Design of a Tension Infiltrometer with Automated Data Collection Using a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
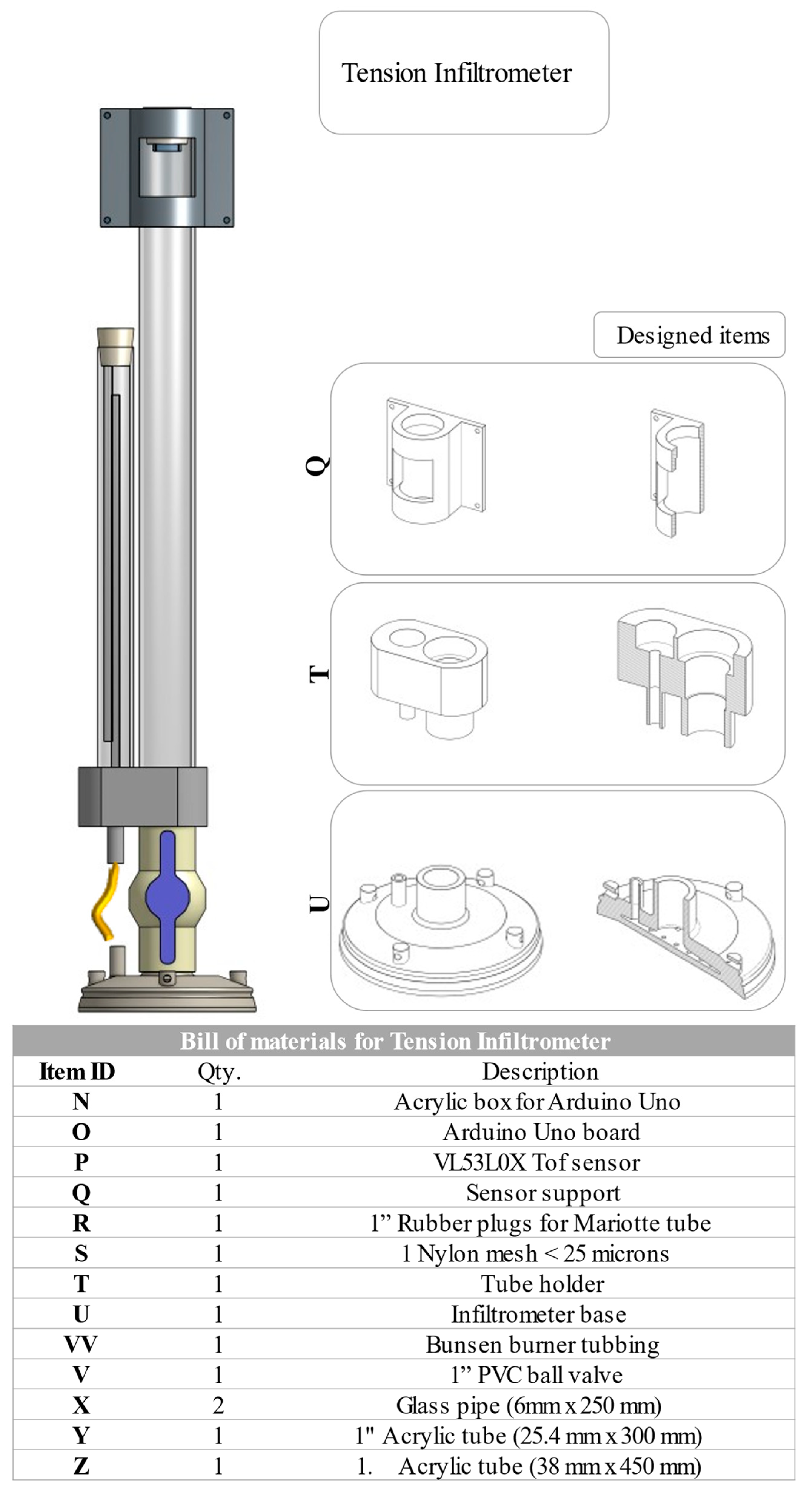
2. Materials
2.1. Mechanical Pieces
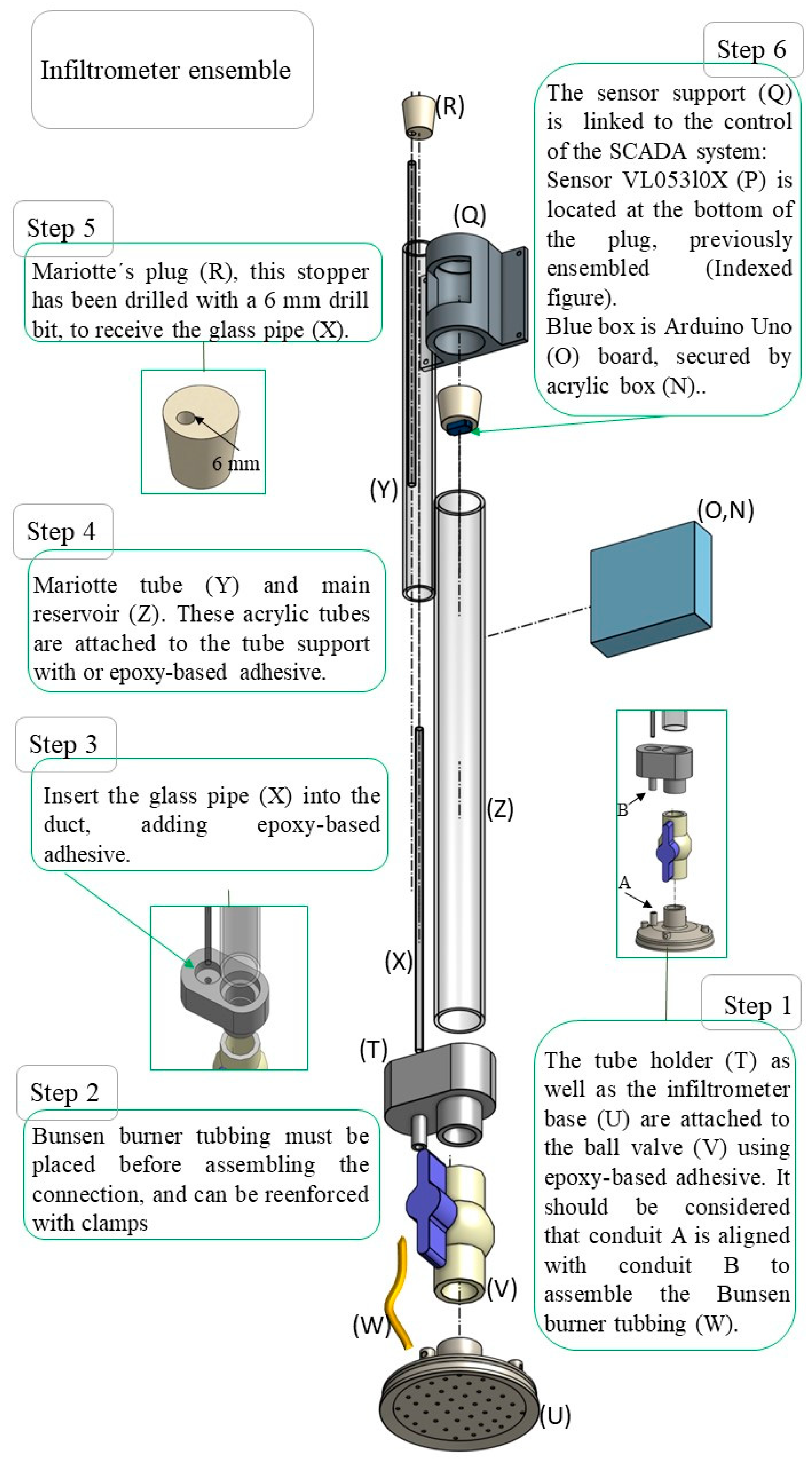
2.1.1. Infiltrometer Base
