Development of Low-Contact-Impedance Dry Electrodes for Electroencephalogram Signal Acquisition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Fabrication and Packaging
3.1. Fabrication of Dry EEG Electrodes
3.2. Fabrication of Dry EEG Head Caps
4. Test Results and Discussion
4.1. Impedance Test
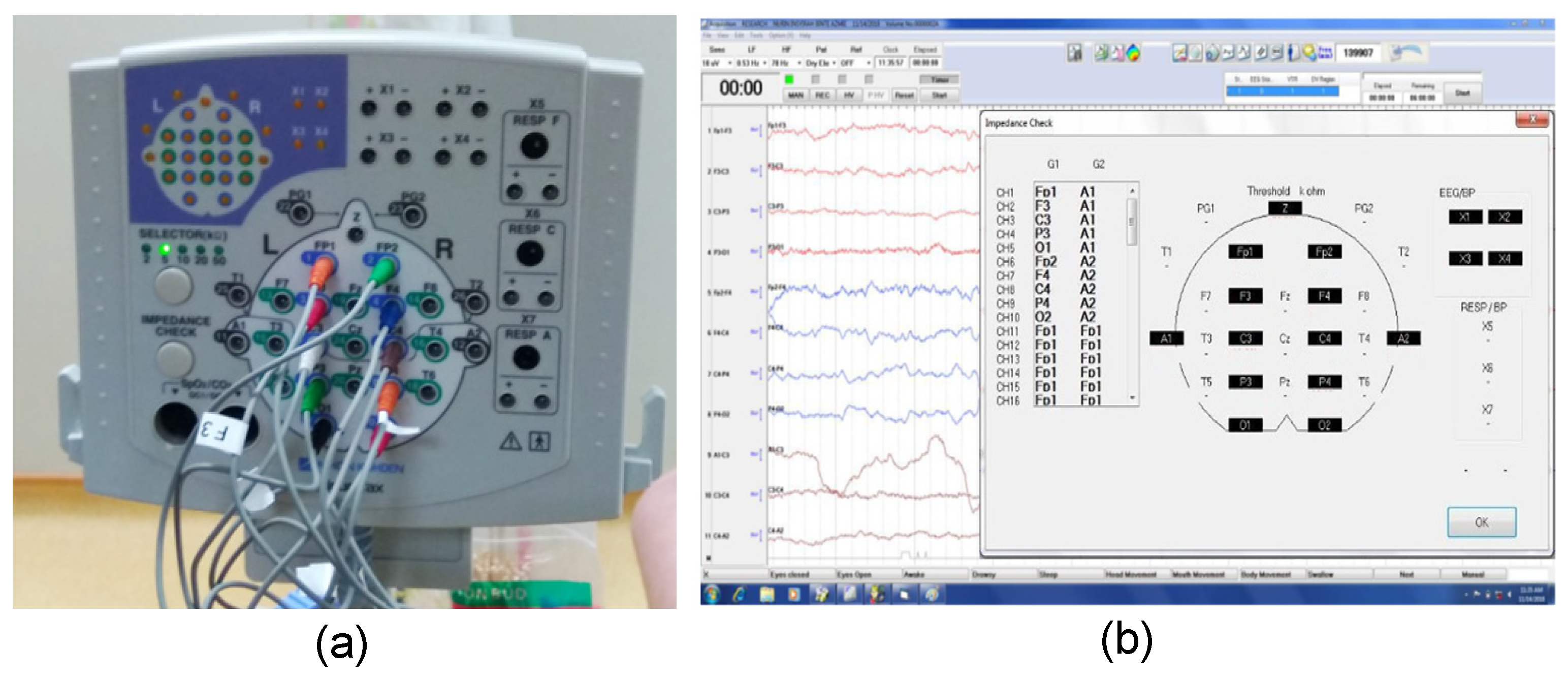
4.1.1. Impedance Readings Obtained Using the Nihon Kohden EEG System
- Testing was performed using only dry EEG electrodes attached to the fabricated 10-channel head cap. The ground electrode (Z) and reference electrodes (A1 and A2) were also dry electrodes.
- Testing was performed again by replacing five dry electrodes, namely A1, A2, C3, C4, and Z, with wet electrodes.
- Testing was reperformed using only conventional wet electrodes.
