Quantification and Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect in Immersive Virtual Reality: A Validation Study in Healthy Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
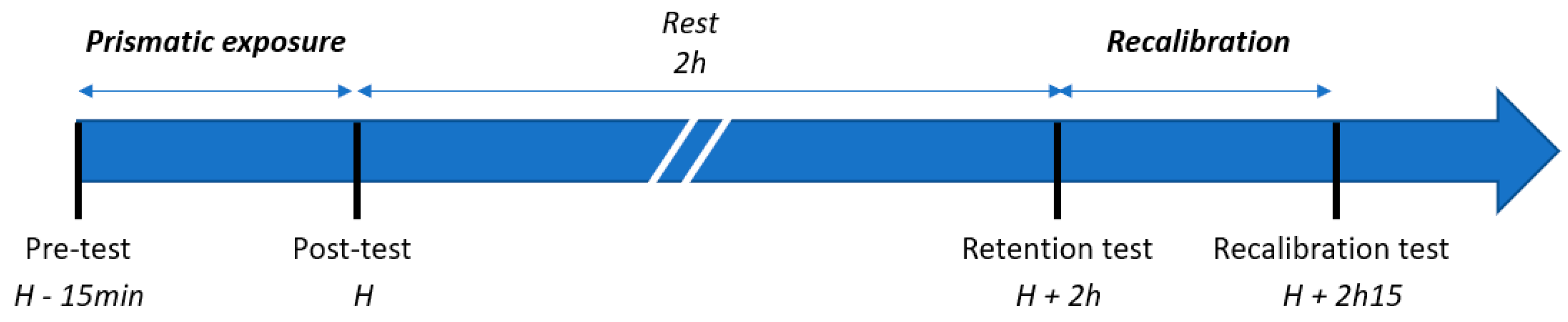
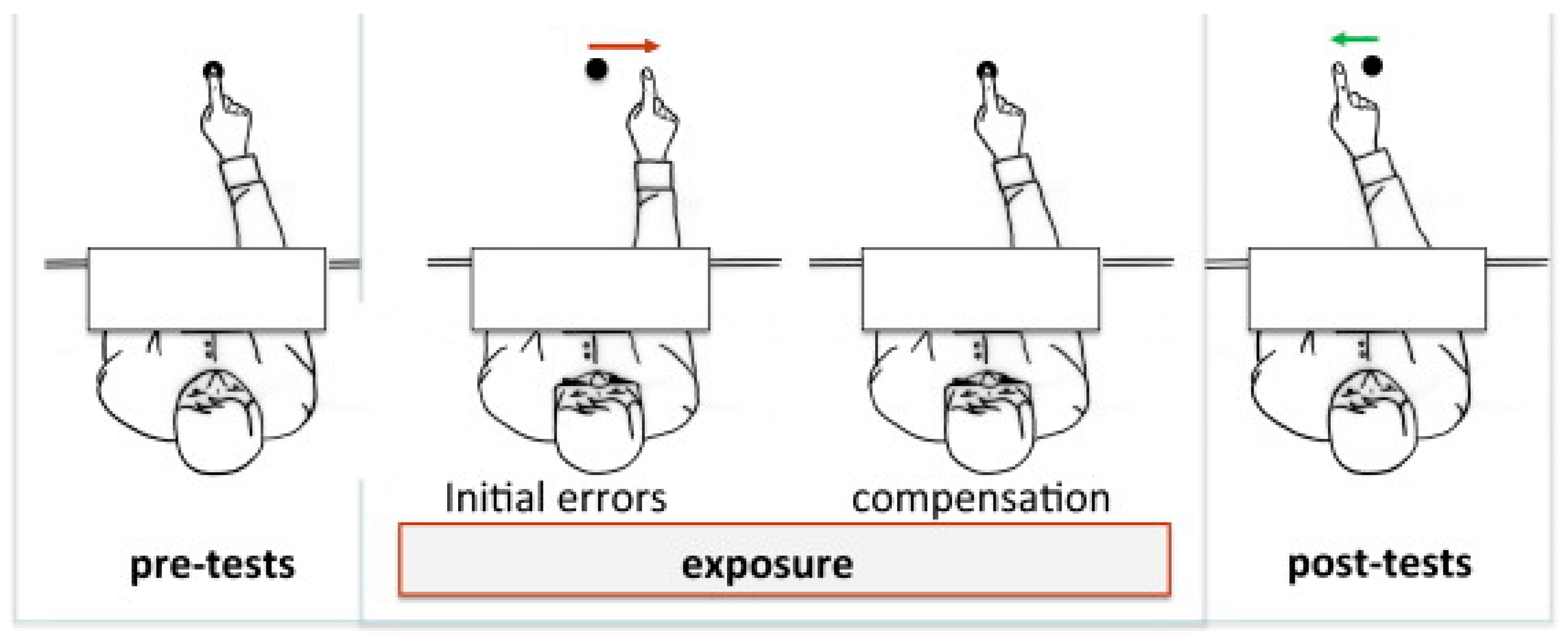
2.2. Experimental Protocol
- -
- The Real Set: measurements performed under real conditions with exposure to real prisms.