2.1.2. Connection for Reservoir and Mariotte
2.1.3. Sensor Support
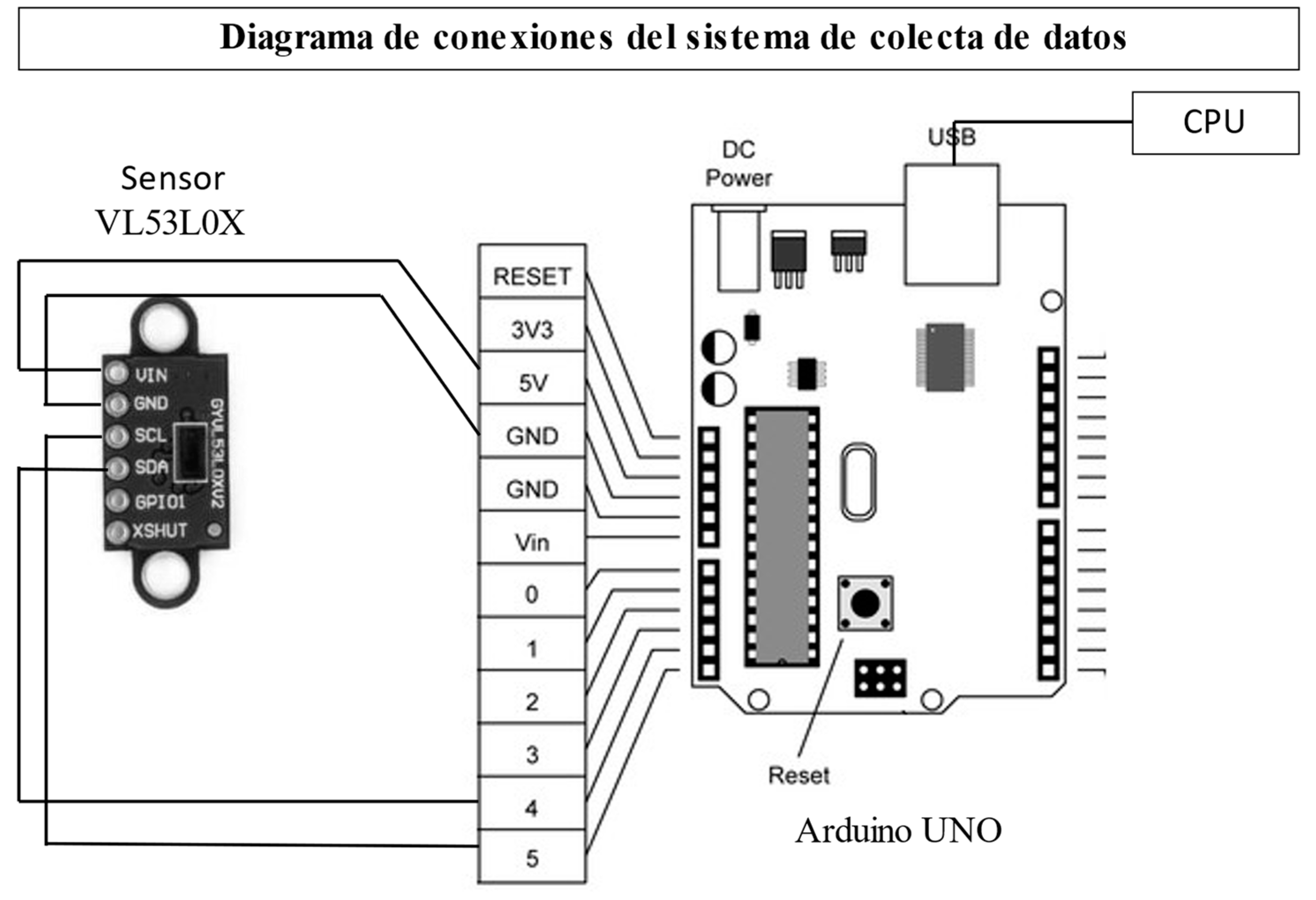
2.2. Electronic Items for SCADA System
2.3. Sensor Assembly
2.4. Infiltrometer Installation to Surface
3. Experimental Program of the Automated Data Collection System, SCADA