4.1.2. Impedance Readings Obtained Using the NuAmps Amplifier
4.2. EEG Signal Recording
4.2.1. Verification of the Pairing of the Fabricated Dry EEG Electrodes
4.2.2. Capturing EEG Signals by Using Self-Developed Circuitry
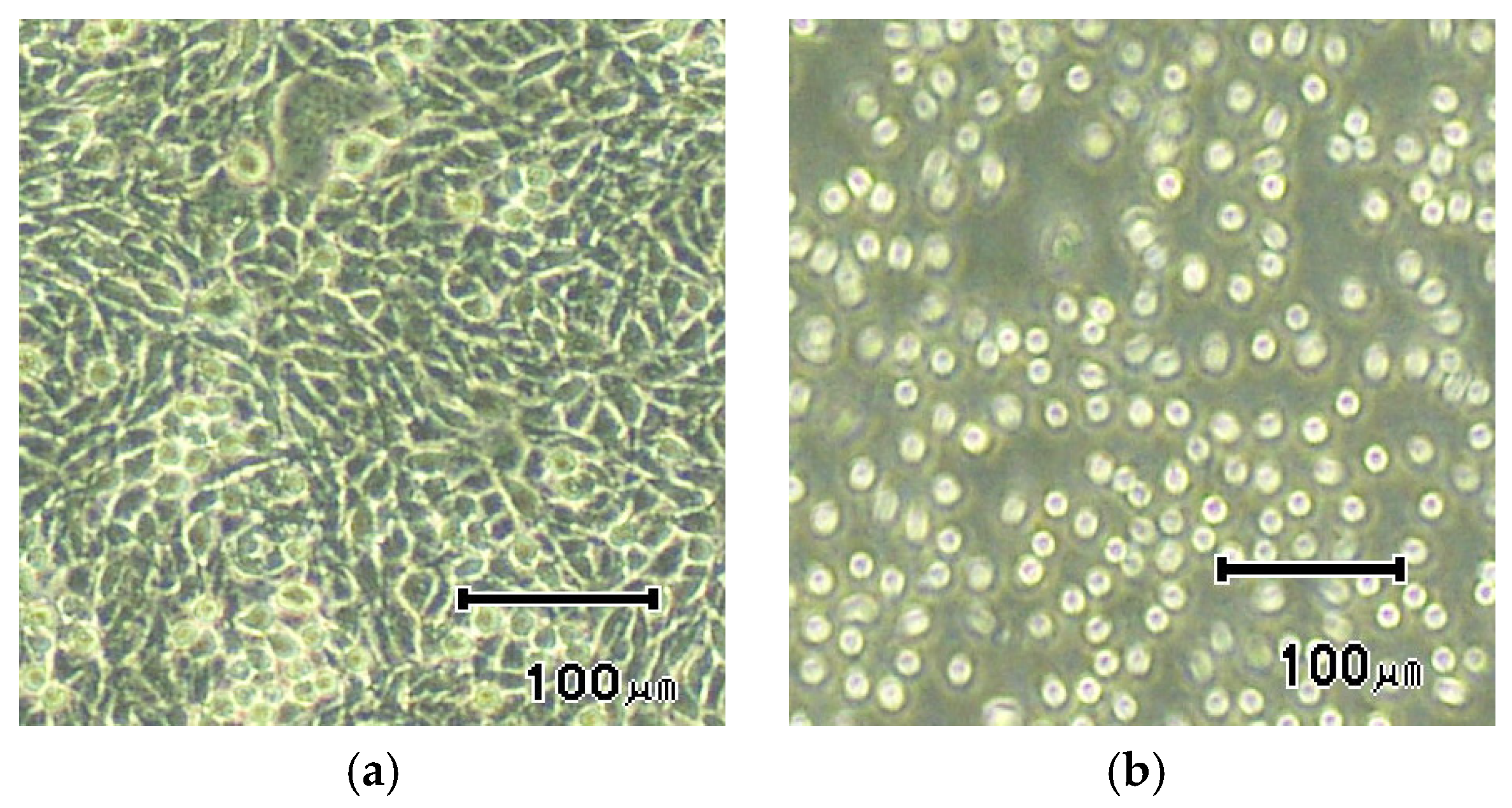
4.3. Primary Skin Irritation Tests and Biocompatibility Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, M.; Tiwari, J.; Acharya, U. Automatic Sleep-Stage Scoring in Healthy and Sleep Disorder Patients Using Optimal Wavelet Filter Bank Technique with EEG Signals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, M.; Schindler, K.; Rao, V. Under-sampling in epilepsy: Limitations of conventional EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2021, 6, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Reyes, L.-M.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; Avecilla-Ramírez, G.; García-Gomar, M.-L.; Robles-Ocampo, J.-B. Impact of EEG Parameters Detecting Dementia Diseases: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78060–78074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Simon, L.; Doval, S.; Nebreda, A.; Linas, S.J.; Marsh, E.; Maestu, F. Understanding brain function in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia with EEG and MEG: A systematic review. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 35, 103040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Gómez, M.; Keijzer, H.; Ruijter, B.; Bruña, R.; Tjepkema-Cloostermans, M.; Hofmeijer, J.; van Putten, M. EEG functional connectivity contributes to outcome prediction of postanoxic coma. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcao, S.; Fonseca, M. Emotions recognition using EEG signals: A survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 10, 374–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer; Das, S.; Teotia, R.; Maheshwari, S. CNN and LSTM based ensemble learning for humanemotion recognition using EEG recording. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 4883–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guo, Y.; Hao, S.; Hong, R. Exploring Self-Attention Graph Pooling With EEG-Based Topological Structure and Soft Label for Depression Detection. