Stability, Mounting, and Measurement Considerations for High-Power GaN MMIC Amplifiers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Issues with X HPA Design
2.1. Process NP15-00
2.2. Transistor Selection and Architecture of the HPA
2.3. Load Pull
- Once the adjustments are completed, the impedance tuners are disassembled, and the desired load () and source reflection coefficients () are obtained by measuring the impedances of the impedance tuners;
- The spectrum analyzer and the power meter connected to the output impedance tuner make it possible to measure the exact value of the output power while simultaneously observing the output spectrum in the spectrum analyzer;
- In case of lower harmonics, the optimum load impedances can be obtained easily; however, a problem does occur when the harmonic impedances are considered;
- In general, the maximum output power is determined from the load impedance of the fundamental frequency, but the efficiency varies according to the harmonic load impedance.
2.4. Matching Network Strategy and Design
- Absorb the reactive part in the matching network (higher-bandwidth solution);
- Resonate the reactive part (lower-bandwidth solution).
- Normalize the source and load impedances with a convenient value () and plot them on the Smith chart;
- Plot the Q circle that corresponds to the required overall quality factor (a low value less than 3 is normally selected);
- If the matching network is a network (e.g., the last element is a parallel component), move away from the load along a constant g circle on the immittance chart until the Q circle is reached. If the matching network is a T network (e.g., the last element is a series component), move away from the load along a constant r circle until the Q circle is reached;
- Introduce an element with a sign opposite to that of the first one until the real axis is reached;
- Repeat the previous process, introducing as many elements as required until the source is reached.
- The more elements, the greater the bandwidth but also greater the losses. It is not usually practical for networks to have more than three or four poles (the design determines the number of poles and the used architecture).
- Attempt to integrate the reactive part into the adaptation network; if not, it is then possible to resonate it partially (preferably) or completely.
- Integrate polarization networks into adaptation networks.
- Attempt to use interspersed low-pass and high-pass sections.
- Make intensive use of the Smith chart, looking for short paths.
- Given the above, obtain an initial solution and proceed to refine it through optimization.
- Keep in mind that the limitations on space and values mean that the jumps are not selected according to a clear methodology but the designer’s own knowledge and experience.
2.5. Simulation Setup and Strategy
3. Stability of the Design
- Minimum disturbance of HPA performance;
