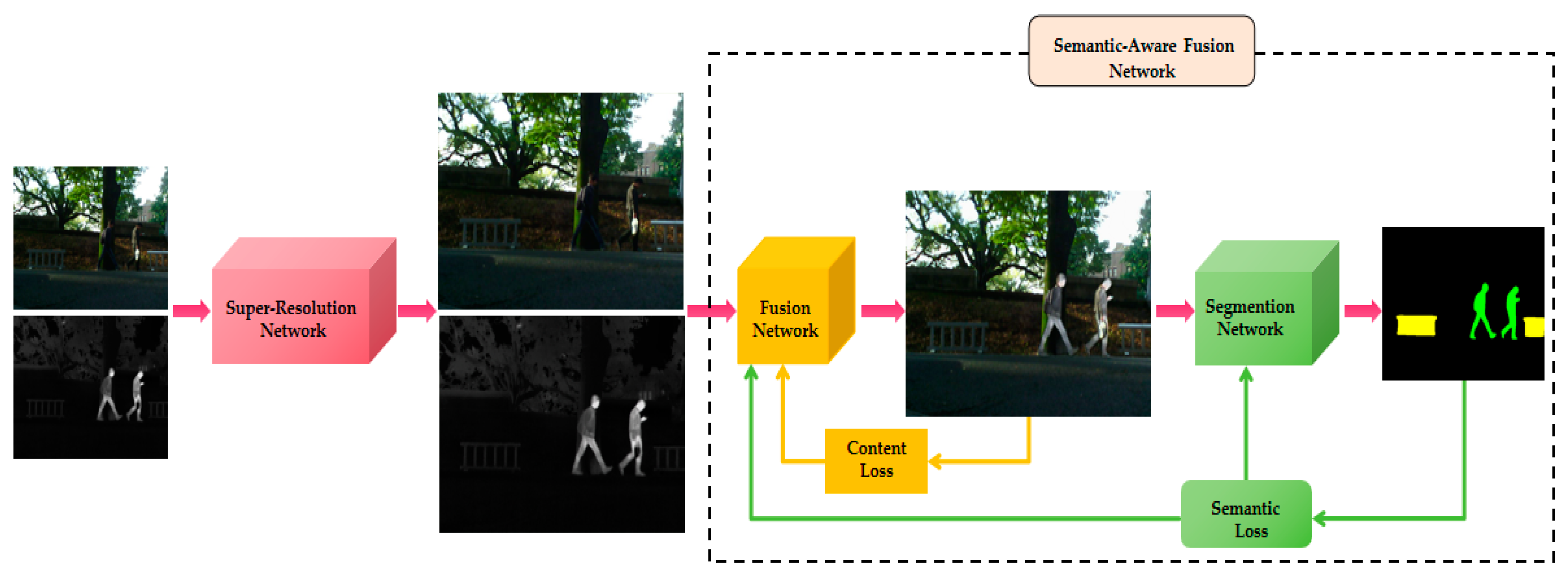
Semantic-Aware Fusion Network Based on Super-Resolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel semantic-aware fusion framework for infrared and visible images based on super-resolution has been ingeniously crafted by integrating super-resolution networks, fusion networks, and segmentation networks. This framework not only excels in image fusion but also achieves outstanding performance in high-level vision tasks.
- In the fusion network, a comprehensive information extraction module is designed, aiming at efficiently processing high-resolution images and achieving more comprehensive fine-grained complementary feature extraction.
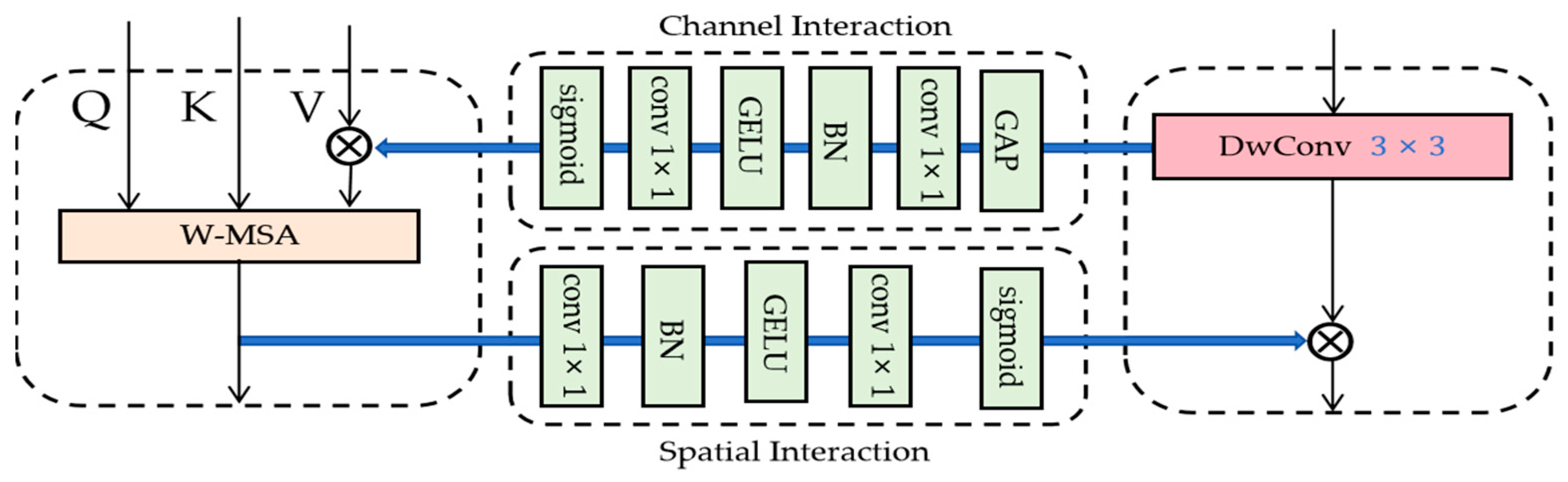
- In the super-resolution network, a multi-branch hybrid attention module is designed to endow the network with strong cross-domain adaptation capability. This means that excellent super-resolution reconstruction results can be achieved even when dealing with cross-modal image super-resolution.
