Experimental Setup for Evaluating Depth Sensors in Augmented Reality Technologies Used in Medical Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
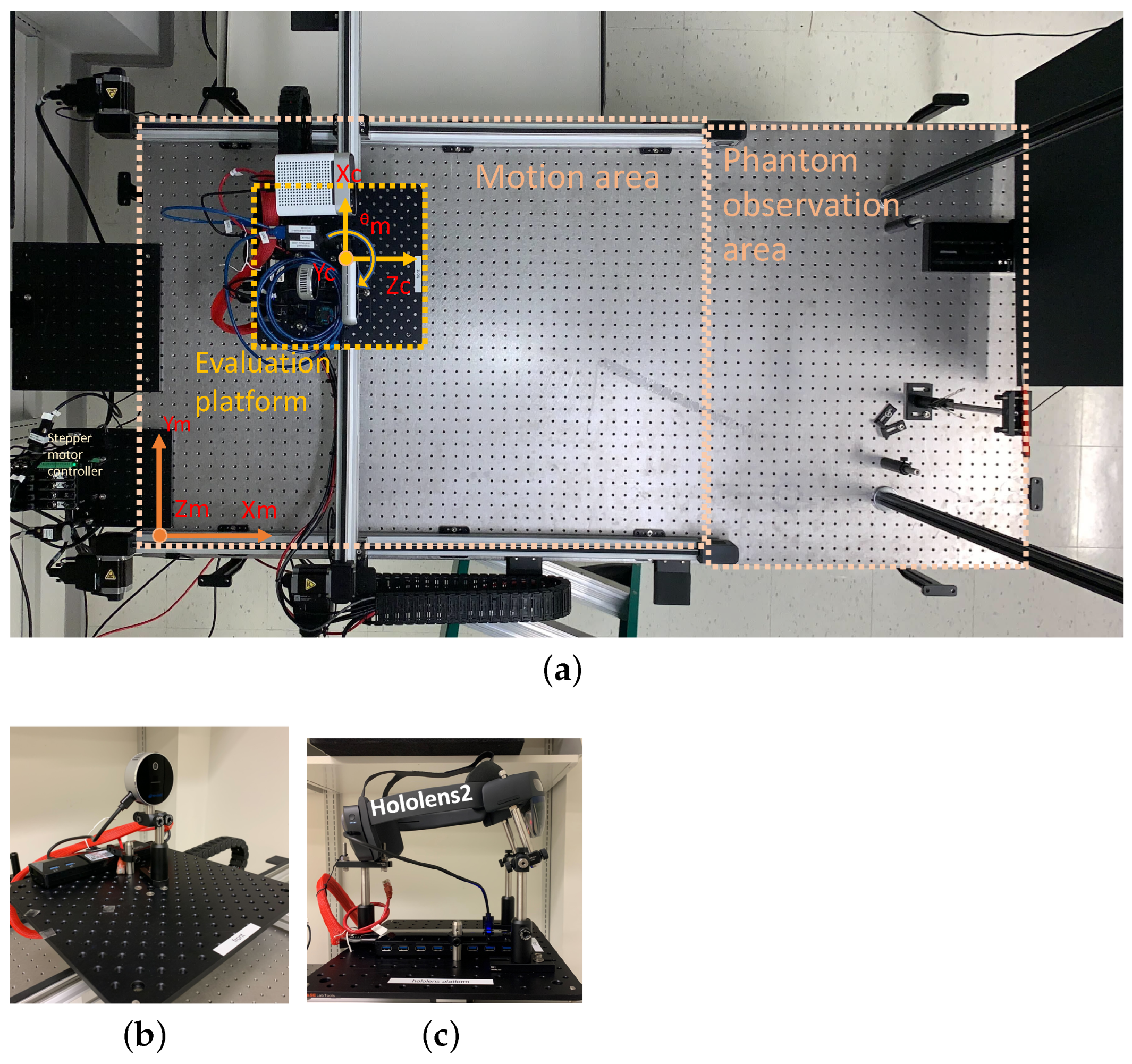
2.2. Modular Experimental Setup with Integrated Control and Data Collection System
Systematic Calibration and Alignment Process for Depth Cameras
3. Examples of Evaluation Studies
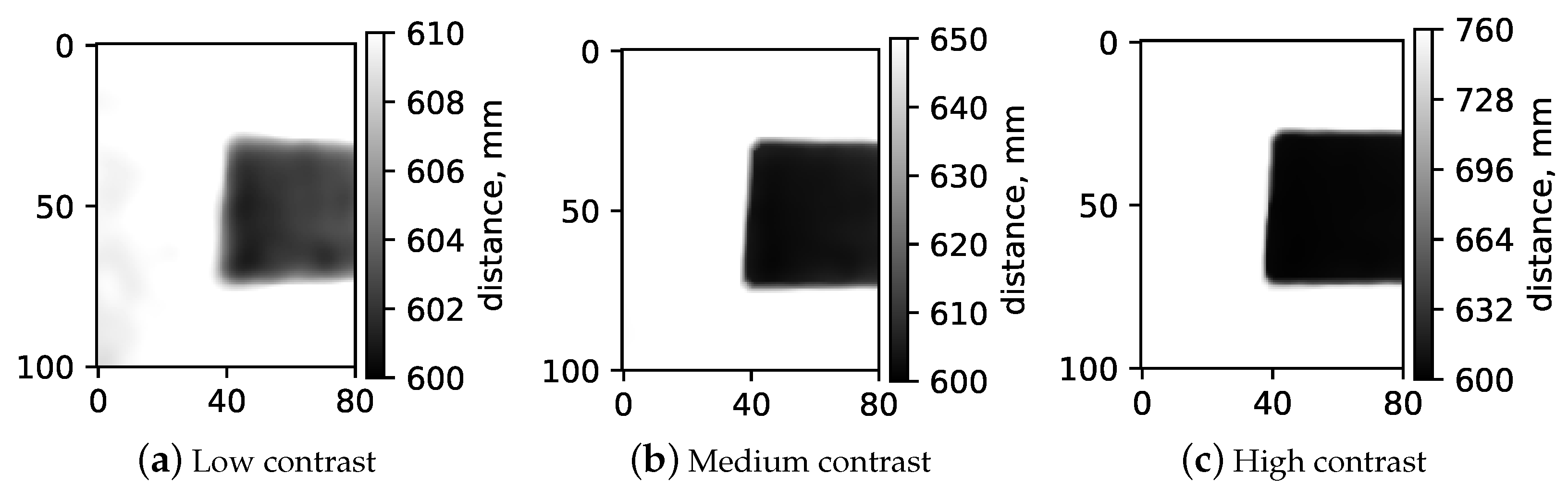
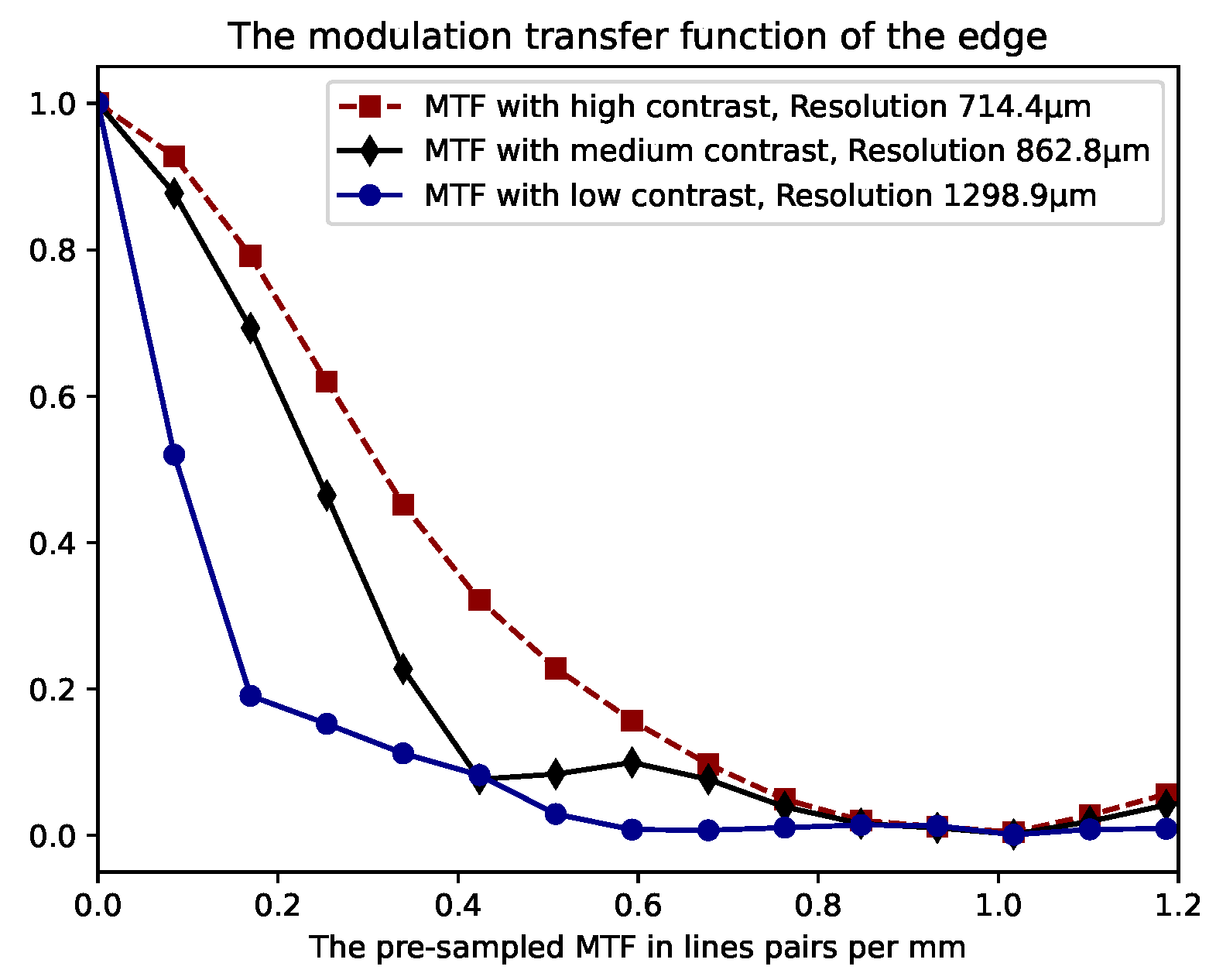
3.1. Image Plane Spatial Resolution
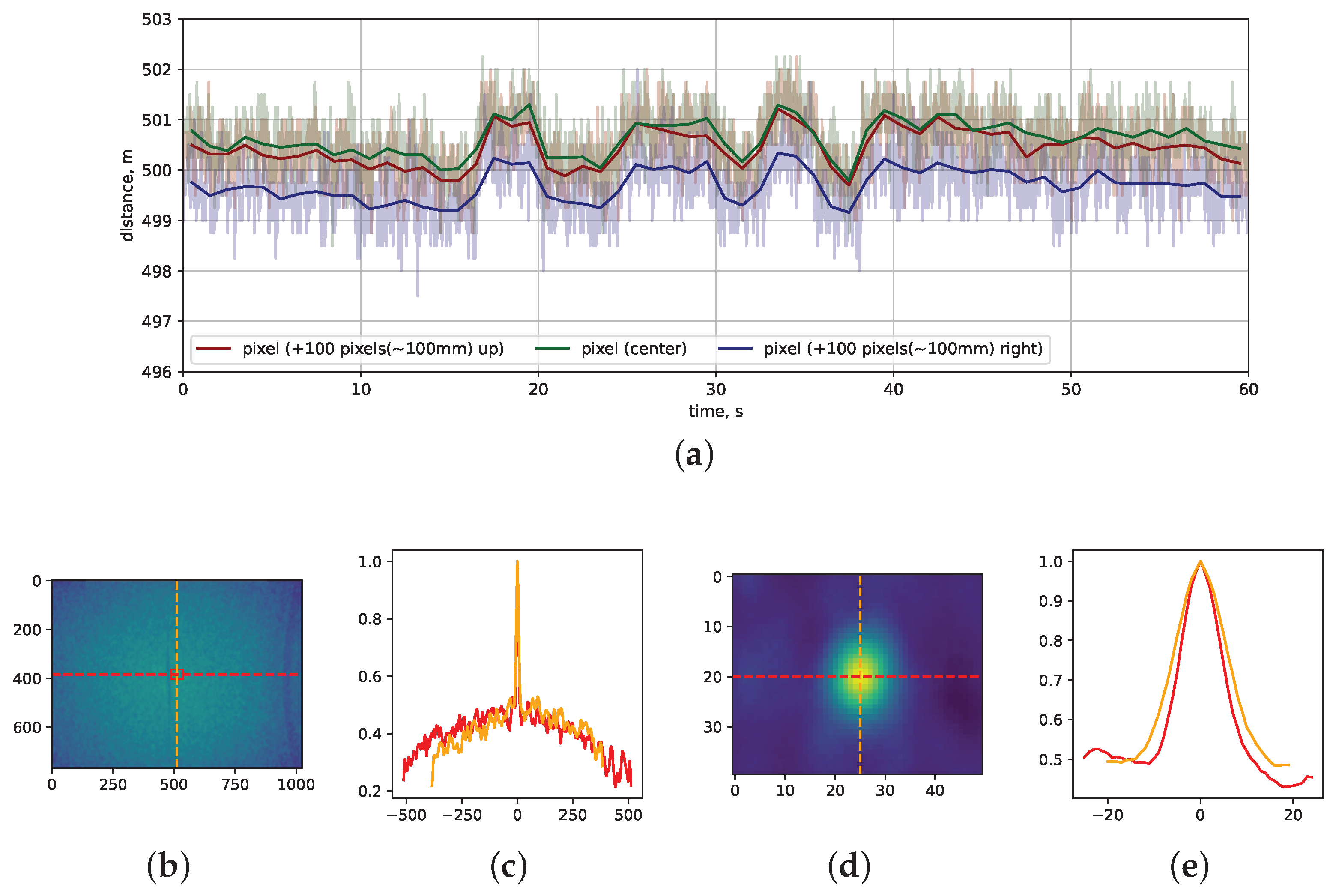
3.2. Z-Precision and Z-Accuracy Measurements
- Root-mean-square error (RMSE) between the observed distance , obtained using a depth sensing camera and the known values of depth camera position, were calculated using a single pixel in the center of the depth image. The RMSE is calculated as follows:
- Accuracy of the z-value measurement, as measured by the depth camera as a deviation of measured mean values and the known camera position, the ground truth. The mean value can be calculated as follows:
- Precision of the z-value measurement, as measured by the depth camera () of measured depth values across different positions of depth camera with respect to the flat wall test object, is calculated as follows:
3.3. Pearson Pixel-to-Pixel Correlation
4. Current State and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| VR | virtual reality |
| XR | Extended Reality |
| MXR | Medical Extended Reality |
| HMD | Head-mounted display |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| CA | California |
| DUT | devices under test |
| GPU | graphics processing unit |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| PD | Power Delivery |
| ROI | region of interest |
| MTF | Modulation Transfer Function |
