Bridged EGFET Design for the Rapid Screening of Sorbents as Sensitisers in Water-Pollution Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. ‘Bridged’ EGFET Desgin
2.2. Processing and Electrical Characterisation
| Bridge Type | Sensitiser | Sensitiser Concentration | Agar Concentration | Fig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Funnel | Clinoptilolite | 150 mg/mL | 20 mg/mL | Figure 2 |
| U-shape | MTS 9140/MTS 9200 1:1 | 200 mg/mL | 40 mg/mL | Figure 3a |
| U-shape | MTS 9140 | 200 mg/mL | 40 mg/mL | Figure 3b |
| U-shape | MTS 9200 | 200 mg/mL | 40 mg/mL | Figure 3c |
| Funnel | MTS 9140/MTS 9200 1:1 | 100 mg/mL | 20 mg/mL | Figure 4 |
3. Results
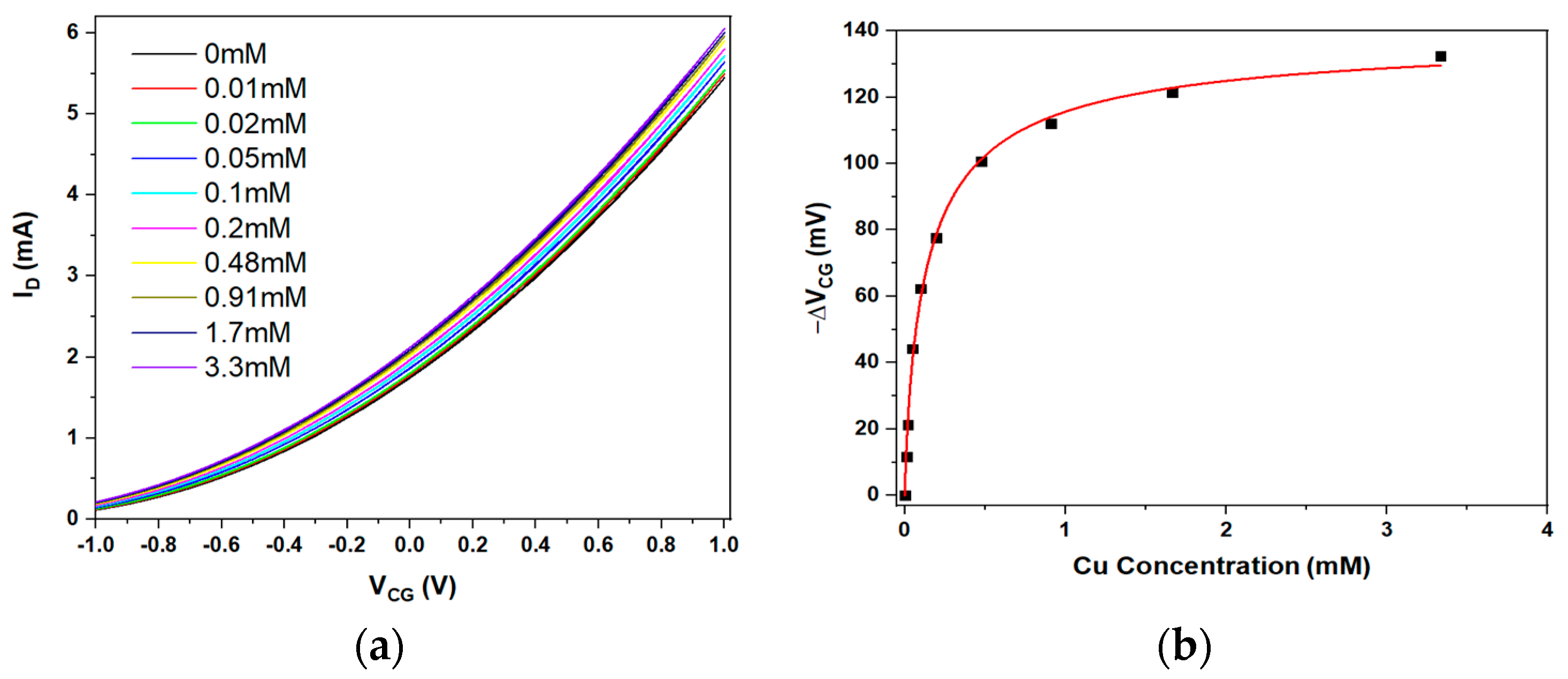
3.1. Sensing Cu2+ with a Funnel-Bridged EGFET Sensitised with Zeolite Sorbent
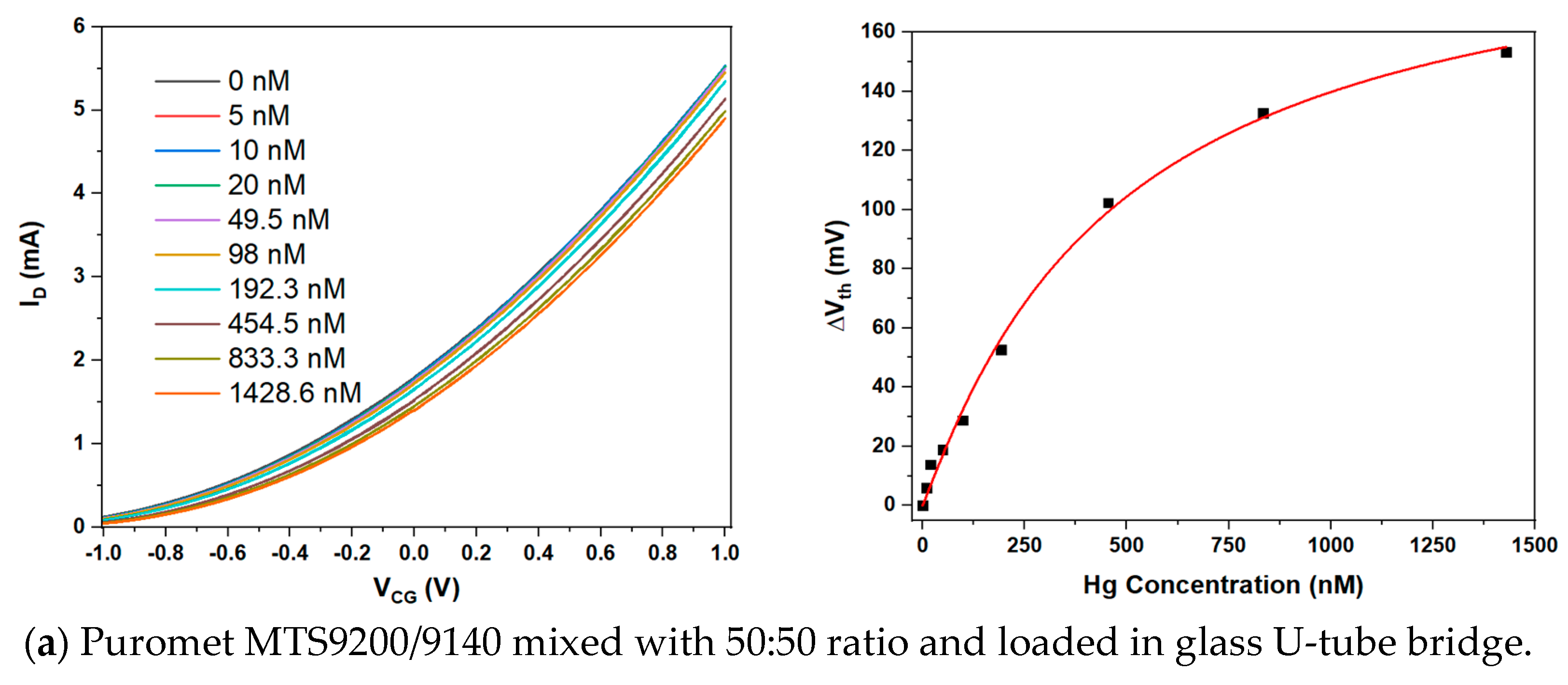
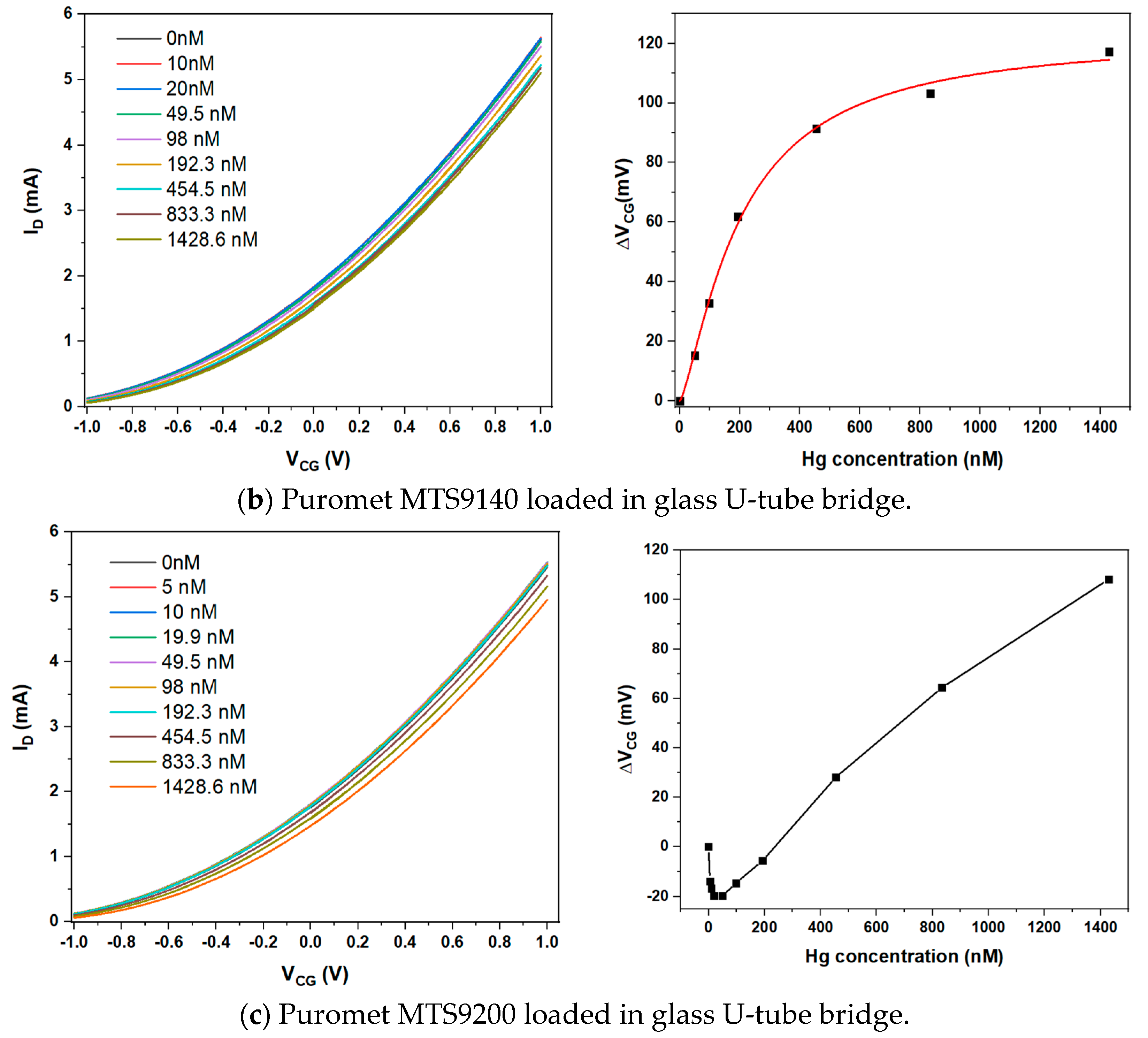
3.2. Sensing Hg2+ with a U-Tube Bridged EGFET Sensitised with Purolite Sorbent Resins
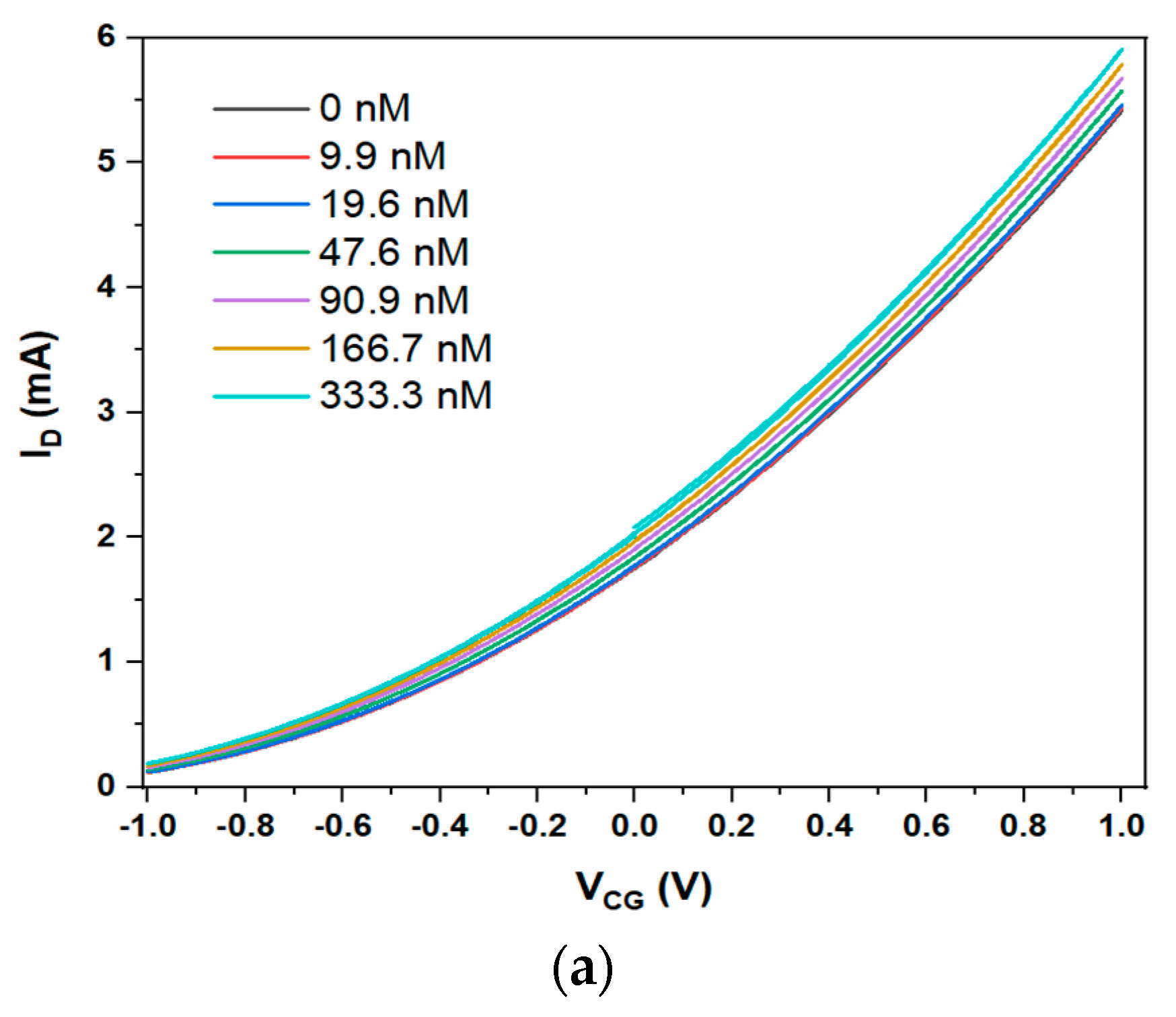
3.3. Sensing Hg2+ with a Funnel-Bridged EGFET Sensitised with Purolite Sorbent Resins

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950 (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Allibone, J.; Fatemian, E.; Walker, P.J. Determination of mercury in potable water by ICP-MS using gold as a stabilising agent. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1999, 14, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P. Development of an Ion-Sensitive Solid-State Device for Neurophysiological Measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1970, BME-17, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, N.; Alqahtani, Z.; Zhou, C.; Sano, N.; Conte, M.; Grell, M. Sensing aromatic pollutants in water with catalyst-sensitized water-gated transistor. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 4169–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, T.; Campana, A.; Leonardi, F.; Casalini, S.; Kyndiah, A.; Murgia, M.; Biscarini, F. Water-gated organic field effect transistors—Opportunities for biochemical sensing and extracellular signal transduction. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3728–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berto, M.; Vecchi, E.; Baiamonte, L.; Condò, C.; Sensi, M.; Di Lauro, M.; Sola, M.; De Stradis, A.; Biscarini, F.; Minafra, A.; et al. Label free detection of plant viruses with organic transistor biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.-H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.-S.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G.; et al. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens Using Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, H.; Alswieleh, A.; Al-Khurayyif, I.; AlGarni, S.; Grell, M. Parallel Potentiometric and Capacitive Response in a Water-Gate Thin Film Transistor Biosensor at High Ionic Strength. Sensors 2021, 21, 5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könemund, L.; Neumann, L.; Hirschberg, F.; Biedendieck, R.; Jahn, D.; Johannes, H.-H.; Kowalsky, W. Functionalization of an extended-gate field-effect transistor (EGFET) for bacteria detection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Qian, D.; Mao, H.; Zhao, J. Novel Graphene Biosensor Based on the Functionalization of Multifunctional Nano-bovine Serum Albumin for the Highly Sensitive Detection of Cancer Biomarkers. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poghossian, A.; Jablonski, M.; Molinnus, D.; Wege, C.; Schöning, M.J. Field-Effect Sensors for Virus Detection: From Ebola to SARS-CoV-2 and Plant Viral Enhancers. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 598103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmoltner, K.; Kofler, J.; Klug, A.; List-Kratochvil, E.J.W. Electrolyte-Gated Organic Field-Effect Transistor for Selective Reversible Ion Detection. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6895–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, K.; Münzer, A.M.; Jaworska, E.; Maksymiuk, K.; Michalska, A.; Scarpa, G. Selective ion-sensing with membrane-functionalized electrolyte-gated carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Analyst 2014, 139, 4947–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althagafi, T.M.; Al Baroot, A.F.; Algarni, S.A.; Grell, M. A membrane-free cation selective water-gated transistor. Analyst 2016, 141, 5571–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alghamdi, N.; Alqahtani, Z.; Grell, M. Sub-nanomolar detection of cesium with water-gated transistor. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 064502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, Z.; Alghamdi, N.; Grell, M. Monitoring the lead-and-copper rule with a water-gated field effect transistor. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, Z.; Alghamdi, N.; Robshaw, T.J.; Dawson, R.; Ogden, M.D.; Buckley, A.; Grell, M. Water-Gated Transistor Using Ion Exchange Resin for Potentiometric Fluoride Sensing. Micromachines 2020, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ye, Z.; Wei, X.; Mao, S. Recent advances in field-effect transistor sensing strategies for fast and highly efficient analysis of heavy metal ions. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2022, 2, e2100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukesan, R.; Chen, Y.-T.; Shahim, S.; Wang, S.-L.; Sarangadharan, I.; Wang, Y.-L. Instant Mercury Ion Detection in Industrial Waste Water with a Microchip Using Extended Gate Field-Effect Transistors and a Portable Device. Sensors 2019, 19, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hardan, N.H.; Abdul Hamid, M.A.; Ahmed, N.M.; Jalar, A.; Shamsudin, R.; Othman, N.K.; Kar Keng, L.; Chiu, W.; Al-Rawi, H.N. High Sensitivity pH Sensor Based on Porous Silicon (PSi) Extended Gate Field-Effect Transistor. Sensors 2016, 16, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Jie, J.; Zhang, W.; He, Z.; Wang, J.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.C.M.; Lee, S.-T. Silicon nanowire sensors for Hg2+ and Cd2+ ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 193101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y. Self-Assembled 1-Octadecanethiol Monolayers on Graphene for Mercury Detection. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4738–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudibya, H.G.; He, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, P. Electrical Detection of Metal Ions Using Field-Effect Transistors Based on Micropatterned Reduced Graphene Oxide Films. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1990–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, E.; Liu, X.; Freeman, R.; Yehezkeli, O.; Willner, I. Label-Free Analysis of Thrombin or Hg2+ Ions by Nucleic Acid-Functionalized Graphene Oxide Matrices Assembled on Field-Effect Transistors. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Kwon, O.S.; Bae, J.; Jang, J. High-Performance Flexible Graphene Aptasensor for Mercury Detection in Mussels. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10563–10571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Kwon, O.S.; Lee, C.; Jang, J. High-performance Hg2+ FET-type sensors based on reduced graphene oxide–polyfuran nanohybrids. Analyst 2014, 139, 3852–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhou, G.; Gao, X.; Mao, S.; Cui, S.; Ocola, L.E.; Yuan, C.; Chen, J. Real-time detection of mercury ions in water using a reduced graphene oxide/DNA field-effect transistor with assistance of a passivation layer. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2015, 5, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Cheng, R.; Ng, R.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. Highly sensitive detection of mercury(II) ions with few-layer molybdenum disulfide. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, B.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J. Graphene field-effect transistors with tunable sensitivity for high performance Hg (II) sensing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 153101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Chang, J.; Pu, H.; Shi, K.; Mao, S.; Sui, X.; Ren, R.; Cui, S.; Chen, J. Ultrasensitive Mercury Ion Detection Using DNA-Functionalized Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheet/Gold Nanoparticle Hybrid Field-Effect Transistor Device. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puromet. Available online: https://www.purolite.com/brand/Puromet (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Amphlett, J.T.M.; Ogden, M.D.; Foster, R.I.; Syna, N.; Soldenhoff, K.; Sharrad, C.A. Polyamine functionalised ion exchange resins: Synthesis, characterisation and uranyl uptake. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, G. Biopolymere, 1st ed.; Vieweg und Teubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, O.; Puliga, S.; Bachan Upadhyay, L.S. Immobilization of watermelon (Citrullus vulgaris) urease in agarose gel for urea estimation. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2007, 12, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, F.; van Beek, T.A.; Zuilhof, H. Key steps towards the oriented immobilization of antibodies using boronic acids. Analyst 2015, 140, 6467–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perić, J.; Trgo, M.; Vukojević Medvidović, N. Removal of zinc, copper and lead by natural zeolite—A comparison of adsorption isotherms. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LND150. Available online: https://www.mouser.com/datasheet/2/268/supertex_lnd150-1181133.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Alrabiah, H.; Al-Majed, A.; Abounassif, M.; Mostafa, G.A.E. Ionophore-based potentiometric PVC membrane sensors for determination of phenobarbitone in pharmaceutical formulations. Acta Pharm. 2016, 66, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Baroot, A.F.; Grell, M. Comparing electron- and hole transporting semiconductors in ion sensitive water- gated transistors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 89, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercury Ionophore I. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/SA/en/product/sial/39075 (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Hill, A.V. The possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of haemoglobin on its dissociationcurves. J. Physiol. 1910, 40 (suppl), i–vii. [Google Scholar]
- van der Spiegel, J.; Lauks, I.; Chan, P.; Babic, D. The extended gate chemically sensitive field effect transistor as multi-species microprobe. Sens. Actuators 1983, 4, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref. | Semiconductor | LoD | Type | Response | Functionalisation/Sensitiser |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | Si NW | 100 nM | ISFET | Nernst | 3-mercaptopropyl triethoxysilane |
| [22] | Graphene | 556 μM | ISFET | NA | 1-octanethiol |
| [23] | red. GO | ≈1 nM | WGTFT | Langmuir | Protein |
