Influence of Normal Aging and Multisensory Data Fusion on Cybersickness and Postural Adaptation in Immersive Virtual Reality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Procedure
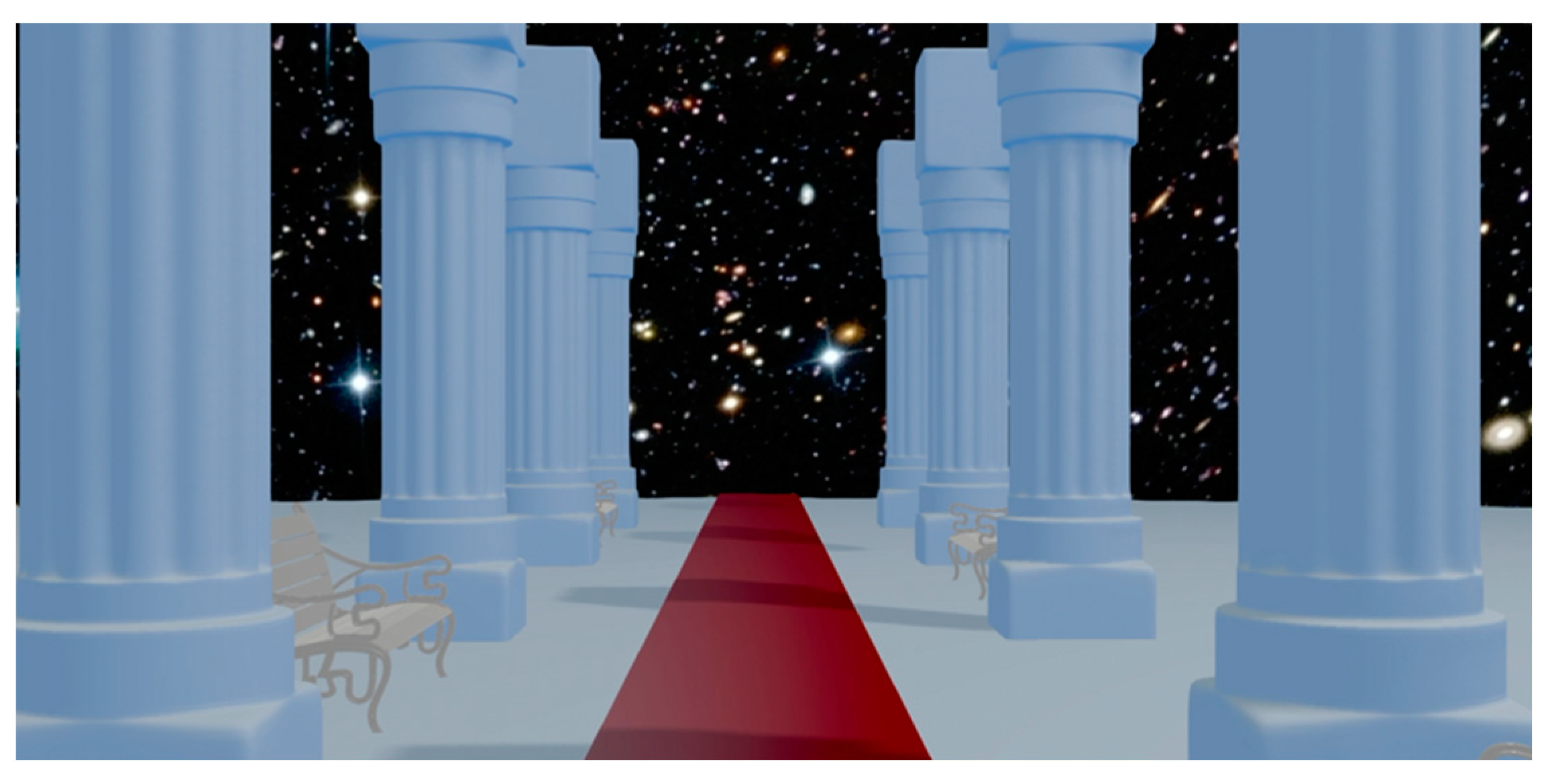
2.2.1. Virtual Reality System
2.2.2. Cybersickness Assessment
2.2.3. Balance Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Cybersickness with Repetition
3.2. Cybersickness, Motion Sickness, Habituation Score, and Age
3.3. Postural Reference Measures
3.4. Postural Changes with Repetition
3.5. Postural Changes and Age
3.6. Postural Adaptation Score and Age
3.7. Evolution of Postural Adaptation and Cybersickness Habituation Scores
3.8. Predicting Cybersickness from Postural Parameters
3.9. Cybersickness and Motion Sickness Susceptibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Høeg, E.R.; Povlsen, T.M.; Bruun-Pedersen, J.R.; Lange, B.; Nilsson, N.C.; Haugaard, K.B.; Faber, S.M.; Hansen, S.W.; Kimby, C.K.; Serafin, S. System Immersion in Virtual Reality-Based Rehabilitation of Motor Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Virtual Real. 2021, 2, 647993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermody, G.; Whitehead, L.; Wilson, G.; Glass, C. The Role of Virtual Reality in Improving Health Outcomes for Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e17331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, P.; Andrade, R. The Influence of Virtual Reality Head-Mounted Displays on Balance Outcomes and Training Paradigms: A Systematic Review. Front. Sports Act. Living 2021, 2, 531535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahmari, K.A.; Marchetti, G.F.; Sparto, P.J.; Furman, J.M.; Whitney, S.L. Estimating Postural Control With the Balance Rehabilitation Unit: Measurement Consistency, Accuracy, Validity, and Comparison With Dynamic Posturography. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phu, S.; Vogrin, S.; Al Saedi, A.; Duque, G. Balance Training Using Virtual Reality Improves Balance and Physical Performance in Older Adults at High Risk of Falls. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, L.E.; Frías-Hiciano, M.; Moreno-Jiménez, M.; Cruz, G.N.; García-Batista, Z.E.; Guerra-Peña, K.; Medrano, L.A. Focusing on Cybersickness: Pervasiveness, Latent Trajectories, Susceptibility, and Effects on the Virtual Reality Experience. Virtual Real. 2022, 26, 1347–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, G. Full-Immersion Virtual Reality: Adverse Effects Related to Static Balance. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 733, 134974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebenitsch, L.; Owen, C. Review on Cybersickness in Applications and Visual Displays. Virtual Real. 2016, 20, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, J.T.; Brand, J.J. Motion Sickness; Academic Press: London, UK, 1975; ISBN 978-0-12-584050-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, J.E.; Bles, W.; Groen, E.L. A Theory on Visually Induced Motion Sickness. Displays 2008, 29, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Son, W. Cybersickness and Its Severity Arising from Virtual Reality Content: A Comprehensive Study. Sensors 2022, 22, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, P.-A.; Patel, M.; Jensen, H.; Lundberg, M.; Tjernström, F.; Magnusson, M.; Ekvall Hansson, E. Postural Instability in an Immersive Virtual Reality Adapts with Repetition and Includes Directional and Gender Specific Effects. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Agundez, A.; Reuter, C.; Becker, H.; Konrad, R.; Caserman, P.; Miede, A.; Göbel, S. Development of a Classifier to Determine Factors Causing Cybersickness in Virtual Reality Environments. Games Health J. 2019, 8, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.; Kim, H.T.; Yoo, B. Virtual Reality Sickness: A Review of Causes and Measurements. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2020, 36, 1658–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockelman, P.; Lingum, D. Factors of Cybersickness. In HCI International 2017—Posters’ Extended Abstracts; Stephanidis, C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easa, S. Human Factor Considerations in Virtual Reality: Adequate or Inadequate? Ergon. Int. J. 2021, 5, 000267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.C.; Van Zandt, E.C. A Meta-Analysis of the Virtual Reality Problem: Unequal Effects of Virtual Reality Sickness across Individual Differences. Virtual Real. 2021, 25, 1221–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtesis, P.; Amir, R.; Linnell, J.; Argelaguet, F.; MacPherson, S.E. Cybersickness, Cognition, & Motor Skills: The Effects of Music, Gender, and Gaming Experience. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar]
- Munafo, J.; Diedrick, M.; Stoffregen, T.A. The Virtual Reality Head-Mounted Display Oculus Rift Induces Motion Sickness and Is Sexist in Its Effects. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazich, B.F.; McPherson, R.; Gorman, E.F.; Chan, T.; Teleb, J.; Galik, E.; Resnick, B. In Too Deep? A Systematic Literature Review of Fully-Immersive Virtual Reality and Cybersickness among Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffert, J.-P.; Niebling, F.; Latoschik, M.E. Latency and Cybersickness: Impact, Causes, and Measures. A Review. Front. Virtual Real. 2020, 1, 582204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saredakis, D.; Szpak, A.; Birckhead, B.; Keage, H.A.D.; Rizzo, A.; Loetscher, T. Factors Associated With Virtual Reality Sickness in Head-Mounted Displays: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, R.; Philippe, F.; Yann, T.; Bahman, A.; Alexandre, C.; Samuel, B.; Philippe, B.; Vincent, B.; Lenaïc, C.; Denis, C.; et al. Charte de Recommandations Sur l’usage de La Réalité Virtuelle. 2019. Available online: https://acrobat.adobe.com/link/review?uri=urn%3Aaaid%3Ascds%3AUS%3A3eb42e51-7889-4ce8-be75-292b29d6ba44 (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Proietti, P.; Allsop, J.; Bloch, M.; Bos, J.; Burov, O.; Clement, D.; French, J.; Kirollos, R.; Lawson, B.; Leoncini, P. Guidelines for Mitigating Cybersickness in Virtual Reality Systems; Technical Report; NATO Science and Technology Organisation, Human Factors and Medicine & Modeling and Simulation Group Specialist Team: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi, L.F.I.; Polastri, P.F.; Penedo, T.; Vieira, L.H.P.; Simieli, L.; Navega, F.R.F.; de Mello Monteiro, C.B.; Rodrigues, S.T.; Barbieri, F.A. Virtual Reality Head-Mounted Goggles Increase the Body Sway of Young Adults during Standing Posture. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 737, 135333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, M.S.; D’Zmura, M. Cybersickness without the Wobble: Experimental Results Speak against Postural Instability Theory. Appl. Ergon. 2017, 58, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assländer, L.; Streuber, S. Virtual Reality as a Tool for Balance Research: Eyes Open Body Sway Is Reproduced in Photo-Realistic, but Not in Abstract Virtual Scenes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshner, E.A.; Slaboda, J.C.; Buddharaju, R.; Lanaria, L.; Norman, J. Augmenting Sensory-Motor Conflict Promotes Adaptation of Postural Behaviors in a Virtual Environment. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.-R.; Xiao, S.-F.; Pan, L.-L.; Mao, Y.-Q.; Su, Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Cai, Y.-L. Profiling of Cybersickness and Balance Disturbance Induced by Virtual Ship Motion Immersion Combined with Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation. Appl. Ergon. 2021, 92, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavgani, A.M.; Nesbitt, K.V.; Blackmore, K.L.; Nalivaiko, E. Profiling Subjective Symptoms and Autonomic Changes Associated with Cybersickness. Auton. Neurosci. 2017, 203, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-L. A Study of Detecting and Combating Cybersickness with Fuzzy Control for the Elderly within 3D Virtual Stores. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2014, 72, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.T.; So, R.H.Y. Cybersickness in the Presence of Scene Rotational Movements along Different Axes. Appl. Ergon. 2001, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, L.J.; Stoffregen, T.A.; Bardy, B.G. Visually Induced Motion Sickness Predicted by Postural Instability. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2002, 44, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berard, J.; Fung, J.; Lamontagne, A. Impact of Aging on Visual Reweighting during Locomotion. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, S.R.; Ward, J.A. Age-Associated Differences in Sensori-Motor Function and Balance in Community Dwelling Women. Age Ageing 1994, 23, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Noppeney, U. Ageing and Multisensory Integration: A Review of the Evidence, and a Computational Perspective. Cortex 2021, 138, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamet, M.; Deviterne, D.; Gauchard, G.C.; Vançon, G.; Perrin, P.P. Higher Visual Dependency Increases Balance Control Perturbation during Cognitive Task Fulfilment in Elderly People. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 359, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesmeier, I.K.; Dalin, D.; Maurer, C. Elderly Use Proprioception Rather than Visual and Vestibular Cues for Postural Motor Control. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eikema, D.J.A.; Hatzitaki, V.; Tzovaras, D.; Papaxanthis, C. Age-Dependent Modulation of Sensory Reweighting for Controlling Posture in a Dynamic Virtual Environment. AGE 2012, 34, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.; Griffin, M.J. Motion Sickness in Public Road Transport: Passenger Behaviour and Susceptibility. Ergonomics 1999, 42, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhare, A.R.; Yang, V.; Stradford, J.; Tsang, I.; Ravichandran, R.; Pa, J. Cycling and Spatial Navigation in an Enriched, Immersive 3D Virtual Park Environment: A Feasibility Study in Younger and Older Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.J.; Chung, W.H.; Park, K.-A.; Kim, J.D.K.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Jeon, H.J. Clinical Predictors of Cybersickness in Virtual Reality (VR) among Highly Stressed People. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilanchian, A.T.; Andringa, R.; Boot, W.R. A Pilot Study Exploring Age Differences in Presence, Workload, and Cybersickness in the Experience of Immersive Virtual Reality Environments. Front. Virtual Real. 2021, 2, 736793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béraud-Peigné, N.; Maillot, P.; Perrot, A. The Effects of a New Immersive Multidomain Training on Cognitive, Dual-Task and Physical Functions in Older Adults. GeroScience 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytönen, M.; Pyykkö, I.; Aalto, H.; Starck, J. Postural Control and Age. Acta Otolaryngol. 1993, 113, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, S.; St-Jacques, J.; Renaud, P.; Wiederhold, B. Side Effects of Immersions in Virtual Reality for People Suffering from Anxiety Disorders. J. Cyber Ther. Rehabil. 2009, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, R.S.; Lane, N.E.; Berbaum, K.S.; Lilienthal, M.G. Simulator Sickness Questionnaire: An Enhanced Method for Quantifying Simulator Sickness. Int. J. Aviat. Psychol. 1993, 3, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, J.F. Predicting Individual Differences in Motion Sickness Susceptibility by Questionnaire. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2006, 41, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Mentiplay, B.F.; Pua, Y.-H.; Bower, K.J. Reliability and Validity of the Wii Balance Board for Assessment of Standing Balance: A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2018, 61, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JASP Team JASP (Version 0.16.2) [Computer Software]. 2022. Available online: https://jasp-stats.