Electromagnetic Sensing Techniques for Monitoring Atopic Dermatitis—Current Practices and Possible Advancements: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Established Methods for Monitoring AD
2.1. Medical Examination and Tests
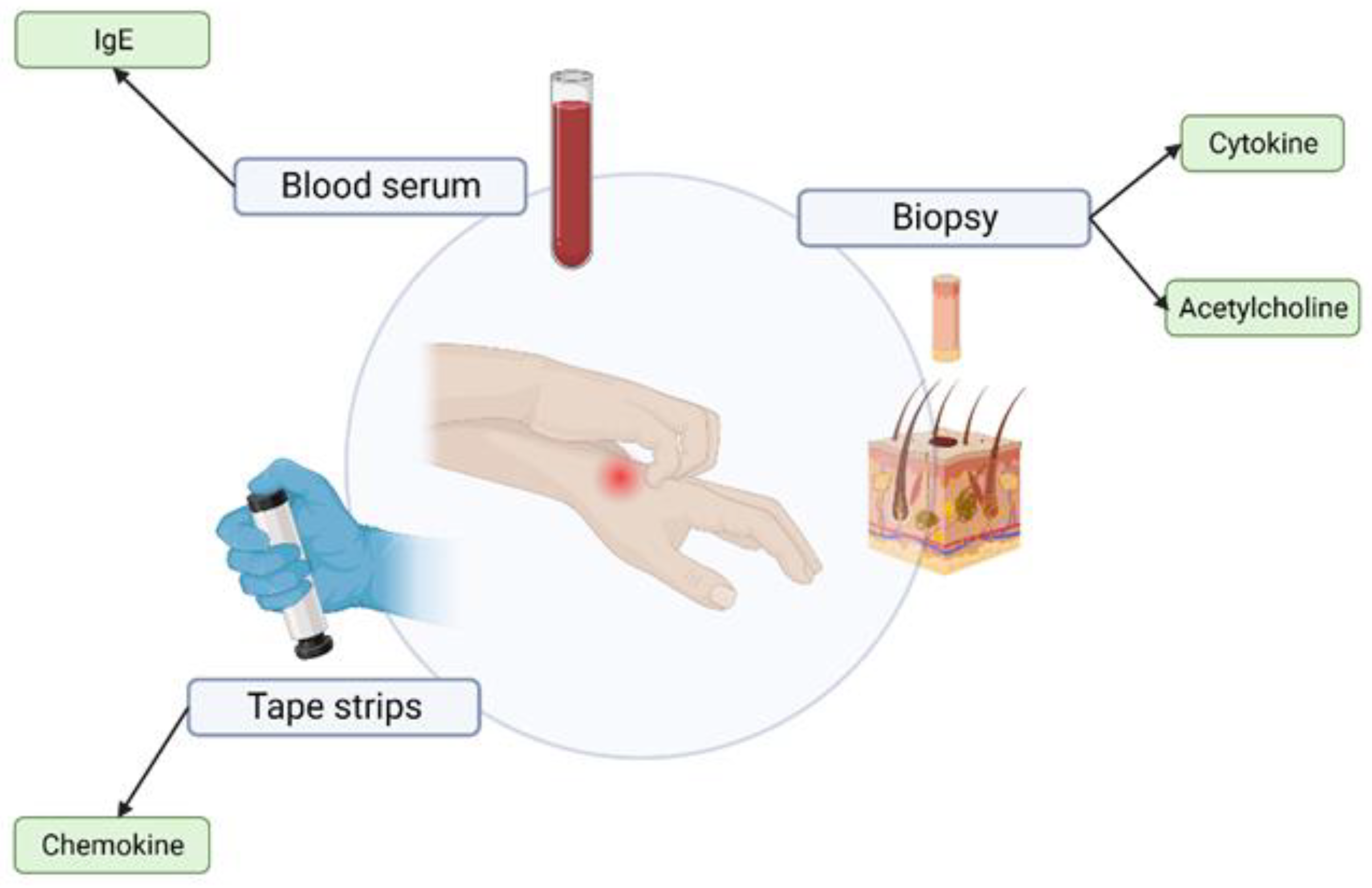
2.1.1. Biopsy
2.1.2. Blood Serum—“Liquid Biopsy”
2.1.3. Tape Stripping
2.1.4. Conclusions
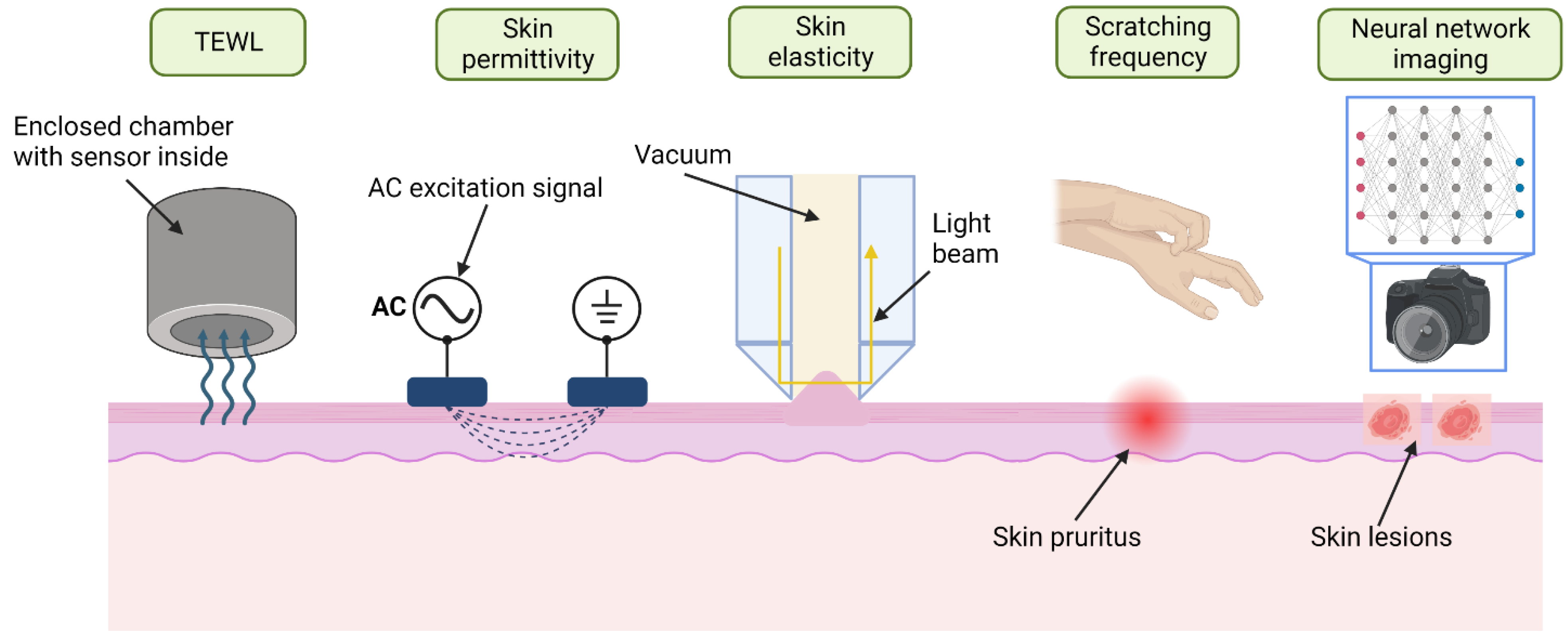
2.2. Telemedical and Non-Invasive Measurements
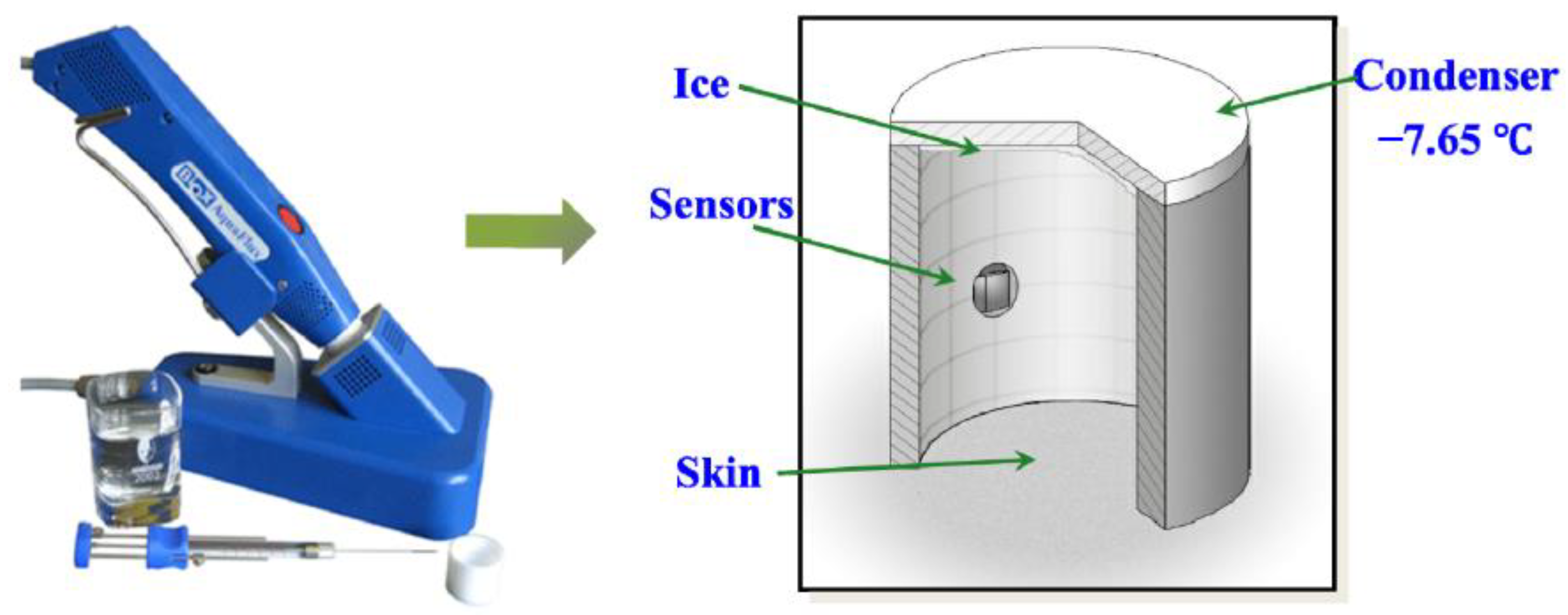
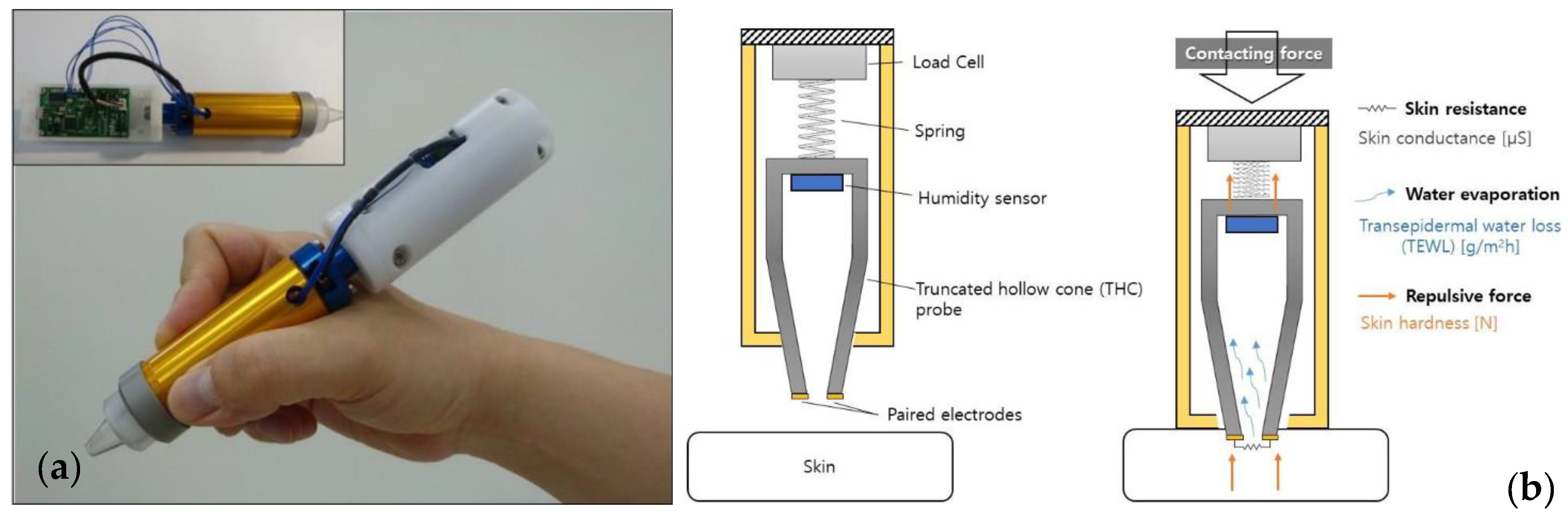
2.2.1. Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL)
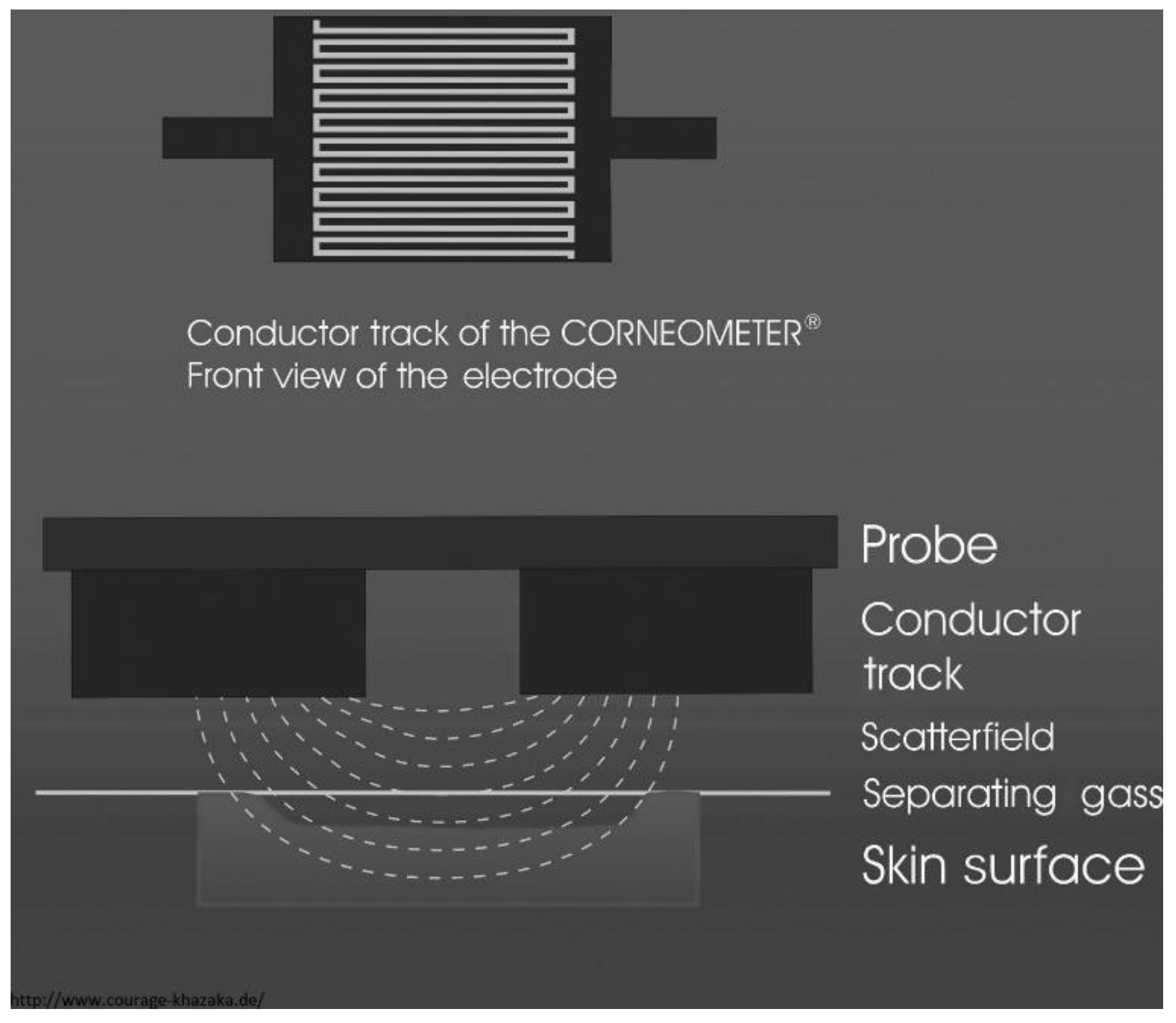
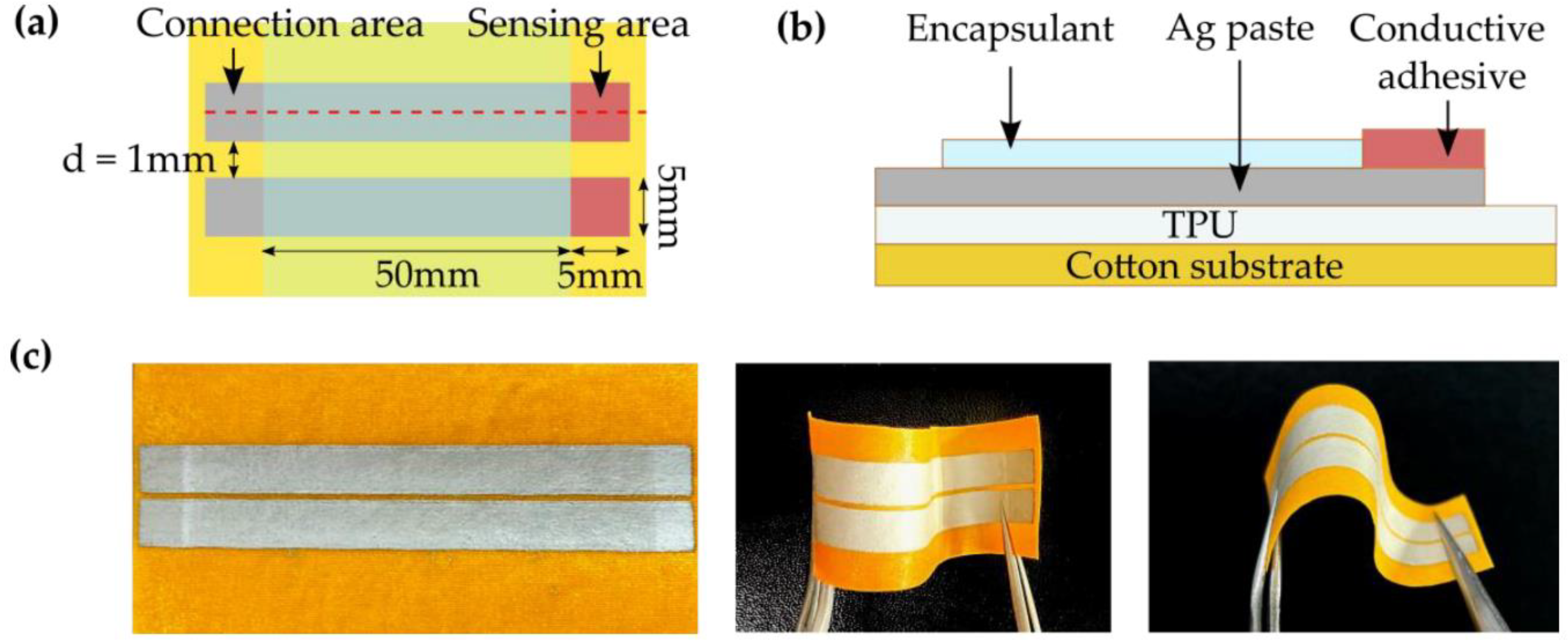
2.2.2. Skin Permittivity and Conductivity
2.2.3. Skin Elasticity
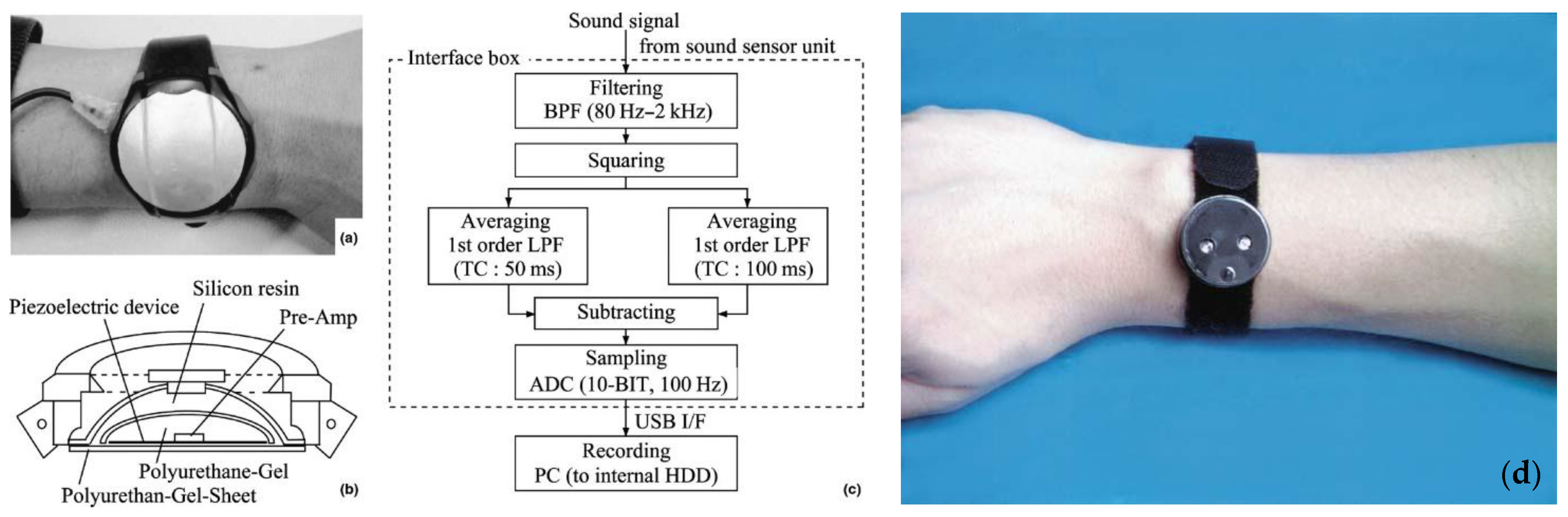
2.2.4. Scratch Activity and Frequency
2.2.5. Neural Network Imaging Systems
2.2.6. Conclusions
3. Future Applicable Technologies
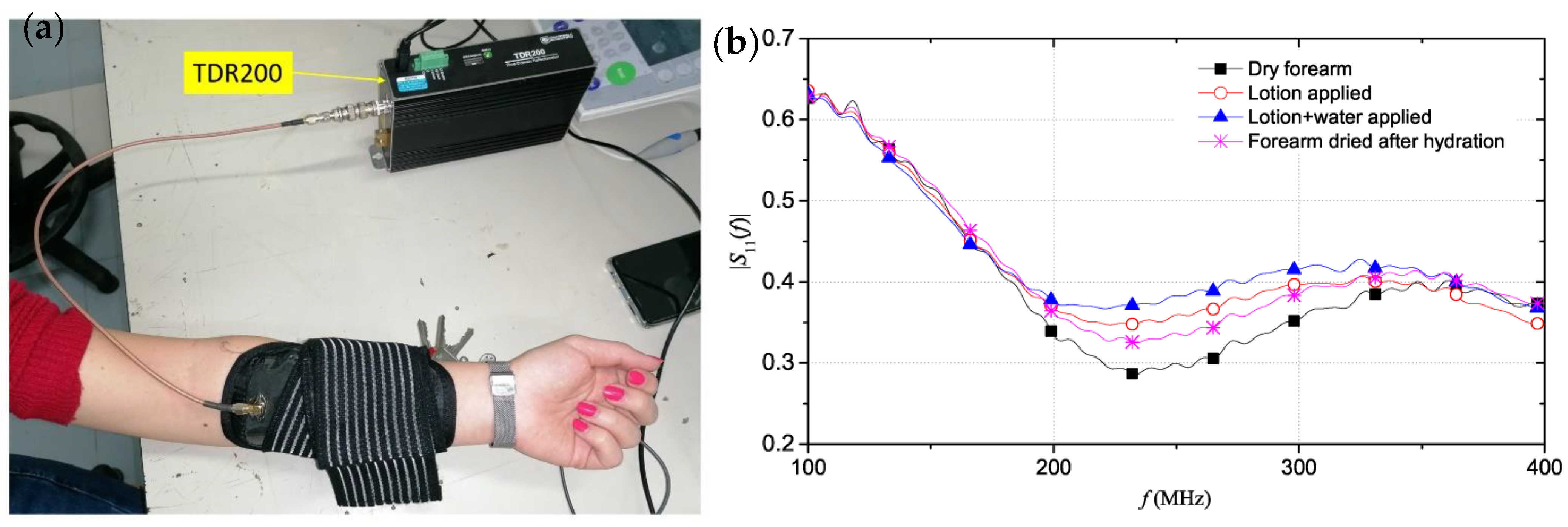
3.1. Radio Frequency Reflectometry
3.2. Optical Spectroscopy
3.2.1. Raman Spectroscopy Measurements on Skin
3.2.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements on Skin
3.2.3. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy Measurements on Skin
3.2.4. Conclusions
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spinazze, P.; Bottle, A.; Car, J. Digital Health Sensing for Personalized Dermatology. Sensors 2019, 19, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, M.; Balocchi, L.; Benassi, F.; Carvalho, N.B.; Chiao, J.-C.; Correia, R.; Costanzo, A.; Cui, Y.; Georgiadou, D.; Gouveia, C.; et al. Microwave-Enabled Wearables: Underpinning Technologies, Integration Platforms, and Next-Generation Roadmap. IEEE J. Microw. 2023, 3, 193–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, D.; Kanwar, A.J.; Handa, S. Comparative efficacy of Hanifin and Rajka’s criteria and the UK working party’s diagnostic criteria in diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in a hospital setting in North India. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2006, 20, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenninkmeijer, E.E.A.; Schram, M.E.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Bos, J.D.; Spuls, P.I. Diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis: A systematic review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, K.; Gilani, S.O.; Waris, A.; Ahmed, A.; Jamil, M.; Khan, M.N.; Sohail Kashif, A. Skin Lesion Segmentation from Dermoscopic Images Using Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Ahmed, F.; Alsuhibany, S.A.; Jamal, S.S.; Zulfiqar Ali, M.; Ahmad, J. Classification of Skin Cancer Lesions Using Explainable Deep Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtava, Z.; Shulaia, T.; Kiladze, N.; Korsantia, N.; Gogitidze, T.; Jorjoliani, D. E-Health/m-Health services for dermatology outpatients screening for skin cancer and follow-up. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Munich, Germany, 14–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khatib, H.; Popescu, D.; Ichim, L. Deep Learning–Based Methods for Automatic Diagnosis of Skin Lesions. Sensors 2020, 20, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelin, A.; Hampton, P. Telemedicine and e-Health in the Management of Psoriasis: Improving Patient Outcomes—A Narrative Review. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.O.; Korsfeldt, A.; Ward, S.; Burla, D.; Dreher, A.; Gautschi, M.; Stolpe, B.; Tan, G.; Bersuch, E.; Melin, D.; et al. Electrical impedance spectroscopy for the characterization of skin barrier in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 3066–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D.; Nomura, I.; Hamid, Q.A. New insights into atopic dermatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.; Paller, A.S. Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, S118–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamouei, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Razban, M.; Qassem, M.; Kyriacou, P.A. Design and Analysis of a Continuous and Non-Invasive Multi-Wavelength Optical Sensor for Measurement of Dermal Water Content. Sensors 2021, 21, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Honeywell-Nguyen, P.L.; Gooris, G.S.; Ponec, M. Structure of the skin barrier and its modulation by vesicular formulations. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Wang, C.; Zhao, R.; Du, L.; Fang, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Z. Review of Stratum Corneum Impedance Measurement in Non-Invasive Penetration Application. Biosensors 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitamo, S.; Luger, T.A.; Steinhoff, M. Textbook of Atopic Dermatitis; Informa Healthcare: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, C.N.A.; Irvine, A.D.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, H.; Lee, S.P.; Goudie, D.R.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Smith, F.J.D.; et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicander, I.; Ollmar, S. Clinically normal atopic skin vs. non-atopic skin as seen through electrical impedance. Ski. Res. Technol. 2004, 10, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qassem, M.; Kyriacou, P. Review of Modern Techniques for the Assessment of Skin Hydration. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Ren, A.; Shah, S.A.; Hu, F.; Zhao, N.; Yang, X.; Haider, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Abbasi, Q.H. Monitoring of atopic dermatitis using leaky coaxial cable. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebata, T.; Iwasaki, S.; Kamide, R.; Niimura, M. Use of a wrist activity monitor for the measurement of nocturnal scratching in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 144, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, B.G.; Leung, S.B.; Leung, D.Y.M. Actigraphy assessment of sleep disturbance in patients with atopic dermatitis: An objective life quality measure. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.D.; Leent, E.J.M.; Smitt, J.H.S. The millennium criteria for the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 1998, 7, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakharia, P.P.; Chopra, R.; Silverberg, J.I. Systematic Review of Diagnostic Criteria Used in Atopic Dermatitis Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herd, R.M.; Tidman, M.J.; Prescott, R.J.; Hunter, J.A.A. The cost of atopic eczema. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 135, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, D.M.; Stratman, E.J.; Miller, S.J. Skin biopsy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessler, I.; Reinheimer, T.; Kilbinger, H.; Bittinger, F.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Saloga, J.; Knop, J. Increased acetylcholine levels in skin biopsies of patients with atopic dermatitis. Life Sci. 2003, 72, 2169–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kägi, M.K.; Wüthrich, B.; Montano, E.; Barandun, J.; Blaser, K.; Walker, C. Differential Cytokine Profiles in Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Supernatants and Skin Biopsies from Patients with Different Forms of Atopic Dermatitis, Psoriasis and Normal Individuals. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1994, 103, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, S.J.F. Atopic Dermatitis in Adults: A Diagnostic Challenge. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 27, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, J.; Marrugo-Ramírez, J.; Rodriguez-Trujillo, R.; Mir, M.; Samitier, J. Sensor-Integrated Microfluidic Approaches for Liquid Biopsies Applications in Early Detection of Cancer. Sensors 2020, 20, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-T.; Goodarzi, H.; Chen, H.-Y. IgE, Mast Cells, and Eosinophils in Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Amp. Immunol. 