- A sufficient stability margin to ensure stable performance, considering the technological dispersion of the circuit parameters;
- A sufficient gain margin to ensure the gain of the X HPA MMIC;
- A sufficient PAE and to ensure HPA performance;
- A minimal chip area.
3.1. Small-Signal Stability Analysis
3.2. Large-Signal Stability Analysis
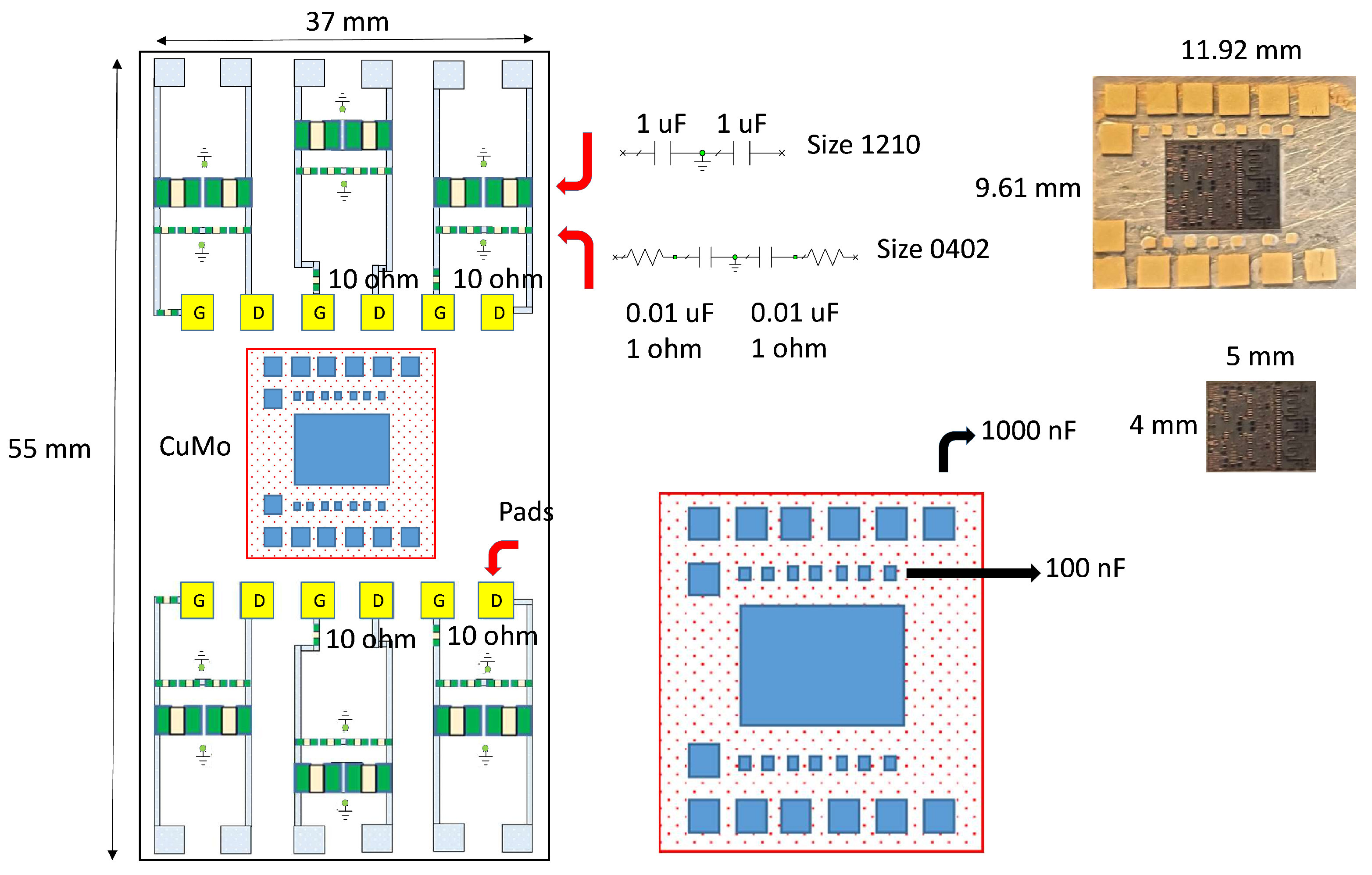
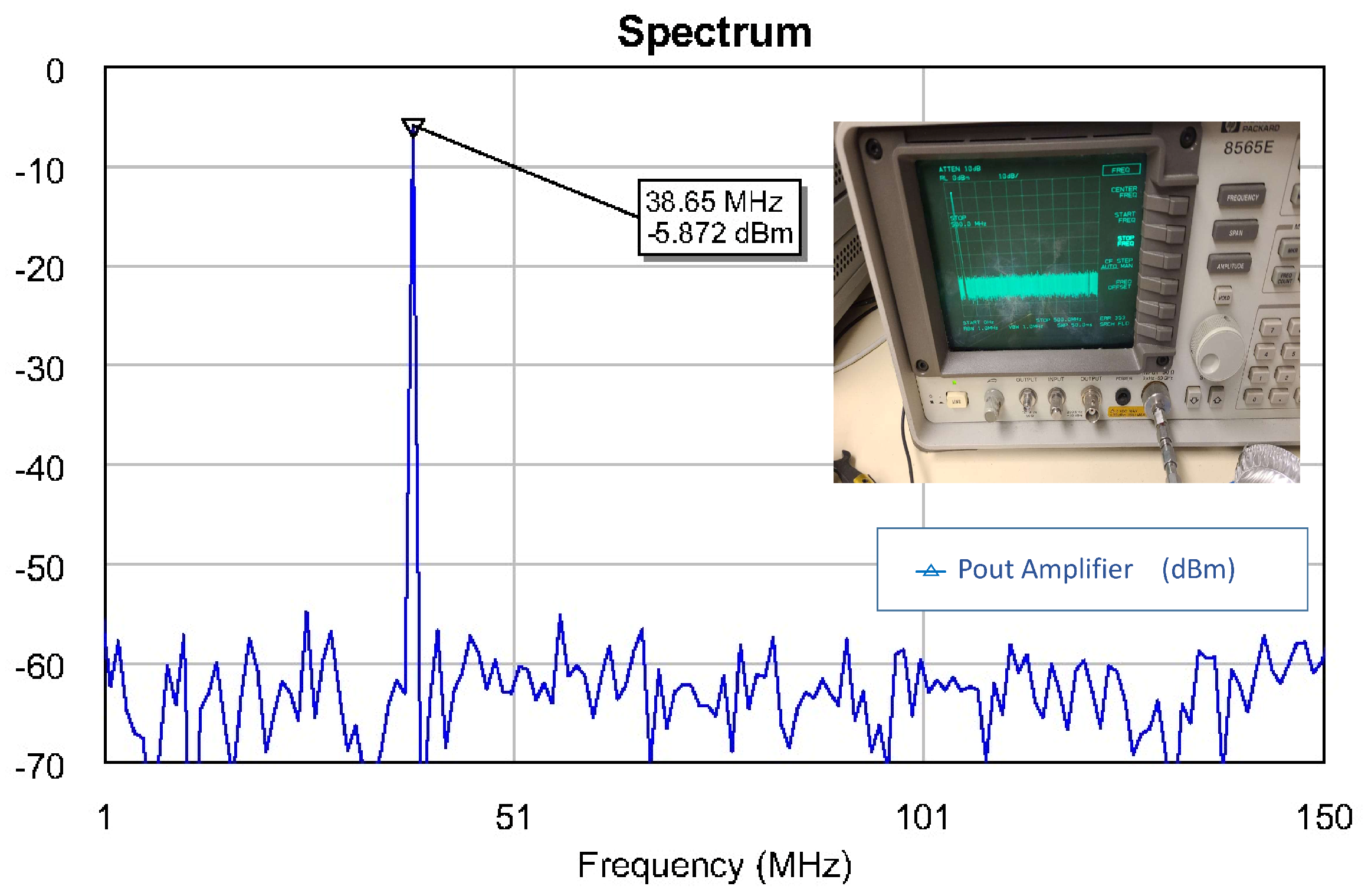
4. Measurement Problems
5. Final Measurements
6. Discussion
| HPA | Technology | (V) | (GHz) | (%) | Operation | Stages | Time/Duty (μs/%) | (W) | Gain (dB) | PAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This | 0.15 μm | 20 | 5.3–12.3 | 100 | AB | 3 | 100/10 | 8–16 | 25–28 | 38–43 |
| Work | GaN | |||||||||
| [35] | 0.25 μm | 25 | 9–11 | 20 | AB | 2 | 20/10 | 35–45 | 19 | 40–52 |
| GaN | ||||||||||
| [36] | 0.25 μm | 28 | 7.8–8.8 | 12 | AB | 2 | CW | 22–22.5 | 26 | 50 |
| GaN | ||||||||||
| [33] | 0.15 μm | 30 | 8.2–8.9 | 8 | AB | 1 | NA/10 | 28–31.5 | 11–12 | 57–60 |
| GaN | ||||||||||
| [34] | 0.15 μm | 44 | 9.8–11.5 | 8 | CascodeF | 1 | NA/10 | 5.8–9.2 | 7–12 | 50–62 |
| GaN | ||||||||||
| [37] | 0.25 μm | 28 | 8–12 | 40 | AB | 3 | 100/10 | 56.2–74 | 21–26 | 40–45 |
| GaN | ||||||||||
| [38] | 0.15 μm | 20 | 8–12.5 | 44 | AB | 2 | 25/10 | 14–17 | 23 | 50–62 |
| GaN |
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miranda, R.F.; Barriquello, C.H.; Reguera, V.A.; Denardin, G.W.; Thomas, D.H.; Loose, F.; Amaral, L.S. Review of Cognitive Hybrid Radio Frequency/Visible Light Communication Systems for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulwali, Z.S.A.; Alqahtani, A.H.; Aladadi, Y.T.; Alkanhal, M.A.S.; Al-Moliki, Y.M.; Aljaloud, K.; Alresheedi, M.T. A High-Performance Circularly Polarized and Harmonic Rejection Rectenna for Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting. Sensors 2023, 23, 7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidaks, J.; Kusnins, R.; Babajans, R.; Cirjulina, D.; Semenjako, J.; Litvinenko, A. Efficient Multi-Hop Wireless Power Transfer for the Indoor Environment. Sensors 2023, 23, 7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, A.; Augello, E.; Battistini, G.; Benassi, F.; Masotti, D.; Paolini, G. Microwave Devices for Wearable Sensors and IoT. Sensors 2023, 23, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouhalvandi, L.; Matekovits, L.; Peter, I. Amplifiers in Biomedical Engineering: A Review from Application Perspectives. Sensors 2023, 23, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Bent, G.; De Hek, A.P.; Van Vliet, F.E.; Ouarch, Z. Single-Chip 100-Watt S-band Power Amplifier in 0.25 μm GaN HEMT MMIC Technology. In Proceedings of the 15th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference, EuMIC2020, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 21–24. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350895537_Single-Chip_100-Watt_S-band_Power_Amplifier_in_025_um_GaN_HEMT_MMIC_Technology (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Qorvo. QPA3069 Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.qorvo.com/products/p/QPA3069 (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Kwiatkowski, P.; Knioła, M.; Szczepaniak, Z. Microwave Frequency Doubler with Improved Stabilization of Output Power. Sensors 2023, 23, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platzker, A.; Struble, W.; Hetzler, K.T. Instabilities diagnosis and the role of k in microwave circuits. In Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–18 June 1993; Volume 3, pp. 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struble, W.; Platzker, A. A rigorous yet simple method for determining stability of linear N-port networks [and MMIC application]. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual GaAs IC Symposium, San Jose, CA, USA, 10–13 October 1993; pp. 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, D. Reappraisal of the unconditional stability criteria for active 2-port networks in terms of s parameters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1976, 23, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.L.; Sinsky, J.H. A new criterion for linear 2-port stability using a single geometrically derived parameter. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1992, 40, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Martín, J.L.; Gonzalez-Posadas, V.; Parra-Cerrada, Á.; Blanco-del-Campo, A.; Segovia-Vargas, D. Transpose Return Relation Method for Designing Low Noise Oscillators. Prog. Electromagn. Res. (PIER) 2012, 127, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Martín, J.L.; Gonzalez-Posadas, V.; Parra-Cerrada, Á.; Segovia-Vargas, D.; Garcia-Munoz, L.E. Provisos for Classic Linear Oscillator Design Methods. New Linear Oscillator Design Based on the NDF/RRT. Prog. Electromagn. Res. (PIER) 2012, 126, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, R.G. A unified analysis of mmic power amplifier stability. In Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE MTT-S Microwave Symposium Digest, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1–5 June 1992; Volume 1, pp. 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jones, M.; Nelson, S. The S-probe-a new, cost-effective, 4-gamma method for evaluating multi-stage amplifier stabilityy. In Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE MTT-S Microwave Symposium Digest, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1–5 June 1992; Volume 2, pp. 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narhi, T.; Valtonen, M. Stability envelope-new tool for generalised stability analysis. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Denver, CO, USA, 8–13 June 1997; Volume 2, pp. 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayllon, N.; Collantes, J.; Anakabe, A.; Lizarraga, I.; Soubercaze-Pun, G.; Forestier, S. A Systematic Approach to the Stabilization of Multitransistor Circuits. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anakabe, A.; Mons, S.; Gasseling, T.; Casas, F.; Quere, R.; Collantes, J.M.; Malet, A.A. Efficient nonlinear stability analysis of microwave circuits using commercially available tools. In Proceedings of the European Microwave Week Conference, Milan, Italy, 23–26 September 2002; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mons, S.; Nallatamby, J.-C.; Quere, R.; Savary, P.; Obregon, J. A unified approach for the linear and nonlinear stability analysis of microwave circuits using commercially available tools. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1999, 47, 2403–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Suarez, A. Systematic methodology for the global stability analysis of nonlinear circuits. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMCAD Engineering. STAN Tool: A Unique Solution for the Stability Analysis of RF & Microwave Circuits. Available online: https://www.amcad-engineering.com/content/uploads/2018/06/Application_Note_STAN.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- WIN Semiconductors Home Page. Available online: https://www.winfoundry.com/en-US (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Pino, J.d.; Khemchandani, S.L.; Mayor-Duarte, D.; San-Miguel-Montesdeoca, M.; Mateos-Angulo, S.; de Arriba, F.; García, M. A Ku-Band GaN-on-Si MMIC Power Amplifier with an Asymmetrical Output Combiner. Sensors 2023, 23, 6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fano, R.M. Theoretical limitations on the broadband matching of arbitrary impedances. J. Frankl. Inst. 1948, 249, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, H.-G.; Le, V.-D.; Nguyen, V.-P.; Song, J.-M.; Lee, B.-H.; Park, J.-D. X-band MMICs for a Low-Cost Radar Transmit/Receive Module in 250 nm GaN HEMT Technology. Sensors 2023, 23, 4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galante-Sempere, D.; Khemchandani, S.L.; del Pino, J. A 2-V 1.4-dB NF GaAs MMIC LNA for K-Band Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhalvandi, L. Directly Matching an MMIC Amplifier Integrated with MIMO Antenna through DNNs for Future Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niclas, W.T.; Wilser, R.R.; Gold, R.B.; Hitchens, W.R. The matched feedback amplifier: Ultrawide-band microwave amplification with GaAs MESFET’s. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1980, 28, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollet, J.M. Stability and power-gain invariants of linear two ports. IRE Trans. Circuit Theory 1962, 9, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysight. PathWave Advanced Design System (ADS). Available online: https://www.keysight.com/us/en/products/software/pathwave-design-software/pathwave-advanced-design-system.html (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Cadence, R.F. Microwave Design with AWR Software. Available online: https://www.cadence.com/en_US/home/tools/system-analysis/rf-microwave-design.html (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Kawamura, Y.; Hangai, M.; Mizutani, T.; Tomiyama, K.; Yamanaka, K. 30W output/60% PAE GaN power amplifier at X-band 8% relative bandwidth. In Proceedings of the 8th 2016 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), New Delhi, India, 5–9 December 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Moon, J.