, P. A cross-sectional study of factors associated with psychosocial wellbeing among older Tai Chi practitioners. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2023, 57, 102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Jais, I.S.; Nadkarni, N.V.; Yee Sien, N.G.; Seow, D.C.C.; Wong, T.H. Investigating the functional grip strength of elderly fallers in Singapore. Proc. Singap. Healthc. 2019, 28, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, B.; Arnold, G.; Alzahrani, A.; Alkhathami, K.; Jastania, R.; Wang, W. Comparison of Limb and Joint Strengths between Tai Chi Chuan Players and Non-Tai Chi Chuan Groups by Using a Force Sensor. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Matsuda, N.; Takahata, M.; Koseki, C.; Yamaki, M.; Sato, T. Relationship between occlusal force and endothelial function in community-dwelling elderly women: A pilot study. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Huang, W.; Jiang, Z. Neuromuscular control strategies of the lower limb during a typical Tai Chi brush knee and twist step in practitioners with and without knee pain: A pilot study. Res. Sports Med. 2023, 32, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currin, J.B.; Hayslip, B.; Temple, J.R. The Relationship between Age, Gender, Historical Change, and Adults’ Perceptions of Mental Health and Mental Health Services. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. 2011, 72, 317–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tang, H.; He, G.; Jin, Z.; He, Y.; Huang, P.; He, N.; Chen, S. Tai Chi enhances cognitive training effects on delaying cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s Dementia J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2023, 19, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, A.K.; Olmstead, R.; López Maya, E.; Banijamali, S. Stress reduction for paid home care aides: A feasibility study of mindfulness meditation and Tai Chi interventions. Home Health Care Serv. Q. 2023, 42, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Precision Intervention Group (n = 21) | Standard Intervention Group (n = 29) | Skilled Tai Chi Practitioner (n = 70) | p-Value for Differences between Groups | p-Value for Normality Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 65.2 ± 4.2 | 64.9 ± 3.7 | 36.1 ± 3.5 | N/A | N/A |
| Height (cm) | 162.85 ± 6.53 | 164.43 ± 7.82 | 169.64 ± 11.85 | N/A | N/A |
| Weight (kg) | 69.31 ± 6.92 | 70.87 ± 7.88 | 75.48 ± 7.11 | N/A | N/A |
