Semi-Supervised Image Stitching from Unstructured Camera Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The development of SandFall, a novel algorithm for data representation that supports an unlimited number of camera inputs while ensuring fixed-size image data.
- A deep learning-based image stitching network capable of processing an unlimited number of input images in a single forward pass, employing semi-supervised learning to optimize training with limited labeled data.
- Adaptations of GAN performance metrics specifically tailored for assessing the quality of image stitching, providing a robust framework for evaluation.
- Comprehensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations of our approach, demonstrating its effectiveness against popular image stitching algorithms using both standard and custom datasets.
2. Related Work
2.1. Image and Video Stitching
2.2. Parallax-Tolerant Stitching
2.3. Gradient Domain Smoothing
2.4. Supervised, Unsupervised, and Semi-Supervised Networks
2.5. Image Quality Assessment (IQA)
3. Method
3.1. Data Representation
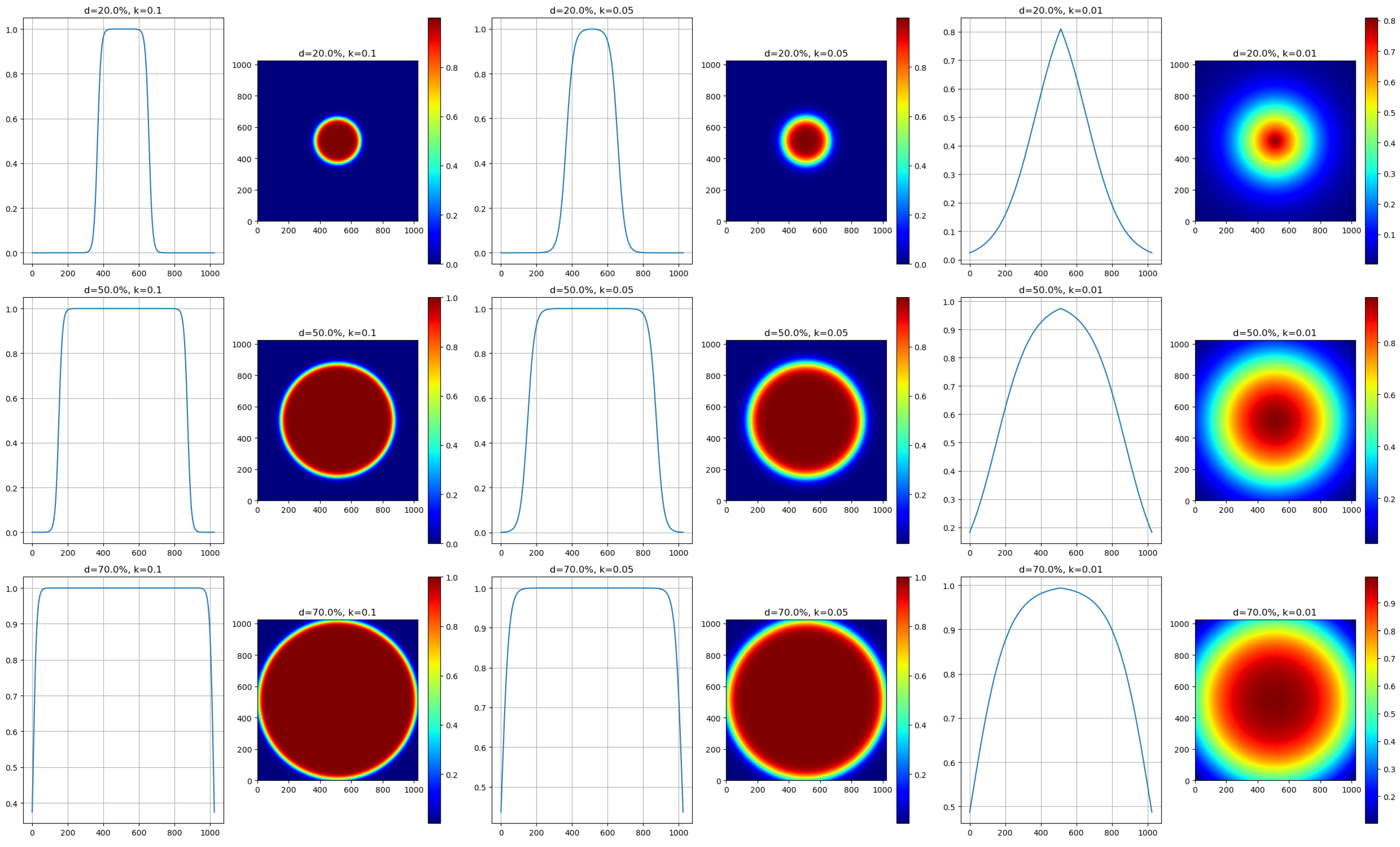
3.1.1. Weighted Mask Integration
- is the Euclidean distance of a pixel from the image center.