3.1. Programming the Data Collection through Ide Arduino
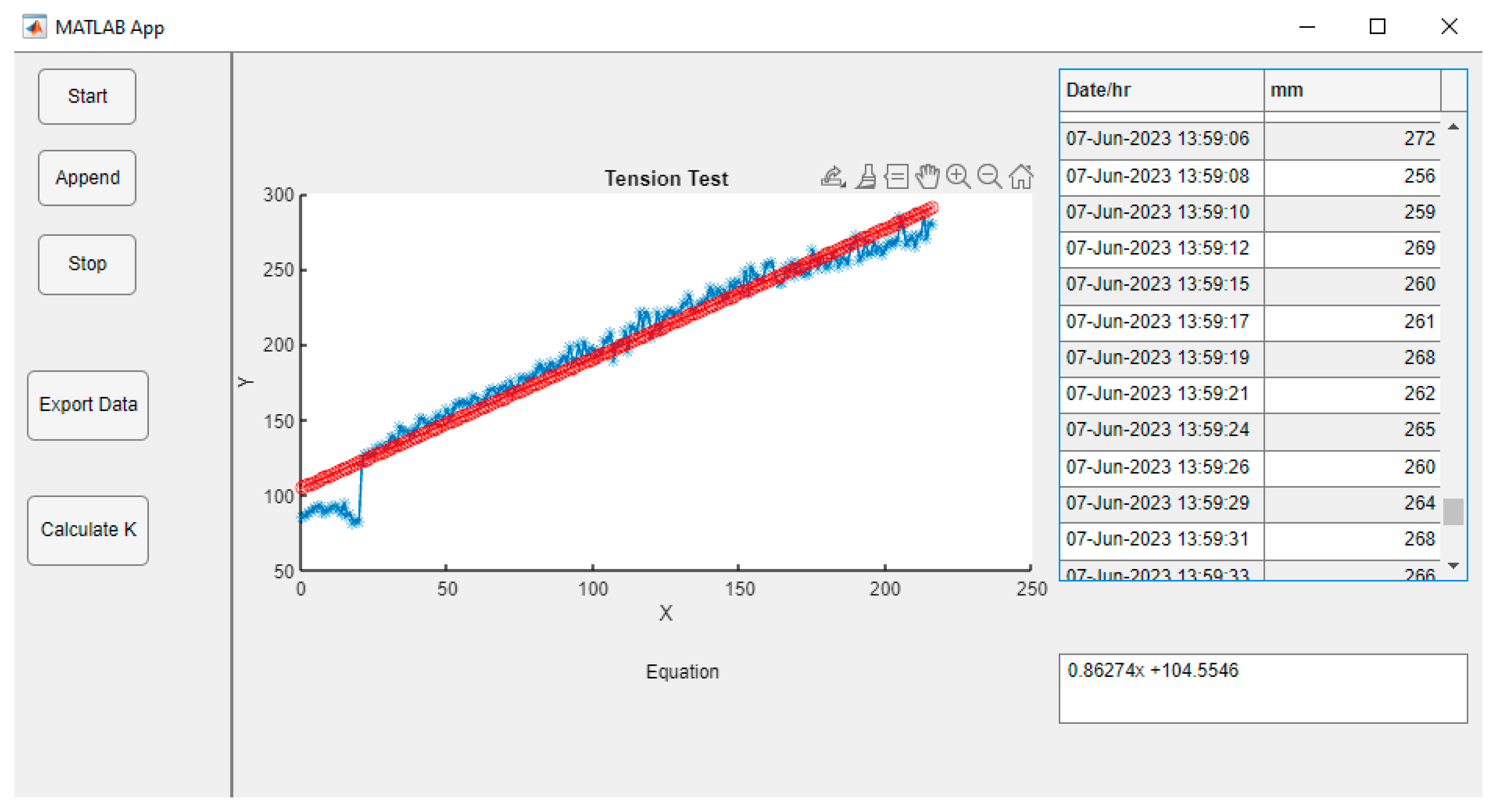
3.2. User Interface in Arduino and Matlab Environment
- ⚬
- The Start button (Start). When pressed, the reading of the data from the serial port begins, and from that moment, the system memory stores the data, ordering them into a table component (Table) and storing them as virtual memory to also graph them (Axes), so that, along the ordinates, the collection time is plotted in hours, minutes, and seconds against the height of the water column in mm along the abscissas.