2011, 41, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Serizawa, S.; Ito, M.; Sato, Y. Stratum corneum lipid abnormalities in atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1991, 283, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røpke, M.A.; Mekulova, A.; Pipper, C.; Eisen, M.; Pender, K.; Spee, P.; Kezic, S. Non-invasive assessment of soluble skin surface biomarkers in atopic dermatitis patients—Effect of treatment. Ski. Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppes, S.A.; Brans, R.; Ljubojevic Hadzavdic, S.; Frings-Dresen, M.H.W.; Rustemeyer, T.; Kezic, S. Stratum Corneum Tape Stripping: Monitoring of Inflammatory Mediators in Atopic Dermatitis Patients Using Topical Therapy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 170, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrer, U.; Manninger, M.; Zirlik, A.; Scherr, D. Multiparameter Monitoring with a Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator. Sensors 2021, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfaramawy, T.; Fall, C.L.; Arab, S.; Morissette, M.; Lellouche, F.; Gosselin, B. A Wireless Respiratory Monitoring System Using a Wearable Patch Sensor Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antali, F.; Kulin, D.; Lucz, K.I.; Szabó, B.; Szűcs, L.; Kulin, S.; Miklós, Z. Multimodal Assessment of the Pulse Rate Variability Analysis Module of a Photoplethysmography-Based Telemedicine System. Sensors 2021, 21, 5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talboom, J.S.; Huentelman, M.J. Big data collision: The internet of things, wearable devices and genomics in the study of neurological traits and disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, R35–R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šalkevicius, J.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliunas, R.; Laukienė, I. Anxiety Level Recognition for Virtual Reality Therapy System Using Physiological Signals. Electronics 2019, 8, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kańtoch, E.; Kańtoch, A. What Features and Functions Are Desired in Telemedical Services Targeted at Polish Older Adults Delivered by Wearable Medical Devices?—Pre-COVID-19 Flashback. Sensors 2020, 20, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulemtafes, A.; Badache, N. Design of Wearable Health Monitoring Systems: An Overview of Techniques and Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Akdeniz, M.; Gabriel, S.; Lichterfeld-Kottner, A.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Kottner, J. TEWL reference values in healthy adults. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mündlein, M.; Nicolics, J.; Chabicovsky, R.; Svasek, P.; Svasek, E.; Komeda, T.; Funakubo, H.; Nagashima, T.; Ito, M. Packaging of a thin-film sensor for transepidermal water loss measurements. In Proceedings of the International Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology, High Tatras, Slovakia, 8–11 May 2003; pp. 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Maibach, H.I. Skin occlusion and irritant and allergic contact dermatitis: An overview. Contact Dermat. 2001, 44, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Park, J.-Y.; Na, G.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, W.-J. Correlation of clinical features and skin barrier function in adolescent and adult patients with atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2006, 45, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, Y.; Lindberg, M. Transepidermal water loss in dry and clinically normal skin in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. -Venereol. 