An Identification Method for Irregular Components Related to Terminal Blocks in Equipment Cabinet of Power Substation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
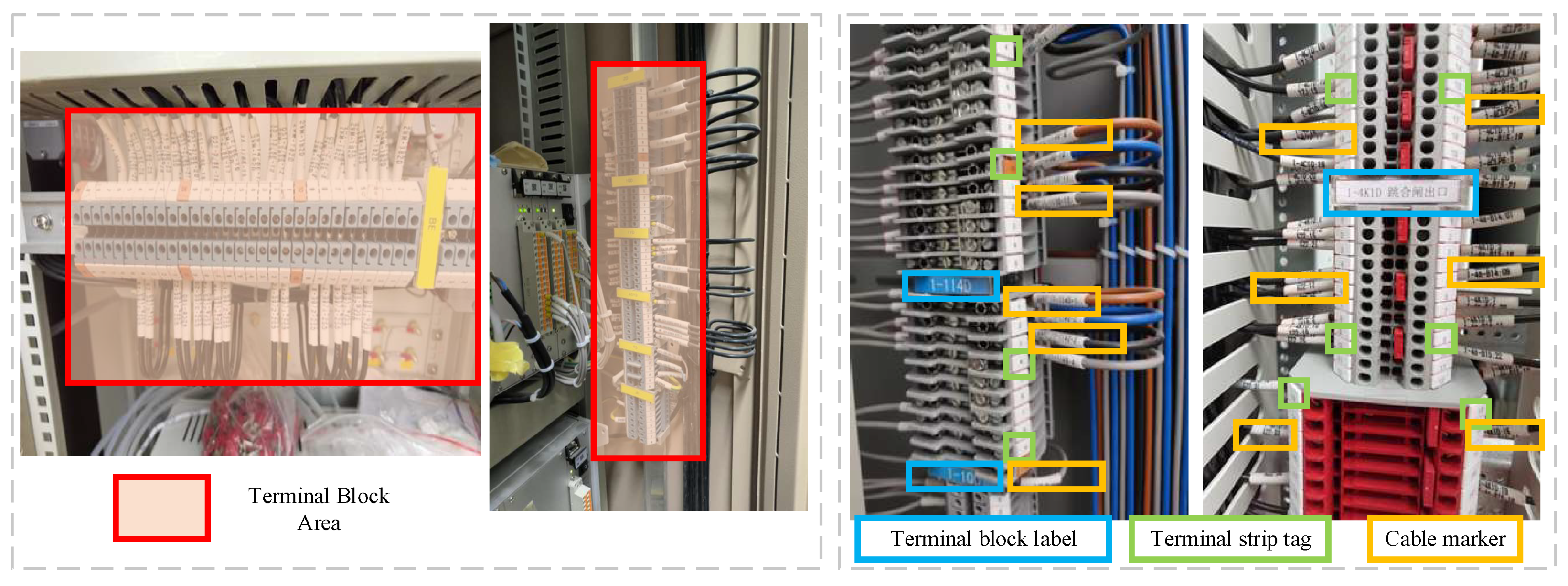
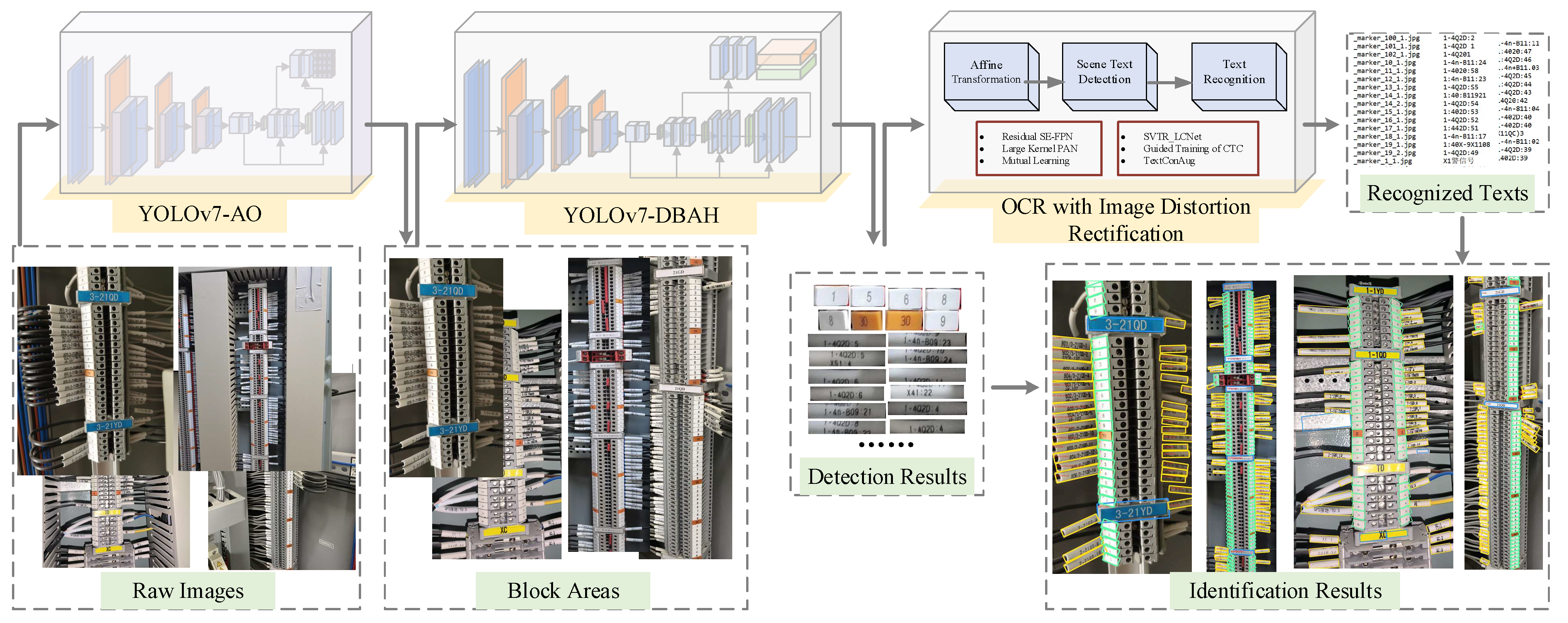
- To address the challenge of identifying minute, irregularly shaped component objects, we devise a three-stage system leveraging deep learning techniques. This system comprises terminal block area extraction, the detection of three categories of terminal block components, and element identity text recognition.
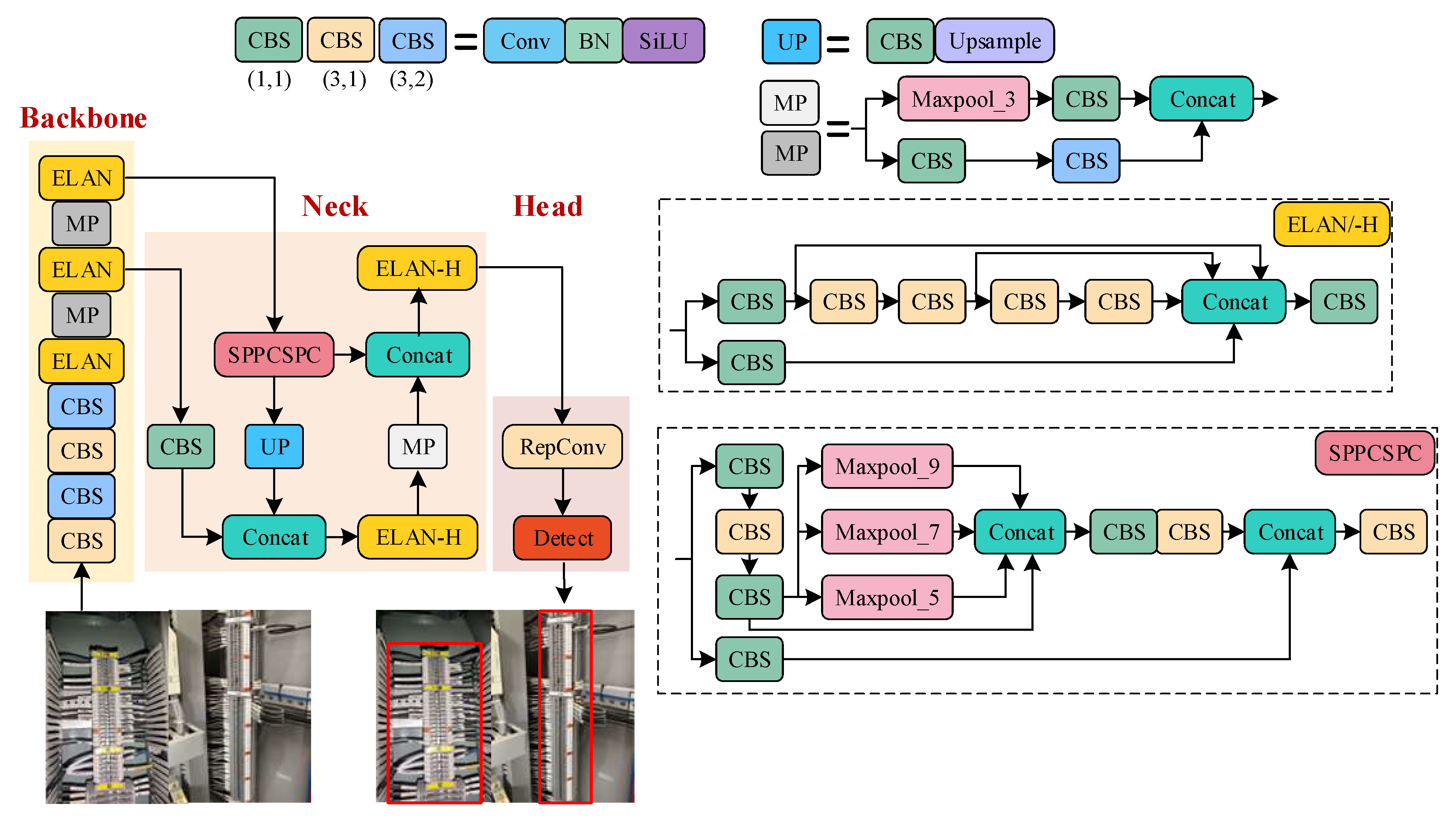
- In response to the distinctive regional characteristics of terminal blocks, we developed the YOLOv7 Area-Oriented (YOLOv7-AO) model for area extraction. This model omits the prediction branches and corresponding feature fusion modules that offer limited value. The streamlined regional detection model efficiently extracts block regions with reduced computational demands.
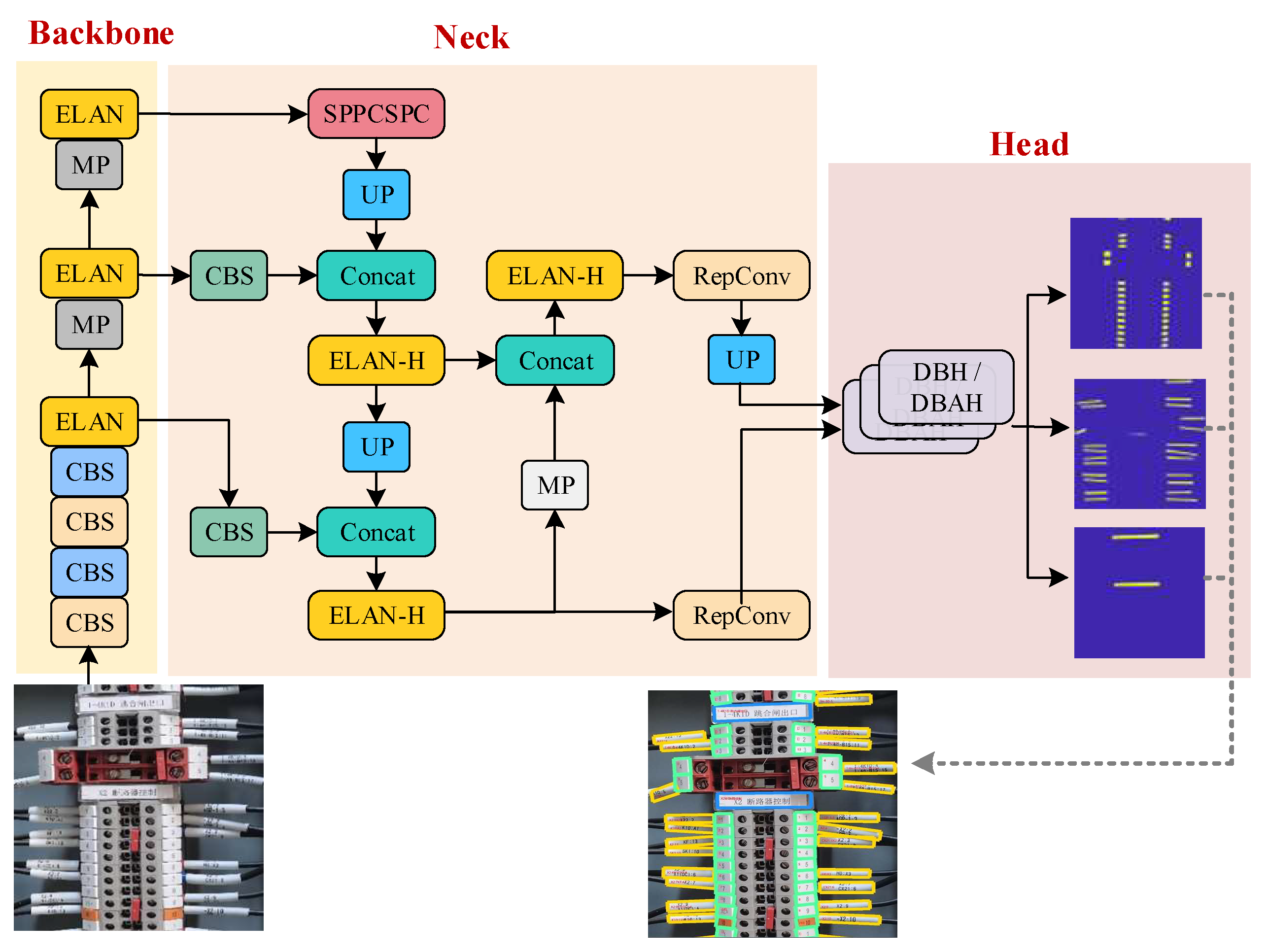
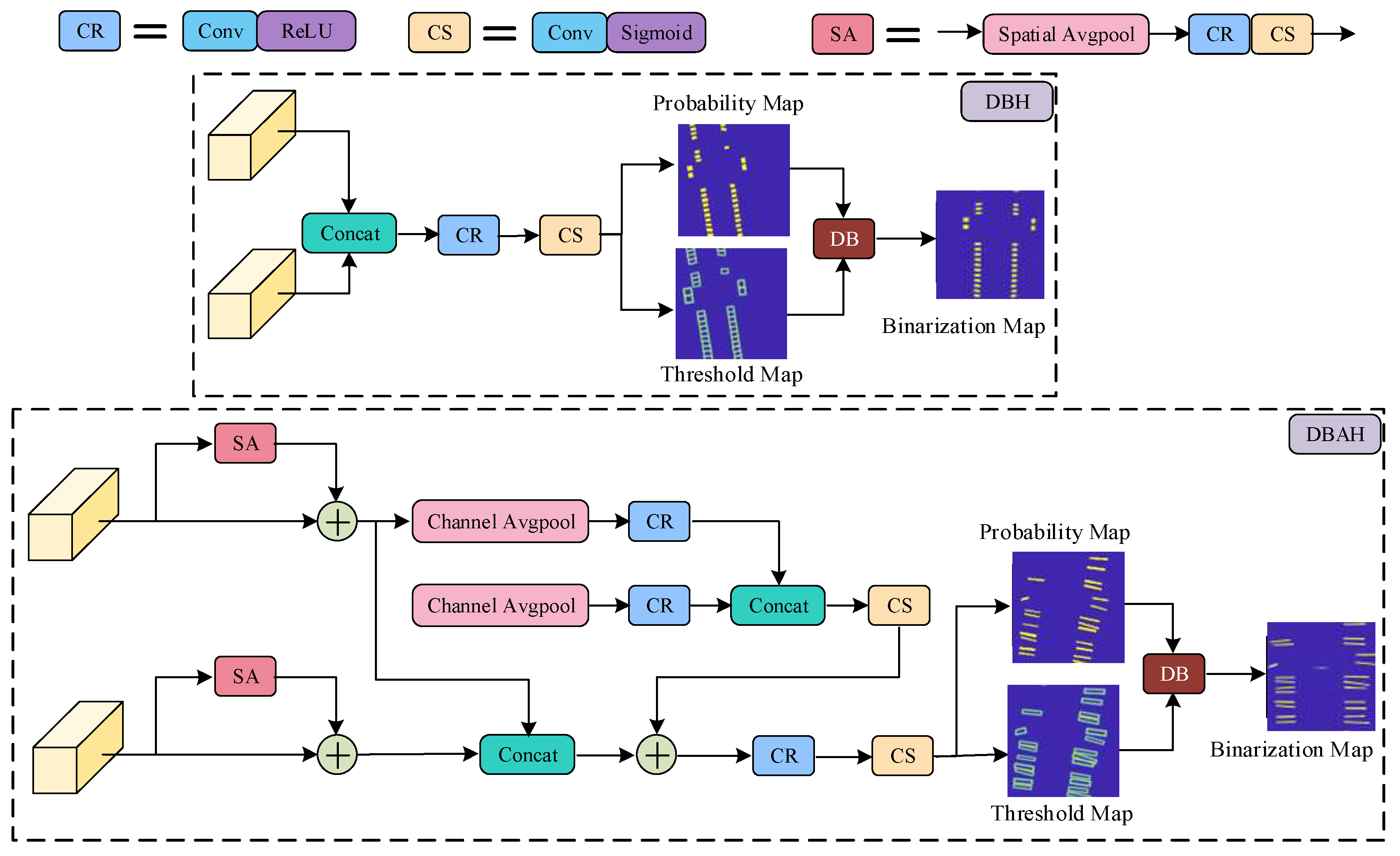
- To accommodate the densely arranged tags and cable markers within terminal blocks, we integrate differentiable binarization (DB) and an attention mechanism into the segmentation heads. This redesigned YOLOv7 model with a differentiable binarization attention head (YOLOv7-DBAH) significantly enhances element detection accuracy by producing results with precise boundaries.
