DRGAN: Dense Residual Generative Adversarial Network for Image Enhancement in an Underwater Autonomous Driving Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A multi-scale feature extraction module is proposed to extract image detail information and expand the receptive field.
- (2)
- A dense residual block is proposed to fuse feature maps into clear images, not only fully utilizing all layers with local dense connections but also adding residual connections to reuse information.
- (3)
- We combine multiple loss functions to facilitate the learning of the generator regarding the generation of clear images. The experimental results show that DRGAN outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of qualitative and quantitative indicators.
2. Related Work
2.1. Generative Adversarial Network
2.2. Residual Network
2.3. Densely Connected Convolutional Network
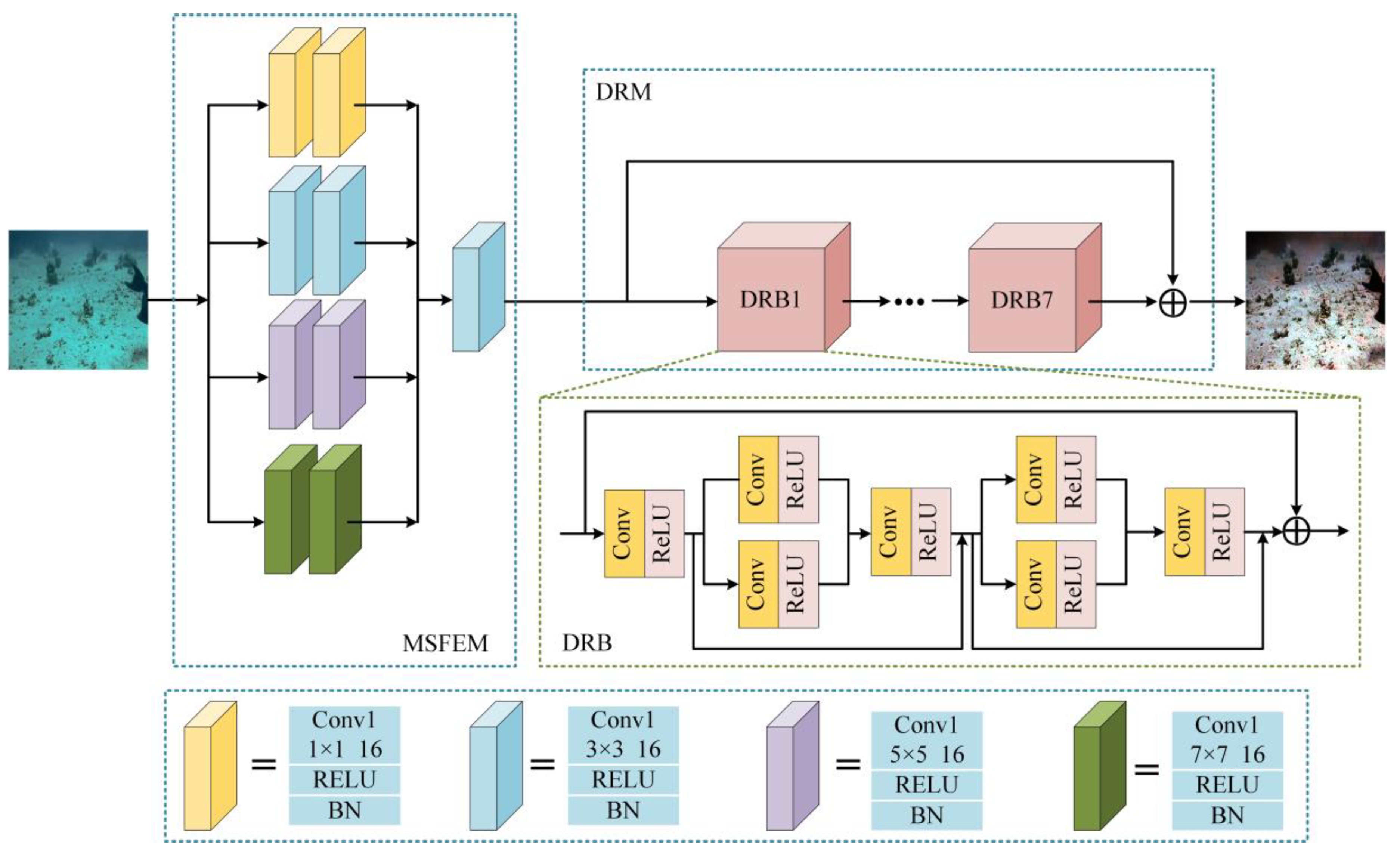
3. Our Method
3.1. Generative Network
3.2. Discrimination Network
3.3. Loss Function
- (1)
- GAN Loss
- (2)
- SSIM Loss
- (3)
- Perceptual Loss
- (4)
- Overall Loss
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Details
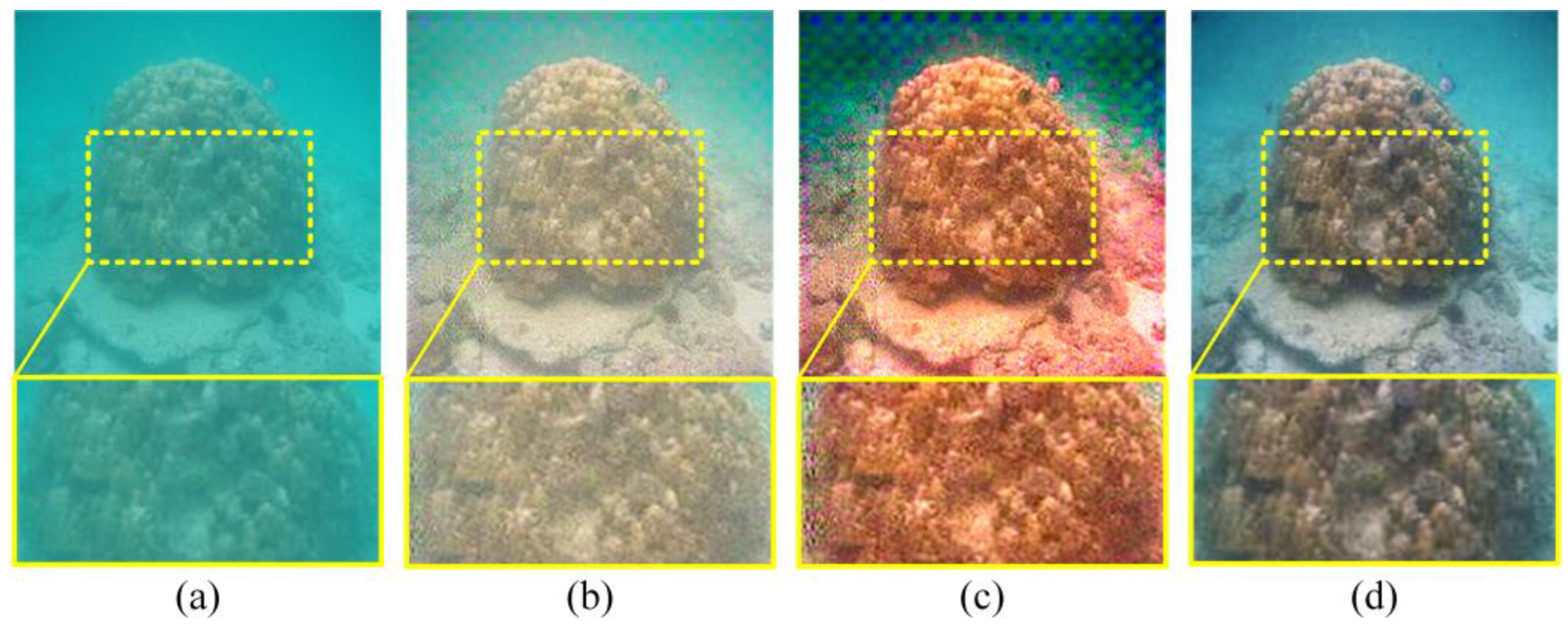
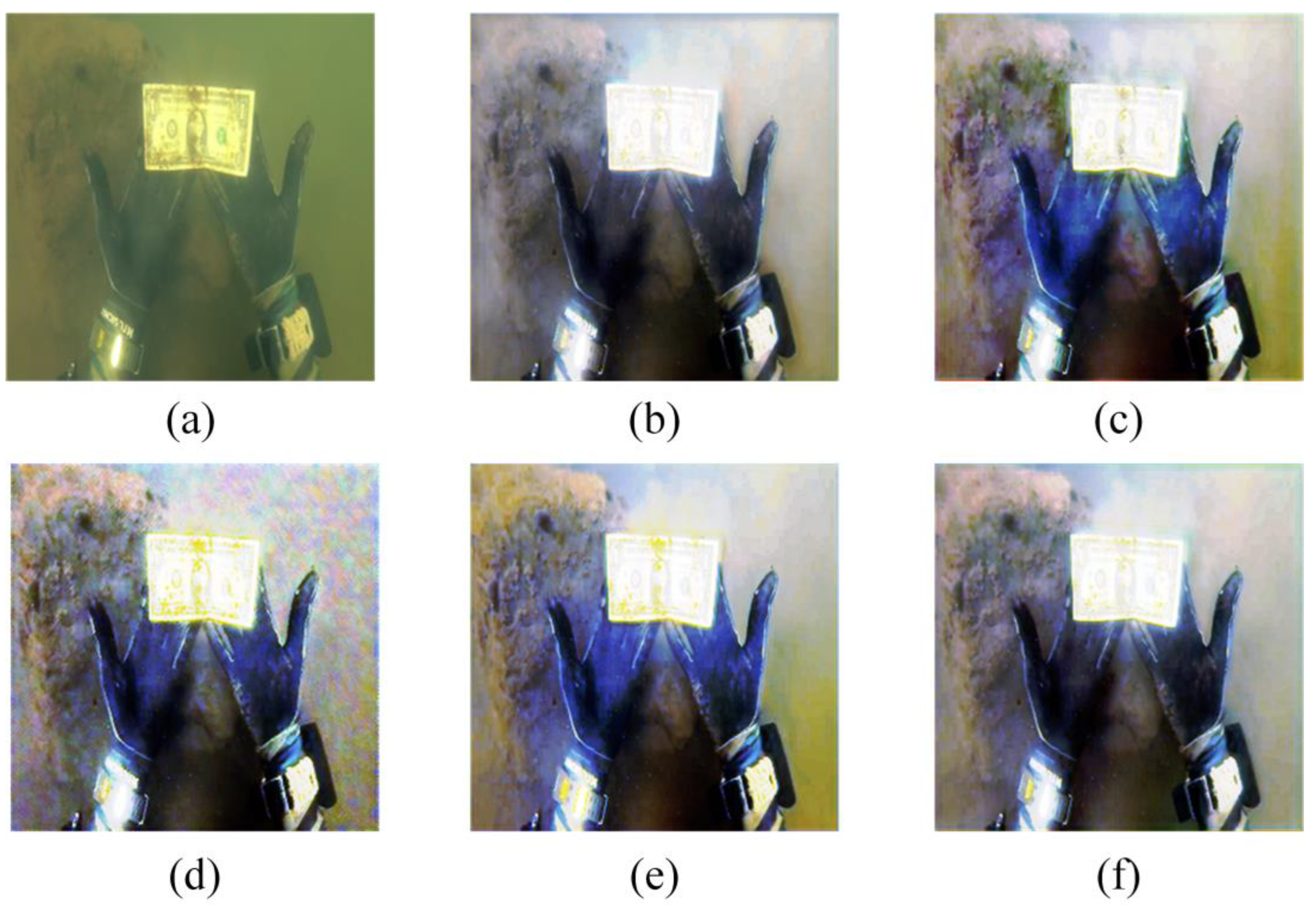
4.2. Subjective Evaluation
4.3. Objective Evaluation
- (1)
- The underwater color image quality evaluation index [24] (UCIQE) is proportional to the underwater picture quality, and the formula for calculating the index is as follows:where is the chromaticity standard deviation, represents the contrast in brightness, represents the average value of saturation, and , , and are weighting coefficients.
- (2)
- The underwater image quality measurement [25] (UIQM) is a quality-evaluated indicator of non-reference underwater images based on human visual system excitation. The calculation formula is as follows:where is set to 0.0282, is set to 0.2953, and is set to 3.5735. The underwater image quality measurement is a linear combination of the underwater image colorfulness measure (UICM), underwater image sharpness measure (UISM), and underwater image contrast measure (UICONM). The higher the UIQM, the better the image’s color balance, sharpness, and contrast.
