Deep Learning and Geometry Flow Vector Using Estimating Vehicle Cuboid Technology in a Monovision Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Proposed Methods
2.2.1. Object Detection Using Deep Learning Model
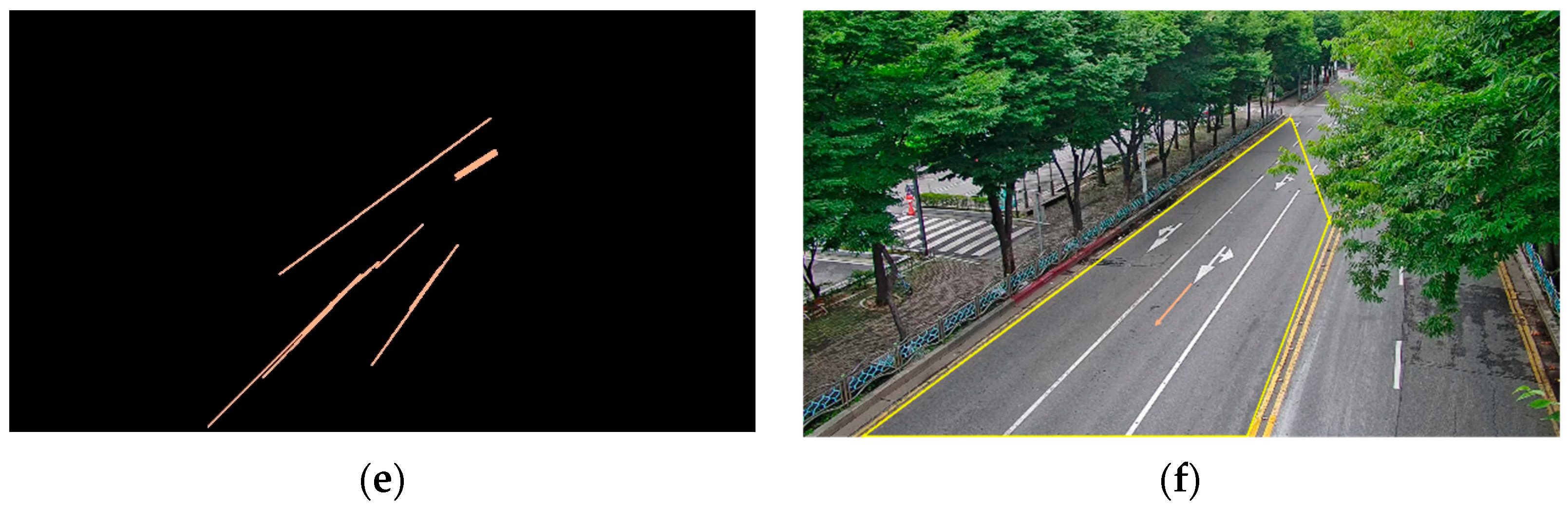
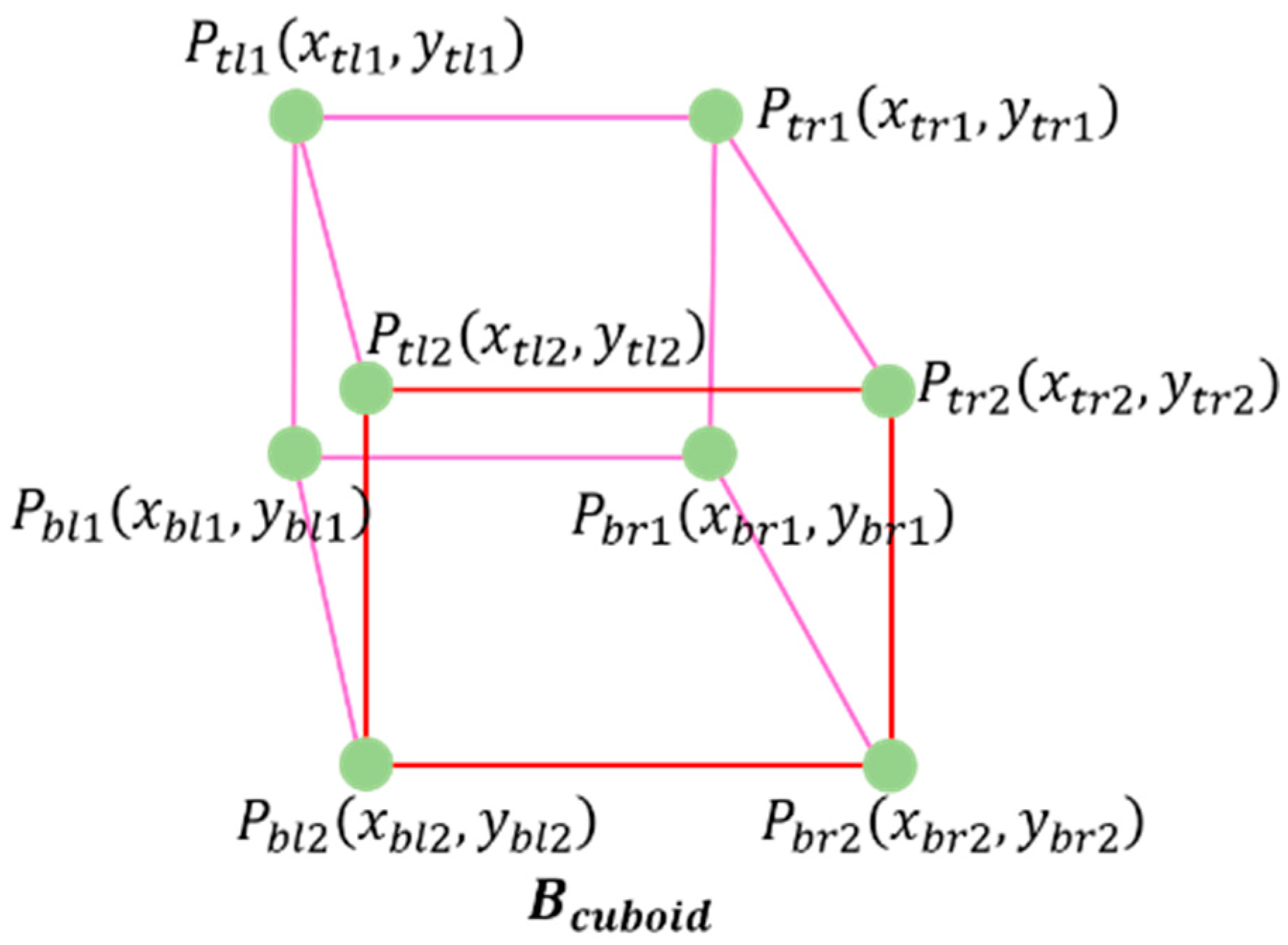
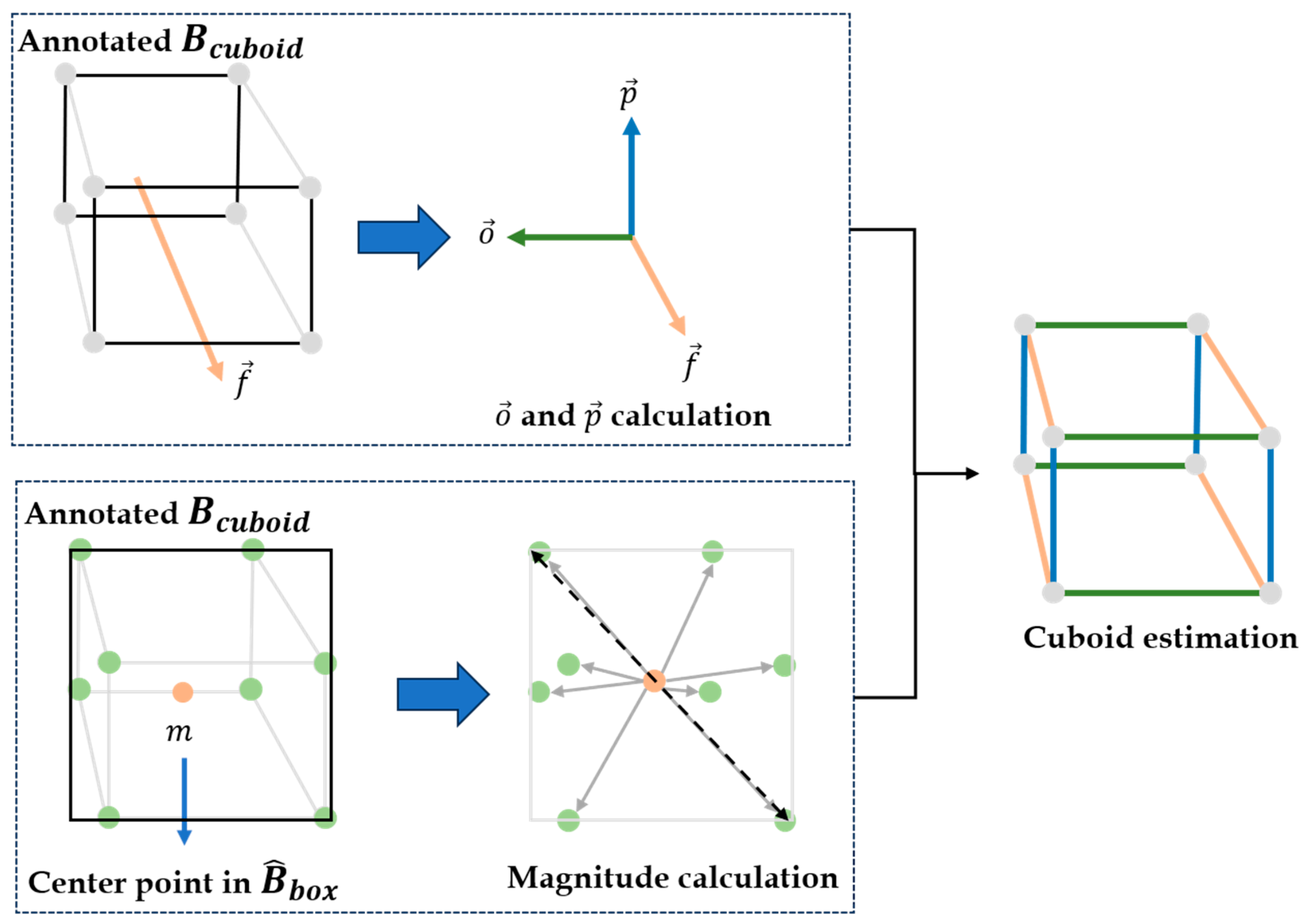
2.2.2. Core Vector Extraction
3. Experiments and Results
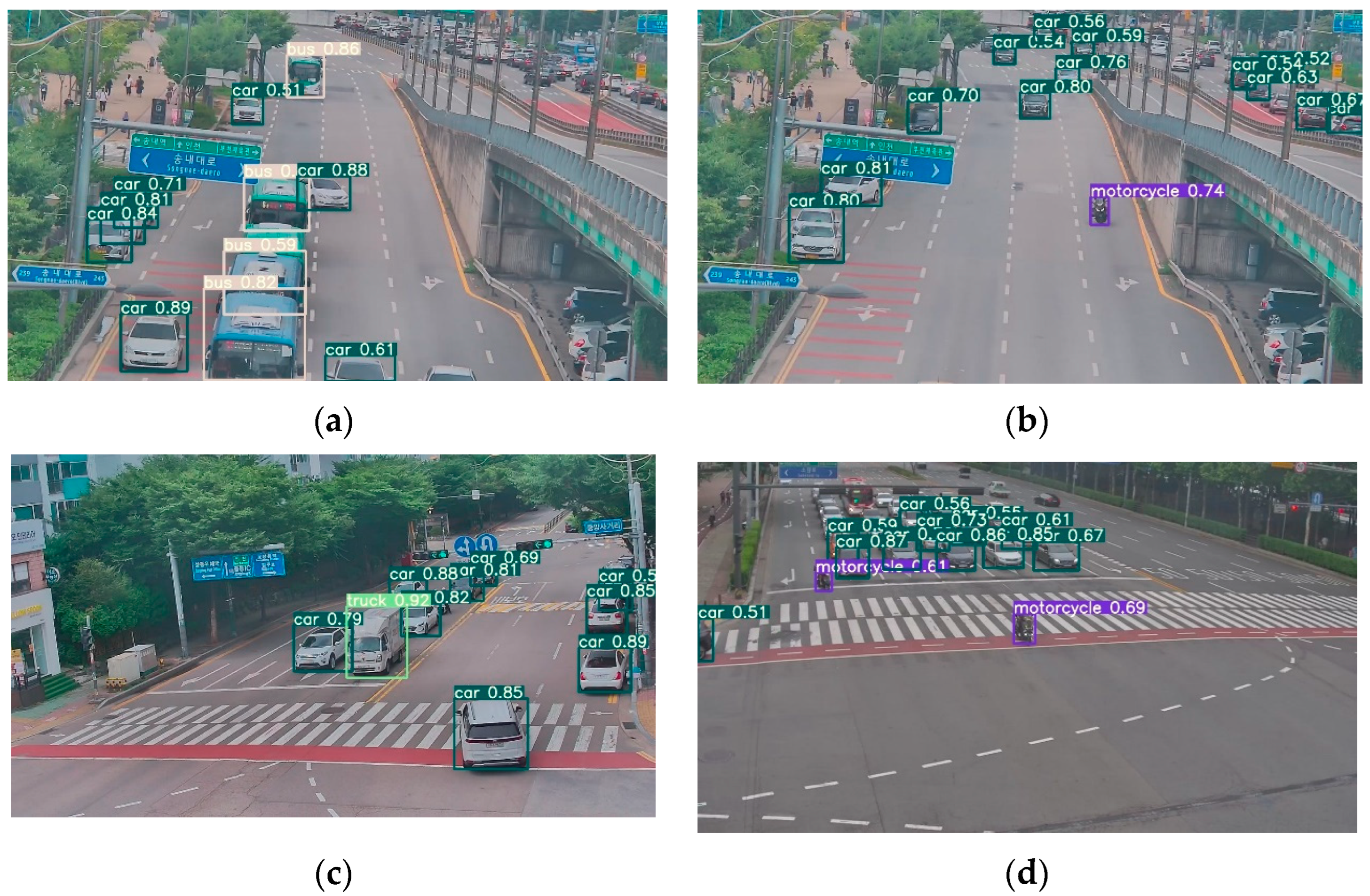
3.1. Experimental Design
- (1)
- To detect road vehicles in video footage and determine their 2D bounding boxes using various object detection models. The aim is to select the most optimal object detection model for this task.
- (2)
- To evaluate the accuracy of the estimated cuboid using core vectors by 3D IoU (Intersection on Union) as the evaluation metric.
3.2. Results
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balfaqih, M.; Alharbi, S.A. Associated Information and Communication Technologies Challenges of Smart City Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, Y.; Han, H.; Lee, S.H. Sejong smart city: On the road to be a city of the future. In Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawany, N.Z.; Shamsi, J.A. Smart City Architecture: Vision and Challenges. 2015. Available online: www.thesai.org (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Telang, S.; Chel, A.; Nemade, A.; Kaushik, G. Intelligent transport system for a smart city. In Studies in Systems, Decision and Control; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Frankfurt, Germany, 2021; pp. 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, K.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Ren, Y.; Hanzo, L. Vehicular Sensing Networks in a Smart City: Principles, Technologies and Applications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 25, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Xiong, N.N.; Zhou, X.; Lin, X.; Ward, T.L. A Robust Vehicle Detection Scheme for Intelligent Traffic Surveillance Systems in Smart Cities. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 139299–139312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.M.; Son, H.; Ahmad, A.; Paul, A. Real-time video processing for traffic control in smart city using Hadoop ecosystem with GPUs. Soft Comput. 2017, 22, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, M.; Hamidkhani, M.; Sadeghi, R. Smart traffic light scheduling in smart city using image and video processing. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Internet of Things and Applications (IoT), Isfahan, Iran, 17–18 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Li, L.; Li, Z. Modeling Vehicle Interactions via Modified LSTM Models for Trajectory Prediction. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38287–38296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthélemy, J.; Verstaevel, N.; Forehead, H.; Perez, P. Edge-Computing Video Analytics for Real-Time Traffic Monitoring in a Smart City. Sensors 2019, 19, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevillano, X.; Màrmol, E.; Fernandez-Arguedas, V. Towards Smart Traffic Management Systems: Vacant On-Street Parking Spot Detection Based on Video Analytics. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Salamanca, Spain, 7–10 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardi, G.; Lupia, M.; Cario, G.; Tedesco, F.; Gaccio, F.C.; Scudo, F.L.; Casavola, A. Advanced Adaptive Street Lighting Systems for Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1495–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. 2022. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696 (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Rahman, M.M.; Chakma, S.; Raza, D.M.; Akter, S.; Sattar, A. Real-Time Object Detection using Machine Learning. In 2021 12th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies, ICCCNT 