2. Materials
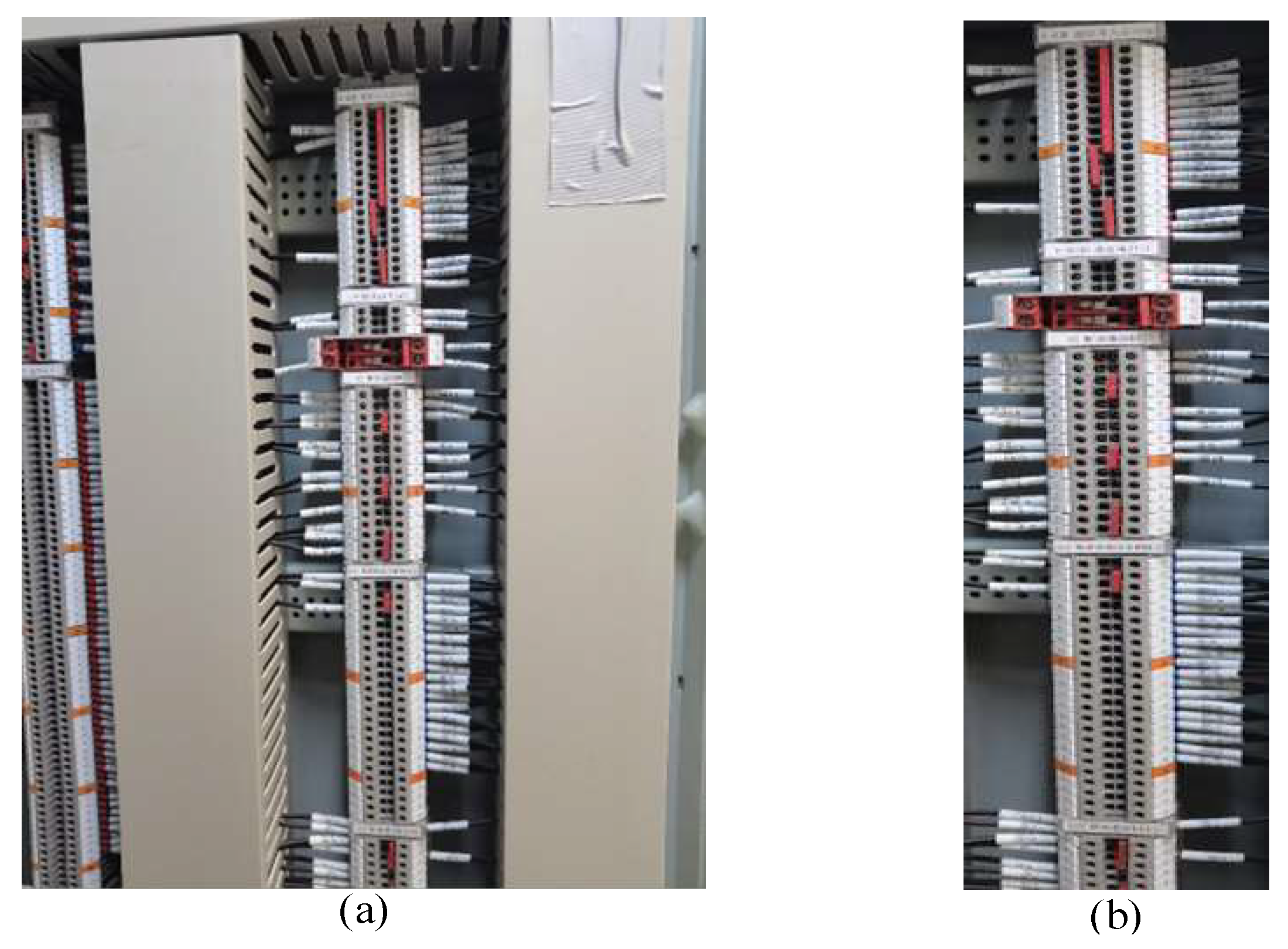
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Dataset Acquisition
2.1.2. Data Enhancement
3. Methods
3.1. Terminal Block Area Extraction
3.2. Terminal Block Components Detection
3.3. Text Recognition with Image Distortion Correction
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Experiment Platform
4.1.2. Experiment Settings
4.1.3. Evaluation Metrics
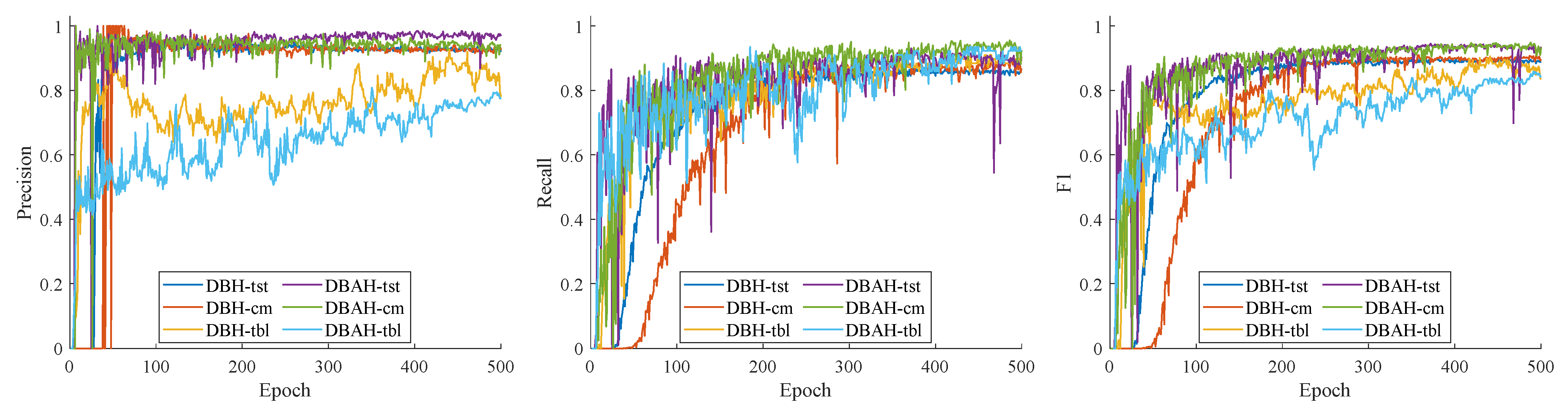
4.2. Experimental Results
4.2.1. Terminal Block Area Exaction Results
4.2.2. Terminal Block Components Detection Results
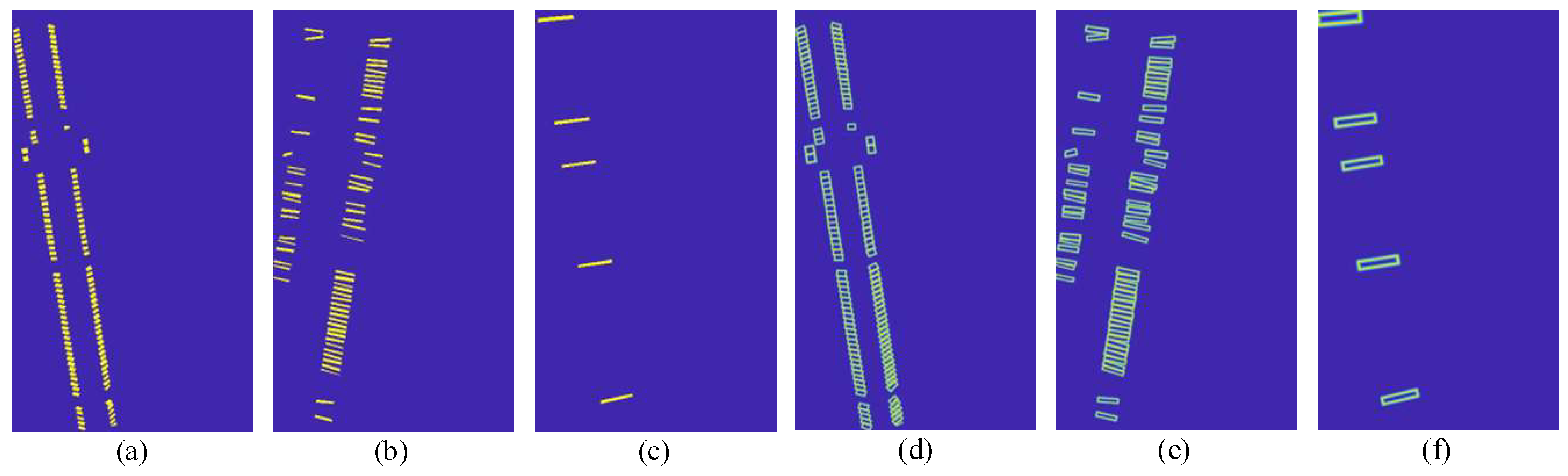
4.2.3. Visualization Analysis of Terminal Block Components Identification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, M.; Xu, J.; Shi, Z. Low carbon economic dispatch of integrated energy system considering extended electric heating demand response. Energy 2023, 278, 127902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Tan, Z.; Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Geng, S.; Pu, L. Study on grid price mechanism of new energy power stations considering market environment. Renew. Energy 2023, 203, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.G.; Madeira, S.C.; Francisco, A.P. Short-term electricity load forecasting—A systematic approach from system level to secondary substations. Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Calderón, A.J.; Folgado, F.J. IoT real time system for monitoring lithium-ion battery long-term operation in microgrids. J. Energy Storage 2022, 51, 104596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daisy, M.; Dashti, R.; Shaker, H.R.; Javadi, S.; Aliabadi, M.H. Fault location in power grids using substation voltage magnitude differences: A comprehensive technique for transmission lines, distribution networks, and AC/DC microgrids. Measurement 2023, 220, 113403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, M.; Shirmohammadi, S. Applied AI in instrumentation and measurement: The deep learning revolution. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2020, 23, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Shakeel, I.; Mehfuz, S.; Ahmad, J. Deep learning models for cloud, edge, fog, and IoT computing paradigms: Survey, recent advances, and future directions. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2023, 49, 100568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.A.S.; Neto, A.P.D.F.; Fernandino, R.M.A.; Carvalho, R.F.; Fernandes, A.L.; Guimaraes, F.G. Automated Monitoring of Construction Sites of Electric Power Substations Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19195–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lan, H.; Niu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Qian, T.; Tang, W. Detection and Location of Safety Protective Wear in Power Substation Operation Using Wear-Enhanced YOLOv3 Algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 125540–125549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Fang, Y.; Xing, L.; Yang, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhou, C. Deep learning-based substation remote construction management and AI automatic violation detection system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2022, 16, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27-30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Chun, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.-J. Gaussian YOLOv3: An Accurate and Fast Object Detector Using Localization Uncertainty for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 502–511. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Lyu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. TPH-YOLOv5: Improved YOLOv5 Based on Transformer Prediction Head for Object Detection on Drone-captured Scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, B.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, D. State identification of transfer learning based Yolov4 network for isolation switches used in substations. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 1000459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Luan, T.