- (3)
- The structural similarity index measurement [26] (SSIM) is an index for determining how similar the two images are. When two images, and , are given, the calculation formula is:where and are the average of and , respectively; are the variance of and ; and is a constant to maintain stability. is the covariance of and ; .
- (4)
- The peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is an index to measure image quality. The calculation formula for the mean square error (MSE) is:where two images, , are compared. The PSNR is obtained through the MSE, and the calculation formula is:
- (5)
- The CIEDE2000 evaluation index [27], which has a range of [0, 100], measures the color changes between the standard color card and each processed color block. The color differences are reduced when the index decreases. For the evaluation in Figure 8, we used the CIEDE2000 evaluation index. Table 1 displays the results.
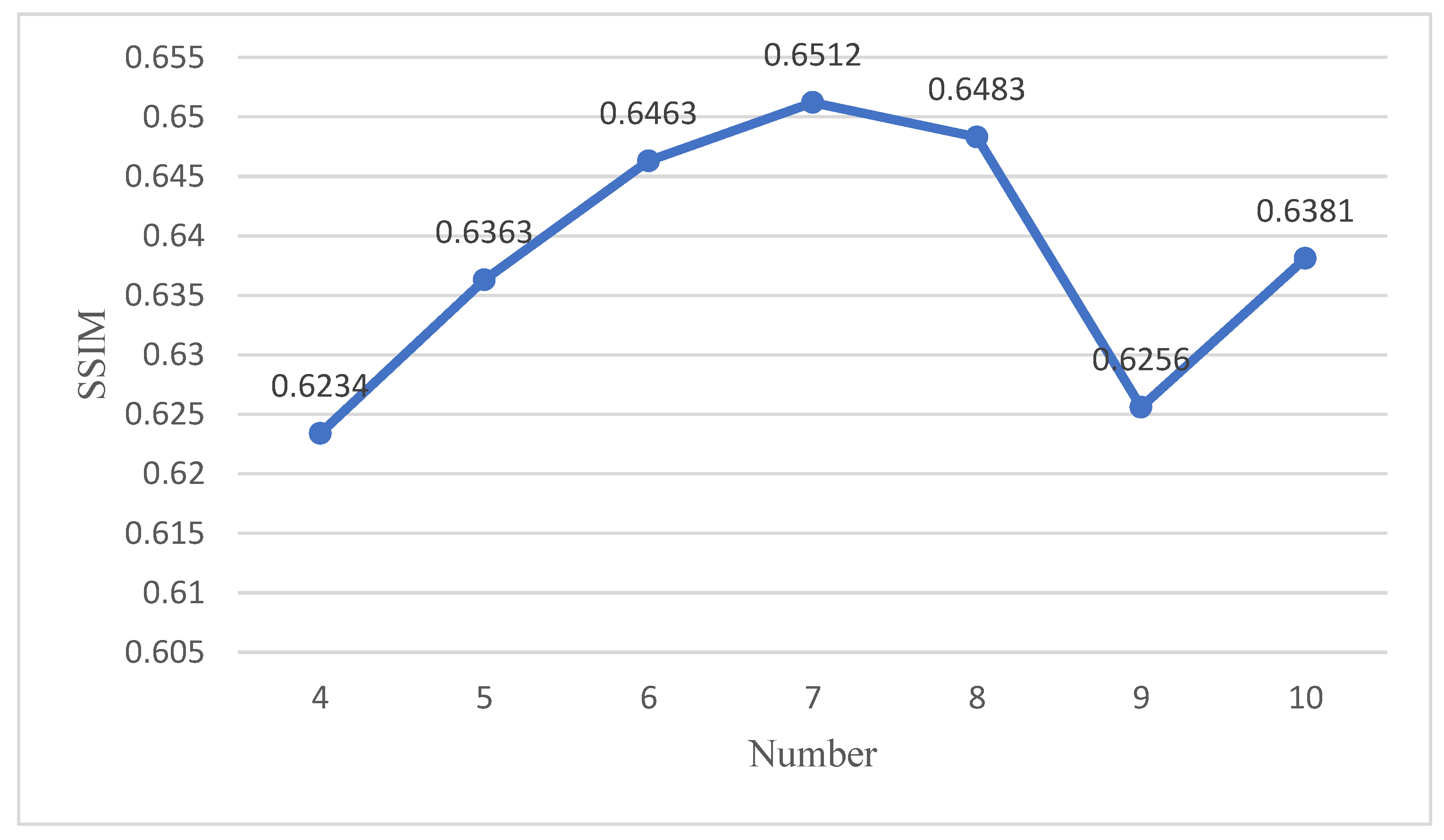
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Additional Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, B.; Cong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Single underwater image enhancement based on color cast removal and visibility restoration. J. Electron. Imaging 2016, 25, 033012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Sun, C.; Wang, R.; Zhao, X. Object Detection Based on Roadside LiDAR for Cooperative Driving Automation: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drews, P.; Nascimento, E.; Moraes, F.; Botelho, S.; Campos, M. Transmission estimation in underwater single images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2–8 December 2013; pp. 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single Image Haze Removal Using Dark Channel Prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Z. Underwater image restoration through a combination of improved dark channel prior and gray world algorithms. J. Electron. Imaging 2019, 28, 053033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; De Vleeschouwer, C.; Bekaert, P. Color balance and fusion for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Mi, Z.; Fu, X. Single underwater image enhancement by attenuation map guided color correction and detail preserved dehazing. Neurocomputing 2021, 425, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, T.P.; Albu, A.B. L2UWE: A Framework for the Efficient Enhancement of Low-Light Underwater Images Using Local Contrast and Multi-Scale Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 538–539. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Skinner, K.A.; Eustice, R.M.; Johnson-Roberson, M. WaterGAN: Unsupervised Generative Network to Enable Real-time Color Correction of Monocular Underwater Images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 3, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, C.; Islam, M.J.; Sattar, J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 7159–7165. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Zhuang, P. Underwater Image Enhancement Using a Multiscale Dense Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 45, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Xia, Y.; Sattar, J. Fast Underwater Image Enhancement for Improved Visual Perception. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Kong, S.; Wu, Z.; Fang, X.; Wen, L. Towards Real-Time Advancement of Underwater Visual Quality With GAN. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9350–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Contrastive Semi-Supervised Learning for Underwater Image Restoration via Reliable Bank. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 18145–18155. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Mu Lee, K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. Single Image Desnow Based on Vision Transformer and Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Internet of Vehicles. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2023, 137, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wand, M. Precomputed Real-Time Texture Synthesis with Markovian Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 17 September 2016; pp. 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tian, J.; Li, P. Image color correction based on double transmission underwater imaging model. Acta Opt. Sin. 2019, 39, 0901002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Upadhyay, M.; Singh, G. Underwater Image Enhancement Using Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.08916. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M.; Hou, M.; Luo, Z. Real-World Underwater Enhancement: Challenges, Benchmarks, and Solutions Under Natural Light. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 4861–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.D.M.; Peña, F.A.G.; Ren, T.I.; Leandro, J.J. Fast and robust multiple ColorChecker detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Image Vis. Comput. 2019, 81, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Sowmya, A. An Underwater Color Image Quality Evaluation Metric. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 6062–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panetta, K.; Gao, C.; Agaian, S. Human-Visual-System-Inspired Underwater Image Quality Measures. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 41, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Wu, W.; Dalal, E.N. The CIEDE2000 color-difference formula: Implementation notes, supplementary test data, and mathematical observations. Color Res. Appl. 2005, 30, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Method |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | Avg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fusion | 26.34 | 33.74 | 33.02 | 32.27 | 35.44 | 22.70 | 29.93 | 19.05 | 27.23 |
