The Great Wall Vibration Monitoring of Traffic and Natural Hazards Using MEMS Accelerometers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Equipment for Vibration Monitoring
3. Analysis of Potential Hazards
3.1. Analysis of Traffic Vibrations Impact
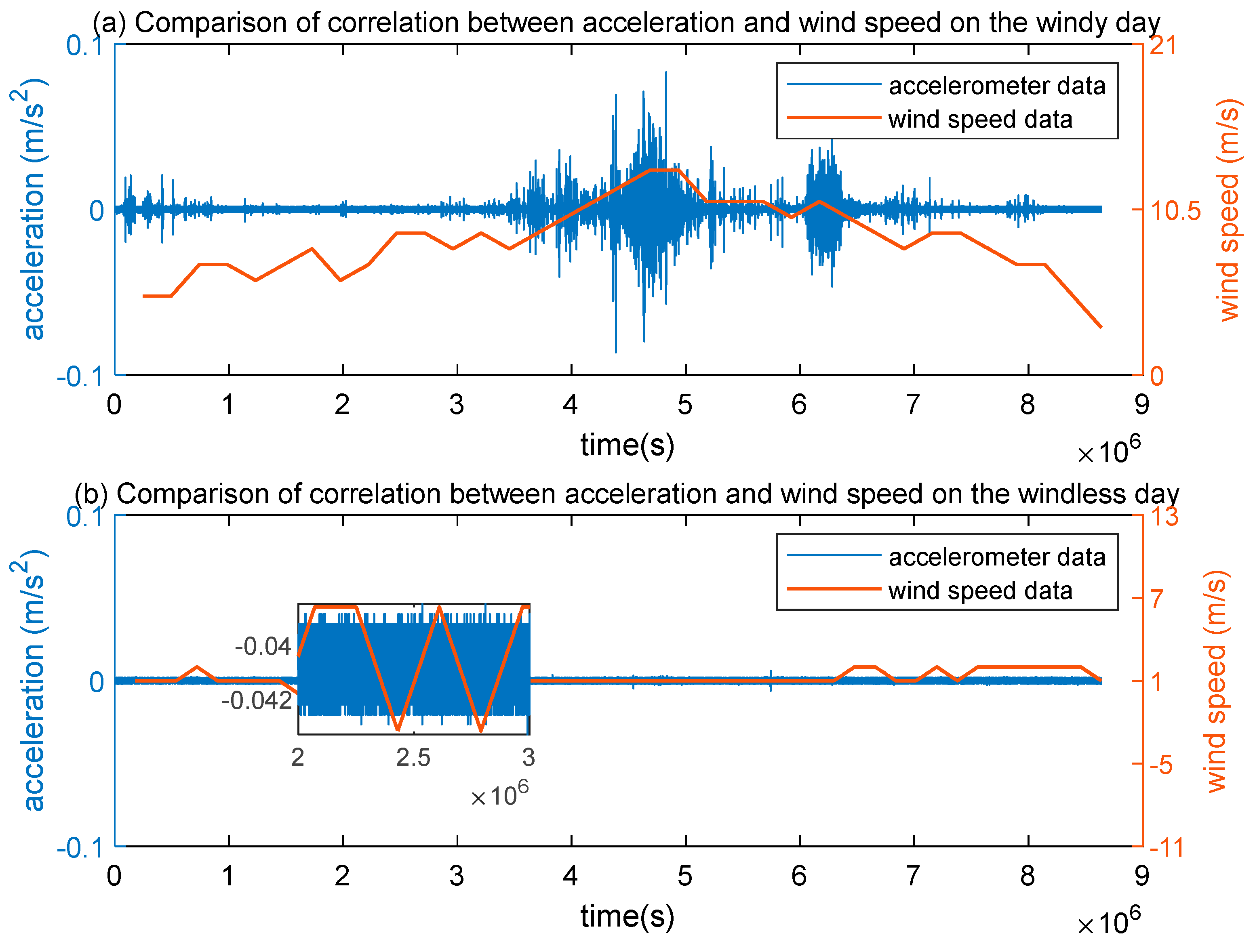
3.2. Analysis of Wind Load Impact
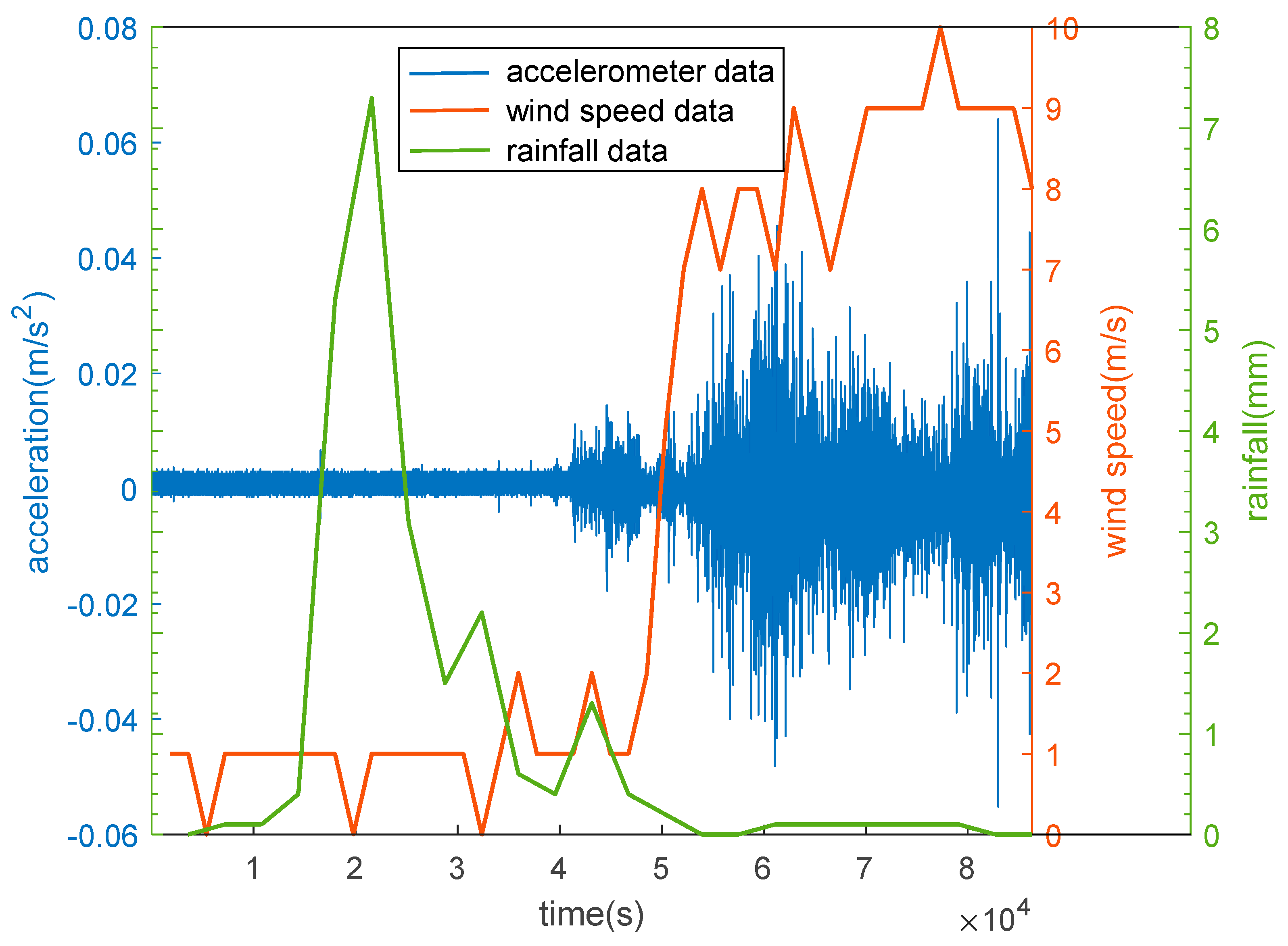
3.3. Analysis of Thunderstorms Impact
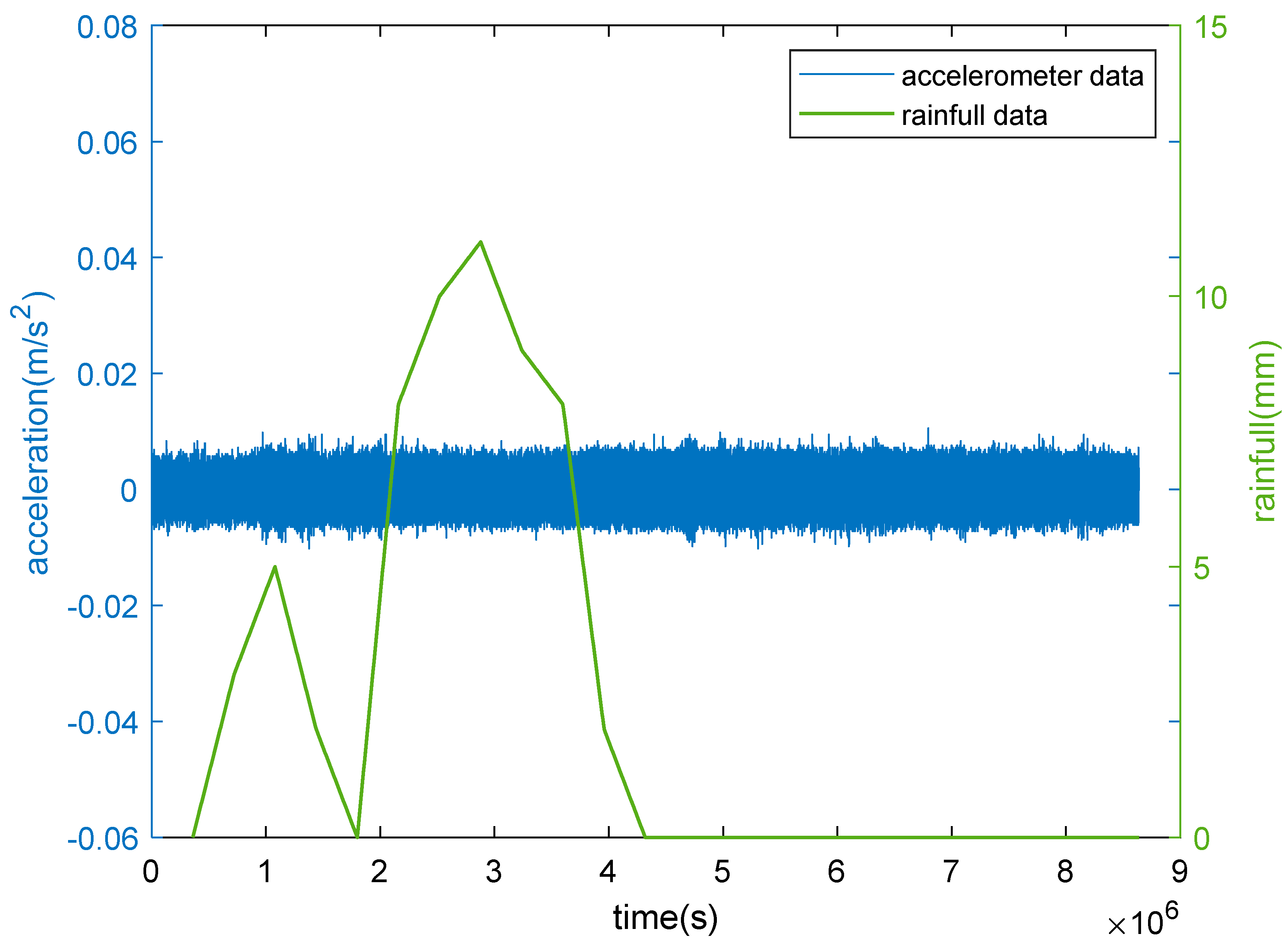
3.4. Analysis of Rain Load Impact
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.F.; Dong, Y.Q.; Hou, M.L. Basic issues and research directions of the digital restoration of the Great Wall. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 2365–2380. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.K. Impact Analysis and Evaluation of Vehicle-driving-induced Vibration on the Ancient Great Wall. Chin. Earthq. Eng. J. 2019, 41, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Agata, S.; Anna, J.G.; Robert, J. The idea of using Bayesian networks in forecasting impact of traffic-induced vibration transmitted through the ground on residential buildings. Geosciences 2019, 9, 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Giacomo, Z.; Michele, B.; Gianni, B. Experimental analysis of the traffic-induced-vibration on an ancient lodge. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2022, 29, e2900. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. Study on the Dynamic Response of the Ming Great Wall under the Vibration of Ground Traffic. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L. The Vibration Influence of the Nanwan Great Wall by Train and the Evaluation of Vibration Reduction Measures. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Research on Vibration Property of Jia Yuguan Great Wall Induced by Ballastless Track. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.L.; Da, Z.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, D.P. Intelligent Monitoring of Structural Safety of Badaling Great Wall Station on Beijing-Zhangjiakou High-speed Railway. Railw. Stand. Des. 2020, 64, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xia, H.; Cao, Y.; Wei, P. Experimental study on the vibration effect of running train on surrounding buildings. J. Vib. Eng. 2008, 05, 476–481. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Shen, C.; Li, J.S.; Wu, J.S.; Mao, N.; Sun, Y.Q. Modal parameter identification and analysis of Xi’an City Wall under complex traffic environment. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2022, 44, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.H.; Liu, Q.P.; Zhou, Y.Q. Mechanical properties and cracking analysis of brick-clay structure of ancient building. J. Build. Struct. 2019, 40, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. Study on the Impact of Zhanghu Railway Construction Vibration on the Cultural Relics of the Great Wall. Railway Energy Conservation. Environ. Prot. Saf. Health 2018, 8, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zanelli, F.; Mauri, M.; Castelli-Dezza, F.; Tarsitano, D.; Manenti, A.; Diana, G. Analysis of Wind-Induced Vibrations on HVTL Conductors Using Wireless Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Shi, Y.C.; Lu, Y.X. Study on seismic performance of a wall construction for the Yumenguan Great Wall in Han dynasty. World Earthq. Eng. 2010, 26, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.R.; Wei, P.; Liu, J.Y. Prediction and analysis for the influence of blasting vibration of Beijing-Zhangjiakou High-speed Railway Badaling Tunnel underneath the Great Wall. Railw. Surv. 2020, 46, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Zhao, F.; Sun, M. Experimental study on the pattern of rainfall on the destruction mode of single building of Ming Great Wall in Yuyang District. Cult. Relics Conserv. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 27, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.F.; Liu, J.; Li, F. The researches on shaking table test of Yongning Gate embrasure watch-tower of Xi’an City wall. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Dyn. 2014, 34, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.M. Evaluation the Influence of Tunnel Excavation Blasting on Ancient Great Wall. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.R. Classification and Identification of Failure modes of ancient city walls. J. Eng. Geol. 2017, 25, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya, H.; Kimura, K.; Miki, C. Technique for Determining Bridge Displacement Response Using MEMS Accelerometers. Sensors 2016, 16, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-F.