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Sotelo, M.A.; Li, Z. YOLOv4-5D: An Effective and Efficient Object Detector for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Quan, W.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G.; Feng, K.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.X. A Segmentation-Based Multitask Learning Approach for Isolating Switch State Recognition in High-Speed Railway Traction Substation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 15922–15939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L. A Method of Identifying Rust Status of Dampers Based on Image Processing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 5407–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassu, B.T.; Marchesi, B.; Wagner, R.; Gomes, V.B.; Zarnicinski, V.; Lippmann, L. A Computer Vision System for Monitoring Disconnect Switches in Distribution Substations. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 37, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Djike, C.L.T.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Xu, K.; Zhang, C. Infrared Image Detection of Substation Insulators Using an Improved Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2020, 36, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Cui, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Ji, L.; Ping, Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, X. An Infrared Image Detection Method of Substation Equipment Combining Iresgroup Structure and CenterNet. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 4757–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wu, G.; Lei, J.; Fan, F.; Ye, X. Detecting Inspection Objects of Power Line from Cable Inspection Robot LiDAR Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Ke, Y. A detection and recognition system of pointer meters in substations based on computer vision. Measurement 2020, 152, 107333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Huang, T.; Lin, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, R.; Jing, W. Automatic Meter Reading from UAV Inspection Photos in the Substation by Combining YOLOv5s and DeeplabV3+. Sensors 2022, 22, 7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, A.; Xie, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Hong, W. A Lightweight Complex-Valued DeepLabv3+ for Semantic Segmentation of PolSAR Image. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Shi, L.; Xi, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, G. Real Time Power Equipment Meter Recognition Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, P. An Improved YOLOv7 Model Based on Visual Attention Fusion: Application to the Recognition of Bouncing Locks in Substation Power Cabinets. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, T.; Xue, C.; Zhou, L. Mvit-pcd: A lightweight vit-based network for martian surface topographic change detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, T.; Rassõlkin, A.; Kallaste, A.; Arsénio, P.; Pánek, D.; Kaska, J.; Karban, P. Robust Design Optimization and Emerging Technologies for Electrical Machines: Challenges and Open Problems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, S.P.; Alexandropoulos, S.N.; Pardalos, P.M.; Vrahatis, M.N. No free lunch theorem: A review. In Approximation and Optimization: Algorithms, Complexity and Applications; Demetriou, I.C., Pardalos, P.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 57–82. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Ke, Z.; Wu, N. Modelskg: A Design and Research on Knowledge Graph of Multimodal Curriculum Based on Paddleocr and Deepke. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Wuhan, China, 15–17 July 2022; pp. 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, M.; Zou, Z.; Wan, Z.; Yao, C.; Bai, X. Real-Time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization and Adaptive Scale Fusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Train | Valid | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Images | 1306 | 194 | 194 |
| Terminal block label | 2661 | 346 | 352 |
| Terminal strip tag | 25,836 | 1621 | 1635 |
| Cable marker | 19,894 | 1386 | 1403 |
| mAP@0.5:0.95 | FPS | |
|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7 | 0.816 | 16.7 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 0.746 | 68.5 |