| 29.39 | 19.34 | 38.37 | 39.61 | 13.52 | 39.20 | 19.63 | 40.03 | ||
| 25.31 | 28.82 | 21.08 | 22.20 | 26.48 | 30.73 | 19.30 | 8.02 | ||
| ICCB | 26.18 | 29.71 | 40.49 | 35.84 | 27.65 | 32.60 | 11.15 | 48.19 | 24.04 |
| 21.58 | 40.94 | 14.31 | 20.06 | 28.25 | 29.16 | 8.77 | 9.24 | ||
| 16.10 | 31.84 | 11.43 | 17.52 | 27.40 | 21.04 | 14.57 | 12.85 | ||
| L^2UWE | 18.20 | 17.17 | 16.06 | 22.58 | 13.12 | 11.54 | 20.94 | 15.96 | 16.35 |
| 17.20 | 7.34 | 25.42 | 27.60 | 10.04 | 27.67 | 7.86 | 25.79 | ||
| 8.20 | 11.54 | 15.30 | 14.80 | 14.22 | 18.52 | 14.89 | 10.67 | ||
| FUnIE | 17.91 | 18.17 | 15.06 | 23.58 | 12.52 | 10.64 | 21.28 | 16.23 | 16.82 |
| 17.80 | 8.36 | 27.45 | 28.20 | 9.07 | 29.65 | 6.82 | 27.79 | ||
| 8.30 | 11.94 | 15.15 | 15.50 | 15.19 | 20.47 | 15.88 | 10.63 | ||
| UWCNN | 23.11 | 40.23 | 31.11 | 32.63 | 37.51 | 38.10 | 33.11 | 17.54 | 28.40 |
| 24.50 | 16.21 | 46.90 | 54.85 | 18.02 | 38.71 | 15.21 | 16.21 | ||
| 23.61 | 26.54 | 41.91 | 18.11 | 37.60 | 31.74 | 15.14 | 3.80 | ||
| Semi-UIR | 21.80 | 10.90 | 13.13 | 15.81 | 12.24 | 10.51 | 24.82 | 13.91 | 14.14 |
| 17.21 | 14.92 | 10.62 | 17.94 | 7.94 | 2.72 | 15.20 | 17.50 | ||
| 12.91 | 9.41 | 15.60 | 9.22 | 7.3 | 26.21 | 21.91 | 10.51 | ||
| Ours | 19.11 | 9.27 | 8.34 | 13.90 | 9.85 | 13.41 | 22.80 | 11.40 | 13.79 |
| 39.34 | 12.91 | 11.2 | 16.81 | 3.90 | 15.61 | 7.2 | 13.51 | ||
| 2.71 | 7.10 | 5.30 | 8.10 | 37.63 | 13.71 | 15.10 | 13.81 |
| No. | Fusion | ICCB | L^2UWE | FUnIE | UWCNN | Semi-UIR | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5970 | 0.5579 | 0.6057 | 0.5791 | 0.5272 | 0.5891 | 0.5982 |
| 2 | 0.5024 | 0.5646 | 0.6063 | 0.6012 | 0.5258 | 0.5746 | 0.6012 |
| 3 | 0.5184 | 0.5101 | 0.5331 | 0.5331 | 0.5118 | 0.6316 | 0.6470 |
| 4 | 0.4361 | 0.3777 | 0.4971 | 0.4971 | 0.5189 | 0.6198 | 0.6200 |
| 5 | 0.5504 | 0.6930 | 0.6863 | 0.5359 | 0.5006 | 0.6066 | 0.6012 |
| 6 | 0.5403 | 0.5572 | 0.6826 | 0.6741 | 0.5920 | 0.5950 | 0.6976 |
| 7 | 0.4914 | 0.5312 | 0.5404 | 0.5404 | 0.4605 | 0.5736 | 0.5821 |
| 8 | 0.4770 | 0.5548 | 0.5694 | 0.5694 | 0.4563 | 0.7085 | 0.6072 |
| Average | 0.5117 | 0.5433 | 0.5901 | 0.5674 | 0.5083 | 0.6124 | 0.6218 |
| No. | Fusion | ICCB | L^2UWE | FUnIE | UWCNN | Semi-UIR | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.8645 | 5.0569 | 4.5500 | 4.2465 | 4.4736 | 4.8277 | 4.8126 |
| 2 | 4.7372 | 5.0987 | 5.1155 | 5.2598 | 4.4404 | 4.7455 | 4.8373 |
| 3 | 5.4121 | 5.8937 | 4.9376 | 3.7809 | 4.2900 | 4.7741 | 4.3680 |
| 4 | 4.0254 | 4.0917 | 3.3799 | 4.0478 | 4.1496 | 4.6246 | 4.6264 |
| 5 | 4.3309 | 4.7002 | 3.5894 | 4.0904 | 4.4431 | 4.6995 | 4.8586 |
| 6 | 3.8358 | 3.9490 | 3.0448 | 4.6219 | 4.2285 | 4.3388 | 4.9539 |