| Blance (s) | 8.61 ± 4.21 | 7.06 ± 3.13 | N/A | 0.14 | 0.33/0.07 |
| Gripstrength (kg) | 36.17 ± 4.82 | 33.69 ± 6.88 | N/A | 0.16 | 0.97/0.75 |
| SF-12 | 30.39 ± 1.61 | 30.07 ± 4.68 | N/A | 0.76 | 0.42/0.20 |
| BDI | 19.13 ± 8.03 | 19.92 ± 7.07 | N/A | 0.71 | 0.53/0.98 |
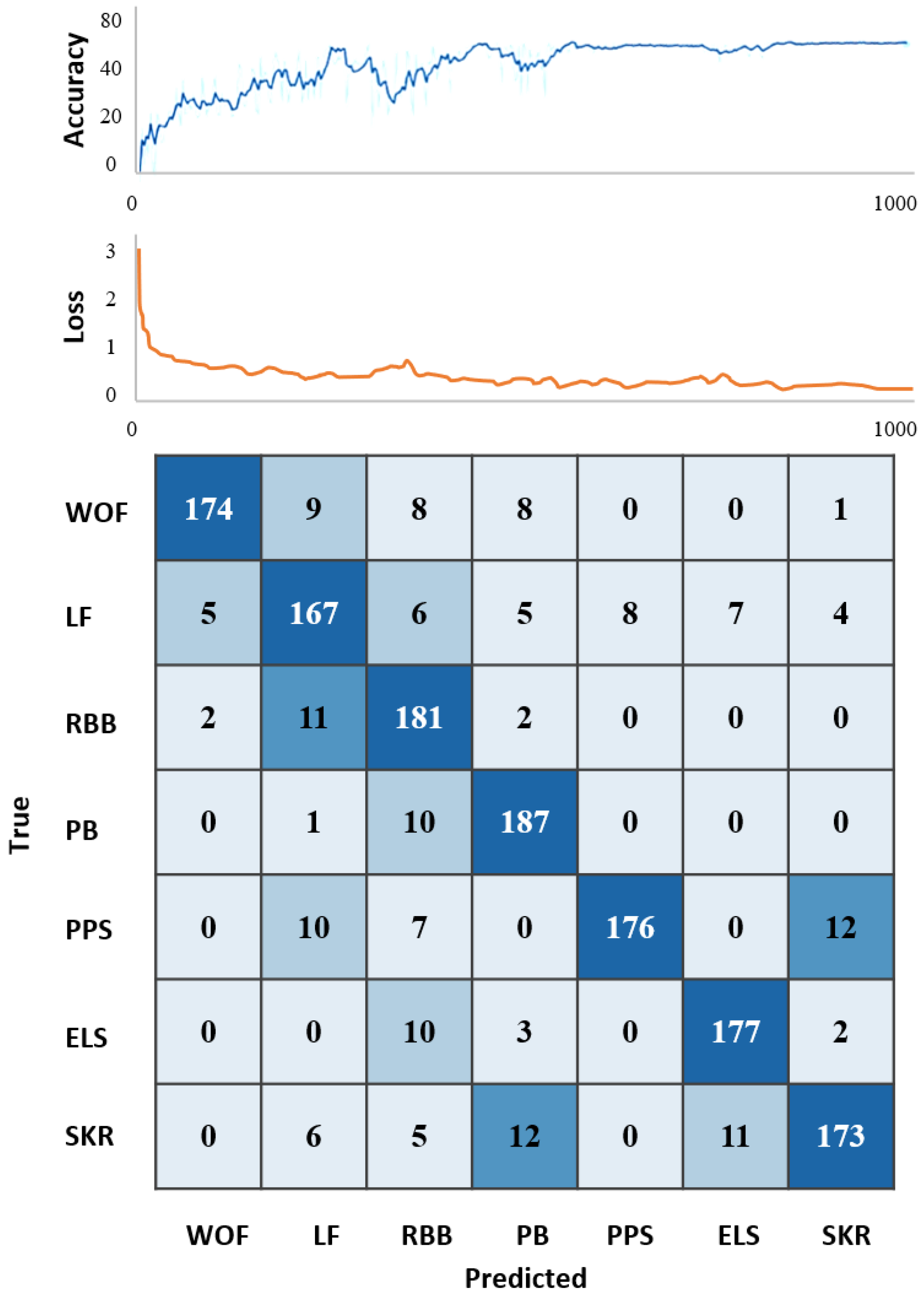
| Motion | True Count | False Count | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| WOF | 174 | 26 | 87.0% |
| LF | 167 | 35 | 82.6% |
| RBB | 181 | 15 | 92.3% |
| PB | 187 | 11 | 94.4% |
| PPS | 176 | 29 | 85.8% |
| ELS | 177 | 15 | 92.1% |
| SKR | 173 | 34 | 83.6% |
| Precision Intervention Group (n = 21) | Standard Intervention Group (n = 29) | Interaction | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | P | Pre | Post | P | P | η2p | |
| Blance (s) | 8.61 ± 4.21 | 10.72 ± 3.50 | 0.010 | 7.06 ± 3.13 | 7.21 ± 2.18 * | 0.136 | 0.059 | 0.075 |
| Gripstrength (kg) | 36.17 ± 4.82 | 39.78 ± 3.22 | 0.000 | 33.69 ± 6.88 | 38.98 ± 5.15 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.196 |
| SF-12 | 30.39 ± 1.61 | 31.46 ± 2.57 | 0.005 | 30.07 ± 4.68 | 30.87 ± 5.94 | 0.005 | 0.670 | 0.004 |
| BDI | 19.13 ± 8.03 | 16.06 ± 3.44 | 0.000 | 19.92 ± 7.07 | 17.90 ± 5.90 | 0.001 | 0.241 | 0.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zou, L.; Li, H. Tai Chi Movement Recognition and Precise Intervention for the Elderly Based on Inertial Measurement Units and Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2024, 24, 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134208
Li X, Zou L, Li H. Tai Chi Movement Recognition and Precise Intervention for the Elderly Based on Inertial Measurement Units and Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors. 2024; 24(13):4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134208
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiongfeng, Limin Zou, and Haojie Li. 2024. "Tai Chi Movement Recognition and Precise Intervention for the Elderly Based on Inertial Measurement Units and Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks" Sensors 24, no. 13: 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134208
APA StyleLi, X., Zou, L., & Li, H. (2024). Tai Chi Movement Recognition and Precise Intervention for the Elderly Based on Inertial Measurement Units and Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors, 24(13), 4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134208






