Novel Sensing Technique for Stem Cells Differentiation Using Dielectric Spectroscopy of Their Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Biological Samples and Experimental Setup
2.1. Preparation of Biological Samples
2.1.1. Cell Culture
2.1.2. Sample Preparation for Dielectric Spectroscopy
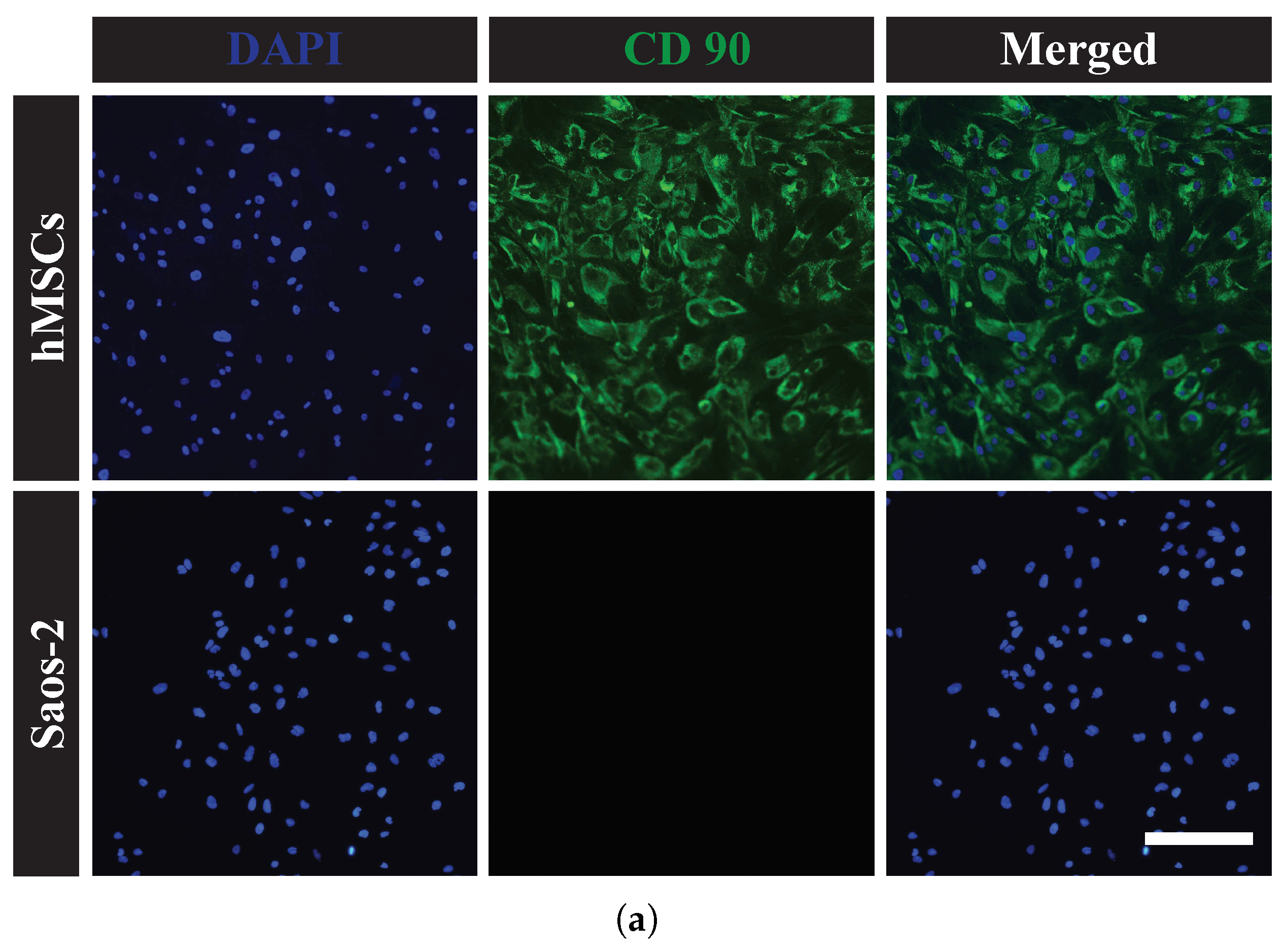
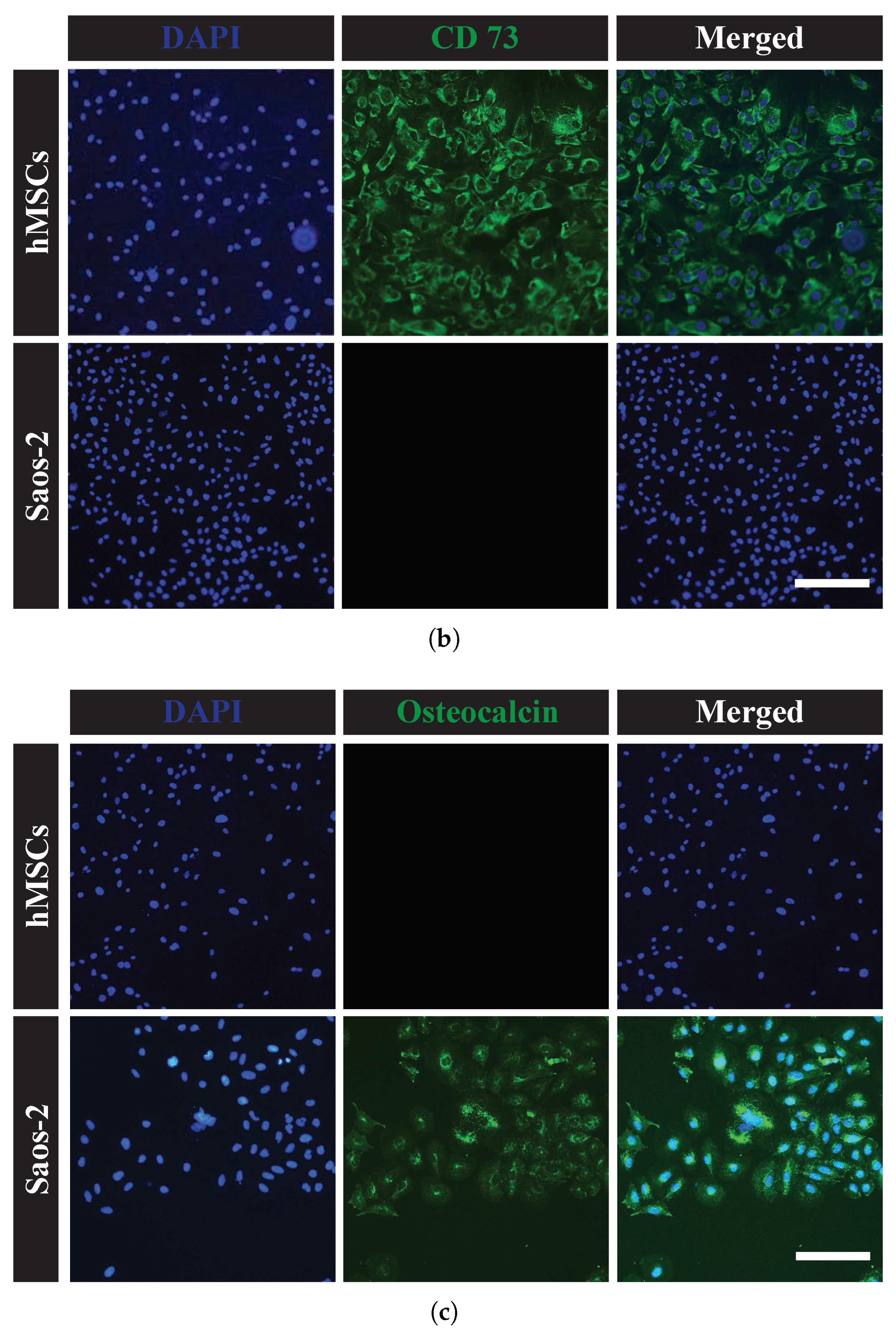
2.1.3. Cell Characterization by Immunohistochemistry
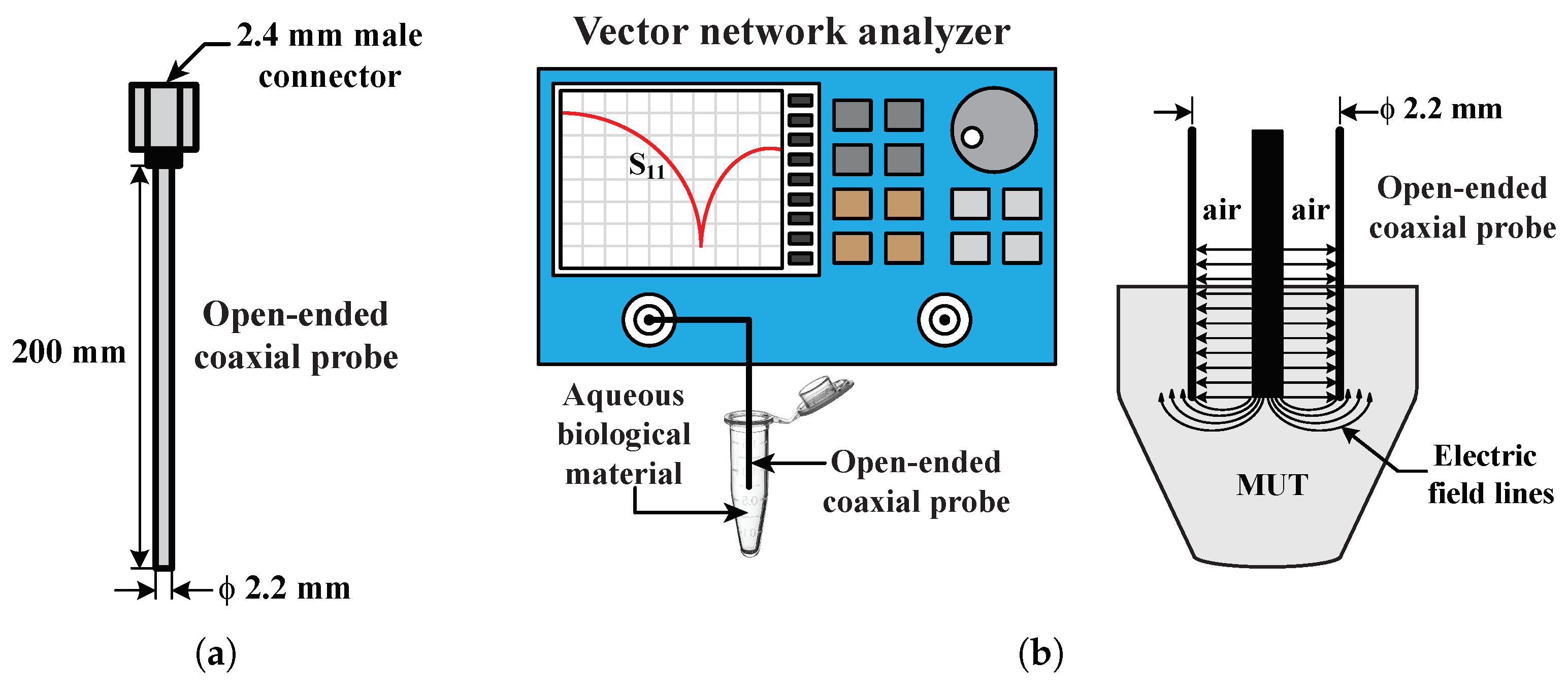
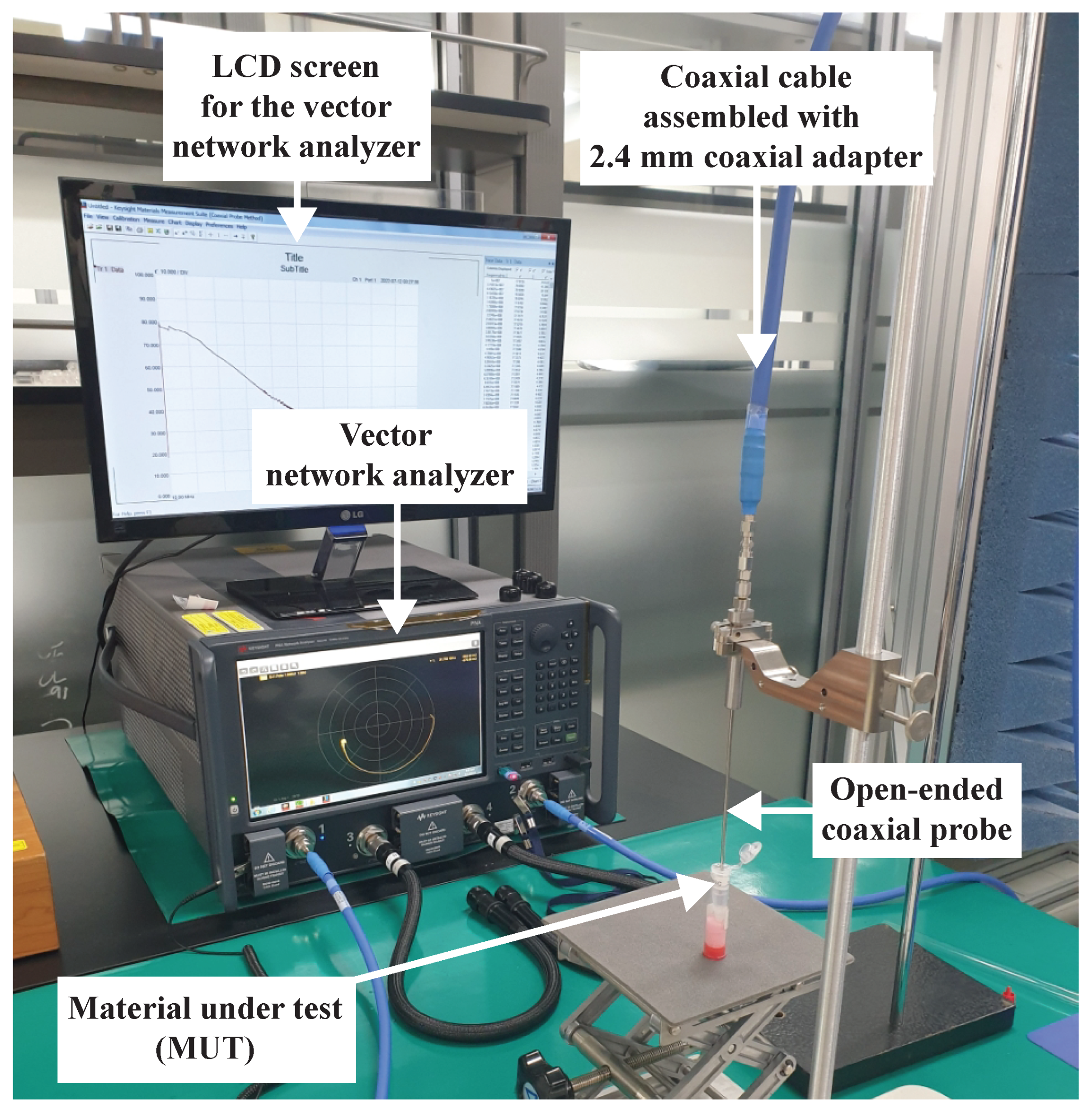
2.2. Experimental Setup for Dielectric Spectroscopy
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Biological Characterizations
3.2. Electrical Characterizations
3.2.1. Measurements Results
3.2.2. Single Shell Model for Protein Suspensions
3.2.3. Dielectrophoresis Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodward, W.H.H. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy—A Practical Guide. In Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy: A Modern Analytical Technique; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; Chapter 1; pp. 3–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, H.P. Electrical properties of tissue and cell suspensions. Adv. Biol. Med. Phys. 1957, 5, 147–209. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, C.; Gabriel, S.; Corthout, E. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: I. Literature survey. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: III. Parametric models for the dielectric spectrum of tissues. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Takashima, S. Dielectric properties of mouse lymphocytes and erythrocytes. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1989, 1010, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Wakamatsu, H.; Koyanagi, N. Dielectric spectroscopy of biological cells. Bioelectrochemistry Bioenerg. 