- k is a constant that adjusts the transition’s steepness.
- is a distance threshold that determines the transition’s starting point between high and low weights.
3.1.2. SandFall Algorithm
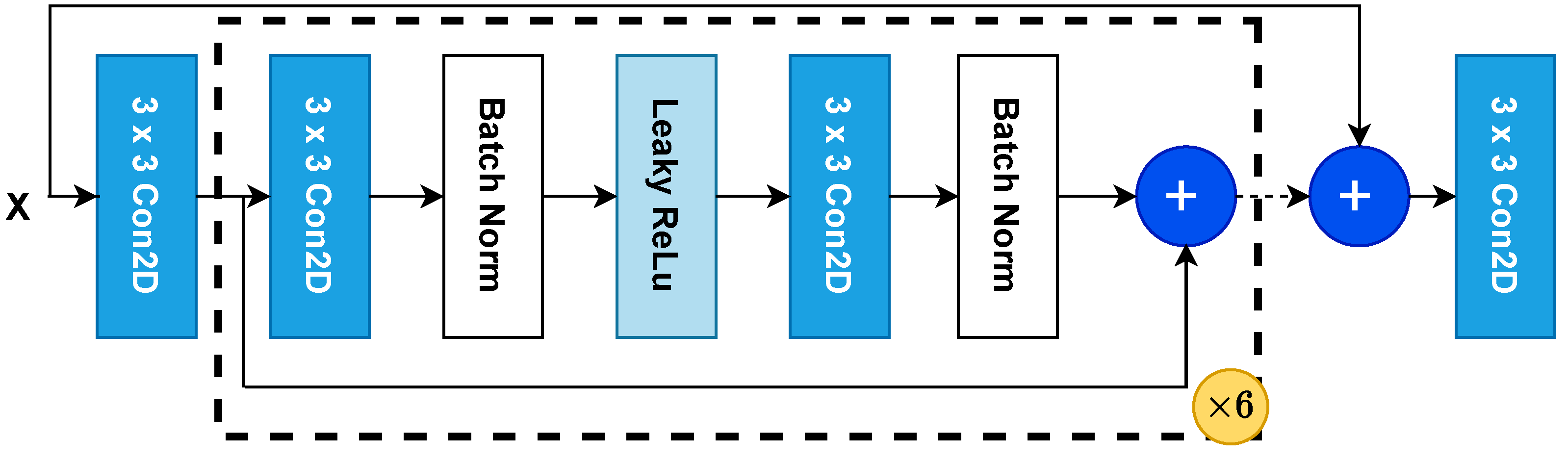
3.2. Image Transformation Network
| Algorithm 1: The SandFall Algorithm |
|
3.2.1. Overview
3.2.2. Objective Function for Supervised Learning
- is the content loss function as defined in Equation (6).
- is the mean square error per pixel loss function as defined in Equation (9).
- represents the total variation as defined in Equation (8)
- is the reconstruction loss function as defined in Equation (7)
- , , , and control the contribution of each function to the overall loss calculated by the model.
