Evaluation of Novel Embroidered Textile-Electrodes Made from Hybrid Polyamide Conductive Threads for Surface EMG Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
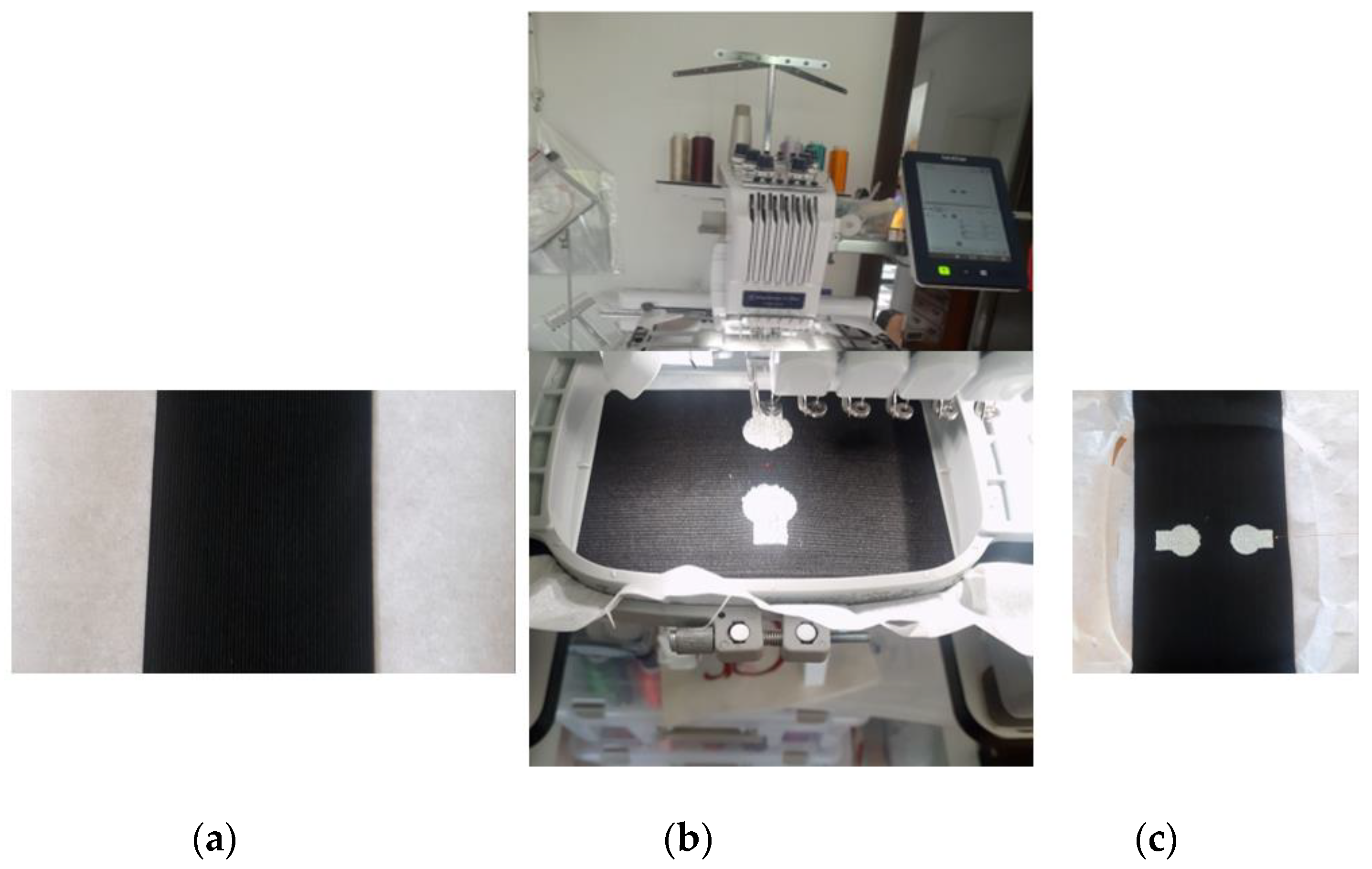
2.1. Materials