1985, 65, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Chen, D. The Effect of Sun Tan Lotion on Skin by Using Skin TEWL and Skin Water Content Measurements. Sensors 2022, 22, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfin Technologies. VapoMeter; Delfin Technologies: Kuopio, Finland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Biox Systems, Ltd. AquaFlux™ Model AF200 TEWL Measurement Device; Biox Systems, Ltd.: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, D.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.S.; Doh, I. Portable Skin Analyzers with Simultaneous Measurements of Transepidermal Water Loss, Skin Conductance and Skin Hardness. Sensors 2019, 19, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K. In vivo Measurements of Water in Skin by Near-Infrared Reflectance. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 52, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Y. A Portable Dual-Parameter Tester for Assessing Electrical Properties of Human Skin Surface. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, S.; Ruzgas, T.; Nowacka, A.; Dahi, I.; Topgaard, D.; Sparr, E.; Engblom, J. Skin Membrane Electrical Impedance Properties under the Influence of a Varying Water Gradient. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 2639–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokus, M.A.; Daniele, M.A. Skin Hydration Sensor for Customizable Electronic Textiles. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 2671–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Myers, A.; Malhotra, A.; Lin, F.; Bozkurt, A.; Muth, J.F.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, S.; Myers, A.; Zhu, Y.; et al. A Wearable Hydration Sensor with Conformal Nanowire Electrodes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Nishizawa, M. Electrical aspects of skin as a pathway to engineering skin devices. APL Bioeng. 2021, 5, 041509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidado, I.M.; Qassem, M.; Triantis, I.F.; Kyriacou, P.A. Review of Advances in the Measurement of Skin Hydration Based on Sensing of Optical and Electrical Tissue Properties. Sensors 2022, 22, 7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: III. Parametric models for the dielectric spectrum of tissues. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2271–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, C.; Peyman, A.; Grant, E.H. Electrical conductivity of tissue at frequencies below 1 MHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SciBase Holding AB. Nevisense; SciBase Holding AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Courage+Khazaka Electronic GmbH. Corneometer® CM 825; Courage+Khazaka Electronic GmbH: Köln, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nova Technology. Novameter DPM 9003; Nova Technology: Suzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scalar Corporation. Skin Moisture Sensor MY-808S; Scalar Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Anthonissen, M.; Daly, D.; Peeters, R.; Van Brussel, M.; Fieuws, S.; Moortgat, P.; Flour, M.; Van Den Kerckhove, E. Reliability of Repeated Measurements on Post-Burn Scars with Corneometer CM 825®. Ski. Res. Technol. 2015, 21, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinich, E.E.; Topham, C.; Haynes, D.; Chung, J.; Latour, E.; Simpson, E.L. Validation of a novel patient-operated device for measuring skin barrier function in atopic dermatitis. Ski. Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPower Inc. gpskin Barrier. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T.; Yuasa, H.; Kai, R.; Ueda, H.; Ogura, S.; Honda, Y. Skin capacitance in normal and atopic infants, and effects of moisturizers on atopic skin. J. Dermatol. 2007, 34, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sator, P.G.; Schmidt, J.B.; Hönigsmann, H. Comparison of epidermal hydration and skin surface lipids in healthy individuals and in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.; Eichenfield, L.F. Quantitative Assessment of Combination Bathing and Moisturizing Regimens on Skin Hydration in Atopic Dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2009, 26, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Kim, H.