Validation of the Short Physical Performance Battery via Plantar Pressure Analysis Using Commercial Smart Insoles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
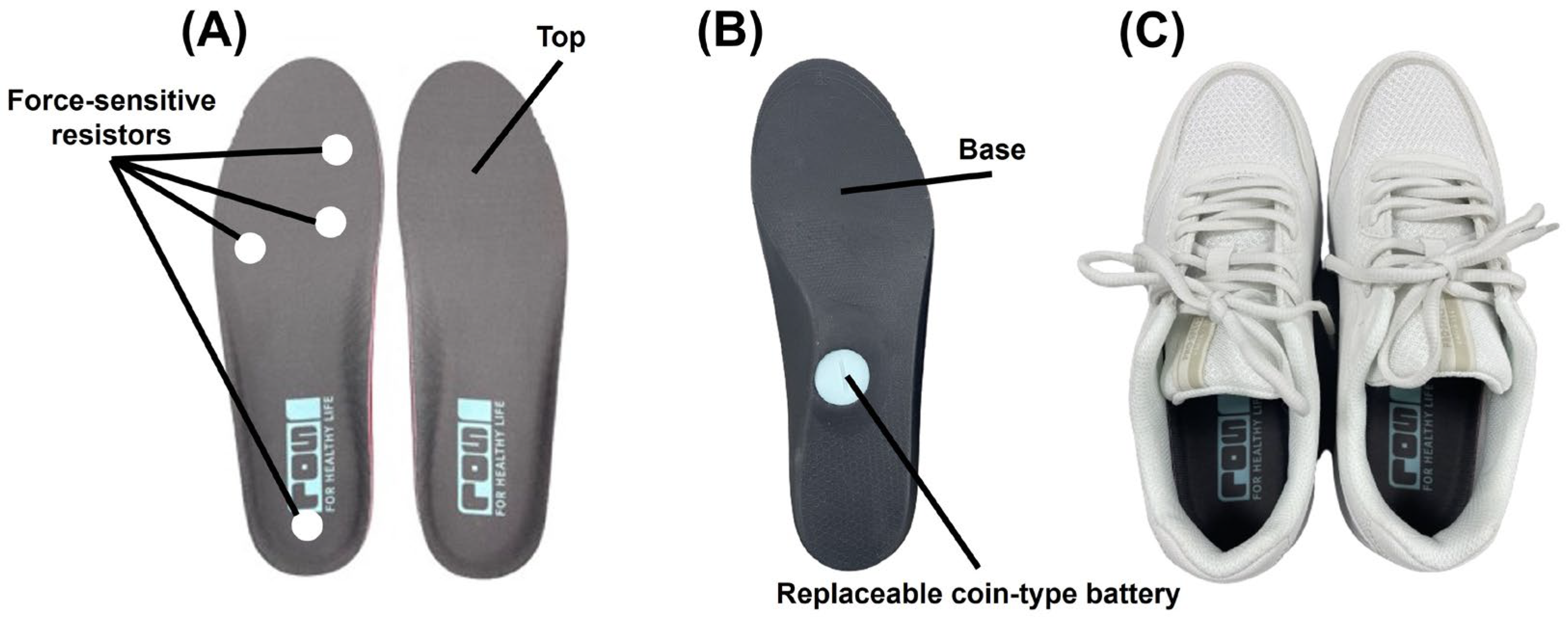
2.2. Commercial Smart Insoles
2.3. SPPB Measurement (the Balance, Gait Speed, and Five Chair Stand Tests)
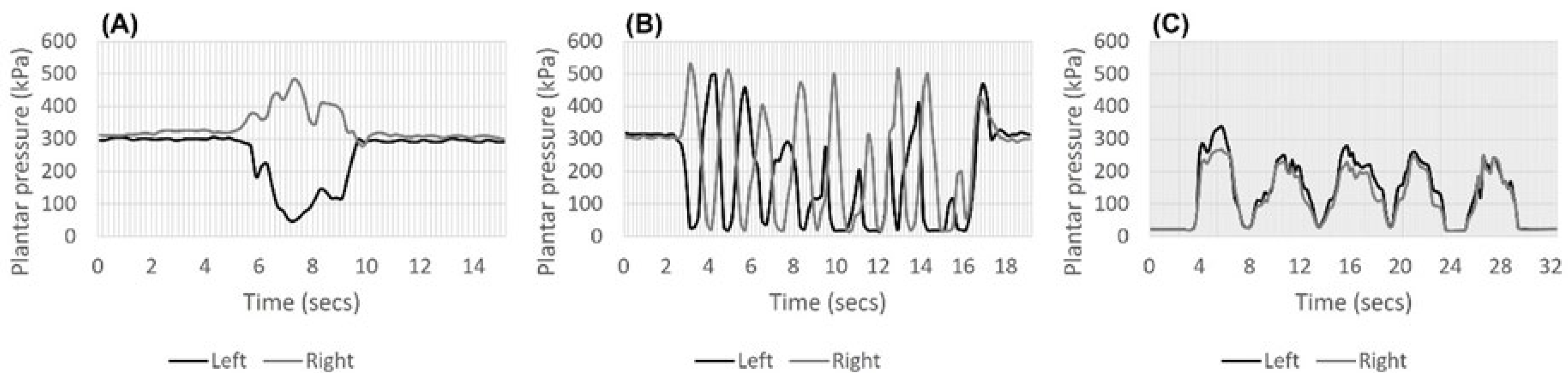
2.4. Interpretation of Plantar Pressure Graphs
2.5. Covariables
2.6. Statistical Analysis
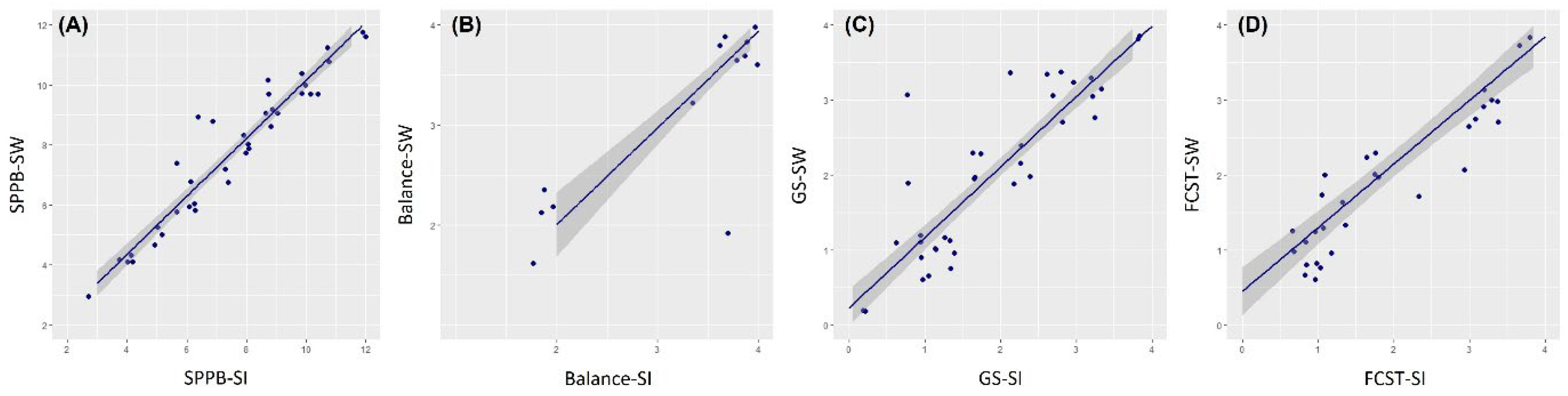
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

References
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: Association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruyère, O.; Buckinx, F.; Beaudart, C.; Reginster, J.Y.; Bauer, J.; Cederholm, T.; Cherubini, A.; Cooper, C.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Landi, F.; et al. How clinical practitioners assess frailty in their daily practice: An international survey. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronai, P.; Gallo, P.M. The short physical performance battery (assessment). ACSM’s Health Fit. J. 2019, 23, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Pérez-Sousa, M.A.; Venegas-Sanabria, L.C.; Cano-Gutierrez, C.A.; Hernández-Quiñonez, P.A.; Rincón-Pabón, D.; García-Hermoso, A.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Sáez de Asteasu, M.L.; Izquierdo, M. Normative values for the short physical performance battery (SPPB) and their association with anthropometric variables in older Colombian adults. The SABE study, 2015. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.W.; Roh, H.; Cho, Y.; Jeong, J.; Shin, Y.S.; Lim, J.Y.; Guralnik, J.M.; Park, J. Validation of a Multi-Sensor-Based Kiosk for Short Physical Performance Battery. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 2605–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musci, M.; Aresta, S.; Sardone, R.; Bortone, I. Technology-based assessment of Short Physical Performance Battery in elderly population. Gait Posture 2022, 97, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Regterschot, G.R.H.; Schaabova, H.; Baldus, H.; Zijlstra, W. Test-retest reliability of a pendant-worn sensor device in measuring chair rise performance in older persons. Sensors 2014, 14, 8705–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmers, S.; Fudickar, S.; Lau, S.; Elgert, L.; Diekmann, R.; Bauer, J.M.; Hein, A. Measurement of the chair rise performance of older people based on force plates and IMUs. Sensors 2019, 19, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellec, J.; Chorin, F.; Castagnetti, A.; Colson, S.S. Sit-to-stand movement evaluated using an inertial measurement unit embedded in smart glasses—A validation study. Sensors 2020, 20, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Yang, J.; Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, J. Multi-Task Deep Learning for Human Activity, Speed, and Body Weight Estimation using Commercial Smart Insoles. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 16121–16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziagkas, E.; Loukovitis, A.; Zekakos, D.X.; Chau, T.D.-P.; Petrelis, A.; Grouios, G. A novel tool for gait analysis: Validation study of the smart insole podosmart®. Sensors 2021, 21, 5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manupibul, U.; Charoensuk, W.; Kaimuk, P. Design and development of SMART insole system for plantar pressure measurement in imbalance human body and heavy activities. In Proceedings of the 7th 2014 Biomedical Engineering International Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 26–28 November 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Alfonso, A.R.; Rao, S.; Everett, B.; Chiu, E.S. Novel pressure-sensing smart insole system used for the prevention of pressure ulceration in the insensate foot. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.G.; Lee, S.H.; Min, S.D. Smart helmet and insole sensors for near fall incidence recognition during descent of stairs. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucharas, D.; Androutsos, C.; Gkois, G.; Tsakanikas, V.; Pezoulas, V.; Manousos, D.; Skaramagkas, V.; Chatzaki, C.; Kontogiannis, S.; Spandonidis, C. Smart insole: A gait analysis monitoring platform targeting Parkinson disease patients based on insoles. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.00109. [Google Scholar]
- Bencheikh, M.A.; Boukhenous, S. A low Cost Smart Insole for Diabetic Foot Prevention. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Applied Smart Systems (ICASS), Medea, Algeria, 24–25 November 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Im Yi, T.; Lee, E.C.; Son, N.H.; Sohn, M.K. Comparison of the Forefoot Pressure-Relieving Effects of Foot Orthoses. Yonsei Med. J. 2022, 63, 864. [Google Scholar]
- Almuteb, I.; Hua, R.; Wang, Y. Smart insoles review over the last two decade: Applications, potentials, and future. Smart Health 2022, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; An, Y.L.; Kim, D.-Y.; Lee, D.-O.; Park, G.Y.; Lee, D.Y. Assessment of Validity and Reliability of Plantar Pressure in Smart Insole. J. Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2022, 26, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-W.; Yoo, H.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Choi, J.-Y.; Yoon, S.-J.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, K.-i. The Korean version of the FRAIL scale: Clinical feasibility and validity of assessing the frailty status of Korean elderly. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.Y.; Jung, H.W.; Lee, C.K.; Jang, K.H.; Cho, E.I.; Jung, J.J.; Park, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, E. Korean version of the Fatigue, Resistance, Ambulation, Illnesses and Loss of weight questionnaire versus the Modified Kihon Checklist for Frailty Screening in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The Aging Study of PyeongChang Rural Area. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.Y.; Park, B.K.; Shin, H.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Pyun, S.B.; Paik, N.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Han, T.R. Development of the Korean version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI): Multi-center study for subjects with stroke. J. Korean Acad. Rehabil. Med. 2007, 31, 283–297. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-I.; Kim, W.-H.; Park, E.-Y.; Kim, E.-J. The validity, reliability and discriminative index of the Korean version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI) in stroke patients. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2012, 13, 4119–4125. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.J.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Han, E.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, H.Y. The Korean Version of Berg Balance Scale as an Index of Activity Related to Ambulation in Subjects with Stroke. J. Korean Acad. Rehabil. Med. 2007, 31, 400–403. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Shim, J.J.; Kim, M.J.; Hwang, M.R.; Kim, S.H. Reliability Test of Korean Version of Berg Balance Scale. J. Korean Acad. Rehabil. Med. 2006, 30, 611–618. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, B.; Cameron, M. Evaluation of walking speed and functional ambulation categories in geriatric day hospital patients. Clin. Rehabil. 1996, 10, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Jhoo, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.L.; Ryu, S.H.; Moon, S.W.; Choo, I.H.; Lee, D.W.; Yoon, J.C.; Do, Y.J. Korean version of mini mental status examination for dementia screening and its’ short form. Psychiatry Investig. 2010, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Jo, S.A.; Jo, I.; Kim, E.; Park, M.H.; Kang, Y. An adaptation of the Korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) in elderly Koreans: Demographic influence and population-based norms (the AGE study). Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2008, 47, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G. Sample size formulas for estimating intraclass correlation coefficients with precision and assurance. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 3972–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlon, Y.; Campo, E.; Brulin, D. Design and evaluation of a smart insole: Application for continuous monitoring of frail people at home. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 95, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piau, A.; Steinmeyer, Z.; Charlon, Y.; Courbet, L.; Rialle, V.; Lepage, B.; Campo, E.; Nourhashemi, F. A smart shoe insole to monitor frail older adults’ walking speed: Results of two evaluation phases completed in a living lab and through a 12-week pilot study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2021, 9, e15641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, C.; Ye, B.; Mihailidis, A. The development and concurrent validity of a multi-sensor-based frailty toolkit for in-home frailty assessment. Sensors 2022, 22, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Seo, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Cha, Y.; Kim, J.-T.; Kim, J.-W.; Ha, Y.-C.; Yoo, J.-I. Assessing physical abilities of sarcopenia patients using gait analysis and smart insole for development of digital biomarker. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimkhani, B.; Mirtalaie, S.H. Analysis of Orthotic Insoles Manufacturing for Treating Flatfoot Using Smart Orthotic Insole in Comparison with Traditional Methods. J. Mod. Process. Manuf. Prod. 2023, 12, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Volpato, S.; Cavalieri, M.; Sioulis, F.; Guerra, G.; Maraldi, C.; Zuliani, G.; Fellin, R.; Guralnik, J.M. Predictive value of the Short Physical Performance Battery following hospitalization in older patients. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2011, 66, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.J.; Stoecklein, H.; Yu, J.C.; Syrkin, G.; Hillstrom, H.; Deland, J.T. The accuracy of an automasking algorithm in plantar pressure measurements. HSS J. 2011, 7, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Kim, C.H. Fall-detection algorithm using plantar pressure and acceleration data. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 21, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Dai, Y.N.; Grimaldi, N.S.; Lin, J.J.; Hu, B.Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Gao, S. Plantar Pressure-Based Insole Gait Monitoring Techniques for Diseases Monitoring and Analysis: A Review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Pérez de Villar, L.; Martínez-Olmos, F.J.; Junqué-Jiménez, A.; Amer-Cuenca, J.J.; Martínez-Gramage, J.; Mercer, T.; Segura-Ortí, E. Test-retest reliability and minimal detectable change scores for the short physical performance battery, one-legged standing test and timed up and go test in patients undergoing hemodialysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total (N = 40) |
|---|---|
| Gender, women | 24 (60%) |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 72.98 (9.27) |
| 55–64 | 6 (15%) |
| 65–74 | 11 (28%) |
| 75–84 | 23 (57%) |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 23.51 (2.33) |
| K-FRAIL score, mean (SD) | 1.55 (1.13) |
| Grip strength (kg), mean (SD) | 19.95 (8.89) |
| K-MBI score, mean (SD) | 86.83 (16.74) |
| K-BBS score, mean (SD) | 43.55 (12.61) |
| FAC score, mean (SD) | 4.03 (1.23) |
| K-MMSE score, mean (SD) | 27.15 (1.78) |
| SPPB-SI score, mean (SD) | |
| Total score | 7.72 (2.50) |
| Balance test score | 3.76 (0.63) |
| Gait speed test score | 2.08 (1.19) |
