Analysis of Intentional Electromagnetic Interference on GENEC Model Using Cylindrical Mode Matching
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cylindrical Mode Matching Formulation
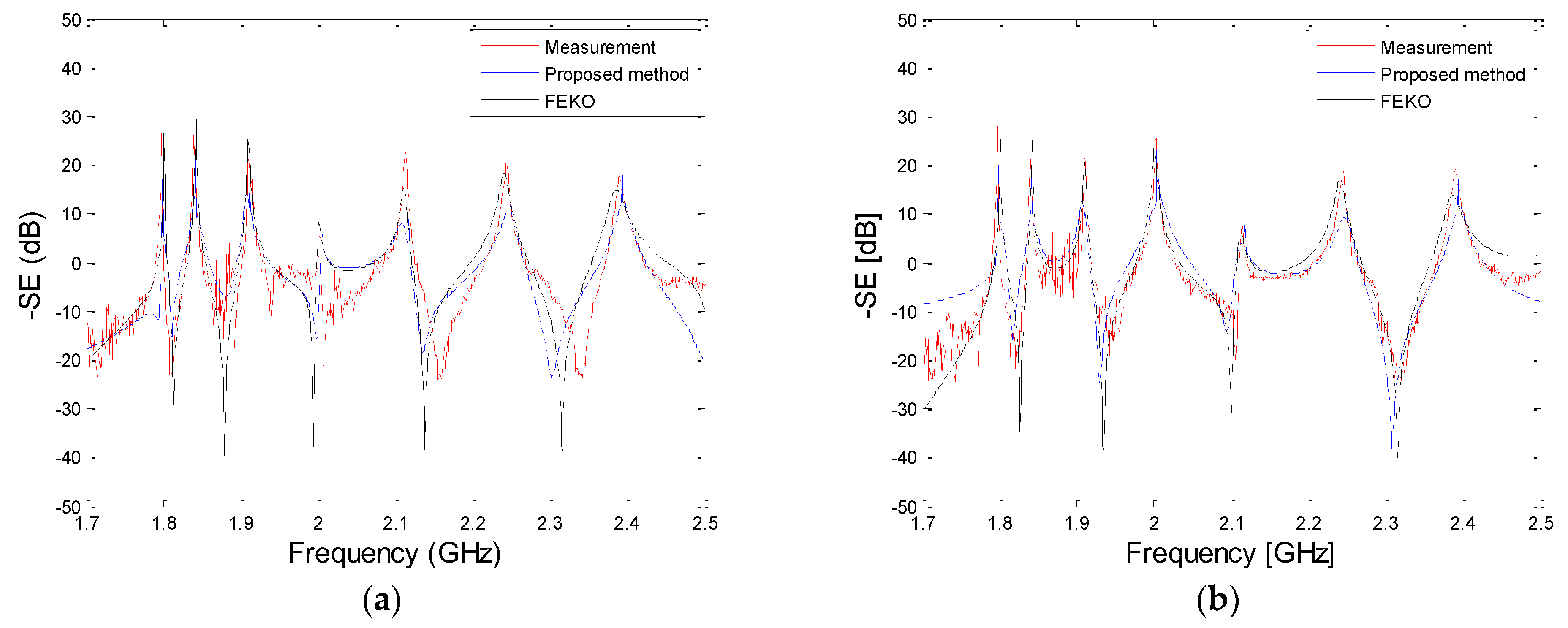
3. Simulation and Measurement Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radasky, W.A.; Baum, C.E.; Wik, M.W. Introduction to the special issue on high-power electromagnetics (HPEM) and intentional electromagnetic interference (IEMI). IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2004, 46, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.-J.; Lee, K.-I.; Shin, J.-W.; So, J.-H.; Chung, Y.-S. An analysis of electromagnetic interference on RF circuits based on electromagnetic topology. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2014, 56, 2784–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Lee, Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Cheon, C.; Jung, H.K. Electromagnetic field penetration analysis of a rectangular aperture-backed cavity based on combination of electromagnetic topology and mode matching. Electromagnetics 2009, 29, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, C.E. Electromagnetic topology for the analysis and design of complex electromagnetic systems. Fast Electr. Opt. Meas. 1986, 108/109, 467–547. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, C.E. Electromagnetic Topology: A Formal Approach to the Analysis and Design of Complex Electronic Systems. Interact. Notes 1980, 400, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, C.E.; Liu, T.K.; Tesche, F.M. On the Analysis of General Multiconductor Transmission-line Networks. Interact. Notes 1978, 350, 467–547. [Google Scholar]
- Parmantier, J.-P. First realistic simulation of effects of EM coupling in commercial aircraft wiring. Comput. Control Eng. J. 1998, 9, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.J.; Lee, V.O.; Mun, S.K.; Chung, Y.S.; Cheon, C.Y. A study for the influence of the EM waves on the cavity with multi-rectangular apertures using BLT equation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–17 July 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rabat, A.; Bonnet, P.; Drissi, K.E.K.; Girard, S. An analytical evaluation of the shielding effectiveness of enclosures containing complex apertures. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 147191–147200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.A.; Komnatnov, M.E. Analytical model for estimating the shielding effectiveness of cylindrical connectors. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 560, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Gao, M.; Zhou, X. A model for the prediction of the shielding effectiveness of cylindrical enclosure. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 085309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y. Calculation and Analysis of Characteristic Parameters for Lossy Resonator. Electronics 2023, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.L.S.; Rosa, G.S.; Bergmann, J.R. A mode-matching solution for the study of cylindrical waveguide bifurcation via closed-form coupling integrals. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 118, 153135. [Google Scholar]