3.2.3. Objective Function for Unsupervised Learning
3.2.4. Formulation of Each Objective Function
3.2.5. Generating the Dataset for Training
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Dataset and Preprocessing
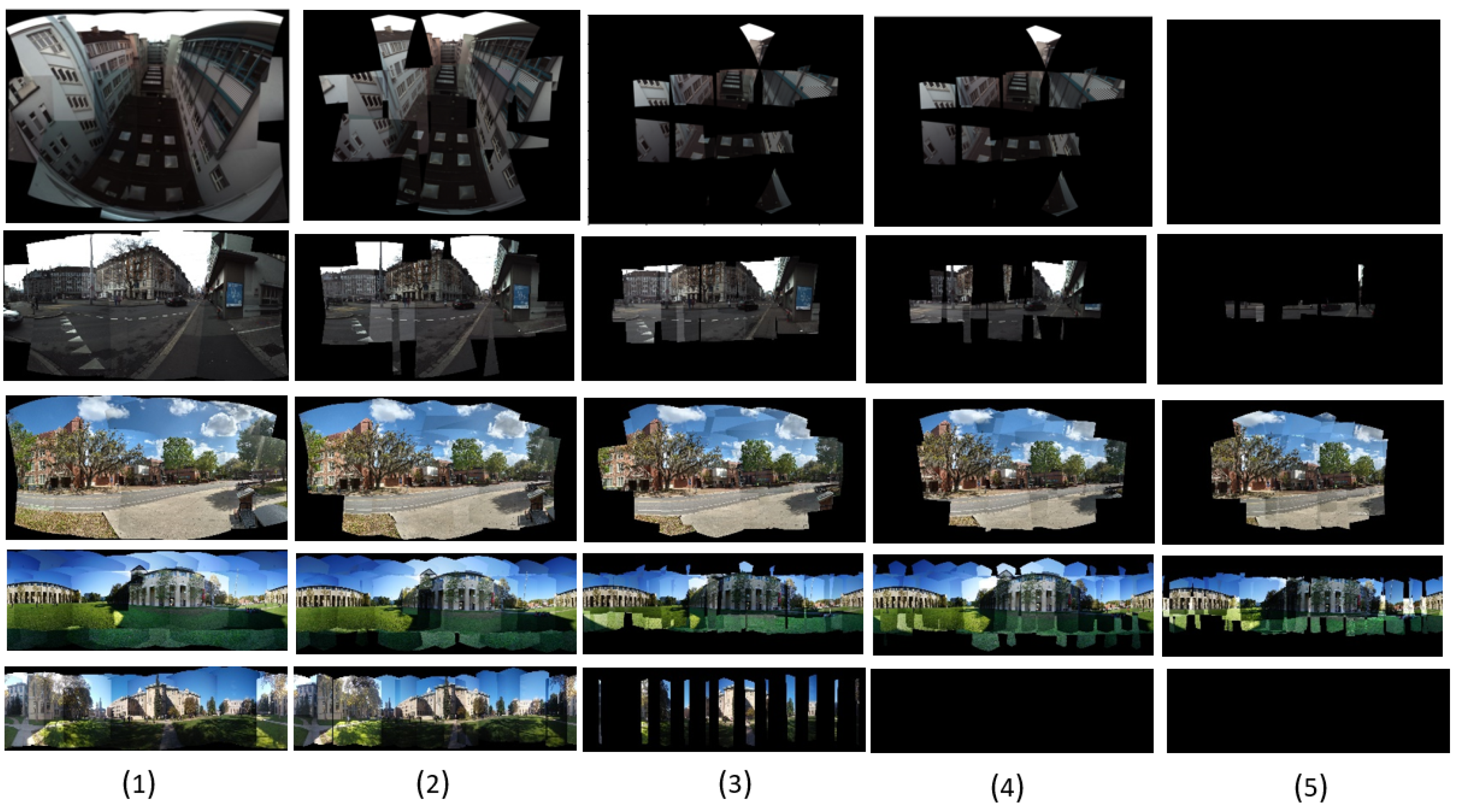
4.2. SandFall Results
4.3. Experimental Setup and Training Parameters
4.4. Model Performance
4.4.1. Quantitative Comparisons
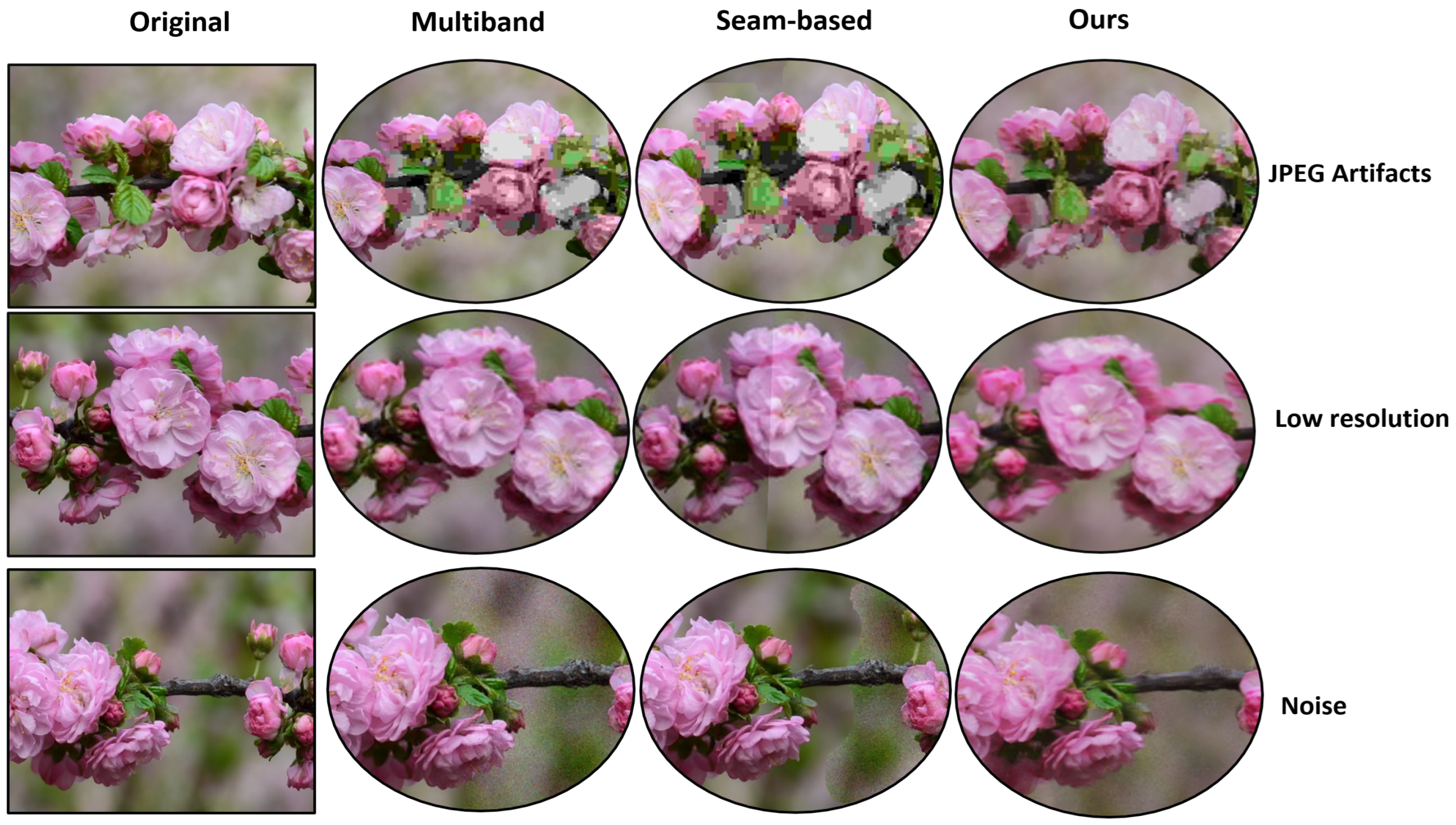
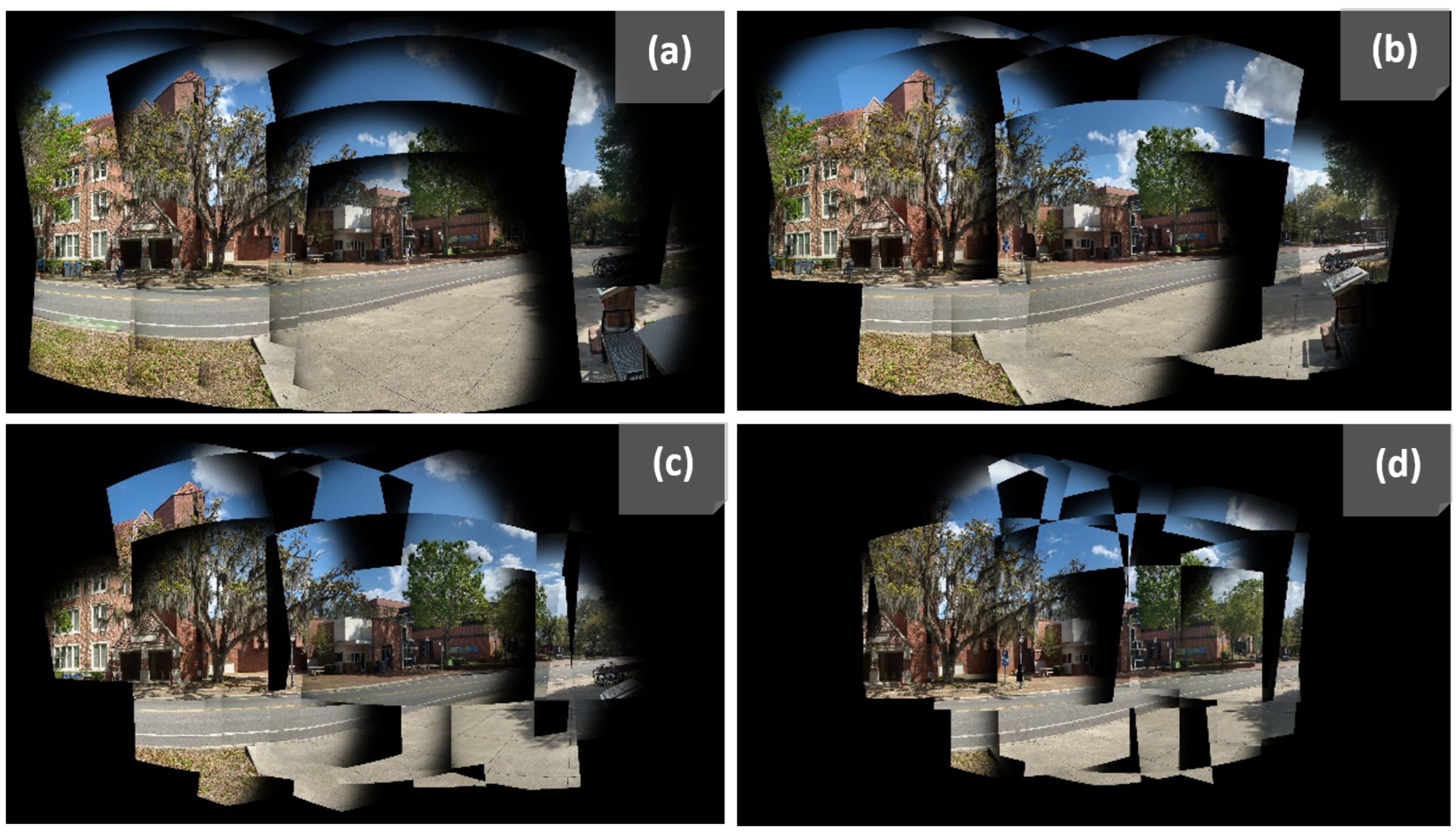
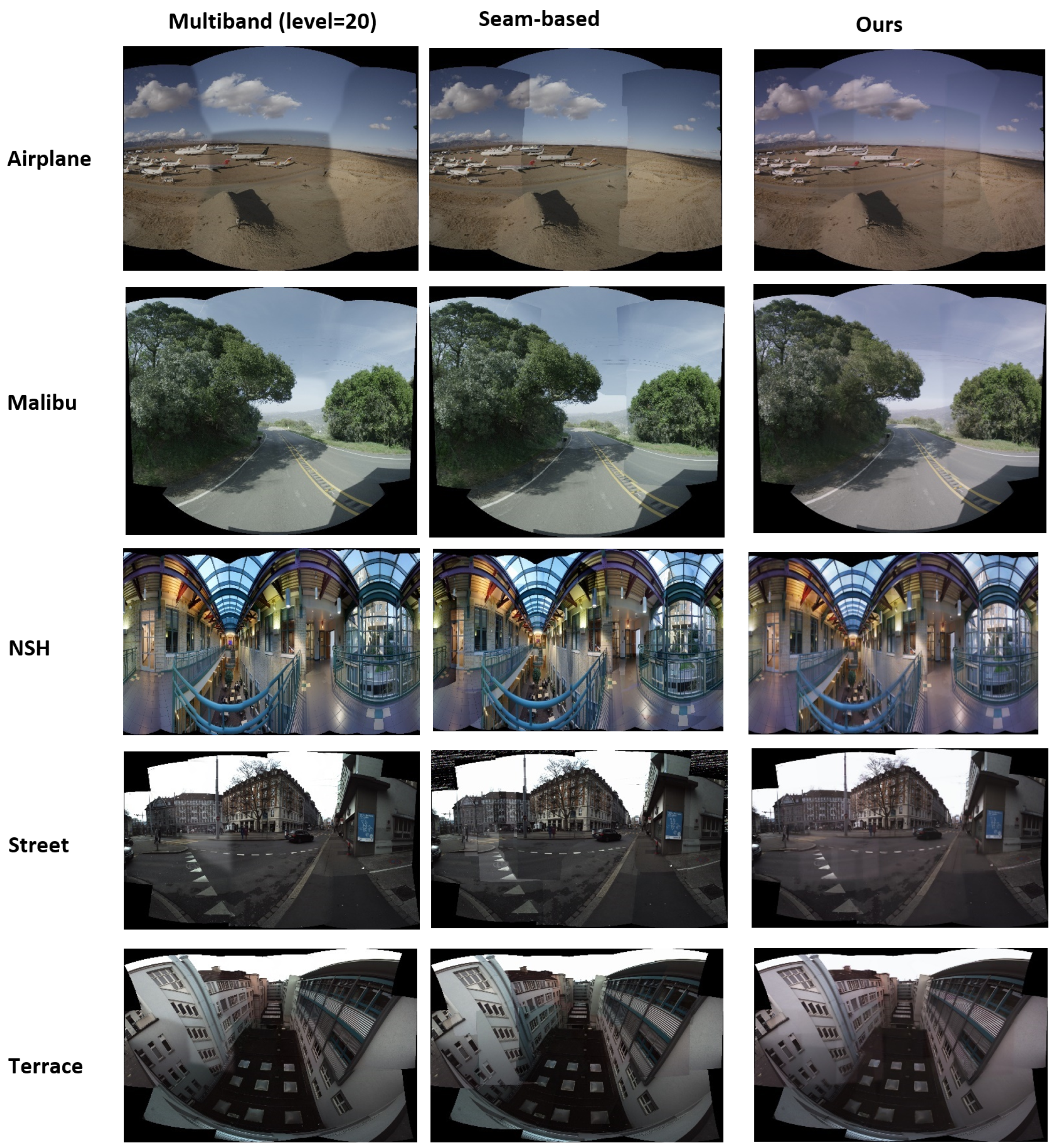
4.4.2. Qualitative Comparisons
5. Discussion
5.1. Image Quality Assessment (IQA)
5.2. SandFall
Intrinsic Artifact Mitigation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szeliski, R. Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications; Springer: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.; Lowe, D.G. Automatic Panoramic Image Stitching using Invariant Features. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwatra, V.; Schödl, A.; Essa, I.; Turk, G.; Bobick, A. Graphcut Textures: Image and Video Synthesis Using Graph Cuts. ACM Trans. Graph. 2003, 22, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, P.; Gangnet, M.; Blake, A. Poisson Image Editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2003, 22, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeliski, R. Image Alignment and Stitching: A Tutorial. Found. Trends. Comput. Graph. Vis. 2006, 2, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchinda, E.N.; Kwadjo, D.T.; Bobda, C. A Distributed Smart Camera Apparatus to Enable Scene Immersion: Work-in-progress. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Hardware/Software Codesign and System Synthesis Companion, New York, NY, USA, 13–18 October 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019. CODES/ISSS ’19. pp. 18:1–18:2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.T.; Chen, H.I.; Chen, M.S.; Shen, I.C.; Chen, B.Y. High-resolution 360 Video Foveated Stitching for Real-time VR. Comput. Graph. Forum 2017, 36, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qian, Y.; Kämäräinen, J.; Cricri, F.; Fan, L. Object Detection in Equirectangular Panorama. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Sim, J.Y. Warping Residual Based Image Stitching for Large Parallax. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Perazzi, F.; Sorkine-Hornung, A.; Zimmer, H.; Kaufmann, P.; Wang, O.; Watson, S.; Gross, M.H. Panoramic Video from Unstructured Camera Arrays. Comput. Graph. Forum 2015, 34, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Yu, S. Parallax-Robust Surveillance Video Stitching. Sensors 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.S.; Gallo, O.; Gu, J.; Sun, D.; Yang, M.H.; Kautz, J. Video stitching for linear camera arrays. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.13622. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Gu, J. Video stitching with spatial-temporal content-preserving warping. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Efficient Video Stitching Based on Fast Structure Deformation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 45, 2707–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilukuri, P.K.; Padala, P.; Padala, P.; Desanamukula, V.S.; Pvgd, P.R. l, r-Stitch Unit: Encoder-Decoder-CNN Based Image-Mosaicing Mechanism for Stitching Non-Homogeneous Image Sequences. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 16761–16782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.Y.; Um, G.M.; Lee, H.K.; Cho, D. End-to-End Image Stitching Network via Multi-Homography Estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Lin, C.; Liao, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Deep Rectangling for Image Stitching: A Learning Baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 5740–5748. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.Y.; Lee, G.; Lee, H.; Um, G.M.; Cho, D. Weakly-Supervised Stitching Network for Real-World Panoramic Image Generation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 54–71. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, USA, 8–13 December 2014; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Weinberger, K., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Ji, X.; Miao, C. Real-Time Image Stitching with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Irkutsk, Russia, 4–9 August 2019; pp. 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.C.; Sung, W.K. Understanding geometry of encoder-decoder CNNs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 7064–7073. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Tang, C. Image Stitching Using Structure Deformation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Mao, J.; Huang, Z.; Huang, C.; Xu, W. Cnn-rnn: A unified framework for multi-label image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NA, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2285–2294. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using Part Affinity Fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, J.M.; Petro, A.; Sbert, C. Fourier implementation of Poisson image editing. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, J.M.; Facciolo, G.; Meinhardt-Llopis, E. Poisson Image Editing. Image Process. Line 2016, 6, 300–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petro, A.B.; Sbert, C. Selective Contrast Adjustment by Poisson Equation. Image Process. Line 2013, 3, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbman, Z.; Hoffer, G.; Lipman, Y.; Cohen-Or, D.; Lischinski, D. Coordinates for Instant Image Cloning. ACM Trans. Graph. 2009, 28, 67:1–67:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A. Sparse autoencoder. CS294A Lect. Notes 2011, 72, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Goldberg, A.B. Introduction to semi-supervised learning. Synth. Lect. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. 2009, 3, 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved Techniques for Training GANs. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.03498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Klambauer, G.; Hochreiter, S. GANs Trained by a Two Time-Scale Update Rule Converge to a Nash Equilibrium. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, S.; Sharma, R. A Note on the Inception Score. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.01973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wei, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J. An Improved Evaluation Framework for Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.07474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Lin, C.; Liao, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Unsupervised Deep Image Stitching: Reconstructing Stitched Features to Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 6184–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C.; Wang, C.; Bowen, R.S.; Keyder, E.; Krainin, M.; Liu, C.; Zabih, R. Robust image stitching with multiple registrations. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Mahendran, A.; Vedaldi, A. Understanding Deep Image Representations by Inverting Them. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual Losses for Real-Time Style Transfer and Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]






| Image Set | # of Cameras | Multi-Band Blending (5) | Multi-Band Blending (20) | Seam-Based Stitching | Our Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrace | 14 | 17.35 s | 74.7 s | 187.6 s | 12.77 s |
| Malibu | 5 | 24.8 s | 101.19 s | 126.4 s | 15.5 s |
| Airplane | 14 | 25.55 s | 106.16 s | 122.3 s | 15.14 s |
| Street | 5 | 16.89 s | 81.6 s | 177.6 s | 9.2 s |
| Indoor | 14 | 1.21 s | 5.04 s | 19.25 s | 1.80 s |
| Averages | N\A | 17.16 s | 73.4 s | 126.63 s | 10.89 s |
| LPIPS ↓ | FID ↓ | IS ↑ | SG ↑ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Seam | Multiband | Ours | Seam | Multiband | Ours | Seam | Multiband | Ours | Seam | Multiband | Ours |