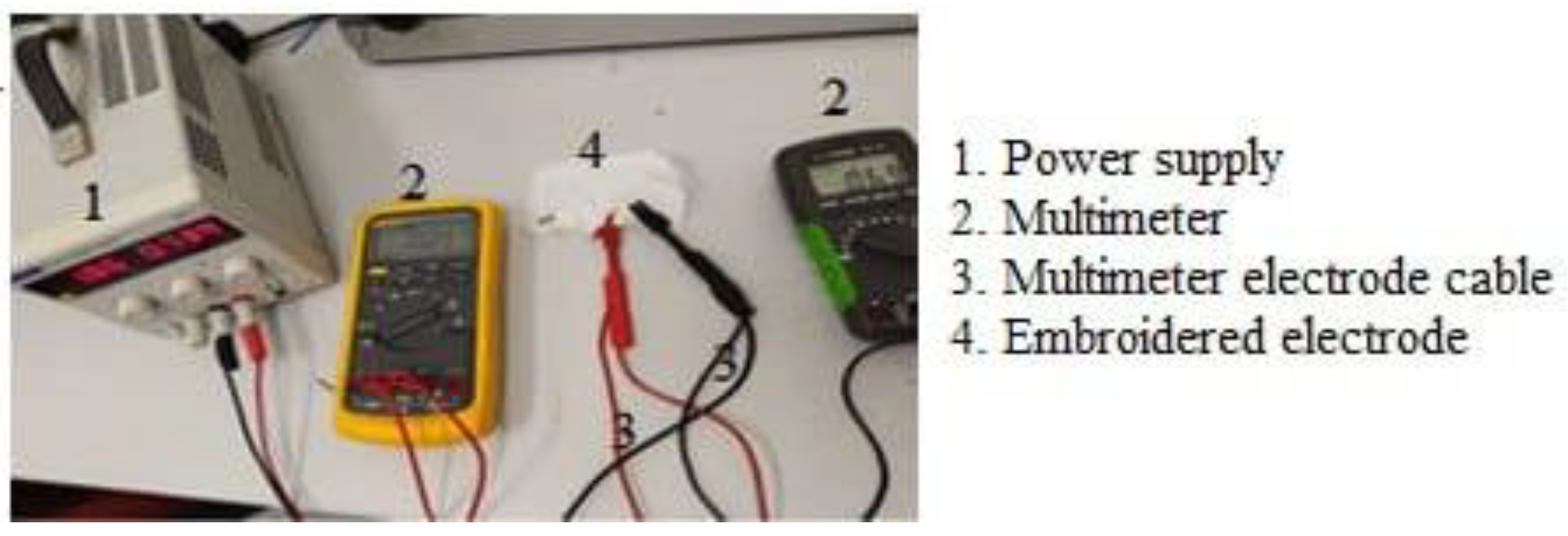
2.2. Experimental Setup for Surface Resistance and Impedance
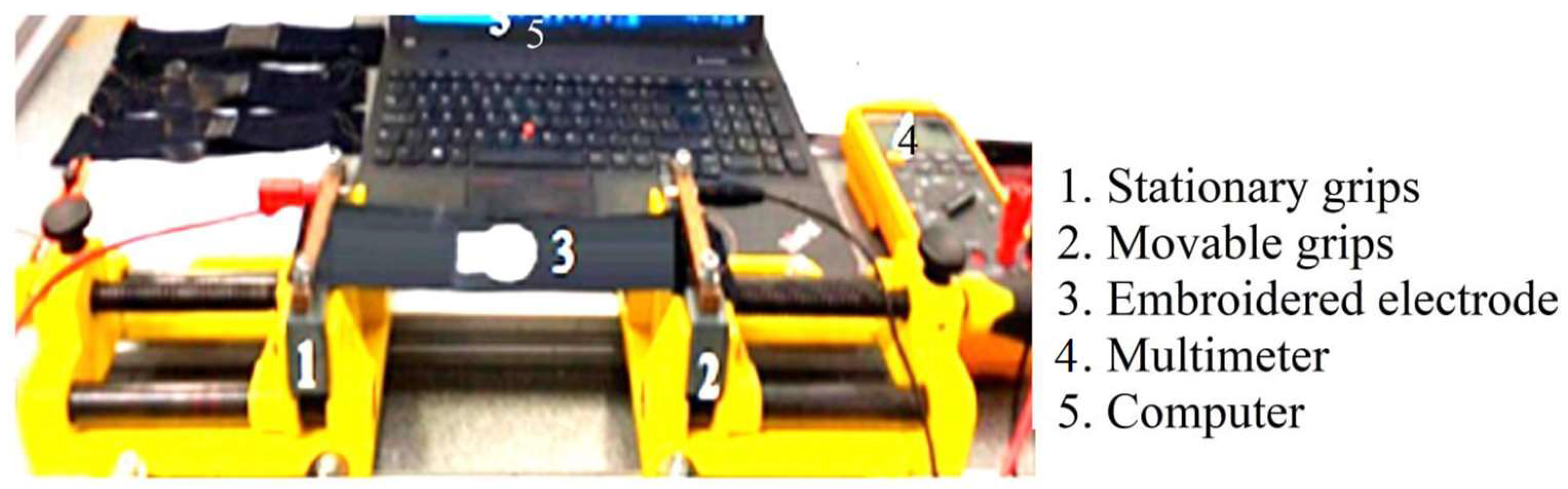
2.3. EMG Recording Protocol
2.4. Impedance Measurement Protocol
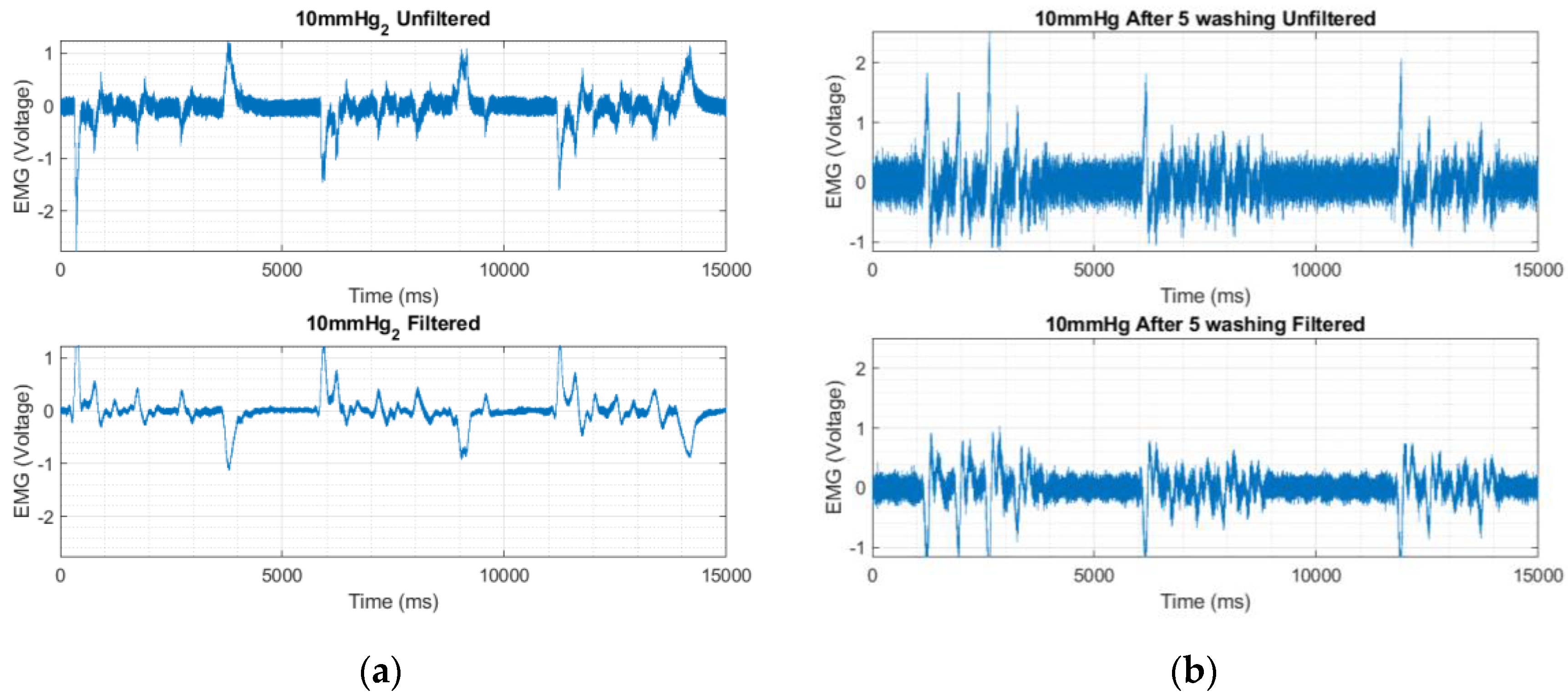