2. Related Works
2.1. Image Fusion Algorithms
2.1.1. Traditional Image Fusion Methods
2.1.2. AE-Based Image Fusion Methods
2.1.3. CNN-Based Image Fusion Methods
2.1.4. GAN-Based Image Fusion Methods
2.2. Image Super-Resolution
2.3. Task-Driven Low-Level Vision Algorithms
3. Proposed Methods
3.1. Problem Formulation
3.2. Loss Function
3.2.1. Content Loss
3.2.2. Semantic Loss
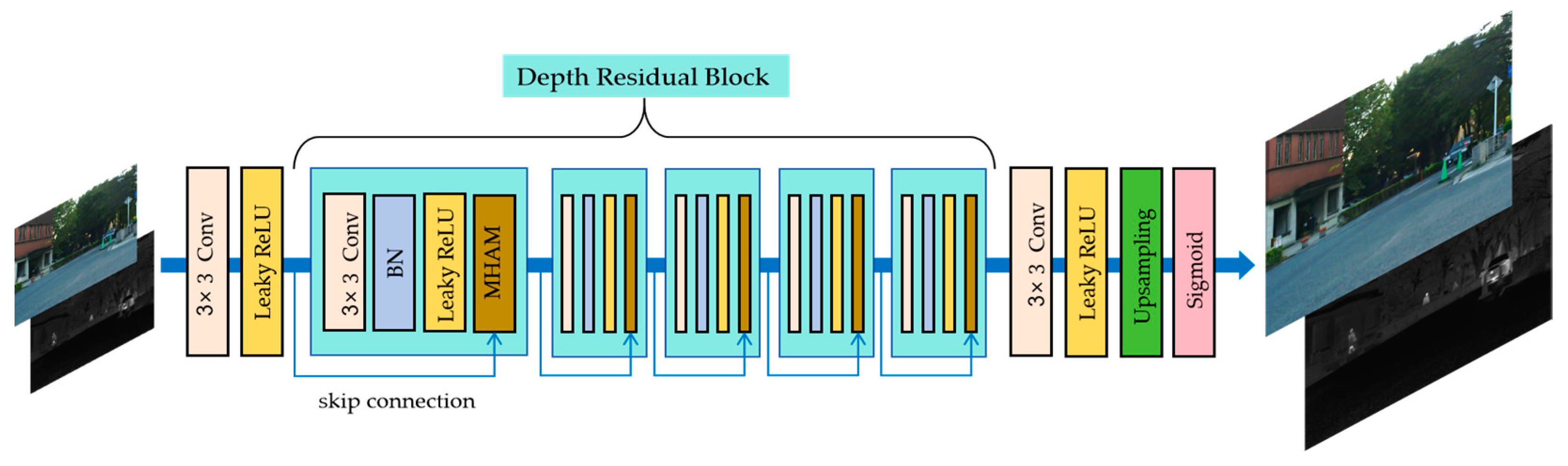
3.3. Super-Resolution Network Framework
3.4. Fusion Network Framework
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Configurations
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparative Experiment
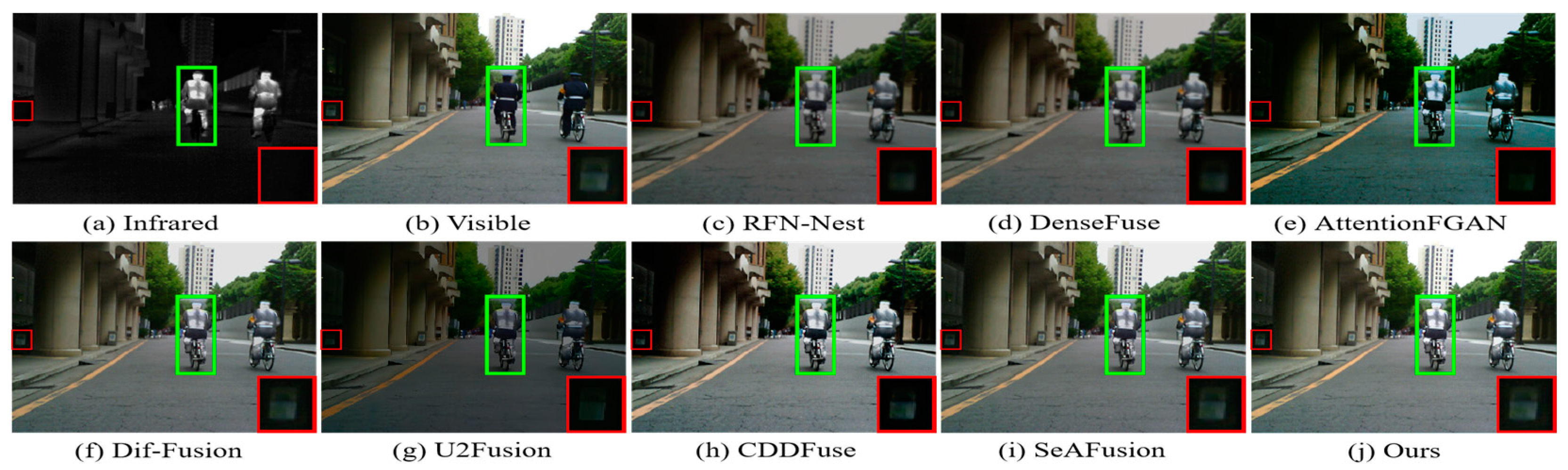
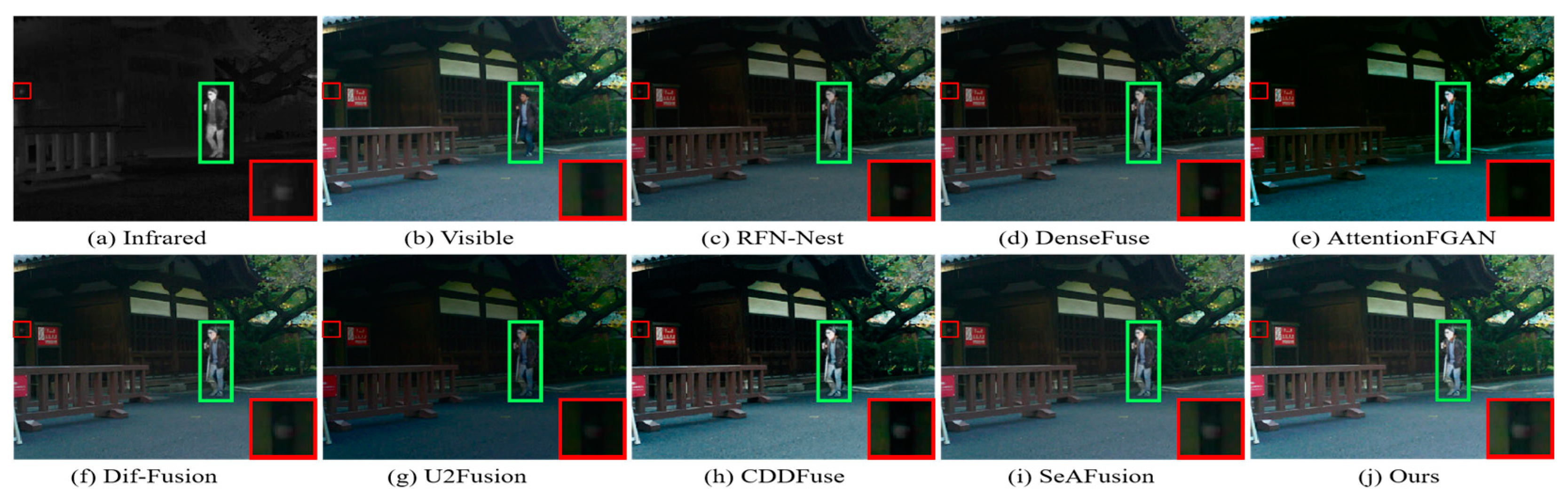
4.3.1. Qualitative Results
4.3.2. Qualitative Results
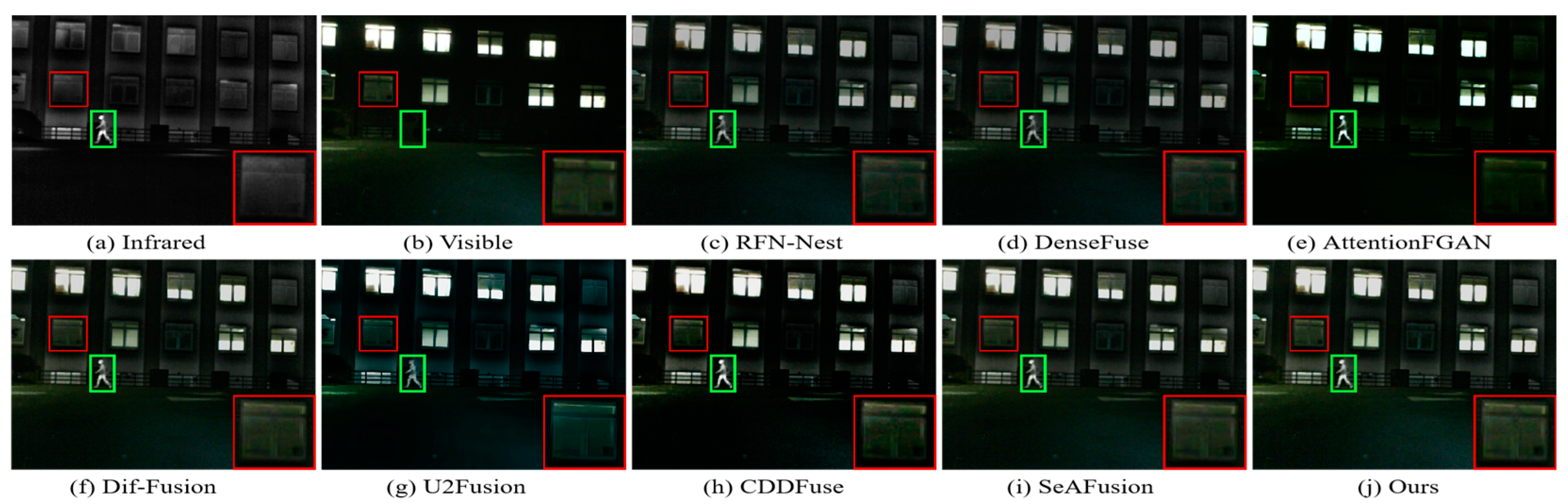
4.4. Generalization Experiment
4.4.1. Qualitative Results
4.4.2. Qualitative Results
4.4.3. Efficiency Comparison
4.4.4. Overfitting Analysis
4.4.5. Parameters Analysis
4.5. Task-Driven Evaluation
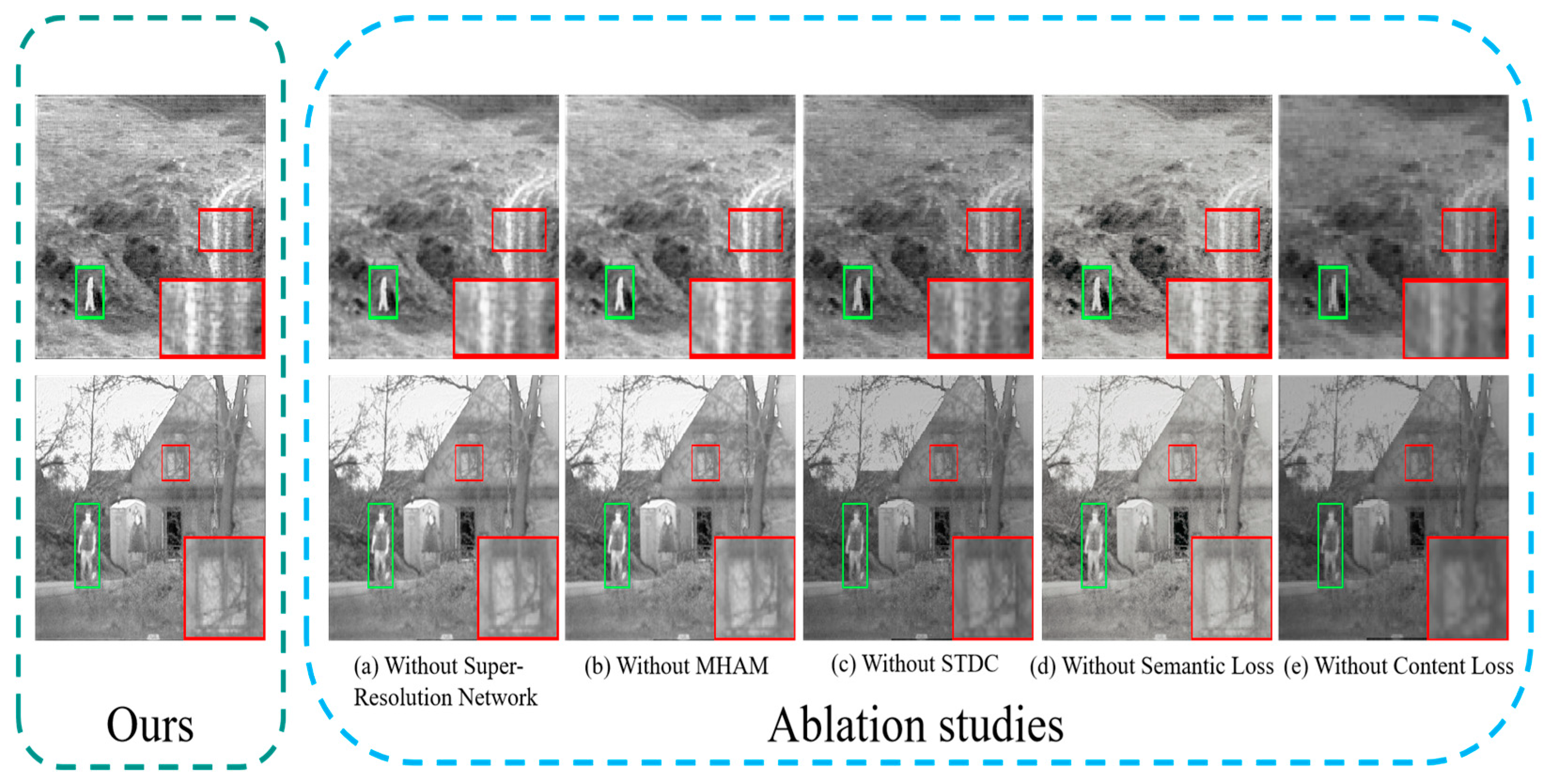
4.6. Ablation Studies
4.6.1. Super-Resolution Network Analysis
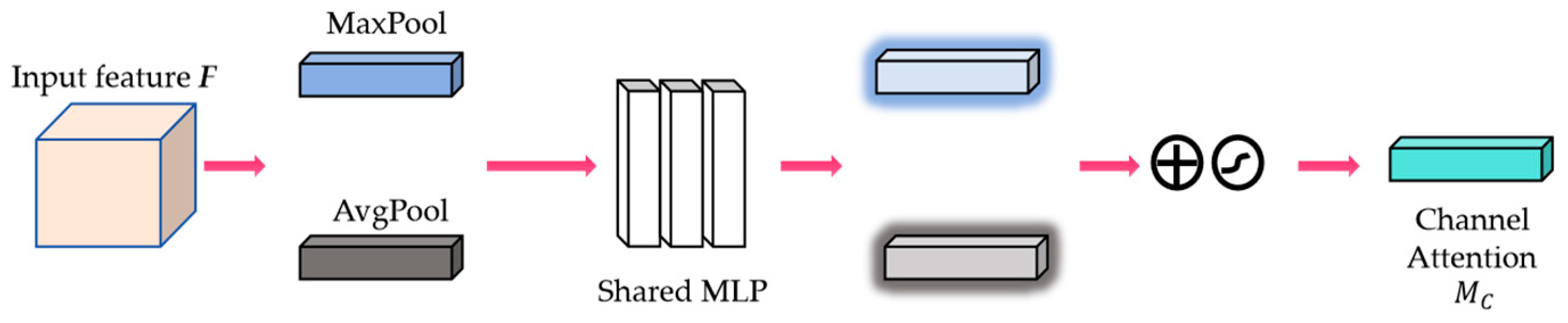
4.6.2. Multi-Branch Hybrid Attention Module Analysis
4.6.3. Comprehensive Information Extraction Module Analysis
4.6.4. Semantic Loss Analysis
4.6.5. Content Loss Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Chu, Q.; Yu, N. Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, DC, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13379–13389. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Guan, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Qiao, Y. Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multispectral feature learning using deep neural networks. Inf. Fusion 2019, 46, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, L. Cross-modal ranking with soft consistency and noisy labels for robust RGB-T tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6 October 2018; pp. 831–847. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Q.; Watanabe, K.; Karasawa, T.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5108–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Dong, X. Region level based multi-focus image fusion using quaternion wavelet and normalized cut. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, D.; Sert, E.; Özyurt, F.; Avcı, E. MFIF-DWT-CNN: Multi-focus image fusion based on discrete wavelet transform with deep convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 10951–10968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamaleki, J.; Ghorbani, A. Image fusion using dual tree discrete wavelet transform and weights optimization. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xi, X.; Li, D.; Li, F.; Zhang, G. GRPAFusion: A gradient residual and pyramid attention-based multiscale network for multimodal image fusion. Entropy 2023, 25, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Li, W.; Xiao, B.; Nawaz, Q. Union Laplacian pyramid with multiple features for medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 2016, 194, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.; Xue, L.; Lin, L.; Xiao, M.; Jia, M. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sadjadi, F. Comparative image fusion analysais. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Maldague, X. An adaptive fusion approach for infrared and visible images based on NSCT and compressed sensing. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 74, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, B. Multifocus image fusion by combining curvelet and wavelet transform. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2008, 29, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jin, S.; Bian, G.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B. A curvelet-transform-based image fusion method incorporating side-scan sonar image features. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.; Kittler, J. MDLatLRR: A novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.; Wang, Z. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Patel, V.; Nasrabadi, N.; Chellappa, R. Joint sparse representation for robust multimodal biometrics recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvejic, N.; Bull, D.; Canagarajah, N. Region-based multimodal image fusion using ICA bases. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J.; Gao, W.; Song, Z. Image fusion based on non-negative matrix factorization and infrared feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (CISP), Hangzhou, China, 16–18 December 2013; pp. 1046–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, Y. Infrared and visible images fusion based on RPCA and NSCT. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 77, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Zong, H. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, B. Hybrid multiresolution method for multisensor multimodal image fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Feng, X.; He, G.; Wu, J.; Yan, K. Image fusion with nonsubsampled contourlet transform and sparse representation. J. Electron. Imaging 2013, 22, 043019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Tang, L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via parallel scene and texture learning. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 132, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J. Classification saliency-based rule for visible and infrared image fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, J. DRF: Disentangled representation for visible and infrared image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5006713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, H. An end-to-end multi-scale network based on autoencoder for infrared and visible image fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 20139–20156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5009513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, Y. RXDNFuse: A aggregated residual dense network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 69, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, M.; Ma, J. DIVFusion: Darkness-free infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.; Xu, T.; Wu, X. TGFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion approach based on transformer and generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Lu, G. Feature dynamic alignment and refinement for infrared–visible image fusion: Translation robust fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 95, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liang, P.; Yu, W.; Chen, C.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via detail preserving adversarial learning. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X. DDcGAN: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Tian, X.; Ma, J. GAN-FM: Infrared and visible image fusion using GAN with full-scale skip connection and dual Markovian discriminators. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, R. Unsupervised misaligned infrared and visible image fusion via cross-modality image generation and registration. arXiv 2022. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Fang, L.; Xia, S.; Deng, Y.; Ma, J. Dif-fusion: Towards high color fidelity in infrared and visible image fusion with diffusion models. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 5705–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Lin, Z.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Cddfuse: Correlation-driven dual-branch feature decomposition for multi-modality image fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5906–5916. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, accepted. arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6 October 2018; pp. 286–301. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Gu, S.; Duan, Y. Deep coupled feedback network for joint exposure fusion and image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3098–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, R.; Yang, K.; Zou, K.J.T.V.C. MFFN: Image super-resolution via multi-level features fusion network. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Xue, F.; Gao, D. No-Reference Hyperspectral Image Quality Assessment via Ranking Feature Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Kan, Z.; Sanchez, A.; Zhao, Q.; He, G. Image Quality Assessment of UAV Hyperspectral Images Using Radiant, Spatial, and Spectral Features Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 5501805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wei, L.; Yang, L.; Xu, L. A method to improve full-resolution remote sensing pansharpening image quality assessment via feature combination. Signal Process. 