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.-X.; Hu, X.-X.; Liu, J.-X. Study of Building Safety Monitoring by Using Cost-Effective MEMS Accelerometers for Rapid After-Earthquake Assessment with Missing Data. Sensors 2021, 21, 7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, G.; D’Alessandro, A.; Di Benedetto, A.; Figlioli, A.; Costanzo, A.; Speciale, S.; Piattoni, Q.; Cipriani, L. Urban Seismic Network Based on MEMS Sensors: The Experience of the Seismic Observatory in Camerino (Marche, Italy). Sensors 2022, 22, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafazade, A.; Pandit, M.; Zhao, C.; Sobreviela, G.; Du, Z.; Steinmann, P. A vibrating beam MEMS accelerometer for gravity and seismic measurements. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, A.J.; Woods, R.; Hester, D. Detecting Vehicle Loading Events in Bridge Rotation Data Measured with Multi-Axial Accelerometers. Sensors 2022, 22, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanè, D.; Tusa, G.; Yang, W.; Astuti, A.; Colino, A.; Costanza, A.; D’Anna, G.; Di Prima, S.; Fertitta, G.; Mangiagli, S.; et al. The Urban Seismic Observatory of Catania (Italy): A Real-Time Seismic Monitoring at Urban Scale. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | Condition | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement range | ±1.5 g, ±3 g, ±6 g | g | |
| Size | 7.6 × 8.6 × 3.3 mm | ||
| Offset | 0 | LSB | |
| Offset error | −40 °C … +125 °C | −20~+20 | mg |
| Sensitivity | ±3 g Mode 1 ±6 g Mode 2 ±1.5 g Mode 3 | 2700 1350 5400 | LSB/g |
| Sensitivity error | −40 °C … +125 °C Mode 1 (±3 g 70 Hz) | −0.7–+0.7 | % |
| Linearity error | −1 g … +1 g range −6 g … +6 g range | −1–+1 −15–+15 | mg |
| Integrated noise | 0.44 | mg RMS | |
| Noise density | 37 | ||
| Updating frequency | 100 | Hz |
| Beijing Time | Times (s) | Traffic Flow |
|---|---|---|
| 6:00–7:00 | 82,801 | 50 |
| 7:00–8:00 | 86,401 | 52 |
| 8:00–9:00 | 90,001 | 58 |
| 9:00–10:00 | 93,601 | 85 |
| 10:00–11:00 | 97,201 | 90 |
| 11:00–12:00 | 100,801 | 94 |
| 12:00–13:00 | 104,401 | 110 |
| 13:00–14:00 | 108,001 | 121 |
| 14:00–15:00 | 111,601 | 78 |
| 15:00–16:00 | 115,201 | 77 |
| 16:00–17:00 | 118,801 | 94 |
| 17:00–18:00 | 122,401 | 100 |
| 18:00–19:00 | 126,001 | 102 |
| 19:00–20:00 | 129,601 | 78 |