1996, 40, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, K.; Gheorghiu, E.; Yonezawa, T. Real-Time Monitoring of Yeast Cell Division by Dielectric Spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 3345–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, K. Characterization of biological cells by dielectric spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2002, 305, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.Z.; Davis, C.C.; Schmukler, R.E. Frequency domain impedance measurements of erythrocytes. Constant phase angle impedance characteristics and a phase transition. Biophys. J. 1992, 61, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.Z.; Davis, C.; Schmukler, R. Impedance spectroscopy of human erythrocytes: System calibration, and nonlinear modeling. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.Z.; Davis, C.C.; Swicord, M.L. Microwave dielectric measurements of erythrocyte suspensions. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, S.; Gabriel, C.; Sheppard, R.; Grant, E. Dielectric behavior of DNA solution at radio and microwave frequencies (at 20 degrees C). Biophys. J. 1984, 46, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermilova, E.; Bier, F.F.; Hölzel, R. Dielectric measurements of aqueous DNA solutions up to 110 GHz. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 11256–11264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laux, E.M.; Ermilova, E.; Pannwitz, D.; Gibbons, J.; Hölzel, R.; Bier, F.F. Dielectric Spectroscopy of Biomolecules up to 110 GHz. Frequenz 2018, 72, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagl, D.; Popovic, D.; Hagness, S.; Booske, J.; Okoniewski, M. Sensing volume of open-ended coaxial probes for dielectric characterization of breast tissue at microwave frequencies. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2003, 51, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, A.; Thomas, V.; Bindu, G.; Jacob, J.; Rajasekaran, C.; Mathew, K.T. New method of detecting lymphatic disease using microwaves. