Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticle Ensembles for Rapidly Identifying S. epidermidis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria Culture
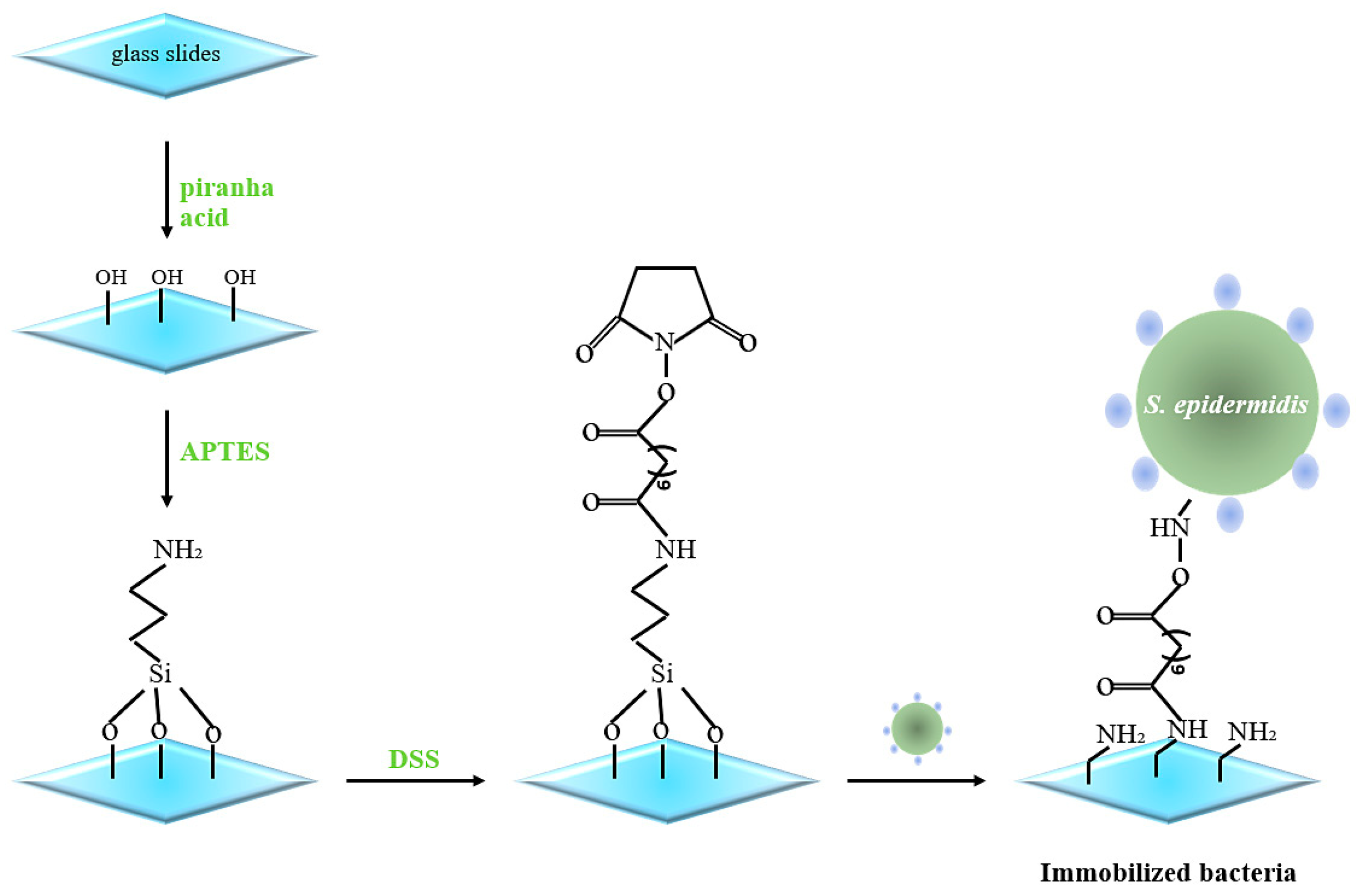
2.2. Immobilizing S. epidermidis
2.3. MIP Nanoparticle Synthesis
2.4. MIP Nanoparticle Rebinding
2.5. Assessing Surface Roughness by AFM Imaging
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Fluorescence Imaging
3. Results
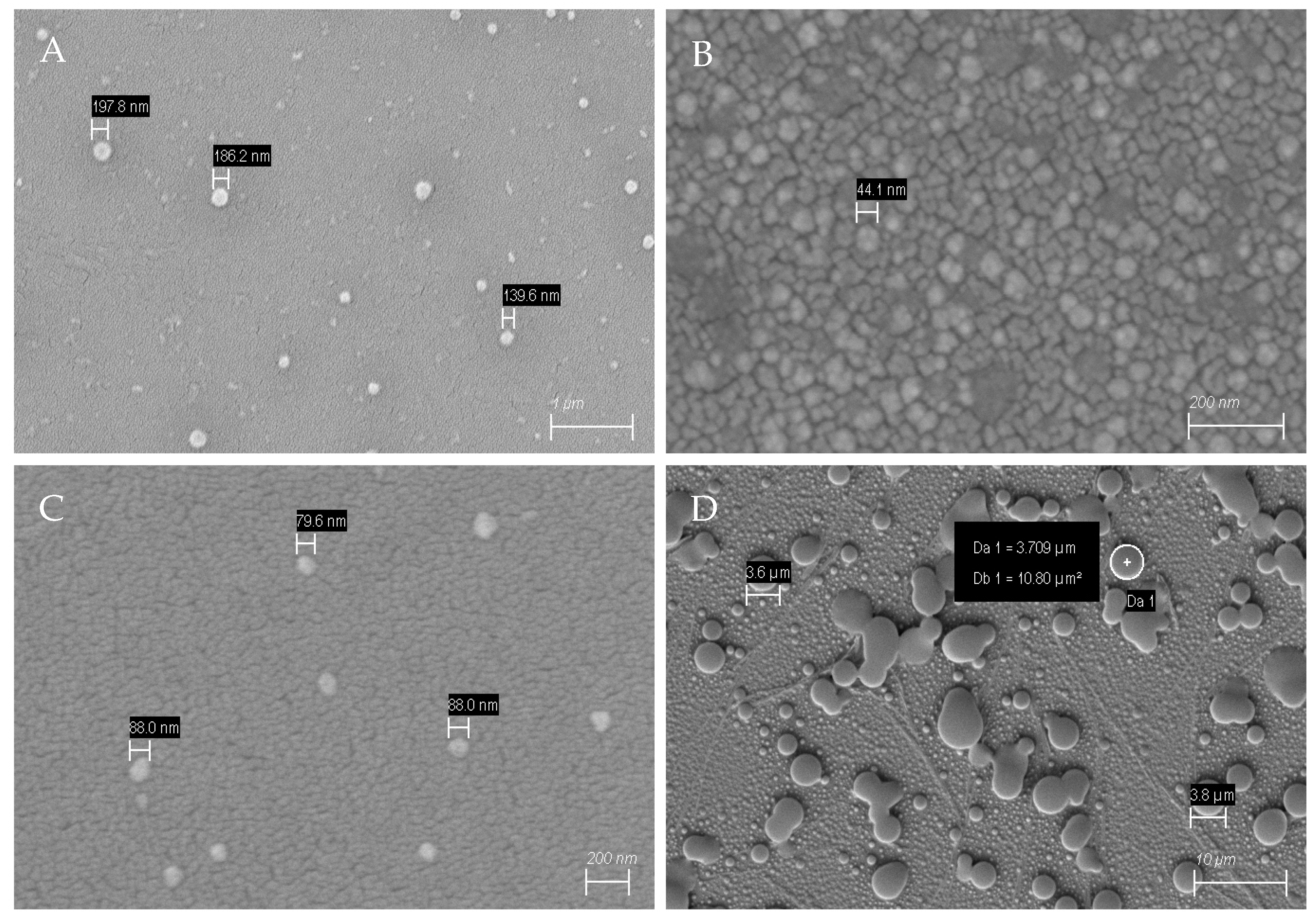
3.1. MIP Characterization by SEM and AFM
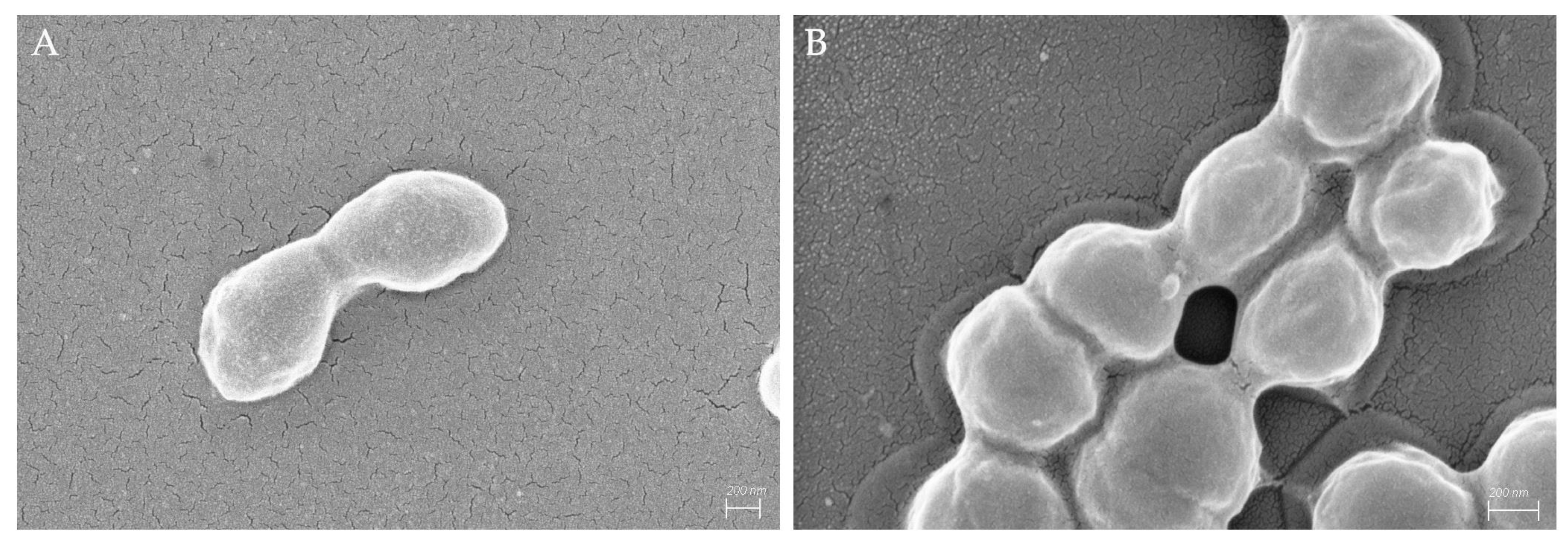
3.2. Bacterial Cell Surface and Morphology Changes
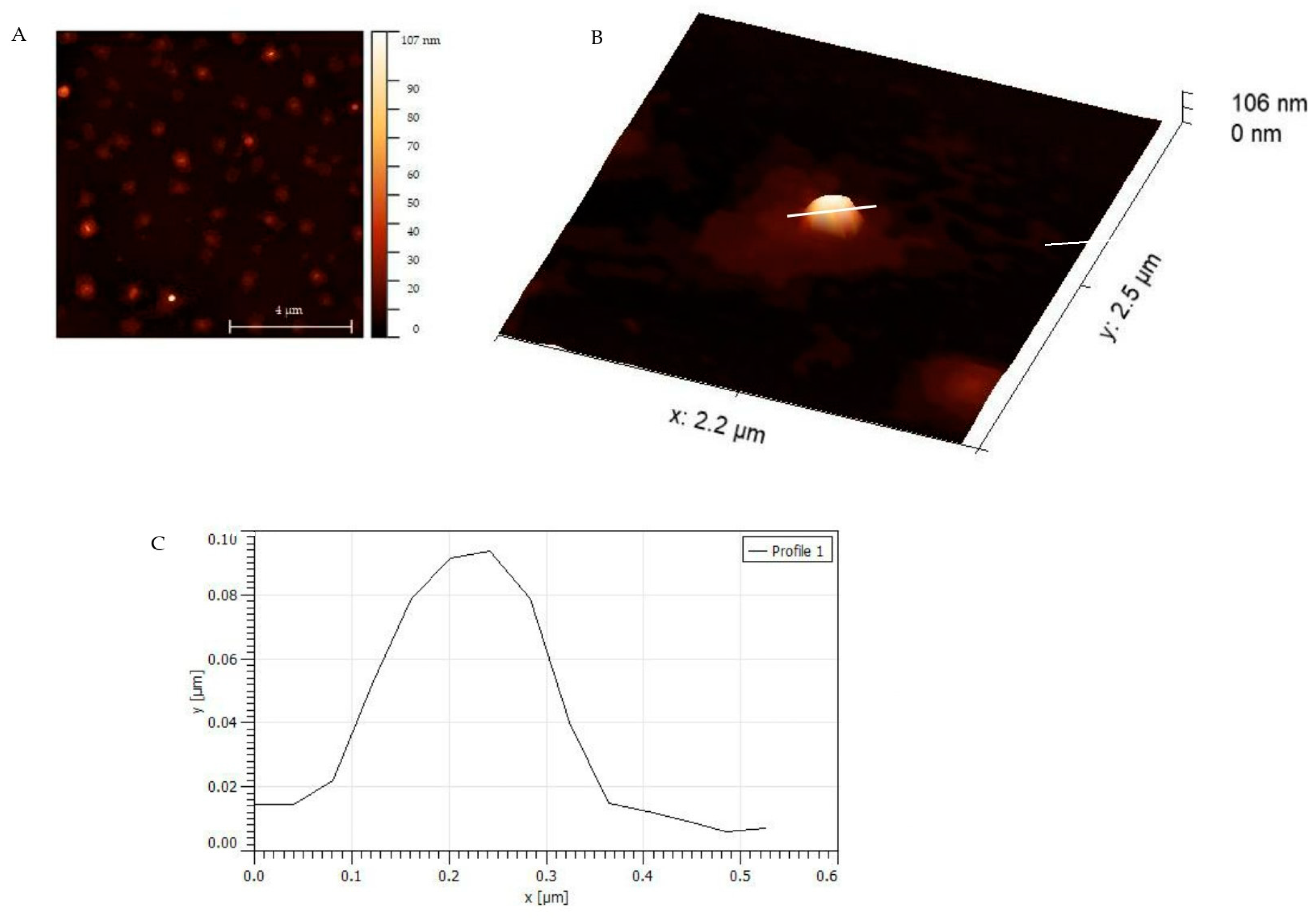
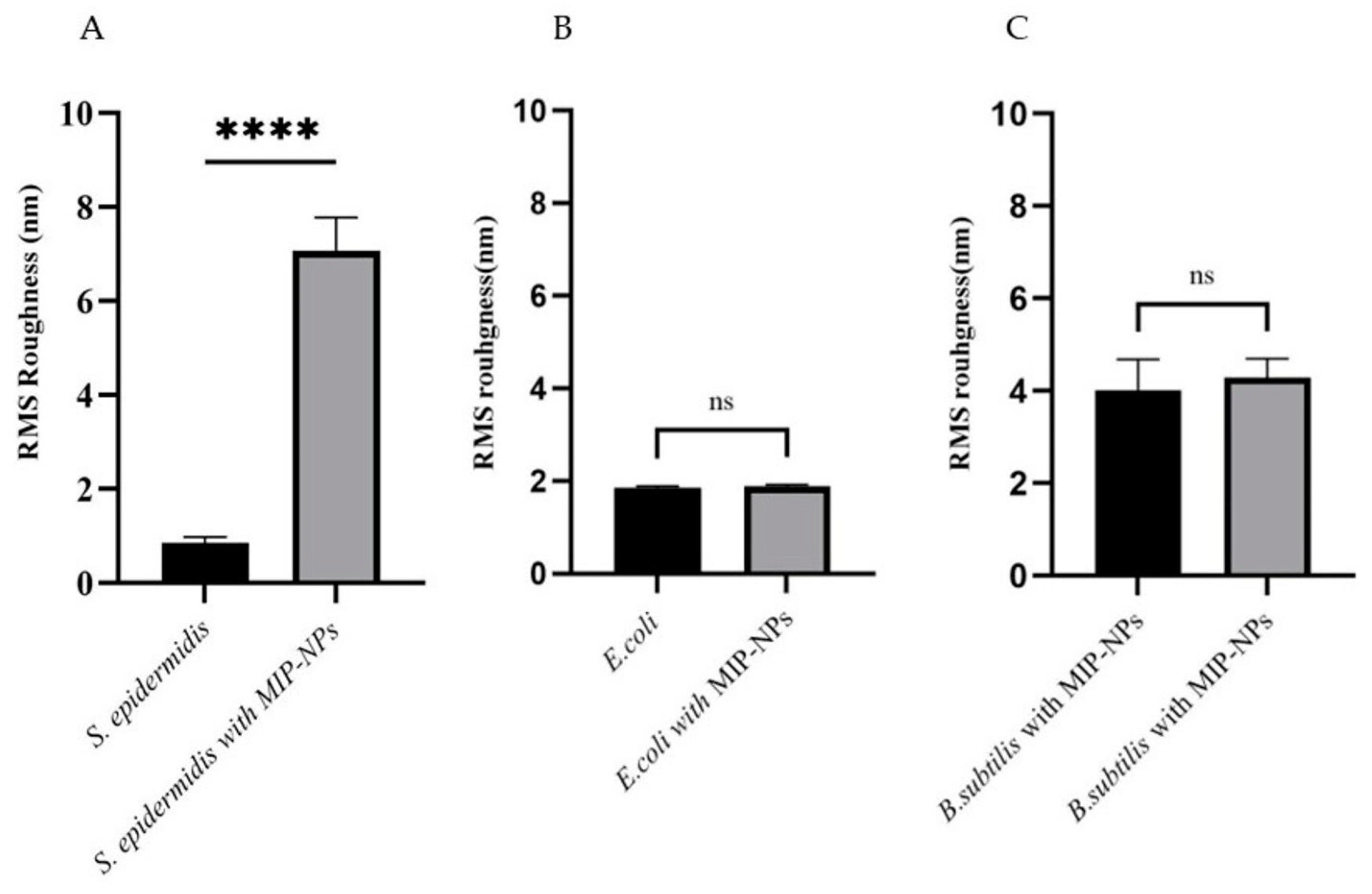
3.3. AFM Characterization of Binding
3.4. Fluorescence Characterization of Binding
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabrera, J.N.; Ruiz, M.M.; Fascio, M.; D’Accorso, N.; Mincheva, R.; Dubois, P.; Lizarraga, L.; Negri, R.M. Increased Surface Roughness in Polydimethylsiloxane Films by Physical and Chemical Methods. Polymers 2017, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornazari, F.; Guimarães, F.; Teixeira, C.; Langoni, H. Isolation of Staphylococcus epidermidis from inflamed upper respiratory tract of an orange-spined hairy dwarf porcupine (Sphiggurus villosus). J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 18, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.Y.; Jiang, Y.E.; Scott, D.A. Culturable bacteria in the entire acne lesion and short-chain fatty acid metabolites of Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 622, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Colín-Castro, C.A.; Hernández-Durán, M.; López-Jácome, L.E.; Franco-Cendejas, R. Staphylococcus epidermidis small colony variants, clinically significant quiescent threats for patients with prosthetic joint infection. Microbes Infect. 2021, 23, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogo, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Sumiyoshi, S.; Iwamoto, N.; Aoki, K.; Motobayashi, H.; Tochitani, K.; Shimizu, T.; Murashima, T.; Nishikawa, N.; et al. Two cases of pyelonephritis with bacteremia by Staphylococcus epidermidis in male patients with nephrolithiasis: Case reports and a literature review. J. Infect. Chemother. 2022, 28, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, M.E.; Fey, P.D. Staphylococcus epidermidis and Other Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci; E-Sun Technologies: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 2579–2589. Available online: http://www.antimicrobe.org/b234.asp#top (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Pagano, L.; Gkartziou, F.; Aiello, S.; Simonis, B.; Ceccacci, F.; Sennato, S.; Ciogli, A.; Mourtas, S.; Spiliopoulou, I.; Antimisiaris, S.G.; et al. Resveratrol loaded in cationic glucosylated liposomes to treat Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2022, 243, 105174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukes, L.; Mikhail, J.; Bome-Mannathoko, N.; Hadfield, S.J.; Harris, L.; El-Bouri, K.; Davies, A.; Mack, D. Rapid differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and other coagulase-negative staphylococci and meticillin susceptibility testing directly from growth-positive blood cultures by multiplex real-time PCR. J. Med Microbiol. 