2023, 208, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lin, W.; Xu, X.; Lin, L.; Zhao, T. Face Super-Resolution Quality Assessment Based On Identity and Recognizability. IEEE T-BIOM 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, R. RISTRA: Recursive Image Super-resolution Transformer with Relativistic Assessment. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2024, 26, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G. Multispectral and hyperspectral image fusion in remote sensing: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2023, 89, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5792–5801. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Q. Detfusion: A detection-driven infrared and visible image fusion network. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 4003–4011. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Tian, T.; Chen, C.; Guo, X.; Ma, J. Bilateral attention decoder: A lightweight decoder for real-time semantic segmentation. Neural Netw. 2021, 137, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, W.; Jong, P.; Joon, L.; In, S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6 October 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.; Kittler, J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Q. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and visible image fusion using attention-based generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2020, 23, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toet, A. The TNO multiband image data collection. Data Brief 2017, 15, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.; Van, J.; Ahmed, F. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023522. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, G.; Zhang, D.; Yan, P. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, A.; Fisher, P. Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 2959–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, K.; Sai, V.; Venkatesh, R. Deepfuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4714–4722. [Google Scholar]







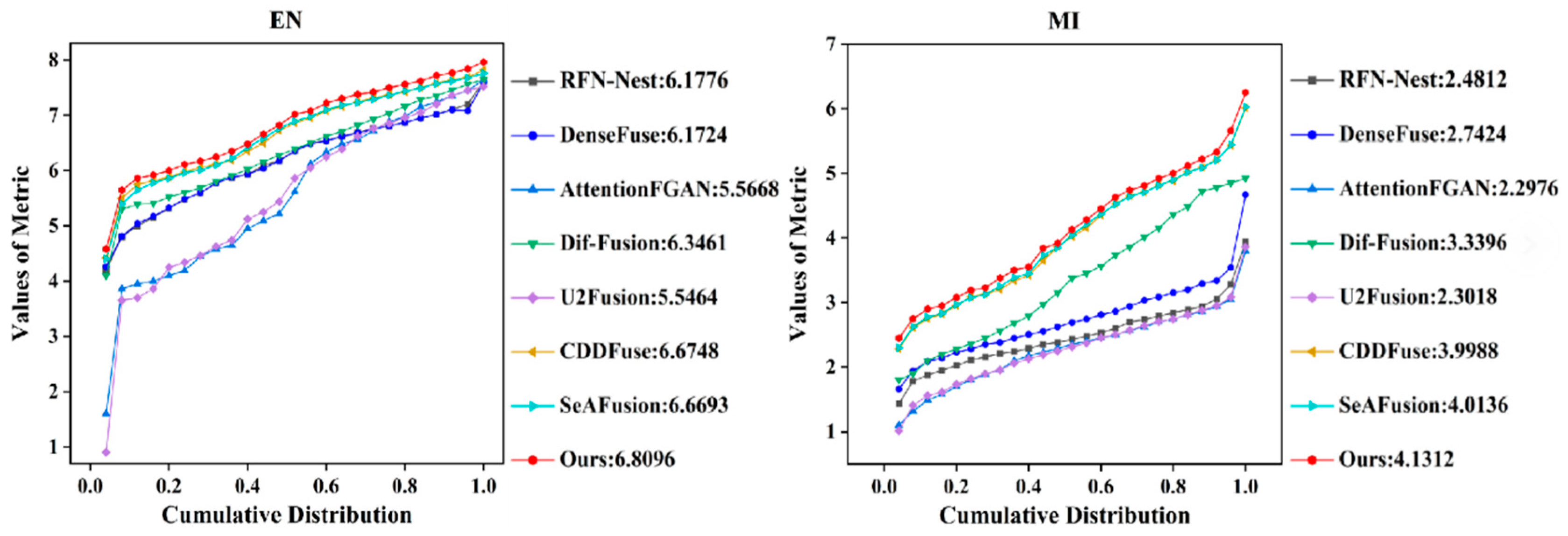