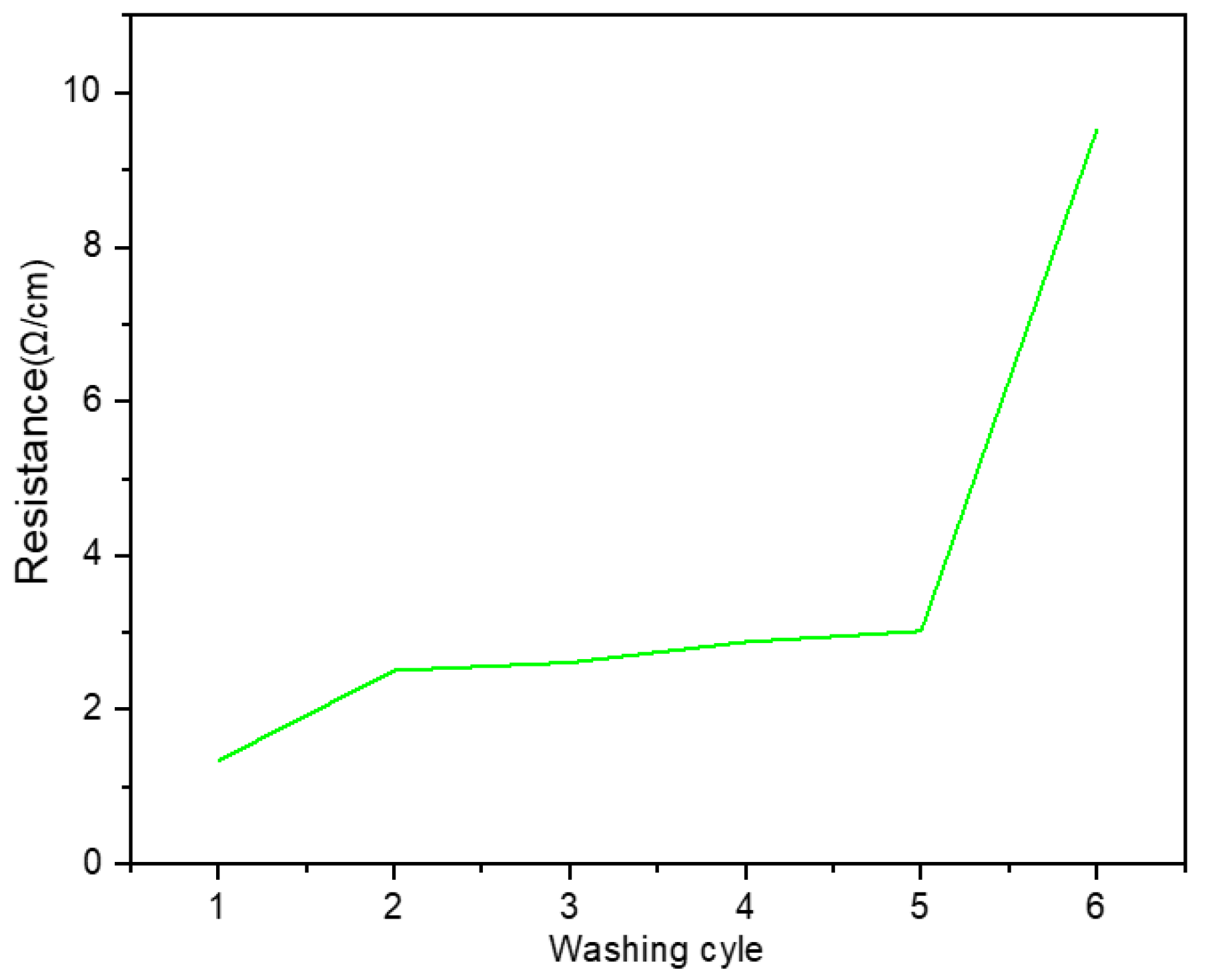
2.5. Effect of Washing on Textile Electrode Performance
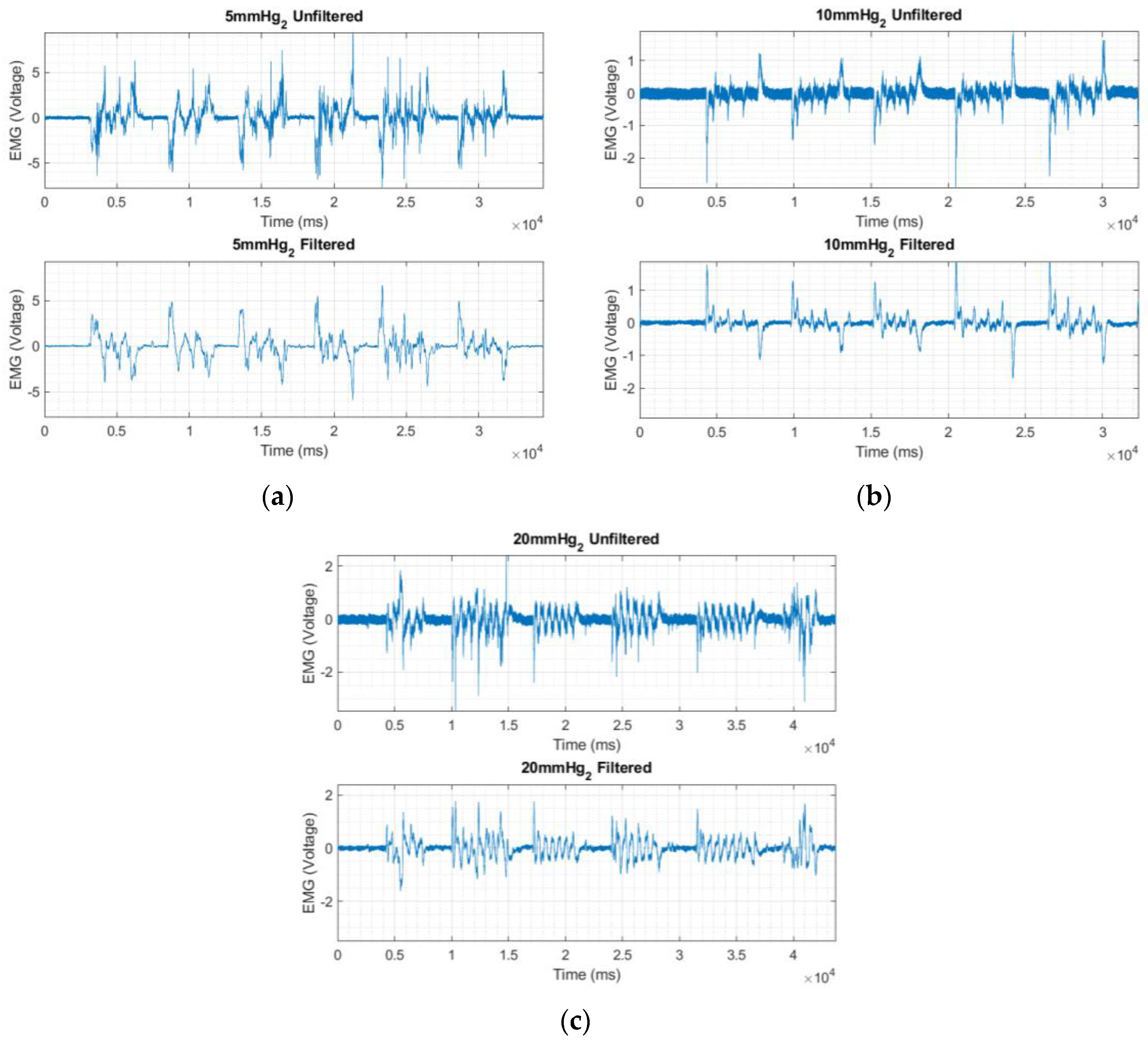
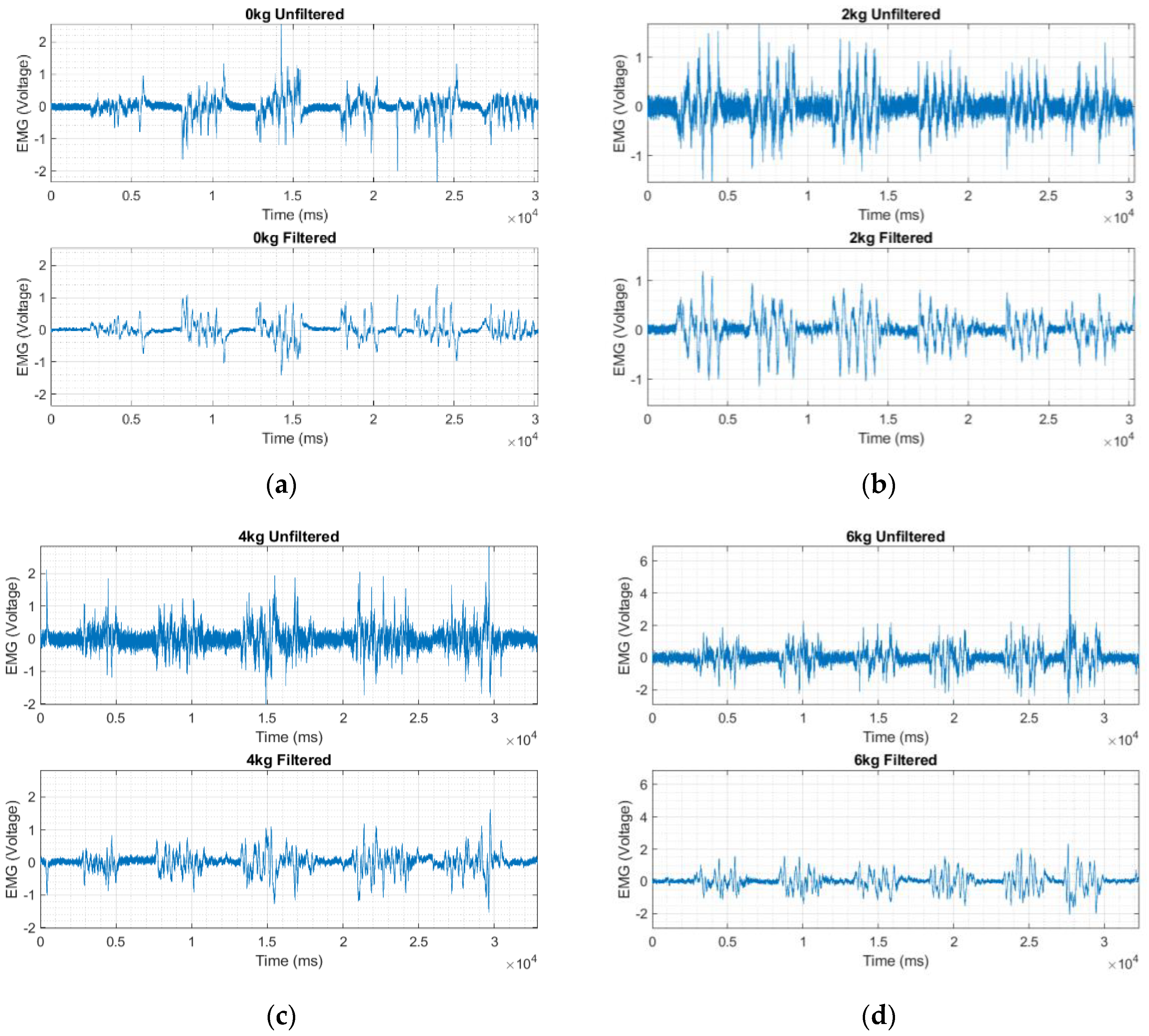
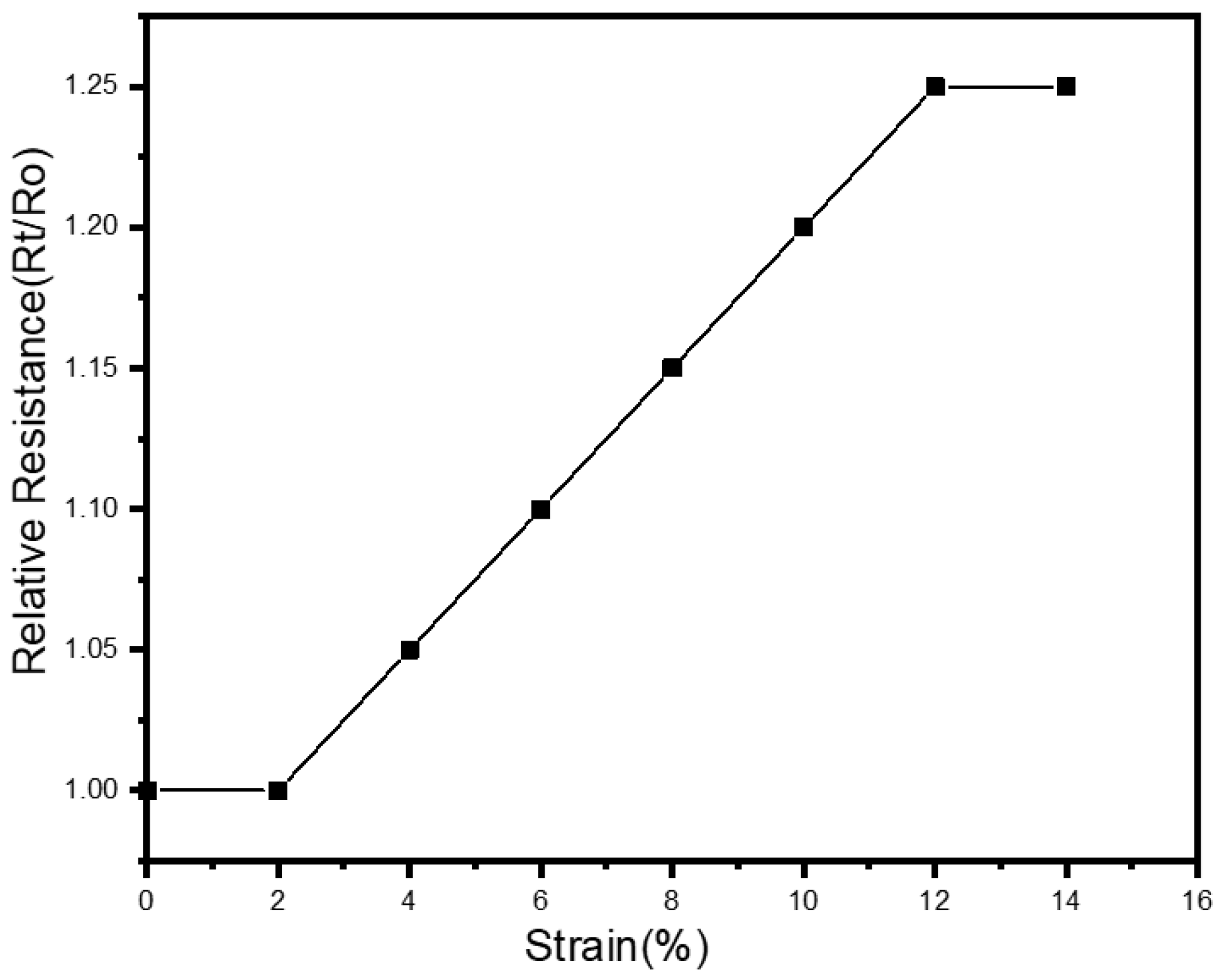
2.6. Effect of Stretching on Textile Electrode Performance
3. Results
3.1. Electrode Impedance Characterization
3.2. EMG Signal Acquired Using Textile Electrodes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albulbul, A. Evaluating Major Electrode Types for Idle Biological Signal Measurements for Modern Medical Technology. Bio-Eng. 2016, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Designing and Evaluating a Wearable Semg Device for the Elderly. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on ICT, Society and Human Beings (ICT 2021), the 18th International Conference Web Based Communities and Social Media (WBC 2021), Online, 20 July 2021; IADIS Press: Porto, Portugal, 2021.