2010, 59, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Peng, H.; Barton, M. Antibiotic resistance in staphylococci associated with cats and dogs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Hossain, M.; Bilkis, L.; Musa, A.K.; Mahamud, C.; Bari, M.S.; Haque, N.; Muhammad, N.; Parvin, U.S.; Islam, M.T.; I Khan, S.; et al. Antibiotic susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Mymensingh Med. J. 2009, 18, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.H.; Ranken, R.; Sefers, S.E.; Lovari, R.; Quinn, C.D.; Meng, S.; Carolan, H.E.; Toleno, D.; Li, H.; Lee, J.N.; et al. Detection, Identification, and Distribution of Fungi in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Specimens by Use of Multilocus PCR Coupled with Electrospray Ionization/Mass Spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.; Friedrich, J.; Adhikari, N.; Day, A.; Verdant, C.; Heyland, D.K. Utility of Gram stain in the clinical management of suspected ventilator-associated pneumonia: Secondary analysis of a multicenter randomized trial. J. Crit. Care 2008, 23, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzicka, F.; Hola, V.; Votava, M.; Tejkalová, R.; Horvát, R.; Heroldová, M.; Woznicová, V. Biofilm detection and the clinical significance ofStaphylococcus epidermidis isolates. Folia Microbiol. 