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2007, 49, 3166–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirbeik-Sabzevari, A.; Tavassolian, N. Ultrawideband, Stable Normal and Cancer Skin Tissue Phantoms for Millimeter-Wave Skin Cancer Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Tien, T.T.T.; Yeo, S.J. Dielectric spectroscopy technique for detection of human respiratory syncytial virus. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019, 61, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, M.; Mulero, L.; Pardo, C.; Morera, C.; Carrió, M.; Laricchia-Robbio, L.; Esteban, C.R.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Characterization of pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer Nardi, N.; da Silva Meirelles, L. Mesenchymal stem cells: Isolation, in vitro expansion and characterization. In Stem Cells; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 249–282. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Im, C.S.; Guo, M.; Cui, Z.K.; Fartash, A.; Kim, S.; Patel, N.; Bezouglaia, O.; Wu, B.M.; Wang, C.Y.; et al. Enhanced Osteogenesis of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by Regulating Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Antagonists and Agonists. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpornmaeklong, P.; Brown, S.E.; Wang, Z.; Krebsbach, P.H. Phenotypic characterization, osteoblastic differentiation, and bone regeneration capacity of human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009, 18, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamatani, T.; Hagizawa, H.; Yarimitsu, S.; Morioka, M.; Koyamatsu, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Kodama, J.; Yamane, J.; Ishiguro, H.; Shichino, S.; et al. Human iPS cell-derived cartilaginous tissue spatially and functionally replaces nucleus pulposus. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychlinska, M.A.