A Robust GPS Navigation Filter Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion with Adaptive Kernel Bandwidth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Maximum Correntropy Criterion
3. Extended Kalman Filter with Maximum Correntropy Criterion
- (1)
- Initialization of state vector and state covariance matrix .
- (2)
- Predictions of the state vector and state covariance matrix are
- (3)
- Computation of the Kalman gain matrix: .
- (4)
- Updating of the state vector: .
- (5)
- Updating of the error covariance: .
- (1)
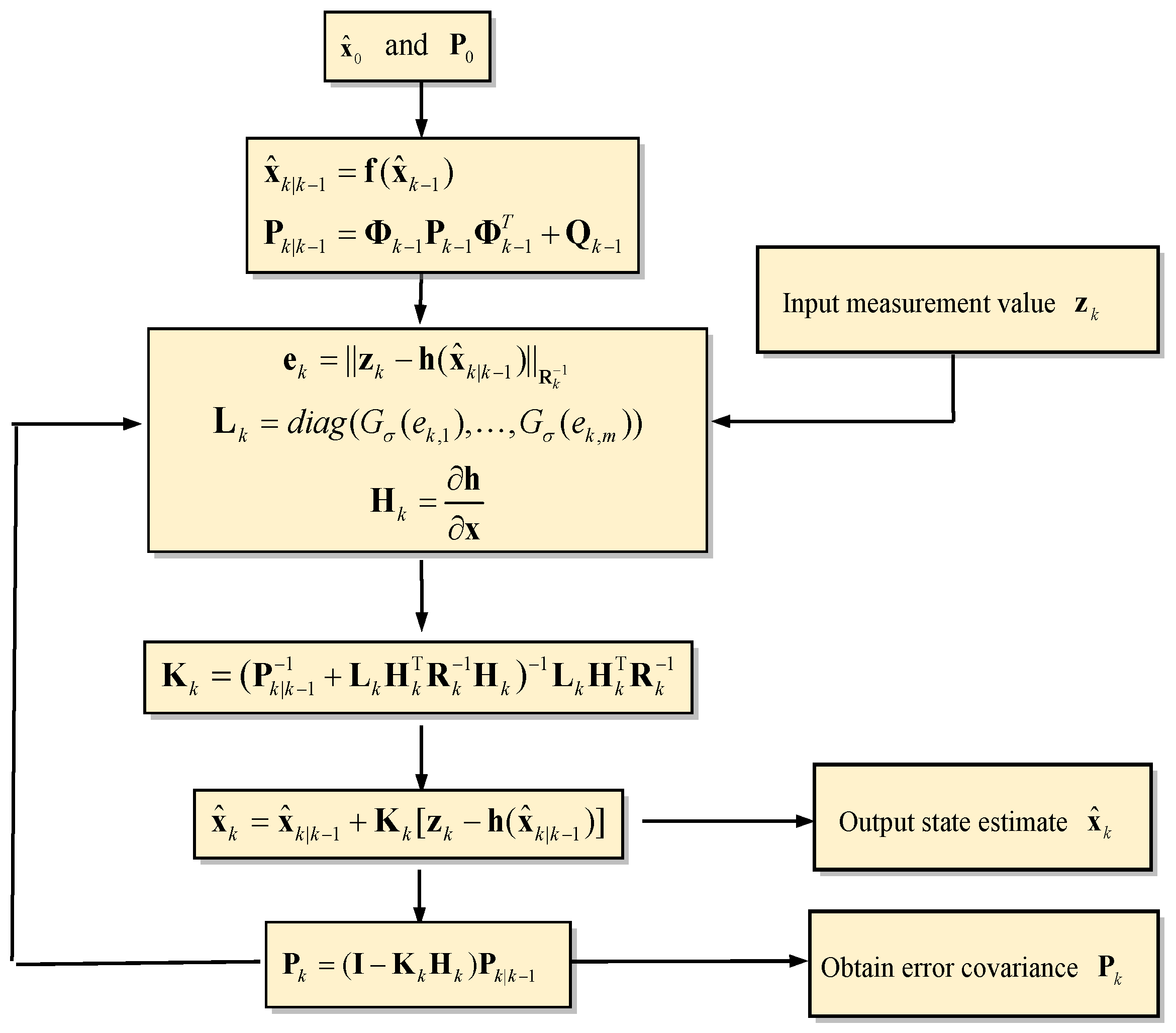
- Initialization of the state vector and state covariance matrix: and ;
- (2)
- Prediction of the state vector and the state covariance matrix: and ;
- (3)
- Computation of the measurement innovation based on MCC to obtain the factor: ;
- (4)
- Computation of the modified Kalman gain matrix: ;
- (5)
- Updating the state vector and the error covariance: and ;
- (6)
- Repeating from Step (2) to evaluate the subsequent estimation cycle.