| Five chair stand test score | 2.13 (1.34) |
| SPPB-M score | |
| Total score | 7.95 (2.63) |
| Balance test score | 3.68 (0.73) |
| Gait speed test score | 2.18 (1.17) |
| Five chair stand test score | 2.25 (1.26) |
| Intra-Interpreter Reliability | Inter-Interpreter Reliability | |
|---|---|---|
| SPPB-SI times | ||
| Balance test times | 0.989 * | 0.957 * |
| Gait speed test times | 0.996 * | 0.993 * |
| Five chair stand test times | 0.999 * | 0.999 * |
| SPPB-SI scores | ||
| Balance test scores | 0.889 * | 0.889 * |
| Gait speed test scores | 0.868 * | 0.868 * |
| Five chair stand test scores | 0.899 * | 0.865 * |
| K-FRAIL | K-BBS | FAC | K-MBI | Grip Strength | K-MMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPPB-SI | ||||||
| Total score | −0.333 (0.036) | 0.686 (<0.001) | 0.829 (<0.001) | 0.743 (<0.001) | 0.260 (<0.105) | 0.303 (<0.058) |
| Balance test score | −0.272 (0.094) | 0.360 (0.025) | 0.516 (0.001) | 0.432 (0.006) | 0.246 (0.131) | 0.091 (0.584) |
| Gait speed test score | −0.349 (0.027) | 0.620 (<0.001) | 0.775 (<0.001) | 0.742 (<0.001) | 0.276 (0.085) | 0.194 (0.230) |
| Five chair stand test score | −0.165 (0.310) | 0.658 (<0.001) | 0.737 (<0.001) | 0.632 (<0.001) | 0.201 (0.215) | 0.365 (0.021) |
| SPPB-M | ||||||
| Total score | −0.355 (0.025) | 0.678 (<0.001) | 0.836 (<0.001) | 0.737 (<0.001) | 0.233 (0.148) | 0.304 (0.056) |
| Balance test score | −0.342 (0.031) | 0.424 (0.006) | 0.554 (<0.001) | 0.471 (0.002) | 0.156 (0.338) | 0.094 (0.565) |
| Gait speed test score | −0.419 (0.007) | 0.682 (<0.001) | 0.801 (<0.001) | 0.749 (<0.001) | 0.289 (0.071) | 0.199 (0.219) |
| Five chair stand test score | −0.220 (0.172) | 0.571 (<0.001) | 0.697 (<0.001) | 0.568 (<0.001) | 0.157 (0.334) | 0.401 (0.010) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, C.W.; Park, K.; Paek, M.-C.; Jee, S.; Park, J.H. Validation of the Short Physical Performance Battery via Plantar Pressure Analysis Using Commercial Smart Insoles. Sensors 2023, 23, 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249757
Jang CW, Park K, Paek M-C, Jee S, Park JH. Validation of the Short Physical Performance Battery via Plantar Pressure Analysis Using Commercial Smart Insoles. Sensors. 2023; 23(24):9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249757
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Chan Woong, Kyoungmin Park, Min-Chul Paek, Sanghyun Jee, and Jung Hyun Park. 2023. "Validation of the Short Physical Performance Battery via Plantar Pressure Analysis Using Commercial Smart Insoles" Sensors 23, no. 24: 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249757
APA StyleJang, C. W., Park, K., Paek, M.-C., Jee, S., & Park, J. H. (2023). Validation of the Short Physical Performance Battery via Plantar Pressure Analysis Using Commercial Smart Insoles. Sensors, 23(24), 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23249757