- Mautz, J.R.; Harrington, R.F. EM penetration into a conducting circular cylinder through a narrow slot, TE case. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 1989, 3, 307–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautz, J.R.; Harrington, R.F. EM penetration into a conducting circular cylinder through a narrow slot, TM case. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 1988, 2, 269–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.F.; Mautz, J.R. A generalized network formulation for aperture problem. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1976, 24, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.F. Time-Harmonic Electromagnetic Fields; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hajj, A.; Kabalan, K.Y.; Harrington, R.F. Characteristic modes of a slot in a conducting cylinder and their use for penetration and scattering, TE case. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1992, 40, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalan, K.Y.; El-Haji, A.; Harrington, R.F. Characteristic modes of a slot in a conducting cylinder and their use for penetration and scattering, TM case. IEE Proc. H (Microw. Antennas Propag.) 1992, 139, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumpert, J.D.; Butler, C.M. Penetration through slots in conducting cylinders—Part 1: TE case. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1998, 46, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumpert, J.D.; Butler, C.M. Penetration through slots in conducting cylinders—Part 2: TM case. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1998, 46, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, A. Partial Differential Equations in Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Senior, T.B. Electromagnetic field penetration into a cylindrical cavity. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1976, 18, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi-Naini, S.; Lee, S.W.; Mittra, R. Transmission of an EM wave through the aperture of a cylindrical cavity. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1977, 19, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisahn, S.; Garbe, H.; Sabath, F. Protective properties of a generic missile enclosure to different electromagnetic influences. In Proceedings of the IEEE international Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Qingdao, China, 23–26 October 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fisahn, S.; Koj, S.; Garbe, H. Analysis of the coupling of electromagnetic pulses into shielded enclosures of vulnerable systems. Adv. Radio Sci. 2019, 16, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Ju, S.H.; Kang, N.W.; Lee, W.S.; Choi, J.S. Wideband Coupling Modeling Analysis by Arbitrarily Incoming Source Fields Based on the Electromagnetic Topology Technique. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 67, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqua, I.; Guibert, L.; Parmantier, J.P. Assessment of high frequency coupling in a generic object by the power balance method. In Proceedings of the 18th International Zurich Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Munich, Germany, 24–28 September 2007; pp. 