-D.; Koo, H.-J.; So, J.-H. Textile-Based Wearable Sensor for Skin Hydration Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rie, H.N.; Cho, J.; Lee, J.; Gandla, S.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J. CMOS Skin Sensor for Mobile Skin Diagnosis Using an Electronic Cotton Pad. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 178816–178824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezic, S. Skin barrier in atopic dermatitis. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courage+Khazaka Electronic GmbH. Cutometer® Dual MPA 580; Courage+Khazaka Electronic GmbH: Köln, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Cuenca-Barrales, C.; Rodriguez-Pozo, J.-A.; Diaz-Calvillo, P.; Tercedor-Sanchez, J.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Epidermal Barrier Function and Skin Homeostasis in Atopic Dermatitis: The Impact of Age. Life 2022, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Segura-Fernández-Nogueras, M.-V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, I.; Soler-Gongora, M.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: Transepidermal Water Loss and Temperature as Useful Tools to Assess Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M.-M.; Bucur, S.; Serban, E.-D.; Olteanu, R.; Bratu, O.; Constantin, T. Measurement of skin viscoelasticity: A non-invasive approach in allergic contact dermatitis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, N.; Christakis, Y.; Di, J.; Bruno, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dorsey, E.R.; Pigeon, W.R.; Beck, L.A.; Thomas, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Development of digital measures for nighttime scratch and sleep using wrist-worn wearable devices. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noro, Y.; Omoto, Y.; Umeda, K.; Tanaka, F.; Shiratsuka, Y.; Yamada, T.; Isoda, K.; Matsubara, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Gabazza, E.C.; et al. Novel acoustic evaluation system for scratching behavior in itching dermatitis: Rapid and accurate analysis for nocturnal scratching of atopic dermatitis patients. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-E.; Lee, J.; Bessho, M.; Sakamura, K. Field Trial of a Wearable Itch Monitoring System for the Self-Management of Atopic Dermatitis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Melbourne, Australia, 17–20 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerstein, J.; Austin, D.; Sack, R.; Hayes, T.L. Wrist actigraphy for scratch detection in the presence of confounding activities. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-P.; Chiu, C.-W.; Lu, C.-W.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tseng, Y.S.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Wang, H.-C. Identification of Skin Lesions by Using Single-Step Multiframe Detector. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, D.; Yumang, A.; Diaz, A.L.; Inlong, G. Differentiating Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Chronic Plaque using Convolutional Neural Network MobileNet Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 11th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment, and Management (HNICEM), Laoag, Philippines, 29 November–1 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Hurault, G.; Arulkumaran, K.; Williams, H.C.; Tanaka, R.J. EczemaNet: Automating Detection and Severity Assessment of Atopic Dermatitis; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 220–230. [Google Scholar]