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2022, 13, 2106–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygin, M.; Yaman, O.; Tuncer, T.; Dogan, S.; Barua, P.D.; Acharya, U.R. Automated accurate schizophrenia detection system using Collatz pattern technique with EEG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.; Chua, K.; Guan, C.; Ang, B.; Kuah, C.; Wang, C.; Phua, K.; Chin, Z.; Zhang, H. Clinical study of neurorehabilitation in stroke using EEG-based motor imagery brain-computer interface with robotic feedback. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cincotti, F.; Pichiorri, F.; Arico, P.; Aloise, F.; Leotta, F.; de Vico Fallani, F.; del R. Millán, J.; Molinari, M.; Mattia, D. EEG-based Brain-Computer Interface to support post-stroke motor rehabilitation of the upper limb. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, G.; Antonioni, A.; Baroni, A.; Malerba, P.; Straudi, S. Relation Between EEG Measures and Upper Limb Motor Recovery in Stroke Patients: A Scoping Review. Brain Topogr. 2022, 35, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foong, R.; Ang, K.; Quek, C.; Guan, C.; Phua, K.; Kuah, C.; Deshmukh, V.; Yam, L.; Rajeswaran, D.; Tang, N.; et al. Assessment of the Efficacy of EEG-Based MI-BCI with Visual Feedback and EEG Correlates of Mental Fatigue for Upper-Limb Stroke Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badcock, N.; Mousikou, P.; Mahajan, Y.; de Lissa, P.; Thie, J.; McArthur, G. Validation of the Emotiv EPOC® EEG gaming system for measuring research quality auditory ERPs. PeerJ 2013, 1, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miah; Shin, J.; Islam, M.; Abdullah; Molla, M. Natural Human Emotion Recognition Based on Various Mixed Reality(MR) Games and Electroencephalography (EEG) Signals. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE Eurasian Conference on Educational Innovation 2022, Taipei, Taiwan, 10–12 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lau-Zhu, A.; Lau, M.; McLoughlin, G. Mobile EEG in research on neurodevelopmental disorders: Opportunities and challenges. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 36, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, T.; Lehne, M.; Ihme, K.; Jatzev, S.; Correia, J.; Kothe, C.; Picht, B.; Nijboer, F. A dry EEG-system for scientific research and brain-computer interfaces. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M.; Temko, A.; Bocchino, A.; O’Mahony, C.; Boylan, G.; Popovici, E. Analysis of a Low-Cost EEG Monitoring System and Dry Electrodes toward Clinical Use in the Neonatal ICU. Sensors 2019, 19, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiblanco Jimenez, I.A.; Gomez Acevedo, J.S.; Olivetti, E.C.; Marcolin, F.; Ulrich, L.; Moos, S.; Vezzetti, E. User Engagement Comparison between Advergames and Traditional Advertising Using EEG: Does the User’s Engagement Influence Purchase Intention? Electronics 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, J.N.; Hani, A.J.; Cheek, J.; Thirumala, P.; Tsuchida, T.N. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Guideline 2: Guidelines for Standard Electrode Position Nomenclature. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Ding, J.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Wen, Z.; Shi, X. Optimal combination of electrodes and conductive gels for brain electrical impedance tomography. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, T.; da Silva, H. Characterization and Validation of Flexible Dry Electrodes for Wearable Integration. Sensors 2023, 23, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.R.; Fiedler, P.; Kuhlmann, L.; Liley, D.; Vasconcelos, B.; Fonseca, C.; Tamburro, G.; Comani, S.; Lui, T.K.-Y.; Tse, C.-Y.; et al. Multi-Center Evaluation of Gel-Based and Dry Multipin EEG Caps. Sensors 2022, 22, 8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, E.H.T.; Molinas, M.; Ytterdal, T. Impedance and Noise of Passive and Active Dry EEG Electrodes: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 14565–14577. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Sanchez-Morillo, D.; Valle, F.P. Dry EEG Electrodes. Sensors 2014, 14, 12847–12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debener, S.; Scanlon, J.; Jacobsen, N.; Maack, M. Does the electrode amplification style matter? A comparison of active and passive EEG system configurations during standing and walking. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 8381–8395. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, R. Dry EEG Electrode for Use on a Hair-Covered Portion of a Person’s Head. U.S. Patent US 2022/0233124 A1, 28 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, K.; Ueda, K.; Li, Z.; Nakao, M. Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Brain Networks Related to Creative Thinking. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 541052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocay, D.D.; Teel, E.F.; Luo, O.D.; Savignac, C.; Mahdid, Y.; Blain-Moraes, S.; Ferland, C.E. Electroencephalographic characteristics of children and adolescents with chronic musculoskeletal pain. Pain Rep. 2022, 7, e1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, J.; Farkas, I.; Ujbanyi, T.; Dukan, P.; Kovari, A. Evaluation Of The Neurosky MindFlex EEG Headset Brain Waves Data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), Herl’any, Slovakia, 23–25 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.M.; Elconin, M.H.; Kerth, T.A. Transducer Assemblies for Dry Applications of Transducers. WIPO Patent WO2013/142316 A1, 26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Damalerio, R.; Cheng, M.-Y. Development of Dry EEG Electrodes and Dry EEG Cap for Neuromonitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE 70th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Orlando, FL, USA, 3–30 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tallgren, P.; Vanhatalo, S.; Kaila, K.; Voipio, J. Evaluation of commercially available electrodes and gels for recording of slow EEG potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow. SYLGARD™ 160 Silicone Elastomer Kit Technical Data Sheet; The Dow Chemical Company: Midland, MI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dow. SYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer Kit Technical Data Sheet; The Dow Chemical Company: Midland, MI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brereton, R. ANOVA tables and statistical significance of models. J. Chemom. 2019, 33, e3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, G.; Sardanelli, F. Statistical significance: P value, 0.05 threshold, and applications to radiomics—Reasons for a conservative approach. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2020, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhang, P.; Gawali, B.; Mehrota, S. Book Chapter 2—Technological Basics of EEG Recording and Operation of Apparatus. In Introduction to EEG- and Speech-Based Emotion Recognition; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 19–50. [Google Scholar]
