A Dual-Path Cross-Modal Network for Video-Music Retrieval
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A video-music retrieval dataset has been constructed and will be published on the website. The dataset is derived from films with a certain level of popularity, and each video–music pair includes an emotional descriptor and polarity labels.
- (2)
- A dual path video–music retrieval network combining content information and emotional information is designed. It can effectively learn various information and use this information to perform retrieval tasks.
- (3)
- A more task-consistent metric loss function was designed and used. By adding penalty factors to the data pairs, the metric loss function is optimized differently for different data pairs, achieving a dynamic optimization of the objective.
2. Related Work
2.1. Cross-Modal Video Music Retrieval
2.2. Video, Music and Emotion
3. Methodology
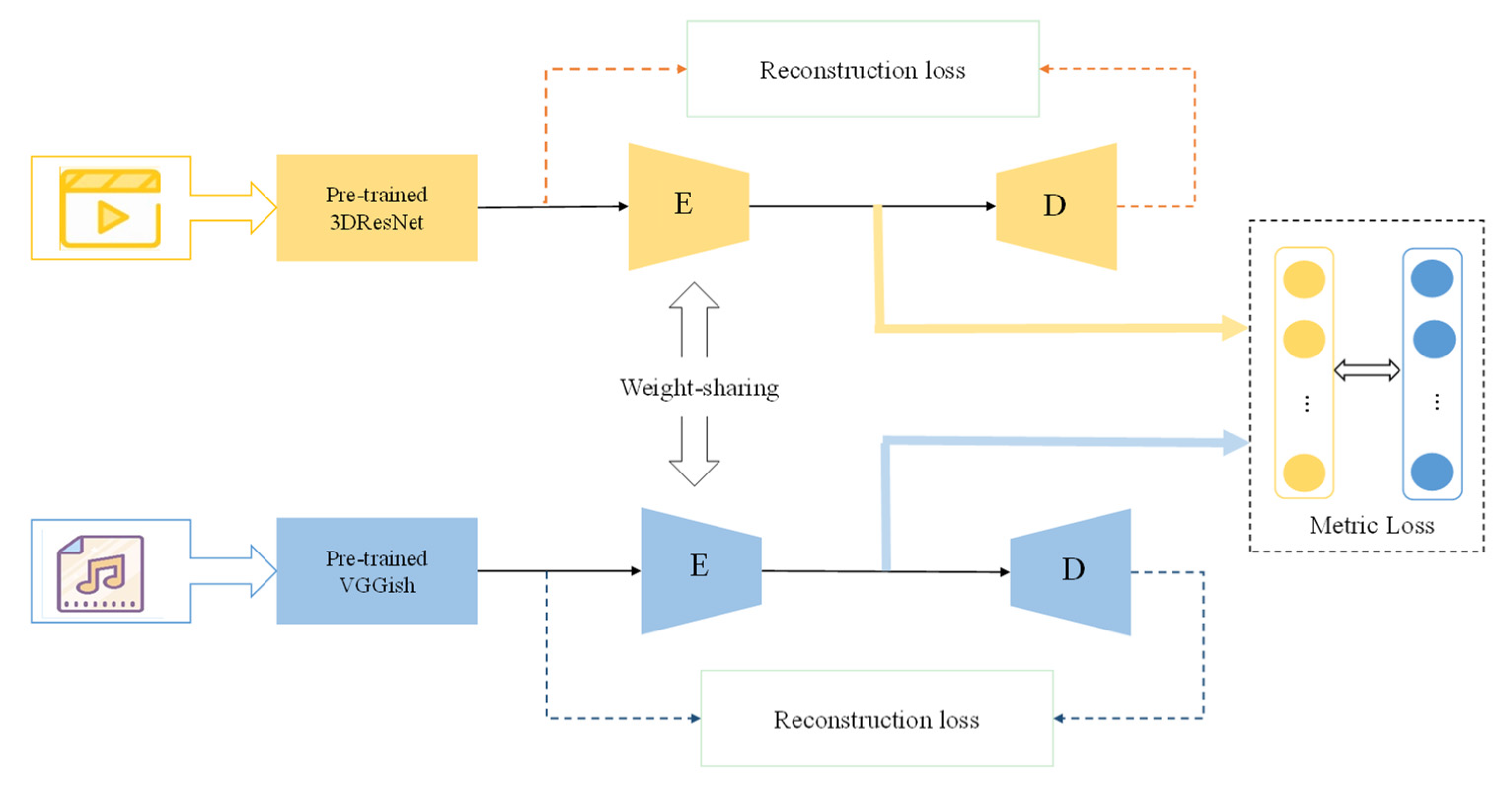
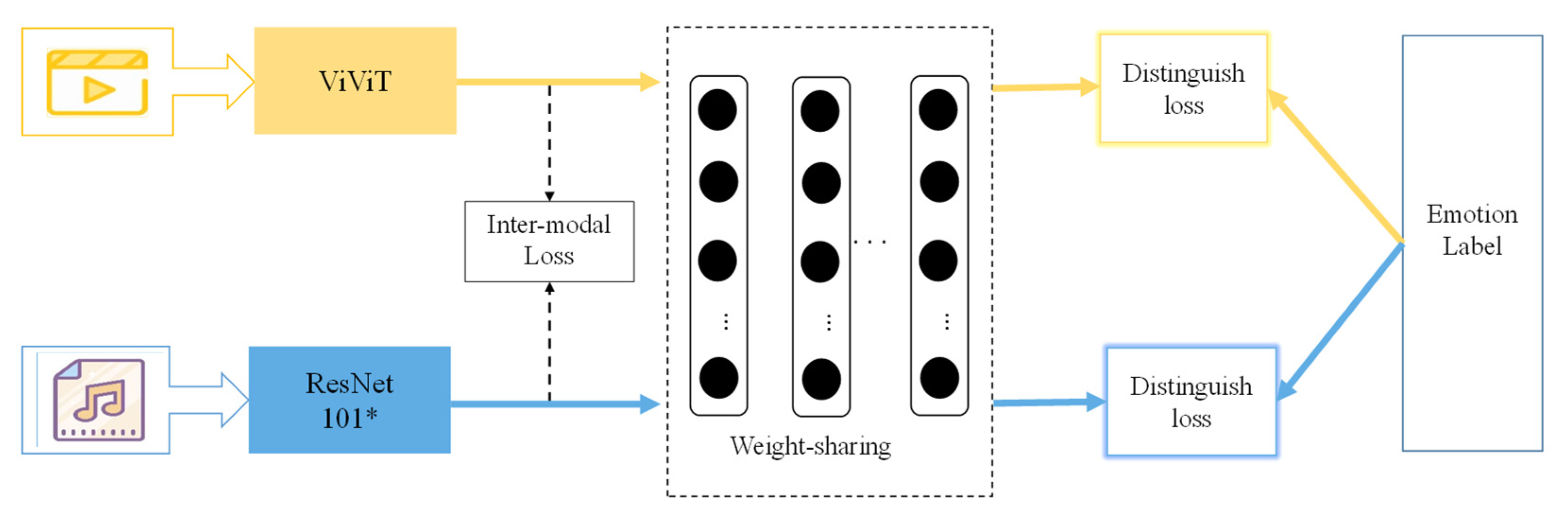
3.1. The Network Overview
3.2. The Content Common Network
3.3. The Emotion Common Network
3.4. The Fusion Common Network
3.5. The Polarity Penalty Metric Loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparison to Other Methods
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, S.; Woobin, I.; Hyun, S.Y. Cbvmr: Content-based video-music retrieval using soft intra-modal structure constraint. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Yokohama, Japan, 11–14 June 2018; pp. 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Pretet, L.; Richard, G.; Peeters, G. Cross-Modal Music-Video Recommendation: A Study of Design Choices. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prétet, L.; Richard, G.; Peeters, G. “Is there a" language of music-video clips”? A qualitative and quanti-tative study. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.00970. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, K.H.; Lee, I.K. Music synchronization with video using emotion similarity. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 13–16 February 2017; pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, D.; Yu, Y.; Oyama, K. Audio-Visual Embedding for Cross-Modal Music Video Retrieval through Supervised Deep CCA. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), Taichung, Taiwan, 10–12 December 2018; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Aparna, K. Query by Video: Cross-modal Music Retrieval. In Proceedings of the International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference, Delft, The Netherlands, 4–8 November 2019; pp. 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, J.; Chen, Z. Cross-modal variational auto-encoder for content-based micro-video background music recommenda-tion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doersch, C. Tutorial on variational autoencoders. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.05908. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Tang, S.; Wu, J.; Li, W. Variational Autoencoder with CCA for Audio-Visual Cross-Modal Retrieval. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surís, D.; Vondrick, C.; Russell, B.; Salamon, J. It’s Time for Artistic Correspondence in Music and Video. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10564–10574. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual. 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Bryan, N.J.; Salamon, J.; Jin, Z.; Nam, J. Metric learning vs classification for disentangled music representation learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.03729. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, L.; Yue, Z.D.; Karim, K.S.; Shen, J.; Wang, D. Camr: Towards connotation-aware music retrieval on social media with visual inputs. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), The Hague, The Netherlands, 7–10 December 2020; pp. 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Shen, Y.; Xu, J. Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Deep Learning: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Culture-oriented Science & Technology (ICCST), Beijing, China, 18–21 November 2021; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, B.; Sigal, L. Heterogeneous Knowledge Transfer in Video Emotion Recognition, Attribution and Summarization. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 9, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X. Video emotion recognition based on Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1738, 012129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; He, L.; Wang, F. Dual Focus Attention Network for Video Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Virtual. 6–10 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. Affective Video Content Analysis With Adaptive Fusion Recurrent Network. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2019, 22, 2454–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Meng, H.; Li, M. Emotion extraction and recognition from music. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD), Changsha, China, 13–15 August 2016; pp. 1728–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Pandeya, Y.R.; Lee, J. Deep learning-based late fusion of multimodal information for emotion classification of music video. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2020, 80, 2887–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Choudhury, S.; Dutta, S.; Roy, A.; Saha, S.K. Recognition of emotion in music based on deep convolutional neural network. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2019, 79, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Kraljević, L.; Stella, M.; Sikora, M. Cochleogram-based approach for detecting perceived emotions in music. Inf. Process. Manag. 