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfram Research, BesselK. Available online: https://functions.wolfram.com/Bessel-TypeFunctions/BesselK/introductions/Bessels/ShowAll.html (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Wolfram MathWorld, Hankel Function of the Second Kind. Available online: https://mathworld.wolfram.com/HankelFunctionoftheSecondKind.html (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Yang, K.; David, G.; Yook, J.G.; Papapolymerou, I.; Katehi, L.P.; Whitaker, J.F. Electrooptic mapping and finite-element modeling of the near-field pattern of a microstrip patch antenna. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2000, 48, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Kwon, J.Y.; Kang, N.W.; Whitaker, J.F. Calibrated 100-dB-dynamic-range electro-optic probe for high-power microwave applications. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 14437–14450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzarella, A.; Qadri, S.B.; Wu, D.H. Optimal electro-optic sensor configuration for phase noise limited, remote field sensing applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 221113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Kang, N.W.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.; Whitaker, J.F. Recent advances in the design of electro-optic sensors for minimally destructive microwave field probing. Sensors 2011, 11, 806–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.J.; Cho, C.H.; Shin, J.W.; Kang, N.W. Photonic-assisted diagnosis of electromagnetic coupling into a generic object. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 125207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, H.W. Noise Reduction Techniques in Electronic Systems; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]

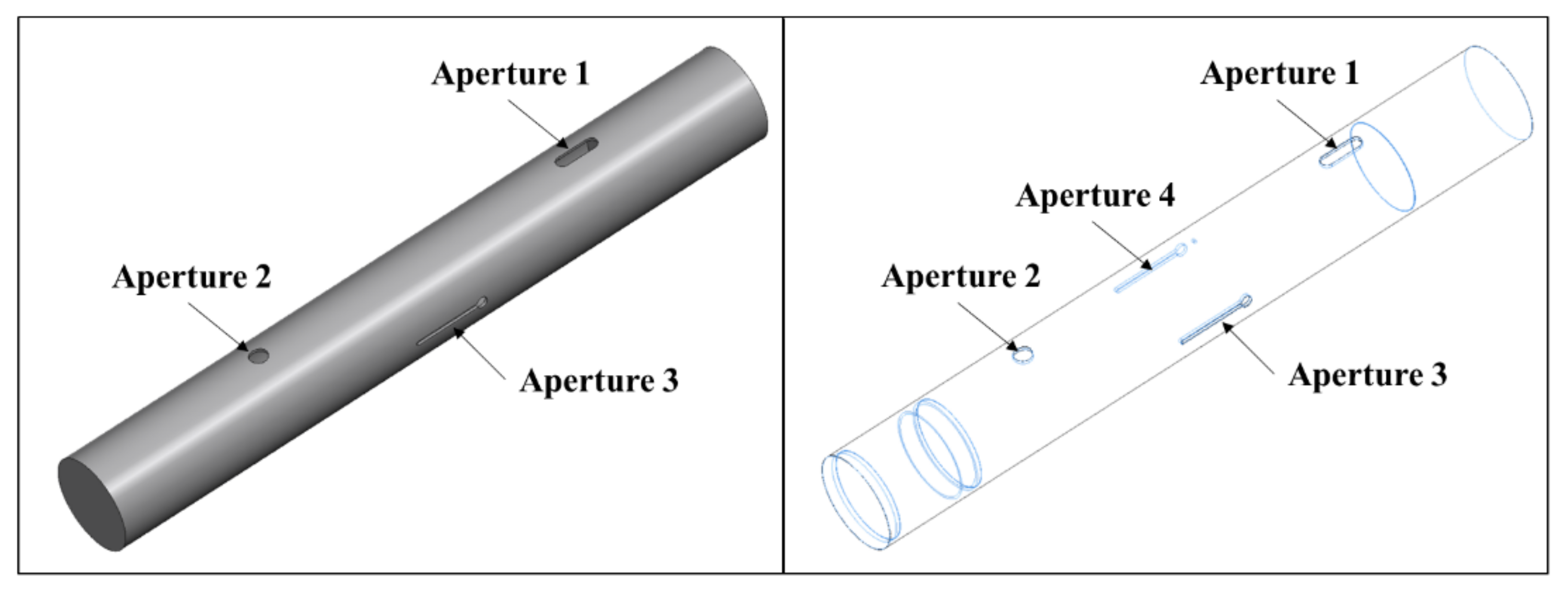




| Aperture Index | Aperture Size | Center of Each Aperture Position (ρ, φ, z) |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture 1 | 46.8 mm × 15 mm | 49.25 mm, 0, 607 mm |
| Aperture 2 | 17.72 mm × 17.72 mm | 49.25 mm, 0, 207 mm |
| Aperture 3 | 88.75 mm × 5 mm | 49.25 mm, π/2, 408.6 mm |
| Aperture 4 | 88.75 mm × 5 mm | 49.25 mm, −π/2, 408.6 mm |
| Analysis Method | Computing Time (s) |
|---|---|
| Proposed method | 62 |
| FEKO (MoM based) | 6240 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, W.; Kang, N.-W.; Lee, W.; Cheon, C.; Chung, Y.-S. Analysis of Intentional Electromagnetic Interference on GENEC Model Using Cylindrical Mode Matching. Sensors 2023, 23, 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063278
Kang W, Kang N-W, Lee W, Cheon C, Chung Y-S. Analysis of Intentional Electromagnetic Interference on GENEC Model Using Cylindrical Mode Matching. Sensors. 2023; 23(6):3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063278
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Wonjune, No-Weon Kang, Woosang Lee, Changyul Cheon, and Young-Seek Chung. 2023. "Analysis of Intentional Electromagnetic Interference on GENEC Model Using Cylindrical Mode Matching" Sensors 23, no. 6: 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063278
APA StyleKang, W., Kang, N.-W., Lee, W., Cheon, C., & Chung, Y.-S. (2023). Analysis of Intentional Electromagnetic Interference on GENEC Model Using Cylindrical Mode Matching. Sensors, 23(6), 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063278