- Patella, V.; Florio, G.; Palmieri, M.; Bousquet, J.; Tonacci, A.; Giuliano, A.; Gangemi, S. Atopic dermatitis severity during exposure to air pollutants and weather changes with an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) analysis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, A.; De Benedetto, E.; Schiavoni, R.; Monti, G.; Tedesco, A.; Masciullo, A.; Piuzzi, E.; Tarricone, L. Portable Microwave Reflectometry System for Skin Sensing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 4003308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.; Chioukh, L.; Dashti Ardakani, M.; Dufour, S.; Tatu, S.O. Early-Stage Detection of Melanoma Skin Cancer Using Contactless Millimeter-Wave Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7310–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Shin, W.J.; Fan, J.A.; Liu, Z.; Lu, C.J.; Kong, G.W.; Chen, K.; Patnaik, D.; et al. Materials and Designs for Wireless Epidermal Sensors of Hydration and Strain. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zoughi, R. Millimeter Wave Reflectometry and Imaging for Noninvasive Diagnosis of Skin Burn Injuries. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendtke, R.; Wiehl, M.; Groeber, F.; Schwarz, T.; Walles, H.; Hansmann, J. Feasibility Study on a Microwave-Based Sensor for Measuring Hydration Level Using Human Skin Models. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavoni, R.; Monti, G.; Piuzzi, E.; Tarricone, L.; Tedesco, A.; De Benedetto, E.; Cataldo, A. Feasibility of a Wearable Reflectometric System for Sensing Skin Hydration. Sensors 2020, 20, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, G.; Schiavoni, R.; De Benedetto, E.; Cataldo, A.; Tarricone, L. Low-cost System for Skin Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and RF Conference (IMARC), Kanpur, India, 17–19 December 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Chand, K.; Narayanswamy, D.; Beetner, D.G.; Zoughi, R.; Stoecker, W.V. Microwave Reflectometry as a Novel Diagnostic Tool for Detection of Skin Cancers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2006, 55, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavoni, R.; Monti, G.; Tedesco, A.; Tarricone, L.; Piuzzi, E.; de Benedetto, E.; Masciullo, A.; Cataldo, A. Microwave Wearable System for Sensing Skin Hydration. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Glasgow, UK, 17–20 May 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, A.J.; Tunnell, J.W. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy and Imaging. In Imaging in Dermatology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Yakimov, B.P.; Davydov, D.A.; Fadeev, V.V.; Budylin, G.S.; Shirshin, E.A. Comparative analysis of the methods for quantitative determination of water content in skin from diffuse reflectance spectroscopy data. Quantum Electron. 2020, 50, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, K.; Ho, C.J.H.; Bi, R.; Yew, Y.W.; Dinish, U.S.; Attia, A.B.E.; Moothanchery, M.; Guan, S.T.T.; Olivo, M. Machine Learning Assisted Handheld Confocal Raman Micro-Spectroscopy for Identification of Clinically Relevant Atopic Eczema Biomarkers. Sensors 2022, 22, 4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Meyers, C.L.; Subramanyan, K.; Hancewicz, T.M. Near infrared imaging for measuring and visualizing skin hydration. A comparison with visual assessment and electrical methods. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 031107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitdidier, N.; Koenig, A.; Gerbelot, R.; Grateau, H.; Gioux, S.; Jallon, P. Contact, high-resolution spatial diffuse reflectance imaging system for skin condition diagnosis. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.J.H.; Yew, Y.W.; Dinish, U.S.; Kuan, A.H.Y.; Wong, M.K.W.; Bi, R.; Dev, K.; Li, X.; Singh, G.; Moothanchery, M.; et al. Handheld confocal Raman spectroscopy (CRS) for objective assessment of skin barrier function and stratification of severity in atopic dermatitis (AD) patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 98, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F.J.; Alda, J.; Moreno-Cruz, B.; Martínez-Escanamé, M.; Ramírez-Elías, M.G.; Torres-Álvarez, B.; Moncada, B. Use of Raman spectroscopy for the early detection of filaggrin-related atopic dermatitis. Ski. Res. Technol. 