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Nsir, H.; Di Rosa, M.; Guglielmino, C.; Parenti, R.; Calabrese, G.; Pricoco, E.; Salvatorelli, L.; Magro, G.; et al. Engineered cartilage regeneration from adipose tissue derived-mesenchymal stem cells: A morphomolecular study on osteoblast, chondrocyte and apoptosis evaluation. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 357, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.W.; Gwak, S.J.; Kang, S.W.; Bhang, S.H.; Won Song, K.W.; Yang, Y.S.; Choi, C.Y.; Kim, B.S. Enhancement of angiogenic efficacy of human cord blood cell transplantation. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Gorjup, E.; Thielecke, H. Chip-based time-continuous monitoring of toxic effects on stem cell differentiation. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2009, 191, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.E.; Kim, D.; Koh, H.S.; Cho, S.; Sung, J.S.; Kim, J.Y. Real-time monitoring of neural differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by electric cell-substrate impedance sensing. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 485173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macit, Z.; Aydinalp, C.; Yilmaz, T.; Sert, A.B.O.; Kok, F.N. Broadband Microwave Dielectric Property Comparison of Human Fetal Osteoblastic (hFOB) and Osteosarcoma (SaOS-2) Cell Lines. In Proceedings of the 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidro, I.A.; Vicente, P.; Pais, D.A.M.; Almeida, J.I.; Domingues, M.; Abecasis, B.; Zapata-Linares, N.; Rodriguez-Madoz, J.R.; Prosper, F.; Aspegren, A.; et al. Online monitoring of hiPSC expansion and hepatic differentiation in 3D culture by dielectric spectroscopy. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 3610–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzel, R.; Pethig, R. Protein dielectrophoresis: Key dielectric parameters and evolving theory. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 513–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R. Protein Dielectrophoresis: A Tale of Two Clausius-Mossottis—Or Something Else? Micromachines 2022, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colburn, T.; Matyushov, D. Trapping proteins on nanopores by dielectrophoresis. ChemRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Aoi, N.; Sato, T.; Yamauchi, Y.; Suga, H.; Eto, H.; Kato, H.; Araki, J.; Yoshimura, K. Differential expression of stem-cell-associated markers in human hair follicle epithelial cells. Lab Investig. 2009, 89, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Tang, J.; Yi, C. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis and promote fat retention in fat grafting via polarized macrophages. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pautke, C.; Schieker, M.; Tischer, T.; Kolk, A.; Neth, P.; Mutschler, W.; Milz, S. Characterization of osteosarcoma cell lines MG-63, Saos-2 and U-2 OS in comparison to human osteoblasts. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 3743–3748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaatze, U. Reference liquids for the calibration of dielectric sensors and measurement instruments. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raicu, V.; Feldman, Y. Dielectric Relaxation in Biological Systems: Physical Principles, Methods, and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entesari, K.; Helmy, A.A.; Moslehi-Bajestan, M. Integrated Systems for Biomedical Applications: Silicon-Based RFMicrowave Dielectric Spectroscopy and Sensing. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2017, 18, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimajiri, A.; Doida, Y.; Hanai, T.; Inouye, A. Passive electrical properties of cultured murine lymphoblast (L5178Y) with reference to its cytoplasmic membrane, nuclear envelope, and intracellular phases. J. Membr. Biol. 1978, 38, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimajiri, A.; Hanai, T.; Inouye, A. A dielectric theory of “multi-stratified