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Brown, P.; Spronck, P.; Powell, W. The Simulator Sickness Questionnaire, and the Erroneous Zero Baseline Assumption. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 3, 945800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, G.; Kemeny, A.; Paillot, D.; Colombet, F. A Simulation Sickness Study on a Driving Simulator Equipped with a Vibration Platform. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2020, 68, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.; Choi, R.; Ferrè, E.R. Multisensory Interactions in Virtual Reality: Optic Flow Reduces Vestibular Sensitivity, but Only for Congruent Planes of Motion. Multisens. Res. 2020, 33, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, P.P.; Jeandel, C.; Perrin, C.A.; Béné, M.C. Influence of Visual Control, Conduction, and Central Integration on Static and Dynamic Balance in Healthy Older Adults. Gerontology 1997, 43, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brech, G.C.; Bobbio, T.G.; Cabral, K.d.N.; Coutinho, P.M.; de Castro, L.R.; Mochizuki, L.; Soares-Junior, J.M.; Baracat, E.C.; Leme, L.E.G.; Greve, J.M.D.; et al. Changes in Postural Balance Associated with a Woman’s Aging Process. Clinics 2022, 77, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Fransson, P.A.; Magnusson, M. Effects of Ageing on Adaptation during Vibratory Stimulation of the Calf and Neck Muscles. Gerontology 2009, 55, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantin, L.; Ceyte, G.; Maïni, E.; Hossu, G.; Ceyte, H. Do Individual Constraints Induce Flexibility of Visual Field Dependence Following a Virtual Immersion? Effects of Perceptive Style and Cybersickness. Virtual Real. 2022, 27, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooij, S.A.E.; Bockisch, C.J.; Bülthoff, H.H.; Straumann, D. Beyond Sensory Conflict: The Role of Beliefs and Perception in Motion Sickness. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarz, B.; Hecht, H. Validating an Efficient Method to Quantify Motion Sickness. Hum. Factors 2011, 53, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtesis, P.; Linnell, J.; Amir, R.; Argelaguet, F.; MacPherson, S.E. Cybersickness in Virtual Reality Questionnaire (CSQ-VR): A Validation and Comparison against SSQ and VRSQ. Virtual Worlds 2023, 2, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.W.; Gilbert, S.B.; Dorneich, M.C.; Costabile, K.A. Gender Differences in Cybersickness: Clarifying Confusion and Identifying Paths Forward. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW), Shanghai, China, 25–29 March 2023; pp. 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassini, S.; Laumann, K. Are Modern Head-Mounted Displays Sexist? A Systematic Review on Gender Differences in HMD-Mediated Virtual Reality. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Séba, M.-P.; Maillot, P.; Hanneton, S.; Dietrich, G. Influence of Normal Aging and Multisensory Data Fusion on Cybersickness and Postural Adaptation in Immersive Virtual Reality. Sensors 2023, 23, 9414. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239414
Séba M-P, Maillot P, Hanneton S, Dietrich G. Influence of Normal Aging and Multisensory Data Fusion on Cybersickness and Postural Adaptation in Immersive Virtual Reality. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9414. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239414
Chicago/Turabian StyleSéba, Marie-Philippine, Pauline Maillot, Sylvain Hanneton, and Gilles Dietrich. 2023. "Influence of Normal Aging and Multisensory Data Fusion on Cybersickness and Postural Adaptation in Immersive Virtual Reality" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9414. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239414
APA StyleSéba, M.-P., Maillot, P., Hanneton, S., & Dietrich, G. (2023). Influence of Normal Aging and Multisensory Data Fusion on Cybersickness and Postural Adaptation in Immersive Virtual Reality. Sensors, 23(23), 9414. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239414