2011, 17, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioravanti, V.; Brandhoff, L.; Van Den Driesche, S.; Breiteneder, H.; Kitzwögerer, M.; Hafner, C.; Vellekoop, M. An Infrared Absorbance Sensor for the Detection of Melanoma in Skin Biopsies. Sensors 2016, 16, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, Y. Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine as a clinical biomarker in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, S.J.; Nam, S.H. Non-invasive method to monitor molecular changes in human stratum corneum during acute barrier disruption using reflectance NIR spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, P.; Fésűs, L.; Kiss, N.; Noll, J.; Becker, K.; Kuroli, E.; Mayer, B.; Bozsányi, S.; Lőrincz, K.; Lihacova, I.; et al. Visualization of Keratin with Diffuse Reflectance and Autofluorescence Imaging and Nonlinear Optical Microscopy in a Rare Keratinopathic Ichthyosis. Sensors 2021, 21, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hu, S.; Alzahrani, A.; Alharbi, S.; Blanos, P. A Multi-Wavelength Opto-Electronic Patch Sensor to Effectively Detect Physiological Changes against Human Skin Types. Biosensors 2017, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbunge, E.; Muchemwa, B.; Jiyane, S.E.; Batani, J. Sensors and healthcare 5.0: Transformative shift in virtual care through emerging digital health technologies. Glob. Health J. 2021, 5, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P.; Singha, M.K. IoT Based Wearable Healthcare System: Post COVID-19; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 305–321. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Huanyu, C.; Kaile, C.; Yilin, Z.; Yihui, Z.; Yuhao, L.; Chenqi, Z.; Shao-chi, O.; Gil-Woo, K.; Cunjiang, Y.; et al. Epidermal Impedance Sensing Sheets for Precision Hydration Assessment and Spatial Mapping. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2848–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Monitor and Distinguish? | Estimate Severity | Can Predict Condition? | Biomarker | Invasive? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biopsy [26,27,28,29] | Yes | Yes | Yes | IgE | Yes |
| Blood serum [11,28,30,31] | Yes | No | Yes | Cytokine Acetylcholine | Yes |
| Tape stripping [32,33,34] | Yes | Yes | No | Chemokine Ceramide | Yes |
| Method | Monitor and Distinguish? | Estimate Severity | Monitor Treatment | Allows Continuous Monitoring | Wearable or Portable? | Occlusive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEWL [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Skin permittivity [10,18,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Skin elasticity [72,73,74,75,76] | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | N/A |
| Scratching frequency [22,77,78,79,80] | No | Yes | Yes | During nighttime | Yes | No |
| Neural network [81,82,83,84] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Can be | No |
| Authors | Probe Type | Measurement Frequency | Sensor Placement | Range in S11 Values between Dry and Wet Skin States | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cataldo, A. et al., 2022 [85] | Tri-electrode array | 0–600 MHz | Forearm and leg | 0.165–0.268 | Predicts values for extra-dehydrated skin. |
| Schiavoni, R. et al., 2021 [93] | Tri-electrode array | 100–400 MHz | Forearm | 0.185–0.290 | Explores three skin hydration states. Housed in a wearable and flexible patch |
| Arab, H. et al., 2020 [86] | Open-ended coaxial | 77 GHz | Hand | 0.2–0.26 | Tested on melanoma skin. |
| Brendtke, R. et al., 2016 [89] | Open-ended coaxial | 7.35 GHz | Tested on phantom | - | Tested on various saline solutions in contact with skin phantom. |
| Monti, G. et al., 2021 [92] | Tri-electrode array | 20–2000 MHz | Forearm, leg, arm, palm | 0.224–0.282 | Uses a compact VNA for mobile measurements. |