shell” model with its application to a lymphoma cell. J. Theor. Biol. 1979, 78, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimajiri, A.; Asami, K.; Ichinowatari, T.; Kinoshita, Y. Passive electrical properties of the membrane and cytoplasm of cultured rat basophil leukemia cells. I. Dielectric behavior of cell suspensions in 0.01–500 MHz and its simulation with a single-shell model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 1987, 896, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R.; Kell, D.B. The passive electrical properties of biological systems: Their significance in physiology, biophysics and biotechnology. Phys. Med. Biol. 1987, 32, 933–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, H.P. Electrical properties of bound water. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1965, 125, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, M.; Srsen, V.; Waterfall, M.; Downes, A.; Pethig, R. Biomarker-free dielectrophoretic sorting of differentiating myoblast multipotent progenitor cells and their membrane analysis by Raman spectroscopy. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 34113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velugotla, S.; Pells, S.; Mjoseng, H.K.; Duffy, C.R.E.; Smith, S.; De Sousa, P.; Pethig, R. Dielectrophoresis based discrimination of human embryonic stem cells from differentiating derivatives. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 44113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cametti, C.; Marchetti, S.; Gambi, C.; Onori, G. Dielectric Relaxation Spectroscopy of Lysozyme Aqueous Solutions: Analysis of the δ-Dispersion and the Contribution of the Hydration Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 7144–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, C. The Antigen-Antibody Reaction in Immunohistochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.R.; Imam, S.A.; Young, L.; Cote, R.J.; Taylor, C.R. Antigen retrieval immunohistochemistry under the influence of pH using monoclonal antibodies. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1995, 43, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.C.; Woods, A.L.; Levison, D.A. The assessment of cellular proliferation by immunohistochemistry: A review of currently available methods and their applications. Histochem. J. 1992, 24, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaki, S.; Hojat, S.A.; Wei, B.; So, A.; Yong, W.H. An Introduction to the Performance of Immunohistochemistry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1897, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, S.J.; Bhang, S.H.; Kim, I.K.; Kim, S.S.; Cho, S.W.; Jeon, O.; Yoo, K.J.; Putnam, A.J.; Kim, B.S. The effect of cyclic strain on embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.Y.; Shin, R.L.Y.; Chen, J.C.H.; Assunção, M.; Wang, D.; Nilsson, S.K.; Tuan, R.S.; Blocki, A. Dextran sulfate-amplified extracellular matrix deposition promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappmann, B.; Gautrot, J.E.; Connelly, J.T.; Strange, D.G.T.; Li, Y.; Oyen, M.L.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Boehm, H.; Li, B.; Vogel, V.; et al. Extracellular-matrix tethering regulates stem-cell fate. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilak, F.; Cohen, D.M.; Estes, B.T.; Gimble, J.M.; Liedtke, W.; Chen, C.S. Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentze, H.; Graichen, R.; Colman, A. Cell therapy and the safety of embryonic stem cell-derived grafts. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickman, J.M.; Burdon, T.G. Pluripotency and tumorigenicity. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
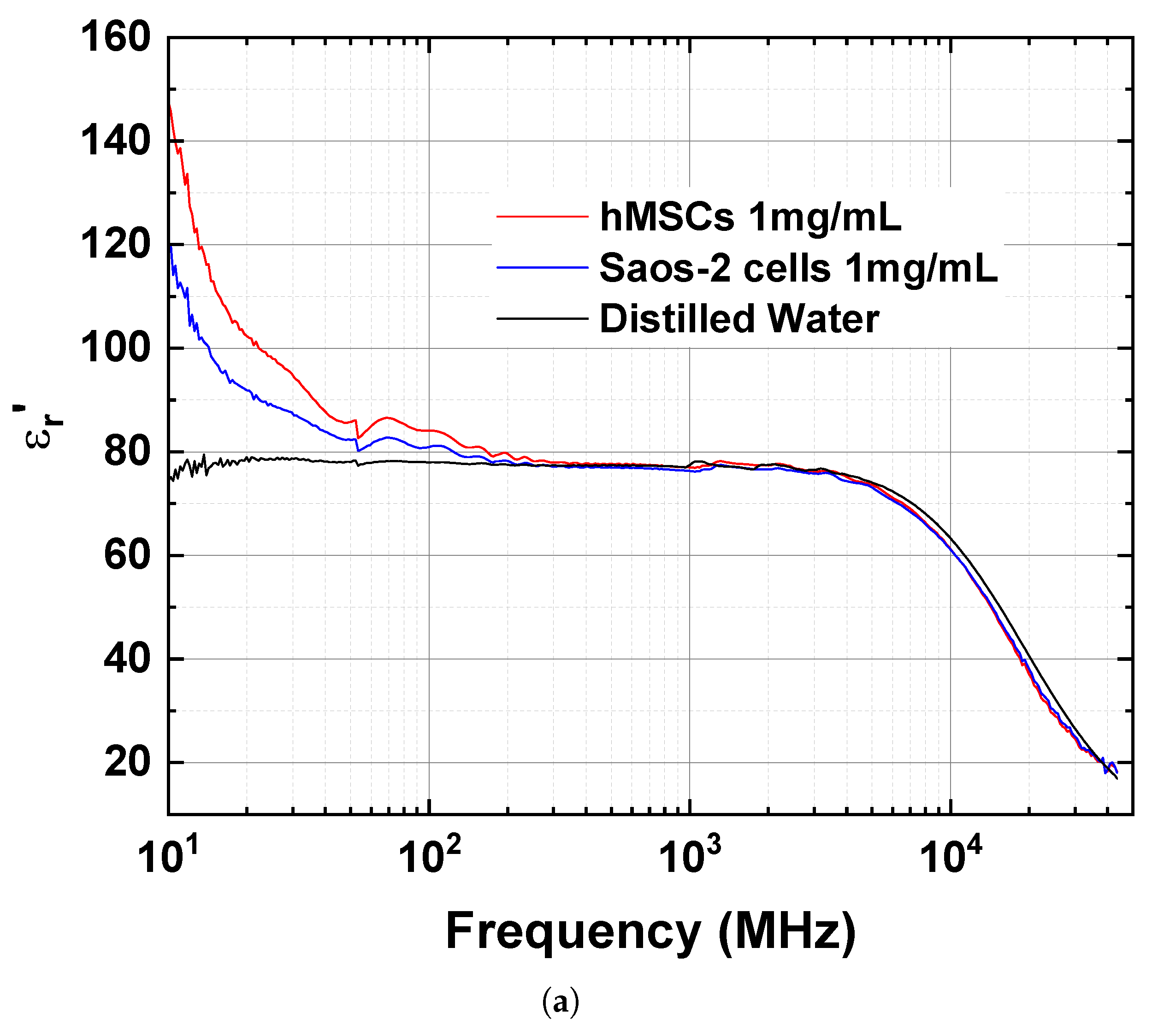
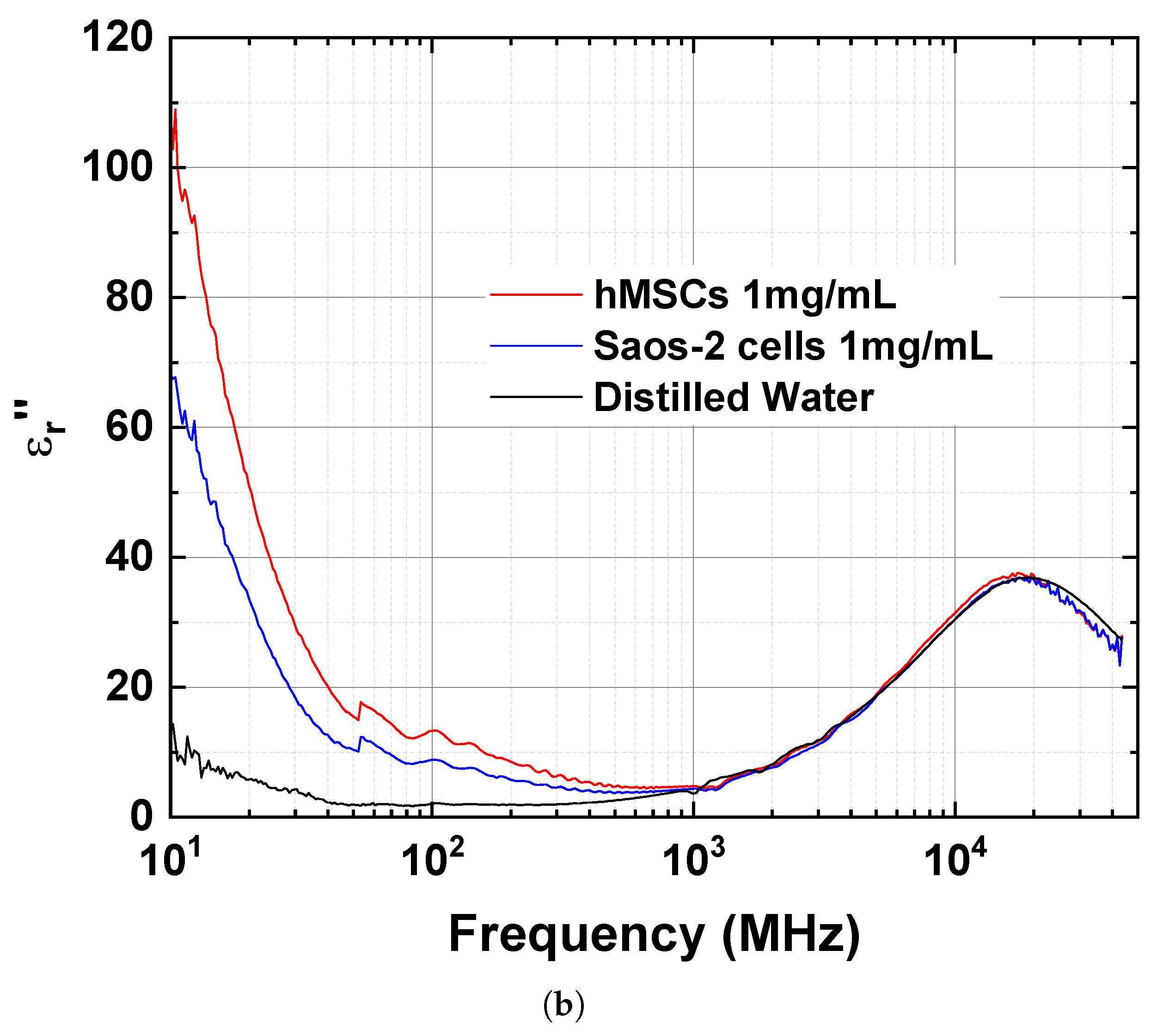
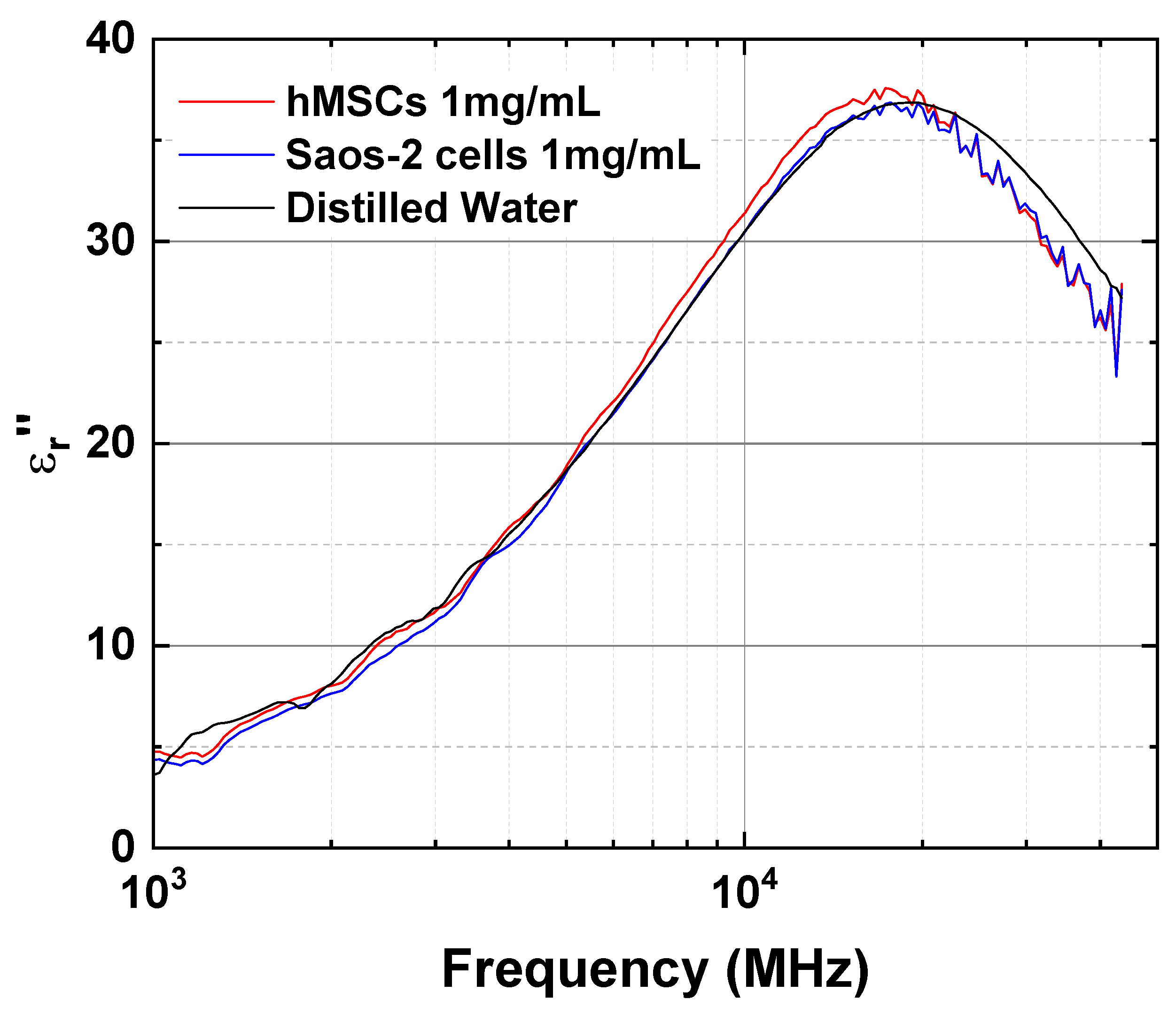

| Frequency | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MHz) | Suspension of hMSCs | Suspension of Saos-2 Cells | Distilled Water | Suspension of hMSCs | Suspension of Saos-2 Cells | Distilled Water |
