EEG Amplitude Modulation Analysis across Mental Tasks: Towards Improved Active BCIs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Protocol
2.2. Dataset Pre-Processing
2.3. Feature Extraction
2.3.1. Power Spectral Density (Baseline) Features
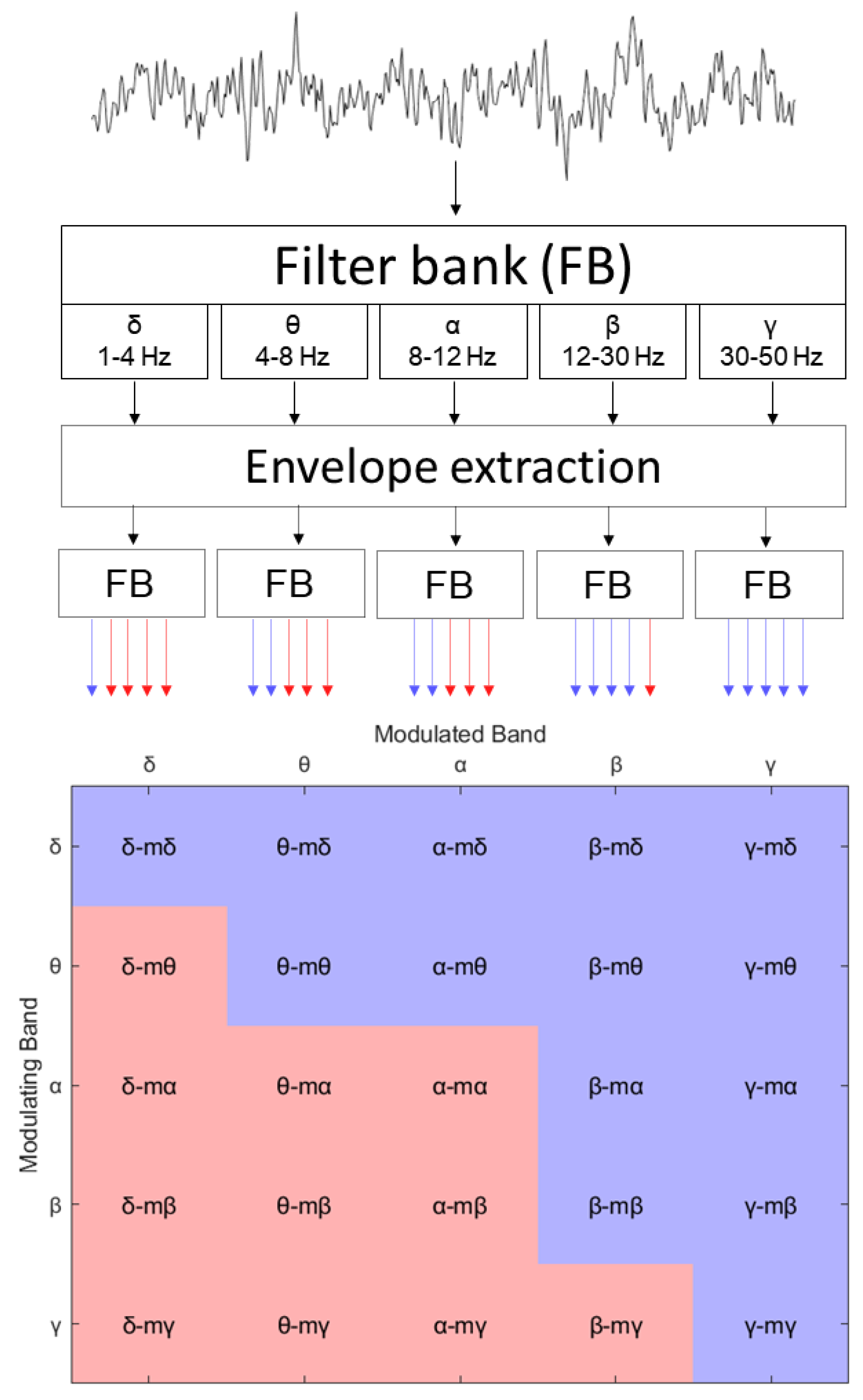
2.3.2. Proposed Amplitude Modulation Power Features
2.3.3. Phase Circular Correlation of Amplitude Modulated Signals
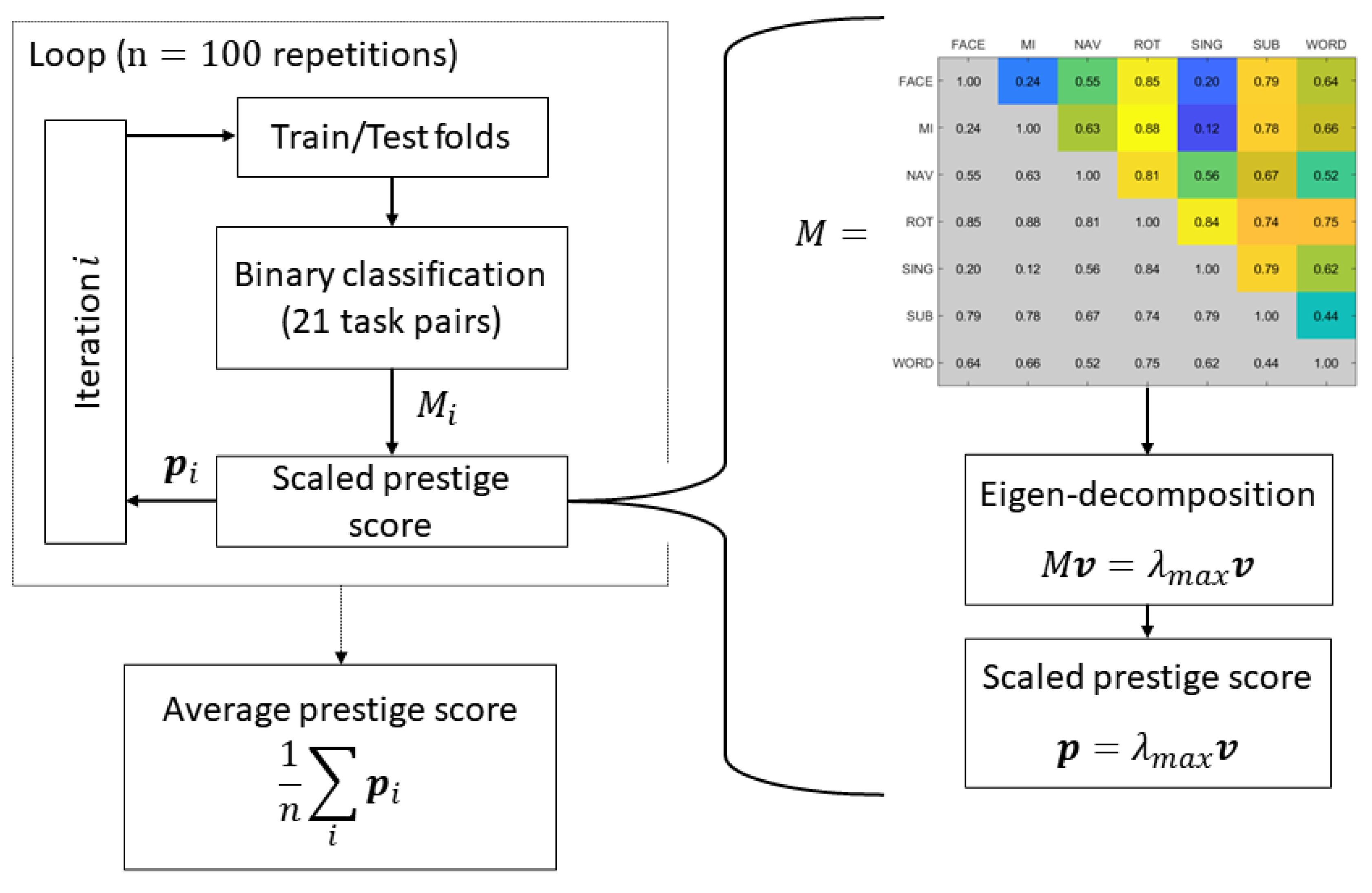
2.4. Feature Selection, Classification, and Figures of Merit
2.5. Eigendecomposition-Based Ranking of Binary Classifications
3. Experimental Results
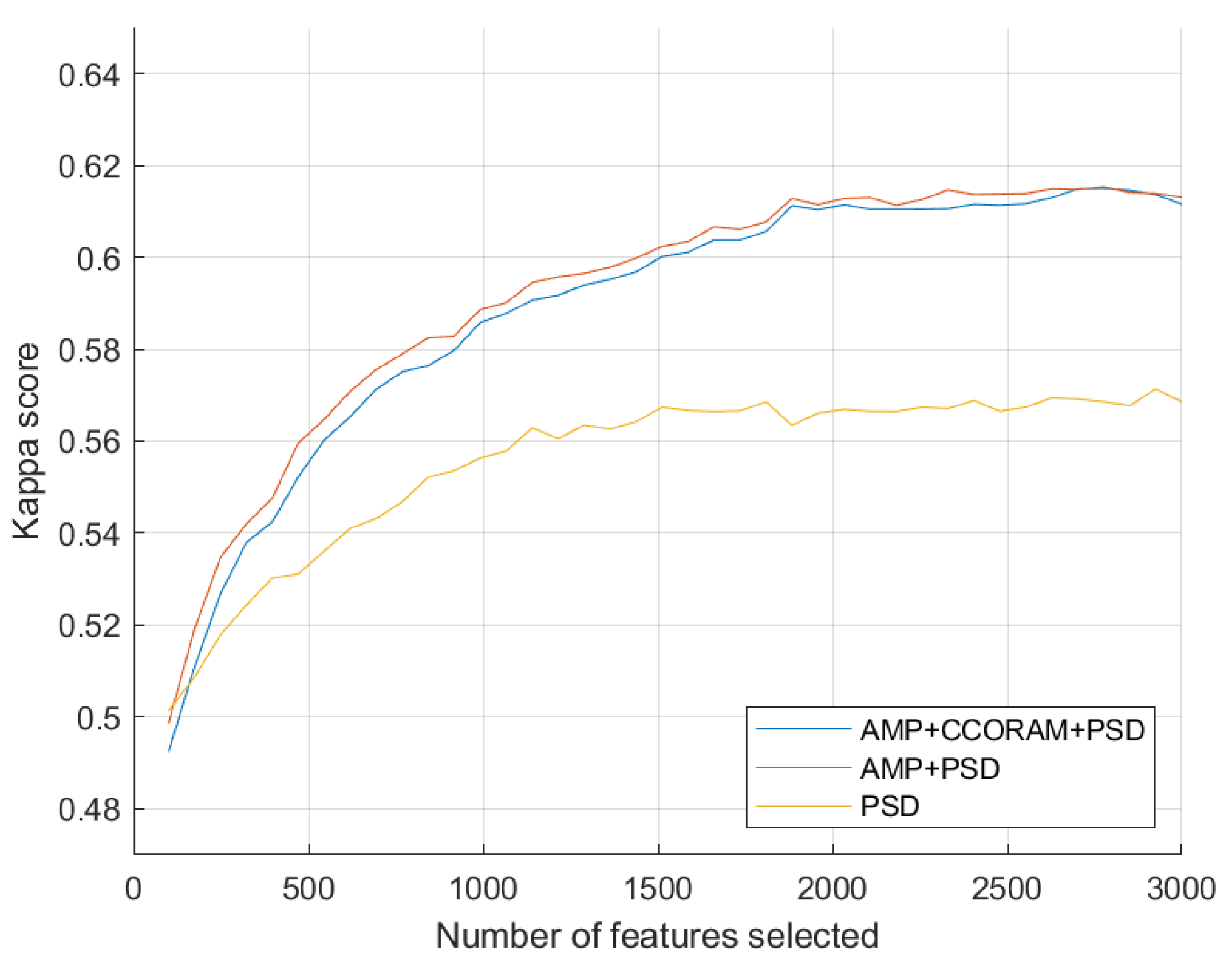
3.1. Estimation of Optimal Feature Set Size
3.2. Impact of Proposed Features on Classification Performance
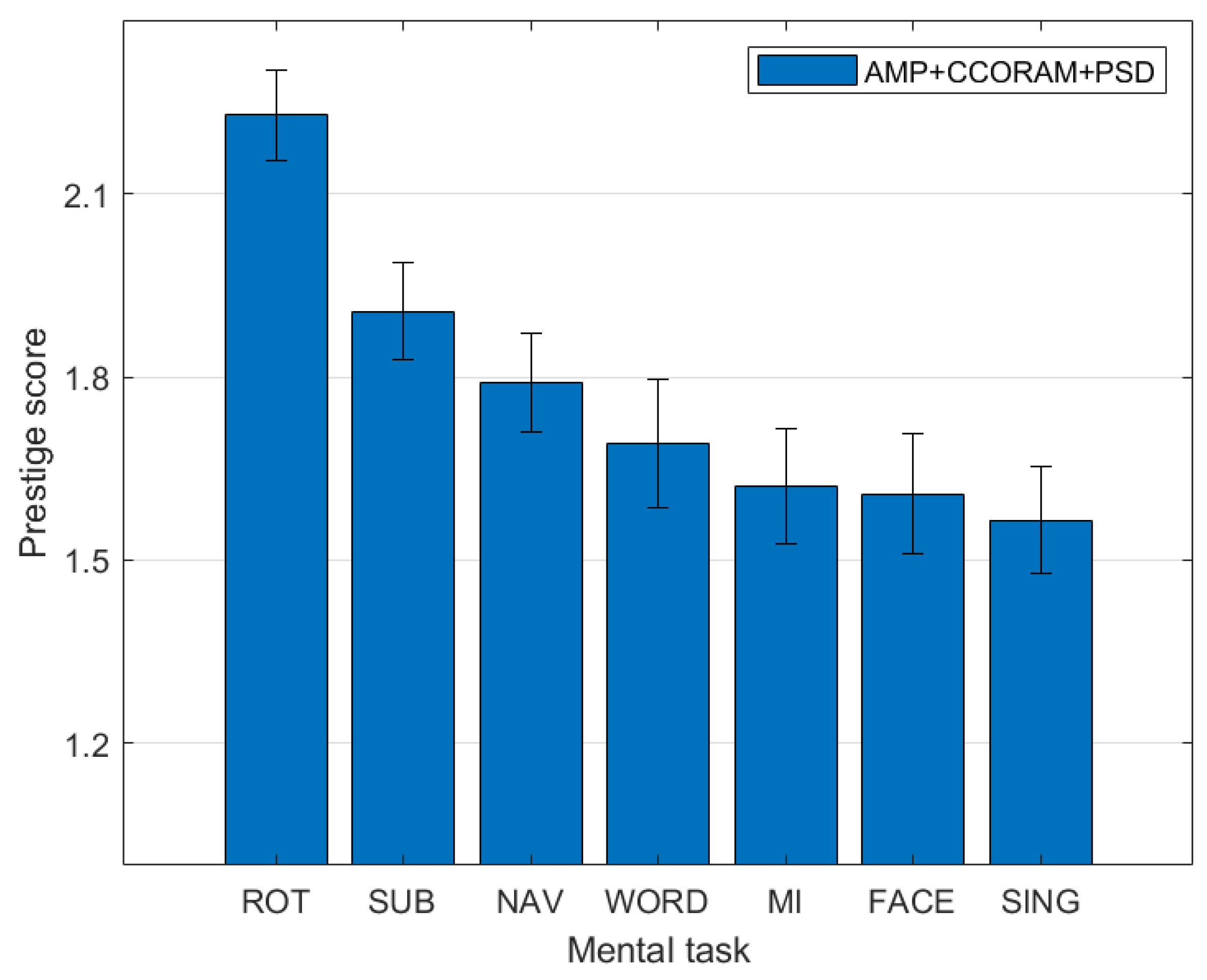
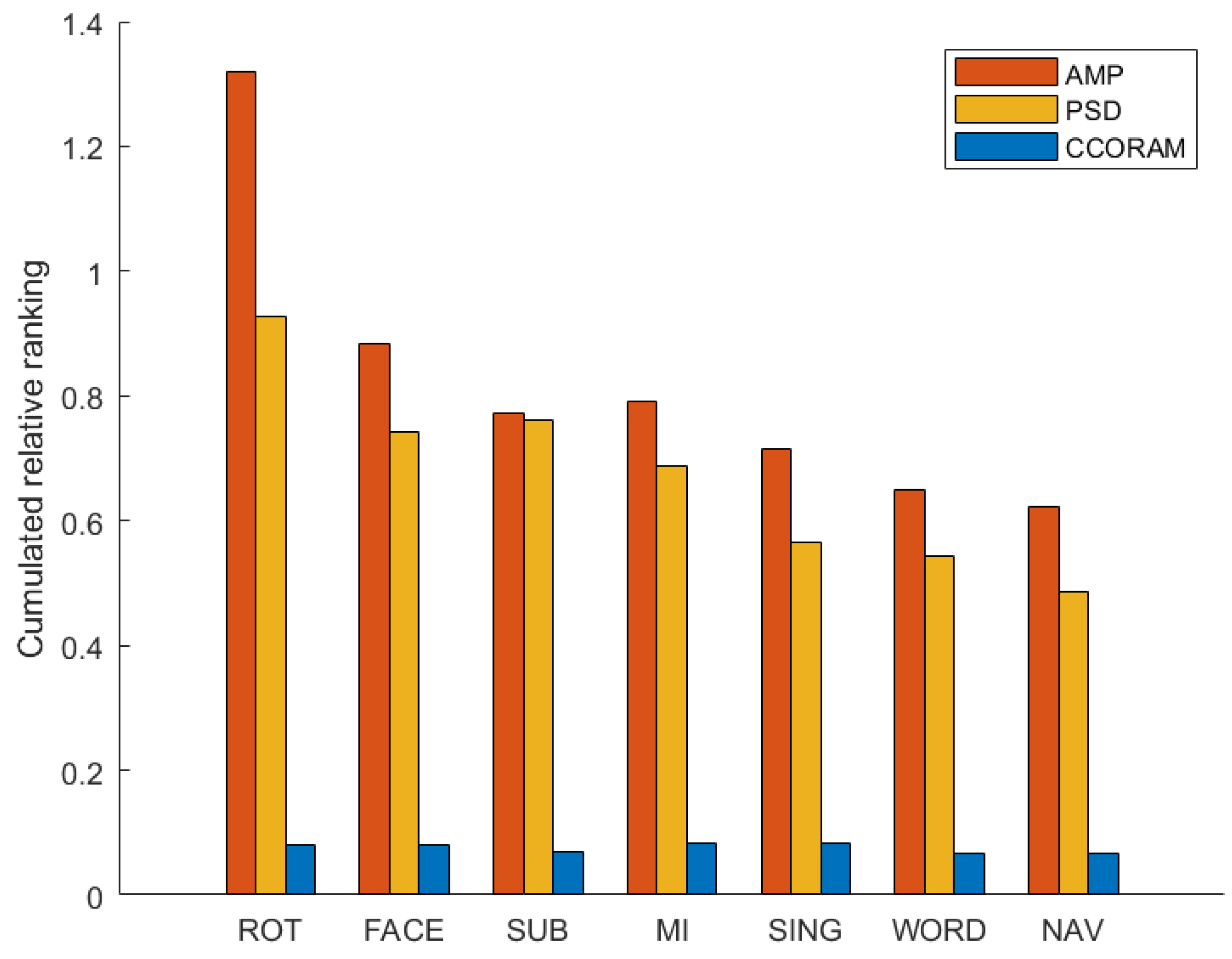
3.3. Ranking of Mental Task Kappa Scores
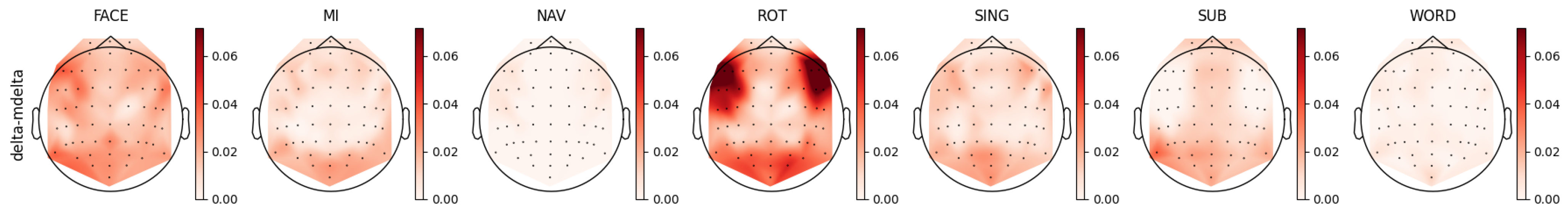
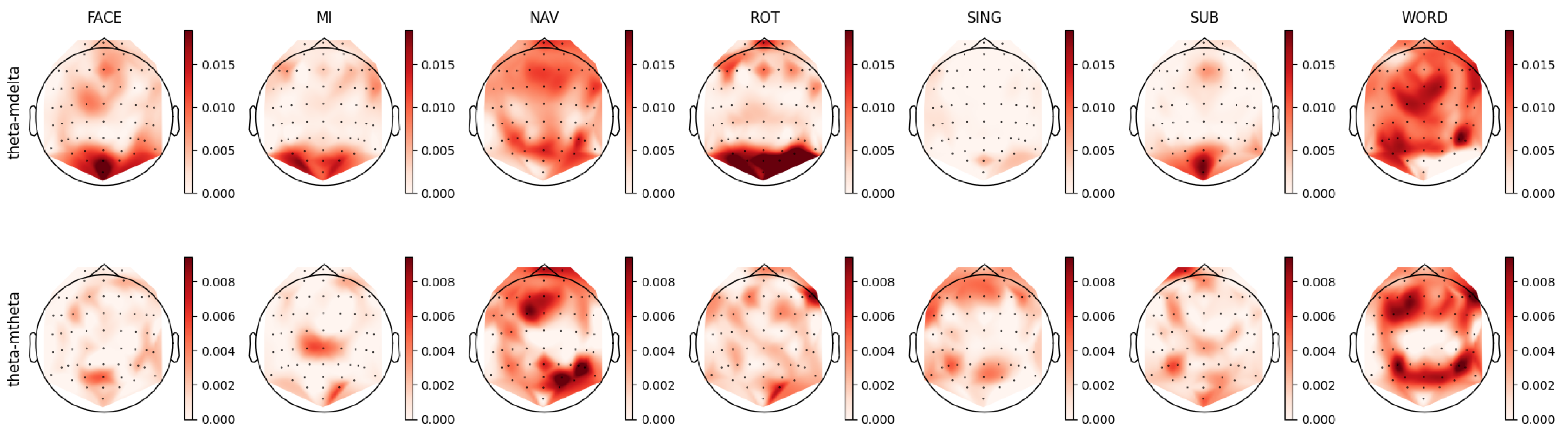
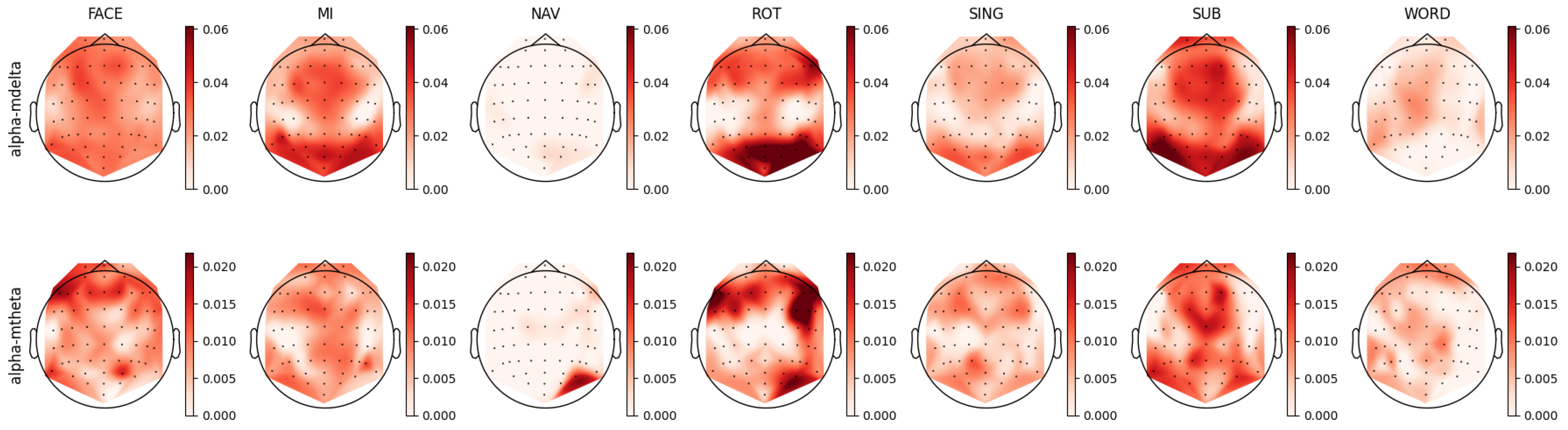
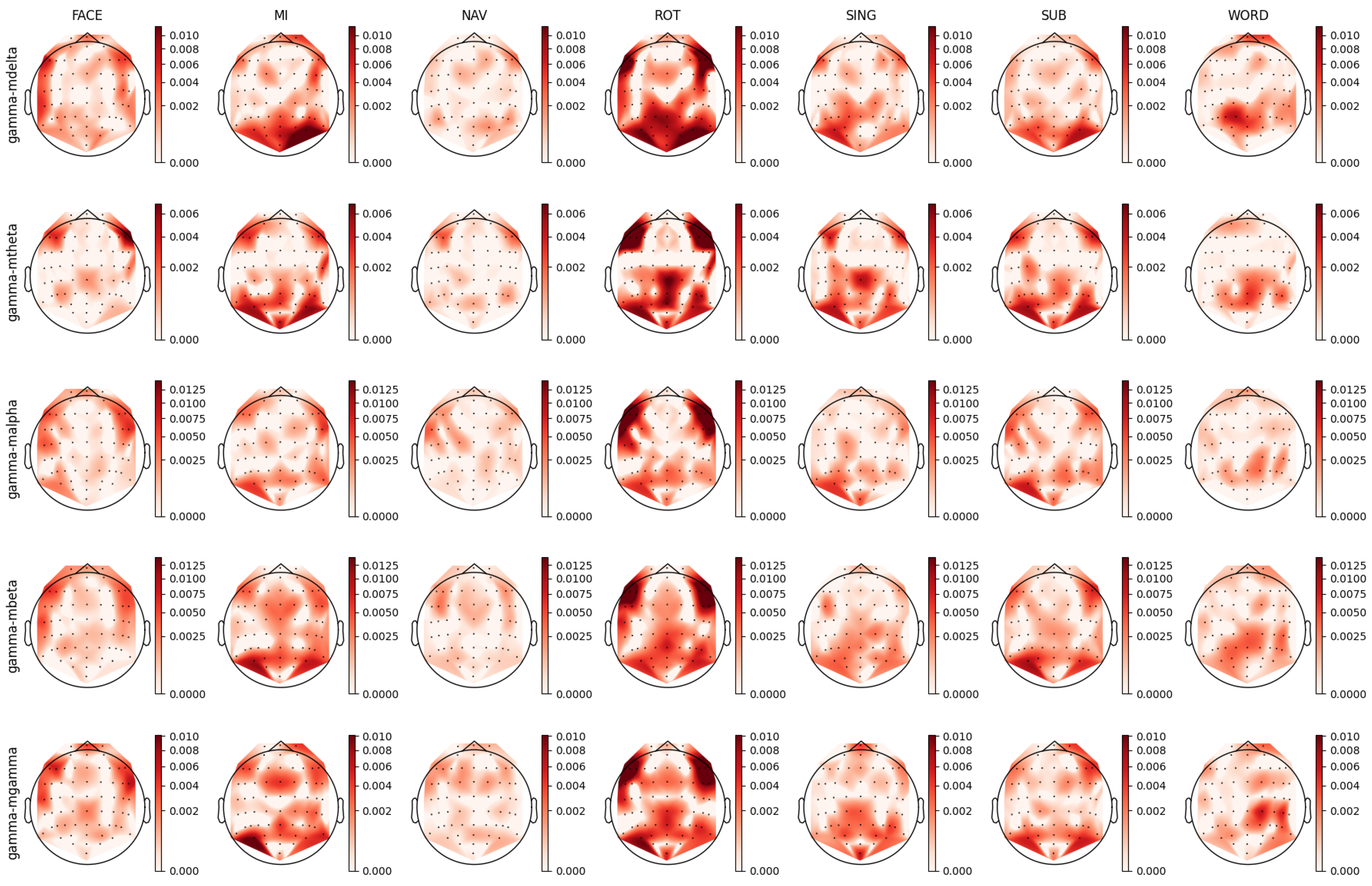
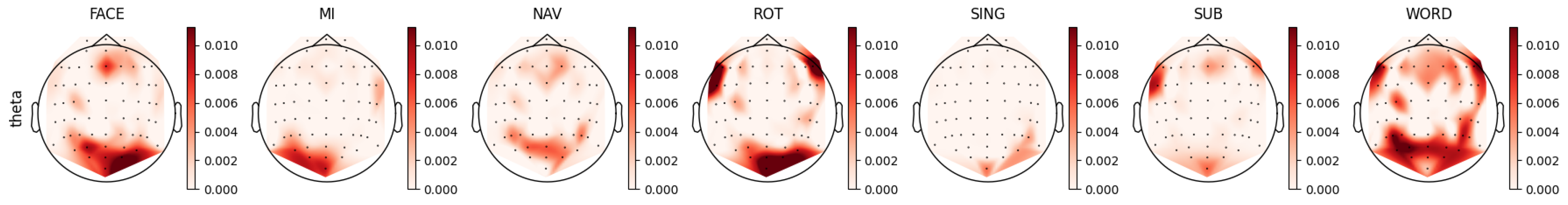
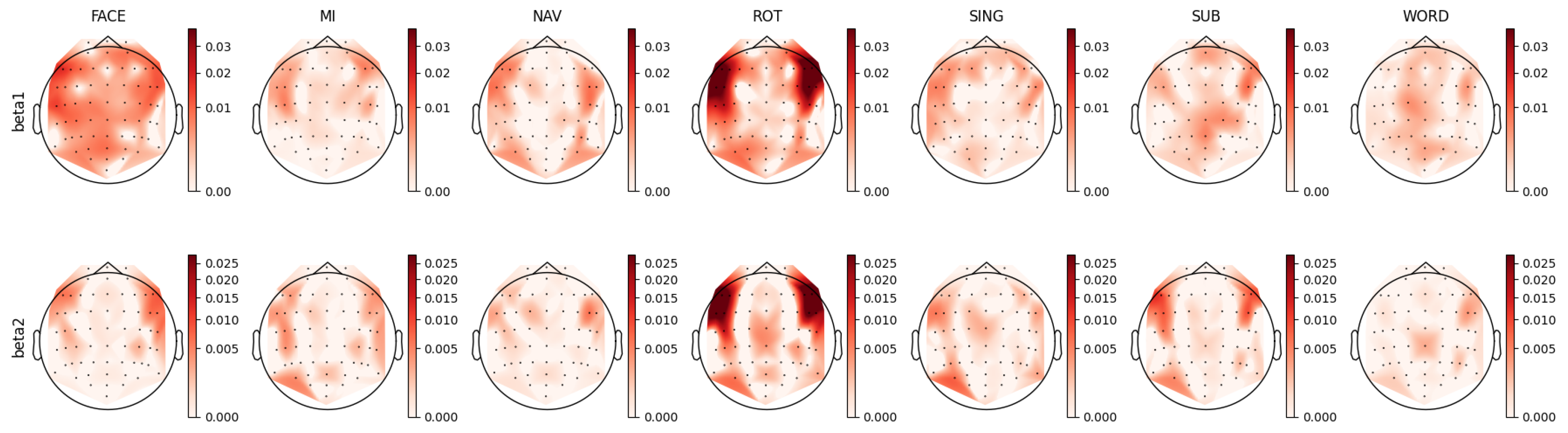
3.4. Mental Task Feature Analysis
3.5. Multidimensional Analysis of Relevant Features
4. Discussion
4.1. Beta Band Analysis
4.2. Theta Band Analysis
4.3. Alpha Band Analysis
4.4. Delta Band Analysis
4.5. Gamma Band Analysis
4.6. Performance Interpretation
4.7. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Amplitude Modulation |
| AMP | Amplitude Modulation Power |
| CCORAM | Circular Correlation of Amplitude Modulation |
| PSD | Power Spectral Density |
| BCI | Brain–Computer Interface |
| ROT | Rotation Imagery Task |
| SING | Sing Imagery Task |
| FACE | Face Imagery Task |
| MI | Motor Imagery Task |
| NAV | Navigational Imagery Task |
| SUB | Arithmetic Task |
| WORD | Word Completion Task |
| EOG | Electrooculography |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
References
- Rashid, M.; Sulaiman, N.; Abdul Majeed, A.P.P.; Musa, R.M.; Ab Nasir, A.F.; Bari, B.S.; Khatun, S. Current status, challenges, and possible solutions of EEG-based brain-computer interface: A comprehensive review. Front. Neurorobot. 2020, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Phang, C.R.; Stevenson, C.; Chen, I.P.; Jung, T.P.; Ko, L.W. Diversity and Suitability of the State-of-the-Art Wearable and Wireless EEG Systems Review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 3830–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, G.A.M.; De Miranda, L.C. Brain–computer interface games based on consumer-grade EEG Devices: A systematic literature review. Int. J.-Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2020, 36, 105–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRocco, J.; Le, M.D.; Paeng, D.G. A systemic review of available low-cost EEG headsets used for drowsiness detection. Front. Neuroinform. 2020, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, R.R.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Song, K.; Tian, C.; Wu, Z. A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality and Robot Therapy as Recent Rehabilitation Technologies Using EEG-Brain—Computer Interface Based on Movement-Related Cortical Potentials. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Värbu, K.; Muhammad, N.; Muhammad, Y. Past, present, and future of EEG-based BCI applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, G.; Antonioni, A.; Baroni, A.; Malerba, P.; Straudi, S. Relation Between EEG Measures and Upper Limb Motor Recovery in Stroke Patients: A Scoping Review. Brain Topogr. 