- Mamdiwar, S.D.; R, A.; Shakruwala, Z.; Chadha, U.; Srinivasan, K.; Chang, C.-Y. Recent Advances on IoT-Assisted Wearable Sensor Systems for Healthcare Monitoring. Biosensors 2021, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, K.T.; Alsahlany, A.M.; Wadi, S.M.; Kadhum, H.T. An Overview of Patient’s Health Status Monitoring System Based on Internet of Things (IoT). Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 2235–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmalek, S.; Nasir, A.; Jabbar, W.A.; Almuhaya, M.A.M.; Bairagi, A.K.; Khan, M.A.-M.; Kee, S.-H. IoT-Based Healthcare-Monitoring System towards Improving Quality of Life: A Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, G.; Ehrmann, A. Textile-Based Sensors for Biosignal Detection and Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gou, L.; Zou, Y. A Novel Wearable Flexible Dry Electrode Based on Cowhide for ECG Measurement. Biosensors 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euler, L.; Guo, L.; Persson, N.-K. A Review of Textile-Based Electrodes Developed for Electrostimulation. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 1300–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, G.; Ozturk, O.; Golparvar, A.J.; Elboshra, T.A.; Böhringer, K.; Yapici, M.K. Wearable and Flexible Textile Electrodes for Biopotential Signal Monitoring: A Review. Electronics 2019, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitou, S.; Michael, B.; Thompson, K.; Howard, M. Hand-Made Embroidered Electromyography: Towards a Solution for Low-Income Countries. Sensors 2020, 20, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncu-Berk, G.; Tuna, B.G. The Effect of Sleeve Pattern and Fit on E-Textile Electromyography (EMG) Electrode Performance in Smart Clothing Design. Sensors 2021, 21, 5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.; Malengier, B.; Hertleer, C.; Van Langenhove, L. Validation of Devices for Characterization of Hybrid 3D Printed Embroidery TENG for Energy Harvesting. Commun. Dev. Assem. Text. Prod. 2022, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamavuako, E.N.; Brown, M.; Bao, X.; Chihi, I.; Pitou, S.; Howard, M. Affordable Embroidered EMG Electrodes for Myoelectric Control of Prostheses: A Pilot Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cömert, A.; Honkala, M.; Hyttinen, J. Effect of Pressure and Padding on Motion Artifact of Textile Electrodes. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2013, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, A.; Hyttinen, J. A Motion Artifact Generation and Assessment System for the Rapid Testing of Surface Biopotential Electrodes. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-J.; Chang, W.-T.; Wu, W.-H.; Lin, B.-S. Applying Noncontact Sensing Technology in the Customized Product Design of Smart Clothes Based on Anthropometry. Sensors 2021, 21, 7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, M.d.; Domingo, R. EMG Characterization and Processing in Production Engineering. Materials 2020, 13, 5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Tangsirinaruenart, O.; Stylios, G.K. Investigating the Performance of Dry Textile Electrodes for Wearable End-Uses. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, N.; Gao, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. Design, Characterization, and Performance of Woven Fabric Electrodes for Electrocardiogram Signal Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.J.; Kuznetsov, M.; Gilmore, L.D.; Roy, S.H. Inter-Electrode Spacing of Surface EMG Sensors: Reduction of Crosstalk Contamination during Voluntary Contractions. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, I.; Fernandez-Garcia, R.; Troynikov, O.; Dabnichki, P.; Pirogova, E.; Gil, I. Embroidered Electrodes for Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Impact of Surface Area and Stitch Parameters. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannaian, T.; Neelaveni, R.; Thilagavathi, G. Design and Development of Embroidered Textile Electrodes for Continuous Measurement of Electrocardiogram Signals. J. Ind. Text. 2013, 42, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Jeong, W. EMG Measurement with Textile-Based Electrodes in Different Electrode Sizes and Clothing Pressures for Smart Clothing Design Optimization. Polymers 2020, 12, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigusse, A.B.; Malengier, B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Tseghai, G.B.; Van Langenhove, L. Development of Washable Silver Printed Textile Electrodes for Long-Term ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Meghrazi, M.; Ying, B.; Schlums, A.; Lam, E.; Eskandarian, L.; Abbas, F.; Sidhu, G.; Mahnam, A.; Moineau, B.; Popovic, M.R. Evaluation of Dry Textile Electrodes for Long-Term Electrocardiographic Monitoring. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2021, 20, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medrano, G.; Ubl, A.; Zimmermann, N.; Gries, T.; Leonhardt, S. Skin Electrode Impedance of Textile Electrodes for Bioim-pedance Spectroscopy. In 13th International Conference on Electrical Bioimpedance and the 8th Conference on Electrical Impedance Tomography; Scharfetter, H., Merwa, R., Eds.; IFMBE Proceedings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 17, pp. 260–263. ISBN 978-3-540-73840-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, E.; Alizadeh-Meghrazi, M.; Schlums, A.; Eskandarian, L.; Mahnam, A.; Moineau, B.; Popovic, M.R. Exploring Textile-Based Electrode Materials for Electromyography Smart Garments. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2022, 9, 205566832110619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, F.; Cè, E.; Gobbo, M.; Veicsteinas, A.; Orizio, C. Surface EMG and Mechanomyogram Disclose Isokinetic Training Effects on Quadriceps Muscle in Elderly People. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 94, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, M.; Arsenault, A.B.; Gravel, D.; Bourbonnais, D. EMG Power Spectrum of Elbow Extensors: A Reliability Study. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1994, 34, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Blijham, P.J.; ter Laak, H.J.; Schelhaas, H.J.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Stegeman, D.F.; Zwarts, M.J. Relation between Muscle Fiber Conduction Velocity and Fiber Size in Neuromuscular Disorders. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 1837–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, M.; Cincera, M.; Gervais, S.; Arsenault, A.B.; Gravel, D.; Lepage, Y.; McKinley, P. Changes in the Electromyographic Spectrum Power Distribution Caused by a Progressive Increase in the Force Level. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 71, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafti, A.; Ribas Manero, R.B.; Borg, A.M.; Althoefer, K.; Howard, M.J. Embroidered Electromyography: A Systematic Design Guide. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manero, R.B.R.; Shafti, A.; Michael, B.; Grewal, J.; Fernandez, J.L.R.; Althoefer, K.; Howard, M.J. Wearable Embroidered Muscle Activity Sensing Device for the Human Upper Leg. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 6062–6065. [Google Scholar]






| Ag/AgCl | EM (15 mm) | EM (20 mm) | EM (25 mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/AgCl (25 mm) | 1.000 | 0.943 | 0.971 | 0.993 |
| EM (15 mm) | 1.000 | 0.943 | 0.953 | |
| EM (20 mm) | 1.000 | 0.986 | ||
| EM (25 mm) | 1.000 |
| Ag/AgCl | EM01 | EM02 | EM03 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/AgCl (25 mm) | 1.000 | 0.972 | 0.969 | 0.993 |
| EM01 | 1.000 | 0.954 | 0.988 | |
| EM02 | 1.000 | 0.970 | ||
| EM03 | 1.000 |
| Holding Contact Pressure (mmHg) | RMS (mV) | ARV (mV) | SNR (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 21.33 ± 1.13 |
| 10 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 23.34 ± 1.44 |
| 20 | 1.83 ± 0.1 | 1.06 ± 0.4 | 17.45 ± 1.43 |
| Ag/AgCl (0 mmHg) | 1.89 ± 0.05 | 1.07 ± 0.06 | 23.10 ± 1.33 |
| Load (Kg) | Root Mean Square (RMS, mV) | Average Rectified Value (ARV, mV) | Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR, dB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.29 ± 0.05 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 17.12 ± 1.74 |
| 2 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 19.53 ± 1.60 |
| 4 | 0.34 ± 0.05 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 19.89 ± 1.91 |
| 6 | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 0.35 ± 0.05 | 20.18 ± 1.93 |
| Ag/AgCl (0 Kg) | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.04 | 21.18 ± 1.72 |
| Subjects | RMS (mV) | ARV (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.14 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| 3 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| 4 | 0.106 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| 5 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.089 ± 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.010 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| 7 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.00 |
| 8 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| 9 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| Parameters | Before Washing | After Washing |
|---|---|---|
| RMS (MV) | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.31 ± 0.03 |
| ARV (MV) | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.05 |
| SNR dB | 24.81 ± 1.19 | 21.00 ± 1.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Etana, B.B.; Malengier, B.; Kwa, T.; Krishnamoorthy, J.; Langenhove, L.V. Evaluation of Novel Embroidered Textile-Electrodes Made from Hybrid Polyamide Conductive Threads for Surface EMG Sensing. Sensors 2023, 23, 4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094397
Etana BB, Malengier B, Kwa T, Krishnamoorthy J, Langenhove LV. Evaluation of Novel Embroidered Textile-Electrodes Made from Hybrid Polyamide Conductive Threads for Surface EMG Sensing. Sensors. 2023; 23(9):4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094397
Chicago/Turabian StyleEtana, Bulcha Belay, Benny Malengier, Timothy Kwa, Janarthanan Krishnamoorthy, and Lieva Van Langenhove. 2023. "Evaluation of Novel Embroidered Textile-Electrodes Made from Hybrid Polyamide Conductive Threads for Surface EMG Sensing" Sensors 23, no. 9: 4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094397
APA StyleEtana, B. B., Malengier, B., Kwa, T., Krishnamoorthy, J., & Langenhove, L. V. (2023). Evaluation of Novel Embroidered Textile-Electrodes Made from Hybrid Polyamide Conductive Threads for Surface EMG Sensing. Sensors, 23(9), 4397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094397