-S. Highly efficient wideband X-band MMIC class-F power amplifier with cascode FP GaN HEMT. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 1207–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowicz, S.; Ouarch, Z.; Chartier, E.; Aubry, R.; Callet, G.; Floriot, D.; Jacquet, J.C.; Jardel, O.; Morvan, E.; Reveyrand, T.; et al. 43W, 52% PAE X-Band AlGaN/GaN HEMTs MMIC amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Anaheim, CA, USA, 23–28 May 2010; pp. 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, A.M.; Poitrenaud, N.; Serru, V.; Dionisio, R.; Fontecavc, J.J.; Camiade, M. 50 % High Efficiency X-Band GaN MMIC Amplifier for Space Applications. In Proceedings of the 48th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Madrid, Spain, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.-Q.; Hong, W.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.-M. A Compact 60W X-Band GaN HEMT Power Amplifier MMIC. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2017, 27, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.; Poitrenaud, N.; Serru, V.; Camiade, M.; Gruenenpuett, J.; Riepe, K.J. A High Efficiency MMIC X-band GaN Power Amplifier. In Proceedings of the 50th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 12–14 January 2021; pp. 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



























Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Posadas, V.; Jiménez-Martín, J.L.; Parra-Cerrada, A.; Espinosa Adams, D.; Hernandez, W. Stability, Mounting, and Measurement Considerations for High-Power GaN MMIC Amplifiers. Sensors 2023, 23, 9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239602
González-Posadas V, Jiménez-Martín JL, Parra-Cerrada A, Espinosa Adams D, Hernandez W. Stability, Mounting, and Measurement Considerations for High-Power GaN MMIC Amplifiers. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239602
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Posadas, Vicente, José Luis Jiménez-Martín, Angel Parra-Cerrada, David Espinosa Adams, and Wilmar Hernandez. 2023. "Stability, Mounting, and Measurement Considerations for High-Power GaN MMIC Amplifiers" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239602
APA StyleGonzález-Posadas, V., Jiménez-Martín, J. L., Parra-Cerrada, A., Espinosa Adams, D., & Hernandez, W. (2023). Stability, Mounting, and Measurement Considerations for High-Power GaN MMIC Amplifiers. Sensors, 23(23), 9602. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239602