2022, 35, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatinno, A.A.; Simpson, A.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Bonilha, H.S.; Bonilha, L.; Seo, N.J. The prognostic utility of electroencephalography in stroke recovery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2022, 36, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Ang, K.K.; Nair, K.P.; Phua, K.S.; Arvaneh, M. Efficacy of brain–computer interface and the impact of its design characteristics on poststroke upper-limb rehabilitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2022, 53, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián-Romagosa, M.; Cho, W.; Ortner, R.; Sieghartsleitner, S.; Von Oertzen, T.J.; Kamada, K.; Laureys, S.; Allison, B.Z.; Guger, C. Brain–computer interface treatment for gait rehabilitation in stroke patients. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1256077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, U.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N.; Birbaumer, N. Neuropsychological and neurophysiological aspects of brain-computer-interface (BCI) control in paralysis. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanutelli, M.E.; Salvadore, M.; Lucchiari, C. BCI Applications to Creativity: Review and Future Directions, from little-c to C2. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Lin, T.; Wu, M.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Jing, Y.; Ren, X.; Gong, Y.; Xu, G.; Lan, Y. Influence of iTBS on the acute neuroplastic change after BCI training. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 653487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrden, A.; Chau, T. Effects of user mental state on EEG-BCI performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijboer, F.; Birbaumer, N.; Kübler, A. The influence of psychological state and motivation on brain–computer interface performance in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—A longitudinal study. Front. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleih, S.C.; Kübler, A. Psychological factors influencing brain-computer interface (BCI) performance. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Hong Kong, China, 9–12 October 2015; pp. 3192–3196. [Google Scholar]
- Jeunet, C.; N’Kaoua, B.; Lotte, F. Advances in user-training for mental-imagery-based BCI control: Psychological and cognitive factors and their neural correlates. Prog. Brain Res. 2016, 228, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; He, F.; Jung, T.P.; Gu, X.; Ming, D. Current challenges for the practical application of electroencephalography-based brain–computer interfaces. Engineering 2021, 7, 1710–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.E.; Kwak, N.S.; Lee, S.W. A real-time movement artifact removal method for ambulatory brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 2660–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, M.Y.; Bhattacharya, S. Towards Practical BCI-Driven Wheelchairs: A Systematic Review Study. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 1030–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shore, J.; Wang, M.; Yuan, F.; Buss, A.; Zhao, X. A systematic review on hybrid EEG/fNIRS in brain-computer interface. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Pan, J. Advances in hybrid brain-computer interfaces: Principles, design, and applications. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 3807670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Padhy, S.; Tripathy, R.K.; Acharya, U.R. Automated classification of mental arithmetic tasks using recurrent neural network and entropy features obtained from multi-channel EEG signals. Electronics 2021, 10, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angsuwatanakul, T.; O’Reilly, J.; Ounjai, K.; Kaewkamnerdpong, B.; Iramina, K. Multiscale entropy as a new feature for EEG and fNIRS analysis. Entropy 2020, 22, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Kumar, S. EEG-based imagined words classification using Hilbert transform and deep networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 20, 026040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzianok, P.; Kołodziej, M.; Kublik, E. Detecting attention in Hilbert-transformed EEG brain signals from simple-reaction and choice-reaction cognitive tasks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 21st International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Kragujevac, Serbia, 25–27 October 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, W.; Jeon, E.; Jeong, S.; Suk, H.I. Multi-scale neural network for EEG representation learning in BCI. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2021, 16, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascil, M.S.; Tesneli, A.Y.; Temurtas, F. Spectral feature extraction of EEG signals and pattern recognition during mental tasks of 2-D cursor movements for BCI using SVM and ANN. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2016, 39, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Goel, S.; Bhardwaj, A. MIDNN—A classification approach for the EEG based motor imagery tasks using deep neural network. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 4824–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattai, T.; Colonnese, S.; Corsi, M.C.; Bassett, D.S.; Scarano, G.; Fallani, F.D.V. Phase/amplitude synchronization of brain signals during motor imagery BCI tasks. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Yi, W.; Wang, K.; He, F.; Qi, H. Inter-stimulus phase coherence in steady-state somatosensory evoked potentials and its application in improving the performance of single-channel MI-BCI. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 046088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, H.; Boon, K.W.; Ho, Y.K.; Khang, T.S. Brain-Computer Interface: Feature Extraction and Classification of Motor Imagery-Based Cognitive Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Control and Intelligent Systems (I2CACIS), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 25–25 June 2022; pp. 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chakladar, D.D.; Dey, S.; Roy, P.P.; Dogra, D.P. EEG-based mental workload estimation using deep BLSTM-LSTM network and evolutionary algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 60, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C. Temporal-spatial-frequency depth extraction of brain-computer interface based on mental tasks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 58, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Du, W. Data augmentation for deep neural networks model in EEG classification task: A review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 765525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, N.D.; Long, N.M.H.; Chung, W.Y. 1D-CNN-based BCI system for detecting Emotional states using a Wireless and Wearable 8-channel Custom-designed EEG Headset. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 20–23 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, Y.; Banville, H.; Albuquerque, I.; Gramfort, A.; Falk, T.H.; Faubert, J. Deep learning-based electroencephalography analysis: A systematic review. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Jiang, X.; Wu, D. Adversarial robustness benchmark for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 143, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Ding, L.; Luo, H.; Lin, C.T.; Jung, T.P.; Chavarriaga, R. Tiny noise, big mistakes: Adversarial perturbations induce errors in brain–computer interface spellers. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassani, R.; Falk, T.H. Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and severity level detection based on electroencephalography modulation spectral “patch” features. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1982–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, B., Jr.; Cassani, R.; McGeown, W.J.; Cecchi, M.; Fadem, K.; Falk, T.H. Multimodal prediction of Alzheimer’s disease severity level based on resting-state EEG and structural MRI. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 700627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerico, A.; Tiwari, A.; Gupta, R.; Jayaraman, S.; Falk, T.H. Electroencephalography amplitude modulation analysis for automated affective tagging of music video clips. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, A.M.; Gibbs, F.A. A Fourier transform of the electroencephalogram. J. Neurophysiol. 1938, 1, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsáki, G.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents—EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.S. Methods of analysis of nonstationary EEGs, with emphasis on segmentation techniques: A comparative review. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 2, 267–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassani, R.; Falk, T.H. Spectrotemporal modeling of biomedical signals: Theoretical foundation and applications. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; University of Quebec: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trambaiolli, L.R.; Cassani, R.; Falk, T.H. EEG spectro-temporal amplitude modulation as a measurement of cortical hemodynamics: An EEG-fNIRS study. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 3481–3484. [Google Scholar]
- Banville, H.; Gupta, R.; Falk, T.H. Mental task evaluation for hybrid NIRS-EEG brain-computer interfaces. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017, 2017, 3524208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, C.S.; Senkowski, D.; Röttger, S. Phase-locking and amplitude modulations of EEG alpha: Two measures reflect different cognitive processes in a working memory task. Exp. Psychol. 2004, 51, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, R.W. Coherence, phase differences, phase shift, and phase lock in EEG/ERP analyses. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2012, 37, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, C.C.; Beaumont, J.G. A critical review of EEG coherence studies of hemisphere function. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1984, 1, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydore, S.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. A note on the phase locking value and its properties. Neuroimage 2013, 74, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvarinen, A. Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mognon, A.; Jovicich, J.; Bruzzone, L.; Buiatti, M. ADJUST: An automatic EEG artifact detector based on the joint use of spatial and temporal features. Psychophysiology 2011, 48, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramfort, A.; Luessi, M.; Larson, E.; Engemann, D.A.; Strohmeier, D.; Brodbeck, C.; Goj, R.; Jas, M.; Brooks, T.; Parkkonen, L.; et al. MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, J.J.; Thiagarajan, T.C. EEG frequency bands in psychiatric disorders: A review of resting state studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajin, B.; Chabert, M.; Régnier, J.; Faucher, J. Space vector analysis for the diagnosis of high frequency amplitude and phase modulations in induction motor stator current. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Condition Monitoring and Machinery Failure Prevention Technologies—CM/MFPT 200810, Stratford-upon-Avon, UK, 22–24 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, F.J.; Falk, T.H.; Kanda, P.A.; Anghinah, R. Characterizing Alzheimer’s disease severity via resting-awake EEG amplitude modulation analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.P. On the interpretation of synchronization in EEG hyperscanning studies: A cautionary note. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murias, M.; Webb, S.J.; Greenson, J.; Dawson, G. Resting state cortical connectivity reflected in EEG coherence in individuals with autism. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 62, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Peng, H. Minimum redundancy feature selection from microarray gene expression data. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2005, 3, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Tian, Y.; Shi, P.; Bao, T. Automatic detection of epileptic seizures in EEG using sparse CSP and fisher linear discrimination analysis algorithm. J. Med. Syst. 2020, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikarwar, R.; Shakya, H.K.; Singh, S.S. A Review on Social Network Analysis Methods and Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Lima, Peru, 22–23 September 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Keener, J.P. The Perron–Frobenius theorem and the ranking of football teams. SIAM Rev. 1993, 35, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trambaiolli, L.; Cassani, R.; Biazoli, C.; Cravo, A.; Sato, J.; Falk, T. Resting-awake EEG amplitude modulation can predict performance of an fNIRS-based neurofeedback task. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1128–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Autthasan, P.; Du, X.; Arnin, J.; Lamyai, S.; Perera, M.; Itthipuripat, S.; Yagi, T.; Manoonpong, P.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. A single-channel consumer-grade EEG device for brain–computer interface: Enhancing detection of SSVEP and its amplitude modulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 3366–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilla, Y.; Von Mankowski, J.; Föcker, J.; Sauseng, P. Faster visual information processing in video gamers is associated with EEG alpha amplitude modulation. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 599788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.; Mazaheri, A. Shaping functional architecture by oscillatory alpha activity: Gating by inhibition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, L.; Barcelo, F.; Herrmann, C.S.; Escera, C. EEG delta oscillations index inhibitory control of contextual novelty to both irrelevant distracters and relevant task-switch cues. Psychophysiology 2014, 51, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarjam, P.; Epps, J.; Lovell, N.H.; Chen, F. Characterization of memory load in an arithmetic task using non-linear analysis of EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 3519–3522. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S.; Mueller, H.M. “Too many betas do not spoil the broth”: The role of beta brain oscillations in language processing. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palva, J.M.; Palva, S. Functional integration across oscillation frequencies by cross-frequency phase synchronization. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daume, J.; Gruber, T.; Engel, A.K.; Friese, U. Phase-amplitude coupling and long-range phase synchronization reveal frontotemporal interactions during visual working memory. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweg, N.A.; Apitz, T.; Leicht, G.; Mulert, C.; Fuentemilla, L.; Bunzeck, N. Theta-alpha oscillations bind the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and striatum during recollection: Evidence from simultaneous EEG–fMRI. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 3579–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, W.J.; Vitello, G. Matter and mind are entangled in EEG amplitude modulation and its double. Soc. Mind Matter Res. 2016, 14, 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmony, T.; Fernández, T.; Silva, J.; Bernal, J.; Díaz-Comas, L.; Reyes, A.; Marosi, E.; Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez, M. EEG delta activity: An indicator of attention to internal processing during performance of mental tasks. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1996, 24, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, R.B. Dynamic sculpting of brain functional connectivity and mental rotation aptitude. Prog. Brain Res. 2006, 159, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuhara, H.; Wang, L.Q.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamaguchi, Y. Long-range EEG phase synchronization during an arithmetic task indexes a coherent cortical network simultaneously measured by fMRI. Neuroimage 2005, 27, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plank, M.; Müller, H.J.; Onton, J.; Makeig, S.; Gramann, K. Human EEG correlates of spatial navigation within egocentric and allocentric reference frames. In Proceedings of the Spatial Cognition VII: International Conference, Spatial Cognition 2010, Mt. Hood/Portland, OR, USA, 15–19 August 2010; Proceedings 7; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuhara, H.; Yamaguchi, Y. Human cortical circuits for central executive function emerge by theta phase synchronization. Neuroimage 2007, 36, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Luo, J.; Li, L.; Li, X. A classification method for EEG motor imagery signals based on parallel convolutional neural network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Huang, Y.Y.; Duann, J.R. The sensitivity of single-trial mu-suppression detection for motor imagery performance as compared to motor execution and motor observation performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmari, A. Neuroimaging Role in Mental Illnesses. Int. J. Neural Plast. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuhara, H.; Wang, L.Q.