4. MCCEKF with Adaptive Kernel Bandwidth
4.1. Innovation Information for Failure Detection and Adaptive Algorithms
4.2. MCCEKF Based on Adaptive Kernel Bandwidth Mechanism
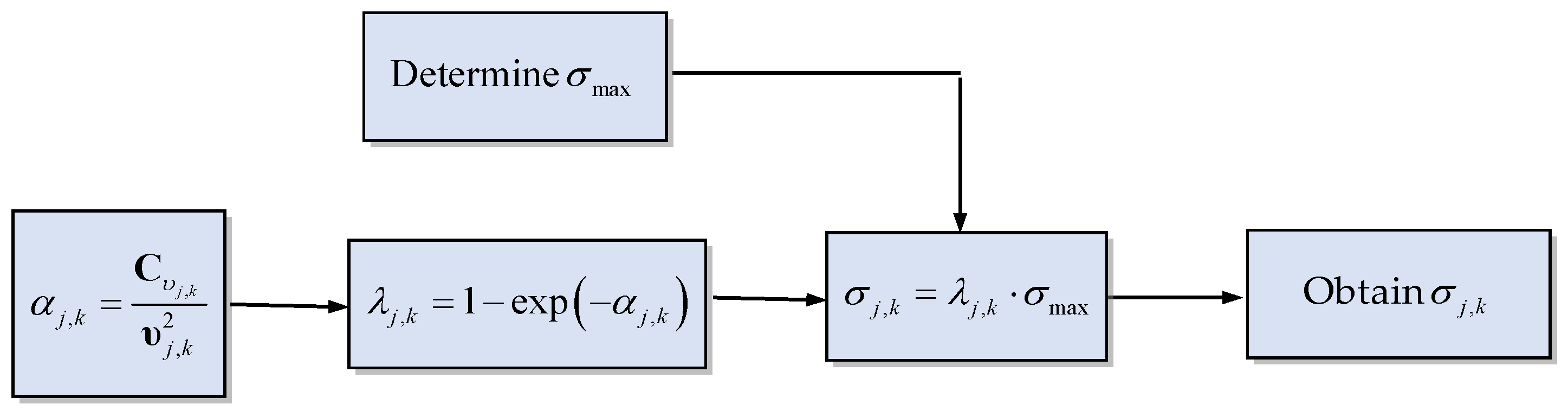
- Case 1: If <>, then < is increased> (this indicates that if is larger than , then the kernel bandwidth increases for maintaining the optimal performance).
- Case 2: If <>, then < is decreased> (this indicates that if is less than , then the kernel bandwidth decreases for maintaining the robustness performance).
- (1)
- Initialization of the state vector and state covariance matrix: and ;
- (2)
- Prediction of the state vector and the state covariance matrix: and ;
- (3)
- Obtaining based on the adaptive factor according to ;
- (4)
- Computation of the measurement innovation based on MCC to obtain the factor: ;
- (5)
- Computation of the modified Kalman gain matrix: ;
- (6)
- Updating the state vector and the error covariance: and ;
- (7)
- Repeating from Step (2) to perform the subsequent estimation cycle.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Scenario 1: Pseudorange Observable Errors Based on Gaussian Mixture Distribution
5.2. Scenario 2: Pseudorange Observable Involving Outlier Type of Multipath Interferences with Time-Varying Variance in Measurement Noise
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Wasle, E. GNSS—Global Navigation Satellite Systems, GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and More; Springer: Vienna, Austria; New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderhauf, N.; Obst, M.; Wanielik, G.; Protzel, P. Multipath Mitigation in GNSS-based Localization Using Robust Optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Alcalá de Henares, Spain, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 784–789. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.G.; Hwang, P.Y.C. Introduction to Random Signals and Applied Kalman Filtering; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, R.K. On-line Identification of Linear Dynamic Systems with Applications to Kalman Filtering. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1970, AC-16, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.H.; Schwarz, K.P. Adaptive Kalman Filtering for INS/GPS. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, J.C. Information Theoretic Learning, Renyi’s Entropy and Kernel Perspectives; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Principe, J.C. Maximum correntropy Kalman filter. Automatica 2017, 76, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qu, H.; Zhao, H.; Chen, B. Extended Kalman filter under maximum correntropy criterion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 1733–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ren, Z.; Lyu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Ren, P.; Chen, B. Linear and Nonlinear Regression-Based Maximum Correntropy Extended Kalman Filtering. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Pokharel, P.P.; Principe, J.C. Correntropy: Properties and Applications in Non-Gaussian Signal Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 5286–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izanloo, R.; Fakoorian, S.A.; Yazdi, H.S.; Simon, D. Kalman filtering based on the maximum correntropy criterion in the presence of non-Gaussian noise. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual Conference on Information Science and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 15–18 March 2016; pp. 500–505. [Google Scholar]
- Fakoorian, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Azimi, V.; Simon, D. Robust Kalman-type filter for non-Gaussian noise: Performance analysis with unknown noise covariances. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2019, 141, 091011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakoorian, S.; Izanloo, R.; Shamshirgaran, A.; Simon, D. Maximum correntropy criterion Kalman filter with adaptive kernel size. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON), Dayton, OH, USA, 15–19 July 2019; pp. 581–584. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive multikernel size-based maximum correntropy cubature Kalman filter for the robust state esitimation. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19835–19844. [Google Scholar]