2004, 49, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.M.; Schuenck, R.P.; Malvar, K.L.; Iorio, N.L.; Matos, P.D.; Olendzki, A.N.; Oelemann, W.M.; dos Santos, K.R. Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus haemolyticus: Methicillin-resistant isolates are detected directly in blood cultures by multiplex PCR. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 165, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Koide, H.; Urakami, T.; Kanazawa, H.; Kodama, T.; Oku, N.; Shea, K.J. Recognition, Neutralization, and Clearance of Target Peptides in the Bloodstream of Living Mice by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles: A Plastic Antibody. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6644–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suedee, R.; Seechamnanturakit, V.; Canyuk, B.; Ovatlarnporn, C.; Martin, G.P. Temperature sensitive dopamine-imprinted (N,N-methylene-bis-acrylamide cross-linked) polymer and its potential application to the selective extraction of adrenergic drugs from urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1114, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräuer, B.; Thier, F.; Bittermann, M.; Baurecht, D.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Raman Studies on Surface-Imprinted Polymers to Distinguish the Polymer Surface, Imprints, and Different Bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 5, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.E.; Dennison, S.R.; Tully, M.; Crossley, S.; Mwangi, W.; Bailey, D.; Graham, S.; Reddy, S.J. Evaluation of electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers (E-MIPs) on disposable electrodes for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1206, 339777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idil, N.; Mattiasson, B. Imprinting of Microorganisms for Biosensor Applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Ng, S.-C.; Chan, H.S.-O. Enantioselective molecular imprinting polymer coated QCM for the recognition of l-tryptophan. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2006, 113, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.-X.; Ma, X.-T.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Smart surface imprinting polymer nanospheres for selective recognition and separation of glycoprotein. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 433, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Xue, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, H.; Wu, Z. Recognition property and preparation of Staphylococcus aureus protein A-imprinted polyacrylamide polymers by inverse-phase suspension and bulk polymerization. Polymer 2009, 50, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, P.X.M.; Laclef, S.; Xu, J.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Kovensky, J.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer nanolabels: Affinity tools for cellular bioimaging of glycans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, K.K.; Shao, S.; Tan, T.; Lv, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective recognition of microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 45, 107640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.S.; Piletska, E.; Poblocka, M.; Macip, S.; Jones, D.J.; Braga, M.; Cao, T.H.; Singh, R.; Spivey, A.C.; Aboagye, E.O.; et al. Snapshot imprinting: Rapid identification of cancer cell surface proteins and epitopes using molecularly imprinted polymers. Nano Today 2021, 41, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, A.P.F.; Gonçalves, S.; Santos, N.C.; de Mishima, B.A.L.; Dalmasso, P.R.; Hollmann, A. Studies on interaction of green silver nanoparticles with whole bacteria by surface characterization techniques. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, T.; Cui, K.; Shen, F.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Mao, H. Evolution of surface morphology, roughness and texture of tungsten disilicide coatings on tungsten substrate. Vacuum 2021, 191, 110297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jung, G.B.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, G.-J.; Park, H.-K. Medical applications of atomic force microscopy and Raman spectroscopy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajini, T.; Mathew, B. A brief overview of molecularly imprinted polymers: Highlighting computational design, nano and photo-responsive imprinting. Talanta Open 2021, 4, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Rao, T.S. AFM studies on surface morphology, topography and texture of nanostructured zinc aluminum oxide thin films. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2012, 7, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ng, A.K.; Xu, R.; Wei, J.; Tan, C.M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial action of dispersed single-walled carbon nanotubes on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis investigated by atomic force microscopy. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2744–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.H.; Chitra, E.; Ramamurthy, S.; Ling, C.C.S.; Ambu, S.P.; Davamani, F. Cationic chitosan-propolis nanoparticles alter the zeta potential of S. epidermidis, inhibit biofilm formation by modulating gene expression and exhibit synergism with antibiotics. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, B.R. Review of surface roughness prediction in machining process by using various parameters. Int. J. Recent Trends Eng. Res. 2020, 6, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
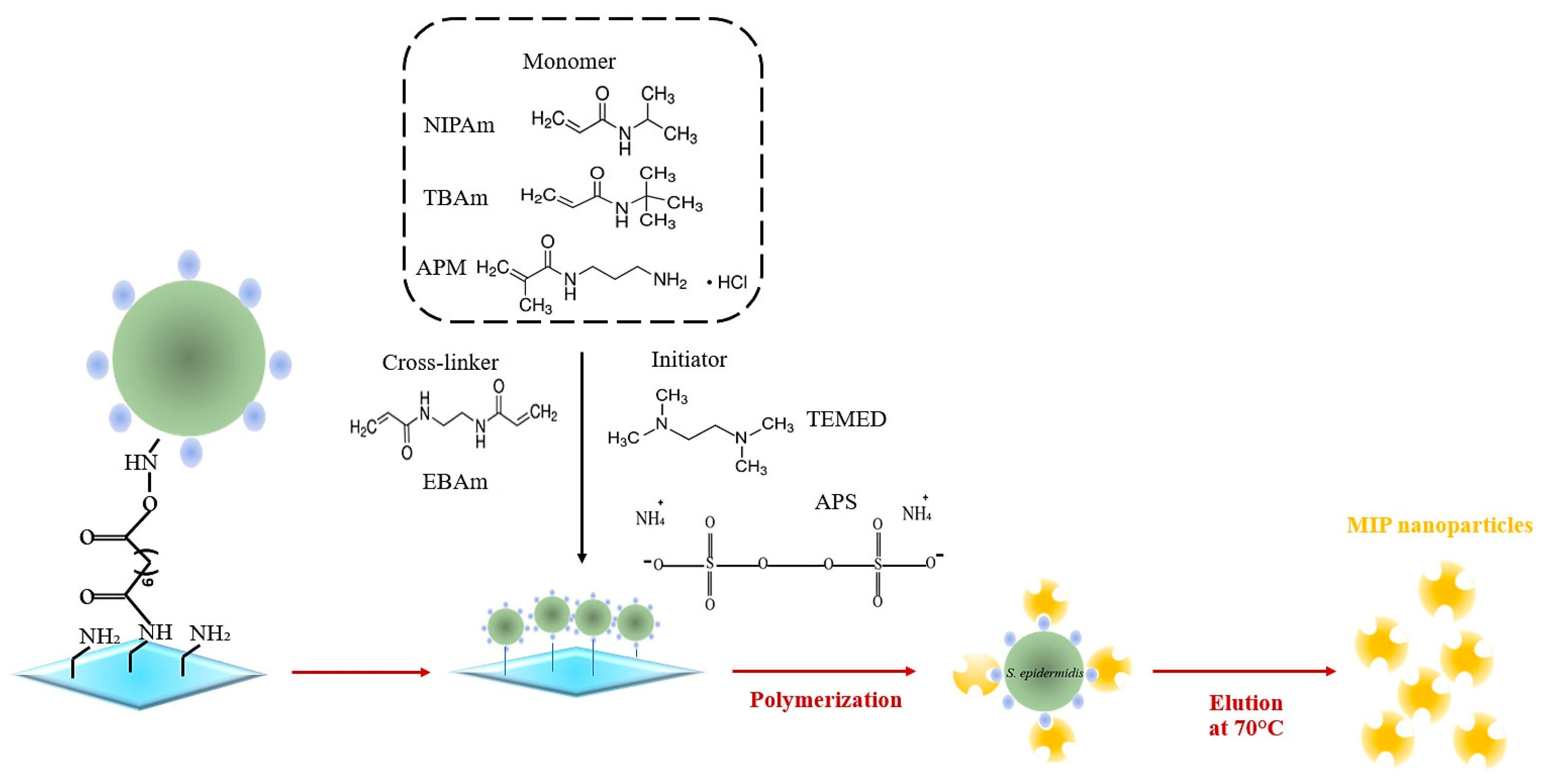




| Protocol | NIPAM (mmol) | TBAM (mmol) | APM (mmol) | EBAM (mmol) | Zeta Pot mV | Size (nm) | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.66 | - | - | 0.06 | −20.9 | ~200 | ~4.7% |
| 2 | 0.6 | 0.06 | - | 0.06 | −11.8 | ~50 | ~7.5% |
| 3 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | +7.5 | ~70–110 | ~3.0% |
| Bacteria Cell | Native Bacteria | Bacteria Incubated with MIP Nanoparticles | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS Roughness (nm) | Ra Roughness (nm) | RMS Roughness (nm) | Ra Roughness (nm) | |
| S. epidermidis | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 7.0 ± 1.5 | 5.9 ± 1.5 |