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamaguchi, Y. A long-range cortical network emerging with theta oscillation in a mental task. Neuroreport 2004, 15, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.A.; O’Reilly, R.C. Modeling hippocampal and neocortical contributions to recognition memory: A complementary-learning-systems approach. Psychol. Rev. 2003, 110, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, E.; Robinson, A.K.; Behrmann, M. Distinct neural processes for the perception of familiar versus unfamiliar faces along the visual hierarchy revealed by EEG. NeuroImage 2018, 181, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanlou, M.; Artemenko, C.; Dresler, T.; Haeussinger, F.B.; Fallgatter, A.J.; Ehlis, A.C.; Nuerk, H.C. Increased arithmetic complexity is associated with domain-general but not domain-specific magnitude processing in children: A simultaneous fNIRS-EEG study. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.R.; Muthalib, M.; Perrey, S.; Galka, A.; Granert, O.; Wolff, S.; Heute, U.; Deuschl, G.; Raethjen, J.; Muthuraman, M. Effective connectivity of cortical sensorimotor networks during finger movement tasks: A simultaneous fNIRS, fMRI, EEG study. Brain Topogr. 2016, 29, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebolla, A.M.; Palmero-Soler, E.; Leroy, A.; Cheron, G. EEG spectral generators involved in motor imagery: A swLORETA study. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukundan, C.; Sumit, S.; Chetan, S. Brain Electrical Oscillations Signature profiling (BEOS) for measuring the process of remembrance. EC Neurol. 2017, 8, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Vukovic, N.; Feurra, M.; Shpektor, A.; Myachykov, A.; Shtyrov, Y. Primary motor cortex functionally contributes to language comprehension: An online rTMS study. Neuropsychologia 2017, 96, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauseng, P.; Klimesch, W.; Stadler, W.; Schabus, M.; Doppelmayr, M.; Hanslmayr, S.; Gruber, W.R.; Birbaumer, N. A shift of visual spatial attention is selectively associated with human EEG alpha activity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ba, S.; Guo, Y.; Guo, L.; Xu, G. Effects of motor imagery tasks on brain functional networks based on EEG Mu/Beta rhythm. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, M.K.I.; Al Shiam, A.; Islam, M.R.; Tanaka, T. Discriminative feature selection-based motor imagery classification using EEG signal. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 98255–98265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spüler, M.; Walter, C.; Rosenstiel, W.; Gerjets, P.; Moeller, K.; Klein, E. EEG-based prediction of cognitive workload induced by arithmetic: A step towards online adaptation in numerical learning. ZDM 2016, 48, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riès, S.K.; Dronkers, N.F.; Knight, R.T. Choosing words: Left hemisphere, right hemisphere, or both? Perspective on the lateralization of word retrieval. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1369, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, O.; Tonellato, M.; Del Felice, A.; Di Marco, R.; Fingleton, C.; Korik, A.; Guanziroli, E.; Molteni, F.; Guger, C.; Otner, R.; et al. A systematic review establishing the current state-of-the-art, the limitations, and the DESIRED checklist in studies of direct neural interfacing with robotic gait devices in stroke rehabilitation. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saegh, A.; Dawwd, S.A.; Abdul-Jabbar, J.M. Deep learning for motor imagery EEG-based classification: A review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 63, 102172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, P.; Esposito, A.; Natalizio, A.; Parvis, M. How to successfully classify EEG in motor imagery BCI: A metrological analysis of the state of the art. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 031002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.; Binli, M.; Ozbay, E.; Yanar, H.; Mishchenko, Y. A large electroencephalographic motor imagery dataset for electroencephalographic brain computer interfaces. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, E.M.; San-Martin, R.; Fraga, F.J. Comparison of subject-independent and subject-specific EEG-based BCI using LDA and SVM classifiers. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2023, 61, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śliwowski, M.; Martin, M.; Souloumiac, A.; Blanchart, P.; Aksenova, T. Impact of dataset size and long-term ECoG-based BCI usage on deep learning decoders performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1111645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Dong, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Identifying bidirectional total and non-linear information flow in functional corticomuscular coupling during a dorsiflexion task: A pilot study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hougaard, B.I.; Rossau, I.G.; Czapla, J.J.; Miko, M.A.; Skammelsen, R.B.; Knoche, H.; Jochumsen, M. Who willed it? decreasing frustration by manipulating perceived control through fabricated input for stroke rehabilitation BCI games. Proc. ACM-Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2021, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Évain, A.; Argelaguet, F.; Strock, A.; Roussel, N.; Casiez, G.; Lécuyer, A. Influence of error rate on frustration of BCI users. In Proceedings of the International Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces, Bari, Italy, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 248–251. [Google Scholar]



| Mental Task | Task Description |
|---|---|
| Mental Rotation (ROT) | Participants had to imagine the 3D rotation of two objects and determine whether the objects were identical |
| Word Generation (WORD) | A letter was presented randomly and the participants needed to find as many words as possible |
| beginning with this letter | |
| Subtraction (SUB) | Participants had to execute the mental subtraction of 1 to 2 digit numbers from a 3 digit number |
| Singing (SING) | Participants had to choose a song and then mentally sing it while paying attention to |
| the emotions that they felt | |
| Navigation (NAV) | Participants had to imagine walking from one room to another in their past or current residence |
| Motor Imagery (MI) | Participants had to imagine moving their fingers |
| Face Imagery (FACE) | Participants had to remember the face of a friend |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosanne, O.; Alves de Oliveira, A.; Falk, T.H. EEG Amplitude Modulation Analysis across Mental Tasks: Towards Improved Active BCIs. Sensors 2023, 23, 9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239352
Rosanne O, Alves de Oliveira A, Falk TH. EEG Amplitude Modulation Analysis across Mental Tasks: Towards Improved Active BCIs. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239352
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosanne, Olivier, Alcyr Alves de Oliveira, and Tiago H. Falk. 2023. "EEG Amplitude Modulation Analysis across Mental Tasks: Towards Improved Active BCIs" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239352
APA StyleRosanne, O., Alves de Oliveira, A., & Falk, T. H. (2023). EEG Amplitude Modulation Analysis across Mental Tasks: Towards Improved Active BCIs. Sensors, 23(23), 9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239352