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, Y. The object detection based on deep learning. In 2017 4th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering, ICISCE 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimutai, G.; Ngenzi, A.; Said, R.N.; Kiprop, A.; Förster, A. An Optimum Tea Fermentation Detection Model Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Data 2020, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, A.; Birardi, G.; Manca, F.; Marin, C.; Birardi, V.; Giannone, D.; Galiano, A.M. Innovative DSS for intelligent monitoring and urban square design approaches: A case of study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 65, 102653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. 2018. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767 (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. Available online: http://pjreddie.com/yolo/ (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. 2020. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934 (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: Fully Convolutional One-Stage Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: A Simple and Strong Anchor-free Object Detector. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, E.; Al-Jarrah, O.Y.; Dianati, M.; Fallah, S.; Oxtoby, D.; Mouzakitis, A. A Survey on 3D Object Detection Methods for Autonomous Driving Applications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 3782–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, X.; Shen, S. Stereo R-CNN based 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Longin, Z.D.; Latecki, J. Amodal Detection of 3D Objects: Inferring 3D Bounding Boxes from 2D Ones in RGB-Depth Images. Available online: https://github.com/phoenixnn/ (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Ku, J.; Mozifian, M.; Lee, J.; Harakeh, A.; Waslander, S.L. Joint 3d proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Ouyang, W.; Simonelli, A.; Ricci, E. 3D Object Detection from Images for Autonomous Driving: A Survey. 