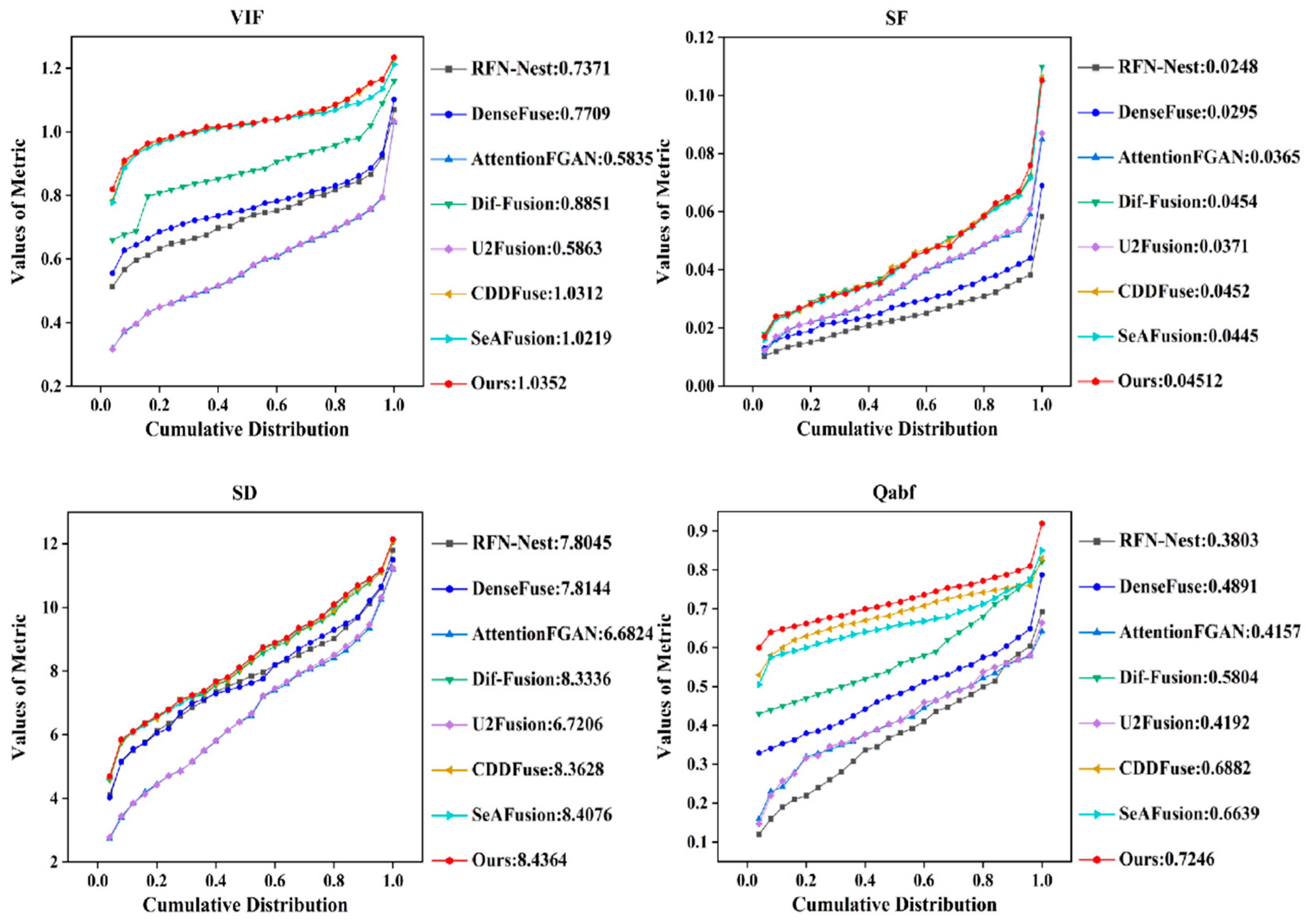








| Methods | EN | MI | VIF | SF | SD | Qabf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFN-Nest | 7.2978 | 2.7287 | 0.7234 | 0.0288 | 9.9871 | 0.3465 |
| DenseFuse | 7.1293 | 2.9048 | 0.7343 | 0.0375 | 9.9172 | 0.4763 |
| AttentionFGAN | 7.1521 | 2.7203 | 0.7041 | 0.0451 | 10.0182 | 0.4821 |
| Dif-Fusion | 7.4284 | 3.3072 | 0.8053 | 0.0516 | 10.1067 | 0.5181 |
| U2Fusion | 7.1681 | 2.7193 | 0.7053 | 0.0498 | 10.0191 | 0.4901 |
| CDDFuse | 7.4396 | 3.1493 | 0.8321 | 0.0523 | 10.6732 | 0.5198 |
| SeAFusion | 7.5947 | 3.2389 | 0.9182 | 0.0643 | 10.6648 | 0.4922 |
| Ours | 7.6326 | 3.2903 | 0.9191 | 0.0648 | 10.6714 | 0.5215 |
| Methods | EN | MI | VIF | SF | SD | Qabf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFN-Nest | 6.8676 | 2.0234 | 0.7678 | 0.0252 | 9.2451 | 0.3392 |
| DenseFuse | 6.7388 | 2.1961 | 0.7653 | 0.0375 | 9.1376 | 0.4346 |
| AttentionFGAN | 6.8382 | 2.7203 | 0.7441 | 0.0463 | 9.3148 | 0.4821 |
| Dif-Fusion | 7.0865 | 2.6213 | 0.9248 | 0.0541 | 9.4341 | 0.4594 |
| U2Fusion | 6.8915 | 1.9876 | 0.7661 | 0.0486 | 9.3268 | 0.4293 |
| CDDFuse | 7.1986 | 2.1886 | 0.8713 | 0.0511 | 9.4152 | 0.5068 |
| SeAFusion | 7.1241 | 2.7654 | 0.9512 | 0.0522 | 9.4458 | 0.4876 |
| Ours | 7.1832 | 2.8235 | 0.9636 | 0.0534 | 9.4762 | 0.5209 |
| Methods | MSRS | RoadScene | TNO |
|---|---|---|---|
| RFN-Nest | 0.1924 ± 0.0901 | 0.1146 ± 0.0224 | 0.1951 ± 0.0979 |
| DenseFuse | 0.2828 ± 0.1532 | 0.6064 ± 0.0804 | 0.6791 ± 0.2955 |
| U2Fusion | 0.1351 ± 0.1350 | 0.7484 ± 0.0929 | 0.5507 ± 0.5186 |
| SeAFusion | 0.0115 ± 0.1081 | 0.0060 ± 0.0025 | 0.0049 ± 0.0017 |
| Ours | 0.0107 ± 0.1069 | 0.0053 ± 0.0018 | 0.0043 ± 0.0012 |
| EN | MI | VIF | SF | SD | Qabf | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y = 1, β = 0 | 5.5134 | 2.9752 | 0.8653 | 0.0337 | 6.9865 | 0.5793 |
| y = 2, β = 1 | 5.9431 | 3.3268 | 0.9173 | 0.0376 | 7.4578 | 0.6263 |
| y = 3, β = 2 | 6.4576 | 3.7454 | 0.9662 | 0.0402 | 7.9376 | 0.6763 |
| y = 4, β = 3 | 6.7868 | 4.1128 | 1.0216 | 0.0442 | 8.4275 | 0.7174 |
| y = 5, β = 4 | 6.8096 | 4.1312 | 1.0352 | 0.0451 | 8.4364 | 0.7246 |