| YOLOv7-AO | 0.809 | 74.3 |
| Precision | Recall | F1 | Time Cost (h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 0.7930 | 0.8037 | 0.7983 | 1.21 |
| YOLACT | 0.8398 | 0.8571 | 0.8483 | 4.52 |
| YOLOv7-DBH | 0.8768 | 0.8743 | 0.8735 | 4.61 |
| YOLOv7-DBAH | 0.9257 | 0.9173 | 0.9208 | 5.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, W.; Chen, Z.; Deng, X.; Wu, C.; Li, T. An Identification Method for Irregular Components Related to Terminal Blocks in Equipment Cabinet of Power Substation. Sensors 2023, 23, 7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187739
Cao W, Chen Z, Deng X, Wu C, Li T. An Identification Method for Irregular Components Related to Terminal Blocks in Equipment Cabinet of Power Substation. Sensors. 2023; 23(18):7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187739
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Weiguo, Zhong Chen, Xuhui Deng, Congying Wu, and Tiecheng Li. 2023. "An Identification Method for Irregular Components Related to Terminal Blocks in Equipment Cabinet of Power Substation" Sensors 23, no. 18: 7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187739
APA StyleCao, W., Chen, Z., Deng, X., Wu, C., & Li, T. (2023). An Identification Method for Irregular Components Related to Terminal Blocks in Equipment Cabinet of Power Substation. Sensors, 23(18), 7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187739