2022. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2202.02980 (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Fayyaz, M.A.B.; Alexoulis-Chrysovergis, A.C.; Southgate, M.J.; Johnson, C. A review of the technological developments for interlocking at level crossing. In Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 2021; Volume 235, pp. 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kundu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R. Monocular 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chabot, F.; Chaouch, M.; Rabarisoa, J.; Teulière, C.; Chateau, T. Deep MANTA: A Coarse-to-Fine Many-Task Network for Joint 2D and 3D Vehicle Analysis from Monocular Image. 2017. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1703.07570 (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Mousavian, A.; Anguelov, D.; Flynn, J.; Kosecka, J. 3D Bounding Box Estimation Using Deep Learning and Geometry. 2016. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.00496 (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- AI-Hub Platform. Available online: https://www.aihub.or.kr/aihubdata/data/view.do?currMenu=115&topMenu=100 (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Newman, W.; Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E. Graphics and Use of the Hough Transformation To Detect Lines and Curves in Pictures. Commun. ACM 1972, 15, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, N.; Karl, W. Line detection in images through regularized hough transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conservatoire national des arts et métiers (France). IEEE Systems, and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT’19)), Le Cnam, Paris, France, 23–26 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, D.; Xie, M.; Mo, Q.; Han, Z.; Wan, Y. An improved Hough transform for line detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling (ICCASM 2010), Taiyuan, China, 22–24 October 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 2, p. V2-354. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Han, Q.; Zhang, C.B.; Xu, J.; Cheng, M.M. Deep Hough Transform for Semantic Line Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 4793–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]





| Class | # of Objects in Test | Accuracy | mIoU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground truth | General vehicle | 182,109 | - | - |
| Bus | 12,031 | - | - | |
| Trucks | 18,699 | - | - | |
| Bikes | 5319 | - | - | |
| Object detection model (YOLOv7) | General vehicle | 179,377 | 0.985 | 0.871 |
| Bus | 11,429 | 0.950 | 0.910 | |
| Trucks | 18,025 | 0.964 | 0.870 | |
| Bikes | 4584 | 0.862 | 0.774 | |
| Average | 0.978 | 0.871 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noh, B.; Lin, T.; Lee, S.; Jeong, T. Deep Learning and Geometry Flow Vector Using Estimating Vehicle Cuboid Technology in a Monovision Environment. Sensors 2023, 23, 7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177504
Noh B, Lin T, Lee S, Jeong T. Deep Learning and Geometry Flow Vector Using Estimating Vehicle Cuboid Technology in a Monovision Environment. Sensors. 2023; 23(17):7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177504
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoh, Byeongjoon, Tengfeng Lin, Sungju Lee, and Taikyeong Jeong. 2023. "Deep Learning and Geometry Flow Vector Using Estimating Vehicle Cuboid Technology in a Monovision Environment" Sensors 23, no. 17: 7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177504
APA StyleNoh, B., Lin, T., Lee, S., & Jeong, T. (2023). Deep Learning and Geometry Flow Vector Using Estimating Vehicle Cuboid Technology in a Monovision Environment. Sensors, 23(17), 7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177504