- ⚬
- The end of data collection button (Stop). When this button is pressed, it ends the functions of reading data in the serial port, as well as graphing and ordering in the table.
- ⚬
- A button exports the data obtained (Export) to a suitable file for Microsoft Excel for further processing.
3.3. Calibration of the Measurement System
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Arduino Measurement Program
Appendix B. Matlab GUI Program
References
- Rodríguez-Iturbe, J. Ecohydrology: A hydrologicperspective of climate-soil-vegetation dynamics. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.A. Bosques, suelo y agua: Explorando sus interacciones: Ecosistemas. Ecosistemas 2017, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongmei, H.; Currell, M.; Guoliang, C.; Hall, B. Alterations to groundwater recharge due to anthropogenic landscape change. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 545–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Shao, M.A. Change of soil physical properties under long-term natural vegetation restoration in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Arid. Environ. 2006, 64, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.; Elsenbeer, H. Spatial and temporal variability of soil saturated hydraulic conductivity in gradients of disturbance. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Tagle, A.; Geissert, D.; Enriquez, E. Manual de Infiltrometría: Infiltrómetro de Tensión INDI; Instituto de Ecología, A.C.: Xalapa, Mexico, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Tagle, A. Linking hydropedology and ecosystem services: Differential controls of surface field saturated hydraulic conductivity in a volcanic setting in central Mexico. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2009, 6, 2499–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB, 11436441 (R2023a); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2023.
- Gómez-Tagle Chávez, A.; Gutiérrez Gnecchi, J.A.; Zepeda Castro, H. Dispositivo de automatización para un infiltrómetro de campo con funcionamiento de mariotte. Terra Latinoam. 2010, 28, 193–202. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Ortega, D.A.; Cambrón-Sandoval, V.H.; Ruiz-González, I.; Luna-Soria, H.; Hernández-Guerrero, J.A.; García-Guzmán, G. Design of a Tension Infiltrometer with Automated Data Collection Using a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System. Sensors 2023, 23, 9489. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239489
Morales-Ortega DA, Cambrón-Sandoval VH, Ruiz-González I, Luna-Soria H, Hernández-Guerrero JA, García-Guzmán G. Design of a Tension Infiltrometer with Automated Data Collection Using a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9489. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239489
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Ortega, David Alberto, Víctor Hugo Cambrón-Sandoval, Israel Ruiz-González, Hugo Luna-Soria, Juan Alfredo Hernández-Guerrero, and Genaro García-Guzmán. 2023. "Design of a Tension Infiltrometer with Automated Data Collection Using a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9489. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239489
APA StyleMorales-Ortega, D. A., Cambrón-Sandoval, V. H., Ruiz-González, I., Luna-Soria, H., Hernández-Guerrero, J. A., & García-Guzmán, G. (2023). Design of a Tension Infiltrometer with Automated Data Collection Using a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System. Sensors, 23(23), 9489. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239489