| [24] | GO | 1.2 μM | ISFET | Nernst | Tailored nucleic acid |
| [25] | Graphene | 10 pM | WGTFT | Nernst | Aptamer |
| [26] | red. GO | 10 pM | WGTFT | Nernst | Polyfuran |
| [27] | red. GO | 1 nM | ISFET | NA | DNA |
| [28] | MoS2 | 30 pM | ISFET | Nernst | Innate (S in MoS2) |
| [29] | Graphene | 5.6 nM | WGTFT | Langmuir | Innate Ionophore |
| [30] | MoS2/Au NPs | 100 pM | ISFET | Langmuir | DNA |
| [19] | LND150 | ≈0.3 pM | EGFET | Nernst | Diaza crown ether |
| Fig. No. | Analyte | Sensitiser | ΔVsat [mV] | β | k [L/mol] | c1/2 [nM] | LoD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 2 | Cu2+ | clinoptilolite | 139.8 ± 3.9 | 0.807 ± 0.05 | (6.95 ± 0.73) × 103 | (144 ± 15) × 103 | 8.3 μM |
| Figure 3a | Hg2+ | MTS9140+ | 203.2 ± 20.1 | 1.06 ± 0.11 | (2.11 ± 0.48) × 106 | 474 ± 108 | 17.7 nM |
| MTS9200 | |||||||
| Figure 3b | Hg2+ | MTS9140 | 122.9 ± 4.6 | 1.34 ± 0.12 | (4.94 ± 0.44) × 106 | 202 ± 18 | 73.7 nM |
| Figure 4 | Hg2+ | MTS9140+ | 103.6 ± 5 | 1.5 ± 0.14 | (1.21 ± 0.1) × 107 | 82.6 ± 6.8 | 17.1 |
| MTS9200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlQahtani, H.R.; Al-Odayni, A.-B.M.; Alhamed, Y.; Grell, M. Bridged EGFET Design for the Rapid Screening of Sorbents as Sensitisers in Water-Pollution Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 7554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177554
AlQahtani HR, Al-Odayni A-BM, Alhamed Y, Grell M. Bridged EGFET Design for the Rapid Screening of Sorbents as Sensitisers in Water-Pollution Sensors. Sensors. 2023; 23(17):7554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177554
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlQahtani, Hadi Rasam, Abdel-Basit M. Al-Odayni, Yusif Alhamed, and Martin Grell. 2023. "Bridged EGFET Design for the Rapid Screening of Sorbents as Sensitisers in Water-Pollution Sensors" Sensors 23, no. 17: 7554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177554
APA StyleAlQahtani, H. R., Al-Odayni, A.-B. M., Alhamed, Y., & Grell, M. (2023). Bridged EGFET Design for the Rapid Screening of Sorbents as Sensitisers in Water-Pollution Sensors. Sensors, 23(17), 7554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177554