| 7 | 3.5990 | 1.6884 | 3.2024 | 3.8366 | 2.4250 | 3.6705 | 4.4406 |
| 8 | 3.5839 | 2.8450 | 2.3827 | 2.2734 | 1.8241 | 3.8842 | 4.5264 |
| Average | 4.2986 | 4.1654 | 3.7752 | 4.0196 | 3.7842 | 4.4706 | 4.8029 |
| Method | SSIM | PSNR | UIQM | UCIQE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fusion | 0.636 | 25.794 | 4.266 | 0.541 |
| ICCB | 0.748 | 31.341 | 4.376 | 0.608 |
| L^2UWE | 0.746 | 26.387 | 4.338 | 0.601 |
| FUnIE | 0.774 | 34.257 | 4.995 | 0.588 |
| UWCNN | 0.648 | 28.868 | 4.463 | 0.507 |
| Semi-UIR | 0.827 | 31.033 | 5.037 | 0.592 |
| Ours | 0.661 | 37.592 | 5.087 | 0.630 |
| Method | Blue | Green | Atomization | Normal | Average | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (M) | (E) | (M) | (E) | (M) | (E) | (M) | (E) | (M) | (E) | |
| Fusion | 3.770 | 0.580 | 4.400 | 0.533 | 4.516 | 0.495 | 4.701 | 0.587 | 4.350 | 0.545 |
| ICCB | 5.422 | 0.588 | 4.272 | 0.568 | 4.742 | 0.582 | 4.450 | 0.610 | 4.698 | 0.585 |
| L^2UWE | 4.394 | 0.575 | 4.606 | 0.578 | 5.336 | 0.519 | 5.273 | 0.583 | 5.003 | 0.545 |
| FUnIE | 3.836 | 0.628 | 4.165 | 0.602 | 4.286 | 0.599 | 4.395 | 0.617 | 4.170 | 0.611 |
| UWCNN | 4.189 | 0.564 | 4.147 | 0.524 | 4.096 | 0.521 | 5.058 | 0.590 | 4.339 | 0.547 |
| Semi-UIR | 5.059 | 0.576 | 4.973 | 0.586 | 5.069 | 0.576 | 5.47 | 0.629 | 5.101 | 0.597 |
| Ours | 5.680 | 0.653 | 4.830 | 0.634 | 4.767 | 0.640 | 5.870 | 0.640 | 5.360 | 0.641 |
| Modules | Baselines | PSNR | SSIM | UCIQE | UIQM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSFEM | w/o MSFEM | 34.372 | 0.653 | 0.615 | 4.734 |
| DRB | w/o RES | 35.132 | 0.651 | 0.619 | 4.833 |
| w/o DEN | 34.876 | 0.651 | 0.614 | 4.791 | |
| w/o DRB | 32.195 | 0.649 | 0.609 | 4.592 | |
| DRGAN | full model | 37.592 | 0.661 | 0.630 | 5.087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Lin, S.; Xing, X. DRGAN: Dense Residual Generative Adversarial Network for Image Enhancement in an Underwater Autonomous Driving Device. Sensors 2023, 23, 8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198297
Qian J, Li H, Zhang B, Lin S, Xing X. DRGAN: Dense Residual Generative Adversarial Network for Image Enhancement in an Underwater Autonomous Driving Device. Sensors. 2023; 23(19):8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198297
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Jin, Hui Li, Bin Zhang, Sen Lin, and Xiaoshuang Xing. 2023. "DRGAN: Dense Residual Generative Adversarial Network for Image Enhancement in an Underwater Autonomous Driving Device" Sensors 23, no. 19: 8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198297
APA StyleQian, J., Li, H., Zhang, B., Lin, S., & Xing, X. (2023). DRGAN: Dense Residual Generative Adversarial Network for Image Enhancement in an Underwater Autonomous Driving Device. Sensors, 23(19), 8297. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23198297