- Jwo, D.-J.; Cho, T.-S. A practical note on evaluating Kalman filter performance optimality and degradation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 193, 482–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, P. Statistical Multipath Model Based on Experimental GNSS Data in Static Urban Canyon Environment. Sensors 2018, 18, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwo, D.-J.; Biswal, A. Implementation and Performance Analysis of Kalman Filters with Consistency Validation. Mathematics 2023, 11, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwo, D.-J.; Cho, T.-S.; Biswal, A. Geometric Insights into the Multivariate Gaussian Distribution and Its Entropy and Mutual Information. Entropy 2023, 25, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwo, D.J.; Lai, J.H.; Chang, Y. Interacting Multiple Model Filter with a Maximum Correntropy Criterion for GPS Navigation Processing. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Ma, W. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter with Correntropy Loss for Robust Power System State Estimation. Entropy 2019, 21, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Xu, L.; Gao, B.; Chang, L.; Zhong, Y. Robust unscented Kalman filter based decentralized multi-sensor information fusion for INS/GNSS/CNS integration in hypersonic vehicle navigation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 8504011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Hu, G.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, X. Cubature Kalman filter with both adaptability and robustness for tightly-coupled GNSS/INS integration. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 14997–15011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Hu, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, Y. A robust cubature Kalman filter with abnormal observations identification using the Mahalanobis distance criterion for vehicular INS/GNSS integration. Sensors 2019, 19, 5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Gao, B.; Gao, S.; Hu, G.; Zhong, Y. A hypothesis test-constrained robust Kalman filter for INS/GNSS integration with abnormal measurement. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 72, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, S.; Gao, B. Double-channel sequential probability ratio test for failure detection in multisensor integrated systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3514814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zong, H.; Gao, S. Maximum Correntropy based Spectral Redshift Estimation for Spectral Redshift Navigation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 8503110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, J.; Wang, H. Outlier-robust Kalman filters with mixture correntropy. Journal of the Franklin Institute 2020, 357, 5058–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, O.A.; Litvinenko, Y.A.; Vasiliev, V.A.; Toropov, A.B.; Basin, M.V. Polynomial filtering algorithm applied to navigation data processing under quadratic nonlinearities in system and measurement equations. Part 1. Description and comparison with Kalman type algorithms. Gyroscopy Navig. 2021, 12, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Technol. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPSoft LLC. Inertial Navigation System Toolbox 3.0 User’s Guide; GPSoft LLC: Athens, OH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- GPSoft LLC. Satellite Navigation Toolbox 3.0 User’s Guide; GPSoft LLC: Athens, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jwo, D.-J.; Chen, Y.-L.; Cho, T.-S.; Biswal, A. A Robust GPS Navigation Filter Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion with Adaptive Kernel Bandwidth. Sensors 2023, 23, 9386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239386
Jwo D-J, Chen Y-L, Cho T-S, Biswal A. A Robust GPS Navigation Filter Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion with Adaptive Kernel Bandwidth. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239386
Chicago/Turabian StyleJwo, Dah-Jing, Yi-Ling Chen, Ta-Shun Cho, and Amita Biswal. 2023. "A Robust GPS Navigation Filter Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion with Adaptive Kernel Bandwidth" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239386
APA StyleJwo, D.-J., Chen, Y.-L., Cho, T.-S., & Biswal, A. (2023). A Robust GPS Navigation Filter Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion with Adaptive Kernel Bandwidth. Sensors, 23(23), 9386. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239386