| RMSE | Root-mean-square error |
| U.S. | United States |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
References
- Sutherland, I.E. A head-mounted three dimensional display. In Proceedings of the AFIPS ’68, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–11 December 1968; pp. 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuscinski, T.; Oszust, M.; Wysocki, M.; Warchol, D. Recognition of Hand Gestures Observed by Depth Cameras. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2015, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.; Eniola, R.O.; Golightly, L.; Xu, Q.A. An Exploration into Human–Computer Interaction: Hand Gesture Recognition Management in a Challenging Environment. SN Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchantchane, R.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Alici, G. A review of hand gesture recognition systems based on noninvasive wearable sensors. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2300207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beams, R.; Brown, E.; Cheng, W.C.; Joyner, J.S.; Kim, A.S.; Kontson, K.; Badano, A. Evaluation Challenges for the Application of Extended Reality Devices in Medicine. J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennler, C.; Bauer, D.E.; Scheibler, A.G.; Spirig, J.; Götschi, T.; Fürnstahl, P.; Farshad, M. Augmented reality in the operating room: A clinical feasibility study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, W.O.C.; Navarro, P.A.; Crispin, S. Intraoperative clinical application of augmented reality in neurosurgery: A systematic review. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 177, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollen, E.; Awad, L.; Langridge, B.; Butler, P.E.M. The intraoperative use of augmented and mixed reality technology to improve surgical outcomes: A systematic review. Int. J. Med Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2022, 18, e2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.; Knight, S.; Guetter, C.; Davis, C.; Moller, M.; Slama, E.; Crandall, M. Telemedicine and telementoring in the surgical specialties: A narrative review. Am. J. Surg. 2019, 218, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, E.; Stein, A.; Levihn-Coon, A.; Pogue, J.; Rothbaum, B.; Emmelkamp, P.; Asmundson, G.; Carlbring, P.; Powers, M. Virtual reality exposure therapy for anxiety and related disorders: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Anxiety Disord. 2019, 61, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkin, D.; Sherman, K.; Balderson, B.; Cook, A.; Anderson, M.; Hawkes, R.; Hansen, K.; Turner, J. Effect of mindfulness-based stress reduction vs cognitive behavioral therapy or usual care on back pain and functional limitations in adults with chronic low back pain: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, B.; Fuller, G.; Lopez, M.; Dupuy, T.; Noah, B.; Howard, A.; Albert, M.; Tashjian, V.; Lam, R.; Ahn, J.; et al. Virtual reality for management of pain in hospitalized patients: A randomized comparative effectiveness trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, A.P.; Addison, P.S.; Smit, P.; Jacquel, D.; Borg, U.R. Noncontact Respiratory Monitoring Using Depth Sensing Cameras: A Review of Current Literature. Sensors 2021, 21, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier Cejnog, L.W.; Marcondes Cesar, R.; de Campos, T.E.; Meirelles Carril Elui, V. Hand range of motion evaluation for Rheumatoid Arthritis patients. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Arteaga-Marrero, N.; Villa, E.; Fabelo, H.; Callicó, G.M.; Ruiz-Alzola, J. Automatic Segmentation Based on Deep Learning Techniques for Diabetic Foot Monitoring Through Multimodal Images. In Image Analysis and Processing—ICIAP 2019; Ricci, E., Rota Bulò, S., Snoek, C., Lanz, O., Messelodi, S., Sebe, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 414–424. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, L.; Sharan, L.; Karl, R.; Wang, C.; Karck, M.; Simone, R.D.; Ivo Wolf, G.R.; Engelhardt, S. Comparative evaluation of three commercially available markerless depth sensors for close-range use in surgical simulation. Int. J. CARS 2023, 18, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Farid, F.; Hashim, N.; Abdullah, J.; Bhuiyan, M.R.; Shahida Mohd Isa, W.N.; Uddin, J.; Haque, M.A.; Husen, M.N. A Structured and Methodological Review on Vision-Based Hand Gesture Recognition System. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, S.B. Optical see-through holographic near-eye-display with eyebox steering and depth of field control. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 27076–27088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarthula, P.; Peng, Y.; Kollin, J.; Fuchs, H.; Heide, F. Wirtinger holography for near-eye displays. Acm Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intel® RealSense™ LiDAR Camera L515 User Guide. Available online: https://support.intelrealsense.com/hc/en-us/articles/360051646094-Intel-RealSense-LiDAR-Camera-L515-User-Guide (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Herrera, C.D.; Kannala, J.; Heikkilä, J. Accurate and Practical Calibration of a Depth and Color Camera Pair. In Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, B.; Bai, X.; Wu, W.; Liu, H. Analysis of the Slanted-Edge Measurement Method for the Modulation Transfer Function of Remote Sensing Cameras. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granton, P. Slant Edge Script. MATLAB Central File Exchange. 2023. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/28631-slant-edge-script (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Janse, R.J.; Hoekstra, T.; Jager, K.J.; Zoccali, C.; Tripepi, G.; Dekker, F.W.; van Diepen, M. Conducting correlation analysis: Important limitations and pitfalls. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2332–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Pearson Education: Noida, India, 1999. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stadnytskyi, V.; Ghammraoui, B. Experimental Setup for Evaluating Depth Sensors in Augmented Reality Technologies Used in Medical Devices. Sensors 2024, 24, 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123916
Stadnytskyi V, Ghammraoui B. Experimental Setup for Evaluating Depth Sensors in Augmented Reality Technologies Used in Medical Devices. Sensors. 2024; 24(12):3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123916
Chicago/Turabian StyleStadnytskyi, Valentyn, and Bahaa Ghammraoui. 2024. "Experimental Setup for Evaluating Depth Sensors in Augmented Reality Technologies Used in Medical Devices" Sensors 24, no. 12: 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123916
APA StyleStadnytskyi, V., & Ghammraoui, B. (2024). Experimental Setup for Evaluating Depth Sensors in Augmented Reality Technologies Used in Medical Devices. Sensors, 24(12), 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24123916