| Mehta, P. et al., 2006 [92] | Open-ended coaxial | 300 MHz–3 GHz | Forearm, cheek, palm, chest | 0.08–0.14 | Used for melanoma detection. Differentiates malignant and benign lesions. |
| Gao, Y. et al., 2017 [88] | Open-ended coaxial | 26.5–75 GHz | Tested on pig skin | - | Classifies burn degrees. |
| Authors | Technique | Sensor Placement | Sensor Footprint | Skin Condition | Wavelength | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dev et al., 2022 [96] | Confocal Raman Micro-Spectroscopy | Volar forearm | Handheld probe, connected to bench spectrometer | AD | 5550–25,000 | Highest sensitivity to urocanic acid. |
| Ho et al., 2020 [99] | Confocal Raman Micro-Spectroscopy | Volar forearm | Handheld probe with built in spectrometer and light source; bulky package | AD | 5000–16,000 | Compares device to TEWL and conventional AD scoring system. |
| Gonzalez et al., 2011 [100] | Raman Spectroscopy | Right thigh | Commercial benchtop Raman spectrometer | AD | 5550–50,000 | Tested on infants. |
| Fioravanti et al., 2016 [101] | Near-Infrared Spectroscopy | Biopsy | Multi-lens benchtop setup, connected to a computer and IR emitter | Melanoma | 3350–3550 | Detects abnormalities of methylene absorption in melanoma patients. |
| Shin et al., 2018 [103] | Near-Infrared Spectroscopy | Facial cheek | Commercial benchtop spectrometer | Barrier disruption | 1450–2500 | Performs skin stripping to induce barrier disruption. Can monitor protein and lipid alterations. |
| Zhang et al., 2005 [97] | Near-Infrared Spectroscopy | Outer lower leg | Benchtop detector and camera setup with two separate light sources | Skin hydration | 1100–1630 | Claims NIR cannot be used to target individual layers. Compares against electrical methods. |
| Anker et al., 2021 [104] | Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy | Various locations on infants’ skin | LEDs around a camera. | Ichthyosis | 405 | Monitors mutations of keratin-forming genes. |
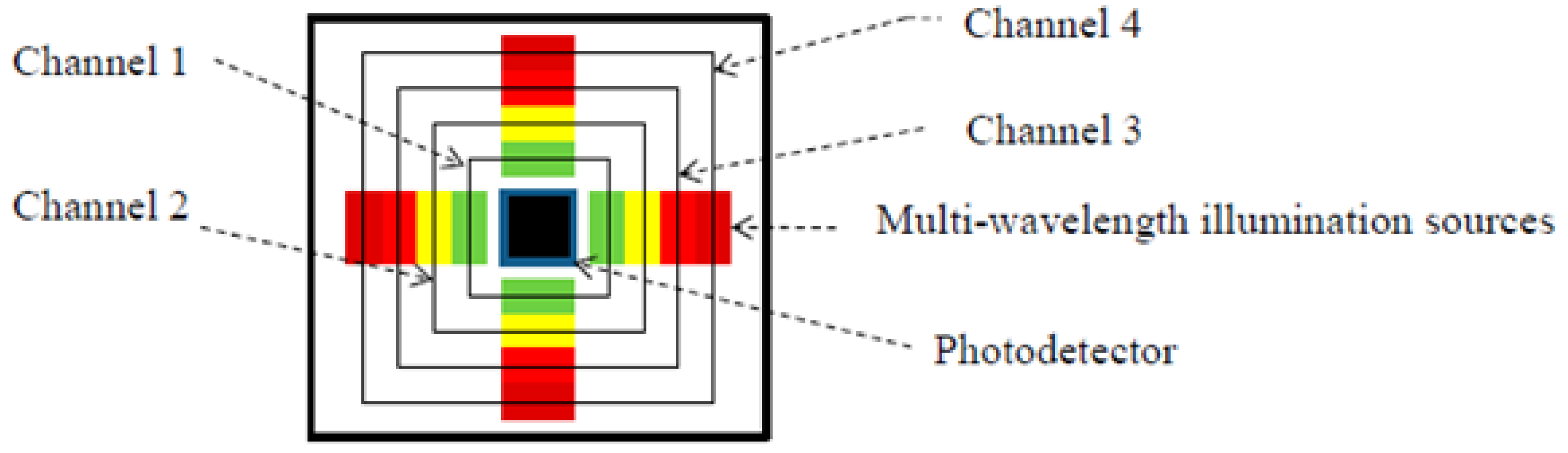
| Yan et al., 2017 [105] | Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy | Palm | Multi-LED and PD patch of size 324 mm2 | Physiological skin changes | 525–870 | Compact and wearable package. |
| Mamouei et al., 2021 [13] | Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy | Skin phantom | Coin-sized Multi-LED and PD probe | Skin hydration | 970–1450 | Has not been used on skin, only on fake tissue to predict water evaporation. |
| Petitdidier et al., 2021 [98] | Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy | Skin phantom | Coin-sized pixelated sensor with holder | Physiological skin changes | 645 | Uses CMOS technology for very small separation distances. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Todorov, A.; Torah, R.; Wagih, M.; Ardern-Jones, M.R.; Beeby, S.P. Electromagnetic Sensing Techniques for Monitoring Atopic Dermatitis—Current Practices and Possible Advancements: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083935
Todorov A, Torah R, Wagih M, Ardern-Jones MR, Beeby SP. Electromagnetic Sensing Techniques for Monitoring Atopic Dermatitis—Current Practices and Possible Advancements: A Review. Sensors. 2023; 23(8):3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083935
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodorov, Alexandar, Russel Torah, Mahmoud Wagih, Michael R. Ardern-Jones, and Steve P. Beeby. 2023. "Electromagnetic Sensing Techniques for Monitoring Atopic Dermatitis—Current Practices and Possible Advancements: A Review" Sensors 23, no. 8: 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083935
APA StyleTodorov, A., Torah, R., Wagih, M., Ardern-Jones, M. R., & Beeby, S. P. (2023). Electromagnetic Sensing Techniques for Monitoring Atopic Dermatitis—Current Practices and Possible Advancements: A Review. Sensors, 23(8), 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083935