| Windmills | 1.241 | 1.172 | 1.239 | 16.18 | 15.45 | 16.90 | 4.10 | 1.89 | 1.87 | 1.41 | 0.63 | 0.62 |
| Terrace | 0.531 | 0.517 | 0.533 | 5.66 | 5.60 | 4.92 | 1.357 | 1.337 | 1.344 | 0.305 | 0.290 | 0.295 |
| Airplanes | 1.238 | 1.163 | 1.234 | 11.74 | 11.60 | 12.32 | 1.61 | 1.57 | 1.48 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.39 |
| Street | 0.694 | 0.67 | 0.696 | 13.35 | 13.46 | 11.67 | 5.84 | 2.86 | 2.45 | 1.76 | 1.05 | 0.89 |
| Malibu | 1.177 | 1.10 | 1.174 | 16.48 | 16.91 | 16.07 | 4.65 | 2.57 | 2.83 | 1.53 | 0.94 | 1.04 |
| Averages | 0.9762 | 0.9244 | 0.9752 | 12.682 | 12.604 | 12.376 | 3.5114 | 2.0454 | 1.9948 | 1.097 | 0.672 | 0.647 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nghonda Tchinda, E.; Panoff, M.K.; Tchuinkou Kwadjo, D.; Bobda, C. Semi-Supervised Image Stitching from Unstructured Camera Arrays. Sensors 2023, 23, 9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239481
Nghonda Tchinda E, Panoff MK, Tchuinkou Kwadjo D, Bobda C. Semi-Supervised Image Stitching from Unstructured Camera Arrays. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239481
Chicago/Turabian StyleNghonda Tchinda, Erman, Maximillian Kealoha Panoff, Danielle Tchuinkou Kwadjo, and Christophe Bobda. 2023. "Semi-Supervised Image Stitching from Unstructured Camera Arrays" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239481
APA StyleNghonda Tchinda, E., Panoff, M. K., Tchuinkou Kwadjo, D., & Bobda, C. (2023). Semi-Supervised Image Stitching from Unstructured Camera Arrays. Sensors, 23(23), 9481. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239481