- -
- The Mixed Set: measurements performed under real conditions with exposure to virtual prisms.
- -
- The Virtual Set: measurements performed under virtual conditions with exposure to virtual prisms.
2.3. Description of Exposure and Tests Used
2.4. Description of the Equipment
2.4.1. Prism Exposure
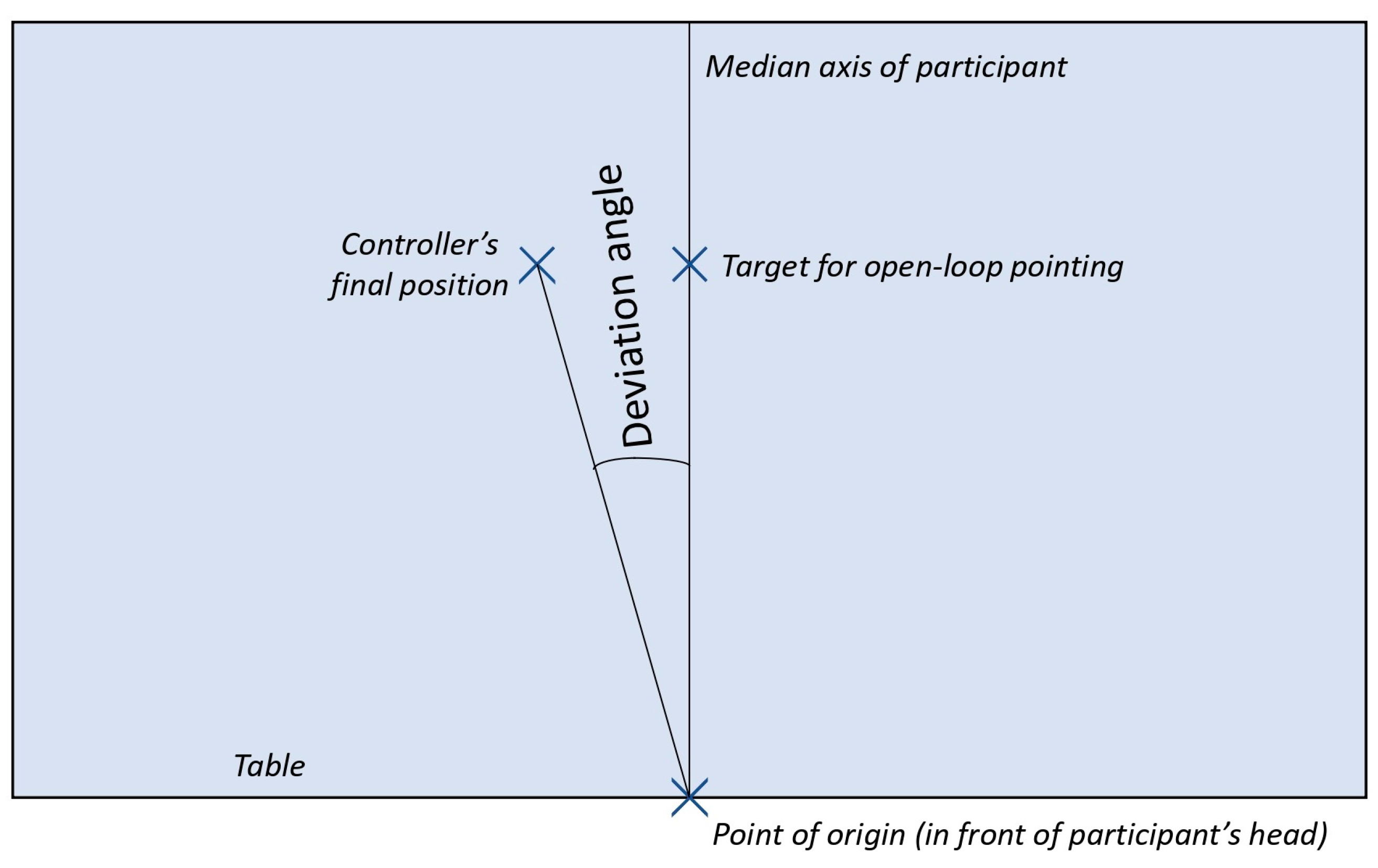
2.4.2. Measuring Tool
2.5. Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
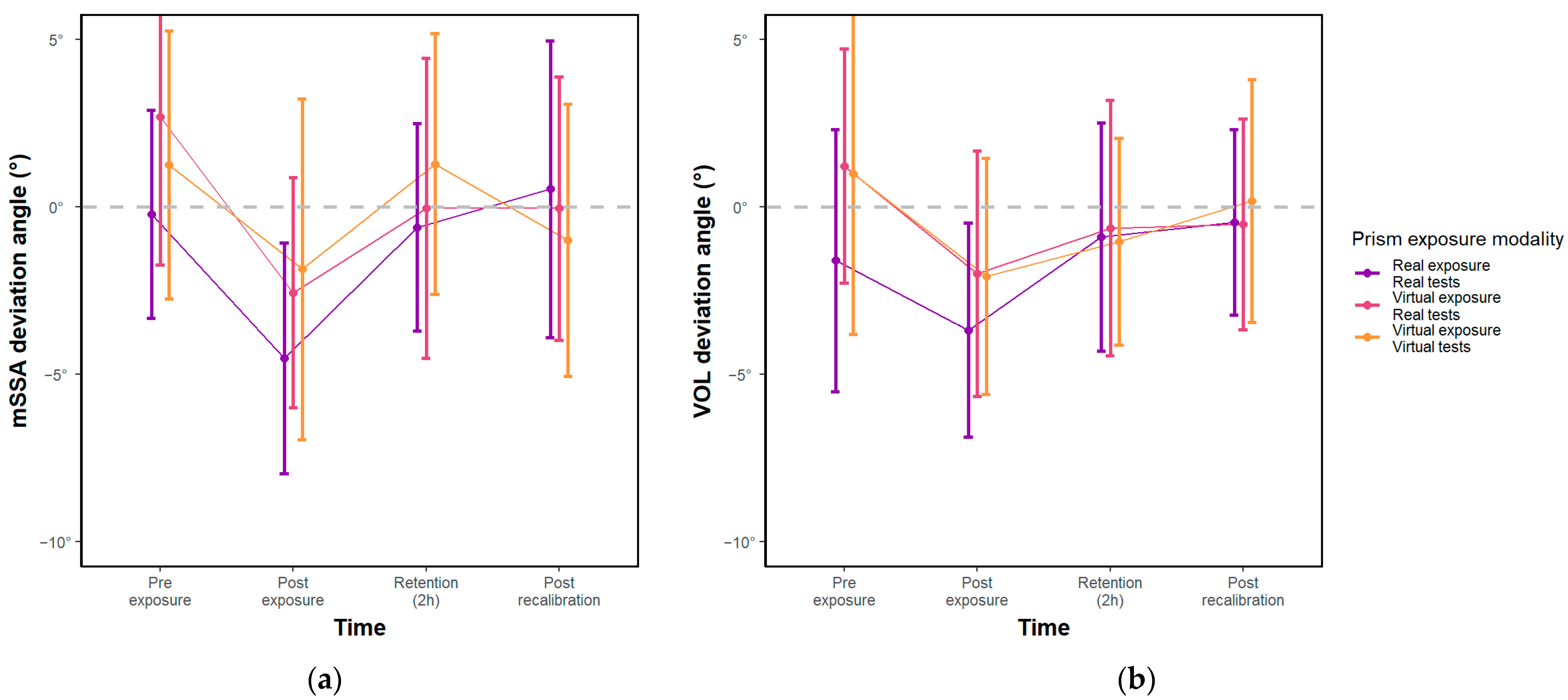
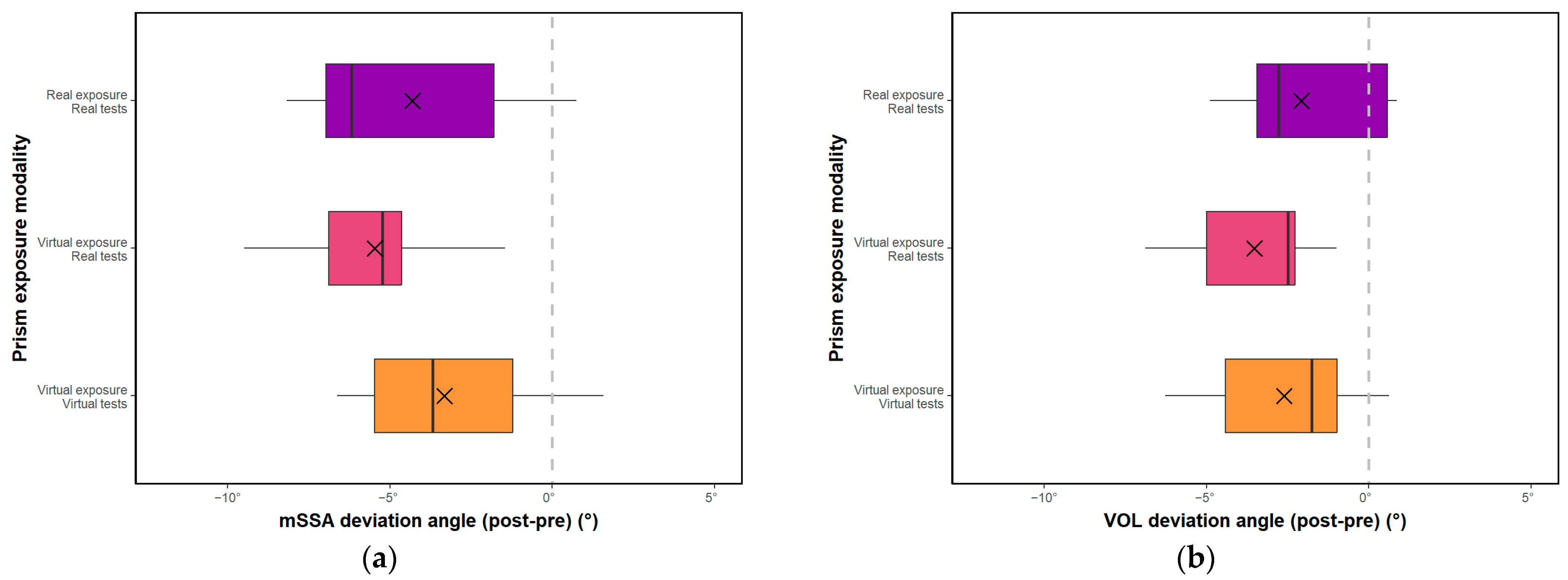
3.1. Effect of Exposure Modality and Time
3.2. Equivalence Hypothesis
3.3. Is the Angle Given by the HTC Vive® System the Same as the Angle Given by the Zebris?
4. Discussion
4.1. For Hypothesis H1: “The Deviation Induced under Virtual Conditions Is at Least as Large as the Deviation Induced in the Real Condition”
4.2. Mechanism of Deviation
4.2.1. The Specific Case of the vSSA
4.2.2. The Importance of Visual Recalibration
4.3. For Hypothesis H2: “The Angle of Deflection Measured by the HTC Vive® System Is the Same as the Angle Measured by the ZEBRIS System”
4.4. Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heilman, K.M.; Valenstein, E. Mechanisms Underlying Hemispatial Neglect. Ann. Neurol. 1979, 5, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.; McKenna, K.; Tallis, R.C. Reasons for Variability in the Reported Rate of Occurrence of Unilateral Spatial Neglect After Stroke. Stroke 1999, 30, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, E.; Shekhtman, G.; Chen, P. Prevalence of Spatial Neglect Post-Stroke: A Systematic Review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 64, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halligan, P.W.; Marshall, J.C.; Wade, D.T. Visuospatial neglect: Underlying factors and test sensitivity. Lancet 1989, 334, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, N.; Hartman-Maeir, A.; Ring, H.; Soroker, N. Functional Disability and Rehabilitation Outcome in Right Hemisphere Damaged Patients with and without Unilateral Spatial Neglect. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longley, V.; Hazelton, C.; Heal, C.; Pollock, A.; Woodward-Nutt, K.; Mitchell, C.; Pobric, G.; Vail, A.; Bowen, A. Non-pharmacological Interventions for Spatial Neglect or Inattention Following Stroke and Other Non-progressive Brain Injury. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD003586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassinetti, F.; Angeli, V.; Meneghello, F.; Avanzi, S.; Làdavas, E. Long-lasting Amelioration of Visuospatial Neglect by Prism Adaptation. Brain 2002, 125, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossetti, Y.; Rode, G.; Pisella, L.; Farné, A.; Li, L.; Boisson, D.; Perenin, M.T. Prism Adaptation to a Rightward Optical Deviation Rehabilitates Left Hemispatial Neglect. Nature 1998, 395, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zanca, J.; Esposito, E.; Barrett, A.M. Barriers and Facilitators to Rehabilitation Care of Individuals With Spatial Neglect: A Qualitative Study of Professional Views. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2021, 3, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieri, G.; Morone, G.; Paolucci, S.; Iosa, M. Virtual Reality in Cognitive and Motor Rehabilitation: Facts, Fiction and Fallacies. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2018, 15, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardsson, M.; Alt Murphy, M.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Commercial Head-Mounted Display Virtual Reality for Upper Extremity Rehabilitation in Chronic Stroke: A Single-Case Design Study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, H.; Ren, Z. Application of Wearable Device HTC VIVE in Upper Limb Rehabilitation Training. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2018; pp. 1460–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Borrego, A.; Latorre, J.; Alcañiz, M.; Llorens, R. Comparison of Oculus Rift and HTC Vive: Feasibility for Virtual Reality-Based Exploration, Navigation, Exergaming, and Rehabilitation. Games Health J. 2018, 7, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, D.; Barlow, M.; Lakshika, E. Prosthetic Rehabilitation Training in Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 7th International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Kyoto, Japan, 5–7 August 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniappan, S.M.; Duerstock, B.S. Developing Rehabilitation Practices Using Virtual Reality Exergaming. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Louisville, KY, USA, 6–8 December 2018; pp. 090–094. [Google Scholar]