| 20:00–21:00 | 133,201 | 72 |
| 21:00–22:00 | 136,801 | 74 |
| Beijing Time | 4 August 2022 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Speed (m/s) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Severe Weather | |
| 0:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | Light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 0:30 | calm | light air (1 m/s) | |
| 1:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | light air (1 m/s) | |
| 1:30 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 2:00 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light air (1 m/s) | |
| 2:30 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light air (1 m/s) | |
| 3:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | light air (1 m/s) | |
| 3:30 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 4:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 4:30 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 5:00 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 5:30 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | (weak) shower, rain |
| 6:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | |
| 6:30 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 7:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 7:30 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 8:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 8:30 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | |
| 9:00 | Light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | |
| 9:30 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 10:00 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 10:30 | gentle breeze (3 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 11:00 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | |
| 11:30 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | |
| 12:00 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 12:30 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 13:00 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 13:30 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 14:00 | Light breeze (2 m/s | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 14:30 | Light breeze (2 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 15:00 | gentle breeze (3 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 15:30 | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 16:00 | gentle breeze (5 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 16:30 | moderate breeze (6 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | |
| 17:00 | gentle breeze (4 m/s | gentle breeze (5 m/s) | |
| 17:30 | light breeze (2 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 18:00 | gentle breeze (5 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | |
| 18:30 | moderate breeze (7 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 19:00 | moderate breeze (6 m/s) | moderate breeze (7 m/s) | thunderstorm |
| 19:30 | gentle breeze (5 m/s) | gentle breeze (5 m/s) | (Weak) thunderstorm, rain |
| 20:00 | light breeze (3 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | (Weak) thunderstorm, rain |
| 20:30 | light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | thunderstorm, rain |
| 21:00 | light air (1 m/s) | gentle breeze (4 m/s) | (Weak) thunderstorm, gust, rain |
| 21:30 | light breeze (3 m/s) | light breeze (3 m/s) | thunderstorm |
| 22:00 | light air (1 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s | |
| 22:30 | light breeze (3 m/s) | light breeze (2 m/s) | |
| 23:00 | light breeze (3 m/s) | light air (1 m/s) | |
| 23:30 | light breeze (3 m/s) | light air (1 m/s) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, C.; Tang, Y. The Great Wall Vibration Monitoring of Traffic and Natural Hazards Using MEMS Accelerometers. Sensors 2023, 23, 2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042179
Wang J, Liu X, Liu F, Chen C, Tang Y. The Great Wall Vibration Monitoring of Traffic and Natural Hazards Using MEMS Accelerometers. Sensors. 2023; 23(4):2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042179
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Xu Liu, Fei Liu, Cai Chen, and Yuyang Tang. 2023. "The Great Wall Vibration Monitoring of Traffic and Natural Hazards Using MEMS Accelerometers" Sensors 23, no. 4: 2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042179
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, X., Liu, F., Chen, C., & Tang, Y. (2023). The Great Wall Vibration Monitoring of Traffic and Natural Hazards Using MEMS Accelerometers. Sensors, 23(4), 2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042179