| Backgroud | Car | Person | Bike | Curve | Car Stop | Guardrail | Color Tone | Bump | mIoU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visible | 98.27 | 89.05 | 59.96 | 70.05 | 60.72 | 71.46 | 77.91 | 63.43 | 75.34 | 74.02 |
| Infrared | 98.23 | 87.34 | 70.51 | 69.27 | 58.77 | 68.91 | 65.57 | 56.95 | 72.76 | 72.03 |
| RFN-Nest | 98.51 | 89.94 | 72.12 | 71.41 | 62.07 | 74.91 | 74.86 | 63.42 | 79.55 | 76.31 |
| DenseFuse | 98.51 | 89.35 | 72.79 | 71.71 | 63.41 | 72.17 | 74.45 | 64.89 | 80.12 | 76.38 |
| AttentionFGAN | 98.50 | 89.29 | 72.08 | 70.99 | 62.82 | 73.63 | 76.12 | 63.17 | 77.05 | 75.96 |
| Dif-Fusion | 98.53 | 90.11 | 74.22 | 72.04 | 64.18 | 73.72 | 82.14 | 63.42 | 80.95 | 77.70 |
| U2Fusion | 98.52 | 89.80 | 72.91 | 71.12 | 62.19 | 72.16 | 79.25 | 63.61 | 77.14 | 76.38 |
| CDDFuse | 98.54 | 90.15 | 74.18 | 72.06 | 64.14 | 74.01 | 82.84 | 66.38 | 81.14 | 78.16 |
| SeAFusion | 98.60 | 90.41 | 74.30 | 72.16 | 65.01 | 74.08 | 85.21 | 66.50 | 81.40 | 78.63 |
| Ours | 98.63 | 90.61 | 74.56 | 72.45 | 65.38 | 74.48 | 85.38 | 66.63 | 81.58 | 78.86 |
| Car | Person | Bike | mIoU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Super-Resolution Network | 90.46 | 74.38 | 72.26 | 78.67 |
| Without MHAM | 90.56 | 74.48 | 72.37 | 78.81 |
| Without STDC | 90.53 | 74.45 | 72.35 | 78.78 |
| Without Semantic Loss | 89.52 | 71.57 | 71.05 | 76.41 |
| Without Content Loss | 89.94 | 73.02 | 71.65 | 77.11 |
| Ours | 90.61 | 74.56 | 72.45 | 78.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Zou, Q. Semantic-Aware Fusion Network Based on Super-Resolution. Sensors 2024, 24, 3665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113665
Xu L, Zou Q. Semantic-Aware Fusion Network Based on Super-Resolution. Sensors. 2024; 24(11):3665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113665
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Lingfeng, and Qiang Zou. 2024. "Semantic-Aware Fusion Network Based on Super-Resolution" Sensors 24, no. 11: 3665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113665
APA StyleXu, L., & Zou, Q. (2024). Semantic-Aware Fusion Network Based on Super-Resolution. Sensors, 24(11), 3665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113665