- Elor, A.; Kurniawan, S.; Teodorescu, M. Towards an Immersive Virtual Reality Game for Smarter Post-Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Taormina, Italy, 18–20 June 2018; pp. 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.-L.; Chen, M.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Liao, C.-M.; Yang, T. Satisfaction of the Immersive Virtual Reality in Upper Limb Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research, Tokyo, Japan, 7–9 September 2020; Shoji, H., Koyama, S., Kato, T., Muramatsu, K., Yamanaka, T., Lévy, P., Chen, K., Lokman, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Niehorster, D.C.; Li, L.; Lappe, M. The Accuracy and Precision of Position and Orientation Tracking in the HTC Vive Virtual Reality System for Scientific Research. Iperception 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borges, M.; Symington, A.; Coltin, B.; Smith, T.; Ventura, R. HTC Vive: Analysis and Accuracy Improvement. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 2610–2615. [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill, S.; Nguyen, A.; Rodriguez, S.T.; Menendez, M.; Wang, E.; Lawrence, K.; Caruso, T.J. Mobilization and Calibration of the HTC VIVE for Virtual Reality Physical Therapy. Digit. Health 2020, 6, 2055207620950929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdelet, G.; Desoche, C.; Volland, F.; Farnè, A.; Coudert, A.; Hermann, R.; Truy, E.; Gaveau, V.; Pavani, F.; Salemme, R. Assessing Spatial and Temporal Reliability of the Vive System as a Tool for Naturalistic Behavioural Research. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on 3D Immersion (IC3D), Brussels, Belgium, 11 December 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Suznjevic, M.; Mandurov, M.; Matijasevic, M. Performance and QoE Assessment of HTC Vive and Oculus Rift for Pick-and-Place Tasks in VR. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Erfurt, Germany, 31 May–2 June 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Gammeri, R.; Turri, F.; Ricci, R.; Ptak, R. Adaptation to Virtual Prisms and Its Relevance for Neglect Rehabilitation: A Single-Blind Dose-Response Study with Healthy Participants. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2020, 30, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, T. Can Virtual Reality Mimic Prism Adaptation? Locus Seton Hall J. Undergrad. Res. 2020, 3, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, A.A.; Hørning, E.C.; Wilms, I.L. Simulated Prism Exposure in Immersed Virtual Reality Produces Larger Prismatic After-Effects than Standard Prism Exposure in Healthy Subjects. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarri, M.; Greenwood, R.; Kalra, L.; Papps, B.; Husain, M.; Driver, J. Prism Adaptation Aftereffects in Stroke Patients with Spatial Neglect: Pathological Effects on Subjective Straight Ahead but Not Visual Open-Loop Pointing. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazilleau, S. Développement d’un Outil de Quantification et de Rééducation de la Négligence Spatiale Unilatérale par Adaptation Prismatique en Réalité Virtuelle Immersive. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 2019; 132p. [Google Scholar]
- Rode, G.; Lacour, S.; Jacquin-Courtois, S.; Pisella, L.; Michel, C.; Revol, P.; Alahyane, N.; Luauté, J.; Gallagher, S.; Halligan, P.; et al. Long-Term Sensorimotor and Therapeutical Effects of a Mild Regime of Prism Adaptation in Spatial Neglect. A Double-Blind RCT Essay. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, Y.; Koga, K.; Mano, T. Prismatic Displacement of Vision Induces Transient Changes in the Timing of Eye-Hand Coordination. Percept. Psychophys. 1993, 54, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Measurement in Medicine: The Analysis of Method Comparison Studies. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D 1983, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redding, G.M.; Rossetti, Y.; Wallace, B. Applications of Prism Adaptation: A Tutorial in Theory and Method. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Díaz, R. Prism Adaptation and Aftereffect: Specifying the Properties of a Procedural Memory System. Learn. Mem. 1999, 6, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukrina, O.; Chen, P. Neural Mechanisms of Prism Adaptation in Healthy Adults and Individuals with Spatial Neglect after Unilateral Stroke: A Review of FMRI Studies. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, G.M.; Wallace, B. Adaptive Spatial Alignment and Strategic Perceptual-Motor Control. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1996, 22, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, G.M.; Wallace, B. Components of Prism Adaptation in Terminal and Concurrent Exposure: Organization of the Eye-Hand Coordination Loop. Percept. Psychophys. 1988, 44, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, G.; Romack, J.L. The Rate of Adaptation to Displacement Prisms Remains Constant despite Acquisition of Rapid Calibration. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1999, 25, 1331–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, G.M.; Wallace, B. Adaptive Coordination and Alignment of Eye and Hand. J. Mot. Behav. 1993, 25, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, J.W.; Hadjiosif, A.M.; Xu, J.; Wong, A.L.; Haith, A.M. Motor Learning. In Comprehensive Physiology; Terjung, R., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 613–663. ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sidahmed, Y. Étude de Validation Chez le Sujet Sain d’un Outil de Quantification et de Rééducation de la Négligence Spatiale Unilatérale par Adaptation Prismatique en Réalité Virtuelle Immersive. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 2021; 75p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Hreha, K.; Gonzalez-Snyder, C.; Rich, T.J.; Gillen, R.W.; Parrott, D.; Barrett, A.M. Impacts of Prism Adaptation Treatment on Spatial Neglect and Rehabilitation Outcome: Dosage Matters. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair. 2022, 36, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faity, G.; Sidahmed, Y.; Laffont, I.; Froger, J. Quantification and Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect in Immersive Virtual Reality: A Validation Study in Healthy Subjects. Sensors 2023, 23, 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073481
Faity G, Sidahmed Y, Laffont I, Froger J. Quantification and Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect in Immersive Virtual Reality: A Validation Study in Healthy Subjects. Sensors. 2023; 23(7):3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073481
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaity, Germain, Yasmine Sidahmed, Isabelle Laffont, and Jérôme Froger. 2023. "Quantification and Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect in Immersive Virtual Reality: A Validation Study in Healthy Subjects" Sensors 23, no. 7: 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073481
APA StyleFaity, G., Sidahmed, Y., Laffont, I., & Froger, J. (2023). Quantification and Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect in Immersive Virtual Reality: A Validation Study in Healthy Subjects. Sensors, 23(7), 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073481