2020, 57, 102270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Li, X.; Gao, Y. Dynamic Music emotion recognition based on CNN-BiLSTM. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; pp. 1372–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Rachman, F.H.; Sarno, R.; Fatichah, C. Music Emotion Detection using Weighted of Audio and Lyric Features. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th Information Technology International Seminar (ITIS), Surabaya, Indonesia, 14–16 October 2020; pp. 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Hirokatsu, K.; Yutaka, S. Can spatiotemporal 3d cnns retrace the history of 2d cnns and imagenet? In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6546–6555. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Gemmeke, J.F.; Ellis, D.P.W.; Freedman, D.; Jansen, A.; Lawrence, W.; Moore, R.C.; Plakal, M.; Ritter, M. Audio Set: An ontology and human-labeled dataset for audio events. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnab, A.; Dehghani, M.; Heigold, G.; Sun, C.; Lučićm, M.; Schmid, C. Vivit: A video vision transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6836–6846. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Hu, H. Video swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, N.; Ferguson, S. Multi-view Neural Networks for Raw Audio-based Music Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia, Naples, Italy, 2–4 December 2020; pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Qi, J. CM-GANs: Cross-modal generative adversarial networks for common representation learning. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2019, 15, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ji, L.; Zhong, M.; Chen, Y.; Lei, W.; Duan, N.; Li, T. CLIP4Clip: An empirical study of CLIP for end to end video clip retrieval and captioning. Neurocomputing 2022, 508, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, C.; Bui, T.; Berg, T.L. Visual to sound: Generating natural sound for videos in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3550–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, W.; Carreira, J.; Simonyan, K.; Zhang, B.; Hillier, C.; Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Viola, F.; Green, T.; Back, T.; Natsev, P.; et al. The kinetics human action video dataset. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.06950. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, Y. User-generated video emotion recognition based on key frames. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 14343–14361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadsell, R.; Chopra, S.; LeCun, Y. Dimen-sionality reduction by learning an invariant mapping. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Visionand Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 1735–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-El-Haija, S.; Kothari, N.; Lee, J.; Natsev, P.; Toderici, G.; Varadarajan, B.; Vijayanarasimhan, S. Youtube-8m: A large-scale video classification benchmark. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.08675. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, J.; Wu, H.H.; Salamon, J.; Bello, J.P. Look, listen, and learn more: Design choices for deep audio embeddings. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 3852–3856. [Google Scholar]

| Data | Video Clip Source | Interception Period | Emotional Descriptions | Polarity Labels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100,601 | Titanic | 01:21:40–01:22:00 | Happy | Positive |
| 206,202 | The Shining | 00:10:37–00:10:52 | Depress | Neutral |
| 119,907 | Oceans | 01:01:50–01:02:05 | Nervous | Negative |
| 100,304 | Forrest Gump | 01:44:42–01:44:57 | Happy | Positive |
| 220,405 | Stand by Me | 01:11:20–01:11:30 | Sad | Negative |
| Method | Recall@1↑ | Recall@5↑ | Recall@10↑ | Recall@15↑ | Recall@20↑ | Recall@25↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-Emotion [6] | 5.39 | 10.61 | 15.37 | 20.08 | 23.53 | 26.17 |
| B-Emotion [6] +PPML | 5.64 | 11.25 | 16.80 | 21.58 | 24.93 | 27.33 |
| B-Connect [2] | 7.59 | 15.23 | 20.31 | 26.25 | 30.13 | 34.27 |
| B-Connect [2] +PPML | 7.91 | 16.43 | 22.92 | 27.53 | 31.29 | 35.90 |
| 9.13 | 16.94 | 22.33 | 29.50 | 37.41 | 42.35 | |
+PPML | 10.42 | 18.34 | 24.07 | 31.74 | 38.26 | 43.19 |
| 10.94 | 18.84 | 24.39 | 34.32 | 43.26 | 49.97 | |
+PPML | 11.53 | 20.11 | 26.67 | 36.01 | 44.87 | 50.63 |
| Method | Recall@1↑ | Recall@5↑ | Recall@10↑ | Recall@15↑ | Recall@20↑ | Recall@25↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-Emotion [6] +PPML | 5.64 | 11.25 | 16.80 | 21.58 | 24.93 | 27.33 |
| B-Connect [2] +PPML | 7.91 | 16.43 | 22.92 | 27.53 | 31.29 | 35.90 |
| 6.43 | 13.54 | 20.26 | 25.09 | 31.41 | 37.26 | |
+PPML | 7.17 | 14.85 | 21.44 | 26.73 | 32.05 | 38.16 |
| 8.31 | 16.42 | 21.21 | 27.99 | 33.94 | 39.01 | |
+PPML | 9.29 | 17.86 | 23.21 | 28.65 | 34.30 | 39.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, X.; Shen, Y.; Lv, C. A Dual-Path Cross-Modal Network for Video-Music Retrieval. Sensors 2023, 23, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020805
Gu X, Shen Y, Lv C. A Dual-Path Cross-Modal Network for Video-Music Retrieval. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020805
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Xin, Yinghua Shen, and Chaohui Lv. 2023. "A Dual-Path Cross-Modal Network for Video-Music Retrieval" Sensors 23, no. 2: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020805
APA StyleGu, X., Shen, Y., & Lv, C. (2023). A Dual-Path Cross-Modal Network for Video-Music Retrieval. Sensors, 23(2), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020805