| E. coli | 1. 8 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| B. subtillis | 4.4 ± 1.9 | 3.5 ± 1.3 | 4.5 ± 2.2 | 3.6 ± 1.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hlaoperm, C.; Sudjarwo, W.A.A.; Ehrenbrandtner, J.; Kiss, E.; Del Favero, G.; Choowongkomon, K.; Rattanasrisomporn, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticle Ensembles for Rapidly Identifying S. epidermidis. Sensors 2023, 23, 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073526
Hlaoperm C, Sudjarwo WAA, Ehrenbrandtner J, Kiss E, Del Favero G, Choowongkomon K, Rattanasrisomporn J, Lieberzeit PA. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticle Ensembles for Rapidly Identifying S. epidermidis. Sensors. 2023; 23(7):3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073526
Chicago/Turabian StyleHlaoperm, Chularat, Wisnu Arfian A. Sudjarwo, Jakob Ehrenbrandtner, Endre Kiss, Giorgia Del Favero, Kiattawee Choowongkomon, Jatuporn Rattanasrisomporn, and Peter A. Lieberzeit. 2023. "Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticle Ensembles for Rapidly Identifying S. epidermidis" Sensors 23, no. 7: 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073526
APA StyleHlaoperm, C., Sudjarwo, W. A. A., Ehrenbrandtner, J., Kiss, E., Del Favero, G., Choowongkomon, K., Rattanasrisomporn, J., & Lieberzeit, P. A. (2023). Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticle Ensembles for Rapidly Identifying S. epidermidis. Sensors, 23(7), 3526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073526