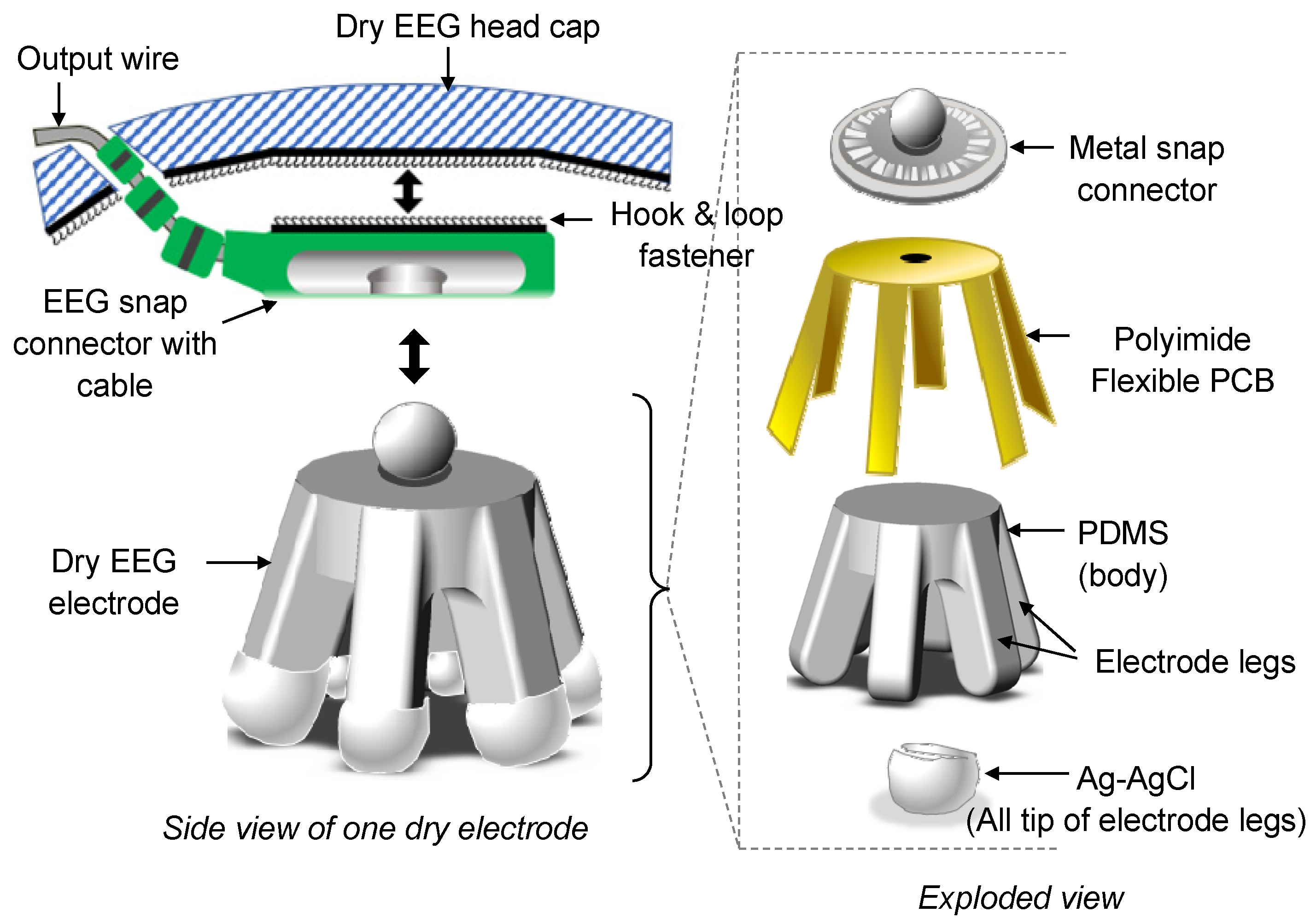
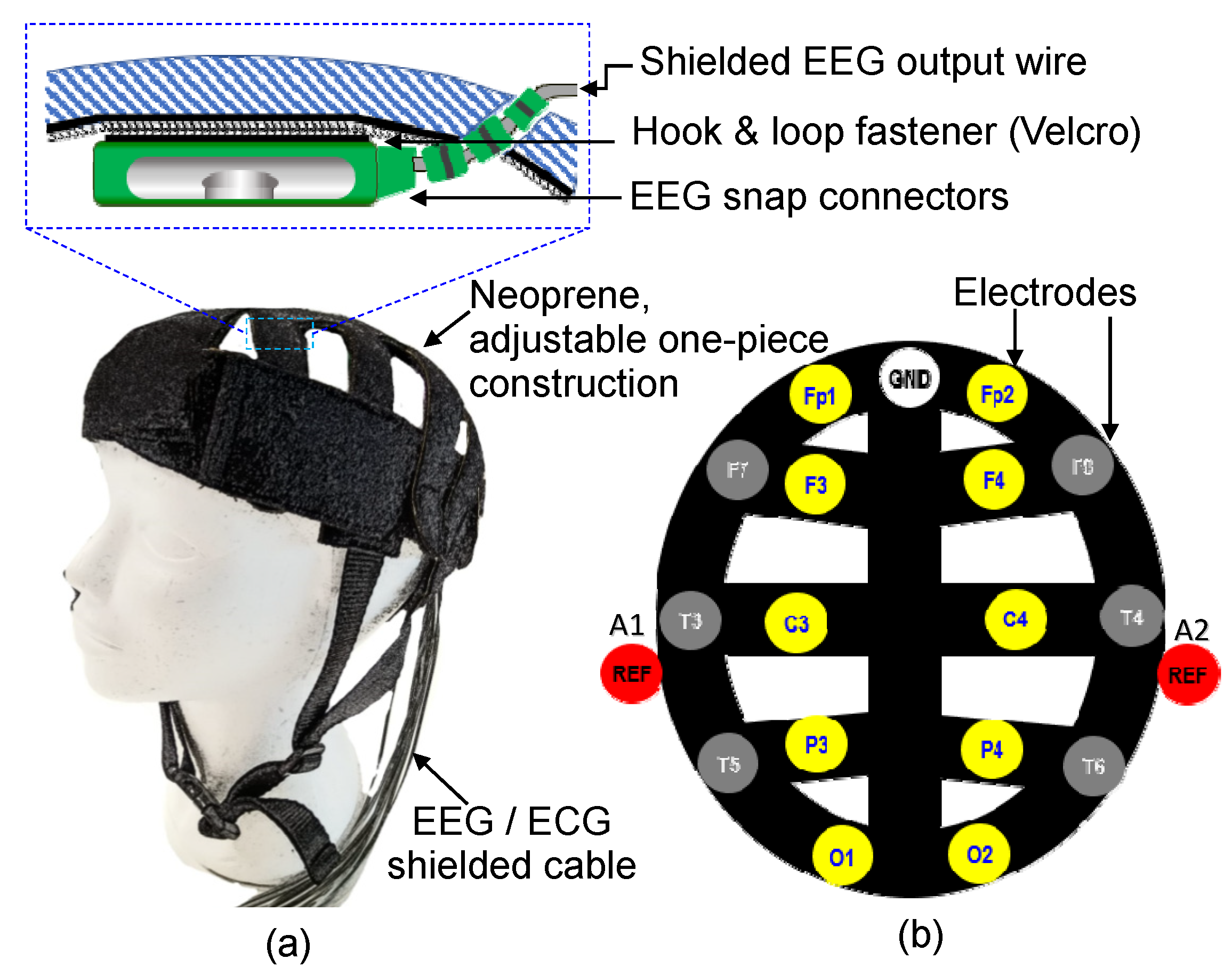







| Description | Design A (Legged) | Design B (Disc Type) |
|---|---|---|
| Span (as is) | 16.0 mm | 16.0 mm |
| Total Thickness 1 | 13.6 mm | 4.5 mm |
| Span 2 | 22.0 mm | 16.0 mm |
| No. of Legs/Bumps | 6 legs | 6 bumps |
| Leg Length | 7.0 mm | N/A |
| Leg Thickness | 3.5 mm | N/A |
| Leg/Bump Width | 3.0 mm | 3.0 mm |
| Ag–AgCl on Tip/Bumps | Yes | Yes |
| Electrode | Dry Electrodes (kΩ) | Dry (8 Electrodes) + Wet (A1, A2, C3, C4, Z) Electrodes (kΩ) | Wet Electrodes 1 (kΩ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z | 50.52 | 2.46 | 2.88 |
| Fp1 | 58.60 | 17.79 | 4.79 |
| F3 | 56.30 | 56.41 | 4.53 |
| C3 | 13.68 | 2.48 | 1.23 |
| P3 | 57.63 | 11.74 | 2.57 |
| O1 | 57.51 | 8.00 | 4.81 |
| Fp2 | 60.57 | 59.50 | 4.68 |
| F4 | 63.84 | 63.84 | 4.08 |
| C4 | 11.79 | 2.42 | 1.19 |
| P4 | 60.67 | 22.80 | 2.26 |
| O2 | 60.44 | 12.98 | 3.61 |
| A1 | 60.56 | 1.68 | 2.07 |
| A2 | 61.09 | 1.52 | 1.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Damalerio, R.B.; Lim, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, T.-T.; Cheng, M.-Y. Development of Low-Contact-Impedance Dry Electrodes for Electroencephalogram Signal Acquisition. Sensors 2023, 23, 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094453
Damalerio RB, Lim R, Gao Y, Zhang T-T, Cheng M-Y. Development of Low-Contact-Impedance Dry Electrodes for Electroencephalogram Signal Acquisition. Sensors. 2023; 23(9):4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094453
Chicago/Turabian StyleDamalerio, Ramona B., Ruiqi Lim, Yuan Gao, Tan-Tan Zhang, and Ming-Yuan Cheng. 2023. "Development of Low-Contact-Impedance Dry Electrodes for Electroencephalogram Signal Acquisition" Sensors 23, no. 9: 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094453
APA StyleDamalerio, R. B., Lim, R., Gao, Y., Zhang, T.-T., & Cheng, M.-Y. (2023). Development of Low-Contact-Impedance Dry Electrodes for Electroencephalogram Signal Acquisition. Sensors, 23(9), 4453. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094453