| 10 | 147.7 | 119.6 | 74.3 | 108.6 | 68.1 | 14.5 |
| 30 | 94.4 | 87.0 | 78.7 | 28.7 | 17.9 | 4.3 |
| 300 | 77.9 | 77.1 | 77.4 | 6.4 | 4.6 | 2.0 |
| 1000 | 77.0 | 76.3 | 77.5 | 4.8 | 4.4 | 3.6 |
| 3000 | 76.2 | 75.8 | 76.5 | 11.9 | 11.4 | 11.9 |
| Material | (GHz) | (ps) |
|---|---|---|
| (Relaxation Frequency) | (Relaxation Time) | |
| Suspension of hMSCs | 17.3 | 9.20 |
| Suspension of Saos-2 cells | 17.7 | 8.99 |
| Distilled water | 19.6 | 8.12 |
| Material | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ns) | (MHz) | (S/m) | ||||
| Suspension of hMSCs | 6.364 | 188.865 | 23.680 | 6.721 | 72.435 | 0.01666 |
| Suspension of Saos-2 cells | 6.594 | 132.555 | 26.535 | 5.998 | 71.381 | 0.01333 |
| Material | R | d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Å) | (Å) | (F/m) | (kHz) | ||
| hMSCs protein | 20.5 | 2.97 | 786.8 | 23.5 | 14.95 |
| Saos-2 protein | 21.3 | 3.08 | 613.9 | 17.6 | 19.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.S.; Gwak, S.-J. Novel Sensing Technique for Stem Cells Differentiation Using Dielectric Spectroscopy of Their Proteins. Sensors 2023, 23, 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052397
Cho YS, Gwak S-J. Novel Sensing Technique for Stem Cells Differentiation Using Dielectric Spectroscopy of Their Proteins. Sensors. 2023; 23(5):2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052397
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Young Seek, and So-Jung Gwak. 2023. "Novel Sensing Technique for Stem Cells Differentiation Using Dielectric Spectroscopy of Their Proteins" Sensors 23, no. 5: 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052397
APA StyleCho, Y. S., & Gwak, S.-J. (2023). Novel Sensing Technique for Stem Cells Differentiation Using Dielectric Spectroscopy of Their Proteins. Sensors, 23(5), 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052397






